Culture Evolution – Workshop 1 (Your Culture Evolution)

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Culture Evolution is provided by Mr. Bonnes (B.Sc.) Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
If you would like to view the Client Information Hub (CIH) for this program, please Click Here
Learning Provider Profile
Mr. Bonnes (B.Sc.) is a highly accomplished business professional with over 25 years of expertise in Project Management, Sales, Marketing, Leadership, and Learning & Development (L&D). With 18 years of hands-on experience in the business world, he possesses unparalleled clarity on what truly adds value in terms of people and organizational development efforts and investments.
As a Change Management and Culture Development Expert, Mr. Bonnes has an impressive track record of guiding leaders and their teams through global change workshops while reinforcing and nurturing the enterprise’s culture. His ability to drive disciplined action during periods of transformation is widely recognized.
Furthermore, Mr. Bonnes is a certified Executive Coach, specializing in coaching CEOs and senior executives. He has successfully worked with global businesses across diverse country, cultural, and language divides, assisting teams and their leaders in achieving personal and professional growth.
Mr. Bonnes’ expertise extends to being an experienced and influential Facilitator, Presenter, and Trainer, with a genuine passion for people development. In his previous corporate role as Vice President and Head of Global Training and Learning at the Hilti Corporation, he led a team with global responsibility for world-class Leadership, Talent Development, Sales, and Marketing Programs. Additionally, he held headquarters responsibility for “soft” skills training and development.
Having collaborated with businessmen and women in over 30 different countries throughout his career, Mr. Bonnes possesses a truly global perspective and an exceptional sensitivity and appreciation for individual cultures. This exposure has shaped his ability to navigate diverse business environments with ease.
In summary, Mr. Bonnes is a highly accomplished professional with a wealth of experience in various business domains. His expertise in Change Management, Culture Development, Executive Coaching, and People Development has made him a sought-after leader in the industry. With his global perspective and cultural sensitivity, Mr. Bonnes brings a unique and valuable perspective to every endeavor he undertakes.
MOST Analysis
Mission Statement
The first workshop Your Culture Evolution, provides participants with a comprehensive understanding of organizational culture and its impact on various aspects of business operations. We aim to demonstrate that a strong and healthy culture is vital for any business in today’s competitive arena. Through this workshop, you will obtain a clear picture of where your organization is placed on its culture journey and take the first steps in identifying the processes required to strengthen and leverage the power in your existing culture. Our goal is to empower participants with the knowledge and tools to create a thriving and sustainable organizational culture that drives success and fosters a positive work environment.
Objectives
01. Provide a comprehensive overview of organizational culture and its significance in today’s business landscape. Time Allocated: 1 Month
02. Help participants understand the impact of culture on various aspects of business operations, including employee engagement, productivity, and customer satisfaction. Time Allocated: 1 Month
03. Facilitate a deep dive into the current culture of the organization, identifying strengths and areas for improvement. Time Allocated: 1 Month
04. Foster a shared understanding among participants about the desired culture and its alignment with the organization’s values and goals. Time Allocated: 1 Month
05. Explore the link between culture and business performance, emphasizing the potential for culture to drive success and competitive advantage. Time Allocated: 1 Month
06. Introduce participants to best practices and case studies of organizations that have successfully transformed their culture. Time Allocated: 1 Month
07. Provide tools and frameworks for assessing and measuring culture, enabling participants to track progress and identify areas of focus.. Time Allocated: 1 Month08. Encourage open and honest dialogue among participants, creating a safe space for discussing cultural challenges and opportunities. Time Allocated: 1 Month
09. Develop a roadmap for culture evolution, outlining the steps and processes required to strengthen and leverage the existing culture. Time Allocated: 1 Month
10. Empower participants with practical strategies for fostering a positive work environment, promoting diversity and inclusion, and enhancing employee well-being. Time Allocated: 1 Month
11. Highlight the importance of leadership in shaping and sustaining a healthy culture, emphasizing the role of leaders as culture champions. Time Allocated: 1 Month
12. Inspire participants to take ownership of culture evolution within their organizations, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning. Time Allocated: 1 Month
Strategies
01. Conduct research and gather relevant information on the concept of organizational culture and incorporate real-life examples and case studies to illustrate the impact of culture on business success.
02. Conduct interactive activities and discussions to explore the link between culture and employee engagement, productivity, and customer satisfaction and encourage participants to share their own experiences and insights to foster a deeper understanding.
03. Conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather feedback from employees about the existing culture, and analyze the data collected to identify patterns, strengths, and areas for improvement.
04. Facilitate brainstorming sessions to define the desired culture based on the organization’s values and goals and encourage participants to share their perspectives and ideas on what the desired culture should look like.
05. Share case studies and success stories of organizations that have achieved business success through having a strong culture and present research findings on the impact of culture on key performance indicators. Facilitate discussions to help participants understand how culture can drive success in their specific industry or context.
06. Introduce participants to best practices and case studies of organizations that have successfully transformed their culture, sharing examples highlighting the strategies and approaches they used to achieve their desired culture.
07. Introduce participants to culture assessment tools and frameworks, such as surveys or culture scans with guidance on how to interpret and analyze the results of these assessments.
08. Create a safe and inclusive environment for participants to share their thoughts and experiences, facilitate discussions that encourage active listening and respect for different perspectives, and foster trust and collaboration among participants.
09. Guide participants in creating a step-by-step plan for culture evolution, including specific actions and timelines, identify key stakeholders and champions who will be responsible for driving the culture evolution process and provide templates or tools to assist participants in documenting their roadmap and tracking progress.
10. Share best practices for promoting diversity and inclusion within the organization, and provide resources and recommendations for enhancing employee well-being and work-life balance.
11. Share examples of effective leadership behaviors that contribute to a positive culture and encourage leaders to lead by example and actively promote the desired culture within their teams.
12. Foster a sense of ownership and accountability among participants for driving culture change and encourage participants to share their progress and success stories with the larger organization to inspire others.
Tasks
01. Conduct research on organizational culture theories and models. Develop presentation training materials Schedule and organize the delivery of the overview session.
02. Prepare interactive activities or case studies to illustrate the impact of culture. Facilitate discussions and encourage participants to share their experiences. Prepare relevant research findings and statistics to support the discussion.
03. Design and distribute surveys or questionnaires to gather feedback from employees. Conduct interviews or focus groups to gather qualitative insights. Analyze the data collected and identify patterns and areas for improvement.
04. Facilitate brainstorming sessions to define the desired culture. Create visual aids or diagrams to illustrate the alignment between culture, values, and goals. Document the agreed-upon desired culture for future reference.
05. Research and gather case studies of organizations that have achieved business success through culture. Prepare presentations summarizing the case studies. Facilitate discussions and encourage participants to draw connections between culture and performance in their own organizations.
06. Research and gather case studies of successful culture transformations. Prepare presentations summarizing the best practices, and facilitate discussions that encourage participants to identify relevant strategies for their own organizations.
07. Research and select appropriate culture assessment tools or frameworks. Customize the tools or frameworks to fit the organization’s specific needs. Develop guidelines or instructions for participants on how to use the assessment tools or frameworks.
08. Create a safe and inclusive environment for discussions. Foster trust and collaboration, and facilitate discussions using active listening techniques encouraging respect for different perspectives.
09. Provide templates or tools for participants to document their roadmap and schedule follow-up sessions or check-ins to review progress and adjust the roadmap as needed.
10. Research and gather best practices for promoting diversity and inclusion. Compile resources and recommendations for enhancing employee well-being and facilitate discussions and brainstorming sessions for participants to develop initiatives or programs.
11. Provide coaching or mentoring for leaders to understand their role in culture evolution. Facilitate discussions and role-playing exercises to practice effective leadership behaviors.
12. Create a platform or forum for participants to share their progress and success stories. Provide ongoing support and resources for participants to continue their culture evolution to maintain momentum and accountability.
Introduction
Why your organizational culture matters
In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of business, there is one factor that sets successful organizations apart from the rest: their organizational culture. Culture is not just a buzzword; it is the heartbeat of an organization, the driving force behind its success.
A strong and positive organizational culture creates an environment where employees are engaged, motivated, and inspired to give their best. It fosters collaboration, innovation, and a sense of belonging, leading to higher productivity, better customer satisfaction, and ultimately, increased profitability.
 But the benefits of a strong culture go beyond the bottom line. It creates a workplace where employees feel valued, supported, and empowered. It attracts and retains top talent, enhances employee morale and well-being, and builds a strong employer brand.
But the benefits of a strong culture go beyond the bottom line. It creates a workplace where employees feel valued, supported, and empowered. It attracts and retains top talent, enhances employee morale and well-being, and builds a strong employer brand.
In today’s competitive landscape, organizations must adapt and evolve to stay ahead. And it is through a strong culture that organizations can navigate change, embrace innovation, and thrive in the face of challenges.
Culture matters because it shapes the way we work, the way we communicate, and the way we thrive. It sets the tone for the entire organization, influencing decision-making, behavior, and ultimately, the success of the business.
So, whether you’re a small startup or a multinational corporation, investing in your organizational culture is not just a nice-to-have; it is a strategic imperative. It is the key to unlocking the full potential of your organization and creating a workplace where everyone can thrive.
Join us on this journey of culture evolution, and together, let’s build a culture that drives success, inspires greatness, and transforms your organization into a powerhouse of innovation and excellence.
What Workshop 1 is about in a nutshell:
In a nutshell, Workshop 1 “Your Culture Evolution – Building a Foundation for Success” is a comprehensive program that provides participants with a deep understanding of organizational culture and its impact on various aspects of the organization.
The workshop begins by explaining what culture is and why it is crucial for organizational success. It explores the different elements that make up culture, such as values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors, and how they shape the organization’s identity and operations.
The workshop will analyze the organization’s current culture and assess its strengths and weaknesses. In the workshop, we will also explore how internal and external perceptions of the organization’s culture can impact its reputation and performance.
The workshop dives into the impact of culture on employee behavior and decision-making processes. Insights will be gained into how culture influences employee engagement, motivation, and productivity. Participants will also learn how to align culture with the organization’s goals and values to drive desired behaviors and outcomes.
Throughout the workshop, there will be engaging and interactive exercises, case studies, and discussions to deepen understanding of culture and its implications. There will be the opportunity to assess the organization’s culture and identify areas for improvement.
By the end of the workshop, participants will have a solid foundation in understanding and analyzing organizational culture. They will be equipped with strategies and tools to transform their culture and create a strong foundation for success in their organization.

Participant benefits in a nutshell:
Participants in Workshop 1 will develop a range of skills that will empower them to unlock the power of organizational culture within their organization. These benefits include a deep understanding of culture and its impact, the ability to assess and analyze their organization’s culture, and the skills to drive culture transformation and create a foundation for success.
Participants will gain a deep understanding of organizational culture and its significance in driving organizational success. They will learn about the various elements that make up culture and how they shape behavior, decision-making processes, and overall performance. This understanding will enable participants to appreciate the importance of culture and its impact on the organization.
They will develop the skills to assess and analyze their organization’s current culture. They will learn how to identify the strengths and weaknesses of their culture and understand how internal and external perceptions can influence the organization’s reputation and performance. This assessment will provide participants with valuable insights into their organization’s culture and areas for improvement.
Participants will learn strategies and tools to drive culture transformation within their organization. They will gain the skills to align culture with the organization’s goals and values, fostering desired behaviors and outcomes. Participants will also learn how to bridge gaps in their culture and develop strategies to create a strong foundation for success.
By the end of the workshop, participants will be equipped with the knowledge and skills to unlock the power of organizational culture. They will have a deep understanding of culture and its impact, the ability to assess and analyze their organization’s culture, and the skills to drive culture transformation. These benefits will empower participants to create a positive and thriving culture within their organization, leading to increased employee engagement, productivity, and overall success.
How the training program is set up:
The training program is thoughtfully designed to provide participants with a comprehensive and engaging learning experience. The program is structured in a way that allows participants to delve into the depths of organizational culture, assess their current culture, and develop strategies for culture transformation. Through a combination of interactive sessions, case studies, and discussions, participants will gain the knowledge and skills needed to unlock the power of organizational culture.
The training program is divided into several modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of organizational culture. These modules build upon one another, creating a cohesive and progressive learning journey. The program begins with an introduction to culture and its significance in organizational success. Participants will gain a foundational understanding of culture and its impact on behavior, decision-making processes, and overall performance.
The subsequent modules dive deeper into the elements of culture and how they shape the organization. Participants will explore topics such as values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors, and understand how these elements contribute to the organization’s identity and operations. They will also learn how to assess their organization’s current culture, identify strengths and weaknesses, and analyze internal and external perceptions.
The interactive exercises and case studies will allow participants to apply their learning to real-world scenarios. They will have the opportunity to discuss and share insights with their peers, fostering a collaborative and enriching learning environment. The program also includes opportunities for the participants to seek clarification and deepen their understanding.
The training program concludes with a focus on culture transformation and creating a foundation for success. Participants will learn strategies and tools to align culture with the organization’s goals and values, fostering desired behaviors and outcomes. They will develop action plans to bridge gaps in their culture and drive culture transformation within their organization.
Throughout the training program, participants receive comprehensive materials to support their learning journey. They will also have access to ongoing support and guidance from the facilitator, ensuring that they can apply their learning effectively in their organization.
By the end of the training program, participants will have gained a deep understanding of organizational culture and its impact. They will have the skills and knowledge to assess and analyze their organization’s culture, as well as the strategies and tools to drive culture transformation. This comprehensive and engaging program sets participants on a path towards unlocking the power of organizational culture and creating a foundation for success within their organization.
Executive Summary
The first workshop Culture Evolution will serve as a Beginning and Big Picture and will provide participants from your business with a comprehensive understanding of organizational culture and its impact on various aspects of your operations. This workshop will begin your journey by demonstrating that a strong and healthy culture is absolutely vital for any business in today’s competitive arena. We will hold up a mirror to obtain a realistic picture of where your business is placed on its culture journey and take the first steps in identifying the processes we require to strengthen and leverage the power of your existing culture.

Chapter 1: Understanding Culture
Culture is a fundamental aspect of any organization, influencing its values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors. In this phase, participants gain a deep understanding of culture and its significance in shaping organizational behavior and performance. They explore the various components of culture and how they influence employee attitudes and actions. By understanding culture, organizations can better align their values and behaviors to achieve their desired outcomes.
Chapter 2: Organizational Analysis
To initiate culture evolution, organizations must conduct a thorough analysis of their existing culture. This focus area emphasizes the importance of assessing the alignment between the current culture and desired outcomes. Participants learn how to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of their culture, identifying areas for improvement. Through this analysis, organizations can identify the gaps that need to be addressed to foster a culture that supports their goals.

Chapter 3: Internal & External Perception
The perception of an organization, both internally and externally, plays a crucial role in culture development. Participants explore how culture impacts employee engagement, customer satisfaction, and overall reputation. They learn strategies to align internal and external perceptions for a cohesive culture. By understanding how their culture is perceived, organizations can make informed decisions to shape their culture in a way that positively impacts their stakeholders.
Chapter 4: Elements of Culture
Culture is composed of various elements, including artifacts, rituals, language, and stories. In this focus area, participants delve deeper into these elements and their role in shaping culture. They explore how artifacts, such as office layout and symbols, can reinforce desired behaviors and values. They also learn how rituals and language contribute to the formation and maintenance of culture. By leveraging these elements, organizations can create a culture that aligns with their vision and values.

Chapter 5: Impact on Behavior
Culture has a profound influence on employee behavior. In this focus area, participants explore the relationship between culture and behavior, understanding how cultural norms and expectations shape individual and collective actions. They learn strategies to align culture with desired behaviors for improved performance. By fostering a culture that supports the desired behaviors, organizations can create an environment where employees thrive and contribute to the organization’s success.
Chapter 6: Decision-making Processes
Culture significantly impacts decision-making processes within organizations. Participants examine how cultural factors, such as risk tolerance, hierarchy, and communication channels, influence decision-making. They learn techniques to align decision-making processes with the desired culture. By aligning decision-making processes with the cultural values and goals, organizations can ensure that decisions are made in a way that supports the overall vision and direction.
Chapter 7: Overall Performance
Culture plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of an organization. In this focus area, participants explore how culture impacts key performance indicators, such as productivity, innovation, and employee retention. They gain insights into leveraging culture to drive sustainable success. By aligning culture with performance goals, organizations can create an environment that fosters high performance and continuous improvement.

Chapter 8: Assessing Existing Culture
To initiate culture evolution, organizations must assess their current culture. Workshop participants consider various assessment methods, including surveys, interviews, and observations, to gain a comprehensive understanding of their existing culture. They also explore tools to measure cultural alignment with organizational goals. By conducting a thorough assessment, organizations can identify the strengths and weaknesses of their culture and develop targeted strategies for improvement.

Chapter 9: Identifying Gaps
Identifying gaps between the current and desired culture is crucial for effective culture development. Participants learn techniques to identify gaps in cultural values, behaviors, and practices. They gain insights into the importance of involving employees in this process to ensure a shared understanding of the gaps. By involving employees in the gap identification process, organizations can foster a sense of ownership and commitment to the culture development efforts.

Chapter 10: Bridging the Gaps
Once gaps are identified, organizations must develop strategies to bridge them. Workshop participants explore various approaches, such as training programs, communication initiatives, and leadership development, to bridge cultural gaps effectively. They learn how to create an action plan for culture transformation. By implementing targeted strategies to bridge the identified gaps, organizations can create a culture that aligns with their desired outcomes.

Chapter 11: Transforming Culture
Culture transformation requires a systematic approach. Participants gain insights into the stages of culture transformation and the challenges associated with it. They learn strategies to overcome resistance to change and create a culture that aligns with the organization’s vision and goals. By understanding the stages of culture transformation and addressing the challenges proactively, organizations can navigate the transformation process successfully.

Chapter 12: Culture for Success
The final focus area emphasizes the importance of aligning culture with organizational success. During the workshop participants have explored case studies of organizations that have successfully transformed their culture to achieve sustainable success. They learn how to create a culture that fosters innovation, collaboration, and adaptability. By aligning culture with the organization’s vision and goals, organizations can create a competitive advantage and drive long-term success.
By exploring the 12 focus areas outlined above, participants will gain insights into understanding the dynamic power of a positive culture in driving organizational success. This workshop serves as a crucial foundation for the subsequent workshops in the “Culture Evolution” series, enabling organizations to embark on a journey of culture development and evolution. Through a systematic, process-driven approach to culture development, organizations can create a culture that aligns with their vision, values, and goals, fostering high performance and sustainable success.
Curriculum
Culture Evolution – WDP1 – Culture Evolution
- Understanding Culture
- Organizational Analysis
- Internal & External Perception
- Elements of Culture
- Impact on Behavior
- Decision-Making Processes
- Overall Performance
- Assessing Existing Culture
- Identifying Gaps
- Bridging the Gaps
- Transforming Culture
- Culture for Success
Distance Learning
Introduction
Welcome to Appleton Greene and thank you for enrolling on the Culture Evolution corporate training program. You will be learning through our unique facilitation via distance-learning method, which will enable you to practically implement everything that you learn academically. The methods and materials used in your program have been designed and developed to ensure that you derive the maximum benefits and enjoyment possible. We hope that you find the program challenging and fun to do. However, if you have never been a distance-learner before, you may be experiencing some trepidation at the task before you. So we will get you started by giving you some basic information and guidance on how you can make the best use of the modules, how you should manage the materials and what you should be doing as you work through them. This guide is designed to point you in the right direction and help you to become an effective distance-learner. Take a few hours or so to study this guide and your guide to tutorial support for students, while making notes, before you start to study in earnest.
Study environment
You will need to locate a quiet and private place to study, preferably a room where you can easily be isolated from external disturbances or distractions. Make sure the room is well-lit and incorporates a relaxed, pleasant feel. If you can spoil yourself within your study environment, you will have much more of a chance to ensure that you are always in the right frame of mind when you do devote time to study. For example, a nice fire, the ability to play soft soothing background music, soft but effective lighting, perhaps a nice view if possible and a good size desk with a comfortable chair. Make sure that your family know when you are studying and understand your study rules. Your study environment is very important. The ideal situation, if at all possible, is to have a separate study, which can be devoted to you. If this is not possible then you will need to pay a lot more attention to developing and managing your study schedule, because it will affect other people as well as yourself. The better your study environment, the more productive you will be.
Study tools & rules
Try and make sure that your study tools are sufficient and in good working order. You will need to have access to a computer, scanner and printer, with access to the internet. You will need a very comfortable chair, which supports your lower back, and you will need a good filing system. It can be very frustrating if you are spending valuable study time trying to fix study tools that are unreliable, or unsuitable for the task. Make sure that your study tools are up to date. You will also need to consider some study rules. Some of these rules will apply to you and will be intended to help you to be more disciplined about when and how you study. This distance-learning guide will help you and after you have read it you can put some thought into what your study rules should be. You will also need to negotiate some study rules for your family, friends or anyone who lives with you. They too will need to be disciplined in order to ensure that they can support you while you study. It is important to ensure that your family and friends are an integral part of your study team. Having their support and encouragement can prove to be a crucial contribution to your successful completion of the program. Involve them in as much as you can.
Successful distance-learning
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes or workshops, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. But unlike traditional internal training courses, it is the student’s responsibility, with a distance-learning program, to ensure that they manage their own study contribution. This requires strong self-discipline and self-motivation skills and there must be a clear will to succeed. Those students who are used to managing themselves, are good at managing others and who enjoy working in isolation, are more likely to be good distance-learners. It is also important to be aware of the main reasons why you are studying and of the main objectives that you are hoping to achieve as a result. You will need to remind yourself of these objectives at times when you need to motivate yourself. Never lose sight of your long-term goals and your short-term objectives. There is nobody available here to pamper you, or to look after you, or to spoon-feed you with information, so you will need to find ways to encourage and appreciate yourself while you are studying. Make sure that you chart your study progress, so that you can be sure of your achievements and re-evaluate your goals and objectives regularly.
Self-assessment
Appleton Greene training programs are in all cases post-graduate programs. Consequently, you should already have obtained a business-related degree and be an experienced learner. You should therefore already be aware of your study strengths and weaknesses. For example, which time of the day are you at your most productive? Are you a lark or an owl? What study methods do you respond to the most? Are you a consistent learner? How do you discipline yourself? How do you ensure that you enjoy yourself while studying? It is important to understand yourself as a learner and so some self-assessment early on will be necessary if you are to apply yourself correctly. Perform a SWOT analysis on yourself as a student. List your internal strengths and weaknesses as a student and your external opportunities and threats. This will help you later on when you are creating a study plan. You can then incorporate features within your study plan that can ensure that you are playing to your strengths, while compensating for your weaknesses. You can also ensure that you make the most of your opportunities, while avoiding the potential threats to your success.
Accepting responsibility as a student
Training programs invariably require a significant investment, both in terms of what they cost and in the time that you need to contribute to study and the responsibility for successful completion of training programs rests entirely with the student. This is never more apparent than when a student is learning via distance-learning. Accepting responsibility as a student is an important step towards ensuring that you can successfully complete your training program. It is easy to instantly blame other people or factors when things go wrong. But the fact of the matter is that if a failure is your failure, then you have the power to do something about it, it is entirely in your own hands. If it is always someone else’s failure, then you are powerless to do anything about it. All students study in entirely different ways, this is because we are all individuals and what is right for one student, is not necessarily right for another. In order to succeed, you will have to accept personal responsibility for finding a way to plan, implement and manage a personal study plan that works for you. If you do not succeed, you only have yourself to blame.
Planning
By far the most critical contribution to stress, is the feeling of not being in control. In the absence of planning we tend to be reactive and can stumble from pillar to post in the hope that things will turn out fine in the end. Invariably they don’t! In order to be in control, we need to have firm ideas about how and when we want to do things. We also need to consider as many possible eventualities as we can, so that we are prepared for them when they happen. Prescriptive Change, is far easier to manage and control, than Emergent Change. The same is true with distance-learning. It is much easier and much more enjoyable, if you feel that you are in control and that things are going to plan. Even when things do go wrong, you are prepared for them and can act accordingly without any unnecessary stress. It is important therefore that you do take time to plan your studies properly.
Management
Once you have developed a clear study plan, it is of equal importance to ensure that you manage the implementation of it. Most of us usually enjoy planning, but it is usually during implementation when things go wrong. Targets are not met and we do not understand why. Sometimes we do not even know if targets are being met. It is not enough for us to conclude that the study plan just failed. If it is failing, you will need to understand what you can do about it. Similarly if your study plan is succeeding, it is still important to understand why, so that you can improve upon your success. You therefore need to have guidelines for self-assessment so that you can be consistent with performance improvement throughout the program. If you manage things correctly, then your performance should constantly improve throughout the program.
Study objectives & tasks
The first place to start is developing your program objectives. These should feature your reasons for undertaking the training program in order of priority. Keep them succinct and to the point in order to avoid confusion. Do not just write the first things that come into your head because they are likely to be too similar to each other. Make a list of possible departmental headings, such as: Customer Service; E-business; Finance; Globalization; Human Resources; Technology; Legal; Management; Marketing and Production. Then brainstorm for ideas by listing as many things that you want to achieve under each heading and later re-arrange these things in order of priority. Finally, select the top item from each department heading and choose these as your program objectives. Try and restrict yourself to five because it will enable you to focus clearly. It is likely that the other things that you listed will be achieved if each of the top objectives are achieved. If this does not prove to be the case, then simply work through the process again.
Study forecast
As a guide, the Appleton Greene Culture Evolution corporate training program should take 12-18 months to complete, depending upon your availability and current commitments. The reason why there is such a variance in time estimates is because every student is an individual, with differing productivity levels and different commitments. These differentiations are then exaggerated by the fact that this is a distance-learning program, which incorporates the practical integration of academic theory as an as a part of the training program. Consequently all of the project studies are real, which means that important decisions and compromises need to be made. You will want to get things right and will need to be patient with your expectations in order to ensure that they are. We would always recommend that you are prudent with your own task and time forecasts, but you still need to develop them and have a clear indication of what are realistic expectations in your case. With reference to your time planning: consider the time that you can realistically dedicate towards study with the program every week; calculate how long it should take you to complete the program, using the guidelines featured here; then break the program down into logical modules and allocate a suitable proportion of time to each of them, these will be your milestones; you can create a time plan by using a spreadsheet on your computer, or a personal organizer such as MS Outlook, you could also use a financial forecasting software; break your time forecasts down into manageable chunks of time, the more specific you can be, the more productive and accurate your time management will be; finally, use formulas where possible to do your time calculations for you, because this will help later on when your forecasts need to change in line with actual performance. With reference to your task planning: refer to your list of tasks that need to be undertaken in order to achieve your program objectives; with reference to your time plan, calculate when each task should be implemented; remember that you are not estimating when your objectives will be achieved, but when you will need to focus upon implementing the corresponding tasks; you also need to ensure that each task is implemented in conjunction with the associated training modules which are relevant; then break each single task down into a list of specific to do’s, say approximately ten to do’s for each task and enter these into your study plan; once again you could use MS Outlook to incorporate both your time and task planning and this could constitute your study plan; you could also use a project management software like MS Project. You should now have a clear and realistic forecast detailing when you can expect to be able to do something about undertaking the tasks to achieve your program objectives.
Performance management
It is one thing to develop your study forecast, it is quite another to monitor your progress. Ultimately it is less important whether you achieve your original study forecast and more important that you update it so that it constantly remains realistic in line with your performance. As you begin to work through the program, you will begin to have more of an idea about your own personal performance and productivity levels as a distance-learner. Once you have completed your first study module, you should re-evaluate your study forecast for both time and tasks, so that they reflect your actual performance level achieved. In order to achieve this you must first time yourself while training by using an alarm clock. Set the alarm for hourly intervals and make a note of how far you have come within that time. You can then make a note of your actual performance on your study plan and then compare your performance against your forecast. Then consider the reasons that have contributed towards your performance level, whether they are positive or negative and make a considered adjustment to your future forecasts as a result. Given time, you should start achieving your forecasts regularly.
With reference to time management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual time taken in your study plan; consider your successes with time-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; consider your failures with time-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to time planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your time expectations. You need to be consistent with your time management, otherwise you will never complete your studies. This will either be because you are not contributing enough time to your studies, or you will become less efficient with the time that you do allocate to your studies. Remember, if you are not in control of your studies, they can just become yet another cause of stress for you.
With reference to your task management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual tasks that you have undertaken in your study plan; consider your successes with task-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case; take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; consider your failures with task-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to task planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your task expectations. You need to be consistent with your task management, otherwise you will never know whether you are achieving your program objectives or not.
Keeping in touch
You will have access to qualified and experienced professors and tutors who are responsible for providing tutorial support for your particular training program. So don’t be shy about letting them know how you are getting on. We keep electronic records of all tutorial support emails so that professors and tutors can review previous correspondence before considering an individual response. It also means that there is a record of all communications between you and your professors and tutors and this helps to avoid any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation. If you have a problem relating to the program, share it with them via email. It is likely that they have come across the same problem before and are usually able to make helpful suggestions and steer you in the right direction. To learn more about when and how to use tutorial support, please refer to the Tutorial Support section of this student information guide. This will help you to ensure that you are making the most of tutorial support that is available to you and will ultimately contribute towards your success and enjoyment with your training program.
Work colleagues and family
You should certainly discuss your program study progress with your colleagues, friends and your family. Appleton Greene training programs are very practical. They require you to seek information from other people, to plan, develop and implement processes with other people and to achieve feedback from other people in relation to viability and productivity. You will therefore have plenty of opportunities to test your ideas and enlist the views of others. People tend to be sympathetic towards distance-learners, so don’t bottle it all up in yourself. Get out there and share it! It is also likely that your family and colleagues are going to benefit from your labors with the program, so they are likely to be much more interested in being involved than you might think. Be bold about delegating work to those who might benefit themselves. This is a great way to achieve understanding and commitment from people who you may later rely upon for process implementation. Share your experiences with your friends and family.
Making it relevant
The key to successful learning is to make it relevant to your own individual circumstances. At all times you should be trying to make bridges between the content of the program and your own situation. Whether you achieve this through quiet reflection or through interactive discussion with your colleagues, client partners or your family, remember that it is the most important and rewarding aspect of translating your studies into real self-improvement. You should be clear about how you want the program to benefit you. This involves setting clear study objectives in relation to the content of the course in terms of understanding, concepts, completing research or reviewing activities and relating the content of the modules to your own situation. Your objectives may understandably change as you work through the program, in which case you should enter the revised objectives on your study plan so that you have a permanent reminder of what you are trying to achieve, when and why.
Distance-learning check-list
Prepare your study environment, your study tools and rules.
Undertake detailed self-assessment in terms of your ability as a learner.
Create a format for your study plan.
Consider your study objectives and tasks.
Create a study forecast.
Assess your study performance.
Re-evaluate your study forecast.
Be consistent when managing your study plan.
Use your Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) for tutorial support.
Make sure you keep in touch with those around you.

Tutorial Support
Programs
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. They are implemented over a sustainable period of time and professional support is consistently provided by qualified learning providers and specialist consultants.
Support available
You will have a designated Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and an Accredited Consultant and we encourage you to communicate with them as much as possible. In all cases tutorial support is provided online because we can then keep a record of all communications to ensure that tutorial support remains consistent. You would also be forwarding your work to the tutorial support unit for evaluation and assessment. You will receive individual feedback on all of the work that you undertake on a one-to-one basis, together with specific recommendations for anything that may need to be changed in order to achieve a pass with merit or a pass with distinction and you then have as many opportunities as you may need to re-submit project studies until they meet with the required standard. Consequently the only reason that you should really fail (CLP) is if you do not do the work. It makes no difference to us whether a student takes 12 months or 18 months to complete the program, what matters is that in all cases the same quality standard will have been achieved.
Support Process
Please forward all of your future emails to the designated (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit email address that has been provided and please do not duplicate or copy your emails to other AGC email accounts as this will just cause unnecessary administration. Please note that emails are always answered as quickly as possible but you will need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general tutorial support emails during busy periods, because emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. You will also need to allow a period of up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Please therefore kindly allow for this within your time planning. All communications are managed online via email because it enables tutorial service support managers to review other communications which have been received before responding and it ensures that there is a copy of all communications retained on file for future reference. All communications will be stored within your personal (CLP) study file here at Appleton Greene throughout your designated study period. If you need any assistance or clarification at any time, please do not hesitate to contact us by forwarding an email and remember that we are here to help. If you have any questions, please list and number your questions succinctly and you can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each and every query.
Time Management
It takes approximately 1 Year to complete the Culture Evolution corporate training program, incorporating 12 x 6-hour monthly workshops. Each student will also need to contribute approximately 4 hours per week over 1 Year of their personal time. Students can study from home or work at their own pace and are responsible for managing their own study plan. There are no formal examinations and students are evaluated and assessed based upon their project study submissions, together with the quality of their internal analysis and supporting documents. They can contribute more time towards study when they have the time to do so and can contribute less time when they are busy. All students tend to be in full time employment while studying and the Culture Evolution program is purposely designed to accommodate this, so there is plenty of flexibility in terms of time management. It makes no difference to us at Appleton Greene, whether individuals take 12-18 months to complete this program. What matters is that in all cases the same standard of quality will have been achieved with the standard and bespoke programs that have been developed.
Distance Learning Guide
The distance learning guide should be your first port of call when starting your training program. It will help you when you are planning how and when to study, how to create the right environment and how to establish the right frame of mind. If you can lay the foundations properly during the planning stage, then it will contribute to your enjoyment and productivity while training later. The guide helps to change your lifestyle in order to accommodate time for study and to cultivate good study habits. It helps you to chart your progress so that you can measure your performance and achieve your goals. It explains the tools that you will need for study and how to make them work. It also explains how to translate academic theory into practical reality. Spend some time now working through your distance learning guide and make sure that you have firm foundations in place so that you can make the most of your distance learning program. There is no requirement for you to attend training workshops or classes at Appleton Greene offices. The entire program is undertaken online, program course manuals and project studies are administered via the Appleton Greene web site and via email, so you are able to study at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office as long as you have a computer and access to the internet.
How To Study
The how to study guide provides students with a clear understanding of the Appleton Greene facilitation via distance learning training methods and enables students to obtain a clear overview of the training program content. It enables students to understand the step-by-step training methods used by Appleton Greene and how course manuals are integrated with project studies. It explains the research and development that is required and the need to provide evidence and references to support your statements. It also enables students to understand precisely what will be required of them in order to achieve a pass with merit and a pass with distinction for individual project studies and provides useful guidance on how to be innovative and creative when developing your Unique Program Proposition (UPP).
Tutorial Support
Tutorial support for the Appleton Greene Culture Evolution corporate training program is provided online either through the Appleton Greene Client Support Portal (CSP), or via email. All tutorial support requests are facilitated by a designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). They are responsible for deciding which professor or tutor is the most appropriate option relating to the support required and then the tutorial support request is forwarded onto them. Once the professor or tutor has completed the tutorial support request and answered any questions that have been asked, this communication is then returned to the student via email by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). This enables all tutorial support, between students, professors and tutors, to be facilitated by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM) efficiently and securely through the email account. You will therefore need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general support queries and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because all tutorial support requests are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Consequently you need to put some thought into the management of your tutorial support procedure in order to ensure that your study plan is feasible and to obtain the maximum possible benefit from tutorial support during your period of study. Please retain copies of your tutorial support emails for future reference. Please ensure that ALL of your tutorial support emails are set out using the format as suggested within your guide to tutorial support. Your tutorial support emails need to be referenced clearly to the specific part of the course manual or project study which you are working on at any given time. You also need to list and number any questions that you would like to ask, up to a maximum of five questions within each tutorial support email. Remember the more specific you can be with your questions the more specific your answers will be too and this will help you to avoid any unnecessary misunderstanding, misinterpretation, or duplication. The guide to tutorial support is intended to help you to understand how and when to use support in order to ensure that you get the most out of your training program. Appleton Greene training programs are designed to enable you to do things for yourself. They provide you with a structure or a framework and we use tutorial support to facilitate students while they practically implement what they learn. In other words, we are enabling students to do things for themselves. The benefits of distance learning via facilitation are considerable and are much more sustainable in the long-term than traditional short-term knowledge sharing programs. Consequently you should learn how and when to use tutorial support so that you can maximize the benefits from your learning experience with Appleton Greene. This guide describes the purpose of each training function and how to use them and how to use tutorial support in relation to each aspect of the training program. It also provides useful tips and guidance with regard to best practice.
Tutorial Support Tips
Students are often unsure about how and when to use tutorial support with Appleton Greene. This Tip List will help you to understand more about how to achieve the most from using tutorial support. Refer to it regularly to ensure that you are continuing to use the service properly. Tutorial support is critical to the success of your training experience, but it is important to understand when and how to use it in order to maximize the benefit that you receive. It is no coincidence that those students who succeed are those that learn how to be positive, proactive and productive when using tutorial support.
Be positive and friendly with your tutorial support emails
Remember that if you forward an email to the tutorial support unit, you are dealing with real people. “Do unto others as you would expect others to do unto you”. If you are positive, complimentary and generally friendly in your emails, you will generate a similar response in return. This will be more enjoyable, productive and rewarding for you in the long-term.
Think about the impression that you want to create
Every time that you communicate, you create an impression, which can be either positive or negative, so put some thought into the impression that you want to create. Remember that copies of all tutorial support emails are stored electronically and tutors will always refer to prior correspondence before responding to any current emails. Over a period of time, a general opinion will be arrived at in relation to your character, attitude and ability. Try to manage your own frustrations, mood swings and temperament professionally, without involving the tutorial support team. Demonstrating frustration or a lack of patience is a weakness and will be interpreted as such. The good thing about communicating in writing, is that you will have the time to consider your content carefully, you can review it and proof-read it before sending your email to Appleton Greene and this should help you to communicate more professionally, consistently and to avoid any unnecessary knee-jerk reactions to individual situations as and when they may arise. Please also remember that the CLP Tutorial Support Unit will not just be responsible for evaluating and assessing the quality of your work, they will also be responsible for providing recommendations to other learning providers and to client contacts within the Appleton Greene global client network, so do be in control of your own emotions and try to create a good impression.
Remember that quality is preferred to quantity
Please remember that when you send an email to the tutorial support team, you are not using Twitter or Text Messaging. Try not to forward an email every time that you have a thought. This will not prove to be productive either for you or for the tutorial support team. Take time to prepare your communications properly, as if you were writing a professional letter to a business colleague and make a list of queries that you are likely to have and then incorporate them within one email, say once every month, so that the tutorial support team can understand more about context, application and your methodology for study. Get yourself into a consistent routine with your tutorial support requests and use the tutorial support template provided with ALL of your emails. The (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit will not spoon-feed you with information. They need to be able to evaluate and assess your tutorial support requests carefully and professionally.
Be specific about your questions in order to receive specific answers
Try not to write essays by thinking as you are writing tutorial support emails. The tutorial support unit can be unclear about what in fact you are asking, or what you are looking to achieve. Be specific about asking questions that you want answers to. Number your questions. You will then receive specific answers to each and every question. This is the main purpose of tutorial support via email.
Keep a record of your tutorial support emails
It is important that you keep a record of all tutorial support emails that are forwarded to you. You can then refer to them when necessary and it avoids any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Individual training workshops or telephone support
Please be advised that Appleton Greene does not provide separate or individual tutorial support meetings, workshops, or provide telephone support for individual students. Appleton Greene is an equal opportunities learning and service provider and we are therefore understandably bound to treat all students equally. We cannot therefore broker special financial or study arrangements with individual students regardless of the circumstances. All tutorial support is provided online and this enables Appleton Greene to keep a record of all communications between students, professors and tutors on file for future reference, in accordance with our quality management procedure and your terms and conditions of enrolment. All tutorial support is provided online via email because it enables us to have time to consider support content carefully, it ensures that you receive a considered and detailed response to your queries. You can number questions that you would like to ask, which relate to things that you do not understand or where clarification may be required. You can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each individual query. You will also then have a record of these communications and of all tutorial support, which has been provided to you. This makes tutorial support administration more productive by avoiding any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Tutorial Support Email Format
You should use this tutorial support format if you need to request clarification or assistance while studying with your training program. Please note that ALL of your tutorial support request emails should use the same format. You should therefore set up a standard email template, which you can then use as and when you need to. Emails that are forwarded to Appleton Greene, which do not use the following format, may be rejected and returned to you by the (CLP) Program Administration Manager. A detailed response will then be forwarded to you via email usually within 20 business days of receipt for general support queries and 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Your tutorial support request, together with the corresponding TSU reply, will then be saved and stored within your electronic TSU file at Appleton Greene for future reference.
Subject line of your email
Please insert: Appleton Greene (CLP) Tutorial Support Request: (Your Full Name) (Date), within the subject line of your email.
Main body of your email
Please insert:
1. Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) Tutorial Support Request
2. Your Full Name
3. Date of TS request
4. Preferred email address
5. Backup email address
6. Course manual page name or number (reference)
7. Project study page name or number (reference)
Subject of enquiry
Please insert a maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Briefly outline the subject matter of your inquiry, or what your questions relate to.
Question 1
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 3
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 4
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 5
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Please note that a maximum of 5 questions is permitted with each individual tutorial support request email.
Procedure
* List the questions that you want to ask first, then re-arrange them in order of priority. Make sure that you reference them, where necessary, to the course manuals or project studies.
* Make sure that you are specific about your questions and number them. Try to plan the content within your emails to make sure that it is relevant.
* Make sure that your tutorial support emails are set out correctly, using the Tutorial Support Email Format provided here.
* Save a copy of your email and incorporate the date sent after the subject title. Keep your tutorial support emails within the same file and in date order for easy reference.
* Allow up to 20 business days for a response to general tutorial support emails and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because detailed individual responses will be made in all cases and tutorial support emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received.
* Emails can and do get lost. So if you have not received a reply within the appropriate time, forward another copy or a reminder to the tutorial support unit to be sure that it has been received but do not forward reminders unless the appropriate time has elapsed.
* When you receive a reply, save it immediately featuring the date of receipt after the subject heading for easy reference. In most cases the tutorial support unit replies to your questions individually, so you will have a record of the questions that you asked as well as the answers offered. With project studies however, separate emails are usually forwarded by the tutorial support unit, so do keep a record of your own original emails as well.
* Remember to be positive and friendly in your emails. You are dealing with real people who will respond to the same things that you respond to.
* Try not to repeat questions that have already been asked in previous emails. If this happens the tutorial support unit will probably just refer you to the appropriate answers that have already been provided within previous emails.
* If you lose your tutorial support email records you can write to Appleton Greene to receive a copy of your tutorial support file, but a separate administration charge may be levied for this service.

How To Study
Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can help you to plan a task list for getting started so that you can be clear about your direction and your priorities in relation to your training program. It is also a good way to introduce yourself to the tutorial support team.
Planning your study environment
Your study conditions are of great importance and will have a direct effect on how much you enjoy your training program. Consider how much space you will have, whether it is comfortable and private and whether you are likely to be disturbed. The study tools and facilities at your disposal are also important to the success of your distance-learning experience. Your tutorial support unit can help with useful tips and guidance, regardless of your starting position. It is important to get this right before you start working on your training program.
Planning your program objectives
It is important that you have a clear list of study objectives, in order of priority, before you start working on your training program. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance here to ensure that your study objectives have been afforded due consideration and priority.
Planning how and when to study
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. This approach is designed to let you study efficiently away from the traditional classroom environment. It is important however, that you plan how and when to study, so that you are making the most of your natural attributes, strengths and opportunities. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance and useful tips to ensure that you are playing to your strengths.
Planning your study tasks
You should have a clear understanding of the study tasks that you should be undertaking and the priority associated with each task. These tasks should also be integrated with your program objectives. The distance learning guide and the guide to tutorial support for students should help you here, but if you need any clarification or assistance, please contact your tutorial support unit.
Planning your time
You will need to allocate specific times during your calendar when you intend to study if you are to have a realistic chance of completing your program on time. You are responsible for planning and managing your own study time, so it is important that you are successful with this. Your tutorial support unit can help you with this if your time plan is not working.
Keeping in touch
Consistency is the key here. If you communicate too frequently in short bursts, or too infrequently with no pattern, then your management ability with your studies will be questioned, both by you and by your tutorial support unit. It is obvious when a student is in control and when one is not and this will depend how able you are at sticking with your study plan. Inconsistency invariably leads to in-completion.
Charting your progress
Your tutorial support team can help you to chart your own study progress. Refer to your distance learning guide for further details.
Making it work
To succeed, all that you will need to do is apply yourself to undertaking your training program and interpreting it correctly. Success or failure lies in your hands and your hands alone, so be sure that you have a strategy for making it work. Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can guide you through the process of program planning, development and implementation.
Reading methods
Interpretation is often unique to the individual but it can be improved and even quantified by implementing consistent interpretation methods. Interpretation can be affected by outside interference such as family members, TV, or the Internet, or simply by other thoughts which are demanding priority in our minds. One thing that can improve our productivity is using recognized reading methods. This helps us to focus and to be more structured when reading information for reasons of importance, rather than relaxation.
Speed reading
When reading through course manuals for the first time, subconsciously set your reading speed to be just fast enough that you cannot dwell on individual words or tables. With practice, you should be able to read an A4 sheet of paper in one minute. You will not achieve much in the way of a detailed understanding, but your brain will retain a useful overview. This overview will be important later on and will enable you to keep individual issues in perspective with a more generic picture because speed reading appeals to the memory part of the brain. Do not worry about what you do or do not remember at this stage.
Content reading
Once you have speed read everything, you can then start work in earnest. You now need to read a particular section of your course manual thoroughly, by making detailed notes while you read. This process is called Content Reading and it will help to consolidate your understanding and interpretation of the information that has been provided.
Making structured notes on the course manuals
When you are content reading, you should be making detailed notes, which are both structured and informative. Make these notes in a MS Word document on your computer, because you can then amend and update these as and when you deem it to be necessary. List your notes under three headings: 1. Interpretation – 2. Questions – 3. Tasks. The purpose of the 1st section is to clarify your interpretation by writing it down. The purpose of the 2nd section is to list any questions that the issue raises for you. The purpose of the 3rd section is to list any tasks that you should undertake as a result. Anyone who has graduated with a business-related degree should already be familiar with this process.
Organizing structured notes separately
You should then transfer your notes to a separate study notebook, preferably one that enables easy referencing, such as a MS Word Document, a MS Excel Spreadsheet, a MS Access Database, or a personal organizer on your cell phone. Transferring your notes allows you to have the opportunity of cross-checking and verifying them, which assists considerably with understanding and interpretation. You will also find that the better you are at doing this, the more chance you will have of ensuring that you achieve your study objectives.
Question your understanding
Do challenge your understanding. Explain things to yourself in your own words by writing things down.
Clarifying your understanding
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your understanding.
Question your interpretation
Do challenge your interpretation. Qualify your interpretation by writing it down.
Clarifying your interpretation
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your interpretation.
Qualification Requirements
The student will need to successfully complete the project study and all of the exercises relating to the Culture Evolution corporate training program, achieving a pass with merit or distinction in each case, in order to qualify as an Accredited Culture Evolution Specialist (ACES). All monthly workshops need to be tried and tested within your company. These project studies can be completed in your own time and at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office. There are no formal examinations, assessment is based upon the successful completion of the project studies. They are called project studies because, unlike case studies, these projects are not theoretical, they incorporate real program processes that need to be properly researched and developed. The project studies assist us in measuring your understanding and interpretation of the training program and enable us to assess qualification merits. All of the project studies are based entirely upon the content within the training program and they enable you to integrate what you have learnt into your corporate training practice.
Culture Evolution – Grading Contribution
Project Study – Grading Contribution
Customer Service – 10%
E-business – 05%
Finance – 10%
Globalization – 10%
Human Resources – 10%
Information Technology – 10%
Legal – 05%
Management – 10%
Marketing – 10%
Production – 10%
Education – 05%
Logistics – 05%
TOTAL GRADING – 100%
Qualification grades
A mark of 90% = Pass with Distinction.
A mark of 75% = Pass with Merit.
A mark of less than 75% = Fail.
If you fail to achieve a mark of 75% with a project study, you will receive detailed feedback from the Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and/or Accredited Consultant, together with a list of tasks which you will need to complete, in order to ensure that your project study meets with the minimum quality standard that is required by Appleton Greene. You can then re-submit your project study for further evaluation and assessment. Indeed you can re-submit as many drafts of your project studies as you need to, until such a time as they eventually meet with the required standard by Appleton Greene, so you need not worry about this, it is all part of the learning process.
When marking project studies, Appleton Greene is looking for sufficient evidence of the following:
Pass with merit
A satisfactory level of program understanding
A satisfactory level of program interpretation
A satisfactory level of project study content presentation
A satisfactory level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
A satisfactory level of the practical integration of academic theory
Pass with distinction
An exceptional level of program understanding
An exceptional level of program interpretation
An exceptional level of project study content presentation
An exceptional level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
An exceptional level of the practical integration of academic theory
Preliminary Analysis
Reading
Here are some specific readings to prepare you to enter the context of Culture Evolution. They are not an essential prerequisite but will prepare you with insights from thought leaders into various elements of organizational culture.
Books – Examples of Companies
• Collins, J. C. (2001). Good to Great: Why Some Companies Make the Leap… and Others Don’t. HarperBusiness.
(This book examines the culture of successful companies and how it contributes to their long-term success.)
• Collins, J. C. (2009). How the Mighty Fall: And Why Some Companies Never Give In. HarperBusiness.
(In this book, Collins explores the downfall of once-successful companies and how their culture played a role in their decline.)
• Fishman, C. (2006). The Wal-Mart Effect: How the World’s Most Powerful Company Really Works–and How It’s Transforming the American Economy. Penguin Books.
(This book delves into the culture and practices of Walmart and how they have shaped the company’s success and impact on the economy.)
• Hsieh, T. (2010). Delivering Happiness: A Path to Profits, Passion, and Purpose. Business Plus.
(This book shares the story of Zappos and its unique culture, highlighting how a strong emphasis on customer service and employee happiness can drive success.)
• Catmull, E., & Wallace, A. (2014). Creativity, Inc.: Overcoming the Unseen Forces That Stand in the Way of True Inspiration. Random House.
(This book explores the culture of Pixar Animation Studios and how it fosters creativity and innovation, leading to their success in the film industry.)
• Reed Hastings & Erin Meyer (2020). No Rules Rules: Netflix and the Culture of Reinvention. Penguin Press.
(This book provides insights into the unique culture and management practices of Netflix, which have contributed to its success as a disruptive force in the entertainment industry.)
• O’Reilly, C. A. & Pfeffer, J. (2000). Hidden Value: How Great Companies Achieve Extraordinary Results with Ordinary People. Harvard Business Review Press.
(This book examines the culture and management practices of successful companies and how they leverage their people to achieve exceptional results.)

Books – General
• Lencioni, P. (2002). The Five Dysfunctions of a Team: A Leadership Fable. Jossey-Bass.
(This book uses a fictional story to illustrate the impact of team dynamics and culture on organizational success.)
• “The Culture Code: The Secrets of Highly Successful Groups” by Daniel Coyle
(This book explores the key elements that contribute to a strong and successful organizational culture.)
• “The Culture Code: Creating a High-Performing Culture” by Daniel Coyle
(Coyle’s book delves into the science behind building a high-performing culture and provides practical strategies for creating a culture of excellence.)
• “Organizational Culture and Leadership” by Edgar H. Schein
(Schein’s book provides a comprehensive understanding of organizational culture and its impact on leadership and performance.)
• “The Corporate Culture Survival Guide” by Edgar H. Schein
(This book offers practical advice and strategies for managing and transforming
organizational culture.)
• “The Advantage: Why Organizational Health Trumps Everything Else in Business” by Patrick Lencioni
(Lencioni discusses the importance of a healthy organizational culture and how it can drive business success.)
• “The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization” by Peter M. Senge
(Senge’s book discusses the concept of a learning organization and how it can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.)

Video Reference Links
• Simon Sinek: How to start a cultural transformation?
• How Southwest Airlines built its culture | Herb Kelleher | WOBI
• Why Your Organizational Culture Should Always be Evolving
• 3 ways to create a work culture that brings out the best in employees

Metrics Available within Your Organization
In order to prepare for and maximize the value of Workshop 1 of Culture Innovation, it will be useful to start by taking stock of the metrics currently available within your organization to measure and evaluate your existing culture, such as:
• Employee engagement surveys
• Information flows and channels within the organization
• Cross-functional collaboration measures
• Innovation and creativity metrics such as the number of ideas generated, successful implementation of innovative projects, and level of risk-taking within the organization
• Diversity and inclusion measures such as representation of different demographics, employee satisfaction with diversity measures, and the presence of inclusive policies and practices
• Employee well-being metrics such as absenteeism rates, employee assistance program utilization, and employee satisfaction with work-life balance
• Assessment of the extent to which employees understand, align with and demonstrate the organization’s values
• Measures of the opportunities provided for employee development and growth, training participation, promotion rates, and employee satisfaction with learning & development programs
• Evaluate the organization’s ability to attract and retain talent, looking at turnover rates, exit interview feedback, clearly communicated employee value proposition, and employee satisfaction with career progression opportunities
• Any other metrics that you feel provide insights into the health of your organization’s culture, and which will help in identifying areas for improvement or reinforcement
Course Manuals 1-12
Course Manual 1: Understanding Culture
Why is understanding Culture so important?
Culture is a fundamental aspect of any organization, shaping its values, beliefs, and behaviors. In this section, we will delve into the concept of organizational culture, exploring its definition, importance, and various dimensions. Through quotes, analysis, and charts, we will gain a comprehensive understanding of culture’s impact on organizations.
Quote: “Culture eats strategy for breakfast.” – Peter Drucker
Understanding culture is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, culture shapes employee behavior and attitudes, impacting their motivation, engagement, and productivity. Secondly, culture influences decision-making processes, as individuals make choices based on the values and norms embedded in the organization’s culture. Lastly, culture plays a significant role in attracting and retaining talent, as employees seek organizations with cultures that align with their own values.
What is the definition of Organizational Culture?
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and assumptions that guide the behavior of individuals within an organization. It is the collective personality of the organization, influencing how employees interact, make decisions, and perceive their work environment.

Exercise
– Divide the participants into two teams of five.
1. Introducing the exercise:
“We have a competitive exercise for each team that will test your collective knowledge and experience. Teamwork will be required, and your analytical skills will be tested. The team that demonstrates the best understanding of sensory perception will be declared the winner!”
– Explain that each team will take turns describing a scent or aroma without using any visual or physical cues.
– The other team will then try to guess the scent based solely on the verbal description.
– Each team will have 1 minute to describe and guess the scent.
– After 1 minute, switch roles, and the other team will describe a different scent.
– As the facilitator, you can intervene if necessary to clarify any points that affect both teams.
– Encourage participants to focus on using descriptive language and paying attention to subtle cues and nuances.
– After the exercise, gather the participants and announce the winning team.
– Ask the question: “In what ways can identifying scents through sensory perception and identifying the culture of an organization be similar?”
– Facilitate a discussion and encourage participants to share their thoughts on the similarities between sensory perception and understanding organizational culture.
– Summarize the key takeaways on a flipchart or similar.
1. Sensory Perception: Just like identifying scents requires a keen sense of smell, identifying the culture of an organization requires a keen sense of observation. Both processes involve paying attention to subtle cues and nuances.
By exploring the concept of sensory perception, this exercise helps participants understand the similarities between identifying scents and identifying organizational culture. It highlights the importance of paying attention to subtle cues, using descriptive language, and recognizing the complexity and subjective nature of understanding organizational culture.
What are some of the dimensions or facets of Organizational Culture?
To understand culture, it is crucial to recognize its multifaceted nature. Edgar Schein’s model of organizational culture provides some valuable insights. Schein’s Model was developed while a professor at MIT, in 1980. The model focuses on how company culture impacts an organization’s functioning, emphasizing learning and group dynamics.
Quote: Culture is both a dynamic phenomenon that surrounds us at all times, being constantly enacted and created by our interactions with others and shaped by leadership behavior, and a set of structures, routines, rules, and norms that guide and constrain behavior.— Organisational Culture and Leadership, 3rd edition – Edgar Schein, 2004
Culture Evolution: According to Schein, organizational culture evolves as employees adapt to changes, handle external challenges, and solve problems. This culture affects how employees feel and behave within the organization.
Schein identifies three levels of culture that each represent different depths of cultural understanding: artifacts and behaviors, espoused values, and underlying assumptions. These levels interact to shape the overall culture of an organization.
Artifacts: These are visible elements like office layout, dress code, and behaviors. They provide surface insights into culture but altering them doesn’t necessarily lead to significant change.
Espoused Values: These are deeper than artifacts and include values communicated through mission statements, charters, and values. They offer more insight into culture and can be changed to influence culture.
Underlying Assumptions/Beliefs: These are the deepest and hardest-to-change cultural elements. They encompass subconscious assumptions about work, success, and failure. They significantly shape culture but aren’t usually documented.
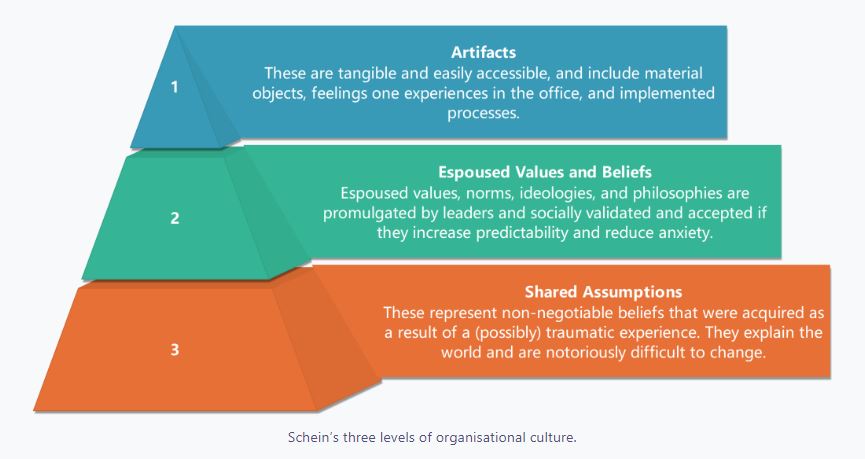
Credit: Georges Lteiff (2023)
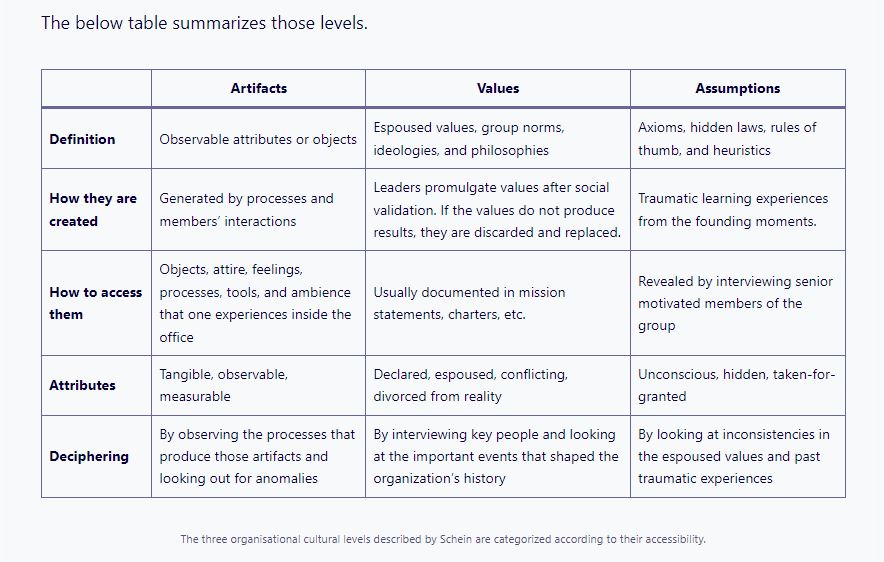
Credit: Georges Lteiff (2023)
These charts can be used to facilitate discussions and encourage participants to identify examples of artifacts, values, and assumptions within their own organizations.
Organizational culture can be examined through various lenses.
Another commonly used framework is the Competing Values Framework (CVF). Researchers Robert Quinn and Kim Cameron came to the conclusion that one must examine two factors when describing an organization’s cultural typology; the degree of flexibility versus controlling behavior and internal focus versus external orientation.
The CVF identifies four cultural types: Clan, Adhocracy, Hierarchy, and Market. Each type represents different values and behaviors, providing a framework for understanding and assessing organizational culture.
Below is a brief explanation of each culture to understand the context of Competing Values Framework:
Clan culture: high degree of flexibility and internally focused. In these organizations, the relationship between people is central. There is a friendly working environment, in which employees have a lot in common. Think of start-ups, family businesses, or small Information Technology (ICT) companies. These organizations resemble a large family. The leaders of these organizations are considered to be mentors or even father figures, who employees can approach very easily. These organizations are held together by loyalty and tradition. Mutual commitment is large, and operations focus on human resources. Relationships, loyalty, and morality are very strong, and success is partly defined on the basis of customer satisfaction. The organization places great value on teamwork, participation, flexibility, and consensus.
Hierarchical culture: high degree of controlling behavior and internally focused. Hierarchical cultures are extremely formal and have a structured working environment. Government agencies are perfectly suited to this culture. Procedures determine employee actions, and the focus is on managing control systems. As a result, there are clearly structured hierarchical layers present in the organization. All work processes are efficiently organized, so that everything is under control and can easily be adjusted. It is important that the organization runs smoothly. Formal rules and policies stabilize the organization. Stability and results are associated with efficient and smooth execution of tasks. Success is generated from reliable supply, tight scheduling, and low costs.
Market culture: high degree of controlling behavior and externally focused. In these types of organizations, it is all about results and the completion of the work. Employees are competitive people and extremely goal oriented. Examples of such organizations are trade associations, insurance companies, and banks. Managers are often demanding and closely follow employee activities. Simultaneously, there is a lot of mutual competition. Within these organizations, the emphasis is on reputation, success, and winning. They will always strive to achieve measurable goals and objectives. Success is translated into market share and penetration. To the outside world, these organizations want to profile themselves through competitive pricing and market leadership. To stay ahead of the competition, there is ruthless competition to maintain customer retention. Customer service and satisfaction are terms that all employees are aware of.
Adhocracy culture: high degree of flexibility and externally focused. In these organisations innovation is key; constant innovation with the aim to remain visible in the market. Research organizations such as the Dutch TNO (Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research) or marketing and advertising agencies usually have such a culture. There is a dynamic, enterprising, and creative work environment, in which employees are encouraged to strive for innovation and use their creativity to create new ideas. Besides innovators, the managers are also risk takers. Such organizations wish to be leaders and at the forefront of new products and/or services. For this reason, they encourage individual initiative and allow the freedom to determine which tasks to execute.
In summary, the Competing Values Framework (CVF) offers valuable insights into the dimensions of organizational culture. The Clan culture emphasizes collaboration, teamwork, and employee development. The Adhocracy culture focuses on innovation, risk-taking, and adaptability. The Hierarchy culture values stability, rules, and efficiency. The Market culture emphasizes competition, results, and customer focus.
By analyzing these cultural types, organizations can identify their dominant culture and assess its alignment with their goals and values.
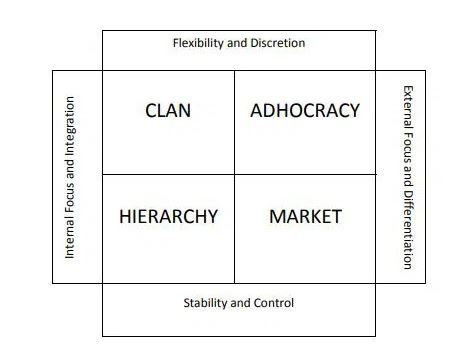
This chart can be used to facilitate discussions and encourage participants to identify which cultural type(s) resonate with that of their own organization.

Supplementary Exercise 1:2 – The “Culture Iceberg Activity.”

Case Study
Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, is renowned for its unique organizational culture, which has played a significant role in its success. Here is a brief case study highlighting some key aspects of Zappos’ culture and its impact:
1. Core Values: Zappos places a strong emphasis on its core values, which include delivering “WOW” through exceptional customer service, embracing and driving change, creating fun and a little weirdness, and being adventurous, creative, and open-minded. These values guide the company’s decisions and actions.
2. Employee Empowerment: Zappos believes in empowering its employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work. Customer service representatives are not bound by scripts and are encouraged to go above and beyond to satisfy customers. This autonomy fosters a sense of ownership and accountability.
3. Cultural Fit: Zappos places great importance on hiring individuals who align with its culture. During the hiring process, candidates go through multiple interviews, including a cultural fit interview, where they are assessed based on their alignment with the company’s values and culture.
4. Holacracy: Zappos implemented a unique management structure called Holacracy, which replaces traditional hierarchical systems with self-organizing teams. This approach promotes autonomy, transparency, and collaboration, allowing employees to contribute and make decisions at all levels.
5. Customer Loyalty: Zappos’ strong focus on customer service has resulted in exceptional customer loyalty. The company is known for its free shipping and returns policy, which has contributed to a high customer retention rate. In fact, repeat customers account for a significant portion of Zappos’ sales.
6. Financial Success: Zappos’ commitment to its culture has translated into financial success. In 2009, the company reported annual revenues of over $1 billion, and by 2019, it had reached $3 billion in annual sales. This growth can be attributed, in part, to the positive impact of its unique culture on customer satisfaction and employee engagement.
Zappos’ organizational culture has not only contributed to its financial success but has also garnered recognition and accolades. The company has been consistently ranked among the best places to work and has received numerous awards for its customer service and company culture.

Understanding Organizational Culture: A Crucial Element Impacting Every Aspect of Business
Organizational culture plays a pivotal role in shaping the success and sustainability of any business. It encompasses the shared values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors that define how individuals within an organization interact and work towards common goals. Understanding and effectively managing organizational culture is essential as it influences employee engagement, productivity, innovation, decision-making, and overall business performance. Let us explore the significance of comprehending organizational culture and its impact on various aspects of a business.
1. The Definition and Components of Organizational Culture:
Organizational culture is a complex concept that encompasses various elements. As we have considered, according to Edgar Schein, a renowned organizational culture expert, it consists of three levels: artifacts and behaviors, espoused values, and underlying assumptions. Artifacts and behaviors are visible manifestations of culture, such as dress code, office layout, and communication styles. Espoused values represent the stated beliefs and principles of an organization, while underlying assumptions are the unconscious beliefs and perceptions that guide behavior.
Understanding the different components of organizational culture is crucial for leaders to effectively manage and shape it. By recognizing the visible artifacts and behaviors, leaders can gain insights into the prevailing culture. However, it is equally important to delve deeper into the espoused values and underlying assumptions to truly understand the essence of the culture.
2. Employee Engagement and Productivity:
Organizational culture significantly impacts employee engagement and productivity. A positive culture that fosters trust, collaboration, and open communication encourages employees to be more engaged and motivated. Research by Gallup shows that engaged employees are 21% more productive than their disengaged counterparts. When employees feel a sense of belonging and alignment with the organizational culture, they are more likely to invest their time and effort into their work.
By understanding and aligning with the organizational culture, leaders can create an environment that promotes employee satisfaction, loyalty, and commitment. This can be achieved by establishing clear expectations, providing opportunities for growth and development, and recognizing and rewarding employees’ contributions. When employees feel valued and connected to the culture, they are more likely to go above and beyond in their roles, leading to increased productivity and overall business success.
3. Innovation and Adaptability:
Organizational culture plays a crucial role in fostering innovation and adaptability. A culture that encourages risk-taking, experimentation, and learning from failures promotes innovation and creativity. In contrast, a culture that is resistant to change and stifles new ideas can hinder growth and competitiveness.
Understanding the existing culture enables leaders to identify areas for improvement and create an environment that supports innovation and adaptability. By promoting a culture of continuous learning, encouraging diverse perspectives, and providing resources for experimentation, organizations can foster a culture that embraces change and drives innovation. This, in turn, enables businesses to stay ahead of the competition and adapt to evolving market dynamics.
4. Decision-Making and Problem-Solving:
Organizational culture influences decision-making processes and problem-solving approaches within a business. Different cultures may prioritize different decision-making styles, such as hierarchical, participative, or consensus-based. By understanding the prevailing culture, leaders can adapt their decision-making processes to align with the organization’s values and norms.
For instance, in a hierarchical culture, decisions may be made by top-level executives, while in a participative culture, decisions may involve input from various levels of the organization. By aligning decision-making processes with the culture, leaders can enhance decision quality, reduce conflicts, and improve overall organizational effectiveness. This ensures that decisions are made in a manner that resonates with employees and promotes a sense of ownership and commitment.
5. Organizational Communication and Collaboration:
Effective communication and collaboration are vital for the success of any business. Organizational culture shapes communication patterns, channels, and the overall flow of information within an organization. Understanding the culture helps leaders identify communication gaps, barriers, and opportunities for improvement.
By fostering a culture of open communication and collaboration, organizations can enhance teamwork, knowledge sharing, and overall organizational performance. This can be achieved by promoting transparent communication channels, encouraging feedback and suggestions, and creating platforms for cross-functional collaboration. When employees feel comfortable expressing their ideas and opinions, it leads to increased innovation, better problem-solving, and stronger relationships within the organization.
6. Organizational Change and Transformation:
Organizational culture plays a critical role in managing change and transformation initiatives. Change efforts that are not aligned with the existing culture often face resistance and may fail to achieve desired outcomes. By understanding the culture, leaders can anticipate potential challenges, develop change strategies that resonate with employees, and create a supportive environment for successful transformation.
Leaders must assess the current culture and identify areas that need to be addressed to support the desired change. This may involve aligning values, revising policies and procedures, and providing training and support to employees. By actively involving employees in the change process and ensuring that the new culture aligns with their values and aspirations, organizations can increase the likelihood of successful change implementation.
Conclusion
Understanding organizational culture is paramount as it impacts every aspect of a business. By comprehending the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that define an organization, leaders can shape a positive culture that enhances employee engagement, productivity, innovation, decision-making, and overall business performance. Chapter 1 has highlighted the significance of understanding organizational culture and its role in driving success in today’s dynamic business environment.
Organizational culture is not a static entity but rather an evolving aspect that requires continuous attention and nurturing. By recognizing the importance of understanding and managing culture, leaders can create an environment that fosters employee satisfaction, promotes innovation, facilitates effective decision-making, and supports successful change initiatives. Embracing and leveraging organizational culture can be a powerful tool for businesses to thrive in an ever-changing and competitive landscape.
Understanding organizational culture is essential for creating a thriving and engaged workforce. By exploring the definition, importance, and dimensions of culture, participants gain insights into how it influences employee behavior, decision-making processes, and overall performance.
The provided exercises and case studies further enhance participants’ understanding and provide practical examples of culture in action.
Schein’s Model and The Competing Values Framework (CVF) are valuable tools for assessing and understanding different cultural types.
Recognizing the critical impact of culture on every aspect of the business in all organizations allows for intentional culture development and alignment with strategic goals.
As Peter Drucker famously stated, culture plays a pivotal role in shaping an organization’s success, making it a crucial area of focus for any business strategy.
Course Manual 2: Organizational Analysis
Introduction:
Organizational analysis is a critical step in understanding and assessing the current state of an organization’s culture. In this section, we will explore the importance of conducting an organizational analysis, the methods and tools involved, and how it will contribute to the overall understanding of culture. In this chapter, we will gain insights into the process of organizational analysis and its impact on culture transformation.
Quote: “Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.” – W. Edwards Deming
Importance of Organizational Analysis:
Organizational analysis provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s culture, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. It helps identify gaps between the desired and actual culture, enabling the development of strategies to bridge those gaps effectively. By conducting an analysis, organizations gain valuable insights into their current position and can make informed decisions to align their culture with their business strategy and goals.
Methods and Tools for Organizational Analysis:
There are various methods and tools available for conducting an organizational analysis. One commonly used approach is the Culture Scan, which involves gathering data through surveys, interviews, and observations. This data provides a holistic view of the organization’s culture, including its values, behaviors, and underlying assumptions. Other tools, such as cultural assessments and employee engagement surveys, can also be utilized to gather relevant data.
Analysis:
The above-mentioned Culture Scan is a powerful and effective tool. It allows for a comprehensive examination of the organization’s culture by collecting data from multiple sources. This data can then be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and areas of misalignment, from which organizations can gain insights into the strengths and weaknesses of their culture, enabling them to develop targeted strategies for improvement.
Culture Scan Process:
This chart illustrates the steps involved in the Culture Scan Process to understand the sequence and flow of conducting an organizational analysis. This visual representation can serve as a guide for organizations to follow when embarking on their own analysis journey.
IMAGE TOO DETAILED
1. Define the purpose: Clearly articulate the purpose of conducting the organizational culture analysis. This could be to identify strengths and weaknesses, align culture with strategic goals, or address specific cultural challenges.
2. Identify key stakeholders: Determine the key stakeholders who should be involved in the analysis process. This may include senior leaders, HR professionals, department heads, and employees from various levels and departments.
3. Select data collection methods: Choose the data collection methods that will be used to gather information about the organization’s culture. This could include surveys, interviews, focus groups, document analysis, and observation.
4. Develop data collection tools: Create the necessary tools for data collection, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, and focus group protocols. Ensure that these tools are aligned with the purpose of the analysis and will provide the desired insights.
5. Determine the sample size and selection: Decide on the appropriate sample size and selection criteria for the data collection. Consider factors such as representation across departments, levels, and demographics to ensure a comprehensive analysis.
6. Conduct data collection: Implement the chosen data collection methods, ensuring that participants understand the purpose and confidentiality of the analysis. Collect data through surveys, interviews, focus groups, document reviews, and observations as planned.
7. Analyze the data: Once the data is collected, analyze it using appropriate qualitative and/or quantitative analysis techniques. This may involve coding and categorizing qualitative data, conducting statistical analysis on survey responses, or identifying patterns and themes.
8. Identify key findings: Identify the key findings and insights that emerge from the data analysis. Look for patterns, trends, and areas of strength or improvement in the organization’s culture.
9. Develop recommendations: Based on the findings, develop actionable recommendations to address any identified gaps or challenges in the organization’s culture. These recommendations should be aligned with the purpose of the analysis and the desired outcomes.
10. Create a culture analysis report: Compile the findings, insights, and recommendations into a comprehensive culture analysis report. Include an executive summary, methodology, key findings, recommendations, and any supporting data or visuals.
11. Present the findings: Present the culture analysis findings and recommendations to the key stakeholders and decision-makers in the organization. Use visuals, charts, and graphs to effectively communicate the information and engage the audience.
12. Implement the recommendations: Work with the relevant stakeholders to implement the recommended actions and initiatives to align the culture with the desired outcomes. Monitor progress and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps that outline the sequence and flow of the organizational culture analysis process, you can ensure a systematic and comprehensive approach to understanding and improving the organization’s culture.
The Organizational Culture Assessment Instrument (OCAI)
The Organizational Culture Assessment Instrument (OCAI) is a widely used tool for analyzing an organization’s culture. It was developed by Cameron and Quinn and is based on the Competing Values Framework which we detailed in the previous chapter. The OCAI assesses an organization’s culture based on four dimensions: Clan, Adhocracy, Market, and Hierarchy.
This is a simplified version of the OCAI questionnaire that you can use to analyze your organization’s culture:
Instructions: Please rate your organization on each of the following statements using a scale of 1 to 5, where 1 represents “Strongly Disagree” and 5 represents “Strongly Agree.”
1. Clan Culture:
– Our organization emphasizes teamwork, collaboration, and employee involvement.
– Our organization values loyalty, trust, and a family-like atmosphere.
– Our organization encourages open communication and values employee opinions.
– Our organization focuses on long-term development and employee well-being.
2. Adhocracy Culture:
– Our organization values innovation, creativity, and risk-taking.
– Our organization encourages employees to take initiative and be entrepreneurial.
– Our organization is flexible and adaptable to change.
– Our organization rewards and recognizes employees for their innovative ideas.
3. Market Culture:
– Our organization is results-oriented and focused on achieving goals.
– Our organization values competitiveness and winning in the marketplace.
– Our organization emphasizes customer satisfaction and meeting customer needs.
– Our organization rewards and recognizes employees based on their performance.
4. Hierarchy Culture:
– Our organization values stability, predictability, and efficiency.
– Our organization has clear rules, procedures, and formalized structures.
– Our organization emphasizes following established processes and protocols.
– Our organization rewards and recognizes employees based on their adherence to rules
and procedures.
Scoring: Calculate the average score for each dimension by summing up the ratings for each statement and dividing it by the number of statements in that dimension. The highest possible score for each dimension is 5.
Interpreting the Results: Once you have calculated the average scores for each dimension, you can plot them on a Competing Values Framework grid (find in Chapter 1) to visualize the organization’s culture. The quadrant with the highest score represents the dominant culture of the organization.
Note: This simplified version of the OCAI questionnaire will not capture the full complexity of an organization’s culture. For a more comprehensive analysis, there is great value in considering numerous different data sources.

Case Study: Google’s Organizational Culture Analysis and Transformation
Introduction: Google is a multinational technology company known for its innovative products and services. To maintain its competitive edge and foster a thriving work environment, Google conducted an organizational culture analysis to understand its culture, identify areas for improvement, and drive culture transformation. This analysis played a crucial role in shaping Google’s success and reinforcing its core values.
Organizational Culture Analysis: Google recognized the importance of its culture in driving innovation, collaboration, and employee satisfaction. To gain insights into its culture, Google utilized various data collection methods, including employee surveys, interviews, and focus groups. The analysis aimed to assess the alignment between the desired culture and the actual culture within the organization.
Key Findings: The culture analysis revealed several strengths in Google’s culture, such as a strong emphasis on innovation, a flat organizational structure that encouraged open communication, and a focus on employee well-being. However, it also identified areas for improvement, including the need for more diversity and inclusion, better work-life balance, and increased transparency in decision-making processes.
Culture Transformation Initiatives: Based on the analysis findings, Google implemented several initiatives to transform its culture and address the identified areas for improvement:
1. Diversity and Inclusion: Google launched comprehensive diversity and inclusion programs to foster a more inclusive culture. This included unconscious bias training, diverse hiring practices, and employee resource groups to support underrepresented communities.
2. Work-Life Balance: Recognizing the importance of work-life balance, Google introduced initiatives such as flexible work hours, remote work options, and wellness programs to support employee well-being and reduce burnout.
3. Transparency and Communication: To enhance transparency, Google implemented regular town hall meetings, increased access to information, and encouraged open dialogue between employees and leadership. This helped to improve trust and alignment within the organization.
4. Learning and Development: Google invested in employee learning and development programs to foster continuous growth and skill development. This included providing opportunities for employees to attend conferences, workshops, and internal training sessions.
Results and Organizational Success: The culture transformation initiatives driven by the organizational culture analysis had a significant impact on Google’s success:
1. Innovation and Productivity: By reinforcing its culture of innovation, Google continued to develop groundbreaking products and services, maintaining its position as a market leader.
2. Employee Satisfaction and Retention: The culture transformation initiatives improved employee satisfaction and engagement, leading to higher retention rates and attracting top talent.
3. Reputation and Employer Branding: Google’s commitment to fostering a positive culture and addressing areas for improvement enhanced its reputation as an employer of choice, attracting skilled professionals from diverse backgrounds.
4. Collaboration and Teamwork: The culture transformation initiatives promoted collaboration and teamwork, enabling employees to work together more effectively and drive collective success.
Conclusion: Google’s organizational culture analysis played a pivotal role in driving culture transformation and contributing to its organizational success. By identifying areas for improvement and implementing targeted initiatives, Google was able to align its culture with its core values, foster innovation, enhance employee satisfaction, and maintain its position as a leading technology company. This case study highlights the importance of regularly assessing and evolving
Conducting a comprehensive Culture Scan of an organization:
The Culture Scan would not be complete without utilizing other diverse data sources. Using multiple data points we can gain a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s culture, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to drive Culture Evolution and organizational success.
1. Employee surveys: Conducting anonymous surveys allows employees to provide honest feedback on various aspects of the organization’s culture, such as communication, collaboration, and work environment. Surveys can include Likert scale questions, open-ended questions, and demographic information to gather comprehensive insights.
2. Focus groups: Organizing small group discussions with employees provides an opportunity for in-depth conversations about their perceptions and experiences of the culture. Focus groups encourage participants to share their thoughts, ideas, and suggestions, fostering a collaborative environment for exploring cultural dynamics.
3. Interviews: One-on-one interviews with employees, managers, and leaders allow for more personalized and detailed insights into the organization’s culture. Interviews can be structured or semi-structured, covering topics such as values, norms, leadership styles, and employee experiences.
4. Performance reviews: Analyzing performance review data helps identify how the organization’s culture impacts employee performance and development. It can reveal patterns, strengths, and areas for improvement in relation to cultural alignment and its influence on individual and team achievements.
5. Employee turnover data: Examining turnover rates and conducting exit interviews provides insights into any cultural factors contributing to employee attrition. Understanding why employees leave can help identify areas where the culture may need improvement to enhance employee retention.
6. Employee engagement surveys: Assessing employee engagement levels and their correlation with the organization’s culture helps gauge the overall satisfaction, motivation, and commitment of employees. These surveys often measure factors like job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and willingness to recommend the organization as a place to work.
7. Organizational policies and procedures: Reviewing written policies and procedures helps understand how they reflect and shape the culture. Policies related to communication, decision-making, diversity, and inclusion can provide insights into the organization’s values and how they are operationalized.
8. Organizational structure: Analyzing the formal structure of the organization helps identify any cultural implications. For example, a hierarchical structure may indicate a more traditional and top-down culture, while a flat structure may suggest a more collaborative and decentralized culture.
9. Leadership behavior: Observing and assessing the behavior of leaders provides insights into how they influence the culture. Leaders serve as role models and can shape the organization’s values, norms, and practices through their actions, communication style, and decision-making.
10. Employee onboarding process: Evaluating the onboarding process helps determine how it aligns with the desired culture. A well-designed onboarding program can help new employees understand and embrace the organization’s values, norms, and expectations from the start.
11. Internal communication channels: Reviewing internal communication platforms and messages helps assess their impact on the culture. Effective communication channels that encourage transparency, collaboration, and knowledge sharing can contribute to a positive and inclusive culture.
12. Employee recognition programs: Assessing the effectiveness of recognition programs in reinforcing the desired culture helps determine if they align with the organization’s values and if they are inclusive and equitable. Recognition programs can motivate employees, reinforce positive behaviors, and foster a culture of appreciation.
13. Diversity and inclusion initiatives: Evaluating the organization’s efforts to promote diversity and inclusion helps understand their impact on the culture. This includes assessing diversity in hiring practices, employee resource groups, training programs, and policies that support an inclusive and equitable work environment.
14. Customer feedback: Analyzing customer feedback helps understand how the organization’s culture impacts customer satisfaction. Customer feedback can provide insights into how employees’ behaviors, attitudes, and values influence the customer experience and overall brand perception.
15. Social media presence: Monitoring the organization’s social media channels helps gauge how the culture is portrayed externally. It provides insights into how the organization communicates its values, engages with stakeholders, and showcases its culture to the public.
16. Corporate values and mission statement: Assessing the alignment between the stated values and mission and the actual culture helps determine if there is consistency and authenticity. It involves evaluating whether the organization’s actions and behaviors reflect the espoused values and if the mission statement guides decision-making and strategic direction.
17. Training and development programs: Evaluating the content and delivery of training programs helps determine their impact on the culture. Training programs that focus on cultural awareness, leadership development, and skill-building can contribute to a culture of continuous learning and growth.
18. Employee networks and affinity groups: Assessing the presence and effectiveness of employee networks and affinity groups helps understand their role in fostering a positive culture. These groups provide opportunities for employees to connect, share experiences, and promote diversity, inclusion, and a sense of belonging.
19. Workplace environment: Observing the physical workspace and its impact on the culture and employee well-being helps identify how the environment supports or hinders the desired culture. Factors such as office layout, amenities, and ergonomics can influence collaboration, creativity, and employee satisfaction.
20. External benchmarking: Comparing the organization’s culture to industry benchmarks and best practices helps identify areas for improvement. It involves researching and analyzing how other successful organizations in the same industry or similar contexts have developed and sustained a positive culture.

Exercise 2:1 – Organizational Culture Assessment Instrument
Conclusion:
Organizational analysis is a crucial step in understanding an organization’s culture and identifying areas for improvement. By utilizing methods and tools such as the Culture Scan, organizations can gather data to gain insights into their current culture and make informed decisions for culture transformation. The exercise “Organizational Culture Assessment Instrument” allows participants to engage in hands-on analysis and discussions. The case study on Google further illustrates the impact of organizational analysis on culture transformation. As W. Edwards Deming emphasized, data-driven analysis is essential for making informed decisions and driving meaningful change within an organization.

Course Manual 3: Internal & External Perception
Introduction:
Perception plays a crucial role in shaping an organization’s culture. In this section, we will explore the concept of internal and external perception, understanding how employees perceive their organization’s culture and how it is perceived by external stakeholders. Through analysis, and a case study, we will gain insights into the importance of managing both internal and external perception to create a positive and aligned organizational culture.
Quote: “Your brand is what other people say about you when you’re not in the room.” – Jeff Bezos

Internal Perception:
The internal perception of an organization’s culture plays a vital role in shaping its overall success and effectiveness. It refers to how employees perceive and interpret the values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors that exist within the organization. This perception influences various aspects of the organization, including employee satisfaction, productivity, teamwork, and overall organizational performance. Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture is crucial as it helps leaders and managers create a positive and supportive work environment that fosters employee engagement and drives organizational success.
Influence of Internal Perception on Employee Satisfaction: The internal perception of an organization’s culture significantly impacts employee satisfaction. When employees perceive a positive and supportive culture, they are more likely to feel valued, respected, and motivated. This, in turn, leads to higher job satisfaction levels, increased loyalty, and reduced turnover rates. On the other hand, if employees perceive a negative or toxic culture, it can result in low morale, increased stress levels, and a higher likelihood of turnover. Therefore, understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to identify areas of improvement and create a culture that promotes employee satisfaction and well-being.
Impact on Employee Productivity: When employees perceive a culture that values and rewards hard work, innovation, and collaboration, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged in their work. This leads to increased productivity levels and higher quality output. Conversely, if employees perceive a culture that lacks support, recognition, or opportunities for growth, it can negatively impact their motivation and productivity. Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture helps leaders identify factors that hinder productivity and implement strategies to enhance employee engagement and performance.
Effect on Teamwork and Collaboration: The internal perception of an organization’s culture greatly affects teamwork and collaboration within the organization. When employees perceive a culture that promotes open communication, trust, and cooperation, they are more likely to work together effectively, share knowledge, and support each other. This fosters a collaborative work environment where ideas are freely exchanged, and teams can achieve their goals more efficiently. Conversely, if employees perceive a culture that lacks trust, encourages competition, or promotes silos, it can hinder teamwork and collaboration. Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to create a culture that values teamwork and collaboration, leading to improved organizational performance.
Influence on Organizational Performance: The internal perception of a positive culture that aligns with the organization’s values and goals can drive employee engagement, satisfaction, and productivity. This, in turn, leads to improved customer satisfaction, increased innovation, and a competitive advantage in the market. On the other hand, a negative or toxic culture can result in decreased employee morale, higher turnover rates, and a decline in organizational performance. Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to assess its impact on performance and make necessary changes to enhance organizational effectiveness.
Importance of Understanding Internal Perception: Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps leaders and managers identify gaps between the desired culture and the actual perception of employees. This allows them to address any inconsistencies and align the organization’s culture with its values and goals. Secondly, understanding internal perception enables leaders to identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance employee satisfaction, productivity, and collaboration. It helps create a positive work environment that attracts and retains top talent, leading to improved organizational performance. Additionally, understanding internal perception allows leaders to identify potential issues or challenges within the culture that may hinder the organization’s success. By addressing these issues proactively, leaders can prevent negative consequences and foster a culture that supports the organization’s long-term goals.
In conclusion, the internal perception of an organization’s culture plays a crucial role in shaping its success and effectiveness. It influences various aspects within the organization, including employee satisfaction, productivity, teamwork, and overall organizational performance. Understanding the internal perception of an organization’s culture is essential as it allows leaders to create a positive and supportive work environment that fosters employee engagement and drives organizational success. By aligning the desired culture with the actual perception of employees, leaders can enhance employee satisfaction, productivity, and collaboration, leading to improved organizational performance.
Conducting an Analysis of Internal Perceptions of an Organization’s Culture:
Analyzing the internal perceptions of an organization’s culture is crucial for understanding how employees perceive and interpret the values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors within the organization. This analysis provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the culture, identifies areas for improvement, and helps leaders create a positive and supportive work environment.
10 Steps to Conducting an Effective Analysis of Internal Perceptions:
1. Define the Objectives: Start by clearly defining the objectives of the analysis. Determine what specific aspects of the culture you want to assess, such as employee satisfaction, teamwork, communication, or leadership. This will help guide the analysis and ensure that it aligns with the organization’s goals.
2. Choose the Methodology: Select the most appropriate methodology for gathering data. Common methods include surveys, focus groups, interviews, and observation. Each method has its advantages and limitations, so choose the one that best suits your objectives and resources.
3. Develop Surveys or Interview Questionnaires: If you opt for surveys or interviews, develop a set of questions that will provide insights into employees’ perceptions of the organization’s culture. Include questions about values, communication, leadership, teamwork, and overall satisfaction. Make sure the questions are clear, concise, and unbiased to obtain accurate and meaningful responses.
4. Ensure Anonymity and Confidentiality: To encourage honest and open feedback, assure employees that their responses will remain anonymous and confidential. This will help create a safe space for employees to express their true perceptions without fear of repercussions.
5. Collect the Data: Implement the chosen methodology to collect data on internal perceptions. Distribute surveys, conduct interviews, or facilitate focus groups. Ensure that the data collection process is well-organized, efficient, and inclusive, involving a representative sample of employees from different levels and departments within the organization.
6. Analyze the Data: Once the data is collected, identify patterns, trends, and themes. Use statistical analysis if applicable, and categorize qualitative data into themes or categories. Look for commonalities and differences in perceptions across different employee groups or departments.
7. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: Based on the analysis, identify the strengths and weaknesses of the organization’s culture. Determine which aspects of the culture are positively perceived by employees and contribute to their satisfaction and engagement. Also, identify areas where improvements are needed, such as communication gaps, lack of recognition, or issues with leadership.
8. Seek Employee Feedback: To validate the analysis and gain a deeper understanding of employees’ perceptions, seek their feedback on the findings. This can be done through follow-up surveys, focus groups, or individual interviews. Encourage employees to provide additional insights, suggestions, or examples that can further enhance the analysis.
9. Develop an Action Plan: Based on the analysis and employee feedback, develop action plans to address the identified weaknesses and enhance the strengths of the organization’s culture. Set clear goals, define specific actions, and assign responsibilities to relevant stakeholders. Ensure that the action plans are aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and goals.
10. Monitor Progress and Adapt: Continuously monitor the progress of the action plans and adapt them as needed. Regularly assess the impact of the implemented changes on employees’ perceptions and satisfaction. This will help ensure that the organization’s culture evolves in a positive direction and remains aligned with the changing needs and expectations of employees.
In conclusion, conducting an analysis of internal perceptions of an organization’s culture is essential for understanding how employees perceive and interpret the values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors within the organization. By following these steps, leaders can gain valuable insights, identify areas for improvement, and create a positive and supportive work environment that fosters employee satisfaction and engagement.
External Perception
 The external perception of an organization’s culture refers to how the organization is perceived by external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, investors, and the general public. It encompasses the organization’s reputation, brand image, and the values and behaviors associated with the organization. Understanding the external perception is crucial as it helps leaders and managers shape a positive and favorable image, attract top talent, and build strong relationships with stakeholders.
The external perception of an organization’s culture refers to how the organization is perceived by external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, investors, and the general public. It encompasses the organization’s reputation, brand image, and the values and behaviors associated with the organization. Understanding the external perception is crucial as it helps leaders and managers shape a positive and favorable image, attract top talent, and build strong relationships with stakeholders.
Influence on Customer Loyalty: The external perception of an organization’s culture has a significant impact on customer loyalty. When customers perceive an organization’s culture as customer-centric, ethical, and trustworthy, they are more likely to develop a sense of loyalty towards the brand. This perception influences their purchasing decisions, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth recommendations. On the other hand, if customers perceive an organization’s culture as negative, untrustworthy, or inconsistent with their values, it can lead to a decline in customer loyalty and a negative impact on the organization’s bottom line. Therefore, understanding the external perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to shape a positive image that resonates with customers and fosters long-term loyalty.
Effect on Brand Reputation: A positive perception of an organization’s culture enhances its brand image and reputation in the market. It helps build trust, credibility, and a strong emotional connection with customers. This, in turn, leads to increased brand recognition, customer loyalty, and a competitive advantage. Conversely, if the external perception of an organization’s culture is negative or inconsistent with its desired image, it can damage the brand reputation and erode customer trust. Understanding the external perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to monitor and manage their brand reputation effectively, ensuring alignment between the desired image and the external perception.
Impact on Employee Recruitment and Retention: When an organization’s culture is perceived positively by potential employees, it becomes an attractive employer brand. This perception can help attract high-quality candidates who align with the organization’s values and goals. However, if the external perception of an organization’s culture is viewed negatively or is inconsistent with its desired image, it will hinder the recruitment of top talent. The same applies to employee retention. A positive perception of the culture can contribute to higher employee satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
Influence on Stakeholder Relationships: External perception plays a crucial role in building and maintaining strong relationships with stakeholders. When an organization’s culture is perceived positively by stakeholders, it enhances trust, credibility, and collaboration. This perception fosters strong partnerships with suppliers, investors, and other key stakeholders, leading to mutual benefits and long-term success, whereas if the external perception is negative or inconsistent with stakeholders’ expectations, it can strain relationships and hinder collaboration. Understanding the external perception of an organization’s culture allows leaders to proactively manage stakeholder relationships, address any concerns or misconceptions, and build strong partnerships based on shared values and goals.
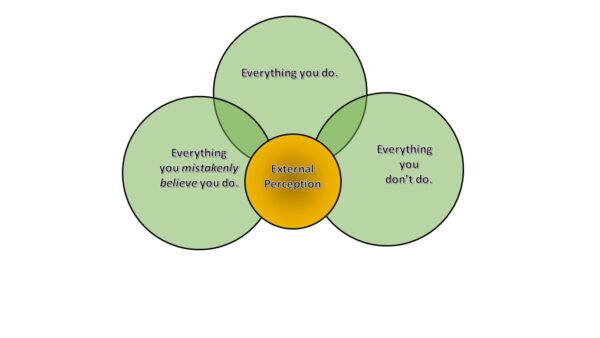
Importance of Understanding External Perception: Understanding the external perception of an organization’s culture is important because it has a significant influence on its success and effectiveness. This perception affects various aspects within the organization, including customer loyalty, brand reputation, employee recruitment, and stakeholder relationships. Understanding the external perception of an organization’s culture is crucial as it allows leaders to shape a positive and favorable image, attract top talent, and build strong relationships with stakeholders. By aligning the desired culture with the external perception, leaders can enhance customer loyalty, brand reputation, and employee satisfaction, leading to improved organizational performance and long-term success.
Conducting an Analysis of External Perceptions of an Organization’s Culture:
Here are some steps to conduct an effective analysis of external perceptions of an organization’s culture:
10 Steps to Conducting an Effective Analysis of External Perceptions:
1. Define the Objectives: Start by clearly defining the objectives of the analysis. Determine what specific aspects of the culture you want to assess, such as brand reputation, customer perception, or stakeholder relationships. This will help guide the analysis and ensure that it aligns with the organization’s goals.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders: Identify the key external stakeholders. This may include customers, suppliers, investors, industry experts, or the general public. Understanding the perspectives of these stakeholders is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the external perception.
3. Choose the Methodology: Select the most appropriate methodology for gathering data on external perceptions. Common methods include surveys, interviews, social media monitoring, online reviews analysis, and market research. Each method has its advantages and limitations, so choose the one that best suits your objectives and resources.
4. Develop a Survey or Interview Questions: If you opt for surveys or interviews, develop a set of questions that will provide insights into stakeholders’ perceptions of the organization’s culture. Include questions about brand reputation, customer satisfaction, perceived values, and overall perception. Make sure the questions are clear, concise, and unbiased to obtain accurate and meaningful responses.
5. Monitor Social Media and Online Platforms: Monitor social media platforms, online review sites, and other relevant online platforms to gather real-time feedback and opinions about the organization’s culture. Pay attention to positive and negative comments, as both can provide valuable insights into the external perception.
6. Analyze the Data: Once the data is collected, analyze it to identify patterns, trends, and themes. Use statistical analysis if applicable, and categorize qualitative data into themes or categories. Look for commonalities and differences in perceptions across different stakeholder groups or platforms.
7. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: Based on the analysis, identify the strengths and weaknesses of the organization’s culture as perceived by external stakeholders. Determine which aspects of the culture are positively perceived and contribute to a favorable reputation and relationships. Also, identify areas where improvements are needed, such as misalignment between perceived and desired values or negative perceptions that may harm the organization’s image.
8. Seek Stakeholder Feedback: To validate the analysis and gain a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perceptions, seek their feedback on the findings. This can be done through follow-up surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Encourage stakeholders to provide additional insights, suggestions, or examples that can further enhance the analysis.
9. Develop Action Plans: Based on the analysis and stakeholder feedback, develop action plans to address the identified weaknesses and enhance the strengths of the organization’s culture. Set clear goals, define specific actions, and assign responsibilities to relevant stakeholders. Ensure that the action plans are aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and goals.
10. Monitor Progress and Adapt: Continuously monitor the progress of the action plans and adapt them as needed. Regularly assess the impact of the implemented changes on external perceptions and reputation.

Case Study: Apple Inc.: Managing Internal and External Perception for Success and Reputation
Introduction: Apple Inc. is a global technology company renowned for its innovative products, including the iPhone, iPad, Mac, and Apple Watch. The company’s success and reputation are not solely based on its cutting-edge technology but also on its strategic management of internal and external perception. This case study explores how Apple effectively manages both internal and external perception, and how this contributes to its success and reputation in the highly competitive technology industry.
Internal Perception Management: Apple places great emphasis on fostering a unique internal culture that aligns with its desired perception. The company’s internal perception management strategies include:
1. Clear Vision and Values: Apple’s leadership ensures that employees understand and embrace the company’s vision and values. This clarity helps create a shared sense of purpose and a strong internal culture.
2. Design-Centric Approach: Apple’s design-centric approach permeates its internal culture. Employees are encouraged to think creatively, challenge conventions, and strive for excellence in product design and user experience.
3. Employee Empowerment: Apple empowers its employees by providing them with opportunities for growth, development, and recognition. This fosters a sense of ownership and pride in their work, leading to higher levels of engagement and commitment.
4. Transparent Communication: Apple maintains open and transparent communication channels, ensuring that employees are well-informed about company updates, strategies, and goals. This transparency builds trust and a sense of belonging among employees.
External Perception Management: Apple’s external perception management strategies are equally crucial in shaping its success and reputation. The company employs various approaches to manage external perception effectively:
1. Branding and Marketing: Apple’s iconic branding and marketing campaigns create a distinct image and perception in the minds of consumers. The company focuses on simplicity, elegance, and innovation, which resonates with its target audience.
2. Product Launch Events: Apple’s meticulously planned and highly anticipated product launch events generate significant media attention and public interest. These events create a sense of excitement and reinforce the perception of Apple as an industry leader.
3. Customer Experience: Apple prioritizes delivering exceptional customer experiences through its retail stores, online platforms, and customer support services. This commitment to customer satisfaction enhances the perception of Apple as a customer-centric company.
4. Strategic Partnerships: Apple strategically partners with other reputable brands, such as Nike and Hermès, to enhance its brand image and expand its reach. These collaborations reinforce the perception of Apple as a premium and lifestyle-oriented brand.
Impact on Success and Reputation: Apple’s effective management of internal and external perception has a profound impact on its success and reputation:
1. Market Leadership: Apple’s ability to shape internal perception and foster a culture of innovation and excellence has enabled the company to consistently introduce groundbreaking products. This has solidified its position as a market leader and contributed to its financial success.
2. Customer Loyalty: By managing external perception through exceptional product design, customer experiences, and branding, Apple has cultivated a loyal customer base. This loyalty translates into repeat purchases, positive word-of-mouth, and a strong market presence.
3. Brand Value: Apple’s meticulous management of internal and external perception has significantly enhanced its brand value. The company consistently ranks among the most valuable brands globally, which strengthens its competitive advantage and attracts top talent.
4. Investor Confidence: Apple’s positive reputation and consistent financial performance have garnered investor confidence. This has resulted in a strong market capitalization and access to capital for future growth and innovation.
Conclusion: Apple’s success and reputation in the technology industry can be attributed, in part, to its effective management of internal and external perception. By fostering a unique internal culture, aligning values, and empowering employees, Apple creates a workforce that is passionate and committed to its vision. Simultaneously, the company strategically manages external perception through branding, marketing, customer experiences, and strategic partnerships. This comprehensive approach has propelled Apple to become a global leader, driving customer loyalty, brand value, and investor confidence.

Exercise 3:1 – “Perception Gap Analysis”
1. How would you describe the organization’s reputation in the industry or market?
1. What are the key differences between the desired perception and the current internal perception of the organization?
Conclusion:
Managing internal and external perception is crucial for creating a positive and aligned organizational culture. By understanding how employees perceive the culture internally and how it is perceived externally, organizations can identify areas of misalignment, strengths, and opportunities for improvement. The provided exercise, “Perception Gap Analysis,” allows participants to engage in discussions and develop strategies to bridge perception gaps. The case study on Apple further illustrates the impact of managing perception on an organization’s success. As Jeff Bezos stated, an organization’s brand is shaped by what others say about it, emphasizing the importance of managing perception to create a strong and positive organizational culture.

Course Manual 4: Elements of Culture
Introduction:
Understanding the elements of organizational culture is essential for shaping and transforming it effectively. In this section, we will explore the key elements that contribute to organizational culture, including values, symbols, rituals, language, and stories. Through analysis, and case studies, we will gain insights into how these elements shape and influence an organization’s culture
Quote: “Culture is the widening of the mind and of the spirit.” – Jawaharlal Nehru
Values:
Values play a crucial role in shaping and influencing the culture of an organization. They serve as guiding principles that define the beliefs, behaviors, and decision-making processes within the organization. When values are clearly defined and consistently upheld, they create a shared sense of purpose and identity among employees, leading to a strong and positive organizational culture. Let’s explore how values shape and influence an organization’s culture with some examples.
Firstly, values provide a framework for decision-making. They help employees understand what is important to the organization, and also guide them in making choices that align with those values. For example, if one of the core values of an organization is integrity, employees are expected to act honestly and ethically in all their interactions. This value influences the culture by fostering trust, transparency, and accountability within the organization.
Values also influence the behavior and attitudes of employees. When values are deeply ingrained in the organization’s culture, they shape the way employees interact with each other, customers, and stakeholders. For instance, if a company values teamwork, employees are encouraged to collaborate, share knowledge, and support each other. This value creates a culture of cooperation, open communication, and mutual respect.
Moreover, values help attract and retain employees who share similar beliefs and principles. Organizations that have a strong and well-defined set of values tend to attract individuals who resonate with those values, For example, a company that values innovation and creativity is likely to attract employees who are passionate about pushing boundaries and finding new solutions. This shared value creates a culture of continuous learning, experimentation, and adaptability.
Values also serve as a benchmark for evaluating performance and recognizing achievements. When an organization’s values are clearly communicated, employees understand the expectations and standards set by the organization. Performance evaluations and recognition programs can be aligned with these values to reinforce and reward behaviors that contribute to the desired culture. For instance, if a company values customer-centricity, employees who consistently go above and beyond to meet customer needs can be recognized and rewarded, reinforcing the importance of customer focus within the culture.
Furthermore, values can influence the way an organization interacts with its external stakeholders. For example, if an organization values sustainability, it may prioritize environmentally friendly practices and engage in socially responsible initiatives. This value shapes the organization’s culture by promoting a sense of responsibility towards the environment and society.
However, it is important to note that values must be more than just words on a wall or a website. They need to be lived and demonstrated by leaders and employees at all levels of the organization. When values are consistently upheld and integrated into everyday practices, they become the foundation of the organizational culture.

Typical Organizational Values
In conclusion, values play a significant role in shaping and influencing an organization’s culture. They provide a framework for decision-making, influence behavior and attitudes, attract and retain employees, serve as a benchmark for evaluating performance, and guide interactions with external stakeholders, When values are deeply embedded in the organization’s culture, they create a shared sense of purpose, identity, and direction.
Analysis:
Analyzing an organization’s values involves examining its mission and vision statements, code of conduct, and leadership behaviors. By assessing the alignment between stated values and actual behaviors, organizations can identify areas of strength and areas that require improvement.
Symbols and Rituals:
Symbols and rituals are two important elements of organizational culture that shape and influence the way an organization operates and its employees behave. Symbols are tangible representations that carry meaning and communicate shared values, beliefs, and identity within the organization. Rituals, on the other hand, are symbolic actions or ceremonies that reinforce and perpetuate the organization’s culture Let’s explore how symbols and rituals shape and influence an organization’s culture with examples.
Symbols play a crucial role in shaping organizational culture by creating a sense of identity and belonging. They serve as visual or auditory cues that employees can identify with and rally around. For example, a company logo represents the organization’s brand and can evoke emotions and associations among employees. When employees wear or display the logo, it reinforces their connection to the organization and fosters a sense of pride and belonging. This symbol becomes a unifying force that strengthens the organizational culture.

Symbols also communicate shared values and beliefs within the organization. They serve as reminders of what the organization stands for and what it aims to achieve. For instance, a company slogan or tagline can encapsulate the organization’s core values and mission. When employees see or hear the slogan, it reinforces the organization’s values and influences their behaviors and decisions. This symbol aligns employees’ actions with the organization’s values, contributing to a strong and positive culture. Symbols can reinforce desired behaviors and norms within the organization.
Symbols also shape the physical environment of the organization, which in turn influences the culture. The layout, design, and decor of the workplace can be symbolic and reflect the organization’s culture. For example, an open office layout with collaborative spaces and vibrant colors can symbolize a culture of teamwork, creativity, and innovation. This symbol influences employees’ behaviors and interactions, fostering a culture of collaboration and idea-sharing.
Rituals, as symbolic actions or ceremonies, also play a significant role in shaping organizational culture. They are repeated behaviors or practices that reinforce and perpetuate the organization’s values, beliefs, and norms. For example, a weekly team meeting where employees share updates and discuss challenges can be a ritual that promotes open communication and collaboration. This ritual influences the culture by fostering a sense of teamwork and accountability.
Rituals can also be seen in the onboarding process of new employees. Orientation programs or induction ceremonies are rituals that introduce new employees to the organization’s culture, values, and expectations. These rituals help new employees understand and assimilate into the organization’s culture, shaping their behaviors and attitudes from the beginning.
Moreover, rituals can be seen in the way organizations celebrate milestones or achievements. For example, an annual company-wide celebration or a monthly event that recognizes employees for their outstanding performance reinforces the value of excellence and hard work. These are rituals that reinforce the organization’s values and recognize employees’ contributions, encouraging employees to strive for excellence and contribute to a culture of high performance. These rituals create a sense of belonging, motivation, and pride among employees, influencing the culture positively.
It is important to note that symbols and rituals must be more than just superficial gestures. They need to be meaningful and authentic representations of the organization’s culture. When symbols and rituals are carefully chosen and consistently upheld, they become integral to the organizational culture, fostering a sense of unity, purpose, and shared understanding among employees.
Symbols and rituals are therefore powerful elements that shape and influence an organization’s culture. Symbols create a sense of identity and belonging, communicate shared values and beliefs, reinforce desired behaviors and norms, shape the physical environment, and influence language and communication. Rituals, as symbolic actions or ceremonies, reinforce and perpetuate the organization’s culture, fostering a sense of unity and shared understanding among employees. When symbols and rituals are aligned with the organization’s values and consistently upheld, they contribute to a strong and positive organizational culture.
Analysis:
Analyzing symbols involves examining the visual elements present within the organization. This can be done through observation and discussions with employees. By understanding the meaning and impact of symbols, organizations can ensure that they align with the desired culture and reinforce the intended values. Analyzing rituals involves identifying the recurring actions and ceremonies within the organization and understanding their purpose and impact. By assessing the alignment between rituals and desired values, organizations can strengthen their culture and foster a sense of belonging.
Language and Stories:
Language and stories are two powerful elements that shape and influence the culture of an organization. Language refers to the words, phrases, and communication patterns used within the organization, while stories are narratives that convey shared experiences, values, and beliefs. Together, they play a significant role in shaping the way employees think, behave, and interact within the organizational context. Let’s explore how language and stories shape and influence an organization’s culture with examples.
Language is a fundamental aspect of organizational culture as it shapes communication patterns and influences the way employees interact and understand each other. The language used within an organization reflects its values, norms, and priorities. For example, if an organization values transparency and open communication, the language used by employees and leaders will likely be direct, honest, and inclusive. This language fosters a culture of trust, collaboration, and effective communication.
Moreover, language can create a sense of belonging and identity within the organization. Certain phrases, jargon, or acronyms can become symbolic and carry specific meanings within the organizational culture. For example, a company may have a unique set of terms or abbreviations that are used by employees to communicate and reinforce shared values or concepts. This language creates a sense of belonging and facilitates effective communication within the organization.

Language also influences the way employees perceive and interpret the organization’s values and expectations. The choice of words and the tone used in communication can shape employees’ understanding and attitudes towards the organization’s culture. For instance, if an organization emphasizes customer-centricity, the language used in customer interactions and internal communications should reflect this value. This language influences employees’ behaviors and attitudes, fostering a culture of customer focus.
Stories, on the other hand, are powerful tools for shaping and transmitting organizational culture. Stories are narratives that convey shared experiences, values, and beliefs within the organization. They provide context, meaning, and a sense of history. For example, stories about the organization’s founders, its journey, or significant milestones can create a sense of pride, purpose, and identity among employees. These stories shape the organization’s culture by reinforcing its values and providing a sense of continuity.
Stories also serve as a means of socialization and onboarding for new employees. When new employees hear stories about the organization’s culture, they gain insights into the values, norms, and expectations. These stories help new employees understand and assimilate into the organization’s culture, shaping their behaviors and attitudes from the beginning. For example, a story about an employee who went above and beyond to solve a customer problem can convey the importance of customer service and inspire new employees to do the same.
Stories can also be used to reinforce desired behaviors and values within the organization. Leaders can share stories that highlight examples of employees who exemplify the organization’s values. These stories serve as role models and inspire others to emulate those behaviors. For instance, a story about an employee who demonstrated exceptional teamwork and collaboration can reinforce the value of collaboration within the organization’s culture.
Stories also play a role in organizational learning and knowledge sharing. They provide a context for understanding past experiences, successes, and failures. When employees share stories about their challenges, lessons learned, and innovative solutions, it fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement. These stories shape the organization’s culture by promoting a mindset of curiosity, experimentation, and adaptability.
It is important to note that language and stories must be authentic and aligned with the organization’s values and goals. Inauthentic or misleading language and stories can erode trust and undermine the organization’s culture. Therefore, leaders must ensure that the language used and the stories shared reflect the reality and values of the organization.
As we have seen, language and stories are powerful elements that shape and influence an organization’s culture. Language influences communication patterns, creates a sense of belonging, and shapes employees’ understanding and attitudes towards the organization’s values. Stories convey shared experiences, values, and beliefs, providing context, inspiration, and a sense of identity. When language and stories are carefully chosen and consistently upheld, they become integral to the organizational culture, fostering effective communication, a sense of belonging, and a shared understanding among employees.
Analysis:
Analyzing language and stories involves examining the vocabulary and communication patterns within the organization and collecting stories. By understanding the language and stories being used, organizations can assess their alignment with desired values and identify opportunities for promoting effective communication and inclusivity.

Case Study: Southwest Airlines
Southwest Airlines is a prime example of an organization that effectively incorporates symbols, rituals, language, and stories to reinforce its values and contribute to its success and reputation. The airline has built a strong and distinctive culture that sets it apart from its competitors and has become a key driver of its success. Let’s explore how Southwest Airlines utilizes these elements to shape its culture and achieve its goals.
Symbols play a significant role in Southwest Airlines’ culture. One of the most recognizable symbols is the company’s logo, the heart-shaped Southwest symbol. This symbol represents the airline’s commitment to providing a friendly and caring experience for its customers. It is prominently displayed on the aircraft, uniforms, and various marketing materials, reinforcing the organization’s values and creating a sense of identity and pride among employees.
Another symbol that Southwest Airlines incorporates is the iconic “Southwest Warrior Spirit logo, which represents the company’s employees as warriors who are passionate about their work and dedicated to serving customers. This symbol embodies the airline’s culture of teamwork, resilience, and a can-do attitude. It is used in internal communications, recognition programs, and employee engagement initiatives, reinforcing the organization’s values and motivating employees to go above and beyond.
Rituals are an integral part of Southwest Airlines culture and are used to reinforce its values and create a sense of community among employees. One of the most well-known rituals is the “Spirit Party”, a celebration held at each airport location to recognize outstanding performance, teamwork, and customer service. These parties include music dancing, and speeches, creating a festive atmosphere and fostering a culture of appreciation and camaraderie.
Another ritual is the “Ramp Rodeo”, an annual competition where employees showcase their skills in various operational tasks. This event promotes teamwork, friendly competition, and a sense of pride in their work, The Ramp Rodeo has become a symbol of Southwest Airlines commitment to operational excellence and has contributed to the airline’s reputation for efficiency and reliability.
Language is a crucial element in Southwest Airlines’ culture, The airline has developed a unique and informal communication style that reflects its values of friendliness, humor, and approachability Employees are encouraged to use humor and engage in light-hearted banter with customers, creating a relaxed and enjoyable experience. This language style is also reflected in the company’s advertising campaigns, where witty and humorous slogans are used to convey the airline’s personality and differentiate it from competitors.
Southwest Airlines also incorporates stories to reinforce its values and inspire employees. The airline has a rich history of legendary customer service stories that are shared internally and externally. These stories highlight employees who have gone above and beyond to provide exceptional service, demonstrating the airline’s commitment to its customers. By sharing these stories, Southwest Airlines reinforces its values of customer centricity and inspires employees to deliver outstanding service.
Additionally, Southwest Airlines has a strong focus on employee empowerment and encourages employees to share their own stories and experiences. The company’s internal communication channels provide platforms for employees to share their success stories, innovative ideas, and lessons learned. These stories foster a culture of continuous learning, collaboration, and employee engagement.
The incorporation of symbols, rituals, language, and stories has contributed significantly to the success and reputation of Southwest Airlines. The airline’s distinctive culture characterized by its symbols such as the heart-shaped logo and the Warrior Spirit logo creates a strong sense of identity and pride among employees. The rituals such as the Spirit Party and Ramp Rodeo, foster a sense of community, teamwork, and excellence. The unique language style, infused with humor and friendliness, sets Southwest Airlines apart and creates a memorable customer experience, Lastly, the sharing of stories, both internally and externally, reinforces the airline’s values, inspires employees, and builds a strong reputation for exceptional customer service.
Overall, Southwest Airlines has created a culture that aligns with its values, engages employees, and delivers a unique and memorable customer experience. These elements have played a crucial role in the airline’s success and have contributed to its strong reputation as a customer centric and employee friendly organization

Exercise 4:1 – Exploring Culture Elements – Values, Symbols, Rituals, Language, and Stories
– Flipchart paper or whiteboard
– Markers
– Sticky notes or index cards
– Pens or markers for participants
1. Introduction:
– Divide participants into groups of 5.
– Distribute sticky notes or index cards and pens/markers to each group.
– Instruct each group to brainstorm and write down at least three core values that they believe are important in their personal lives or within their organization.
– Encourage participants to think about values such as integrity, teamwork, innovation, respect, or any other values that resonate with them.
– Emphasize that values are guiding principles that influence behavior and decision-making.
– Ask each group to identify and discuss symbols and rituals that are associated with their chosen values.
– Symbols can be objects, gestures, or images that represent or convey meaning related to the values.
– Rituals are repeated actions or behaviors that reinforce the values and create a sense of belonging or identity.
– Instruct each group to share a story or anecdote that exemplifies their chosen values.
– Encourage participants to discuss how language is used to communicate and reinforce the values within the story.
– Language can include specific words, phrases, or expressions that are associated with the values.
– Invite each group to present their chosen values, symbols, rituals, and share their story with the rest of the participants.
– Encourage participants to ask questions and engage in a brief discussion after each presentation.
– Conclude the exercise by summarizing the key points discussed during the activity.
– Ask participants to reflect on how the elements of culture (values, symbols, rituals, language, and stories) are interconnected and contribute to shaping the culture within their personal lives or organization.
– If time allows, facilitate a brief debriefing session to gather participants’ insights and observations from the exercise.
– Encourage participants to share any new perspectives or connections they have made regarding the elements of culture.
Conclusion:
Understanding the elements of organizational culture, including values, symbols, rituals, language, and stories is crucial for shaping and transforming culture effectively. By analyzing and aligning these elements, organizations can create a strong and cohesive culture that supports their mission and values. The provided exercise, “Exploring Culture Elements”, allows participants to engage in discussions and deepen their understanding of the elements of culture. The case study on Southwest Airlines powerfully illustrates the impact of these elements on organizational culture. As Jawaharlal Nehru stated, culture widens the mind and the spirit, which emphasizes the transformative power of culture within organizations.

Course Manual 5: Impact on Behavior
Introduction:
The impact of organizational culture on employee behavior is significant and far-reaching. In this section, we will explore how culture influences employee behavior, attitudes, and actions within an organization. A strong culture that aligns with employees’ values fosters a sense of belonging, commitment, and motivation. It shapes how employees interact with one another, collaborate, and communicate. Additionally, culture influences employee attitudes towards change, risk-taking, and innovation. Through, analysis, charts and a case study, we will gain insights into the importance of understanding this impact and how organizations can shape behavior through culture.
Quote: “Culture drives great results.” – Jack Welch

Understanding the Impact:
The culture of an organization plays a significant role in shaping the behavior of its employees. It encompasses the shared values, beliefs, norms, and practices that guide how individuals within the organization interact and make decisions. The impact of organizational culture on employee behavior can be seen in various aspects, including their attitudes, motivation, communication, and overall performance.
One of the key ways in which organizational culture influences employee behavior is through the establishment of shared values and beliefs. When employees personal values are aligned with the core values of the organization, they are more likely to exhibit behaviors that are consistent with those values. For example, if an organization values teamwork and collaboration, employees are more likely to engage in cooperative behaviors and work well with others. On the other hand, if an organization promotes individualism and competition, employees may exhibit more self-centered behaviors and be less inclined to collaborate.
Organizational culture also impacts employee behavior through its influence on attitudes and motivation. A positive and supportive culture can foster a sense of belonging and loyalty among employees, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and commitment. This, in turn, can result in employees who are more motivated and engaged in their work. Conversely, a toxic or negative culture can lead to low morale, high turnover, and decreased motivation among employees.
Communication is another area where organizational culture has a significant impact on employee behavior. The communication style and channels within an organization are often shaped by its culture. For example, in a hierarchical culture, communication may be top-down, with little input or feedback from employees. This can lead to a lack of transparency and trust, as well as reduced employee engagement. In contrast, a culture that values open and transparent communication can foster a more inclusive and collaborative environment, where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns.
The impact of organizational culture on employee behavior is also evident in their performance. A culture that promotes high standards of performance and accountability can motivate employees to strive for excellence and deliver their best work. On the other hand, a culture that tolerates mediocrity or lacks clear performance expectations may result in lower productivity and subpar performance.
Furthermore, organizational culture can influence employee behavior through the establishment of norms and practices. These can include things like dress code, work hours, and decision-making processes. When employees perceive that their behavior aligns with the norms and practices of the organization, they are more likely to conform to them. This can create a sense of order and consistency within the organization, but it can also stifle creativity and innovation if the culture is too rigid or resistant to change.
In conclusion, the impact of organizational culture on employee behavior is significant and multifaceted. It shapes attitudes, motivation, communication, and performance, ultimately influencing how employees interact and behave within the organization. A positive and supportive culture can foster employee engagement, satisfaction, and productivity, while a toxic or negative culture can lead to low morale and decreased motivation. Therefore, organizations should strive to cultivate a culture that aligns with their values and promotes behaviors that contribute to their overall success.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on behavior involves examining the alignment between desired behaviors and the actual behaviors exhibited within the organization. By assessing the influence of culture on employee behavior, organizations can identify areas of strength and areas that require improvement.
Chart: Desired / Less-Desired Behaviors
This chart can be used to facilitate discussions and identify opportunities for reinforcing desired behaviors within the organization.
IMAGE TOO DETAILED
Let us now focus on 3 different dimensions of behavior influenced by culture which are critical to any organization’s business success. Collaboration, innovation, and customer focus, are all areas where there is a direct connection between culture and behavior.
Impact on Collaboration:
Organizational culture plays a vital role in fostering collaboration among employees within a company. It sets the tone for how individuals interact, communicate, and work together towards common goals. A strong and positive organizational culture encourages behaviors that promote collaboration, creating an environment where employees feel valued, supported, and motivated to work together effectively.

One crucial behavior that is fostered by a positive organizational culture is open communication. When employees feel comfortable expressing their ideas, concerns, and opinions, it creates an atmosphere of trust and transparency. This open communication allows for the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and different perspectives, which can lead to innovative solutions and better decision-making. Employees are more likely to collaborate and work together when they feel their voices are heard and respected.
Another important behavior that is encouraged by a positive organizational culture is teamwork. Collaboration requires individuals to work together towards a common goal, pooling their skills, knowledge, and resources. A strong organizational culture promotes teamwork by emphasizing the value of collective effort and recognizing the contributions of each team member. When employees feel that their efforts are recognized and appreciated, they are more likely to actively participate in collaborative projects and support their colleagues.
Trust is also a crucial behavior that is fostered by a positive organizational culture. Trust is the foundation of effective collaboration, as it allows individuals to rely on each other, delegate tasks, and share responsibilities. A culture that promotes trust encourages employees to be reliable, accountable, and supportive of one another. When employees trust their colleagues, they are more willing to collaborate, take risks, and share information, leading to increased productivity and better outcomes.
The benefits of fostering collaboration through organizational culture are numerous and significant for a business. Firstly, collaboration enhances creativity and innovation. When employees from different backgrounds and expertise collaborate, they bring diverse perspectives and ideas to the table. This diversity of thought can lead to the generation of innovative solutions, improved processes, and new product ideas. Collaboration also encourages continuous learning and development, as employees have the opportunity to learn from each other’s experiences and expertise.
Collaboration improves problem-solving and decision-making. When employees collaborate, they can leverage their collective knowledge and skills to tackle complex problems and make informed decisions. Different viewpoints and approaches can be considered, leading to more comprehensive and effective solutions. Collaboration also promotes a sense of ownership and accountability, as employees feel invested in the outcomes of their group efforts.
Collaboration also enhances employee engagement and satisfaction. When employees feel valued, supported, and included in team projects, they are more likely to be engaged in their work. Collaboration provides opportunities for personal growth, skill development, and recognition, which can contribute to higher job satisfaction and motivation. Engaged employees are more productive, committed, and loyal to the organization, leading to improved overall performance and business success.
In conclusion, organizational culture plays a vital role in fostering collaboration among employees. The benefits of fostering collaboration include enhanced creativity and innovation, improved problem-solving and decision-making, increased employee engagement and satisfaction, and ultimately, improved business performance. Open communication, teamwork, and trust are some crucial behaviors that are encouraged by a positive organizational culture. By creating a culture that values collaboration, organizations can create a collaborative environment where employees thrive and will therefore contribute to the success of the business.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on collaboration involves assessing the level of teamwork, communication channels, and the presence of collaborative practices within the organization. By understanding the influence of culture on collaboration, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance collaboration.
Impact on Innovation:
Organizational culture has a significant influence on employee attitudes towards innovation. The culture of an organization sets the tone for how employees perceive and approach innovation, and it can either foster or hinder their willingness to take risks, think creatively, and embrace new ideas. A positive and supportive organizational culture can encourage employees to be more innovative, while a negative or restrictive culture can stifle their creativity and hinder their willingness to try new things.

Innovation often involves taking risks and trying new approaches, which can be intimidating for employees if they fear negative consequences or punishment for failure. A positive organizational culture that values and rewards risk-taking can help alleviate these fears and encourage employees to step outside their comfort zones. When employees feel supported and empowered to take risks, they are more likely to explore new ideas, experiment with different approaches, and contribute to the organization’s innovation efforts.
Another important behavior that is crucial for fostering innovation is promoting a growth mindset. A growth mindset is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort and learning. In an organizational culture that promotes a growth mindset, employees are encouraged to embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and see failure as an opportunity for learning and growth. This mindset is essential for innovation because it encourages employees to view obstacles as opportunities, think creatively, and seek out new solutions. When employees believe that their efforts and ideas can make a difference, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged in the innovation process.
In the previous point, we discussed the importance of collaboration, and here too it is noteworthy that a culture that values open communication is also crucial for fostering innovation. Innovation often requires the input and collaboration of multiple individuals with diverse perspectives and expertise. When employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas, collaborating with others, and seeking feedback, it creates an environment that is conducive to innovation. Collaboration allows for the exchange of knowledge, the generation of new ideas, and the refinement of existing ones. When employees feel that their contributions are valued and that they have a voice in the innovation process, they are more likely to actively participate and contribute their unique insights and expertise.
The benefits of fostering innovation through organizational culture are significant for a business. Firstly, innovation can lead to a competitive advantage. In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, organizations that can adapt, innovate, and stay ahead of the curve are more likely to succeed. By fostering a culture of innovation, organizations can encourage employees to think creatively, identify new opportunities, and develop innovative solutions that can differentiate them from their competitors.
Furthermore, innovation can lead to improved efficiency and productivity. When employees are encouraged to think critically and find new ways of doing things, it can lead to process improvements, streamlined workflows, and increased productivity. Innovation can also lead to cost savings, as new ideas and approaches can help identify more efficient ways of operating.
Innovation also enhances employee engagement and satisfaction. When employees are given the opportunity to contribute their ideas and be part of the innovation process, it can increase their sense of ownership and engagement in their work. Innovation provides opportunities for personal growth, skill development, and recognition, which can contribute to higher job satisfaction and motivation. Engaged employees are more likely to be committed, productive, and loyal to the organization, leading to improved overall performance and business success.
Clearly organizational culture has a significant influence on employee attitudes towards innovation. Encouraging risk-taking, promoting a growth mindset, and fostering collaboration and open communication are crucial behaviors for fostering innovation. The benefits of fostering innovation through organizational culture include a competitive advantage, improved efficiency and productivity, and increased employee engagement and satisfaction. By creating a culture that values and supports innovation, organizations can create an environment where employees are motivated, empowered, and inspired to think creatively and contribute to the success of the business.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on innovation involves assessing the organization’s approach to risk, the presence of learning opportunities, and the level of support for new ideas. By understanding the influence of culture on innovation, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to foster a culture of innovation.
Impact on Customer Focus:
Organizational culture has a significant influence on employee attitudes towards customer service and satisfaction. The culture of an organization sets the tone for how employees perceive and approach customer service, and it can either foster or hinder their commitment to providing exceptional service and ensuring customer satisfaction. A positive and customer-centric organizational culture can encourage employees to go above and beyond to meet customer needs, while a negative or indifferent culture can result in poor customer service and low customer satisfaction.
One crucial behavior in fostering exceptional customer service is a customer-centric mindset. This way of thinking places the customer at the center of all decisions and actions, emphasizing the importance of understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations. When employees are encouraged to prioritize customer satisfaction and are provided with the necessary tools and resources to do so, they are more likely to be proactive, attentive, and responsive to customer needs. A customer-centric culture also promotes empathy and understanding, as employees are encouraged to put themselves in the customer’s shoes and provide personalized and tailored solutions.
Another important behavior that is crucial for fostering exceptional customer service is effective communication. Clear and open communication is essential in order to understand customer needs, address concerns, and provide timely and accurate information. A positive organizational culture that values and promotes effective communication ensures that employees have the necessary skills and resources to interact with customers in a professional and empathetic manner. When employees feel supported and empowered to communicate effectively, it enables them to build strong relationships with customers, resolve issues efficiently, and exceed customer expectations.

A positive organizational culture that values and rewards teamwork is also crucial for fostering exceptional customer service. Customer service often requires collaboration and coordination among different departments and individuals within an organization. When employees are encouraged to work together, share knowledge and resources, and support each other, it creates an environment that is conducive to providing seamless and exceptional customer service. Collaboration allows for the sharing of best practices, the identification of innovative solutions, and the delivery of consistent and high-quality service. When employees feel that their contributions are valued and that they are part of a team working towards a common goal, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to providing exceptional customer service.
The benefits of fostering exceptional customer service through organizational culture are significant for a business. Primarily, exceptional customer service leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. When customers receive exceptional service, they are more likely to have a positive perception of the organization, recommend it to others, and continue doing business with it. Satisfied and loyal customers are more likely to become repeat customers, leading to increased sales and revenue.
Exceptional customer service can differentiate an organization from its competitors. In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations that can provide exceptional service and exceed customer expectations are more likely to stand out and gain a competitive advantage. Exceptional customer service can help build a strong brand reputation, attract new customers, and retain existing ones.
Exceptional customer service also leads to improved customer retention and reduced customer churn. When customers receive exceptional service and have positive experiences, they are more likely to remain loyal to the organization and continue doing business with it. This reduces the need for costly customer acquisition efforts and allows the organization to focus on building long-term relationships with its customers.
In conclusion, organizational culture has a significant influence on employee attitudes towards customer service and satisfaction. A customer-centric mindset, effective communication, and teamwork are crucial behaviors for fostering exceptional customer service. The benefits of fostering exceptional customer service through organizational culture include increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, differentiation from competitors, improved customer retention, and reduced customer churn. By creating a culture that values and supports exceptional customer service, organizations can create an environment where employees are motivated, empowered, and inspired to go above and beyond to meet customer needs and ensure their satisfaction.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on customer focus involves assessing the organization’s values, training programs, and customer-centric practices. By understanding the influence of culture on customer focus, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance customer-centric behaviors.

Case Study
Netflix’s culture has had a significant impact on employee behavior and has played a crucial role in the company’s organizational success. The unique and innovative culture at Netflix has fostered a high-performance environment that encourages autonomy, creativity, and accountability among its employees. This culture has contributed to Netflix’s ability to attract and retain top talent, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in the streaming industry.
One key aspect of Netflix’s culture is its emphasis on freedom and responsibility. The company operates under the belief that responsible employees should have the freedom to make their own decisions and take ownership of their work. This culture of autonomy empowers employees to take risks, experiment with new ideas, and make decisions without excessive bureaucracy or micromanagement. By giving employees the freedom to innovate and take ownership of their work, Netflix has created an environment that fosters creativity and encourages employees to think outside the box.
Netflix’s culture also promotes a high-performance mindset. The company values excellence and expects its employees to consistently deliver exceptional results. This culture of high performance is reinforced through a rigorous performance evaluation system that focuses on continuous improvement and rewards top performers. By setting high expectations and providing regular feedback, Netflix motivates its employees to strive for excellence and continuously raise the bar.
Another important aspect of Netflix’s culture is its focus on talent density. The company believes that having a high concentration of top performers is crucial for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive advantage. Netflix actively seeks out and hires top talent, and it is not afraid to let go of employees who do not meet its high-performance standards. This focus on talent density ensures that the company has a strong and capable workforce that can drive innovation and deliver exceptional results.
Netflix’s culture also promotes a culture of candor and open communication. The company encourages employees to speak their minds, challenge ideas, and provide honest feedback. This culture of open communication fosters a collaborative and transparent environment where ideas can be freely shared and debated. By encouraging open communication, Netflix ensures that the best ideas rise to the top and that employees feel valued and heard.
The impact of Netflix’s culture on employee behavior has been instrumental in the company’s success. The culture of autonomy and responsibility has empowered employees to take risks and innovate, leading to the development of groundbreaking products and services. The focus on high performance has motivated employees to consistently deliver exceptional results, driving the company’s growth and success. The emphasis on talent density has ensured that Netflix has a strong and capable workforce that can drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge. The culture of candor and open communication has fostered a collaborative and transparent environment where ideas can flourish and employees can contribute their best work.
Overall, Netflix’s culture has created an environment where employees are empowered, motivated, and inspired to excel. This culture has contributed to the company’s ability to attract and retain top talent, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive advantage in the streaming industry. By fostering a culture of autonomy, high performance, talent density, and open communication, Netflix has created a winning formula that has propelled its organizational success.

Exercise 5:1 – “Behavior Observation Activity.”
Conclusion:
Understanding the impact of organizational culture on employee behavior is crucial for creating a positive and productive work environment. By analyzing the influence of culture on collaboration, innovation, and customer focus, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to shape behavior through culture. The provided exercise, “Behavior Observation Activity,” allows participants to engage in hands-on analysis and discussions. The case study on Netflix further illustrates the impact of culture on behavior. As Jack Welch stated, culture drives great results, emphasizing the transformative power of culture in shaping employee behavior and organizational success.

Course Manual 6: Decision-Making Processes
Introduction:
Culture plays a vital role in decision-making processes within organizations. Decision-making is influenced by the values, norms, and assumptions embedded in the culture. For example, a Clan culture may prioritize consensus-building and participatory decision-making, while a Market culture may emphasize data-driven decision-making and competition. Understanding the cultural influences on decision-making helps organizations make more effective and aligned choices.
In this section, we will explore how organizational culture shapes decision-making processes, and we’ll take a deeper dive into the specific roles of values, communication, and power dynamics. Through a case study, analysis, and exercises, we will gain insights into the importance of understanding these processes and how organizations can foster effective decision-making through culture.
Quote: “Culture is the invisible force that shapes our decision-making processes. It influences the values, beliefs, and norms that guide our choices, ultimately determining the success or failure of our decisions” – Edgar Schein, Organizational Culture and Leadership
Understanding Decision-Making Processes:
One way in which organizational culture shapes decision-making processes is through the establishment of norms and values. These norms and values provide a framework for decision-making and guide individuals on what is considered acceptable or unacceptable behavior. For example, in a culture that values innovation and risk-taking, decision-making processes may be more decentralized, allowing for greater autonomy and creativity. On the other hand, in a culture that values stability and conformity, decision-making processes may be more centralized and focused on maintaining the status quo.
The culture of an organization also determines who is involved in the decision-making process. In some organizations, decision-making is hierarchical, with decisions being made by top-level executives or managers. In others, decision-making is more participatory, involving input from employees at all levels of the organization. The culture of an organization can either encourage or discourage employee involvement in decision-making, which can have a significant impact on the quality and effectiveness of decisions. When employees feel empowered and included in the decision-making process, they are more likely to be committed to the decisions made and to work towards their successful implementation.
The overall effectiveness of decision-making processes is also influenced by organizational culture. A culture that values open communication, collaboration, and learning from mistakes can lead to more effective decision-making. In such a culture, individuals are encouraged to share their ideas and perspectives, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the problem at hand. Additionally, a culture that encourages learning from mistakes allows for continuous improvement and adaptation, leading to better decision-making over time.
On the other hand, a culture that is resistant to change, hierarchical, or focused on individual interests can hinder effective decision-making. In such cultures, individuals may be hesitant to challenge the status quo or voice alternative viewpoints, leading to groupthink and a lack of critical evaluation of decisions. This can result in poor decision-making and missed opportunities for innovation and growth.
In conclusion, organizational culture plays a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within an organization. It establishes the norms and values that guide decision-making, determines who is involved in the process, and influences the overall effectiveness of decisions. Organizations that foster a culture of open communication, collaboration, and learning from mistakes are more likely to make effective decisions that drive success and growth. Conversely, organizations with cultures that resist change, are hierarchical, or prioritize individual interests may struggle with decision-making and miss out on opportunities for improvement and innovation. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to cultivate a positive and supportive culture that encourages employee involvement and fosters effective decision-making.

Analysis:
Analyzing decision-making processes involves examining the alignment between desired decision-making practices and the actual processes followed within the organization. By assessing the influence of culture on decision-making, organizations can identify areas of improvement and implement strategies to foster effective decision-making.
Role of Values:
Values play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes. They provide a foundation for ethical behavior and guide individuals in making choices that align with the organization’s mission and vision. Values serve as a compass, helping individuals navigate complex situations and make decisions that are consistent with the organization’s principles.
One way in which values shape decision-making processes is by providing a framework for evaluating options. When faced with a decision, individuals can refer to the organization’s values to determine which option best aligns with those values. For example, if one of the organization’s core values is integrity, individuals can assess whether a particular decision is honest and transparent. Values help individuals prioritize and make choices that are in line with the organization’s ethical standards.
Consider a company that values sustainability. When making decisions about sourcing materials or manufacturing processes, the organization will prioritize options that have the least negative impact on the environment. This value will guide decision-making and lead to choices that align with the organization’s commitment to sustainability.
Values also influence the decision-making process by setting expectations for behavior. When an organization has clearly defined values, individuals understand the behaviors that are expected of them. This clarity helps guide decision-making and ensures that choices are made in a manner consistent with the organization’s values. For example, if one of the values is teamwork, individuals are more likely to involve others in the decision-making process and seek input from different perspectives. For example, a company that values collaboration will encourage employees to work together and involve multiple stakeholders in decision-making processes. This value will shape the decision-making process by promoting inclusivity and ensuring that decisions are made with input from various perspectives.
Values shape decision-making processes by fostering a sense of purpose and meaning. When individuals understand and embrace the organization’s values, they are more motivated to make decisions that contribute to the organization’s overall mission and vision. Values provide a sense of direction and guide individuals in making choices that are aligned with the organization’s long-term goals. This sense of purpose can enhance decision-making by ensuring that choices are made with the organization’s best interests in mind. For example, a nonprofit organization that values social impact will prioritize decisions that have a positive effect on the community it serves. This value will guide decision-making and lead to choices that align with the organization’s mission of making a difference in people’s lives.
Values also play a role in shaping the culture of an organization, which in turn influences decision-making processes. When an organization’s values are consistently demonstrated and reinforced, they become ingrained in the culture. This culture then shapes how decisions are made and what is considered acceptable behavior. For example, if one of the organization’s values is innovation, the culture may encourage risk-taking and experimentation in decision-making processes. A technology company that values innovation would foster a culture that encourages employees to think outside the box and take risks in their decision-making. On the other hand, if one of the values is stability, the culture may prioritize caution and a more conservative approach to decision-making.
Values can help guide decision-making during times of uncertainty or ambiguity. When faced with complex or challenging situations, individuals can rely on the organization’s values to provide guidance and clarity. Values serve as a moral compass, helping individuals navigate difficult decisions and make choices that are consistent with the organization’s principles. For example, during a crisis, a healthcare organization that values patient safety and well-being will prioritize decisions that prioritize the health and safety of patients. This value will guide decision-making and lead to choices that align with the commitment to providing quality care.
In conclusion, values play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within an organization. They provide a framework for evaluating options, set expectations for behavior, foster a sense of purpose, shape organizational culture, and guide decision-making during times of uncertainty. Organizations that have clearly defined values and promote a culture that aligns with those values are more likely to make ethical and effective decisions. Values serve as a guiding force, ensuring that decisions are made in a manner consistent with the organization’s mission and vision. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to identify and promote their core values to shape decision-making processes and foster a positive and ethical organizational culture.
Analysis:
Analyzing the role of values in decision-making involves examining the organization’s stated values and assessing their influence on decision-making processes. By understanding the impact of values on decision-making, organizations can ensure that decisions are aligned with the desired culture and values.
Chart: Simple Values-Based Decision Making Decision Tree (Credit: Clarkie Consulting)
Communication Channels:
Communication channels play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within an organization. They serve as the means through which information is shared, ideas are exchanged, and decisions are made. Effective communication channels facilitate the flow of information, ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the decision-making process, and promote transparency and accountability. In contrast, poor communication channels can lead to misunderstandings, misalignment, and ineffective decision-making.
One way in which communication channels shape decision-making processes is by facilitating the sharing of information. In order to make informed decisions, individuals need access to relevant and accurate information. Communication channels such as meetings, emails, and reports enable the dissemination of information to the relevant parties. For example, in a product development team, regular meetings and status updates allow team members to share progress, challenges, and insights, which in turn inform decision-making regarding the product’s development and launch.
Communication channels ensure that all the relevant stakeholders are involved in the decision-making process. Effective decision-making requires input from individuals with diverse perspectives and expertise. Communication channels that allow for collaboration and participation, such as brainstorming sessions or online platforms, enable stakeholders to contribute their ideas, insights, and concerns. For instance, in a marketing department, a collaborative platform can be used to gather input from different team members on a new advertising campaign, ensuring that decisions are made collectively and reflect a variety of perspectives.
Communication channels promote transparency and accountability in decision-making processes. When information is shared openly and consistently, individuals feel more informed and engaged, leading to greater trust and buy-in. Communication channels that encourage open dialogue and feedback, such as town hall meetings or suggestion boxes, create an environment where individuals feel comfortable expressing their opinions and concerns. This transparency fosters a sense of accountability, as decisions are made with the knowledge that they will be subject to scrutiny and evaluation. For example, in a nonprofit organization, regular town hall meetings can be held to update employees on the organization’s financial situation and involve them in decision-making regarding budget allocations.
Communication channels can also help to overcome barriers and challenges in decision-making processes. In complex or geographically dispersed organizations, communication channels such as video conferencing or project management software enable real-time collaboration and decision-making across different locations. These channels bridge the gap between individuals and teams, ensuring that decision-making is not hindered by physical distance. In a multinational corporation for example, video conferencing can be used to bring together teams from different countries to make decisions regarding global marketing strategies.
Good communication channels facilitate feedback and learning. Effective decision-making requires a continuous feedback loop, where decisions are evaluated and adjusted based on outcomes and new information. Channels that encourage feedback, such as performance reviews or project retrospectives, provide opportunities for individuals and teams to reflect on their decisions and learn from their experiences. This feedback loop promotes continuous improvement and enhances decision-making over time. An example would be in a software development team where regular retrospectives could be held to evaluate the effectiveness of decision-making processes and identify areas for improvement.
Communication channels clearly play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within an organization. They facilitate the sharing of information, ensure the involvement of relevant stakeholders, promote transparency and accountability, overcome barriers and challenges, and enable feedback and learning. Effective communication channels create an environment where decisions are made based on accurate and relevant information, involve diverse perspectives, and are subject to scrutiny and evaluation. Organizations that prioritize effective communication channels are more likely to make informed and inclusive decisions that drive success and growth. Therefore, it is essential to establish and maintain communication channels that foster open dialogue, collaboration, and feedback to shape decision-making processes positively.
Analysis:
Analyzing the role of communication channels in decision-making involves assessing the organization’s communication practices, such as the frequency and quality of communication, the accessibility of information, and the involvement of stakeholders. By understanding the influence of communication on decision-making, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance communication effectiveness.
Chart: Communication at Work – Selecting Appropriate Channels
(This chart can be used to facilitate discussions on the alignment between communication channels and effective decision-making.)
Power Dynamics:
Power dynamics play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within an organization. The distribution and exercise of power among individuals and groups within an organization can significantly influence the way decisions are made, who has a say in the process, and ultimately, the outcomes of those decisions. Understanding power dynamics is essential for effective decision-making and organizational success.
The hierarchical structure found in many organizations is an example of how power dynamics shape decision-making processes. In a traditional top-down structure, decision-making power is concentrated at the top levels of management, with lower-level employees having limited influence. This power dynamic can lead to decisions being made without considering the perspectives and expertise of those lower down in the organization. For instance, a CEO may make a decision about a new product launch without consulting the sales team, resulting in a product that does not meet customer needs or fails to generate sales.
Another example is the influence of informal power dynamics within teams or departments. In many organizations, there are individuals who hold informal power due to their expertise, relationships, or personal charisma. These individuals may not have formal authority, but their opinions and preferences carry weight and can shape decision-making processes. For example, a team leader who is well-liked and respected by their colleagues may have a significant influence on the decisions made within the team, even if their formal authority is limited. This can lead to decisions being made based on personal relationships rather than objective criteria.
Power dynamics can also impact decision-making through the use of coercive power. Coercive power is the ability to influence others through fear, punishment, or the threat of negative consequences. In organizations where coercive power is prevalent, decision-making processes may be driven by fear or the desire to avoid punishment rather than by a genuine consideration of the best interests of the organization. This can result in decisions that prioritize short-term gains or the interests of those in power over long-term sustainability or the needs of stakeholders.
On the other hand, power dynamics can be harnessed positively to improve decision-making processes. Organizations that embrace a more participatory approach to decision-making, where power is distributed and shared among employees, can benefit from a wider range of perspectives and expertise. This can lead to more informed and innovative decisions. By involving employees at all levels in the decision-making process, organizations can tap into the collective intelligence of their workforce and increase employee engagement and commitment.
In conclusion, power dynamics play a crucial role in shaping decision-making processes within organizations. The distribution and exercise of power can determine who has a say in decision-making, how decisions are made, and the outcomes of those decisions. Understanding and managing power dynamics is essential for effective decision-making and organizational success. By recognizing and addressing power imbalances, organizations can create a more inclusive and collaborative decision-making process that considers a wider range of perspectives and ultimately leads to better outcomes.
Analysis:
Analyzing power dynamics in decision-making involves assessing the organization’s structure, leadership style, and the level of employee involvement in decision-making processes. By understanding the influence of power dynamics on decision-making, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to foster inclusive decision-making.
Chart: Power at Work (Credit: The Democratic Society)
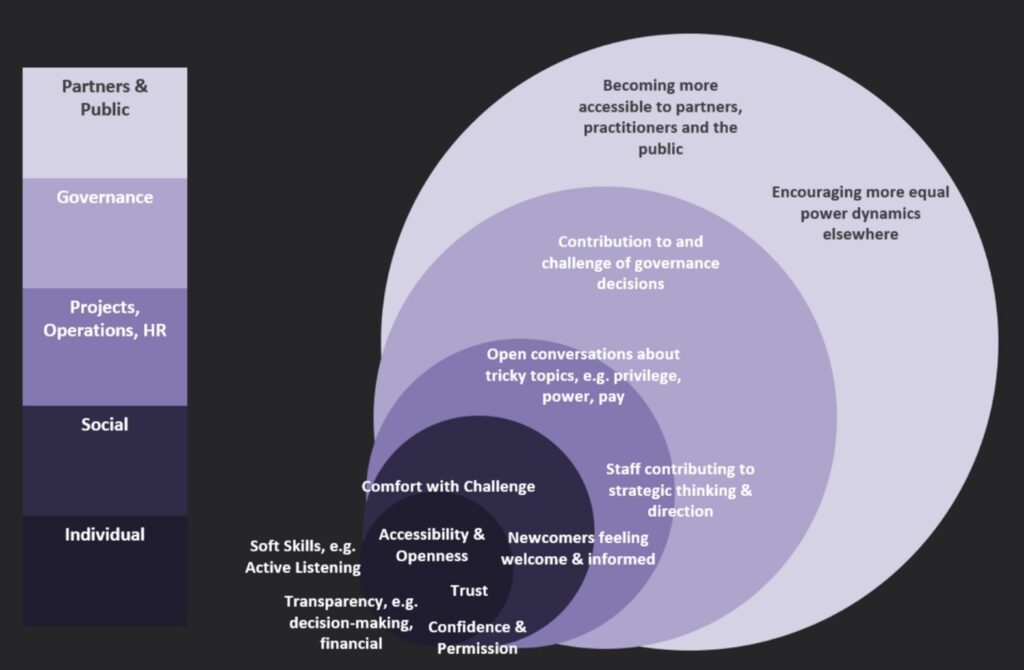
(This chart can be used to facilitate discussions on the alignment between power dynamics and effective decision-making.)

Case Study: Enron Corporation – Poor Organizational Culture and Decision-Making
Background: Enron Corporation was an American energy company that was once one of the largest and most successful companies in the world. However, it collapsed in 2001 due to widespread accounting fraud and unethical business practices. The downfall of Enron is often attributed to a toxic organizational culture that prioritized short-term financial gains over ethical decision-making.
Mistakes Made:
1. Lack of Transparency: Enron had a culture of secrecy and lack of transparency, which allowed unethical practices to thrive. Decision-making processes were often conducted behind closed doors, with limited input or oversight from employees or external stakeholders. This lack of transparency enabled executives to manipulate financial statements and hide debt, leading to the eventual collapse of the company.
2. Emphasis on Financial Performance: Enron had a culture that placed excessive emphasis on financial performance and stock price, often at the expense of ethical considerations. Executives were incentivized to meet aggressive financial targets, leading to unethical practices such as inflating revenues and hiding losses. This focus on short-term financial gains undermined the long-term sustainability and integrity of the company.
3. Lack of Accountability: Enron had a culture that lacked accountability, with executives and employees not being held responsible for their actions. This lack of accountability allowed unethical behavior to go unchecked and created a culture of impunity. Decision-making processes were driven by personal interests and self-preservation rather than the best interests of the company and its stakeholders.
Impact on the Business: The poor organizational culture and decision-making at Enron had severe consequences for the company and its stakeholders. The collapse of Enron resulted in the loss of thousands of jobs, wiped out billions of dollars in shareholder value, and had a significant impact on the broader financial markets. The scandal also eroded public trust in corporations and led to increased scrutiny and regulation of the accounting and financial industries.
The case of Enron serves as a cautionary tale of the importance of a strong ethical culture and sound decision-making processes within organizations. It highlights the devastating impact that a toxic culture can have on a company’s reputation, financial stability, and long-term success.
For a positive case study, Google’s decision-making culture can be examined. Google is known for its data-driven and inclusive decision-making processes. The case study can highlight how Google’s culture influences decision-making, such as the emphasis on data analysis, the involvement of diverse perspectives, and the focus on experimentation. It can provide real-life examples of how culture shapes decision-making and contributes to organizational success.

Exercise 6:1 – “Decision Making Simulation – Cultural Influence on Decision Making”:
1. Divide participants into 2 groups of 5 people.
– What are the key factors to consider when making this decision?
– How might the organizational culture influence the decision-making process?
– How do the cultural values and norms of the organization align with each option?
– Are there any cultural biases or assumptions that may affect the decision-making process?
– How can the group ensure that cultural diversity is taken into account and that decisions are made in a fair and inclusive manner?
Conclusion:
Understanding the impact of organizational culture on decision-making processes is crucial for creating a culture that supports effective decision-making. By analyzing the role of values, communication channels, and power dynamics, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to foster inclusive and transparent decision-making. The provided exercise, “Decision-Making Simulation,” allows participants to engage in hands-on analysis and discussions. The case study on Enron further illustrates the impact of a toxic culture on decision-making. As Edgar Schein states, culture is the invisible force that shapes our decision-making processes emphasizing the transformative power of culture in shaping decision-making within organizations.

Course Manual 7: Overall Performance
Introduction:
Organizational culture has a direct and significant impact on overall performance. A strong and positive culture enhances employee engagement, satisfaction, and retention. It fosters a sense of purpose and shared values, leading to increased productivity and innovation. Moreover, a strong culture attracts customers and stakeholders who align with the organization’s values, contributing to long-term success.
In this chapter, we will explore how culture influences various aspects of an organization’s performance, including employee engagement, productivity, and business outcomes. Through analysis and a case study, we will gain insights into the importance of fostering a positive culture for achieving high levels of overall performance.

Quote: “Culture is the foundation of everything we do in an organization.” – Tricia Griffith
The Impact of Culture on Employee Engagement:
The culture of an organization plays a crucial role in shaping employee engagement and ultimately impacting the overall performance of the organization. A positive and inclusive culture fosters a sense of belonging, motivation, and commitment among employees, leading to improved results and outcomes. In this section, we will explore the specific impact of organizational culture on employee engagement and provide real examples to illustrate its significance.
Employee engagement refers to the level of commitment, passion, and enthusiasm employees have towards their work and the organization they work for. It is a measure of how invested employees are in their roles and how willing they are to go above and beyond to contribute to the organization’s success. A strong organizational culture can significantly influence employee engagement in several ways.
Firstly, a positive and supportive culture promotes a sense of belonging and camaraderie among employees. When employees feel valued, respected, and included, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated to perform at their best. For example, Google is renowned for its inclusive and supportive culture, which encourages employees to bring their whole selves to work. This has resulted in high levels of employee engagement and innovation, leading to Google’s success as a leading technology company.
Secondly, a culture that promotes open communication and transparency fosters trust and engagement among employees. When employees feel that their opinions and ideas are valued and that they have a voice within the organization, they are more likely to be engaged and actively contribute to the organization’s goals. For instance, Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, has a culture that emphasizes open and honest communication. This has created a strong sense of trust and engagement among employees, resulting in exceptional customer service and business growth.
A culture that encourages learning and development also significantly impacts employee engagement. When organizations invest in the growth and development of their employees, it demonstrates a commitment to their success and well-being. This, in turn, motivates employees to engage in their work and strive for continuous improvement. For example, LinkedIn, a professional networking platform, has a culture that promotes learning and development. They provide various opportunities for employees to enhance their skills and knowledge, resulting in high levels of engagement and a highly skilled workforce.
Equally, a culture that recognizes and rewards employee contributions can have a significant impact on engagement. When employees feel appreciated and rewarded for their efforts, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated to perform at their best. For instance, Southwest Airlines has a culture that celebrates and rewards employee achievements. This has created a strong sense of pride and engagement among employees, leading to exceptional customer service and profitability.
The impact of organizational culture on employee engagement is undeniable. A positive and inclusive culture fosters a sense of belonging, trust, and motivation among employees, resulting in improved performance and outcomes for the organization. The above cited real-life examples demonstrate the power of a strong organizational culture in driving employee engagement and ultimately achieving success. Organizations that prioritize and invest in cultivating a positive culture are more likely to reap the benefits of engaged and motivated employees.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on employee engagement involves assessing factors such as communication, recognition, and opportunities for growth within the organization. By understanding the influence of culture on employee engagement, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance engagement levels.
Chart: Dimensions of Employee Engagement
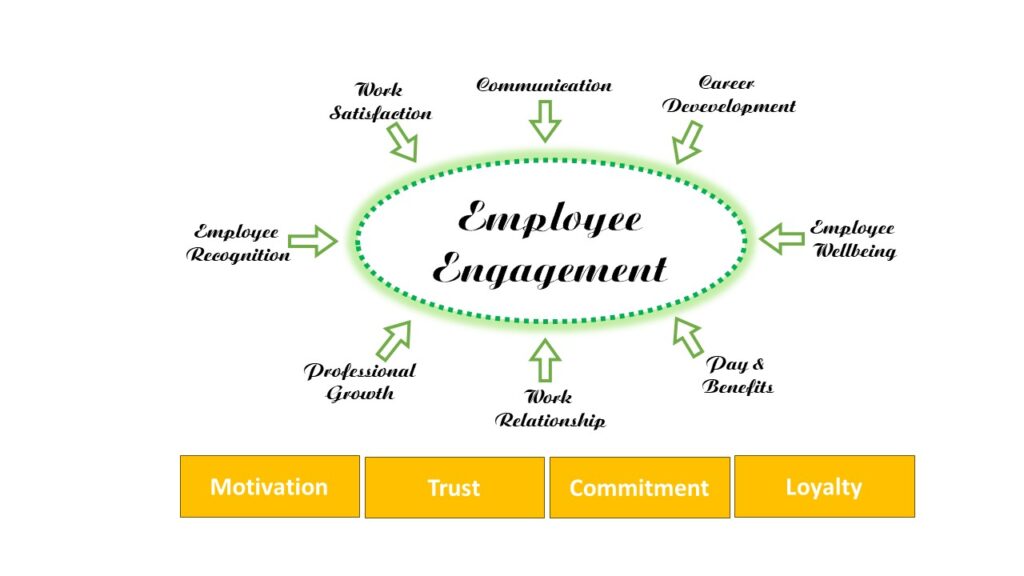
This chart illustrates the different dimensions of employee engagement influenced by culture. This chart can be used to facilitate discussions and identify opportunities for reinforcing desired engagement behaviors within the organization.
The Impact of Culture on Productivity:
The culture of an organization has a significant impact on its overall performance, particularly in terms of productivity and the resulting improvement in results. A positive and supportive culture can enhance productivity by fostering a sense of motivation, collaboration, and commitment among employees. In this section, we will explore the specific impact of organizational culture on productivity and provide real examples to illustrate its significance.
Productivity refers to the efficiency and effectiveness with which employees perform their tasks and contribute to the organization’s goals. A strong organizational culture can greatly influence productivity in several ways.
It is widely acknowledged that a culture that promotes a positive work environment and employee well-being has a direct impact on productivity. When employees feel valued, supported, and cared for, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged in their work. For example, Patagonia, an outdoor clothing and gear company, has a culture that prioritizes work-life balance, employee wellness, and environmental sustainability. This has resulted in high levels of employee satisfaction and productivity, as employees feel a sense of purpose and alignment with the company’s values.
A culture that encourages collaboration and teamwork can also significantly enhance productivity. When employees are encouraged to work together, share ideas, and support one another, it leads to increased efficiency and innovation. For instance, Pixar Animation Studios has a culture that emphasizes collaboration and creativity. Their open and inclusive culture has resulted in highly successful and critically acclaimed films, as employees work together to bring their collective talents and ideas to life.
Promoting autonomy and empowerment can also have a positive impact on productivity. When employees are given the freedom to make decisions, take ownership of their work, and have a sense of control over their tasks, it can lead to increased productivity and innovation. For example, Netflix has a culture that values freedom and responsibility. They empower their employees to make decisions and trust them to do what is best for the company. This has resulted in a highly productive and successful streaming platform.
In addition, a culture that values continuous learning and improvement significantly enhances productivity. When organizations invest in the development of their employees and provide opportunities for growth, it leads to increased knowledge, skills, and efficiency. For instance, Toyota has a culture that emphasizes continuous improvement and employee development through their Toyota Production System. This has resulted in high levels of productivity and quality in their manufacturing processes.
As noted before, a culture that recognizes and rewards employee contributions can have a significant impact on engagement and this is true too for productivity. When employees feel appreciated and rewarded for their efforts, it motivates them to perform at their best and strive for excellence. For example, Microsoft has a culture that values and rewards innovation. They have various recognition programs and incentives in place to acknowledge and celebrate employee contributions. This has resulted in increased productivity and a culture of continuous innovation within the company.
Overall, the impact of organizational culture on productivity and the resulting improvement in results is undeniable. A positive and supportive culture that prioritizes employee well-being, collaboration, autonomy, continuous learning, and recognition can greatly enhance productivity within an organization. The real-life examples of many companies demonstrate the power of a strong organizational culture in driving productivity and achieving exceptional results. Organizations that invest in cultivating a positive culture are more likely to experience increased productivity, innovation, and overall success.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on productivity involves assessing factors such as teamwork, communication, and the presence of performance-driven practices within the organization. By understanding the influence of culture on productivity, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance productivity levels.

Different factors contribute to a productive culture, such as clear goals, effective communication, and a focus on quality, illustrating the importance of culture in fostering productivity.
The Impact of Culture on Business Outcomes:
The culture of an organization has a significant impact on its overall performance and business outcomes. A positive and strong organizational culture can lead to improved results, increased profitability, and sustainable success.
Business outcomes refer to the tangible results and achievements that an organization attains, such as financial performance, customer satisfaction, market share, and employee retention. The culture of an organization plays a crucial role in shaping these outcomes in several ways.
A culture that values customer-centricity and focuses on delivering exceptional customer experiences can have a direct impact on business outcomes. When employees are aligned with the organization’s values and are committed to providing excellent customer service, it leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business growth. For example, Amazon has a culture that prioritizes customer obsession. This has resulted in high customer satisfaction, repeat business and market dominance.
Promoting innovation and risk-taking can significantly impact business outcomes. When employees are encouraged to think creatively, experiment, and take calculated risks, it leads to the development of new products, services, and processes that can drive growth and competitive advantage. For instance, Apple has a culture that fosters innovation and encourages employees to challenge the status quo. This has resulted in groundbreaking products like the iPhone and iPad, leading to Apple’s success as a technology leader.
A culture that values and invests in employee development and engagement can have a positive impact on business outcomes. When employees feel valued, supported, and empowered, they are more likely to be motivated, productive, and committed to the organization’s goals. This, in turn, leads to improved performance, higher employee retention rates, and ultimately, better business results. For example, The Ritz-Carlton Hotel Company has a culture that prioritizes employee training, empowerment, and recognition. This has resulted in exceptional customer service, high employee satisfaction, and a strong brand reputation.
A culture that promotes ethical behavior and corporate social responsibility can also impact business outcomes. When organizations prioritize ethical practices, sustainability, and social impact, it can enhance their reputation, attract customers and investors, and contribute to long-term success. For instance, Patagonia has a culture that emphasizes environmental sustainability and social responsibility. This has resulted in a loyal customer base, strong brand loyalty, and business growth.
Collaboration, teamwork, and diversity can have a positive impact on business outcomes. When employees from diverse backgrounds and perspectives come together to work towards common goals, it leads to increased creativity, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities. This, in turn, can drive business growth and competitiveness. For example, Procter & Gamble (P&G) has a culture that promotes diversity and inclusion. This has resulted in a diverse portfolio of products that cater to a wide range of customer needs, contributing to P&G’s success as a global consumer goods company.
The impact of organizational culture on business outcomes and the resulting improvement in results is significant. A positive and strong culture that values customer-centricity, innovation, employee development, ethical behavior, collaboration, and diversity can lead to improved financial performance, customer satisfaction, market share, and employee retention. Real-life examples such as Amazon and Apple, demonstrate the power of a strong organizational culture in driving business outcomes and achieving sustainable success. Organizations that prioritize and invest in cultivating a positive culture are more likely to experience improved results and long-term growth.
Analysis:
Analyzing the impact of culture on business outcomes involves assessing factors such as customer loyalty, employee retention, and financial performance. By understanding the influence of culture on business outcomes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to enhance overall performance.

Case Study: Patagonia
To support and illustrate the content, a more detailed case study on Patagonia’s culture and its impact on overall performance can be examined. Patagonia is a well-known outdoor clothing and gear company that has gained recognition for its strong organizational culture and commitment to environmental sustainability. The company’s culture has had a direct impact on employee engagement, productivity, and overall business outcomes, leading to its success. Let’s explore the key aspects of Patagonia’s culture and how they have contributed to these outcomes.
1. Environmental Stewardship: Patagonia’s culture is deeply rooted in environmental stewardship. The company’s mission is to “build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.” This mission resonates with employees who are passionate about sustainability and environmental conservation. As a result, employees feel a strong sense of purpose and alignment with the company’s values, leading to high levels of engagement.
2. Work-Life Balance: Patagonia places a strong emphasis on work-life balance and employee well-being. The company offers flexible work schedules, encourages employees to pursue outdoor activities, and provides on-site childcare facilities. This commitment to work-life balance fosters a positive and supportive work environment, leading to increased employee satisfaction and productivity.
3. Employee Empowerment: Patagonia empowers its employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work. The company encourages employees to take risks, experiment, and learn from failures. This culture of empowerment fosters innovation, creativity, and a sense of ownership among employees, leading to increased productivity and the development of innovative products and solutions.
4. Employee Development: Patagonia invests in the development of its employees through various training and development programs. The company provides opportunities for skill-building, career growth, and personal development. This commitment to employee development not only enhances individual capabilities but also contributes to overall business outcomes by creating a highly skilled and motivated workforce.
5. Transparency and Open Communication: Patagonia maintains a culture of transparency and open communication. The company encourages employees to share their ideas, concerns, and feedback openly. This culture of open communication fosters trust, collaboration, and engagement among employees, leading to improved teamwork and overall business outcomes.
The impact of Patagonia’s culture on employee engagement, productivity, and overall business outcomes has been significant. The company has achieved remarkable success, both financially and in terms of its environmental impact. Patagonia’s revenue has consistently grown, and it has become a leading brand in the outdoor industry. The company’s commitment to sustainability and its strong culture have attracted a loyal customer base, resulting in increased market share and brand loyalty.
In conclusion, Patagonia’s organizational culture, which emphasizes environmental stewardship, work-life balance, employee empowerment, development, and open communication, has had a direct impact on employee engagement, productivity, and overall business outcomes. The company’s success can be attributed to its strong culture, which has created a motivated and committed workforce, fostered innovation, and attracted loyal customers. Patagonia serves as a compelling business case study for the power of a positive and values-driven organizational culture in driving success.

Exercise 7:1 – “Culture and Performance Assessment.”
– Revenue growth: Measure the increase in revenue over a specific period.
– Profit margin: Track the percentage of profit generated from sales.
– Return on investment (ROI): Assess the profitability of investments made.
– Customer satisfaction: Measure customer satisfaction through surveys or feedback.
– Customer retention rate: Track the percentage of customers who continue to use your
products or services.
– Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measure customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend
your organization.
– Cycle time: Measure the time it takes to complete a process or deliver a
product/service.
– Quality index: Assess the level of quality in products or services delivered.
– Process efficiency: Track the percentage of waste or rework in internal processes.
– Employee satisfaction: Measure employee satisfaction through surveys or feedback.
– Employee turnover rate: Track the percentage of employees who leave the
organization.
– Training and development: Assess the number of training programs offered and
employee participation.
– Employee engagement: Measure the level of employee engagement through surveys
or feedback.
– Diversity and inclusion: Track the representation of diverse groups within the
organization.
– Alignment with core values: Assess the extent to which employees demonstrate
behaviors aligned with the organization’s core values.
– Number of new products/services: Track the number of new products or services
introduced.
– Research and development (R&D) investment: Measure the percentage of revenue
invested in R&D.
– Idea generation and implementation: Assess the number of ideas generated and
successfully implemented.
1. If your culture emphasizes innovation, an objective could be to foster a culture of continuous improvement and creativity.

Conclusion:
Organizational culture has a profound impact on overall performance. By understanding the influence of culture on employee engagement, productivity, and business outcomes, organizations can create a positive culture that drives high levels of performance. The provided exercise, “Culture and Performance Assessment,” allows participants to engage in hands-on analysis and discussions. The case study on Patagonia further illustrates the impact of culture on overall performance. As Tricia Griffith stated, culture is the foundation of everything we do in an organization, emphasizing the transformative power of culture in achieving exceptional overall performance.

Course Manual 8: Assessing Existing Culture
Introduction:
Assessing the existing culture of an organization is a crucial step in understanding its strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. In this section, we will explore various methods and tools for assessing organizational culture, including surveys, interviews, and observation. Through charts, analysis, a case study and an exercise, we will gain insights into the importance of assessing existing culture and how it can inform culture change efforts.

Quote: “Culture is the foundation upon which great organizations are built.” – Peter Drucker
The Importance of Assessing Existing Culture:
Assessing the existing culture of an organization and understanding its impact on organizational success is of paramount importance. Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors that shape the way people think, act, and interact within an organization. It serves as the foundation upon which the organization’s identity, purpose, and strategy are built. Here are some key reasons why assessing and understanding the existing culture is crucial for organizational success:
1. Alignment with Strategy: Assessing the existing culture helps leaders ensure that the culture aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. A strong alignment between culture and strategy ensures that the organization’s values and behaviors support the desired outcomes. When there is a misalignment, it can hinder the implementation and success of strategic initiatives.
2. Employee Engagement and Productivity: The culture of an organization significantly impacts employee engagement and productivity. A positive and supportive culture fosters a sense of belonging, motivation, and commitment among employees. It creates an environment where employees feel valued, empowered, and motivated to give their best. On the other hand, a toxic or negative culture can lead to disengagement, low morale, and decreased productivity.
3. Talent Attraction and Retention: Assessing the existing culture helps organizations attract and retain top talent. In today’s competitive job market, candidates are not only looking for attractive compensation packages but also for organizations with a positive and inclusive culture. A strong culture that aligns with the values and aspirations of potential employees can be a powerful tool for attracting and retaining the best talent.
4. Innovation and Adaptability: Organizational culture plays a crucial role in fostering innovation and adaptability. A culture that encourages risk-taking, creativity, and continuous learning can drive innovation and help organizations stay ahead in a rapidly changing business environment. Assessing the existing culture allows leaders to identify any barriers or gaps that may hinder innovation and make necessary adjustments to foster a culture of innovation.
5. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: The culture of an organization has a direct impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty. A culture that prioritizes customer-centricity, quality, and service excellence can lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty. Assessing the existing culture helps identify areas where the culture may be hindering customer-centric behaviors and allows leaders to implement strategies to improve the customer experience.
6. Organizational Resilience and Change Management: Assessing the existing culture is crucial for building organizational resilience and effectively managing change. A strong culture that embraces change, encourages learning, and adapts to new circumstances can help organizations navigate through challenges and seize opportunities. Understanding the existing culture allows leaders to identify any cultural barriers to change and develop strategies to overcome resistance and drive successful change initiatives.
In conclusion, assessing the existing culture and understanding its impact on organizational success is essential for leaders to create a positive and high-performing work environment. It enables leaders to align culture with strategy, enhance employee engagement and productivity, attract and retain top talent, foster innovation and adaptability, improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, and build organizational resilience. By proactively assessing and shaping the culture, organizations can create a strong foundation for long-term success and sustainable growth.
Analysis:
Analyzing the importance of assessing existing culture involves understanding the impact of culture on organizational performance, employee engagement, and customer satisfaction. By recognizing the significance of culture in achieving desired outcomes, organizations can prioritize culture assessment as a critical step in their improvement journey.
Chart: Companies known for strong focus on assessing and shaping culture

This chart can be used to facilitate discussions on the importance of assessing existing culture and its impact on organizational success.
Methods for Assessing Organizational Culture:
Assessing organizational culture is a critical step in understanding the values, beliefs, and behaviors that shape the work environment and drive employee performance. There are several methods that organizations can use to assess their culture, each with its own strengths and limitations. Here are some commonly used methods for assessing organizational culture, along with real-world examples:
1. Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires are a popular method for assessing organizational culture. These tools typically consist of a series of questions that employees answer anonymously. The questions may cover various aspects of culture, such as values, communication, teamwork, and leadership. The data collected can provide valuable insights into the prevailing culture within the organization.
Example: Google conducts an annual employee survey called “Googlegeist” to assess its culture. The survey covers a wide range of topics, including employee satisfaction, leadership, and work-life balance. The results of the survey help Google identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their culture.
2. Interviews and Focus Groups: Interviews and focus groups involve direct conversations with employees to gather qualitative data about the organizational culture. These methods allow for in-depth exploration of employees’ experiences, perceptions, and beliefs. They provide a deeper understanding of the underlying values and behaviors that shape the culture.
Example: Zappos, an online retailer, conducts culture fit interviews as part of their hiring process. These interviews assess candidates’ alignment with the company’s core values and cultural expectations. By conducting interviews, Zappos ensures that new hires are a good fit for their unique and customer-centric culture.
3. Observation and Ethnography: Observation and ethnography involve observing employees’ behaviors and interactions in their natural work environment. This method allows researchers to gain firsthand insights into the culture by observing how employees behave, communicate, and collaborate. It provides a holistic view of the culture and can uncover hidden aspects that may not be captured through surveys or interviews alone.
Example: Southwest Airlines is known for its strong culture of customer service and employee engagement. To assess their culture, Southwest Airlines uses a combination of observation and ethnography. Researchers spend time observing employees in various roles and departments to understand how the culture is manifested in their daily activities.
4. Cultural Artefacts and Symbols: Cultural artefacts and symbols are tangible representations of an organization’s culture, such as mission statements, logos, office layout, and rituals. Analyzing these artefacts and symbols can provide insights into the values and beliefs that are important to the organization.
Example: Patagonia, an outdoor clothing company, is committed to environmental sustainability. Their culture is reflected in their mission statement, which states, “Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.” The mission statement serves as a cultural artefact that communicates their values and guides their actions.
5. Employee Feedback and Suggestions: Employee feedback and suggestions can be a valuable source of information for assessing organizational culture. Organizations can create channels for employees to provide feedback, share ideas, and voice their concerns. This feedback can help identify areas where the culture may need improvement or where it aligns well with employees’ needs and expectations.
Example: Netflix has a culture of open and honest communication. They have a “Keeper Test” that encourages managers to ask themselves if they would fight to keep a particular employee. This approach values employee feedback and ensures that the culture is continuously assessed and aligned with employees’ needs.
It’s important to note that assessing organizational culture is an ongoing process. Organizations should use a combination of methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of their culture. By regularly assessing and monitoring their culture, organizations can identify areas for improvement, align their culture with their strategic goals, and create a positive and high-performing work environment.
Analysis:
Analyzing the different methods for assessing organizational culture involves understanding their strengths, limitations, and the type of information they provide. By exploring these methods, organizations can choose the most appropriate approach based on their specific needs and goals.
Chart: Methods for assessing organizational culture – advantages & disadvantages
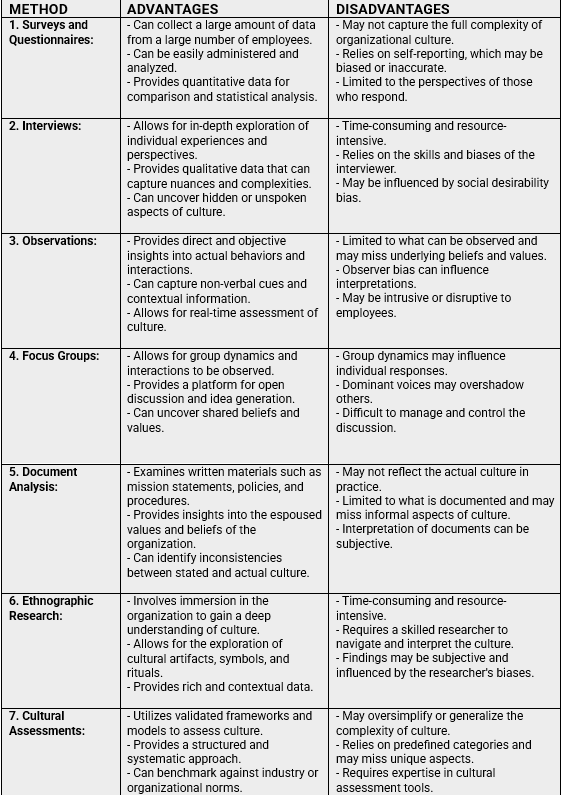
It is important to note that no single method can provide a comprehensive assessment of organizational culture. A combination of methods, such as triangulation, is often recommended to gain a more holistic understanding. The choice of method should align with the specific goals, resources, and constraints of the organization.
This chart can be used to facilitate discussions on the selection of the most suitable method for assessing existing culture.

Case Study: Netflix – Systematically Assessing Existing Culture
Introduction: Netflix, a global streaming giant, has become renowned not only for its vast content library but also for its unique and high-performance culture. The company places a strong emphasis on assessing and cultivating its culture, recognizing that a strong culture is a key driver of business success. This case study explores how Netflix regularly assesses its culture, the methods it employs, and how this contributes to its ongoing success.
Assessing Culture at Netflix:
1. Values and Behaviors: Netflix has a set of core values and behaviors that guide its culture. These values, such as “judgment,” “communication,” and “impact,” are clearly defined and communicated to all employees. Regular assessments are conducted to ensure that employees understand and embody these values in their daily work.
2. 360-Degree Feedback: Netflix utilizes a 360-degree feedback process to assess its culture. This involves gathering feedback from employees at all levels, including peers, subordinates, and managers. The feedback focuses on how well individuals demonstrate the company’s values and behaviors, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
3. Employee Surveys: Netflix conducts regular employee surveys to gauge employee satisfaction, engagement, and alignment with the company’s culture. These surveys provide valuable insights into the overall health of the culture and identify areas for improvement. The company uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative data to analyze survey results and take appropriate actions.
4. Exit Interviews: When employees leave Netflix, they are encouraged to participate in exit interviews. These interviews provide an opportunity for departing employees to share their experiences, insights, and suggestions for improving the culture. Netflix values this feedback and uses it to make necessary adjustments to maintain a positive and engaging work environment.
Cultivating Culture at Netflix:
1. Freedom and Responsibility: Netflix promotes a culture of freedom and responsibility, empowering employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work. This autonomy fosters innovation, creativity, and a sense of ownership, contributing to a high-performance culture.
2. Transparent Communication: Netflix emphasizes transparent and open communication at all levels. Regular company-wide meetings, known as “QBRs” (Quarterly Business Reviews), provide updates on company performance, strategy, and challenges. This transparency ensures that employees are well-informed and aligned with the company’s goals and values.
3. Continuous Learning and Development: Netflix invests in the continuous learning and development of its employees. The company encourages employees to attend conferences, workshops, and training programs to enhance their skills and knowledge. This commitment to employee growth contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
4. Performance-Based Culture: Netflix has a performance-based culture that rewards high performers and encourages underperformers to improve or exit the company. The company emphasizes a “keeper test” philosophy, where managers are encouraged to ask themselves if they would fight to keep a particular employee. This approach ensures that the company maintains a high-performing workforce aligned with its culture and values.
Business Success and Culture Assessment: Netflix’s commitment to regularly assessing and cultivating its culture has played a significant role in its business success. Here are some ways in which culture assessment contributes to Netflix’s achievements:
1. Attracting and Retaining Top Talent: Netflix’s strong culture and reputation as an innovative and high-performing organization attract top talent from around the world. The company’s rigorous culture assessment processes ensure that new hires align with its values, leading to a workforce that is highly motivated and engaged.
2. Agility and Adaptability: By regularly assessing its culture, Netflix remains agile and adaptable in a rapidly changing industry. The company can identify cultural gaps and make necessary adjustments to stay ahead of the competition and respond effectively to market shifts.
3. Innovation and Creativity: Netflix’s culture assessment practices foster a culture of innovation and creativity. By empowering employees and encouraging open communication, the company creates an environment where new ideas can flourish. This culture of innovation has enabled Netflix to disrupt the traditional entertainment industry and continuously deliver new and engaging content to its subscribers.
4. Employee Engagement and Productivity: Regular culture assessments help Netflix identify areas where employee engagement may be lacking. By addressing these issues, the company ensures that its workforce remains motivated, productive, and committed to achieving the company’s goals.
Conclusion: Netflix’s commitment to regularly assessing and cultivating its culture has been instrumental in its ongoing success. By utilizing various assessment methods, such as values and behavior assessments, employee surveys, and exit interviews, Netflix ensures that its culture remains aligned with its values and goals. This focus on culture has contributed to the company’s ability to attract top talent, foster innovation, and maintain a high-performance workforce. As Netflix continues to evolve and expand, its culture assessment practices will remain a critical component of its business strategy.

Exercise 8:1 – “Culture Assessment Survey.”
a. How would you describe the core values of our organization?
b. To what extent do you believe our organization’s values are consistently demonstrated in our daily operations?
c. How well do you think our organization’s values align with your personal values?
a. How would you rate the overall communication within our organization?
b. Do you feel that communication channels are open and transparent?
c. Are you satisfied with the frequency and quality of communication from leadership?
a. How would you describe the leadership style within our organization?
b. Do you feel that leaders in our organization effectively communicate expectations and provide clear direction?
c. How well do you think leaders in our organization support and empower their teams?
a. How would you rate the level of collaboration and teamwork within our organization?
b. Do you feel that there are opportunities for cross-functional collaboration?
c. Are you satisfied with the level of support and cooperation you receive from your colleagues?
a. How would you rate our organization’s openness to new ideas and innovation?
b. Do you feel encouraged to share your ideas and suggestions?
c. Are there processes in place to support and implement innovative ideas?
a. How would you rate our organization’s commitment to diversity and inclusion?
b. Do you feel that everyone is treated fairly and with respect?
c. Are there opportunities for diverse perspectives to be heard and valued?
a. How would you rate the work-life balance within our organization?
b. Do you feel supported in maintaining a healthy work-life balance?
c. Are there policies and practices in place to promote work-life balance?
a. How would you rate the opportunities for professional growth and development within our organization?
b. Do you feel that your skills and talents are recognized and utilized?
c. Are there resources and support available for continuous learning and development?
a. How would you rate our organization’s ability to adapt to change?
b. Do you feel that change is effectively communicated and managed?
c. Are there opportunities for employees to provide input and feedback during times of change?
a. How would you rate your overall level of engagement and satisfaction with your work?
b. Do you feel a sense of pride and connection to our organization?
c. Are there opportunities for employee recognition and appreciation?
Conclusion:
Assessing the existing culture of an organization is a critical step in understanding its strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. By recognizing the importance of culture assessment, organizations can make informed decisions and develop strategies to align culture with their desired goals and values. The provided exercise, “Culture Assessment Survey,” allows participants to engage in hands-on assessment and discussions. The case study on Netflix further illustrates the significance of culture assessment in driving culture change. As Peter Drucker famously said, culture is the foundation upon which great organizations are built., emphasizing the transformative power of culture in shaping organizational success.

Course Manual 9: Identifying Gaps
Introduction:
In order to effectively evolve the culture of an organization, it is crucial to identify the gaps between the current culture and the desired culture. This chapter explores the importance of identifying these gaps and provides insights into various techniques that can be employed to identify gaps in cultural values, behaviors, and practices. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of involving employees in the process to foster a shared understanding of the gaps and to cultivate a sense of ownership and commitment to culture development efforts. Through analysis, an exercise, and a business case study we will gain insights into the importance of a thorough gap analysis.
Quote: “Identifying the gaps between the current and desired culture is a critical step in culture evolution. It provides organizations with a clear vision of the desired culture and helps them set specific goals for cultural change. By acknowledging and addressing these gaps, organizations can align their culture with their strategic objectives, enhance employee engagement, and drive positive outcomes.” – Edgar Schein

Importance of Identifying Gaps:
The importance of identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture cannot be overstated. It is a crucial step in the process of culture evolution and plays a significant role in shaping the success and effectiveness of an organization. Here are several reasons why identifying these gaps is of utmost importance:

1. Clarity of Vision: Identifying gaps helps organizations gain a clear understanding of the desired culture and the areas where the current culture falls short. This clarity enables organizations to set specific goals and objectives for culture evolution. Without a clear vision of the desired culture, organizations may struggle to implement effective change initiatives and may find it challenging to align their culture with their strategic goals.
2. Targeted Interventions: By identifying gaps, organizations can focus their efforts on specific areas that require improvement. This targeted approach allows for more effective and efficient interventions, saving time and resources. Instead of trying to change the entire culture, organizations can prioritize their efforts and concentrate on the areas that will have the most significant impact on achieving the desired culture.
3. Alignment with Strategy: Identifying gaps helps align the culture with the organization’s strategic goals. It ensures that the culture supports and enhances the overall strategy, leading to improved performance and outcomes. When the culture is aligned with the strategy, employees are more likely to understand and embrace the organization’s goals, resulting in increased motivation, productivity, and overall success.
4. Employee Engagement: Involving employees in the process of identifying gaps fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the culture development efforts. When employees are actively engaged in the identification of gaps, they feel valued and recognized for their insights and experiences. This engagement leads to increased motivation and dedication towards achieving the desired culture. Employees become advocates for the culture change, driving it forward and influencing their peers to embrace the desired behaviors and practices.
5. Cultural Insights: Employees possess valuable insights into the day-to-day realities of the organization’s culture. They understand the unwritten rules, norms, and behaviors that shape the culture. Involving employees in the process of identifying gaps allows for a more accurate identification of the gaps and a better understanding of the underlying causes. Their perspectives and experiences provide valuable context and help uncover hidden gaps that may not be apparent to leaders or external consultants.
6. Continuous Improvement: Identifying gaps is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process. It requires organizations to regularly assess their culture and identify areas for improvement. By continuously evaluating the gaps between the current and desired culture, organizations can adapt and refine their culture development strategies. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and ensures that the culture remains aligned with the changing needs and goals of the organization.
In conclusion, identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is crucial for effective culture evolution. It provides clarity of vision, enables targeted interventions, aligns the culture with the strategy, enhances employee engagement, leverages cultural insights, and promotes continuous improvement. By actively involving employees and regularly assessing the gaps, organizations can create a culture that supports their strategic goals, drives positive change, and ultimately leads to long-term success.
Techniques to Identify Gaps:
As we have considered, Identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is crucial for organizations to understand where they stand and what changes need to be made to align their culture with their goals and values. Here are five different techniques that can be used to identify these gaps:
1. Surveys and questionnaires: One of the most common techniques to identify gaps in organizational culture is through surveys and questionnaires. These tools allow organizations to gather feedback from employees at all levels and assess their perceptions of the current culture. Questions can be designed to measure various aspects of culture, such as communication, teamwork, leadership, and values alignment. By comparing the responses to the desired culture, organizations can identify gaps and areas for improvement.

2. Focus groups and interviews: Another effective technique is to conduct focus groups and interviews with employees. This allows for more in-depth discussions and provides an opportunity for employees to share their experiences, opinions, and suggestions. By engaging in open and honest conversations, organizations can gain valuable insights into the current culture and identify gaps that may not have been captured through surveys alone.
3. Observations and shadowing: Sometimes, the best way to understand the current culture is by observing it firsthand. This can be done through shadowing employees in different roles and departments or by simply observing interactions and behaviors within the organization. By paying attention to how people communicate, collaborate, and make decisions, organizations can identify gaps between the current and desired culture.
4. Performance evaluations and feedback: Performance evaluations and feedback processes can also provide valuable information about the organizational culture. By analyzing performance ratings, feedback comments, and development plans, organizations can identify patterns and trends that may indicate gaps in the culture. For example, if employees consistently receive feedback about a lack of teamwork or poor communication, it may indicate a gap between the desired and current culture in these areas.
5. Benchmarking and best practices: Lastly, organizations can identify gaps in their culture by benchmarking against industry best practices and other successful organizations. This involves researching and studying organizations known for their strong cultures and comparing their practices to the current culture. By identifying areas where the organization falls short, organizations can set goals and develop strategies to bridge the gaps and align their culture with the desired state.
In conclusion, identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is essential for organizations to drive meaningful change and improve performance. By utilizing techniques such as surveys, focus groups, observations, performance evaluations, and benchmarking, organizations can gain valuable insights into their culture and identify areas for improvement. It is important to remember that culture is a dynamic and evolving aspect of an organization, and regular assessments are necessary to ensure alignment with the organization’s goals and values.
Importance of Employee Involvement:

We have established that organizational culture plays a vital role in shaping the success and sustainability of any organization. However, organizations often face challenges in aligning their current culture with the desired culture. To bridge this gap effectively, employee involvement is crucial. This section explores the significance of employee involvement in identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture and how it contributes to successful cultural transformation.
1. Enhanced Employee Engagement:
Employee involvement fosters a sense of ownership and engagement among employees. When employees are actively involved in identifying gaps in the organizational culture, they feel valued and empowered. This engagement leads to increased motivation, commitment, and loyalty towards the organization. Engaged employees are more likely to provide honest and constructive feedback, enabling organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current culture and identify areas for improvement.
2. Diverse Perspectives:
Employees at all levels possess unique insights and perspectives on the organizational culture. By involving employees in the gap identification process, organizations can tap into this diverse knowledge base. Different departments, teams, and individuals may have varying experiences and observations, which can provide a holistic view of the current culture. This diversity of perspectives helps organizations identify gaps that may have been overlooked or underestimated by management alone.
3. Accurate Assessment of the Current Culture:
Employees are the primary participants in the organizational culture, experiencing it on a daily basis. Their involvement in identifying gaps ensures a more accurate assessment of the current culture. Surveys, questionnaires, focus groups, and interviews allow employees to express their opinions, share their experiences, and provide feedback on various aspects of the culture. This firsthand information helps organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of the current culture, including its strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
4. Identification of Cultural Misalignments:
Employee involvement enables organizations to identify cultural misalignments that hinder the achievement of desired outcomes. Employees can provide insights into discrepancies between the stated values and actual behaviors within the organization. For example, if the desired culture emphasizes collaboration and teamwork, but employees perceive a lack of cooperation and siloed decision-making, it indicates a misalignment. By involving employees, organizations can identify such gaps and take corrective actions to align the culture with the desired state.
5. Increased Acceptance and Buy-in:
When employees are involved in the gap identification process, they are more likely to accept and support the proposed changes. This is because they feel a sense of ownership and inclusion in the decision-making process. By actively involving employees, organizations can ensure that their perspectives and concerns are considered, leading to a more inclusive and collaborative approach to cultural transformation. This, in turn, increases employee buy-in and reduces resistance to change, facilitating a smoother transition to the desired culture.
6. Identification of Cultural Strengths:
Employee involvement not only helps identify gaps but also highlights the existing strengths within the organizational culture. Employees can provide insights into positive aspects of the current culture that should be preserved and reinforced. By recognizing and leveraging these strengths, organizations can build upon them to create a strong and solid culture. Employee involvement ensures that the desired culture is built on a foundation of existing positive elements, enhancing the chances of successful cultural transformation.
7. Employee Empowerment and Development:
Involving employees in the gap identification process empowers them to contribute to the organization’s success. It provides an opportunity for employees to develop their skills in critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication. By actively participating in discussions, surveys, and interviews, employees enhance their understanding of the organizational culture and its impact on performance. This empowerment and development contribute to a more engaged and capable workforce, ready to embrace the desired culture and drive positive change.
8. Continuous Improvement and Adaptability:
Organizational culture is not a static entity; it evolves over time. Employee involvement in identifying gaps ensures that the process is ongoing and adaptive. By regularly seeking employee feedback and involvement, organizations can continuously monitor and assess the culture’s alignment with the desired state. This enables them to make timely adjustments and improvements, ensuring that the culture remains relevant and supportive of the organization’s goals and values.
Employee involvement is a critical factor in identifying gaps between the current and desired organizational culture. By actively engaging employees in the gap identification process, organizations can tap into their diverse perspectives, enhance employee engagement, and gain a more accurate assessment of the current culture. Employee involvement also facilitates the identification of cultural misalignments, increases acceptance and buy-in, and empowers employees to contribute to the organization’s success. Furthermore, involving employees ensures the recognition and preservation of existing cultural strengths and promotes continuous improvement and adaptability. Ultimately, employee involvement is essential for successful cultural transformation and the achievement of organizational goals.

Case Study: Uber
Uber, a ride-hailing service, experienced significant challenges in aligning its actual culture with the desired culture. The desired culture at Uber was envisioned as one that prioritized diversity, inclusion, and respect for all employees and customers. However, the actual culture within the organization was characterized by a toxic work environment, allegations of sexual harassment, discrimination, and a lack of accountability.
The failure to identify the gaps between the actual and desired culture at Uber can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the rapid growth of the company led to a focus on scaling operations and expanding into new markets, often at the expense of fostering a healthy organizational culture. This growth mindset overshadowed the importance of building a strong internal culture.
Secondly, Uber’s leadership, including former CEO Travis Kalanick, fostered a hyper-competitive and aggressive culture that prioritized results over ethical behavior. This top-down approach trickled down throughout the organization, leading to a culture that tolerated and even encouraged inappropriate conduct.
Additionally, Uber’s lack of effective communication channels and feedback mechanisms further hindered the identification of cultural gaps. Employees were often afraid to speak up about issues due to fear of retaliation or a belief that their concerns would not be addressed.
The impact of this failure to identify cultural gaps was significant for Uber. The company faced numerous lawsuits, public backlash, and a tarnished reputation. The toxic culture led to high employee turnover, difficulty in attracting top talent, and a loss of trust from customers. Uber’s brand image suffered, and it took significant efforts to rebuild trust and reshape the company’s culture.
This case study highlights the importance of proactively identifying and addressing cultural gaps within an organization. Failure to do so can have severe consequences, impacting employee morale, customer perception, and overall business performance.

Exercise 9:1 Gap Analysis Brainstorm
– Flipchart or whiteboard
– Markers
– Sticky notes
1. Begin by briefly summarizing the importance of identifying gaps in current and desired organizational culture, emphasizing the benefits of clarity, targeted interventions, and alignment with strategy.
Conclusion:
Identifying gaps between the current and desired culture is crucial for effective culture evolution. Techniques such as surveys, interviews, observations, benchmarking, and policy reviews can aid in this identification process. Furthermore, involving employees in the process ensures a shared understanding of the gaps and fosters a sense of ownership and commitment. By actively involving employees, organizations can create a culture that aligns with their strategic goals and drives positive change. The case study of Uber serves as a warning example when this gap analysis is not conducted effectively.

Course Manual 10: Bridging the Gaps
Bridging the Gaps – Fostering Alignment in Organizational Culture
Introduction:
After identifying the gaps in organizational culture, the next crucial step is to bridge these gaps effectively. Chapter 10 of Culture Evolution workshop 1, titled “Bridging the Gaps,” focuses on providing participants with strategies and techniques to foster alignment between the current culture and the desired culture. This section aims to equip participants with the necessary tools to develop targeted interventions and initiatives that bridge the gaps and create a cohesive and thriving organizational culture.

Quote: “The distance between your dreams and the reality is called action.” – Unknown
Understanding the Importance of Bridging the Gaps:
Understanding the importance of bridging the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is crucial for the success and growth of any organization. These gaps can arise due to various factors such as changes in leadership, shifts in market dynamics, or the need to adapt to new technologies. Regardless of the cause, it is essential to bridge these gaps to ensure that the organization can effectively navigate the challenges and achieve its goals.
One of the primary reasons why bridging these gaps is important is because it helps in creating a cohesive and unified organizational culture. When there are gaps between the current and desired culture, it can lead to confusion, conflicts, and a lack of direction within the organization. This can result in decreased employee morale, productivity, and overall performance. By bridging these gaps, organizations can align their values, beliefs, and behaviors, creating a shared sense of purpose and direction. This, in turn, fosters a positive work environment, enhances employee engagement, and improves overall organizational performance.
Bridging the gaps between the current and desired culture also helps in managing change effectively. In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, organizations need to be adaptable and responsive to change. However, change can be met with resistance, especially if there is a significant gap between the current and desired culture. By bridging these gaps, organizations can effectively communicate the need for change, address any concerns or resistance, and create a smooth transition. This ensures that employees are on board with the changes and are willing to embrace them, leading to successful change implementation.
Furthermore, bridging these gaps is essential for attracting and retaining top talent. In today’s competitive job market, employees are increasingly looking for organizations that align with their values and offer a positive work culture. If there is a significant gap between the current and desired culture, it can deter potential candidates from joining the organization and lead to high turnover rates. By bridging these gaps, organizations can create an attractive work environment that aligns with the expectations and aspirations of employees. This not only helps in attracting top talent but also in retaining them, reducing recruitment and training costs.
Bridging the gaps between the current and desired culture also promotes innovation and creativity within the organization. When there is a disconnect between the current and desired culture, it can hinder the free flow of ideas and collaboration. Employees may feel hesitant to share their thoughts or take risks, fearing judgment or rejection. By bridging these gaps, organizations can create a culture that encourages open communication, experimentation, and learning. This fosters a sense of psychological safety, where employees feel comfortable expressing their ideas and taking calculated risks. As a result, organizations can tap into the collective intelligence of their workforce, leading to innovation, improved problem-solving, and a competitive edge in the market.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of bridging the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is crucial for the success and growth of any organization. It helps in creating a cohesive and unified culture, managing change effectively, attracting and retaining top talent, and promoting innovation. By bridging these gaps, organizations can create a positive work environment, enhance employee engagement, and improve overall organizational performance.
Developing Targeted Interventions:
Developing targeted interventions to bridge the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture is a critical step in ensuring a successful cultural transformation. These interventions are designed to address the specific areas of misalignment and create a pathway for the organization to move towards its desired culture. By implementing targeted interventions, organizations can effectively bridge the gaps and create a cohesive and unified culture.
One example of a targeted intervention is the implementation of training and development programs. These programs can be designed to address specific areas of misalignment, such as communication, leadership, or teamwork. For instance, if the desired culture emphasizes open and transparent communication, the organization can conduct communication workshops or provide training on effective communication techniques. This intervention helps employees develop the necessary skills and behaviors to align with the desired culture.
Another example of a targeted intervention is the implementation of performance management systems. These systems can be used to align employee goals and behaviors with the desired culture. For instance, if the desired culture emphasizes collaboration and teamwork, the organization can incorporate team-based performance metrics and rewards into its performance management system. This intervention encourages employees to work together towards common goals and reinforces the desired cultural values.
Organizations can also implement targeted interventions through the use of technology. For example, if the desired culture emphasizes innovation and creativity, the organization can invest in collaboration tools or idea management platforms. These technologies facilitate the sharing of ideas, collaboration, and innovation among employees, bridging the gap between the current and desired culture.
In addition to these examples, organizations can also implement targeted interventions through leadership development programs. Leadership plays a crucial role in shaping and driving the organizational culture. By providing leadership training and development programs, organizations can equip their leaders with the necessary skills and behaviors to model and reinforce the desired culture. For instance, if the desired culture emphasizes empowerment and autonomy, leadership development programs can focus on developing leaders who are supportive, inclusive, and empower their teams.
Furthermore, organizations can implement targeted interventions through the redesign of physical spaces and work environments. The physical environment can have a significant impact on the organizational culture. For example, if the desired culture emphasizes collaboration and creativity, the organization can create open and flexible workspaces that encourage interaction and idea sharing. This intervention helps in breaking down silos and fostering a culture of collaboration.
It is important to note that developing targeted interventions requires a thorough understanding of the gaps between the current and desired culture. This understanding can be obtained through various methods such as surveys, focus groups, or interviews. By gathering feedback and insights from employees, organizations can identify the specific areas of misalignment and design interventions that address these gaps effectively.
So, developing targeted interventions is crucial for bridging the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture. These interventions can take various forms such as training and development programs, performance management systems, technology implementation, leadership development, and redesigning physical spaces. By implementing targeted interventions, organizations can address the specific areas of misalignment and create a pathway towards the desired culture. These interventions help in aligning employee behaviors, fostering collaboration, and reinforcing the desired cultural values.
Communicating the Desired Culture:
Effective communication plays a crucial role in bridging the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture. It is through communication that organizations can articulate and convey the desired culture to their employees, ensuring a shared understanding and alignment. By effectively communicating the desired culture, organizations can engage employees, inspire behavior change, and create a sense of purpose and direction.

One of the key roles of effective communication in communicating the desired culture is to provide clarity and understanding. When there is a gap between the current and desired culture, employees may be uncertain about the changes or expectations. Effective communication helps in providing clear and concise information about the desired culture, its values, and the behaviors expected from employees. This clarity helps in reducing ambiguity and confusion, enabling employees to align their actions with the desired culture.
For example, if an organization is transitioning towards a more customer-centric culture, effective communication can involve clearly articulating the importance of customer satisfaction, providing examples of desired customer-centric behaviors, and explaining how these behaviors align with the organization’s values. This communication helps employees understand the desired culture and their role in achieving it.
Another role of effective communication is to create a sense of ownership and involvement among employees. When employees feel involved and engaged in the process of shaping the desired culture, they are more likely to embrace and adopt the desired behaviors. Effective communication can include involving employees in discussions, seeking their input and feedback, and providing opportunities for them to contribute to the development of the desired culture. This involvement creates a sense of ownership and empowers employees to actively participate in the cultural transformation.
For example, an organization that wants to foster a culture of innovation can communicate this desire to employees and invite them to share their ideas and suggestions for fostering innovation. This communication not only demonstrates the organization’s commitment to innovation but also encourages employees to contribute their insights and creativity, fostering a culture of innovation.
Furthermore, effective communication helps in reinforcing the desired culture through consistent messaging and storytelling. By consistently communicating the desired culture and its values, organizations can reinforce the importance of these values and behaviors in the minds of employees. This consistent messaging helps in shaping employee attitudes and beliefs, leading to behavior change and cultural alignment.
For example, an organization that values collaboration can consistently communicate the benefits of collaboration, share success stories of collaborative projects, and recognize and reward collaborative behaviors. This consistent communication reinforces the desired culture and encourages employees to embrace and practice collaboration.
In addition to these roles, effective communication also plays a vital role in addressing any resistance or concerns that employees may have towards the desired culture. Change can often be met with resistance, and effective communication helps in addressing these concerns, providing reassurance, and addressing any misconceptions or fears. By actively listening to employees’ concerns and providing transparent and honest communication, organizations can build trust and create a supportive environment for cultural transformation.
For example, if employees are concerned about the impact of the desired culture on their job roles or responsibilities, effective communication can involve explaining how the desired culture will enhance their skills, provide new opportunities, and contribute to their professional growth. This communication helps in alleviating concerns and gaining employee buy-in.
In conclusion, effective communication plays a crucial role in bridging the gaps between the current and desired organizational culture. It provides clarity and understanding, creates a sense of ownership and involvement, reinforces the desired culture through consistent messaging, and addresses any resistance or concerns. By effectively communicating the desired culture, organizations can engage employees, inspire behavior change, and create a shared sense of purpose and direction.
Leadership’s Role in Bridging the Gaps:
In the previous discussion on targeted interventions and the importance of communication, we touched on leadership’s role. Here we will expand on how leadership plays a crucial role in bridging the gaps in organizational culture. Leaders are responsible for setting the tone, shaping the values, and driving the behaviors that define the culture of an organization. They have the power to influence and inspire employees to align their actions with the desired culture. By effectively leading cultural transformation, leaders can bridge the gaps between the current and desired culture and create a cohesive and unified organizational culture.
One reason why leadership’s role is crucial in bridging the gaps in organizational culture is because leaders serve as role models. Employees look up to their leaders for guidance and direction. When leaders embody the desired culture through their actions and behaviors, it sends a powerful message to employees about the importance of the desired culture. For example, if the desired culture emphasizes collaboration and teamwork, leaders can demonstrate these behaviors by actively seeking input from team members, encouraging open communication, and recognizing and rewarding collaborative efforts. This sets an example for employees to follow and bridges the gap between the current and desired culture.

Leadership’s role in bridging the gaps in organizational culture can also be accomplished through effective communication. Leaders have the responsibility to clearly articulate the desired culture, its values, and the behaviors expected from employees. By effectively communicating the desired culture, leaders ensure that employees have a shared understanding and alignment. For example, leaders can hold town hall meetings, send regular updates, or use other communication channels to consistently communicate the importance of the desired culture and provide clarity on the behaviors that support it. This communication helps bridge the gap between the current and desired culture by providing employees with the information they need to align their actions.
Furthermore, leadership’s role in bridging the gaps in organizational culture can be accomplished through the development of leaders who can champion the desired culture. Leaders can invest in their own development and acquire the necessary skills and behaviors to model and reinforce the desired culture. They can also provide leadership development programs and training to other leaders within the organization. By developing leaders who are aligned with the desired culture, organizations can create a ripple effect that cascades down to all levels of the organization. For example, leaders can participate in workshops or coaching sessions that focus on developing the skills and behaviors that support the desired culture. This development helps bridge the gap between the current and desired culture by ensuring that leaders have the necessary tools to drive cultural transformation.
In addition to these examples, leadership’s role in bridging the gaps in organizational culture can also be accomplished through the establishment of accountability mechanisms. Leaders can set clear expectations and hold themselves and others accountable for demonstrating the desired behaviors. They can establish performance metrics, provide regular feedback, and recognize and reward behaviors that align with the desired culture. By creating a culture of accountability, leaders bridge the gap between the current and desired culture by ensuring that there are consequences for not aligning with the desired culture.
For example, leaders can incorporate cultural alignment into performance evaluations, provide feedback on behaviors that support or hinder the desired culture, and recognize and reward employees who consistently demonstrate the desired behaviors. This accountability mechanism helps bridge the gap between the current and desired culture by reinforcing the importance of the desired culture and creating incentives for employees to align their actions.
In conclusion, leadership plays a crucial role in bridging the gaps in organizational culture. Leaders serve as role models, effectively communicate the desired culture, develop leaders who can champion the desired culture, and establish accountability mechanisms. By effectively leading cultural transformation, leaders bridge the gaps between the current and desired culture and create a cohesive and unified organizational culture.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment:
Employee engagement and empowerment are crucial factors in bridging the gaps between actual and desired organizational culture. These concepts play a significant role in creating a positive work environment, fostering employee satisfaction, and driving organizational success. By empowering and engaging employees, organizations can align their actual culture with the desired culture, resulting in improved productivity, innovation, and overall performance.
Employee engagement refers to the emotional commitment and dedication employees have towards their work and organization. Engaged employees are passionate about their roles, feel valued, and are motivated to contribute their best efforts. When employees are engaged, they are more likely to align with the desired organizational culture and actively work towards its achievement.
One example of how employee engagement bridges the gap between actual and desired culture is through communication. Engaged employees are more likely to communicate openly and honestly, sharing their ideas, concerns, and feedback. This open communication fosters a culture of transparency and collaboration, which can bridge the gap between the actual culture, where communication may be lacking, and the desired culture, which values open dialogue.
Empowerment, on the other hand, involves giving employees the authority, autonomy, and resources to make decisions and take ownership of their work. Empowered employees feel trusted and valued, leading to increased job satisfaction and motivation. When employees are empowered, they are more likely to align their actions with the desired organizational culture, as they have the freedom to make decisions that reflect the organization’s values.
For instance, a company that desires a culture of innovation can empower its employees by providing them with the necessary tools, resources, and support to explore new ideas and take risks. By empowering employees to be innovative, the organization bridges the gap between the actual culture, where employees may feel restricted or discouraged from trying new things, and the desired culture, which encourages creativity and innovation.
Furthermore, employee empowerment and engagement can bridge the gap between actual and desired culture by fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. When employees feel empowered and engaged, they take responsibility for their work and its impact on the organization. This sense of ownership aligns with the desired culture, where employees are accountable for their actions and strive for excellence.
For example, a company that aims to create a culture of continuous improvement can empower employees by involving them in decision-making processes and encouraging them to identify areas for improvement. By empowering employees to take ownership of their work and contribute to the organization’s growth, the actual culture, where employees may be passive or resistant to change, can be bridged with the desired culture, which values continuous learning and improvement.
In conclusion, employee engagement and empowerment are crucial factors in bridging the gaps between actual and desired organizational culture. By fostering engagement, organizations can create a positive work environment where employees are motivated, aligned with the desired culture, and actively contribute to the organization’s success. Empowering employees gives them the authority and autonomy to make decisions that reflect the desired culture, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. Through these practices, organizations can bridge the gaps between actual and desired culture, resulting in improved performance, innovation, and overall success.

Case Study: Zappos
One real-world business case study of an organization that successfully bridged the gaps between current and desired culture is Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer known for its exceptional customer service and unique company culture.
Zappos’ desired culture was centered around delivering “WOW” customer service, fostering a fun and innovative work environment, and promoting a strong sense of employee empowerment and engagement. However, the actual culture at the company was not fully aligned with these desired values.
To bridge this gap, Zappos implemented several strategies:
1. Hiring for culture fit: Zappos recognized the importance of hiring employees who aligned with their desired culture. They developed a rigorous hiring process that focused not only on skills and qualifications but also on cultural fit. Candidates were evaluated based on their alignment with Zappos’ core values, such as delivering WOW through service, embracing and driving change, and creating fun and a little weirdness.
2. Training and development: Zappos invested heavily in training and development programs to ensure that employees understood and embraced the desired culture. They provided extensive onboarding programs that immersed new hires in the company’s values and culture. Additionally, they offered ongoing training and development opportunities to reinforce the desired behaviors and values.
3. Empowering employees: Zappos empowered its employees by giving them the authority and autonomy to make decisions and take ownership of their work. They encouraged employees to go above and beyond to deliver exceptional customer service and empowered them to resolve customer issues without needing to seek approval from supervisors. This empowerment created a sense of ownership and accountability among employees, aligning with the desired culture.
4. Communication and transparency: Zappos fostered a culture of open communication and transparency. They encouraged employees to share their ideas, concerns, and feedback through various channels, such as regular town hall meetings, suggestion boxes, and online forums. This open communication allowed employees to contribute to the shaping of the desired culture and bridged the gap between the actual and desired culture.
As a result of these strategies, Zappos successfully bridged the gaps between their actual and desired culture. The company’s commitment to hiring for culture fit ensured that employees were aligned with the desired values from the start. The training and development programs further reinforced the desired behaviors and values. Empowering employees and fostering open communication created a sense of ownership and engagement among employees, leading to the desired culture of exceptional customer service, innovation, and fun.
Zappos’ success in bridging the gaps between actual and desired culture is evident in their strong customer loyalty, high employee satisfaction, and recognition as a top workplace. The company’s culture has become a key differentiator and a source of competitive advantage in the online retail industry.
Monitoring and Evaluation:
Monitoring and evaluation are crucial components of bridging the gaps between actual and desired organizational culture. By regularly assessing and measuring the progress towards the desired culture, organizations can identify areas of improvement, track the effectiveness of their strategies, and make necessary adjustments to ensure alignment with the desired culture. Here are some ways in which monitoring and evaluation can be done:
1. Surveys and feedback: Organizations can conduct regular surveys and feedback sessions to gather insights from employees about their perceptions of the actual and desired culture. These surveys can include questions about employee satisfaction, engagement, alignment with values, and suggestions for improvement. The feedback received can help identify gaps between the actual and desired culture and provide valuable input for developing strategies to bridge those gaps.
For example, a company may conduct an annual employee engagement survey to measure the level of employee satisfaction and alignment with the desired culture. The survey results can highlight areas where the actual culture is not aligned with the desired culture, such as low levels of empowerment or communication. Based on these findings, the organization can develop action plans to address these gaps and improve the alignment.
2. Key performance indicators (KPIs): Organizations can establish KPIs that reflect the desired culture and regularly track and measure progress towards those goals. These KPIs can be related to employee engagement, customer satisfaction, innovation, or any other aspect that aligns with the desired culture.
For instance, a company that aims to foster a culture of innovation may establish KPIs such as the number of new ideas generated, the percentage of ideas implemented, or the revenue generated from new products or services. By tracking these KPIs, the organization can assess its progress towards the desired culture and make necessary adjustments to bridge any gaps.
3. Performance reviews and assessments: Performance reviews and assessments can be used as a tool to evaluate how well employees are embodying the desired culture. By incorporating cultural alignment as a criterion in performance evaluations, organizations can ensure that employees’ behaviors and actions are aligned with the desired culture.
For example, a company that values teamwork and collaboration may include criteria related to teamwork and collaboration in its performance evaluations. This can include assessing how well employees contribute to team projects, communicate and share information with colleagues, and support their teammates. By evaluating employees’ performance in these areas, the organization can identify any gaps between the actual and desired culture and provide feedback and support to bridge those gaps.
4. Observations and informal feedback: Managers and leaders can regularly observe and provide informal feedback on employees’ behaviors and actions to assess their alignment with the desired culture. This can be done through regular check-ins, team meetings, or informal conversations.
For instance, a manager may observe that an employee consistently demonstrates behaviors that align with the desired culture, such as taking initiative, collaborating with others, and displaying a positive attitude. The manager can provide positive feedback and recognition for these behaviors, reinforcing the alignment with the desired culture. On the other hand, if an employee’s behaviors are not aligned with the desired culture, the manager can provide constructive feedback and support to bridge the gap.
In conclusion, monitoring and evaluation are essential for bridging the gaps between actual and desired organizational culture. By regularly assessing and measuring progress towards the desired culture, organizations can identify areas of improvement, track the effectiveness of their strategies, and make necessary adjustments. Surveys, feedback, KPIs, performance reviews, observations, and informal feedback are some of the methods that can be used to monitor and evaluate cultural alignment. By implementing these practices, organizations can ensure that their actual culture aligns with the desired culture, leading to improved performance, employee satisfaction, and overall success.

Exercise 10:1 – “Bridging the Gaps”
Conclusion:
Bridging the gaps in organizational culture is a critical step toward creating a cohesive and aligned work environment. By developing targeted interventions, communicating the desired culture, and engaging employees, organizations can foster alignment and drive sustainable change. The “Bridging the Gaps” exercise and the case study of Zappos provide practical examples and insights for participants to apply the concepts discussed in this section. By monitoring and evaluating the progress, organizations can ensure the effectiveness of the interventions and continuously bridge any new gaps that may arise. Through these efforts, organizations can cultivate a thriving culture that supports their vision, values, and goals.

Course Manual 11: Transforming Culture
Introduction:
In chapter 10 of the first Culture Evolution Workshop, we discussed the importance of bridging the gaps in organizational culture. Now, in part 11, titled “Transforming Culture,” we will delve into the process of creating lasting change within the organization. This section aims to provide participants with strategies and techniques to effectively transform the organizational culture and embed the desired values and behaviors.

Quote: “Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other time. We are the ones we have been waiting for. We are the change that we seek.” – Barack Obama
Understanding the Need for Culture Transformation: Culture transformation is necessary when organizations recognize the need to align their culture with their strategic goals and adapt to changing external environments. It involves a comprehensive and intentional effort to shift the underlying beliefs, values, and behaviors that shape the organization’s culture. By transforming the culture, organizations can create a more agile, innovative, and resilient work environment.
Creating a Compelling Vision: A compelling vision serves as a guiding light for culture transformation. It articulates the desired future state of the organization and inspires employees to embrace the change. The vision should be communicated clearly and consistently, ensuring that all employees understand and align with the new direction. Quotes such as Peter Senge’s “People don’t resist change. They resist being changed” can be used to emphasize the importance of involving employees in the transformation process.
Leadership’s Role in Culture Transformation: Leadership plays a crucial role in driving culture transformation. Leaders must act as change agents, championing the new culture and modeling the desired behaviors. They should communicate the vision, provide resources and support, and actively engage with employees throughout the transformation process. By demonstrating commitment and consistency, leaders can inspire and motivate employees to embrace the change.
Engaging Employees in the Transformation Process:
Engaging employees in any transformation or change process within an organization is crucial for its success. Employees are the driving force behind the implementation of change initiatives, and their active involvement and commitment can significantly impact the outcome. This section will explore the importance of employee engagement in organizational transformation, highlighting the benefits it brings and providing examples of successful engagement strategies.
1. Ownership and Commitment: When employees are engaged in the transformation process, they develop a sense of ownership and commitment towards the change. They feel valued and empowered, knowing that their opinions and contributions are being heard and considered. This ownership leads to increased motivation and dedication to achieving the desired outcomes. For example, a manufacturing company that involved its employees in the decision-making process for implementing new technology saw a higher level of commitment from employees, resulting in smoother adoption and improved productivity.
2. Knowledge and Expertise: Employees possess valuable knowledge and expertise about their roles, processes, and the organization as a whole. Engaging them in the transformation process allows organizations to tap into this knowledge and leverage it for better decision-making and problem-solving. Employees can provide insights into potential challenges, identify areas for improvement, and suggest innovative solutions. By involving employees in the change process, organizations can benefit from their expertise and make more informed decisions. For instance, a healthcare organization that engaged frontline staff in redesigning patient care processes saw significant improvements in patient satisfaction and quality of care.
3. Collaboration and Teamwork: Engaging employees in the transformation process fosters collaboration and teamwork. When employees are involved in decision-making and problem-solving, they are more likely to work together towards a common goal. This collaboration breaks down silos and encourages cross-functional cooperation, leading to better communication, knowledge sharing, and synergy. An example of this is a technology company that implemented a company-wide change initiative and formed cross-functional teams to address different aspects of the transformation. The collaboration among teams resulted in a seamless transition and improved overall performance.
4. Change Advocates and Influencers: Engaged employees become change advocates and influencers within the organization. When they are involved in the transformation process, they understand the rationale behind the change and its benefits. This understanding enables them to effectively communicate the purpose and goals of the transformation to their colleagues, creating a positive ripple effect throughout the organization. These change advocates can help overcome resistance, address concerns, and inspire others to embrace the change. For instance, a retail company that engaged its store managers as change champions during a rebranding effort saw increased acceptance and enthusiasm from employees, leading to a successful brand transition.
5. Continuous Improvement and Adaptability: Engaging employees in the transformation process fosters a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability. When employees are actively involved, they become more open to change and more willing to embrace new ideas and approaches. This mindset of continuous improvement enables organizations to adapt to evolving market conditions, customer needs, and industry trends. An example of this is a financial institution that involved its employees in a digital transformation initiative. The engagement of employees led to a culture of innovation and agility, allowing the organization to stay ahead of competitors and meet changing customer expectations.
Engaging employees in any transformation or change process within an organization is essential for its success. By fostering ownership, leveraging knowledge and expertise, promoting collaboration, creating change advocates, and nurturing a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can achieve their transformation goals more effectively. Examples from various industries demonstrate the positive impact of employee engagement on organizational transformation. Therefore, organizations should prioritize employee engagement as a critical component of their change management strategies to drive successful and sustainable transformations.
Overcoming Resistance to Change: Strategies to Address Common Reasons

Resistance to change is a natural human response that can hinder culture transformation efforts within organizations. People often resist change due to various reasons such as attachment to old ways, fear of failure, perceived threat, loss of control, curtailed freedom, diminished power, threatened job security, uncertainty, climate of mistrust, concern for co-workers, unclear benefits, forced change, work overload, disruption, poor communication, and mismanagement. In order to successfully overcome resistance to change, organizations need to implement effective strategies that address these reasons. We will briefly explore each reason in detail and suggest strategies to address them.
Attachment to Old Ways:
One of the primary reasons people resist change is their attachment to old ways. They may have become comfortable with the existing processes and fear the unknown. To address this, organizations should focus on creating awareness about the need for change and the benefits it will bring. Communicating the reasons behind the change and providing examples of successful transformations can help individuals understand the necessity of letting go of old ways.
Fear of Failure:
Fear of failure is another common reason for resistance to change. People may worry about their ability to adapt to new processes or fear that they will not be able to perform as well in the changed environment. To overcome this fear, organizations should provide training and support to employees during the transition period. Offering resources, coaching, and mentoring can help individuals build confidence and develop the necessary skills to succeed in the changed circumstances.
Perceived Threat:
Change can often be perceived as a threat to individuals, especially if they believe it will negatively impact their position or status within the organization. To address this, organizations should emphasize the positive aspects of the change and how it can benefit everyone involved. Providing clear communication about the impact on roles and responsibilities can help alleviate perceived threats and create a sense of security.
Loss of Control:
Change can make individuals feel like they are losing control over their work or their environment. To address this, organizations should involve employees in the change process by seeking their input and feedback. By including them in decision-making and giving them a sense of ownership, individuals will feel more in control and be more likely to embrace the change.
Curtailed Freedom:
Change can sometimes restrict individuals’ freedom to work in the way they are accustomed to. To overcome this resistance, organizations should provide individuals with autonomy within the new framework. Allowing flexibility in how tasks are accomplished and encouraging innovation can help individuals feel that they still have some freedom in their work.
Diminished Power:
Change can also lead to a perceived loss of power or influence. To address this, organizations should involve individuals in the change process and provide opportunities for them to contribute their expertise. Recognizing and valuing their contributions can help individuals feel empowered and motivated to support the change.
Threatened Job Security:
One of the most significant reasons for resistance to change is the fear of job loss or reduced job security. To address this, organizations should provide clear communication about the impact of the change on job roles and responsibilities. Offering retraining or upskilling opportunities can help individuals adapt to the new requirements and feel more secure in their positions.
Too Much Uncertainty:
Change often brings uncertainty, which can be unsettling for individuals. To address this, organizations should provide regular and transparent communication about the change process. Sharing information about the timeline, milestones, and expected outcomes can help individuals feel more informed and reduce uncertainty.
Climate of Mistrust:
A climate of mistrust within an organization can significantly contribute to resistance to change. To address this, organizations should focus on building trust through open and honest communication. Leaders should be transparent about the reasons for the change and actively listen to employees’ concerns. Creating a safe space for dialogue and addressing any underlying issues can help rebuild trust and facilitate the change process.
Concern for Co-workers:
Individuals may resist change out of concern for their co-workers who may struggle with the transition. To address this, organizations should provide support and resources to help individuals navigate the change. Offering training, coaching, and mentoring can help individuals feel more confident in supporting their co-workers and alleviate their concerns.
Unclear Benefits:
Resistance to change can also arise when individuals do not understand the benefits of the change. To address this, organizations should clearly communicate the expected outcomes and how they will positively impact individuals and the organization as a whole. Providing real-life examples and success stories can help individuals see the potential benefits and motivate them to embrace the change.
Forced Change:
When change is imposed on individuals without their input or involvement, resistance is likely to occur. To address this, organizations should involve individuals in the change process from the beginning. Seeking their input, involving them in decision-making, and providing opportunities for feedback can help individuals feel more engaged and willing to support the change.
Work Overload:
Change can sometimes lead to an increased workload, which can contribute to resistance. To address this, organizations should assess the workload impact of the change and provide necessary resources or support to manage the increased demands. Prioritizing tasks, redistributing responsibilities, or hiring additional staff can help alleviate work overload and make the change more manageable.
Disruption:
Change often disrupts established routines and processes, which can be challenging for individuals. To address this, organizations should provide support and guidance during the transition period. Offering training, clear instructions, and ongoing communication can help individuals navigate the disruption and adapt to the new ways of working.
Poor Communication:
Lack of effective communication is a significant contributor to resistance to change. To address this, organizations should prioritize clear and consistent communication throughout the change process. Providing regular updates, addressing concerns, and actively listening to feedback can help individuals feel informed and engaged in the change.
Mismanagement:
When change is poorly managed, individuals are more likely to resist. To address this, organizations should ensure that change initiatives are well-planned and executed. Assigning dedicated change management teams, providing training to leaders, and monitoring progress can help ensure that change is implemented effectively and minimize resistance.
In conclusion overcoming resistance to change is crucial for successful culture transformation within organizations. By addressing the common reasons for resistance, organizations can implement effective strategies. These strategies include creating awareness, providing training and support, emphasizing benefits, involving employees, addressing concerns, and ensuring clear communication. By implementing these strategies, organizations can overcome resistance to change and facilitate a smooth transition towards a transformed culture.
Sustaining Culture Transformation: Reinforcing and Embedding the Desired Culture

Once a culture transformation has been initiated within an organization, the next crucial step is to reinforce and embed the desired culture into the organization’s systems, processes, and performance management practices. This involves aligning recognition and reward systems with the new culture to reinforce the desired behaviors. By implementing effective strategies and examples, organizations can ensure that the culture transformation is sustained in the long term.
Aligning Systems and Processes: To reinforce and embed the desired culture, organizations need to align their systems and processes with the new cultural values and behaviors. This can be achieved through the following strategies:
1. Recruitment and Selection:
Organizations should revise their recruitment and selection processes to ensure that they attract and hire individuals who align with the desired culture. This can be done by incorporating cultural fit assessments and behavioral interviews that assess candidates’ alignment with the new cultural values.
Example: A company that values collaboration and teamwork may include group exercises during the recruitment process to assess candidates’ ability to work effectively in a team.
2. Onboarding and Training:
During the onboarding process, organizations should provide new employees with a comprehensive introduction to the desired culture. This can include training sessions, workshops, and mentorship programs that focus on the new cultural values and expected behaviors.
Example: A company that values innovation and creativity may provide training on design thinking methodologies and encourage employees to think outside the box during their onboarding process.
3. Performance Management:
Performance management practices should be aligned with the desired culture to reinforce and reward the desired behaviors. Organizations should set clear performance expectations that reflect the new cultural values and provide regular feedback and coaching to employees.
Example: A company that values customer-centricity may include customer satisfaction metrics as part of the performance evaluation process and provide feedback on how employees can improve their customer service skills.
4. Communication and Collaboration:
Organizations should establish effective communication channels and collaboration platforms that facilitate the sharing of information, ideas, and best practices. This can help foster a culture of transparency, open communication, and knowledge sharing.
Example: A company that values collaboration may implement a digital platform where employees can share their ideas, collaborate on projects, and provide feedback to one another.
Aligning Recognition and Reward Systems: Recognition and reward systems play a crucial role in reinforcing the desired culture and motivating employees to exhibit the desired behaviors. Here are some strategies to align recognition and reward systems with the new culture:
1. Define and Communicate Desired Behaviors:
Organizations should clearly define the behaviors that align with the desired culture and communicate them to all employees. This ensures that everyone understands what is expected of them and what behaviors will be recognized and rewarded.
Example: A company that values teamwork may define behaviors such as actively seeking input from colleagues, sharing knowledge, and supporting team members.
2. Implement a Culture of Appreciation:
Organizations should foster a culture of appreciation where employees are encouraged to recognize and appreciate their colleagues’ contributions. This can be done through peer-to-peer recognition programs, where employees can nominate and acknowledge their colleagues for exhibiting the desired behaviors.
Example: A company may implement a monthly “Employee Appreciation Award” where employees can nominate their peers who have demonstrated exceptional teamwork and collaboration.
3. Tie Recognition to Cultural Values:
Recognition and reward programs should be aligned with the new cultural values. This can be done by linking recognition to specific cultural behaviors and values, and incorporating them into performance evaluations and reward systems.
Example: A company that values innovation may introduce an “Innovation Champion” award, where employees who have implemented innovative ideas or processes are recognized and rewarded.
4. Provide Meaningful Rewards:
Organizations should ensure that the rewards provided align with the desired culture and are meaningful to employees. This can include both monetary and non-monetary rewards, such as bonuses, promotions, flexible work arrangements, or opportunities for professional development.
Example: A company that values work-life balance may offer employees the opportunity to take additional paid time off as a reward for consistently demonstrating a healthy work-life balance.
Reinforcing and embedding the desired culture into an organization’s systems, processes, and performance management practices is crucial for sustaining a culture transformation. By aligning recruitment and selection, onboarding and training, performance management, and communication and collaboration practices with the new culture, organizations can ensure that the desired behaviors are consistently exhibited. Additionally, aligning recognition and reward systems with the new culture reinforces and motivates employees to continue exhibiting the desired behaviors. By implementing these strategies and examples, organizations can sustain the culture transformation and create a positive and thriving work environment.

Case Study: Google – Transforming Organizational Culture for Success
Introduction: Google, a multinational technology company, is renowned for its innovative products, cutting-edge technology, and vibrant work culture. Over the years, Google has successfully transformed its organizational culture, fostering an environment that promotes creativity, collaboration, and employee empowerment. This case study explores the key strategies and initiatives implemented by Google to transform its culture and achieve remarkable success.
Background: In its early years, Google had a culture that emphasized technical expertise and individual brilliance. However, as the company grew rapidly, it faced challenges in maintaining its innovative edge and fostering a collaborative environment. Recognizing the need for cultural transformation, Google embarked on a journey to create a culture that would attract and retain top talent, encourage risk-taking, and promote a sense of purpose among its employees.
Key Strategies and Initiatives:
1. Hiring for Cultural Fit: Google recognized that hiring individuals who aligned with its core values and cultural principles was crucial for cultural transformation. The company implemented a rigorous hiring process that focused not only on technical skills but also on assessing candidates’ alignment with Google’s culture. This approach ensured that new hires would contribute positively to the desired cultural shift.
2. Encouraging Psychological Safety: To foster a culture of innovation and collaboration, Google placed a strong emphasis on psychological safety. The company encouraged open communication, active listening, and respectful feedback among employees. This created an environment where individuals felt comfortable taking risks, sharing ideas, and challenging the status quo without fear of judgment or retribution.
3. Empowering Employees: Google empowered its employees by providing them with autonomy and decision-making authority. The company implemented a 20% time policy, allowing employees to dedicate a portion of their workweek to pursue passion projects outside their core responsibilities. This initiative not only fostered creativity but also gave employees a sense of ownership and purpose, leading to breakthrough innovations such as Gmail and Google News.
4. Creating Collaborative Spaces: Google recognized the importance of physical spaces in shaping its culture. The company designed its offices to promote collaboration, creativity, and serendipitous encounters. Open floor plans, communal areas, and informal meeting spaces encouraged spontaneous interactions and cross-functional collaboration, breaking down silos and fostering a sense of community.
5. Continuous Learning and Development: Google invested heavily in employee development programs to nurture a culture of continuous learning. The company provided numerous training opportunities, mentorship programs, and internal mobility options to help employees grow both personally and professionally. This focus on development not only enhanced employee engagement but also contributed to the overall success of the organization.
Results and Impact: Google’s cultural transformation initiatives have had a profound impact on the company’s success. The company consistently ranks among the top employers globally, attracting top talent from diverse backgrounds. Google’s innovative products and services, such as Google Search, Android, and Google Maps, have revolutionized industries and transformed the way people interact with technology. The company’s culture of collaboration, psychological safety, and employee empowerment has been instrumental in driving innovation, fostering creativity, and maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving tech industry.
Conclusion: Google’s successful cultural transformation serves as a compelling case study for organizations seeking to create a vibrant and innovative work culture. By focusing on hiring for cultural fit, encouraging psychological safety, empowering employees, creating collaborative spaces, and investing in continuous learning, Google has transformed its culture into a key driver of its success. The company’s commitment to fostering a culture that values innovation, collaboration, and employee well-being has positioned it as a global leader in the technology industry.

Exercise 11:1 – “Navigating Resistance to Change: A Reflection Exercise”
– Flipchart or whiteboard
– Markers
– Sticky notes
– Timer
1. Introduction
– Start by explaining the importance of acknowledging and understanding resistance to change when attempting to transform an organization’s culture.
– Emphasize that resistance is a natural response to change and that it can be overcome with the right strategies and mindset.
– Ask participants to take a few moments to reflect individually on the potential resistance and challenges they anticipate facing when trying to transform their organization’s culture.
– Encourage them to consider both internal and external factors that may contribute to resistance, such as fear of the unknown, lack of buy-in, or organizational structures.
– Divide participants into pairs or small groups of 2-3 people.
– Instruct each group to share their reflections and discuss the common themes or challenges they identified.
– Encourage participants to actively listen and take notes on the challenges shared by their group members.
– Bring the groups back together and facilitate a brief discussion around the challenges identified.
– Write down the common challenges on the flipchart or whiteboard, creating a list of potential obstacles to transforming the organization’s culture.
– Instruct participants to brainstorm practical solutions or strategies to overcome the challenges identified.
– Encourage them to think creatively and consider both individual and collective approaches to addressing resistance to change.
– Write down the solutions on sticky notes and place them next to the corresponding challenge on the flipchart or whiteboard.
– Wrap up the exercise by summarizing the challenges and potential solutions identified.
– Emphasize the importance of being prepared and proactive in addressing resistance to change.
– Encourage participants to refer back to the list of solutions as they embark on their journey to transform their organization’s culture.
Conclusion:
Transforming the organizational culture is a complex and ongoing process. By creating a compelling vision, engaging employees, and involving leadership, organizations can drive lasting change. The reflection exercise, ” Navigating Resistance to Change” and the case study of Google provide practical examples and insights for participants to apply the concepts discussed in this section. Overcoming resistance to change and sustaining the transformation are critical factors that organizations must address to ensure the success of the culture transformation efforts. Through these efforts, organizations can create a culture that supports their strategic goals, fosters innovation, and drives long-term success.

Course Manual 12: Culture for Success
Introduction:
In the final part of the first Culture Evolution workshop titled “Culture for Success,” we will explore the importance of sustaining and leveraging organizational culture to drive long-term success. Building on the previous section on transforming culture, this section aims to provide participants with strategies and techniques to sustain the desired culture and harness its power to achieve organizational goals.
Quote: “Culture is not just one aspect of the game, it is the game.” – Lou Gerstner
Sustaining the Desired Culture:
Creating a desired organizational culture is just the first step; sustaining it requires ongoing effort and dedication. Many successful companies have implemented various strategies and techniques to ensure the longevity of their desired culture. Here are some key strategies and examples from different companies:
1. Clear Communication and Reinforcement:
Effective communication is crucial in sustaining a desired culture. Companies need to consistently communicate their values, mission, and expectations to employees. This can be done through regular company-wide meetings, internal newsletters, and other communication channels. Reinforcing the desired culture through recognition programs, rewards, and celebrations can also help to keep employees engaged and aligned with the culture.
Example: Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, places a strong emphasis on its core values, which include delivering “WOW” through service and embracing and driving change. Zappos reinforces these values through regular communication, including weekly emails from CEO Tony Hsieh, highlighting employees who have exemplified the company’s values.
2. Leadership Role Modeling:
Leaders play a critical role in sustaining the desired culture. They need to embody the values and behaviors that are expected from employees. By consistently demonstrating the desired culture, leaders set an example for others to follow. This can be done through active participation in cultural initiatives, regular communication, and leading by example.
Example: Southwest Airlines is known for its strong culture of customer service and employee empowerment. The company’s founder, Herb Kelleher, was known for his hands-on leadership style and his commitment to treating employees well. Kelleher’s leadership and his focus on creating a positive and fun work environment set the tone for the company’s culture, which has been sustained even after his retirement.
3. Employee Engagement and Empowerment:
Engaging and empowering employees is crucial for sustaining a desired culture. Companies need to provide opportunities for employees to contribute, make decisions, and have a sense of ownership. This can be done through initiatives such as employee feedback programs, cross-functional projects, and employee recognition programs.
Example: Patagonia, an outdoor clothing and gear company, has a strong culture of environmental sustainability and employee empowerment. The company encourages employees to take part in environmental initiatives and provides opportunities for them to contribute to the company’s mission. Patagonia’s “Venture Capital Fund” allows employees to pitch and fund projects that align with the company’s values, empowering them to make a difference.
4. Continuous Learning and Development:
Investing in employee development is essential for sustaining a desired culture. Companies need to provide opportunities for employees to learn, grow, and develop new skills. This can be done through training programs, mentorship initiatives, and internal mobility options.
Example: Google is known for its culture of continuous learning and development. The company provides numerous training opportunities, including its “Google University” program, which offers a wide range of courses for employees to enhance their skills. As previously mentioned, Google also encourages employees to pursue passion projects through its “20% time” policy, which allows employees to dedicate a portion of their workweek to projects outside their core responsibilities.
5. Regular Culture Assessments and Feedback:
Regularly assessing the culture and gathering feedback from employees is crucial for sustaining a desired culture. Companies need to have mechanisms in place to measure the alignment of employees with the desired culture and identify areas for improvement. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, and regular feedback sessions.
Example: As we have already considered, Netflix, a streaming entertainment company, conducts regular “360-degree feedback” assessments to gather feedback on how well employees are embodying the company’s culture and values. This feedback is used to identify areas for improvement and provide targeted development opportunities for employees.
In conclusion, sustaining a desired organizational culture requires a combination of clear communication, leadership role modeling, employee engagement and empowerment, continuous learning and development, and regular culture assessments. By implementing these strategies and techniques, companies can ensure that their desired culture remains strong and aligned with their values and goals.
Leveraging Culture for Success:
Creating a desired organizational culture is just the first step; leveraging that culture for success requires a strategic approach. Companies that effectively leverage their culture can gain a competitive advantage, attract top talent, and drive innovation. Here are some key strategies and techniques, along with examples from different companies, on how to leverage the desired organizational culture for success:
1. Aligning Culture with Strategy:
To leverage the desired organizational culture for success, it is crucial to align the culture with the company’s strategic goals. This involves ensuring that the values, behaviors, and norms of the culture support and reinforce the strategic direction of the organization.
Example: Apple is known for its culture of innovation and design excellence. This culture is aligned with Apple’s strategic goal of creating groundbreaking products that disrupt industries. By fostering a culture that encourages risk-taking, creativity, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, Apple has been able to leverage its culture to consistently deliver innovative products such as the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch.
2. Empowering Employees:
Empowering employees is a key strategy for leveraging the desired organizational culture. When employees feel empowered, they are more engaged, motivated, and willing to take ownership of their work. This leads to increased productivity, innovation, and overall success.
Example: Netflix has a culture of freedom and responsibility, where employees are given the autonomy to make decisions and take risks. This empowers employees to be creative, experiment with new ideas, and take ownership of their projects. By empowering its employees, Netflix has been able to foster a culture of innovation and disrupt the traditional entertainment industry with its streaming platform.
3. Encouraging Collaboration and Cross-functional Communication:
Collaboration and cross-functional communication are essential for leveraging the desired organizational culture. When employees from different departments and levels of the organization collaborate and share ideas, it leads to increased innovation, problem-solving, and a more cohesive and aligned workforce.
Example: Google has a culture of collaboration and open communication, which is evident in its office design and work practices. The company’s open floor plans, communal areas, and informal meeting spaces encourage spontaneous interactions and cross-functional collaboration. By fostering a culture of collaboration, Google has been able to leverage the collective intelligence of its employees and drive innovation across its products and services.
4. Recognizing and Rewarding Desired Behaviors:
Recognizing and rewarding desired behaviors is a powerful technique for leveraging the desired organizational culture. When employees are recognized and rewarded for embodying the values and behaviors of the culture, it reinforces those behaviors and motivates others to follow suit.
Example: Southwest Airlines is renowned for it’s culture of customer service and employee empowerment. The company recognizes and rewards employees who go above and beyond to deliver exceptional customer service. This recognition not only reinforces the desired behaviors but also motivates other employees to provide outstanding service, leading to a positive customer experience and business success.
5. Continuous Learning and Development:
Investing in continuous learning and development is crucial for leveraging the desired organizational culture. When employees are provided with opportunities to learn, grow, and develop new skills, it enhances their capabilities and enables them to contribute more effectively to the organization’s success.
Example: Amazon has a culture of continuous learning and development, which is evident in its “Career Choice” program. This program provides employees with opportunities to pursue further education and training in fields that are in high demand, even if those fields are outside of Amazon. By investing in the learning and development of its employees, Amazon has been able to leverage its culture to attract and retain top talent and drive innovation and growth.
In conclusion, leveraging the desired organizational culture for success requires aligning the culture with the company’s strategy, empowering employees, encouraging collaboration, recognizing and rewarding desired behaviors, and investing in continuous learning and development. By implementing these strategies and techniques, companies can leverage their culture to gain a competitive advantage, attract top talent, and drive innovation and success.

Case Study: Southwest Airlines’ Culture for Success
Southwest Airlines is a prime example of how aligning culture with organizational success can lead to sustained growth and profitability. Southwest has consistently been recognized as one of the most admired and successful airlines in the industry, and their unique culture has played a significant role in their achievements.
One of the key elements of Southwest’s culture is its focus on employees. They believe that happy and engaged employees will provide exceptional customer service, which in turn leads to customer loyalty and business success. Southwest has created a work environment that values and empowers its employees, fostering a strong sense of ownership and commitment.
To sustain their culture, Southwest has implemented several practices. First, they have a rigorous hiring process that focuses not only on skills and qualifications but also on cultural fit. They look for individuals who align with their core values, such as a “warrior spirit” and a “servant’s heart.” This ensures that new hires are likely to embrace and contribute to the company’s culture.
Southwest also leverages their culture to drive success by providing extensive training and development opportunities for their employees. They invest in their people, offering ongoing training programs that focus on customer service, teamwork, and leadership. This investment in employee development not only enhances their skills but also reinforces the desired culture.
Furthermore, Southwest reinforces their culture through various initiatives and practices. They have a strong emphasis on teamwork and collaboration, encouraging employees to work together to solve problems and deliver exceptional service. They also have a unique profit-sharing program that rewards employees based on the company’s financial performance, creating a sense of ownership and shared success.
Southwest’s culture is also reinforced through their leadership practices. The company has a flat organizational structure, with a focus on open communication and transparency. Leaders at Southwest actively engage with employees, listen to their ideas and concerns, and involve them in decision-making processes. This inclusive leadership style reinforces the culture of empowerment and collaboration.
The success of Southwest’s culture alignment is evident in its financial performance. Despite operating in a highly competitive industry, Southwest has consistently been profitable and has achieved 47 consecutive years of profitability. They have also been recognized for their exceptional customer service, winning numerous awards and accolades.
In conclusion, Southwest Airlines is a compelling case study that highlights the importance of aligning culture with organizational success. By prioritizing their employees, investing in their development, and fostering a culture of teamwork and empowerment, Southwest has sustained its success and achieved remarkable financial performance. Their focus on culture has not only differentiated them in the market but also created a loyal customer base. Other organizations can learn from Southwest’s example and recognize the significant impact that a strong and aligned culture can have on long-term success.
Celebrating and Reinforcing the Culture:
Celebrating and reinforcing the desired organizational culture is crucial for the long-term success of any company. It helps to create a positive work environment, boosts employee morale, and enhances productivity. In this section, we will explore practical examples from different companies that effectively celebrate and reinforce their desired organizational culture.
One company that excels in celebrating and reinforcing its desired organizational culture is Google. Google is known for its innovative and fun work environment. They have various programs and initiatives in place to foster a culture of creativity and collaboration. As mentioned above, they have “20% time,” where employees are encouraged to spend 20% of their workweek on projects that interest them. This not only allows employees to pursue their passions but also promotes a culture of autonomy and innovation.
Google also celebrates its culture through various events and activities. They have an annual “Google I/O” conference where employees and developers come together to share ideas and showcase new technologies. This event not only reinforces Google’s commitment to innovation but also creates a sense of community among employees.
Another company that effectively reinforces its desired organizational culture is Zappos. Zappos is known for its exceptional customer service and employee-centric culture. They have a unique onboarding process called “The Offer,” where new hires are offered $2,000 to quit if they feel that Zappos is not the right fit for them. This process not only ensures that employees are aligned with the company’s values but also reinforces the importance of cultural fit.
Zappos also celebrates its culture through various initiatives. They have a program called “Zappos Culture Book,” where employees share their experiences and stories about the company’s culture. This book is published annually and distributed to all employees, reinforcing the desired culture and creating a sense of pride and belonging.
Netflix reinforces its desired organizational culture in a unique way. Netflix is known for its high-performance culture and emphasis on freedom and responsibility. They have a culture deck that outlines their values and expectations, which is shared with all employees. This deck serves as a guide for decision-making and reinforces the desired culture.
Netflix makes use of its interesting “Keeper Test.” This test encourages managers to ask themselves if they would fight to keep a particular employee on their team. If the answer is no, then the manager is encouraged to have an open and honest conversation with the employee about their fit within the organization. This reinforces the importance of cultural alignment and ensures that employees who embody the desired culture are retained.
Celebrating and reinforcing the desired organizational culture is essential for the success of any company. Companies like Google, Zappos, and Netflix have effectively implemented various initiatives and programs to celebrate and reinforce their desired culture. Whether it’s through events, unique onboarding processes, or culture decks, these companies have created a positive work environment that fosters innovation, collaboration, and employee engagement. By learning from these practical examples, other companies can also create a strong and vibrant organizational culture that drives success.

Exercise 12:1 – “Sustaining and Leveraging Desired Culture for Organizational Success”
– Flipchart or whiteboard
– Markers
– Sticky notes
– Timer
1. Introduction
– Start by explaining the importance of sustaining, reinforcing, and leveraging the desired culture for organizational success.
– Emphasize that a strong and aligned culture can drive employee engagement, productivity, and overall performance.
– Divide participants into small groups of two or three.
– Provide each group with sticky notes and markers.
– Instruct them to spend a few minutes brainstorming and writing down practical ideas and strategies for sustaining, reinforcing, and leveraging the desired culture in their organization.
– Encourage them to think about specific actions, initiatives, or programs that can be implemented.
– Ask each group to share one or two ideas from their brainstorming session.
– Write down these ideas on the flipchart or whiteboard, creating a visual representation of the different strategies.
– Facilitate a brief discussion on the shared ideas and strategies.
– Ask participants to reflect on the feasibility and potential impact of these strategies in their organization.
– Encourage them to consider how these strategies can sustain, reinforce, and leverage the desired culture for organizational success.
– Summarize the key points discussed during the exercise.
– Reinforce the importance of actively implementing strategies to sustain, reinforce, and leverage the desired culture.
– Encourage participants to take the ideas generated during the exercise and discuss them with their teams or leaders for further action.
Conclusion of Workshop 1:
In conclusion, Workshop 1 of the Culture Evolution series has laid a strong foundation for our journey toward transforming our organizational culture for success and understanding what kind of wind blows through the organization and whether it is in your favor. We have delved into the depths of organizational culture, understanding its significance and the profound impact it has on our business.
Throughout this workshop, we have explored the fundamental elements of organizational culture, recognizing how they shape our daily operations, employee behavior, and overall performance. By gaining insights into our organization’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, we have taken the first crucial step toward culture evolution.
We have learned that identifying gaps between our actual and desired culture is essential for progress. It is through this introspection that we can pinpoint areas that require attention and change. By acknowledging these gaps, we have demonstrated our commitment to growth and improvement.

But our journey does not end here. We must now focus on bridging these gaps and transforming our culture to align with our vision for success. This will require collective effort, open communication, and a shared commitment to change. We must embrace new processes, strategies, and mindsets that will propel us toward a culture that fosters innovation, collaboration, and excellence.
As we move forward, let us remember that culture evolution is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. It requires continuous assessment, adaptation, and refinement. We must remain vigilant, always seeking opportunities for improvement and growth.
Together, we have embarked on a remarkable journey towards cultural transformation. Let us harness the knowledge and insights gained in this workshop to drive positive change within our organization. By embracing this culture evolution, we are paving the way for a brighter future, where our organization thrives, our employees flourish, and our business achieves unprecedented success.
Thank you for your active participation in Workshop 1. Let us carry this momentum forward as we continue our quest for culture excellence in Workshop 2 and beyond.
Project Studies
Project Study (Part 1) – Customer Service
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 2) – E-Business
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 3) – Finance
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 4) – Globalization
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 5) – Human Resources
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 6) – Information Technology
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 7) – Legal
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 8) – Management
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 9) – Marketing
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 10) – Production
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 11) – Logistics
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 12) – Education
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Culture Evolution process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Understanding Culture
02. Organizational Analysis
03. Internal & External Perceptions
04. Elements of Culture
05. Impact of Behavior
06. Decision-making Processes
07. Overall Performance
08. Assessing Existing Culture
09. Identifying Gaps
10. Bridging the Gaps
11. Transforming Culture
12. Culture for Success
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Program Benefits
Human Resources
- Attract talent
- Fuel engagement
- Increase loyalty
- Employee retention
- Values alignment
- Empower talent
- Enhance teamwork
- Improve communication
- Enhance collaboration
- Employee well-being
Executive Management
- Values alignment
- Customer satisfaction
- Increased profitability
- Improve collaboration
- Efficiency gains
- Drive results
- Foster innovation
- Leadership effectiveness
- Thriving workforce
- Competitive advantage
Globalization
- Sustainable Growth
- Process Alignment
- Mergers acquisitions
- Competitive advantage
- Integrated culture
- Expand collaboration
- Foster innovation
- Employee engagement
- Customer-centricity
- Knowledge sharing
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.



































