Managing Risk
Accredited Consulting Service for Mr. Chari Accredited Senior Consultant (ASC)
Executive Summary Video

The Appleton Greene Accredited Consultant Service (ACS) for Managing Risk is provided by Mr. Chari and provides clients with four cost-effective and time-effective professional consultant solutions, enabling clients to engage professional support over a sustainable period of time, while being able to manage consultancy costs within a clearly defined monthly budget. All service contracts are for a fixed period of 12 months and are renewable annually by mutual agreement. Services can be upgraded at any time, subject to individual client requirements and consulting service availability. If you would like to place an order for the Appleton Greene Managing Risk service, please click on either the Bronze, Silver, Gold, or Platinum service boxes below in order to access the respective application forms. If you have any questions or would like further information about this service, please CLICK HERE. A detailed information guide for this service is provided below and you can access this guide by scrolling down and clicking on the tabs beneath the service order application forms.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.
Bronze Client Service
Monthly cost: USD $1,500.00
Time limit: 5 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
SERVICE FEATURES
Bronze service includes:
01. Email support
02. Telephone support
03. Questions & answers
04. Professional advice
05. Communication management
To apply – CLICK HERE

Silver Client Service
Monthly cost: USD $3,000.00
Time limit: 10 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
SERVICE FEATURES
Bronze service plus
01. Research analysis
02. Management analysis
03. Performance analysis
04. Business process analysis
05. Training analysis
To apply – CLICK HERE
Gold Client Service
Monthly cost: USD $4,500.00
Time limit: 15 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
SERVICE FEATURES
Bronze/Silver service plus
01. Management interviews
02. Evaluation and assessment
03. Performance improvement
04. Business process improvement
05. Management training
To apply – CLICK HERE
Consultant Profile

Mr. Chari is an approved Senior Consultant at Appleton Greene and he has experience in management, legal and information technology. He has achieved a Master of Business Administration, a Master of Science in Industrial Engineering, and a Bachelor of Science in Management. He has industry experience within the following sectors: Banking & Financial Services; Consultancy; Technology and Non-Profit & Charities. He has had commercial experience within the following countries: United States of America; United Kingdom; India and Republic of Singapore, or more specifically within the following cities: Los Angeles CA; New York NY; London; Mumbai and Singapore. His personal achievements include: integrated three lines of defence; improved governance over risk management; revamped board risk reporting; authored data breach response plan and implemented global risk policies. His service skills incorporate: risk management; governance; benchmarking; change management and project management.
To request further information about Mr. Chari through Appleton Greene, please CLICK HERE
Executive Summary

Managing Risk
Risk is the effect of uncertainty on the outcomes of an organization’s objectives.
Just in the last 20 years, there have been several risk-related events that have impacted individual organizations, an entire industry, and the entire world – Enron (2001), WorldCom (2002), Financial crisis (2008-09), Madoff (2008), Fukushima (2011), UBS/JP Morgan trading (2011-12), Libor-fixing (2012), Volkswagen diesel (2015), Wells Fargo (2016), COVID-19 (2019-).
Almost every week, there is a news story about the failure of risk management and the resulting impact, both financial and non-financial. Some of these are operational failures – cyber breaches, regulatory issues, fraud; others are strategic – strategic goals not achieved, reputational damage to the brand, etc. In many cases, there may have been ignored warning signs – and in some instances, the risk events were unanticipated.
Effective risk management is how organizations can 1) become more proactive in identifying and managing key risks and 2) get more resilient if risk events, known or unanticipated, impact them.
What makes risk management crucial?
– Just like high-performing automobiles, high-performing businesses require reliable brakes. They enable the driver to slow down the vehicle and stop it safely. They also inspire the motorist to drive faster, which is as crucial.
– The adverse effects of poor risk management are very costly and may lead to a company’s bankruptcy. Pay now or pay later—and paying now is typically less expensive—by investing in risk management.
Service Methodology
Theoretical risk frameworks, such as from the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), are typically industry-agnostic. Based on 20+ years of track record of implementation of such frameworks in different industries and organizations, two critical elements stand out:
– Effectiveness of risk management framework: Understanding the different categories of risks that impact business objectives, implementing appropriate process/control mechanisms, and ensuring adequate resources and accountability to manage/oversee risks.
– Strength of risk culture: Various elements such as values and belief systems, rules and boundaries, psychological safety, escalation, and governance play a role in strong risk culture.
There is no “one size fits all” approach. Risk management will be most effective when it matches the inherent nature and controllability of the organization’s different types of risk. There are three broad risk categories: “Category I/preventable,” “Category 2/strategic,” and “Category 3/external” – each has a different source, a different degree of controllability, and a different approach for identification, mitigation, and management.
The right risk program and leader should be able to execute risk transformations tailored to the maturity and needs of the organization and with the least disruption to the organization possible.
Approach to assessing and improving the state of ERM:
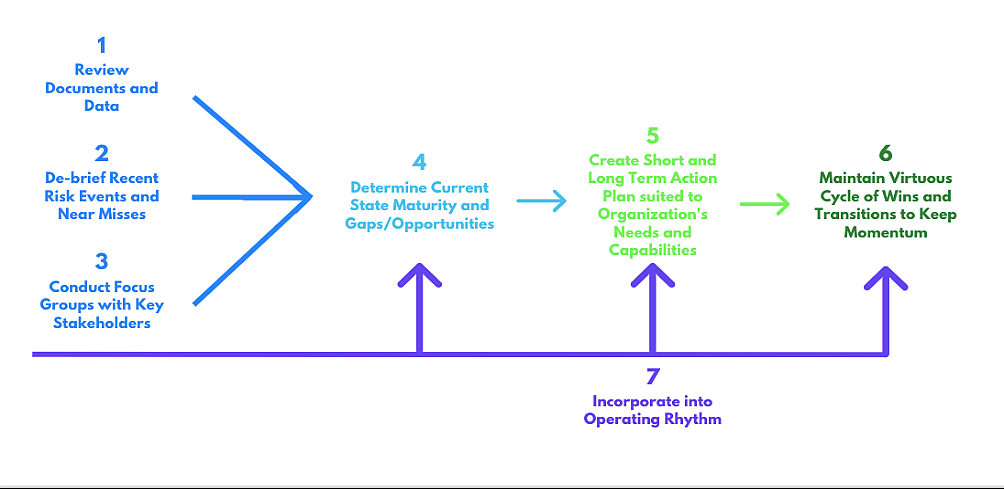
Service Options
Companies can elect whether they just require Appleton Greene for advice and support with the Bronze Client Service, for research and performance analysis with the Silver Client Service, for facilitating departmental workshops with the Gold Client Service, or for complete process planning, development, implementation, management and review, with the Platinum Client Service. Ultimately, there is a service to suit every situation and every budget and clients can elect to either upgrade or downgrade from one service to another as and when required, providing complete flexibility in order to ensure that the right level of support is available over a sustainable period of time, enabling the organization to compensate for any prescriptive or emergent changes relating to: Customer Service; E-business; Finance; Globalization; Human Resources; Information Technology; Legal; Management; Marketing; or Production.
Service Mission
I aspire to help organizations achieve best-in-class risk management suitable for their present circumstances and anticipated future needs. By doing this, I aim to safeguard and increase the value organizations can offer their shareholders and stakeholders.
Proactive risk management (“Avoiding big surprises”), Business partnerships (“Being on speed dial”), and Reduced bureaucracy (“Agile and Efficient”) are three outcomes that I have used to gauge success.
Service Objectives

Objective 1: Risk Diagnostic
Want to assess how your risk program stacks up against the finest in the business?
A typical risk program includes several crucial elements, including:
– Identification of the critical risks and an understanding of risk appetite and tolerance
– Effective handling of significant risks
– Controls
– Governance and Resources
– Reporting and Metrics
– Ongoing improvement, etc.
Different frameworks (such as COSO and ISO – see below) have attempted to define standards for enterprise risk management.
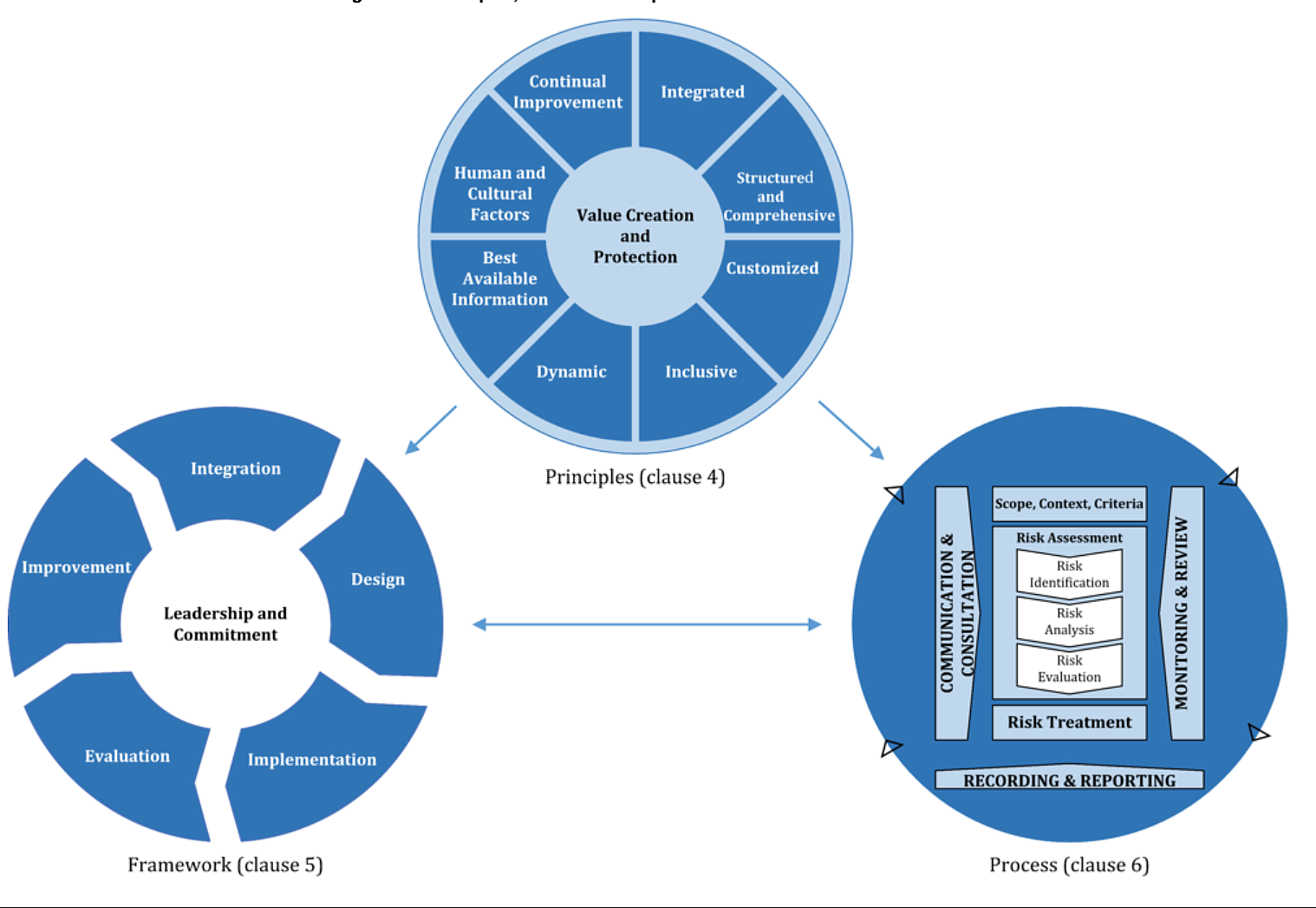
While these are helpful, they do not get into nuances that must be addressed while implementing risk management frameworks. Supplementing these theoretical frameworks with insights from successful practical applications at several leading organizations over 20+ years gives a better assessment methodology.
The organization can choose the targets and subsequent actions for the various program components based on this assessment and what is best for the organization’s requirements.
Objective 2: Risk Deep-Dive
Need help figuring out where to start in identifying and managing key risks for your organization? Have specific concerns on risk topics like culture, crisis management, risk committee effectiveness, etc.?
Risk management is most effective when it matches the inherent nature and controllability of an organization’s different types of risk. Each of an organization’s three typical risk categories — “preventable,” “strategic,” and “external”— has a different source, a different degree of controllability, and a different approach for identification, mitigation, and management.
Different frameworks (such as from COSO and ISO – see below) have attempted to define standards for enterprise risk management.
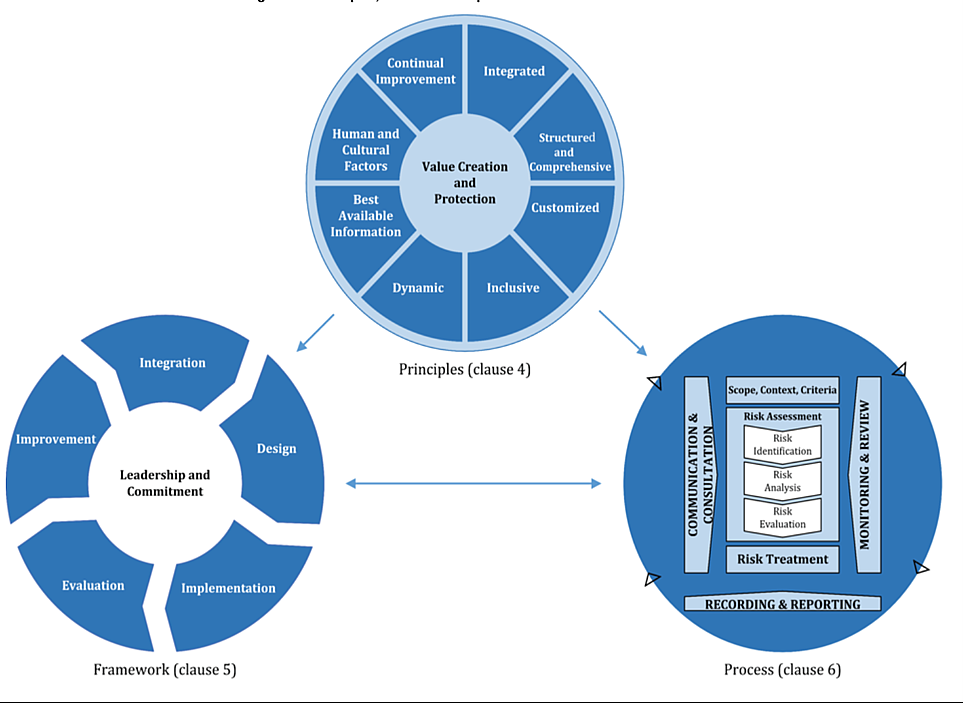
However, such frameworks do not make distinctions in the approach to managing different risk categories under various degrees of uncertainty. The standard risk management approach of “Identify – Assess – Prioritize – Manage” only works when there is a higher degree of certainty about likelihood and impact – for “known knowns” and maybe some “known unknowns.” But this approach does not usually work for “unknown unknowns” (recent examples include COVID-19 and the extended financial crisis in 2008-09).
Supplementing these theoretical frameworks with insights from successful practical applications at several leading organizations over 20+ years gives a better approach for identifying, assessing, and managing significant risks that can impact the achievement of the organization’s strategy.
Based on an assessment of how specific risks are and should be managed, the organization can decide the appropriate targets and next steps for the organization’s needs.
Objective 3: Risk Accountability
Does your organization have the proper ownership and governance over key risks?
Having the proper accountability and governance for critical risks is essential for an effective risk management program.
A typical organization has an operating structure and reporting lines to provide clear roles and responsibilities across the three lines of defense for identifying, managing, and overseeing risks.
Sample operating structure for risk management
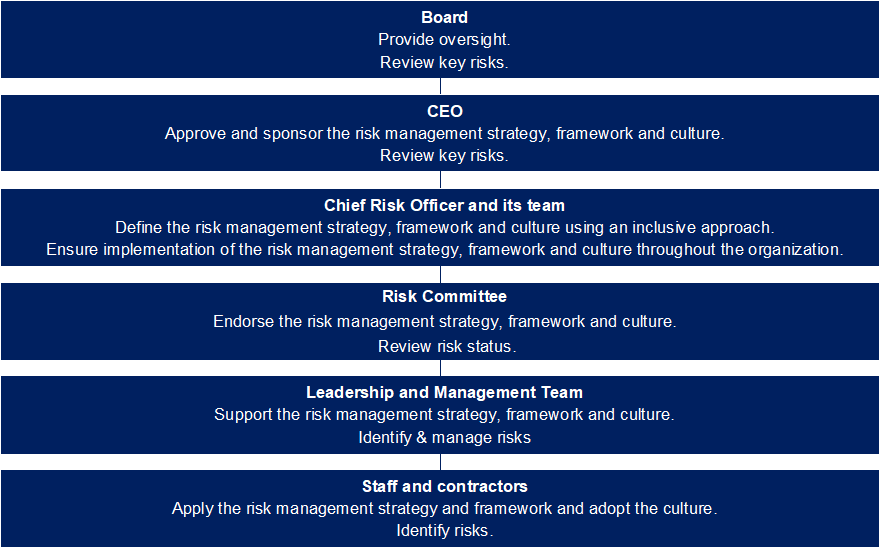
The level of formality depends on the organization’s maturity; however, some structure is necessary, even for smaller organizations such as start-ups. In addition, adjusting the operating structure based on insights from successful practical applications at several leading organizations over 20+ years provides a more effective solution.
Based on an assessment of how the current operating structure works, the organization can decide the appropriate targets and next steps for the organization’s needs.
Objective 4: Fractional Leadership
Have an immediate need for a senior risk executive to step in to bridge the gap to something more permanent?
Sometimes, an organization may have concerns with the current risk environment but may need more resources to invest in a full-time risk leader/organization.
This situation requires a risk leader:
– who has worked in different environments – small and large organizations, various industries, and across geographies – so they can better understand and appreciate the nuances of clients;
– who can hit the ground running to address urgent risk matters while at the same time strengthening the foundation;
– who is well-connected in the risk profession to identify a permanent risk leader; and
– can impact the risk culture in the organization through soft skills such as executive presence, influencing, active listening, and coaching are as important.
Based on the short-term actions and longer-term proposals of the temporary risk leader and discussions with senior leadership, the organization can decide the appropriate targets and next steps for the organization’s needs.
Achievements

Experian
In 6 years of leading risk and compliance programs, Mr. Chari has several success stories across the consulting services he will provide.
A few of these that Mr. Chari has been recognized for (by his direct manager as well as other senior leaders):
– Improving the maturity of the risk and compliance programs, as validated by internal and external benchmarking.
– Building a cohesive three lines of defense by bringing together leaders and teams from across governance functions to serve a common broader objective for the organization.
– Authoring a data breach response plan tailored to the unique needs of Experian and based on lessons learned from external breaches.
– Implementing a risk-based approach to different enterprise risks, including third-party risk.
– Simplifying enterprise governance policies.

PIMCO
In 3 years of starting and leading the enterprise risk program, Mr. Chari has several success stories across the consulting services he will provide.
A few of these that Mr. Chari has been recognized for (by his direct manager as well as other senior leaders):
– Developed Enterprise Risk framework and implemented various components such as risk assessments and key risk indicators.
– Coordinated the agenda and activities of the Global Risk Committee.
– Influenced senior management and embedded functional risk representatives to ensure consistent implementation of all aspects of the Risk Framework.
– Promoted risk awareness through training and newsletters.
– Led various governance forums such as vendor oversight and business continuity.

AllianceBernstein
In 9 years in various roles, including leading the operational risk program, Mr. Chari has had several success stories across the consulting services he will provide.
A few of these that Mr. Chari has been recognized for (by his direct manager as well as other senior leaders):
– Chaired various governance committees, such as Operational Risk Oversight, Error Review, Outsourcing Oversight/Vendor Risk, and Operations Risk Council.
– Contributed to various other committees, such as New Product Initiative and Investment Risk Oversight.
– Maintained “Top Operational Risks” scorecard.
– Worked with senior management to ensure consistent implementation of all aspects of the Operational Risk framework.
– Key Risk liaison for various activities such as SSAE16 and SOX.

Louis Hornick
In 11 years in various roles, including leading the quality assurance program, Mr. Chari has had several success stories across the consulting services he will provide.
A few of these that Mr. Chari has been recognized for (by his direct manager as well as other senior leaders):
– A vital member of the executive steering committee that worked on setting and monitoring goals on labor costs, budgets, and process improvements. Typical savings of $1Millon+ annually.
– Championed culture change for the company using Six Sigma and Lean principles. This resulted in proactively identifying issues and improved process capabilities by more than 25%.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Banking & Financial Services
The financial services sector affects almost everyone, whether directly or indirectly, through employment, personal or business clientele. The worldwide financial services industry is thought to account for around 20 trillion dollars, or about one-fourth, of the global economy. Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, the sector has kept expanding at a healthy rate and is projected to continue through 2025 at a CAGR of 5-6%.
The inherent risks in the sector have increased because of the rise of cryptocurrencies, fintech, and other start-ups in recent years. As more customers become accustomed to digital assets, digital technology—including those utilized in payments—will continue to advance.
As one of the most heavily regulated sectors, internal and external stakeholders have high expectations for effective risk management (including compliance). Despite these expectations, there is a wide range in risk management performance. Risk management is essential because failures and fines have occurred even in banks, which are typically subject to the most intense monitoring.
While the overall risk management process (identification, assessment, management, reporting, and governance) is industry-agnostic, each industry has unique characteristics that should be considered.
Financial services entities may be influenced by any or all of the following external factors:
• Regulatory scrutiny and heightened expectations of staff conduct, lending, and sales practices, and the effectiveness of enterprise risk management programs.
• The local economy’s health is typically strongly correlated to the ability to increase deposits and lending activity and is affected by financial downturns.
• Economic implications from the distribution of wealth and institutions financing new opportunities and businesses.
• Disruptions to the traditional banking models as new technology becomes available (e.g., e-banking).
• Significant capital and liquidity requirements imposed by regulators to solidify financial institutions’ financial foundations and resilience.
• Social expectations of corporate philanthropy and support of community causes.
They may also be influenced by internal factors:
• The need to manage new and increased capital requirements imposed by regulators.
• Competition for talented employees in new areas such as e-banking, model development, and credit risk management to support initiatives and respond to changes in the market.
• Stable, long-standing relationships centered on understanding customers’ businesses, risk profiles, and capacity to meet their financial obligations.
• A relationship-based approach to lending that relies increasingly on qualitative information from customers, given the availability of audited financial statements, tax returns, or other verifiable information.
It is essential to determine the current areas of weaknesses, pick the right opportunities to address them, and embrace a culture of continuous improvement.

Consultancy
The estimated size of the worldwide consulting market is between $200-300 billion. The largest consulting markets are in North America and Europe, while Asia offers promising growth prospects. The highest market share belongs to the Big 4 accounting and management consulting firms, including McKinsey and Boston Consulting Group. The value supplied by consultants (such as strategic industry knowledge, management expertise, and understanding of new trends) should continue to sustain the growth of this market, notwithstanding a slowdown during COVID-19 and subsequent spending reductions because of economic uncertainties.
Recent internal failures in the consulting sector, such as insider trading and “poor advice” (the impact of their services on their clients/end users), have drawn intense regulatory and political scrutiny. Although consulting firms have become experts at offering a range of services to their clients, internal risk management at these firms has occasionally been lacking.
While the overall risk management process (identification, assessment, management, reporting, and governance) is industry-agnostic, each industry has unique characteristics that should be considered.
In the case of consulting entities, external factors (such as economic uncertainty, regulatory scrutiny, political pressure, and social expectations) and internal factors (such as talent shortage, sales practices, ethics, and culture of compliance) can influence risk management.
It is essential to determine the current areas of weaknesses, pick the right opportunities to address them, and embrace a culture of continuous improvement.

Technology
The worldwide IT market is valued at more than $5 trillion, with North America accounting for 35%, Asia for 32%, and Europe for 22% of that total. Global household names include technology giants like FAANG (Facebook/Meta, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, and Google/Alphabet). The technology sector is still expanding despite COVID-19. Services based on the cloud and artificial intelligence (AI) are anticipated to drive this sector’s rapid expansion.
The only “constant” in this sector is change, and both established firms and newcomers are causing enormous upheaval. Regulators are paying more attention to issues like privacy and operational resilience. Technology businesses’ actual risk management performance varies widely, and there are frequent failures in privacy and data protection.
While the overall risk management process (identification, assessment, management, reporting, and governance) is industry-agnostic, each industry has unique characteristics that should be considered.
Technology entities may be influenced by any or all of the following external factors:
• Political and government regulatory approaches to spectrum usage, cloud computing, data privacy, sustainability, and infrastructure.
• Competition from cloud-based products and services that impact the margins of traditional hardware businesses and affect people with lower disposable incomes in developed countries, who are less likely to buy high-end consumer products.
• Consumer demand for end-to-end solutions that make the customer experience seamless and secure, such as cyber security products, services, and technologies that improve overall productivity and efficiency.
• Rapid technological changes, growing technological complexity, and the shortening of product life cycles.
• Regulatory and legal requirements arise from political and government changes and legislation.
• Climate change and sustainability demands push companies to provide incentives to reduce, reuse, and recycle devices.
Internal factors may also influence them:
• Capital demands to sustain merger and acquisitions activities, increased liability in pensions, minimum health benefit requirements, and legacy staff and low-skilled labor.
• The need for skilled employees increases the urgency to retain current talented staff and outsource entry-level jobs.
• Processes required to obtain third-party assistance to deploy and integrate new services and technologies.
• Innovation in technology that drives efficiency and relevancy of companies in the market.
It is essential to determine the current areas of weaknesses, pick the right opportunities to address them, and embrace a culture of continuous improvement.
Non-Profit & Charities
The non-profit sector’s market size is estimated at around $250 billion. Although COVID-19 has affected charitable donations, total revenue is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4-5% through 2027. As corporate social responsibility (CSR) advances, there will be growth in the market for charitable organizations. Businesses that practice CSR consider social and environmental concerns when conducting business and interacting with stakeholders. Additionally, millennials prefer to work for companies that support social causes.
While the overall risk management process (identification, assessment, management, reporting, and governance) is industry-agnostic, each industry has unique characteristics that should be considered.
Not-for-profit entities may be influenced by external factors:
• Political stability required to gain access to infrastructure and local administration, such as permits.
• Government support to provide grants for the types of work that these organizations perform.
• An understanding of what drives disposable income and corporate profits is essential for this sector, as much of the funding is donor generated, and there is significant competition for funds.
• The emotional aspect of giving, which affects what causes donors respond to.
• Advances in technology that allow organizations to deliver services more efficiently.
• Regulations on the delivery of aid from the country the organization is headquartered in and where aid is provided (e.g., medical volunteers must comply with any licensing regulations governing their profession).
They may also be influenced by the following internal factors:
• Capital needs for equipment and machinery.
• The right mix of permanent staff and skilled and non-skilled volunteers.
• Effective processes for training to enable efficient and effective responses.
• The effectiveness and efficiency of response depend on access to current technologies.
It is essential to determine the current areas of weaknesses, pick the right opportunities to address them, and embrace a culture of continuous improvement.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Los Angeles, USA
Los Angeles is a global economic powerhouse, boasting the world’s third-largest metropolitan economy, with a real GDP of over $950 billion. Traditionally the world’s entertainment capital, Los Angeles (and California more broadly) has become an important location for several industries, including technology and financial services. Outstanding academic institutions (such as Caltech, UCLA, and USC) and connectivity to critical areas worldwide through airports and seaports enhance its importance for the global economy.
On the flip side, the cost of doing business (taxes, real estate) has continued to make companies move out of California into states like Texas. Income inequality and associated issues like homelessness have increased in recent years.

New York, USA
The New York metro area’s GDP steadily rose in the last two decades to $1.5 trillion in 2021. New York has been the financial and cultural capital of the world for several decades. The presence of many Fortune 500 companies in various industries, such as financial services, pharmaceuticals, media, real estate, fashion, and entertainment, combined with experienced and new professionals, makes New York a vibrant and exciting location. The region is also home to one of the largest trading industries in the country at the Port of New York and New Jersey, making it well connected to critical cities worldwide.
On the flip side, the cost of doing business (taxes, real estate) has made some companies hesitant to continue having a significant presence in New York. Other cities like London have become more prominent players in financial markets.
London, UK
Service industries generate more than GBP 200 billion in economic production annually and dominate London’s economy. London has become a significant location for global markets and financial services. London is a particularly attractive market for financial service companies due to its highly educated and diversified workforce.
On the other hand, corporations have relocated their offices to mainland Europe and other markets because of the political and economic uncertainties caused by the UK’s exit from the Eurozone. The UK is experiencing stagflation in 2022–2023 (high inflation, negative growth), and unless the government and others act, the UK (particularly London) will experience significant challenges in the near future.

Mumbai, India
Mumbai’s GDP is estimated to be more than $60 billion. Mumbai is the financial capital of India, generates more than 6% of India’s GDP, and is expected to grow more than 10% in the next year. India is one of the world’s fastest-growing economies. It is on track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2027, thanks to global trends and key investments the country has made in technology and energy. Mumbai, and India in general, is also home to many start-ups – making it a second “Bay Area.”
Conversely, issues like income inequality, homelessness, crime, intellectual property rights, and political vagaries make Mumbai (and India overall) challenging for business.
Despite this, the sheer number of opportunities in a market like India and the support India provides to the global economy (in areas such as outsourcing) will keep Mumbai a critical cog of the world economy.

Singapore
Singapore’s GDP is close to $400 billion. It has continued to grow despite the impact of COVID-19; growth is expected to slow down in 2023 amid persistent inflation and global pressures that will impact demand for trade and finance industries.
Singapore is one of the financial capitals of Asia. Due to its business-friendly policies, safety, and connectivity to other key markets in Asia and the world, Singapore is a very attractive market for employers.
On the flip side, there are questions about the authoritarian nature of the Singapore government and freedom of speech.
Despite this, Singapore’s infrastructure and quality of life will make it a global market leader.
Clients
This service’s current clients or employers include:

Experian
We live in a world built on data; it is everywhere, growing in power and influence. Experian believes that data has the potential to transform lives and create a better tomorrow. To do this, data needs to be understood, interpreted, and the knowledge it holds is acted on. Experian works to do just this: unlock the possibilities that data holds and help people and organizations realize the opportunities held within.
Experian serves – Business-to-Business – helping businesses provide great customer experiences by managing and analyzing data that will help them solve problems, drive better decisions and outcomes, and prevent fraud.
Consumer Services – helping millions of people in the USA, UK, Brazil, India, and Colombia to better manage and improve their financial position and help them to protect against fraud and identity theft.

PIMCO
PIMCO manages assets for central banks, sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, corporations, foundations and endowments, and individual investors around the world. For more than 50 years, PIMCO has worked relentlessly to help millions of investors pursue their objectives – regardless of shifting market conditions.
PIMCO believes that active management is the responsible way to invest clients’ assets in fixed income. PIMCO’s active investment process combines a top-down macroeconomic view with bottom-up research and analysis to put the best ideas around the world to work in PIMCO portfolios.

AllianceBernstein
AllianceBernstein (AB) is committed to seeking alpha. A unique combination of expertise across equities, fixed-income, alternatives, and multi-asset strategies and a connected global network helps AB deliver differentiated insights and distinctive solutions to advance investors’ success.
Bernstein Research is Wall Street’s premier independent sell-side research and brokerage firm that delivers trusted investment research and trading execution to drive better outcomes.
The Private Wealth Management division offers sophisticated wealth-planning tools and expert advice for high-net-worth individuals, families, and smaller institutions, helping investors make their money meaningful.
https://www.alliancebernstein.com
Service Benefits
Management
- Achieve strategy
- Enable growth
- Improve culture
- Take risk
- Reduce risk
- Minimize surprises
- Improve governance
- Continuous improvement
- Reduce expenses
- Vendor management
Governance
- Achieve goals
- Improve culture
- Take risk
- Reduce risk
- Minimize surprises
- Reduce expenses
- Screen acquisitions
- Improve governance
- Better compliance
- Continuous improvement
Information Technology
- Achieve goals
- Take risk
- Reduce risk
- Improve culture
- Reduce expenses
- Increase resilience
- Crisis management
- Improve governance
- Vendor management
- Continuous improvement
Bronze Service

Time limit: 5 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze service includes:
01. Email support
02. Telephone support
03. Questions & answers
04. Professional advice
05. Communication management
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Bronze Client Service (BCS) for Manage Risk provides clients with an entry level option and enables client contacts to become personally acquainted with Mr. Chari over a sustainable period of time. We suggest that clients allocate up to a maximum of 5 Key Employees for this service. Your Key Employees can then contact the consultant via email, whenever they feel that they need specific advice or support in relation to the consultant’s specialist subject. The consultant will also be proactive about opening and maintaining communications with your Key Employees. Your Key Employees can list and number any questions that they would like to ask and they will then receive specific answers to each and every query that they may have. Your Key Employees can then retain these communications on file for future reference. General support inquiries will usually receive replies within 48 hours, but please allow a period of up to 10 business days during busy periods. The Bronze Client Service (BCS) enables your Key Employees to get to know their designated Appleton Greene consultant and to benefit from the consultant’s specialist skills, knowledge and experience.
Silver Service

Time limit: 10 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze service plus
01. Research analysis
02. Management analysis
03. Performance analysis
04. Business process analysis
05. Training analysis
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Silver Client Service (SCS) for Manage Risk provides more time for research and development. If you require Mr. Chari to undertake research on your behalf, or on behalf of your Key Employees, then this would understandably require more time and the Silver Client Service (SCS) accommodates this. For example, you may want your consultant to undertake some research into your management, performance, business, or training processes, with a view towards providing an independent analysis and recommendations for improvement. If any research and development, or business analysis is required, then the Silver Client Service (SCS) is for you.
Gold Service

Time limit: 15 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze/Silver service plus
01. Management interviews
02. Evaluation and assessment
03. Performance improvement
04. Business process improvement
05. Management training
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Gold Client Service (GCS) for Manage Risk is intended for more detailed evaluation and assessment, that may require your Key Employees to have monthly meetings or interviews with Mr. Chari. These meetings and interviews can be conducted over the telephone, Skype, or by video conference if required. The consultant can also attend your business premises, an Appleton Greene office, or another mutually beneficial location, but please note that clients are responsible for the costs of any disbursements separately, including travel and accommodation. This service enables you to integrate the specific skills, knowledge and experience of your designated consultant into your Key Employee management team. The Gold Client Service (GCS) can also incorporate training workshops, business presentations and external meetings with customers, suppliers, associations, or any other business-related stakeholders.
Platinum Service

Time limit: 20 hours per month
Contract period: 12 months
Bronze/Silver/Gold service plus
01. Project planning
02. Project development
03. Project implementation
04. Project management
05. Project review
SERVICE DESCRIPTION
The Platinum Client Service (PCS) for Manage Risk is our flagship service and will be required if you need Mr. Chari to facilitate the planning, development, implementation, management, or review of a particular project relating to his specialist subject, which would obviously require more time and dedication. This service enables you to reserve up to 12.5% of the consultant’s working month and provides a more hands-on service as and when required. If you need more time than this, then this can always be arranged, subject of course to the consultant’s ongoing availability. The benefit of having an external consultant involved in projects is they provide an independent perspective and are not influenced by internal politics, day-to-day responsibilities, or personal career interest. They provide objectivity, specific knowledge, skills and experience and will be entirely focused upon the tasks at hand. The Platinum Client Service (PCS) will provide your organization with a valuable resource as and when you need it.
















