Professional Services Advisor – Workshop 1 (Services Trust)
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Professional Services Advisor is provided by Dr. Cherry Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
If you would like to view the Client Information Hub (CIH) for this program, please Click Here
Learning Provider Profile

Prior to his advisory, academic and training career, Dr. Cherry had significant senior management experience, at general manager and managing director level, across manufacturing and service industries. His strong commercial acumen and strategic thinking, coupled with formal business and technical tertiary qualifications, have allowed him to achieve significant revenue and profitability growth through his senior career. Dr Cherry has worked in senior management, executive director, and non-executive director roles across multinationals, listed and private companies as well as not-for-profits. A strong strategic mind-set, coupled with an ability to lead senior and middle management teams have been the keys to Dr Cherry’s commercial success in business, across a range of industries. Throughout his career, Dr Cherry has demonstrated his capability to affect change, turnaround, re-engineer and grow businesses both organically and via acquisition. He has leveraged this corporate experience and success into his professional services career and provides strategic advisory and training services at senior management and board level to clients globally. Outside his professional career, Dr Cherry was a founding director of the Cure Brain Cancer Foundation, established to fund advances in brain tumour treatment and research. He also lectures and supervises at undergraduate and postgraduate levels across several Australian and Irish universities and business schools.
Dr Cherry holds an honours degree in Chemical Engineering, a Master of Commerce degree with a marketing major and a Doctor of Business Administration degree where he researched trust in the professional services context.
To request further information about Dr. Cherry through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
MOST Analysis
Mission Statement
Welcome to Workshop 1 on Services Trust, a foundational program designed to equip professional service providers with the essential knowledge and skills to cultivate and sustain trust in client relationships. Our mission is to foster a deep understanding of trust as the cornerstone of professional services, enabling participants to achieve and maintain the status of trusted advisers.
Trust is the bedrock of successful client relationships in professional services, encompassing reliability, integrity, and competence. This workshop aims to demystify trust, exploring its various dimensions and its paramount importance in the professional context. Participants will gain insights into how trust impacts client satisfaction and loyalty, ultimately benefiting both clients and service providers.
Establishing rapport and credibility is crucial for fostering strong client relationships. Through interactive sessions, participants will learn techniques for building genuine connections and effective communication strategies to enhance credibility. Upholding ethics and integrity are essential for maintaining client trust. This workshop delves into ethical considerations and strategies for handling ethical dilemmas, equipping participants to navigate these challenges effectively.
In an era of prevalent data breaches and privacy concerns, confidentiality and data protection are paramount. This workshop will cover safeguarding client information and implementing best practices for data security. Effective communication and managing client expectations are also crucial for building trust and ensuring satisfaction. Participants will acquire skills to communicate effectively, listen actively, and set realistic expectations through role-playing scenarios and discussions.
Finally, feedback and continuous improvement are essential for maintaining high standards and fostering trust. Participants will learn techniques for soliciting and providing feedback and strategies for empowering clients with knowledge and information. Our commitment is to provide a comprehensive, interactive, and practical learning experience, equipping professionals to build, maintain, and enhance trust in their client relationships, achieving trusted adviser status and fostering long-lasting, successful client relationships.
Objectives
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services: Participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of trust, recognising its crucial role in client relationships within professional services. The module will cover various dimensions of trust, such as reliability, competence, and integrity, helping professionals to enhance client satisfaction and loyalty by navigating complex interactions confidently.
02. Building Rapport and Credibility: This module equips participants with skills to establish and maintain rapport and credibility with clients, essential for fostering long-term relationships. Through learning genuine connection techniques and effective communication, professionals will be able to build trust and ensure lasting client satisfaction.
03. Communication Skills: Participants will develop vital communication skills necessary for building and maintaining strong client relationships. By focusing on active listening, clear expression, and empathetic communication, this module aims to enhance transparency and understanding in client interactions, fostering trust and competence.
04. Ethics and Integrity: This module explores the importance of ethics and integrity in professional services, providing strategies to handle ethical dilemmas and maintain client trust. Participants will learn to uphold high ethical standards, ensuring credibility and reliable service delivery.
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection: Participants will understand the critical aspects of confidentiality and data protection, crucial for maintaining client trust. This module covers data protection regulations and best practices, helping professionals safeguard client information and comply with regulatory standards.
06. Managing Expectations: This module focuses on setting and managing client expectations to enhance satisfaction and build trust. Participants will learn to align expectations with deliverables, reducing misunderstandings and fostering clear communication and realistic goal setting.
07. Conflict Resolution: Participants will acquire skills to identify, address, and resolve conflicts effectively, crucial for maintaining trust and client satisfaction. This module provides techniques to turn disputes into opportunities for trust-building and preserving professional relationships.
08. Risk Management: This module teaches participants to identify and mitigate risks, crucial for maintaining trust in professional services. By developing effective risk management strategies and implementing risk assessments, professionals can safeguard their services and client relationships.
09. Quality Assurance: Participants will learn to ensure quality in service delivery through effective quality control measures and continuous improvement strategies. This module highlights the significance of maintaining high standards to foster client trust and satisfaction.
10. Client Empowerment: This module focuses on empowering clients with knowledge and information to build trust and confidence. Participants will learn strategies to educate clients about services, enhancing relationships and ensuring sustained success through empowerment.
11. Transparency in Processes: Participants will explore the importance of transparency in service delivery, learning techniques for clear communication and openness. This module aims to build trust through transparent processes, ultimately fostering long-term client loyalty.
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement: This module emphasises the role of feedback in fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Participants will learn effective feedback strategies and how to implement them for ongoing service enhancement, strengthening client trust and satisfaction.
Strategies
01. Enhance trust by consistently demonstrating competence, reliability, integrity, and clear communication, supported by digital platforms and data-driven assessments.
02. Build trust by consistently demonstrating expertise, reliability, empathy, and effective communication, fostering strong, credible, and lasting client relationships.
03. Foster effective communication by practising active listening, clear articulation, and empathy to build trust and strong client relationships.
04. Uphold ethics and integrity by demonstrating honesty, transparency, and consistent ethical behaviour, fostering trust and credibility in all professional interactions.
05. Ensure confidentiality and data protection by implementing robust security measures, maintaining strict access controls, and adhering to legal regulations to foster client trust.
06. Maintain clear, transparent communication, set realistic goals, and regularly update clients to effectively manage expectations, fostering trust and long-term relationships.
07. Adopt a transformative conflict resolution strategy, focusing on understanding underlying interests, fostering mutual respect, and employing empathetic communication for proactive, sustainable solutions.
08. Integrate risk management into strategic planning, using comprehensive assessment frameworks and fostering open communication for proactive risk mitigation.
09. Implementing client-centric quality assurance through continuous feedback, employee training, and standardised processes to meet and exceed client expectations consistently.
10. Integrate client feedback, involve them in decision-making, and educate them on relevant information to foster ownership, satisfaction, and stronger service relationships.
11. Promote transparency by setting clear expectations, maintaining consistent communication, documenting processes, and involving clients in decision-making to foster trust and improve service outcomes.
12. Implement structured feedback mechanisms to gather client insights regularly, fostering continuous improvement and enhancing service quality.
Tasks
01. Role-playing trust-building scenarios, active listening and transparent communication drills, ethical dilemma resolution, confidentiality management simulations, and continuous feedback implementation exercises.
02. Participants will engage in role-playing client meetings, practicing active listening, empathy, transparent communication, and receiving feedback to build rapport and credibility.
03. Participants will conduct mock client meetings, practice active listening and empathy, refine clear and concise communication, and receive feedback on presentations and nonverbal communication skills.
04. Participants will engage in ethical dilemma discussions, role-playing scenarios for decision-making, reviewing case studies, and developing strategies for maintaining integrity and transparency in client relationships.
05. Participants will review and enhance data protection policies, conduct risk assessments, implement encryption and access controls, engage in role-playing for handling breaches, and participate in discussions on best practices for confidentiality and data protection.
06. Participants will engage in role-playing to negotiate project expectations, create expectation alignment maps, and participate in a simulation exercise managing dynamic client expectations and challenges to achieve project objectives.
07. Participants engage in role reversal to build empathy, interest-based problem-solving to find mutually beneficial solutions, and joint goal setting to enhance cooperation and accountability, strengthening their conflict resolution skills.
08. Participants will conduct risk identification workshops, develop mitigation plans, practise continuous risk monitoring, and engage in role-play for managing expectations and conflict resolution.
09. Participants will engage in process standardisation workshops, quality assurance simulations, and client feedback analysis to develop standardised service delivery processes, practice quality assurance techniques, and use client feedback to enhance service quality.
10. Participants will brainstorm client empowerment strategies, develop and present action plans, gather and incorporate client feedback, and engage in role-playing scenarios to practice effective communication and decision-making with clients.
11. Participants will identify transparency gaps, develop transparency plans including real-time dashboards and regular updates, present these plans, and receive feedback to enhance transparency, efficiency, and client trust in professional services.
12. Participants will design a comprehensive client feedback survey, role-play feedback review meetings to discuss and create action plans and analyse feedback data to develop an actionable improvement plan with specific steps, responsible team members, and timelines.
Introduction
The first workshop of the Professional Services Advisor program, Services Trust, has been designed to equip professional service providers with the skills and knowledge needed to build, maintain, and enhance trust in their client relationships. Participants will achieve a comprehensive understanding of trust and its critical role in professional services, which will translate into practical benefits, including enhanced client relationships, improved professional competence, greater client satisfaction and loyalty, reduced risk of ethical breaches, enhanced reputation and credibility, increased confidence in managing client interactions, better data protection practices, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By mastering these skills, professionals can achieve trusted adviser status and build long-lasting, successful client relationships, ensuring their long-term success in the industry.
The following paragraphs provide an important grounding on trust, firstly in the general business context, and then the specific area of professional services. They also provide a clear overview of the workshop objectives, what is to be achieved by participants and the benefits of same. A useful assessment of trust from historical, current, and future perspectives is also provided, to better understand the journey to trusted advisor status.
The Importance of Trust in General Business Settings
Trust is a foundational element in any business setting, serving as the glue that holds relationships, processes, and systems together. Without trust, the smooth operation of businesses can be significantly impaired, leading to inefficiencies, decreased morale, and reduced profitability. Several notable writers and scholars have extensively discussed the importance of trust in business, each offering unique perspectives and insights.

Stephen M.R. Covey: Speed of Trust
Stephen M.R. Covey, in his book “The Speed of Trust,” argues that trust is a critical economic driver and not merely a social virtue. Covey suggests that trust affects two measurable outcomes: speed and cost. When trust is present in an organisation, decisions are made faster and more efficiently, and the costs associated with business transactions are reduced. Conversely, a lack of trust slows down operations and increases costs due to the need for additional checks and balances.
Covey provides the example of Warren Buffett, who acquired McLane Distribution without extensive due diligence because of the high level of trust he had in the management team. This move saved considerable time and costs, illustrating how trust can directly impact business efficiency and profitability.
Francis Fukuyama: Trust and Social Virtues
Francis Fukuyama, in his book “Trust: The Social Virtues and the Creation of Prosperity,” explores how trust extends beyond interpersonal relationships to influence the broader economic and social structures. Fukuyama argues that high-trust societies tend to have more robust economies because trust facilitates cooperation and reduces the need for extensive regulation and oversight.
He contrasts high-trust cultures, such as those in Germany and Japan, with low-trust cultures, noting that businesses in high-trust cultures are more likely to engage in long-term strategic partnerships. These partnerships lead to more innovation and economic growth, as seen in the success of companies like Toyota and Siemens, which thrive on collaborative, trust-based relationships with suppliers and partners.
Lencioni’s Five Dysfunctions of a Team
Patrick Lencioni, in “The Five Dysfunctions of a Team,” identifies the absence of trust as the first dysfunction that can cripple a team. Lencioni emphasises that trust is the foundation upon which other critical team dynamics are built, including conflict resolution, commitment, accountability, and results.
In a business setting, when team members do not trust each other, they are less likely to engage in open and honest communication. This lack of communication leads to unresolved conflicts, lack of commitment to decisions, and ultimately, poor performance. Lencioni’s model is often used in team-building exercises to highlight the importance of establishing trust within teams to achieve high performance.
Mayer, Davis, and Schoorman: An Integrative Model of Organisational Trust
Roger C. Mayer, James H. Davis, and F. David Schoorman developed an integrative model of organisational trust that outlines three critical factors: ability, benevolence, and integrity. According to their model, trust is built when employees perceive their leaders as competent (ability), caring (benevolence), and honest (integrity).
This model is particularly useful in understanding how trust can be developed and maintained in business settings. For instance, leaders who consistently demonstrate these three attributes are more likely to earn the trust of their employees, leading to higher levels of engagement and productivity. Conversely, a breach in any of these areas can quickly erode trust and lead to organisational dysfunction.
The Role of Trust in Leadership: Simon Sinek
Simon Sinek, in his book “Leaders Eat Last,” discusses the role of trust in effective leadership. Sinek argues that great leaders prioritise the well-being of their team members, creating a culture of trust and safety. This sense of safety allows employees to take risks, innovate, and collaborate more effectively, knowing that their leaders have their backs.
Sinek provides examples from the military, where leaders are often willing to sacrifice their own well-being for the sake of their team. This level of trust and commitment is what makes teams resilient and high performing. In business, leaders who adopt this mindset can build loyal and motivated teams that drive organisational success.
Trust and Corporate Reputation: Charles Fombrun
Charles Fombrun, a leading scholar on corporate reputation, highlights the importance of trust in building and maintaining a positive corporate reputation. Fombrun argues that trust is a key component of reputation, which in turn influences consumer behaviour, investor confidence, and employee loyalty.
Companies like Johnson & Johnson have demonstrated the importance of trust through their handling of crises. The Tylenol poisoning incident in the 1980s is often cited as a textbook example of how a company can build trust by prioritising customer safety over profits. Johnson & Johnson’s swift and transparent response not only restored trust but also enhanced its reputation overall.
Trust in Digital and Remote Work Environments
In the digital age, trust has taken on new dimensions. The rise of remote work, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has highlighted the need for trust in virtual teams. According to Paul J. Zak, author of “Trust Factor: The Science of Creating High-Performance Companies,” trust in virtual teams can be cultivated through regular communication, transparency, and the use of technology to foster connections.
Zak’s research shows that organisations with high levels of trust enjoy greater employee engagement and productivity, even in remote settings. For example, companies that implement regular video check-ins, transparent communication channels, and recognition programs can maintain elevated levels of trust and cohesion among remote workers.
Trust in the Professional Services Context: Insights from Maister et al.
Trust is the cornerstone of any successful professional services relationship. It is the intangible yet essential element that determines whether clients feel confident in relying on their advisors, be they accountants, consultants, lawyers, or other professionals. In this exploration, we delve into the nature of trust in professional services, drawing on the seminal work of David Maister, along with Charles H. Green and Robert M. Galford, particularly their insights presented in “The Trusted Advisor.”
The Trust Equation
Maister, Green, and Galford introduced a profound framework for understanding trust in their book “The Trusted Advisor.” They broke down trust into four components through what they call the Trust Equation. This equation provides a clear and structured way to analyse and build trust in professional relationships. The components are credibility, reliability, intimacy, and self-orientation. Each of these elements contributes to the overall trustworthiness of a professional.
Credibility
Credibility is about the words we speak. It encompasses the professional’s credentials, expertise, and the ability to deliver on promises. Credibility is established through qualifications, experience, and a proven record of accomplishment of success. For instance, an accountant’s credibility might be reflected in their certifications, their knowledge of tax laws, and their ability to provide accurate financial advice.
Professionals enhance their credibility by continually updating their skills, staying informed about industry developments, and demonstrating a deep understanding of their field. Credibility is not just about what you know; it is also about how you communicate what you know. Clear, concise, and jargon-free communication helps in making complex information accessible to clients, thereby reinforcing the professional’s credibility.
Reliability
Reliability refers to the actions we take. It is about consistency in behaviour and the assurance that the professional will follow through on commitments. Reliable professionals are those who meet deadlines, deliver on promises, and maintain a consistent level of service quality. In accounting, reliability might manifest as timely submission of financial reports, consistent accuracy in calculations, and regular updates to clients about their financial status.
To be perceived as reliable, professionals need to be organised, diligent, and attentive to details. They should also communicate openly about their capabilities and limitations, ensuring that they do not overpromise and underdeliver. Consistency in small actions, such as returning phone calls promptly and following up on client queries, significantly contributes to building a perception of reliability.
Intimacy
Intimacy is about the safety or security that clients feel when confiding in their advisors. It is the dimension of trust that involves building a personal connection and making the client feel comfortable. Intimacy is fostered through empathy, active listening, and a genuine interest in the client’s concerns. For an accountant, this might involve understanding not just the financial aspects but also the personal goals and challenges of a client.
Professionals can build intimacy by creating an environment where clients feel heard and understood. This involves asking open-ended questions, showing empathy, and responding to concerns with compassion. Intimacy is also about maintaining confidentiality and respecting the privacy of the client’s information. When clients feel that their advisor genuinely cares about them and their issues, they are more likely to trust them.
Self-Orientation
Self-orientation reflects where the professional’s focus lies. An elevated level of self-orientation indicates that the professional is more concerned with their own interests rather than those of the client. Conversely, a low level of self-orientation means that the professional prioritises the client’s needs. This component is crucial because clients need to feel that their advisor has their best interests at heart.
Professionals can reduce perceived self-orientation by demonstrating a commitment to the client’s success. This can be achieved by providing unbiased advice, even if it means recommending a service or product from a competitor. Transparency about fees and avoiding hidden charges also contribute to lowering self-orientation. When clients perceive that their advisor is genuinely focused on their needs, their trust in the advisor deepens.
The Dynamics of Trust in Professional Services

The Trust Equation provides a robust framework for understanding how trust is built and maintained in professional services. However, the dynamics of trust are complex and influenced by numerous factors, including the nature of the professional’s work, the context of the client relationship, and external factors such as industry standards and regulatory environments.
Building Trust through Expertise and Knowledge
In professional services, expertise is a significant driver of trust. Clients seek professionals who possess a deep understanding of their field and can offer valuable insights and solutions. Continuous professional development is essential for maintaining and enhancing expertise. This involves staying updated with the latest industry trends, obtaining relevant certifications, and engaging in ongoing education.
For instance, an accountant who is well-versed in the latest tax regulations and financial reporting standards is more likely to be trusted by clients. Demonstrating expertise through thought leadership, such as publishing articles, speaking at industry events, and participating in professional associations, also enhances credibility and trustworthiness.
The Role of Communication in Building Trust
Effective communication is a critical component of trust in professional services. Professionals must be able to convey complex information in a clear and understandable manner. This involves not only technical proficiency but also the ability to listen actively and respond appropriately to client concerns.
Transparency in communication is vital. Professionals should provide clients with all necessary information, including potential risks and uncertainties, to enable informed decision-making. Regular updates and proactive communication help in keeping clients informed and reassured.
Ethical Behaviour and Integrity
Ethical behaviour is foundational to trust. Clients need to be confident that their advisor will act in their best interests and adhere to the highest ethical standards. Integrity involves honesty, transparency, and a commitment to doing what is right, even when it may not be in the professional’s immediate interest.
In accounting, integrity is particularly crucial due to the potential consequences of unethical behaviour. Accountants must avoid conflicts of interest, maintain confidentiality, and ensure the accuracy and honesty of financial reporting. Demonstrating integrity through actions, such as whistleblowing in cases of malpractice, further solidifies trust.
Client-Centred Approach
A client-centred approach is essential for building and maintaining trust. This involves understanding the client’s unique needs, goals, and challenges and providing tailored advice and solutions. Professionals should show empathy and a genuine interest in the client’s welfare.
Building a personal connection with clients can significantly enhance trust. This involves not only understanding their business or personal financial situation but also their broader context, such as their industry, market conditions, and long-term objectives. A holistic understanding of the client’s situation enables the professional to provide more relevant and valuable advice.
Consistency and Dependability
Consistency in delivering high-quality service is crucial for maintaining trust. Clients need to feel that they can depend on their advisor to meet their needs reliably over time. This involves not only meeting deadlines and fulfilling commitments but also maintaining a consistent level of service quality.
Professionals should establish clear processes and standards to ensure consistency. This might include regular training for staff, implementing quality control measures, and using technology to streamline workflows. Consistency also involves being responsive to client needs and concerns, providing timely updates, and addressing issues promptly.
Challenges in Building Trust
While the principles of building trust are clear, professionals often face challenges in implementing them. These challenges can stem from various sources, including the complexity of the client’s situation, competitive pressures, and the inherent uncertainties in the professional’s work.
Complexity and Uncertainty
The complexity of the client’s situation can pose challenges to building trust. For instance, in accounting, clients may have intricate financial structures, multiple revenue streams, and diverse regulatory requirements. Understanding and addressing these complexities require a high level of expertise and diligence.
Uncertainty also plays a significant role. Clients may face uncertain market conditions, regulatory changes, or other external factors that impact their situation. Professionals need to provide clear guidance in navigating these uncertainties, which requires staying informed and adapting to changing circumstances.
Competitive Pressures
Competitive pressures can sometimes lead to ethical dilemmas and conflicts of interest. Professionals may feel pressured to cut corners, overpromise, or engage in aggressive marketing to attract clients. However, such actions can undermine trust overall.
Maintaining ethical standards and focusing on building long-term relationships rather than short-term gains is essential. Professionals should prioritise quality over quantity and ensure that their actions align with their commitment to integrity and client welfare.
Managing Client Expectations
Managing client expectations is crucial for building trust. Professionals need to set realistic expectations about what can be achieved and within what timeframe. Overpromising can lead to disappointment and erode trust, while under promising can result in lost opportunities.
Clear and transparent communication is key to managing expectations. Professionals should provide clients with a realistic assessment of the situation, potential outcomes, and any associated risks. Regular updates and honest feedback help in aligning client expectations with the reality of the situation.
Trust is the foundation of successful professional services relationships. The insights from Maister, Green, and Galford’s Trust Equation provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and building trust. By enhancing credibility, reliability, intimacy, and reducing self-orientation, professionals can build strong, trust-based relationships with their clients.
Implementing these principles requires a commitment to continual learning, ethical behaviour, clear communication, and a client-centred approach. Despite the challenges, professionals who prioritise building and maintaining trust are more likely to achieve long-term success and foster enduring client relationships. Trust is not just an abstract concept; it is a tangible asset that drives client loyalty, satisfaction, and ultimately, the success of professional service firms.

Case Study – Trust and Empathy
A notable case study on the importance of trust in a business setting involves the transformation journey of Microsoft under the leadership of Satya Nadella. Microsoft, a globally recognised multinational technology company, experienced a significant cultural shift that emphasised trust, collaboration, and innovation, leading to remarkable business success.
Background
In 2014, when Satya Nadella became CEO, Microsoft was struggling with internal competition, a siloed culture, and a lack of innovation. The company’s market share was being challenged by emerging technologies and competitors. Nadella’s vision for transforming Microsoft hinged on fostering a culture of trust and empathy within the organisation.
Key Initiatives
1. Cultural Transformation:
o Nadella focused on breaking down silos and promoting a “One Microsoft” culture where collaboration and trust were prioritised. He encouraged employees to embrace a growth mindset, promoting continuous learning and improvement.
o Trust was built through transparent communication and by aligning the company’s mission with employee values. Nadella communicated openly about the company’s direction and challenges, fostering a sense of shared purpose.
2. Customer-Centric Approach:
o Microsoft shifted its focus to understanding and addressing customer needs. This involved listening to customer feedback and incorporating it into product development, thereby building trust with customers and partners.
3. Innovation and Collaboration:
o The company embraced open-source technologies and partnered with competitors, which was a significant shift from its previous insular approach. This openness built trust within the tech community and among stakeholders.
Outcomes
• Financial Performance:
o Microsoft’s market capitalisation increased significantly, from around $300 billion in 2014 to over $2 trillion in 2021, reflecting the success of its transformation strategy.
• Employee Engagement:
o Employee satisfaction and engagement improved as the company culture became more inclusive and collaborative. Trust within teams increased, leading to higher productivity and innovation.
• Market Position:
o Microsoft regained its competitive edge, becoming a leader in cloud computing with its Azure platform, which was a direct result of the company’s renewed focus on innovation and customer trust.
Lessons Learned
• Leadership Commitment:
o The active involvement and commitment of leadership are crucial in driving cultural transformation. Nadella’s consistent emphasis on trust and empathy set the tone for the entire organisation.
• Change Management:
o Effective change management strategies, including clear communication and employee engagement, are vital for overcoming resistance and fostering a culture of trust and continuous improvement.
• Collaboration with External Stakeholders:
o Embracing partnerships and collaboration, even with competitors, can drive innovation and build trust within the broader industry.
This case study of Microsoft under Satya Nadella’s leadership demonstrates the critical role of trust in achieving organisational success and highlights how a strong culture of trust can drive innovation, employee engagement, and overall business performance.
History of Trust
The concept of trust in professional services has long been a cornerstone of successful client relationships. Historically, trust has been integral to professions such as law, accounting, and consulting, where clients must rely heavily on the expertise and integrity of their advisors. The origins of professional trust can be traced back to the early days of these professions when practitioners were often seen as pillars of their communities, entrusted with sensitive information and critical decisions.
In the early 20th century, the formalisation of professional standards and ethics began to take shape, laying the groundwork for trust in these fields. Professional bodies such as the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (ICAEW) and the Law Society established codes of conduct and ethical guidelines, which were designed to ensure that practitioners adhered to exacting standards of integrity and competence. These regulatory frameworks were crucial in building public confidence and trust in professional services.
The post-World War II era saw a significant expansion in the demand for professional services, driven by economic growth and increasing regulatory complexity. This period marked the beginning of the modern professional services industry, characterised by the rise of large multinational firms and the diversification of services offered. Trust remained a fundamental element, as clients sought advisors who could navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing business environment.

Trust in the Current Situation
Today, trust in professional services is more critical than ever. The landscape of professional services has evolved significantly, influenced by globalisation, technological advancements, and shifting client expectations. Despite these changes, the core elements of trust—competence, integrity, and reliability—remain unchanged.
In the contemporary professional services context, competence is demonstrated through continuous professional development and the ability to provide expert advice tailored to the client’s unique needs. Professional service providers are expected to stay abreast of industry trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements to maintain their credibility and effectiveness.
Integrity, another pillar of trust, involves adhering to ethical standards and demonstrating honesty in all client interactions. This includes maintaining confidentiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and ensuring transparency in communications and fee structures. The rise of corporate scandals and financial crises in the late 20th and early 21st centuries have underscored the importance of integrity, as breaches of trust have far-reaching consequences for both clients and service providers.
Reliability is crucial in maintaining trust, requiring professionals to deliver consistent, high-quality service and honour their commitments. This includes meeting deadlines, providing accurate and timely information, and being responsive to client needs. In a highly competitive market, reliability differentiates trusted advisors from their peers.
The digital age has introduced new challenges and opportunities for building and maintaining trust. On one hand, technology has enabled greater transparency and efficiency in service delivery. On the other hand, it has also heightened concerns around data security and privacy. Professional service providers must navigate these complexities to protect client information and build digital trust.
The Future of Trust
The future of trust in professional services is set to be shaped by several emerging trends and developments. As the industry continues to evolve, professionals must adapt to maintain and enhance trust in their client relationships.
1. Technological Integration and Digital Trust: The increasing integration of technology in professional services will play a significant role in the future of trust. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics are transforming how services are delivered, offering opportunities for greater accuracy, efficiency, and transparency. However, these advancements also bring challenges, particularly in terms of data security and ethical considerations. Professionals will need to ensure that technological innovations are implemented responsibly, and that clients’ data is protected against breaches and misuse.
2. Focus on Ethical Standards and Corporate Responsibility: Ethical considerations and corporate responsibility will become even more critical in the future. Clients are increasingly seeking advisors who not only provide expert services but also adhere to high ethical standards and demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. Issues such as environmental sustainability, diversity and inclusion, and corporate governance are becoming more important to clients. Professional service firms will need to integrate these values into their practices to build and maintain trust.
3. Personalisation and Client-Centric Approaches: The future will see a greater emphasis on personalisation and client-centric approaches. Clients are looking for tailored solutions that address their specific needs and challenges. Building trust will involve understanding clients’ unique circumstances and providing bespoke advice and services. Advances in technology, such as data analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, will enable professionals to gain deeper insights into their clients and deliver more personalised services.
4. Continuous Professional Development and Lifelong Learning: As industries and regulations continue to evolve, continuous professional development and lifelong learning will be essential for maintaining competence and trust. Professional service providers will need to invest in ongoing education and training to stay updated with the latest developments in their fields. This commitment to professional growth will demonstrate to clients that their advisors are knowledgeable and capable of navigating new challenges.
5. Transparency and Communication: Transparency and clear communication will remain foundational to building trust in the future. Clients expect honesty and openness in all interactions, from fee structures to service delivery processes. Professionals will need to communicate clearly and regularly with clients, providing updates and addressing any concerns promptly. The use of technology to enhance communication, such as through secure client portals and real-time updates, will become increasingly important.
6. Adaptability and Resilience: The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and demonstrate resilience will be crucial for maintaining trust in the face of uncertainty. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of adaptability in professional services, as firms had to quickly pivot to remote working and digital service delivery. Going forward, professionals will need to be prepared for future disruptions and demonstrate their capacity to adapt while continuing to provide reliable and high-quality services.
Trust in professional services has a rich history rooted in the principles of competence, integrity, and reliability. These core elements remain as relevant today as they were in the past, even as the professional services landscape continues to evolve. The current position of trust is shaped by the need to navigate technological advancements, maintain ethical standards, and meet the growing expectations of clients. Looking to the future, professionals must adapt to emerging trends such as digital trust, ethical responsibility, personalisation, continuous learning, transparency, and adaptability. By embracing these developments, professional service providers can continue to build and maintain the trust that is essential for long-term client relationships and success in the industry.

Workshop – Core Objectives, Expected Achievements & Benefits
The Services Trust Workshop is designed to equip professional service providers with the essential skills and knowledge required to build, maintain, and enhance trust in their client relationships. Trust is the foundation of successful client engagements in professional services, influencing client satisfaction, loyalty, and the overall success of service engagements. The following paragraphs will explore the core objectives of the workshop, what participants will achieve through their participation, and how they will benefit from the insights and skills gained.
Core Objectives of the Workshop
Understanding Trust in Professional Services
The primary objective of the workshop is to deepen participants’ understanding of trust and its critical importance in the professional services context. Trust is a multifaceted concept that encompasses reliability, integrity, and competence. Each of these dimensions plays a crucial role in building and maintaining strong client relationships.
1. Reliability: Clients need to feel confident that their service providers will deliver on their promises consistently. Reliability involves meeting deadlines, providing accurate and timely information, and being dependable in all interactions.
2. Integrity: Ethical behaviour and honesty are at the heart of trust. Clients must believe that their service providers will act in their best interests, maintain confidentiality, and uphold high ethical standards.
3. Competence: Professionals must possess the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver high-quality services. Competence is demonstrated through continuous professional development, staying abreast of industry trends, and providing expert advice tailored to the client’s unique needs.
By understanding these dimensions, participants will learn how trust forms the basis of successful client relationships and how it influences client satisfaction and loyalty. This foundational knowledge will enable professionals to navigate client relationships with greater insight and effectiveness.
Enhancing Communication Skills
Effective communication is fundamental to building trust. The workshop places a strong emphasis on enhancing participants’ communication skills. Active listening, clear and concise expression of ideas, and empathetic communication are core components covered in the training. Participants will engage in practical exercises and role-playing scenarios to hone these skills. By practising these techniques in a controlled environment, professionals can improve their ability to communicate transparently and effectively, ensuring clients feel understood and valued. Improved communication skills lead to fewer misunderstandings, more productive engagements, and a stronger foundation of trust with clients.
Building Rapport and Credibility
Establishing and maintaining rapport and credibility are crucial for developing long-term client relationships. This workshop objective focuses on equipping participants with techniques to build genuine connections and enhance their credibility. Effective communication strategies, active listening, and empathetic interactions are key components of this objective. By mastering these skills, professionals will be better prepared to foster trust through authentic and meaningful engagements with their clients. The goal is to ensure long-term client satisfaction by establishing a solid foundation of trust from the outset.
Ethical Decision-Making and Integrity
Upholding ethical standards and maintaining integrity are non-negotiable in professional services. The workshop delves into ethical considerations, helping participants navigate complex ethical dilemmas. Through case studies and ethical scenarios, professionals will explore real-life situations where ethical behaviour is paramount. This training equips participants with the tools to make sound ethical decisions and act with integrity in all their professional dealings. By consistently demonstrating ethical behaviour, professionals can build and sustain trust, ensuring their clients feel confident in their commitment to honesty and transparency.
Effective Management of Client Expectations
Managing client expectations is crucial for maintaining trust and satisfaction. The workshop provides participants with techniques for setting realistic expectations, aligning client expectations with deliverables, and strategies for managing and exceeding those expectations. Role-playing scenarios allow participants to practise these skills in realistic settings, enhancing their ability to communicate effectively and manage expectations proactively. This training helps professionals avoid misunderstandings and disappointments, ensuring a smoother and more positive client experience.
Conflict Resolution Skills
Conflicts are inevitable in any professional relationship, but effective resolution is key to maintaining trust. The workshop explores techniques for identifying and addressing conflicts, resolving disputes, and turning conflicts into opportunities for trust-building. Interactive activities allow participants to practise conflict resolution strategies, enhancing their ability to manage disputes constructively. By mastering these skills, professionals can address issues promptly and effectively, preserving trust and strengthening their client relationships even in challenging situations.
Confidentiality and Data Protection
In today’s digital age, safeguarding client information is more important than ever. The workshop covers the importance of confidentiality and data protection, providing participants with best practices for managing and protecting sensitive information. Through practical exercises that simulate data protection challenges, professionals gain hands-on experience in maintaining confidentiality and security. This training ensures that participants understand the critical role of data protection in maintaining client trust and compliance with regulatory standards.
Continuous Improvement and Feedback
Continuous improvement is essential for long-term success in professional services. The workshop emphasises the importance of soliciting and providing feedback effectively and using it for ongoing improvement. Participants engage in feedback sessions and continuous improvement exercises, learning how to cultivate a feedback-oriented culture. This training helps professionals identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance service quality and client satisfaction. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, professionals can maintain exacting standards and adapt to evolving client needs, further strengthening trust.
Quality Assurance
Ensuring quality in service delivery is fundamental to building and maintaining trust. The workshop covers quality control measures, continuous improvement strategies, and the significance of quality assurance in professional services. Participants learn how to implement effective quality control measures through case studies and practical exercises. This training helps professionals maintain high standards of service delivery, ensuring clients receive consistent and reliable service. High-quality service delivery enhances client trust and satisfaction, contributing to long-term client loyalty.
Client Empowerment
Empowering clients with knowledge and information is crucial for building trust. The workshop covers strategies for educating clients about services, fostering confidence, and enhancing client relationships through empowerment. Participants engage in activities focused on client education and empowerment strategies, helping them understand the importance of transparency and client empowerment. By empowering clients, professionals can build stronger, trust-based relationships, as clients feel more confident and informed about the services they receive.
Transparency in Processes
Maintaining transparency in service delivery is essential for fostering trust. The workshop covers techniques for effectively communicating processes and methodologies to clients, ensuring openness and transparency. Through interactive discussions and transparency exercises, participants learn how to cultivate open and transparent relationships with clients. This training helps professionals build long-term client loyalty and trust by ensuring clients understand the processes and methodologies involved in service delivery.
Achievements through Participation
Participants in the Services Trust Workshop will achieve several key outcomes that will enhance their professional capabilities and improve their client relationships. These achievements include:
1. A Comprehensive Understanding of Trust: Participants will gain a thorough understanding of the multifaceted nature of trust and its critical role in professional services. They will learn how reliability, integrity, and competence interact to build strong client relationships.
2. Enhanced Communication Skills: Through practical exercises and role-playing scenarios, participants will improve their communication skills. They will learn techniques for active listening, clear and concise expression, and empathetic communication, leading to more effective client interactions.
3. Techniques for Building Rapport and Credibility: Participants will acquire strategies for establishing and maintaining rapport and credibility with clients. They will learn how to build genuine connections and enhance their credibility through effective communication and ethical behaviour.
4. Ethical Decision-Making Skills: The workshop will equip participants with tools for navigating complex ethical dilemmas. They will explore real-life ethical scenarios and learn how to make sound ethical decisions that build and sustain trust.
5. Effective Client Expectation Management: Participants will learn techniques for setting realistic expectations and aligning them with deliverables. They will practise managing and exceeding client expectations through role-playing scenarios, enhancing client satisfaction.
6. Conflict Resolution Skills: The workshop will provide participants with strategies for identifying and resolving conflicts constructively. They will practise conflict resolution techniques in interactive activities, preparing them to manage disputes effectively.
7. Confidentiality and Data Protection Expertise: Participants will gain best practices for safeguarding client information and maintaining data protection. They will engage in practical exercises to manage confidential information securely, reinforcing client trust.
8. Continuous Improvement Mindset: The workshop will emphasise the importance of continuous improvement and feedback. Participants will learn how to solicit and provide feedback effectively and implement changes that enhance service quality.
9. Quality Assurance Knowledge: Participants will acquire knowledge of quality control measures and continuous improvement strategies. They will learn how to maintain exacting standards of service delivery, ensuring consistent and reliable client service.
10. Client Empowerment Strategies: The workshop will cover strategies for educating and empowering clients. Participants will learn how to foster client confidence and build stronger relationships through transparency and education.
11. Transparency in Service Delivery: Participants will learn techniques for maintaining transparency in service delivery. They will engage in discussions and exercises that emphasise the importance of openness and transparency in building long-term client trust.
Practical Benefits for Participants

Enhanced Client Relationships
One of the most significant practical benefits of the workshop is the enhancement of client relationships. By understanding the core elements of trust and how to foster them, participants will be better equipped to build strong, trust-based relationships with their clients. This leads to increased client satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for long-term success in professional services.
Improved Professional Competence
The workshop provides participants with the tools and knowledge needed to improve their professional competence. Enhanced communication skills, ethical decision-making abilities, and conflict resolution strategies contribute to a more competent and confident professional. This competence is essential for delivering high-quality services and maintaining client trust.
Greater Client Satisfaction and Loyalty
By mastering techniques for managing client expectations, resolving conflicts, and ensuring quality service delivery, participants will be able to enhance client satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied clients are more likely to return for future services and recommend the professional to others, leading to increased business opportunities.
Reduced Risk of Ethical Breaches
The workshop’s focus on ethical decision-making and integrity helps participants navigate complex ethical dilemmas. This reduces the risk of ethical breaches, which can have severe consequences for both the professional and the client. By upholding high ethical standards, participants can build and maintain a reputation for integrity and trustworthiness.
Enhanced Reputation and Credibility
Professionals who demonstrate reliability, competence, and integrity are more likely to be seen as credible and trustworthy. The workshop equips participants with the skills needed to build and maintain this credibility, enhancing their reputation in the industry. A strong reputation attracts new clients and business opportunities, contributing to long-term success.
Increased Confidence in Managing Client Interactions
Participants will gain confidence in managing complex client interactions through practical exercises and role-playing scenarios. They will learn how to communicate effectively, manage expectations, and resolve conflicts, leading to more productive and positive client engagements.
Better Data Protection Practices
In an era of increasing data breaches and privacy concerns, the workshop’s focus on confidentiality and data protection is particularly valuable. Participants will learn best practices for managing and protecting sensitive client information, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, and reinforcing client trust.
Commitment to Continuous Improvement
The workshop emphasises the importance of continuous improvement and feedback. Participants will develop a mindset of continuous improvement, seeking out opportunities to enhance their skills and service quality. This commitment to improvement ensures that professionals remain competitive and responsive to evolving client needs.
Conclusion

The Services Trust workshop is a comprehensive training program designed to equip professional service providers with the skills and knowledge needed to build, maintain, and enhance trust in their client relationships. By focusing on key areas such as understanding trust, enhancing communication skills, building rapport and credibility, upholding ethics and integrity, managing client expectations, resolving conflicts, ensuring confidentiality and data protection, continuous improvement, quality assurance, client empowerment, and maintaining transparency, the workshop prepares participants to navigate complex client interactions with confidence and competence.
Participants will achieve a comprehensive understanding of trust and its critical role in professional services, enhanced communication skills, techniques for building rapport and credibility, ethical decision-making abilities, effective client expectation management, conflict resolution skills, confidentiality and data protection expertise, a continuous improvement mindset, quality assurance knowledge, client empowerment strategies, and transparency in service delivery.
These achievements translate into practical benefits, including enhanced client relationships, improved professional competence, greater client satisfaction and loyalty, reduced risk of ethical breaches, enhanced reputation and credibility, increased confidence in managing client interactions, better data protection practices, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By mastering these skills, professionals can achieve trusted adviser status and build long-lasting, successful client relationships, ensuring their long-term success in the industry.
Executive Summary

Chapter 1: Understanding Trust in Professional Services
This topic area is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of trust, the cornerstone of successful client relationships in professional services. Trust is paramount in the professional services context as it ensures clients have confidence in the reliability, integrity, and competence of the service provider. Participants will gain the necessary skills and knowledge to establish, maintain, and enhance trust with clients. The topic covers key areas, including defining trust in the context of professional services, exploring its importance for both clients and service providers, and understanding different dimensions of trust such as reliability, competence, and integrity. Participants will learn to recognise the significance of trust in professional relationships, understand how it impacts client satisfaction and loyalty, and explore the benefits of a trust-based relationship for service providers. This topic will enable professionals to navigate complex client interactions with confidence, integrity, and competence.

Chapter 2: Building Rapport and Credibility
This topic focuses on building rapport and credibility, which are vital for successful client relationships in professional services. Participants will acquire skills to establish, maintain, and enhance rapport and credibility with clients. The topic covers essential topics, including establishing rapport, techniques for building credibility, and fostering long-term client relationships. Participants will learn the importance of genuine connections, effective communication, and tailoring approaches to build trust, ensuring lasting client satisfaction. By mastering these skills, professionals will be able to navigate complex client interactions with confidence, integrity, and competence, ultimately fostering stronger, long-lasting client relationships.

Chapter 3: Communications Skills
This topic focuses on developing effective communication skills crucial for successful client relationships in professional services. Communication is vital in relation to trust in professional services as it ensures transparency, clarity, and fosters understanding, thus building and maintaining strong client relationships. Participants will gain the necessary skills to communicate effectively, listen actively, and express ideas clearly and concisely. Key areas covered include effective communication in professional services, active listening techniques, and clear and concise expression of ideas. Participants will learn the importance of clear, respectful, and empathetic communication, enhancing client interactions. By completing this topic, professionals will be equipped to navigate complex client interactions with confidence, integrity, and competence, fostering stronger, long-lasting client relationships.
Chapter 4: Ethics and Integrity
This topic delves into the crucial aspects of ethics and integrity within professional services, which are essential for fostering successful client relationships. Ethics and integrity are crucial in professional services as they uphold credibility, maintain client trust, and ensure the delivery of reliable and ethical services. Participants will acquire the skills necessary to navigate ethical considerations, maintain integrity in client relationships, and effectively handle ethical dilemmas. The topic covers key topics, including ethical considerations in professional services, the importance of maintaining integrity in client relationships, and strategies for handling ethical dilemmas. Participants will learn the significance of upholding ethical standards, maintaining transparency, and fostering trust with clients. This topic provides professionals with the necessary tools to maintain trust and credibility in the professional services they provide.
Chapter 5: Confidentiality and Data Protection
This topic explores the critical aspects of confidentiality and data protection in professional services, essential for fostering successful client relationships. Recent incidents across the globe have reminded businesses of the necessity to safeguard client information, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, protecting user privacy, and maintaining client trust. Participants will acquire the skills necessary to understand the importance of confidentiality, comply with data protection regulations, and ensure client data security. The topic covers key topics, including the significance of confidentiality in professional services, data protection regulations, and best practices for ensuring client data security. Participants will learn the importance of safeguarding client information, complying with regulations, and implementing best practices to protect client data.
Chapter 6: Managing Expectations
This topic focuses on effectively managing expectations, crucial for successful client relationships in professional, as it ensures clients have a clear understanding of what to expect, reducing the risk of misunderstandings, enhancing satisfaction, and building trust. Participants will acquire skills to set realistic expectations, align client expectations with deliverables, and implement strategies for managing and exceeding expectations. Key topics covered include the importance of setting achievable expectations, techniques for aligning client expectations with deliverables, and strategies for managing and surpassing expectations.
Chapter 7: Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution in professional services is essential as it enables the timely and effective resolution of disputes, fostering trust, maintaining client satisfaction, and preserving professional relationships. This topic explores conflict resolution, a critical aspect for building successful client relationships in professional services. Participants will acquire skills to identify and address conflicts, techniques for resolving disputes, and strategies for turning conflicts into opportunities for trust-building. Key areas covered include the importance of identifying and addressing conflicts, effective techniques for resolving disputes, and strategies for turning conflicts into opportunities to build trust.

Chapter 8: Risk Management
This topic explores risk management, a crucial element in building and maintaining trust in professional services. Participants will learn to identify and mitigate risks, develop effective risk management strategies, and implement risk assessment in service delivery. Key areas covered include the importance of risk identification and mitigation, effective risk management strategies, and the implementation of risk assessment in service delivery.
Chapter 9: Quality Assurance
Effective risk management in professional services provides several benefits, including mitigating potential financial losses, enhancing client trust and satisfaction, maintaining the integrity of the service, and safeguarding the reputation of the service provider. This topic delves into quality assurance, a pivotal element in building and maintaining trust in professional services. Participants will learn to ensure quality in service delivery, implement quality control measures, and drive continuous improvement in professional services. Key areas covered include the significance of ensuring quality, effective implementation of quality control measures, and fostering continuous improvement in service delivery.
Chapter 10: Client Empowerment
This topic focuses on empowering clients with knowledge and information, a critical element for building and maintaining trust in professional services. Participants will learn to educate clients about the services provided and build client confidence through empowerment. Key areas include the significance of empowering clients with knowledge, effective strategies for educating clients, and fostering confidence through empowerment. This topic ensures professionals can foster stronger, long-lasting client relationships, enhancing their professional services and guaranteeing sustained success, ultimately strengthening the foundation of trust between clients and service providers.

Chapter 11: Transparency in Processes
This topic delves into the importance of transparency in service delivery, a cornerstone for fostering trust in professional relationships. Participants will explore techniques for maintaining transparency, including effectively communicating processes and methodologies to clients. Key areas covered include the significance of transparency, strategies for clear communication, and building trust through openness. This topic aims to equip professionals with the tools to cultivate open and transparent relationships, ultimately strengthening trust and fostering long-term client loyalty.
Chapter 12: Feedback and Continuous Improvement
This topic emphasises the importance of feedback in fostering a culture of continuous improvement within professional services. Participants will explore techniques for soliciting and providing feedback effectively and implementing it for improvement. Key areas covered include the significance of feedback, strategies for its implementation, and cultivating a culture of continuous improvement. This topic aims to equip professionals with the tools to foster a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately enhancing client satisfaction and strengthening trust in the services provided.
Curriculum
Professional Services Advisor – Workshop number 1 – Services Trust
- Understanding Trust in Professional Services
- Building Rapport and Credibility
- Communication Skills
- Ethics and Integrity
- Confidentiality and Data Protection
- Managing Expectations
- Conflict Resolution
- Risk Management
- Quality Assurance
- Client Empowerment
- Transparency in Processes
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Detailed Curriculum
This comprehensive training program on professional services trust is crucial for fostering a culture of trust and reliability within the professional services firm. Here are the 12 topic areas included in the Services Trust curriculum:
1. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
• Defining trust in the context of professional services
• Importance of trust for clients and service providers
• Different dimensions of trust (e.g., reliability, competence, integrity)
2. Building Rapport and Credibility
• Establishing rapport with clients
• Techniques for building credibility
• Developing long-term relationships with clients
3. Communication Skills
• Effective communication in professional services
• Active listening techniques
• Clear and concise expression of ideas
4. Ethics and Integrity
• Ethical considerations in professional services
• Maintaining integrity in client relationships
• Handling ethical dilemmas
5. Confidentiality and Data Protection
• Importance of confidentiality in professional services
• Data protection regulations and best practices
• Ensuring client data security
6. Managing Expectations
• Setting realistic expectations
• Aligning client expectations with deliverables
• Strategies for managing and exceeding expectations
7. Conflict Resolution
• Identifying and addressing conflicts
• Techniques for resolving disputes
• Turning conflicts into opportunities for trust-building
8. Risk Management
• Identifying and mitigating risks in professional services
• Strategies for risk management
• Implementing risk assessment in service delivery
9. Quality Assurance
• Ensuring quality in service delivery
• Implementing quality control measures
• Continuous improvement in professional services
10. Client Empowerment
• Empowering clients with knowledge and information
• Educating clients about the services provided
• Building client confidence through empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
• Maintaining transparency in service delivery
• Communicating processes and methodologies to clients
• Building trust through openness
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
• Soliciting and providing feedback
• Implementing feedback for improvement
• Cultivating a culture of continuous improvement
These topic areas form the basis of a comprehensive training program on professional services trust, helping to ensure the delivery of high-quality services and fostering strong, lasting relationships with clients.
Distance Learning
Introduction
Welcome to Appleton Greene and thank you for enrolling on the Professional Services Advisor corporate training program. You will be learning through our unique facilitation via distance-learning method, which will enable you to practically implement everything that you learn academically. The methods and materials used in your program have been designed and developed to ensure that you derive the maximum benefits and enjoyment possible. We hope that you find the program challenging and fun to do. However, if you have never been a distance-learner before, you may be experiencing some trepidation at the task before you. So we will get you started by giving you some basic information and guidance on how you can make the best use of the modules, how you should manage the materials and what you should be doing as you work through them. This guide is designed to point you in the right direction and help you to become an effective distance-learner. Take a few hours or so to study this guide and your guide to tutorial support for students, while making notes, before you start to study in earnest.
Study environment
You will need to locate a quiet and private place to study, preferably a room where you can easily be isolated from external disturbances or distractions. Make sure the room is well-lit and incorporates a relaxed, pleasant feel. If you can spoil yourself within your study environment, you will have much more of a chance to ensure that you are always in the right frame of mind when you do devote time to study. For example, a nice fire, the ability to play soft soothing background music, soft but effective lighting, perhaps a nice view if possible and a good size desk with a comfortable chair. Make sure that your family know when you are studying and understand your study rules. Your study environment is very important. The ideal situation, if at all possible, is to have a separate study, which can be devoted to you. If this is not possible then you will need to pay a lot more attention to developing and managing your study schedule, because it will affect other people as well as yourself. The better your study environment, the more productive you will be.
Study tools & rules
Try and make sure that your study tools are sufficient and in good working order. You will need to have access to a computer, scanner and printer, with access to the internet. You will need a very comfortable chair, which supports your lower back, and you will need a good filing system. It can be very frustrating if you are spending valuable study time trying to fix study tools that are unreliable, or unsuitable for the task. Make sure that your study tools are up to date. You will also need to consider some study rules. Some of these rules will apply to you and will be intended to help you to be more disciplined about when and how you study. This distance-learning guide will help you and after you have read it you can put some thought into what your study rules should be. You will also need to negotiate some study rules for your family, friends or anyone who lives with you. They too will need to be disciplined in order to ensure that they can support you while you study. It is important to ensure that your family and friends are an integral part of your study team. Having their support and encouragement can prove to be a crucial contribution to your successful completion of the program. Involve them in as much as you can.
Successful distance-learning
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes or workshops, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. But unlike traditional internal training courses, it is the student’s responsibility, with a distance-learning program, to ensure that they manage their own study contribution. This requires strong self-discipline and self-motivation skills and there must be a clear will to succeed. Those students who are used to managing themselves, are good at managing others and who enjoy working in isolation, are more likely to be good distance-learners. It is also important to be aware of the main reasons why you are studying and of the main objectives that you are hoping to achieve as a result. You will need to remind yourself of these objectives at times when you need to motivate yourself. Never lose sight of your long-term goals and your short-term objectives. There is nobody available here to pamper you, or to look after you, or to spoon-feed you with information, so you will need to find ways to encourage and appreciate yourself while you are studying. Make sure that you chart your study progress, so that you can be sure of your achievements and re-evaluate your goals and objectives regularly.
Self-assessment
Appleton Greene training programs are in all cases post-graduate programs. Consequently, you should already have obtained a business-related degree and be an experienced learner. You should therefore already be aware of your study strengths and weaknesses. For example, which time of the day are you at your most productive? Are you a lark or an owl? What study methods do you respond to the most? Are you a consistent learner? How do you discipline yourself? How do you ensure that you enjoy yourself while studying? It is important to understand yourself as a learner and so some self-assessment early on will be necessary if you are to apply yourself correctly. Perform a SWOT analysis on yourself as a student. List your internal strengths and weaknesses as a student and your external opportunities and threats. This will help you later on when you are creating a study plan. You can then incorporate features within your study plan that can ensure that you are playing to your strengths, while compensating for your weaknesses. You can also ensure that you make the most of your opportunities, while avoiding the potential threats to your success.
Accepting responsibility as a student
Training programs invariably require a significant investment, both in terms of what they cost and in the time that you need to contribute to study and the responsibility for successful completion of training programs rests entirely with the student. This is never more apparent than when a student is learning via distance-learning. Accepting responsibility as a student is an important step towards ensuring that you can successfully complete your training program. It is easy to instantly blame other people or factors when things go wrong. But the fact of the matter is that if a failure is your failure, then you have the power to do something about it, it is entirely in your own hands. If it is always someone else’s failure, then you are powerless to do anything about it. All students study in entirely different ways, this is because we are all individuals and what is right for one student, is not necessarily right for another. In order to succeed, you will have to accept personal responsibility for finding a way to plan, implement and manage a personal study plan that works for you. If you do not succeed, you only have yourself to blame.
Planning
By far the most critical contribution to stress, is the feeling of not being in control. In the absence of planning we tend to be reactive and can stumble from pillar to post in the hope that things will turn out fine in the end. Invariably they don’t! In order to be in control, we need to have firm ideas about how and when we want to do things. We also need to consider as many possible eventualities as we can, so that we are prepared for them when they happen. Prescriptive Change, is far easier to manage and control, than Emergent Change. The same is true with distance-learning. It is much easier and much more enjoyable, if you feel that you are in control and that things are going to plan. Even when things do go wrong, you are prepared for them and can act accordingly without any unnecessary stress. It is important therefore that you do take time to plan your studies properly.
Management
Once you have developed a clear study plan, it is of equal importance to ensure that you manage the implementation of it. Most of us usually enjoy planning, but it is usually during implementation when things go wrong. Targets are not met and we do not understand why. Sometimes we do not even know if targets are being met. It is not enough for us to conclude that the study plan just failed. If it is failing, you will need to understand what you can do about it. Similarly if your study plan is succeeding, it is still important to understand why, so that you can improve upon your success. You therefore need to have guidelines for self-assessment so that you can be consistent with performance improvement throughout the program. If you manage things correctly, then your performance should constantly improve throughout the program.
Study objectives & tasks
The first place to start is developing your program objectives. These should feature your reasons for undertaking the training program in order of priority. Keep them succinct and to the point in order to avoid confusion. Do not just write the first things that come into your head because they are likely to be too similar to each other. Make a list of possible departmental headings, such as: Customer Service; E-business; Finance; Globalization; Human Resources; Technology; Legal; Management; Marketing and Production. Then brainstorm for ideas by listing as many things that you want to achieve under each heading and later re-arrange these things in order of priority. Finally, select the top item from each department heading and choose these as your program objectives. Try and restrict yourself to five because it will enable you to focus clearly. It is likely that the other things that you listed will be achieved if each of the top objectives are achieved. If this does not prove to be the case, then simply work through the process again.
Study forecast
As a guide, the Appleton Greene Professional Services Advisor corporate training program should take 12-18 months to complete, depending upon your availability and current commitments. The reason why there is such a variance in time estimates is because every student is an individual, with differing productivity levels and different commitments. These differentiations are then exaggerated by the fact that this is a distance-learning program, which incorporates the practical integration of academic theory as an as a part of the training program. Consequently all of the project studies are real, which means that important decisions and compromises need to be made. You will want to get things right and will need to be patient with your expectations in order to ensure that they are. We would always recommend that you are prudent with your own task and time forecasts, but you still need to develop them and have a clear indication of what are realistic expectations in your case. With reference to your time planning: consider the time that you can realistically dedicate towards study with the program every week; calculate how long it should take you to complete the program, using the guidelines featured here; then break the program down into logical modules and allocate a suitable proportion of time to each of them, these will be your milestones; you can create a time plan by using a spreadsheet on your computer, or a personal organizer such as MS Outlook, you could also use a financial forecasting software; break your time forecasts down into manageable chunks of time, the more specific you can be, the more productive and accurate your time management will be; finally, use formulas where possible to do your time calculations for you, because this will help later on when your forecasts need to change in line with actual performance. With reference to your task planning: refer to your list of tasks that need to be undertaken in order to achieve your program objectives; with reference to your time plan, calculate when each task should be implemented; remember that you are not estimating when your objectives will be achieved, but when you will need to focus upon implementing the corresponding tasks; you also need to ensure that each task is implemented in conjunction with the associated training modules which are relevant; then break each single task down into a list of specific to do’s, say approximately ten to do’s for each task and enter these into your study plan; once again you could use MS Outlook to incorporate both your time and task planning and this could constitute your study plan; you could also use a project management software like MS Project. You should now have a clear and realistic forecast detailing when you can expect to be able to do something about undertaking the tasks to achieve your program objectives.
Performance management
It is one thing to develop your study forecast, it is quite another to monitor your progress. Ultimately it is less important whether you achieve your original study forecast and more important that you update it so that it constantly remains realistic in line with your performance. As you begin to work through the program, you will begin to have more of an idea about your own personal performance and productivity levels as a distance-learner. Once you have completed your first study module, you should re-evaluate your study forecast for both time and tasks, so that they reflect your actual performance level achieved. In order to achieve this you must first time yourself while training by using an alarm clock. Set the alarm for hourly intervals and make a note of how far you have come within that time. You can then make a note of your actual performance on your study plan and then compare your performance against your forecast. Then consider the reasons that have contributed towards your performance level, whether they are positive or negative and make a considered adjustment to your future forecasts as a result. Given time, you should start achieving your forecasts regularly.
With reference to time management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual time taken in your study plan; consider your successes with time-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; consider your failures with time-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to time planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your time expectations. You need to be consistent with your time management, otherwise you will never complete your studies. This will either be because you are not contributing enough time to your studies, or you will become less efficient with the time that you do allocate to your studies. Remember, if you are not in control of your studies, they can just become yet another cause of stress for you.
With reference to your task management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual tasks that you have undertaken in your study plan; consider your successes with task-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case; take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; consider your failures with task-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to task planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your task expectations. You need to be consistent with your task management, otherwise you will never know whether you are achieving your program objectives or not.
Keeping in touch
You will have access to qualified and experienced professors and tutors who are responsible for providing tutorial support for your particular training program. So don’t be shy about letting them know how you are getting on. We keep electronic records of all tutorial support emails so that professors and tutors can review previous correspondence before considering an individual response. It also means that there is a record of all communications between you and your professors and tutors and this helps to avoid any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation. If you have a problem relating to the program, share it with them via email. It is likely that they have come across the same problem before and are usually able to make helpful suggestions and steer you in the right direction. To learn more about when and how to use tutorial support, please refer to the Tutorial Support section of this student information guide. This will help you to ensure that you are making the most of tutorial support that is available to you and will ultimately contribute towards your success and enjoyment with your training program.
Work colleagues and family
You should certainly discuss your program study progress with your colleagues, friends and your family. Appleton Greene training programs are very practical. They require you to seek information from other people, to plan, develop and implement processes with other people and to achieve feedback from other people in relation to viability and productivity. You will therefore have plenty of opportunities to test your ideas and enlist the views of others. People tend to be sympathetic towards distance-learners, so don’t bottle it all up in yourself. Get out there and share it! It is also likely that your family and colleagues are going to benefit from your labors with the program, so they are likely to be much more interested in being involved than you might think. Be bold about delegating work to those who might benefit themselves. This is a great way to achieve understanding and commitment from people who you may later rely upon for process implementation. Share your experiences with your friends and family.
Making it relevant
The key to successful learning is to make it relevant to your own individual circumstances. At all times you should be trying to make bridges between the content of the program and your own situation. Whether you achieve this through quiet reflection or through interactive discussion with your colleagues, client partners or your family, remember that it is the most important and rewarding aspect of translating your studies into real self-improvement. You should be clear about how you want the program to benefit you. This involves setting clear study objectives in relation to the content of the course in terms of understanding, concepts, completing research or reviewing activities and relating the content of the modules to your own situation. Your objectives may understandably change as you work through the program, in which case you should enter the revised objectives on your study plan so that you have a permanent reminder of what you are trying to achieve, when and why.
Distance-learning check-list
Prepare your study environment, your study tools and rules.
Undertake detailed self-assessment in terms of your ability as a learner.
Create a format for your study plan.
Consider your study objectives and tasks.
Create a study forecast.
Assess your study performance.
Re-evaluate your study forecast.
Be consistent when managing your study plan.
Use your Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) for tutorial support.
Make sure you keep in touch with those around you.

Tutorial Support
Programs
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. They are implemented over a sustainable period of time and professional support is consistently provided by qualified learning providers and specialist consultants.
Support available
You will have a designated Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and an Accredited Consultant and we encourage you to communicate with them as much as possible. In all cases tutorial support is provided online because we can then keep a record of all communications to ensure that tutorial support remains consistent. You would also be forwarding your work to the tutorial support unit for evaluation and assessment. You will receive individual feedback on all of the work that you undertake on a one-to-one basis, together with specific recommendations for anything that may need to be changed in order to achieve a pass with merit or a pass with distinction and you then have as many opportunities as you may need to re-submit project studies until they meet with the required standard. Consequently the only reason that you should really fail (CLP) is if you do not do the work. It makes no difference to us whether a student takes 12 months or 18 months to complete the program, what matters is that in all cases the same quality standard will have been achieved.
Support Process
Please forward all of your future emails to the designated (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit email address that has been provided and please do not duplicate or copy your emails to other AGC email accounts as this will just cause unnecessary administration. Please note that emails are always answered as quickly as possible but you will need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general tutorial support emails during busy periods, because emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. You will also need to allow a period of up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Please therefore kindly allow for this within your time planning. All communications are managed online via email because it enables tutorial service support managers to review other communications which have been received before responding and it ensures that there is a copy of all communications retained on file for future reference. All communications will be stored within your personal (CLP) study file here at Appleton Greene throughout your designated study period. If you need any assistance or clarification at any time, please do not hesitate to contact us by forwarding an email and remember that we are here to help. If you have any questions, please list and number your questions succinctly and you can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each and every query.
Time Management
It takes approximately 1 Year to complete the Professional Services Advisor corporate training program, incorporating 12 x 6-hour monthly workshops. Each student will also need to contribute approximately 4 hours per week over 1 Year of their personal time. Students can study from home or work at their own pace and are responsible for managing their own study plan. There are no formal examinations and students are evaluated and assessed based upon their project study submissions, together with the quality of their internal analysis and supporting documents. They can contribute more time towards study when they have the time to do so and can contribute less time when they are busy. All students tend to be in full time employment while studying and the Professional Services Advisor program is purposely designed to accommodate this, so there is plenty of flexibility in terms of time management. It makes no difference to us at Appleton Greene, whether individuals take 12-18 months to complete this program. What matters is that in all cases the same standard of quality will have been achieved with the standard and bespoke programs that have been developed.
Distance Learning Guide
The distance learning guide should be your first port of call when starting your training program. It will help you when you are planning how and when to study, how to create the right environment and how to establish the right frame of mind. If you can lay the foundations properly during the planning stage, then it will contribute to your enjoyment and productivity while training later. The guide helps to change your lifestyle in order to accommodate time for study and to cultivate good study habits. It helps you to chart your progress so that you can measure your performance and achieve your goals. It explains the tools that you will need for study and how to make them work. It also explains how to translate academic theory into practical reality. Spend some time now working through your distance learning guide and make sure that you have firm foundations in place so that you can make the most of your distance learning program. There is no requirement for you to attend training workshops or classes at Appleton Greene offices. The entire program is undertaken online, program course manuals and project studies are administered via the Appleton Greene web site and via email, so you are able to study at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office as long as you have a computer and access to the internet.
How To Study
The how to study guide provides students with a clear understanding of the Appleton Greene facilitation via distance learning training methods and enables students to obtain a clear overview of the training program content. It enables students to understand the step-by-step training methods used by Appleton Greene and how course manuals are integrated with project studies. It explains the research and development that is required and the need to provide evidence and references to support your statements. It also enables students to understand precisely what will be required of them in order to achieve a pass with merit and a pass with distinction for individual project studies and provides useful guidance on how to be innovative and creative when developing your Unique Program Proposition (UPP).
Tutorial Support
Tutorial support for the Appleton Greene Professional Services Advisor corporate training program is provided online either through the Appleton Greene Client Support Portal (CSP), or via email. All tutorial support requests are facilitated by a designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). They are responsible for deciding which professor or tutor is the most appropriate option relating to the support required and then the tutorial support request is forwarded onto them. Once the professor or tutor has completed the tutorial support request and answered any questions that have been asked, this communication is then returned to the student via email by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). This enables all tutorial support, between students, professors and tutors, to be facilitated by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM) efficiently and securely through the email account. You will therefore need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general support queries and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because all tutorial support requests are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Consequently you need to put some thought into the management of your tutorial support procedure in order to ensure that your study plan is feasible and to obtain the maximum possible benefit from tutorial support during your period of study. Please retain copies of your tutorial support emails for future reference. Please ensure that ALL of your tutorial support emails are set out using the format as suggested within your guide to tutorial support. Your tutorial support emails need to be referenced clearly to the specific part of the course manual or project study which you are working on at any given time. You also need to list and number any questions that you would like to ask, up to a maximum of five questions within each tutorial support email. Remember the more specific you can be with your questions the more specific your answers will be too and this will help you to avoid any unnecessary misunderstanding, misinterpretation, or duplication. The guide to tutorial support is intended to help you to understand how and when to use support in order to ensure that you get the most out of your training program. Appleton Greene training programs are designed to enable you to do things for yourself. They provide you with a structure or a framework and we use tutorial support to facilitate students while they practically implement what they learn. In other words, we are enabling students to do things for themselves. The benefits of distance learning via facilitation are considerable and are much more sustainable in the long-term than traditional short-term knowledge sharing programs. Consequently you should learn how and when to use tutorial support so that you can maximize the benefits from your learning experience with Appleton Greene. This guide describes the purpose of each training function and how to use them and how to use tutorial support in relation to each aspect of the training program. It also provides useful tips and guidance with regard to best practice.
Tutorial Support Tips
Students are often unsure about how and when to use tutorial support with Appleton Greene. This Tip List will help you to understand more about how to achieve the most from using tutorial support. Refer to it regularly to ensure that you are continuing to use the service properly. Tutorial support is critical to the success of your training experience, but it is important to understand when and how to use it in order to maximize the benefit that you receive. It is no coincidence that those students who succeed are those that learn how to be positive, proactive and productive when using tutorial support.
Be positive and friendly with your tutorial support emails
Remember that if you forward an email to the tutorial support unit, you are dealing with real people. “Do unto others as you would expect others to do unto you”. If you are positive, complimentary and generally friendly in your emails, you will generate a similar response in return. This will be more enjoyable, productive and rewarding for you in the long-term.
Think about the impression that you want to create
Every time that you communicate, you create an impression, which can be either positive or negative, so put some thought into the impression that you want to create. Remember that copies of all tutorial support emails are stored electronically and tutors will always refer to prior correspondence before responding to any current emails. Over a period of time, a general opinion will be arrived at in relation to your character, attitude and ability. Try to manage your own frustrations, mood swings and temperament professionally, without involving the tutorial support team. Demonstrating frustration or a lack of patience is a weakness and will be interpreted as such. The good thing about communicating in writing, is that you will have the time to consider your content carefully, you can review it and proof-read it before sending your email to Appleton Greene and this should help you to communicate more professionally, consistently and to avoid any unnecessary knee-jerk reactions to individual situations as and when they may arise. Please also remember that the CLP Tutorial Support Unit will not just be responsible for evaluating and assessing the quality of your work, they will also be responsible for providing recommendations to other learning providers and to client contacts within the Appleton Greene global client network, so do be in control of your own emotions and try to create a good impression.
Remember that quality is preferred to quantity
Please remember that when you send an email to the tutorial support team, you are not using Twitter or Text Messaging. Try not to forward an email every time that you have a thought. This will not prove to be productive either for you or for the tutorial support team. Take time to prepare your communications properly, as if you were writing a professional letter to a business colleague and make a list of queries that you are likely to have and then incorporate them within one email, say once every month, so that the tutorial support team can understand more about context, application and your methodology for study. Get yourself into a consistent routine with your tutorial support requests and use the tutorial support template provided with ALL of your emails. The (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit will not spoon-feed you with information. They need to be able to evaluate and assess your tutorial support requests carefully and professionally.
Be specific about your questions in order to receive specific answers
Try not to write essays by thinking as you are writing tutorial support emails. The tutorial support unit can be unclear about what in fact you are asking, or what you are looking to achieve. Be specific about asking questions that you want answers to. Number your questions. You will then receive specific answers to each and every question. This is the main purpose of tutorial support via email.
Keep a record of your tutorial support emails
It is important that you keep a record of all tutorial support emails that are forwarded to you. You can then refer to them when necessary and it avoids any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Individual training workshops or telephone support
Please be advised that Appleton Greene does not provide separate or individual tutorial support meetings, workshops, or provide telephone support for individual students. Appleton Greene is an equal opportunities learning and service provider and we are therefore understandably bound to treat all students equally. We cannot therefore broker special financial or study arrangements with individual students regardless of the circumstances. All tutorial support is provided online and this enables Appleton Greene to keep a record of all communications between students, professors and tutors on file for future reference, in accordance with our quality management procedure and your terms and conditions of enrolment. All tutorial support is provided online via email because it enables us to have time to consider support content carefully, it ensures that you receive a considered and detailed response to your queries. You can number questions that you would like to ask, which relate to things that you do not understand or where clarification may be required. You can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each individual query. You will also then have a record of these communications and of all tutorial support, which has been provided to you. This makes tutorial support administration more productive by avoiding any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Tutorial Support Email Format
You should use this tutorial support format if you need to request clarification or assistance while studying with your training program. Please note that ALL of your tutorial support request emails should use the same format. You should therefore set up a standard email template, which you can then use as and when you need to. Emails that are forwarded to Appleton Greene, which do not use the following format, may be rejected and returned to you by the (CLP) Program Administration Manager. A detailed response will then be forwarded to you via email usually within 20 business days of receipt for general support queries and 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Your tutorial support request, together with the corresponding TSU reply, will then be saved and stored within your electronic TSU file at Appleton Greene for future reference.
Subject line of your email
Please insert: Appleton Greene (CLP) Tutorial Support Request: (Your Full Name) (Date), within the subject line of your email.
Main body of your email
Please insert:
1. Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) Tutorial Support Request
2. Your Full Name
3. Date of TS request
4. Preferred email address
5. Backup email address
6. Course manual page name or number (reference)
7. Project study page name or number (reference)
Subject of enquiry
Please insert a maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Briefly outline the subject matter of your inquiry, or what your questions relate to.
Question 1
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 3
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 4
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 5
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Please note that a maximum of 5 questions is permitted with each individual tutorial support request email.
Procedure
* List the questions that you want to ask first, then re-arrange them in order of priority. Make sure that you reference them, where necessary, to the course manuals or project studies.
* Make sure that you are specific about your questions and number them. Try to plan the content within your emails to make sure that it is relevant.
* Make sure that your tutorial support emails are set out correctly, using the Tutorial Support Email Format provided here.
* Save a copy of your email and incorporate the date sent after the subject title. Keep your tutorial support emails within the same file and in date order for easy reference.
* Allow up to 20 business days for a response to general tutorial support emails and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because detailed individual responses will be made in all cases and tutorial support emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received.
* Emails can and do get lost. So if you have not received a reply within the appropriate time, forward another copy or a reminder to the tutorial support unit to be sure that it has been received but do not forward reminders unless the appropriate time has elapsed.
* When you receive a reply, save it immediately featuring the date of receipt after the subject heading for easy reference. In most cases the tutorial support unit replies to your questions individually, so you will have a record of the questions that you asked as well as the answers offered. With project studies however, separate emails are usually forwarded by the tutorial support unit, so do keep a record of your own original emails as well.
* Remember to be positive and friendly in your emails. You are dealing with real people who will respond to the same things that you respond to.
* Try not to repeat questions that have already been asked in previous emails. If this happens the tutorial support unit will probably just refer you to the appropriate answers that have already been provided within previous emails.
* If you lose your tutorial support email records you can write to Appleton Greene to receive a copy of your tutorial support file, but a separate administration charge may be levied for this service.

How To Study
Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can help you to plan a task list for getting started so that you can be clear about your direction and your priorities in relation to your training program. It is also a good way to introduce yourself to the tutorial support team.
Planning your study environment
Your study conditions are of great importance and will have a direct effect on how much you enjoy your training program. Consider how much space you will have, whether it is comfortable and private and whether you are likely to be disturbed. The study tools and facilities at your disposal are also important to the success of your distance-learning experience. Your tutorial support unit can help with useful tips and guidance, regardless of your starting position. It is important to get this right before you start working on your training program.
Planning your program objectives
It is important that you have a clear list of study objectives, in order of priority, before you start working on your training program. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance here to ensure that your study objectives have been afforded due consideration and priority.
Planning how and when to study
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. This approach is designed to let you study efficiently away from the traditional classroom environment. It is important however, that you plan how and when to study, so that you are making the most of your natural attributes, strengths and opportunities. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance and useful tips to ensure that you are playing to your strengths.
Planning your study tasks
You should have a clear understanding of the study tasks that you should be undertaking and the priority associated with each task. These tasks should also be integrated with your program objectives. The distance learning guide and the guide to tutorial support for students should help you here, but if you need any clarification or assistance, please contact your tutorial support unit.
Planning your time
You will need to allocate specific times during your calendar when you intend to study if you are to have a realistic chance of completing your program on time. You are responsible for planning and managing your own study time, so it is important that you are successful with this. Your tutorial support unit can help you with this if your time plan is not working.
Keeping in touch
Consistency is the key here. If you communicate too frequently in short bursts, or too infrequently with no pattern, then your management ability with your studies will be questioned, both by you and by your tutorial support unit. It is obvious when a student is in control and when one is not and this will depend how able you are at sticking with your study plan. Inconsistency invariably leads to in-completion.
Charting your progress
Your tutorial support team can help you to chart your own study progress. Refer to your distance learning guide for further details.
Making it work
To succeed, all that you will need to do is apply yourself to undertaking your training program and interpreting it correctly. Success or failure lies in your hands and your hands alone, so be sure that you have a strategy for making it work. Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can guide you through the process of program planning, development and implementation.
Reading methods
Interpretation is often unique to the individual but it can be improved and even quantified by implementing consistent interpretation methods. Interpretation can be affected by outside interference such as family members, TV, or the Internet, or simply by other thoughts which are demanding priority in our minds. One thing that can improve our productivity is using recognized reading methods. This helps us to focus and to be more structured when reading information for reasons of importance, rather than relaxation.
Speed reading
When reading through course manuals for the first time, subconsciously set your reading speed to be just fast enough that you cannot dwell on individual words or tables. With practice, you should be able to read an A4 sheet of paper in one minute. You will not achieve much in the way of a detailed understanding, but your brain will retain a useful overview. This overview will be important later on and will enable you to keep individual issues in perspective with a more generic picture because speed reading appeals to the memory part of the brain. Do not worry about what you do or do not remember at this stage.
Content reading
Once you have speed read everything, you can then start work in earnest. You now need to read a particular section of your course manual thoroughly, by making detailed notes while you read. This process is called Content Reading and it will help to consolidate your understanding and interpretation of the information that has been provided.
Making structured notes on the course manuals
When you are content reading, you should be making detailed notes, which are both structured and informative. Make these notes in a MS Word document on your computer, because you can then amend and update these as and when you deem it to be necessary. List your notes under three headings: 1. Interpretation – 2. Questions – 3. Tasks. The purpose of the 1st section is to clarify your interpretation by writing it down. The purpose of the 2nd section is to list any questions that the issue raises for you. The purpose of the 3rd section is to list any tasks that you should undertake as a result. Anyone who has graduated with a business-related degree should already be familiar with this process.
Organizing structured notes separately
You should then transfer your notes to a separate study notebook, preferably one that enables easy referencing, such as a MS Word Document, a MS Excel Spreadsheet, a MS Access Database, or a personal organizer on your cell phone. Transferring your notes allows you to have the opportunity of cross-checking and verifying them, which assists considerably with understanding and interpretation. You will also find that the better you are at doing this, the more chance you will have of ensuring that you achieve your study objectives.
Question your understanding
Do challenge your understanding. Explain things to yourself in your own words by writing things down.
Clarifying your understanding
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your understanding.
Question your interpretation
Do challenge your interpretation. Qualify your interpretation by writing it down.
Clarifying your interpretation
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your interpretation.
Qualification Requirements
The student will need to successfully complete the project study and all of the exercises relating to the Professional Services Advisor corporate training program, achieving a pass with merit or distinction in each case, in order to qualify as an Accredited Professional Services AdvisorSpecialist (APSAS). All monthly workshops need to be tried and tested within your company. These project studies can be completed in your own time and at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office. There are no formal examinations, assessment is based upon the successful completion of the project studies. They are called project studies because, unlike case studies, these projects are not theoretical, they incorporate real program processes that need to be properly researched and developed. The project studies assist us in measuring your understanding and interpretation of the training program and enable us to assess qualification merits. All of the project studies are based entirely upon the content within the training program and they enable you to integrate what you have learnt into your corporate training practice.
Professional Services Advisor – Grading Contribution
Project Study – Grading Contribution
Customer Service – 10%
E-business – 05%
Finance – 10%
Globalization – 10%
Human Resources – 10%
Information Technology – 10%
Legal – 05%
Management – 10%
Marketing – 10%
Production – 10%
Education – 05%
Logistics – 05%
TOTAL GRADING – 100%
Qualification grades
A mark of 90% = Pass with Distinction.
A mark of 75% = Pass with Merit.
A mark of less than 75% = Fail.
If you fail to achieve a mark of 75% with a project study, you will receive detailed feedback from the Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and/or Accredited Consultant, together with a list of tasks which you will need to complete, in order to ensure that your project study meets with the minimum quality standard that is required by Appleton Greene. You can then re-submit your project study for further evaluation and assessment. Indeed you can re-submit as many drafts of your project studies as you need to, until such a time as they eventually meet with the required standard by Appleton Greene, so you need not worry about this, it is all part of the learning process.
When marking project studies, Appleton Greene is looking for sufficient evidence of the following:
Pass with merit
A satisfactory level of program understanding
A satisfactory level of program interpretation
A satisfactory level of project study content presentation
A satisfactory level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
A satisfactory level of the practical integration of academic theory
Pass with distinction
An exceptional level of program understanding
An exceptional level of program interpretation
An exceptional level of project study content presentation
An exceptional level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
An exceptional level of the practical integration of academic theory
Preliminary Analysis
Here are some helpful readings which provide participants and other stakeholders with further detail and context in relation to trust in the professional services context. Two readings are provided for each of the course manuals (1 through 12) and presented in course manual order.
Books
01 Understanding Trust in Professional Services
“The Trusted Advisor” by David H. Maister, Charles H. Green, and Robert M. Galford
• This book explores the essential elements of building trust with clients in professional services. It offers practical advice and real-world examples to help professionals establish, maintain, and enhance trust in their client relationships.
“Trust-Based Selling: Using Customer Focus and Collaboration to Build Long-Term Relationships” by Charles H. Green
• This book delves into the principles of trust-based selling, emphasizing the importance of prioritizing clients’ needs and fostering genuine, collaborative relationships. It provides insights and strategies for professionals to build trust and achieve long-term success in their client interactions.

02 Building Rapport and Credibility
“How to Win Friends and Influence People” by Dale Carnegie
• This classic book offers timeless principles for building rapport and credibility in personal and professional relationships. Carnegie’s advice on effective communication, understanding others, and making people feel valued helps readers establish strong connections and gain trust.
“The Speed of Trust: The One Thing That Changes Everything” by Stephen M.R. Covey
• This book focuses on the critical role of trust in successful relationships and organizations. Covey outlines actionable steps for building trust quickly and maintaining credibility, emphasizing transparency, integrity, and consistent behaviour to foster strong, trustworthy connections.

03 Communication Skills
“Crucial Conversations: Tools for Talking When Stakes Are High” by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler
• This book offers practical tools and techniques for handling difficult and high-stakes conversations effectively. It emphasizes the importance of staying calm, being honest, and maintaining respect to achieve positive outcomes in challenging communication situations.
“Nonviolent Communication: A Language of Life” by Marshall B. Rosenberg
• This book introduces the concept of nonviolent communication, which focuses on empathetic listening and expressing oneself honestly without criticism or blame. Rosenberg’s approach helps readers improve their communication skills by fostering understanding and compassion in their interactions.

04 Ethics and Integrity
“The Integrity Dividend: Leading by the Power of Your Word” by Tony Simons
• This book discusses the critical role of integrity in leadership and business success. Tony Simons explores how leaders can build trust, foster loyalty, and drive performance by consistently keeping their promises and maintaining ethical standards.
“Business Ethics: A Stakeholder and Issues Management Approach” by Joseph W. Weiss
• This book provides a comprehensive overview of business ethics, focusing on stakeholder management and ethical decision-making in business contexts. Joseph W. Weiss combines theoretical frameworks with practical applications, offering insights into how businesses can navigate ethical challenges and maintain integrity in their operations.

05 Confidentiality and Data Protection
“Data and Goliath: The Hidden Battles to Collect Your Data and Control Your World” by Bruce Schneier
• Bruce Schneier, a renowned security technologist, explores the extensive reach of data collection and the implications for privacy and confidentiality. This book provides insights into the methods used to collect data, the entities involved, and strategies for protecting data privacy.
“The Data Privacy Law: A Practical Guide to Managing Privacy and Information Security Compliance” by Daniel J. Solove and Paul M. Schwartz
• This comprehensive guide offers practical advice on navigating data privacy laws and implementing effective information security measures. Daniel J. Solove and Paul M. Schwartz provide actionable strategies for businesses to ensure compliance and protect sensitive data.

06 Managing Expectations
“Managing the Professional Service Firm” by David H. Maister
• This book offers insights into managing expectations and delivering exceptional service in professional firms such as consulting, legal, and accounting. It covers topics like client relationships, leadership, and strategic management.
“Professional Services Marketing: How the Best Firms Build Premier Brands, Thriving Lead Generation Engines, and Cultures of Business Development Success” by Mike Schultz and John E. Doerr
• This book focuses on marketing strategies specifically tailored for professional service firms. It covers topics such as branding, lead generation, and cultivating a business development culture, essential for success in competitive markets.

07 Conflict Resolution
“Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In” by Roger Fisher, William Ury, and Bruce Patton
• This classic book on negotiation offers practical strategies for resolving conflicts and reaching mutually beneficial agreements in business and personal situations.
“Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most” by Douglas Stone, Bruce Patton, and Sheila Heen
• This book offers a framework for navigating tough conversations effectively, providing strategies for managing emotions, understanding different perspectives, and achieving constructive outcomes.

08 Risk Management
“Risk Management in Professional Services: Insights from Management Consulting, Legal, and Accounting Firms” by Edward J. Barocas
• This book provides insights into risk management specific to professional services, covering strategies, case studies, and best practices tailored to consulting, legal, and accounting firms.
“The Professional Services Firm Bible: A Guide to Building a Financially Healthy Firm” by John Baschab and Jon Piot
• This book covers various aspects of running a professional services firm, including risk management strategies tailored to financial health and sustainability in consulting, legal, and other professional services contexts.

09 Quality Assurance
“Professional Services Firms: How to Achieve Profitable Growth” by Jean Stephens
• This book covers strategies for quality assurance in professional services firms, focusing on achieving growth through maintaining high-quality service delivery and client satisfaction.
“Managing the Professional Service Firm” by David H. Maister
• While primarily covering management of professional service firms, this book also delves into quality assurance practices essential for sustaining client trust and business success.

10 Client Empowerment
“Clients for Life: How Great Professionals Develop Breakthrough Relationships” by Jagdish Sheth and Andrew Sobel
• This book emphasizes building long-term client relationships by understanding their needs deeply and providing exceptional service, crucial for sustained success in professional services.
“Extreme Trust: Honesty as a Competitive Advantage” by Don Peppers and Martha Rogers
• This book explores how businesses can empower clients by fostering extreme trust through transparency and honesty, which can be crucial in professional services.

11 Transparency in Processes
“The Transparency Sale: How Unexpected Honesty and Understanding the Buying Brain Can Transform Your Results” by Todd Caponi
• This book explores how transparency in sales processes can build trust and improve outcomes, applicable across various professional services.
“Transparency: How Leaders Create a Culture of Candor” by Warren Bennis, Daniel Goleman, and James O’Toole
• This book explores how leaders can create a culture of transparency within organizations, emphasizing its impact on organizational effectiveness and trust in professional services.

12 Feedback and Continuous Improvement
“The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses” by Eric Ries
• While not solely focused on feedback, this book emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement through iterative feedback loops and learning from customer responses.
“Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us” by Daniel H. Pink
• This book explores motivation and how feedback plays a crucial role in enhancing performance and fostering continuous improvement in business contexts.
Course Manuals 1-12
Course Manual 1: Understanding Trust in Professional Services
Trust is a fundamental element in professional relationships or services where the work involves the provision of expert advice. In the professional services sector, where lawyers, accountants, and consultants often handle sensitive information and critical tasks, trust defines the relationship’s quality and longevity. Accenture’s research supports this, showing that employees at high-trust companies experience significantly less stress and are more productive.

Moreover, PwC’s 2024 Trust Survey reveals that 93% of business executives believe that building and maintaining trust directly improves their bottom line, yet there is a noticeable gap between perceived and actual trust. While 90% of executives think their clients have high trust in their companies, only 30% of consumers feel the same.
Dr. Rachel Botsman, a renowned academic and author specialising in trust and technology, offers valuable insights into trust in business relationships. She suggests that trust in the business context is not merely about personal relationships or gut feelings but is increasingly becoming digitised and based on data-driven assessments. In her research, she emphasises the importance of understanding how technology and digital platforms also reshape trust dynamics between businesses.

According to Botsman, business trust involves several dimensions:
1. Competence: Businesses trust each other when they believe the other party has the capability and expertise to deliver on their promises. This can be assessed through factors such as past performance, certifications, and industry reputation.
2. Reliability: Trust in business relationships depends on the consistency and predictability of interactions. Reliable partners consistently meet deadlines, fulfill orders, and maintain communication.
3. Integrity: Integrity refers to the alignment between a business’s actions and its stated values or ethical standards. Businesses trust partners who demonstrate honesty, transparency, and ethical behaviour.
4. Security: In an increasingly digital landscape, security is a critical aspect of trust in BUSINESS relationships. Businesses must ensure the protection of sensitive data, intellectual property, and financial transactions.
5. Mutual Benefit: Trust is strengthened when both parties perceive that the relationship brings mutual benefits and creates value for each other. This could include cost savings, innovation opportunities, or access to new markets.
Botsman’s insights highlight the evolving nature of trust in business interactions, where traditional notions of personal rapport are complemented by digital platforms, data analytics, and cybersecurity measures. Understanding these dimensions of trust is essential for businesses to navigate complex supply chains, partnerships, and collaborative ventures in the modern marketplace.
The Critical Role of Trust in Professional Relationships
Trust is a cornerstone in professional relationships, essential for fostering enduring partnerships. Trust in professional services transcends mere transactional interactions, encompassing dependability, competence, and integrity. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of trust and its pivotal role in professional contexts.
Defining Trust in the Context of Professional Services
The Essence of Trust
Trust in professional services goes beyond the expectation of job completion. Professionals in these roles can become custodians of clients’ business secrets, personal ambitions, and business success. Each piece of advice given, and every decision made carries a responsibility that extends beyond a simple client-service provider dynamic. Trust here is about believing that the hired experts will act in the client’s best interests, handling their aspirations and anxieties with the utmost care.
Trust as a Foundation for Collaboration
This deep level of professional trust transforms agreements into powerful collaborations. It does not arise from credentials alone but from a profound sense of true partnership. This partnership resolves complexities with clarity and purpose, underpinned by a genuine commitment to clients’ objectives.
Components of Trust in Services
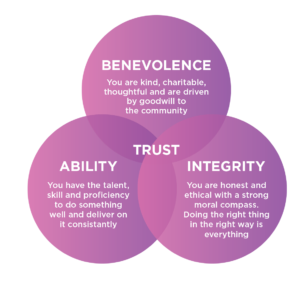
Transparency
Transparency involves making complex actions, decisions, and their underlying reasons understandable. Effective communication ensures clients are informed about the progress of their work and any challenges that arise. A recent survey found that 78% of clients consider clear communication crucial for trusting a service provider. Transparency ensures clients are fully engaged and informed every step of the way.
For example, consider a legal firm handling sensitive cases for its clients. Regular updates, transparent billing practices, and clear explanations of legal strategies and potential outcomes build client trust. This transparency helps clients feel in control and reassured that their case is being handled with utmost professionalism.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is vital for establishing trust, as it assures clients that their sensitive information is safe and managed with care. Data security is a top concern for clients, with 88% stating that how their data is handled directly influences their trust in a service provider. Professionals must employ robust security measures to protect sensitive data, reinforcing clients’ confidence in their discretion.
For instance, in the financial services sector, managing clients’ investment portfolios requires handling confidential financial information. Financial advisors who maintain strict confidentiality protocols earn clients’ trust, as they ensure their financial data is secure and used solely for their benefit.
Ethical Behaviour
Ethical behaviour represents the moral compass of professional services. It involves acting with fairness, respecting others’ rights, and adhering strictly to professional codes of conduct. Research shows that ethical behaviour and integrity are top traits clients seek in a service provider. Ethical standards reassure clients that their welfare is prioritised.
In the medical profession, doctors and healthcare providers are expected to adhere to strict ethical guidelines. Patients trust their healthcare providers to make decisions in their best interests, maintain confidentiality, and provide accurate information. Ethical behaviour in this context is crucial for patient trust and effective healthcare delivery.
Trust as a Strategic Asset
Client Retention
Trust enhances client retention, which is more cost-effective than acquiring new clients. Studies indicate that a mere 5% increase in client retention can boost company revenue by 25-95%. Retained clients tend to buy more over time and are less likely to switch to competitors, even in highly competitive markets.
For example, a marketing agency that consistently delivers results and maintains transparent communication with clients is likely to retain those clients for extended periods. The clients feel valued and confident in the agency’s ability to manage their marketing needs, reducing the likelihood of them seeking services elsewhere.
Reputation Building
A trustworthy reputation attracts new clients and can often be the deciding factor in prospective clients’ decisions. Companies like Heineken and Sweet Fish Media have leveraged trust to transform client interactions into relationships, leading to measurable growth and reduced client churn. Embedding trust within operational and strategic frameworks ensures long-term success.
Consider a consultancy firm known for its integrity and reliability. Such a firm attracts new clients through positive word-of-mouth and a formidable reputation. Prospective clients are more likely to engage with a consultancy firm that has a track record of trustworthiness and ethical behaviour.
Importance of Trust for Clients and Service Providers

For Clients
Confidence in Decision-Making
Clients make better choices when they trust a business. Trust is a determinant of loyalty and commitment. Providers gain trust through honesty, dependability, and quality of services rendered. This trust fosters certainty and security in client dealings.
For instance, an architectural firm trusted by its clients for its innovative designs and adherence to project timelines allows clients to make confident decisions about their building projects. The clients trust that the firm will deliver high-quality results, enabling them to invest in ambitious projects without hesitation.
Impact on Long-term Relationships
Trust is crucial for business. Clients appreciate honesty and openness, leading to repeat business. Trust also enhances teamwork and innovation, forming lasting relationships and aiding career growth.
In the context of educational services, a tutoring centre that builds trust with students and parents through consistent performance and ethical practices will see long-term relationships develop. Parents will continue to enrol their children, and students will return for further assistance, knowing they can rely on the centre’s expertise and integrity.
For Service Providers
Business Growth and Sustainability
Trust is vital for ongoing business success. Clients who trust a company stick around and spread the word, bringing in more business and attracting new clients. This cycle sustains steady company growth.
For example, a software development company that consistently delivers secure, reliable products and maintains transparent communication with clients will experience sustainable growth. Satisfied clients will recommend the company to others, leading to an expanding client base.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Established trust enhances collaboration and communication. Open, honest conversations lead to tailor-made solutions. Trust allows clients to speak freely, fostering creative brainstorming and effective strategies. Clear communication avoids misunderstandings, and feedback helps fine-tune services.
Consider a partnership between a marketing agency and a client. When trust is established, both parties can openly share ideas and feedback, leading to innovative marketing strategies that effectively address the client’s needs. This collaboration results in successful campaigns and a strong, ongoing partnership.

Heineken: Building Trust Through Long-Term Relationships
Heineken has emphasised long-term relationships as a cornerstone of its business strategy. By fostering trust with suppliers, distributors, and consumers, Heineken has created a robust network of partnerships. Their commitment to transparency, ethical practices, and consistent quality has cemented their reputation as a trustworthy brand.

Sweet Fish Media: Reducing Client Churn Through Engagement
Sweet Fish Media reduced its churn rate by actively engaging with clients and continuously adapting to their needs. By prioritising open communication and transparency, the company has built lasting relationships with clients, leading to steady growth and reduced client turnover.
Different Dimensions of Trust
Reliability
Reliability hinges on consistent, dependable actions. Trust grows when promises are kept, deadlines met, and quality maintained. This foundation fosters enduring relationships.
In the construction industry, a contractor who consistently meets project deadlines and maintains high-quality standards builds trust with clients. Reliability in completing projects on time and within budget ensures clients return for future construction needs.
Competence
Professionals’ expertise assures clients of effective solutions. Continuous learning maintains competence, essential for delivering reliable services. Evolving skills and dedication ensure client satisfaction and trust.
In the technology sector, a cybersecurity firm must stay updated with the latest threats and solutions. Clients trust the firm to protect their digital assets because of its demonstrated competence and commitment to ongoing education and improvement.
Integrity
Integrity involves following ethical principles and being honest in all endeavours. Success achieved through fair means sets a strong example, reinforcing trust.
For instance, a public relations agency that handles crises with honesty and transparency earns the trust of its clients. By prioritising ethical practices and maintaining integrity, the agency sets a positive example and secures long-term client relationships.
Building and Maintaining Trust

Key Professional Behaviours
1. Active Listening and Transparent Communication: Engage clients through active listening and clear, honest communication. This approach ensures clients feel heard and understood, fostering trust.
2. Consistent Delivery on Promises: Build trust by reliably fulfilling commitments. Consistency in meeting deadlines and delivering high-quality results strengthens client relationships.
3. Feedback Utilisation: Seek and use feedback for continuous improvement. By valuing client input and making necessary adjustments, professionals demonstrate their commitment to excellence.
4. Integrity, Empathy, and Reliability: Uphold these values consistently. Clients appreciate professionals who show genuine concern for their needs and act with honesty and dependability.
5. Prompt Issue Resolution: Address concerns swiftly and admit mistakes. Taking responsibility and resolving issues promptly maintains trust and shows clients that their satisfaction is a priority.
6. Ethical Practices: Maintain high ethical standards in all dealings. Adhering to professional codes of conduct and acting with fairness builds a solid foundation of trust.
7. Genuine Connections: Build authentic relationships through consistent actions. Developing a personal connection with clients fosters long-term partnerships based on mutual trust and respect.
Common Trust-Building Challenges
1. Transparency and Communication: Ensuring open and honest interactions. Overcoming the challenge of maintaining transparency, especially in complex situations, is crucial for trust-building.
2. Consistency and Reliability: Maintaining dependable service delivery. Consistency in performance can be challenging but is essential for establishing and maintaining trust.
3. Demonstrating Competence and Expertise: Continuously proving professional capabilities. Staying updated with industry trends and best practices ensures ongoing competence.
Actions Recommended
1. Foster Open Communication: Actively listen to concerns, address them transparently, and consistently deliver on promises. This approach builds trust gradually and effectively.
2. Establish Clear Intentions: Ensure mutual understanding to avoid misunderstandings. Clear intentions and transparent communication from the outset save time and foster trust.
3. Prioritise Integrity and Accountability: Admit mistakes and take proactive steps to rectify them. Transparency in acknowledging errors and working to resolve them preserves trustworthiness.
For instance, consider a scenario where a financial advisor makes an error in an investment strategy. By promptly informing the client, explaining the mistake, and presenting a revised plan to mitigate losses, the advisor maintains the client’s trust despite the error.
Conclusion
Professionals can cultivate trust through transparent, ethical practices and expertise. Trust, encompassing reliability, competence, and integrity, fosters client confidence, enhances collaboration, and drives long-term success. Despite challenges, trust-building techniques and a commitment to continuous development are key. Professionals should reflect on their trust-building practices, recognising that trust is earned and nurtured for enduring client partnerships and business success.
Trust is not just a benefit but a necessity in professional services. It transforms ordinary interactions into strong, lasting partnerships, ensuring clients feel secure, valued, and confident in their choices. By embedding trust within operational and strategic frameworks, organisations can foster long-term relationships and drive sustainable business growth. Trust enhances client retention, reputation, and collaboration, leading to business success. Professionals must prioritise trust-building behaviours, address challenges proactively, and maintain high ethical standards to cultivate and sustain trust in professional relationships.
In summary, trust is the bedrock of professional relationships. It is essential for client confidence, long-term partnerships, and business sustainability. Through transparency, confidentiality, and ethical behaviour, professionals can build and maintain trust, ensuring their clients feel secure and valued. By recognising the importance of trust and implementing trust-building practices, professionals can foster enduring relationships that drive success and growth in their respective fields.

Case Study: Building Trust in Legal Services
Background: A law firm specialising in corporate law and intellectual property (IP) services sought to differentiate itself in a highly competitive market. Recognising that trust is paramount in legal services, the firm embarked on a strategic initiative to enhance trust among its clients.
Objectives:
1. Build and maintain trust with existing clients.
2. Attract new clients by establishing the firm as a trusted advisor.
3. Strengthen the firm’s reputation for reliability, integrity, and expertise.
Approach:
1. Client-Centric Communication: The firm implemented a client-centric communication strategy, focusing on transparency and responsiveness. This included regular updates on case progress, clear explanations of legal processes, and prompt responses to client inquiries.
2. Expertise Showcase: The firm emphasised its attorneys’ expertise through thought leadership initiatives, such as publishing articles, hosting webinars, and speaking at industry events. By demonstrating a deep understanding of complex legal issues, the firm aimed to instil confidence in its capabilities.
3. Personalised Service: Recognising that every client has unique needs, the firm prioritised personalised service. Attorneys took the time to understand each client’s goals, concerns, and preferences, tailoring their approach accordingly. This personalised attention helped foster strong client relationships built on mutual respect and understanding.
4. Ethical Standards: Upholding the highest ethical standards was non-negotiable for the firm. It ensured full compliance with legal regulations and codes of conduct, maintaining integrity and trustworthiness in all interactions with clients.
Results:
1. Increased Client Satisfaction: Client feedback indicated higher satisfaction levels with the firm’s services, particularly regarding communication, expertise, and personalised attention.
2. Enhanced Reputation: The firm’s reputation as a trusted advisor grew within its target market, leading to an increase in referrals and new client inquiries.
3. Client Retention: By prioritising trust-building efforts, the firm strengthened its relationships with existing clients, leading to improved client retention rates.
4. Competitive Advantage: In a crowded marketplace, the firm’s reputation for trustworthiness and reliability set it apart from competitors, contributing to its long-term success and sustainability.
Lessons Learned:
1. Trust is Fundamental: In professional services, trust forms the foundation of successful client relationships. Investing in trust-building efforts is essential for long-term growth and client satisfaction.
2. Communication is Key: Open and transparent communication fosters trust and strengthens client relationships. Regular updates, clear explanations, and responsiveness are critical components of effective communication.
3. Expertise Matters: Demonstrating expertise and thought leadership positions a firm as a trusted authority in its field. Clients value working with knowledgeable professionals who can navigate complex legal issues with confidence.
4. Personalisation Drives Engagement: Tailoring services to meet individual client needs fosters deeper connections and enhances client loyalty. Understanding clients’ goals, preferences, and concerns enables firms to deliver personalised experiences that build trust and satisfaction.
By prioritising trust-building initiatives, the law firm successfully differentiated itself in the competitive legal services market, solidifying its reputation as a trusted advisor and partner to its clients.

Exercise: Role-Playing Trust in Professional Services
• Participants (ideally in pairs): One acts as the service provider (e.g., lawyer, financial advisor, consultant), and the other as the client.
• Scenario cards: Pre-written scenarios that simulate common client-provider interactions in professional services.
1. Introduction:
o Explain the purpose of the exercise: to explore the dynamics of trust in professional relationships and highlight behaviours that foster trust.
o Divide participants into pairs, with one person assuming the role of the service provider and the other as the client.
o Distribute scenario cards to each pair.
2. Role-Playing:
o Each pair selects a scenario card and reads it together.
o The service provider and client then role-play the scenario, focusing on building trust through their interactions.
o Encourage participants to embody behaviours that enhance trust, such as active listening, empathy, transparency, and professionalism.
o Emphasise the importance of communication, expertise, and ethical conduct in building trust.
3. Debrief:
o Facilitate a discussion with the whole group to reflect on the role-playing experience.
o Ask participants to share their observations, including what behaviours they found most effective in building trust.
o Discuss the impact of trust on client-provider relationships and the consequences of trust breaches.
o Encourage participants to identify strategies for building and maintaining trust in their professional practice.
4. Key Takeaways:
o Summarise the key learnings from the exercise, emphasising the critical role of trust in professional services.
o Reinforce the importance of trust-building behaviours, such as communication, competence, integrity, and reliability.
o Encourage participants to apply these principles in their interactions with clients to strengthen trust and enhance client satisfaction.
• Service Provider (Attorney): Demonstrates expertise, patience, and clarity in explaining legal concepts.
• Client: Expresses concerns, asks questions, and relies on the attorney’s guidance.

Course Manual 2: Building Rapport and Credibility
Introduction
Building rapport and credibility are essential for developing and maintaining successful client relationships. Rapport involves interpersonal connections and the “chemistry” and confidence between parties. It ensures that both parties feel secure, comfortable, and understood. Credibility, in turn, is a matter of expertise and experience known to the client. Together, they create a foundation upon which a relationship may develop over time. For building rapport and credibility to be successful, communication, listening skills, and empathy are crucial for the quality of exchanges.
Conversely, credibility involves demonstrating expertise, integrity, and reliability in delivering solutions or services. Clients seek partners they can trust to fulfil their needs competently and ethically. This trust is built through consistent performance, transparency, and a history of delivering results. Credibility instils confidence in clients, reinforcing their decision to engage with a particular provider or professional.
Dr. David Maister, a highly respected academic in the field of professional services and business relationships, emphasises the importance of building rapport and credibility. He argues that credibility is the foundation of trust in business relationships. According to Maister, credibility is established through a combination of expertise, reliability, and empathy. Businesses must demonstrate deep knowledge and competence in their field, consistently deliver on promises, and show genuine concern for their clients’ needs and challenges. Building rapport, Maister suggests, involves more than just professional competence; it requires creating a sense of connection and understanding with clients. This can be achieved through active listening, empathy, and personalised attention. In the business context, where transactions often involve significant investments and long-term partnerships, establishing rapport and credibility is crucial for fostering trust and sustaining successful business relationships.
Rapport and credibility form the bedrock of successful client relationships, fostering collaboration, loyalty, and positive outcomes for all parties involved.
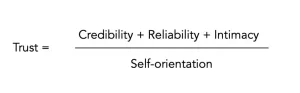
Understanding Rapport
Rapport is the foundation of successful professional interactions, referring to individuals’ connection, understanding, and trust. It is crucial because it fosters open communication, promotes collaboration, and enhances productivity in various settings, such as business negotiations, client meetings, or team collaborations.
The Role of First Impressions
First impressions are pivotal in establishing rapport as they set the tone for future interactions. Body language, tone of voice, and initial conversations contribute significantly to forming positive or negative impressions. Being attentive, maintaining eye contact, and displaying genuine interest in the other person’s thoughts and ideas help create a favourable first impression.
Techniques for Effective Listening and Empathy
Effective listening and empathy are key techniques for building and sustaining rapport. Active listening involves focusing on the speaker, asking clarifying questions, and paraphrasing to ensure understanding. Empathy, on the other hand, involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others, which can be conveyed through acknowledgement, validation, and supportive responses.
To enhance rapport through listening and empathy, practitioners can practice reflective listening, summarising, and reflecting on the speaker’s words to demonstrate understanding and encourage further sharing. Additionally, being mindful of nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, can help tune into the other person’s emotional state, allowing for a more empathetic response.
Building Strong Connections
Rapport is fundamental to professional interactions, facilitated by positive first impressions, effective listening, and empathetic communication. By mastering these techniques, individuals can build strong connections, foster trust, and achieve successful outcomes in their professional endeavours.
Techniques for Building Credibility

Building credibility is crucial in establishing and maintaining strong professional relationships. Credibility refers to the trustworthiness and believability that others attribute to you based on your actions, words, and expertise. It impacts how others perceive your reliability, competence, and integrity in your field.
Consistency and Reliability
Consistency and reliability are fundamental pillars of credibility. Consistently meeting deadlines, delivering on promises, and being dependable in your actions build trust over time. When clients and colleagues can rely on you to follow through consistently, it enhances your credibility and strengthens relationships.
For example, if a consultant consistently meets project deadlines and delivers high-quality work, clients are more likely to trust their capabilities and continue to engage their services.
Highlighting Expertise
Highlighting expertise is another key aspect. Demonstrating your knowledge and skills is essential to ensure clients are satisfied. Tailor your communication to your audience’s level of understanding, using language to which they can relate. Share relevant examples, case studies, or success stories to illustrate your capabilities effectively.
For instance, an IT specialist can highlight their expertise by sharing detailed case studies of past successful projects, demonstrating their ability to solve complex technical issues and deliver value to clients.
Authenticity and Professionalism
Authenticity is vital in building credibility. Be genuine in your interactions, expressing your thoughts and opinions honestly. Avoid exaggerating or misrepresenting facts, as this can quickly erode trust. Admitting mistakes when they occur and taking responsibility demonstrates authenticity and reinforces credibility.
Maintaining professionalism in all aspects of your work, such as punctuality, respect, and ethics, also contributes to building and sustaining credibility. Building credibility is an ongoing process that requires consistency, expertise, authenticity, and professionalism to cultivate strong and lasting professional relationships.
Establishing a Track Record of Success
Establishing a track record of success involves consistently delivering high-quality results over time. This track record serves as proof of your capabilities and reliability. By showcasing a history of successful projects and satisfied clients, you can enhance your credibility and attract new business opportunities.
Engaging in Continuous Learning and Improvement
Continuous learning and improvement are essential for maintaining credibility in a rapidly changing professional landscape. Staying updated with industry trends, acquiring new skills, and adapting to emerging technologies demonstrate your commitment to excellence and professional growth. Clients are more likely to trust professionals who are proactive in enhancing their knowledge and skills.
Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication is essential for building trust in any relationship, especially in professional settings. Clear and open communication fosters transparency, which is crucial for establishing trust between individuals or organisations. Conveying clearly and honestly reduces misunderstandings and allows for better collaboration and decision-making.
Adapting Communication Styles
Adapting communication styles to meet client needs and expectations is also key. Clients have diverse backgrounds, preferences, and communication styles. Understanding these differences and tailoring your communication approach shows respect and enhances the client’s experience. For example, some clients prefer concise emails, while others appreciate more detailed explanations or face-to-face meetings. Flexibility in communication style demonstrates your willingness to accommodate their preferences, leading to stronger relationships and improved outcomes.
The Role of Feedback
Feedback plays a vital role in effective communication. Providing constructive feedback helps individuals and teams identify areas for improvement and encourages growth. Delivering feedback respectfully and constructively is important, as well as focusing on specific behaviours or actions rather than personal attributes. Similarly, being open to receiving feedback demonstrates humility and a commitment to continuous learning and improvement.
For example, in a project management setting, providing timely and constructive feedback to team members can help improve their performance and contribute to the successful completion of projects.
Building a Culture of Open Communication
Effective communication strategies involve clarity, adaptability, and a willingness to give and receive feedback. By prioritising these aspects, individuals and organisations can build trust, enhance client relationships, and foster a culture of open communication and collaboration.
Active Listening and Empathy
Active listening and empathy are crucial components of effective communication. Active listening involves fully focusing on the speaker, understanding their message, and responding thoughtfully. Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others. Together, these skills help build trust and foster meaningful connections.
The Importance of Clarity and Transparency
Clarity and transparency are essential for effective communication. Being clear and transparent in your communications helps prevent misunderstandings and builds trust. This involves clearly articulating your ideas, expectations, and any potential issues that may arise. Transparency also involves being honest about your limitations and the realistic outcomes of your services.
Developing Long-Term Client Relationships
Building long-term client relationships involves more than just one-off transactions; it is about fostering trust, understanding needs, and consistently delivering value. Follow-up and ongoing engagement are crucial in this process.
The Importance of Follow-Up
Follow-up is essential after the initial transaction to ensure client satisfaction, address concerns, and gather feedback. This demonstrates care and commitment to their success, laying the foundation for a lasting connection. Ongoing engagement involves staying in touch regularly, sharing relevant updates or insights, and proactively offering solutions or support.

Case Study: Mindsight
Technology is pivotal in every business’s success, but navigating the details is key. Mindsight, a tech solutions provider, has been instrumental in a long-term partnership with a food processing company, enhancing its IT environment over a decade.
The client initially sought Mindsight’s expertise in upgrading their firewall to a Cisco ASA. Impressed by Mindsight’s efficiency, they expanded the collaboration to upgrade switches and access points across five sites.
As the relationship deepened, Mindsight assisted with larger projects like migrating to a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), refreshing storage and servers, and providing ongoing technical support.
Recognising the value, the client transitioned to a managed services agreement with Mindsight in 2014. Over time, the scope of services expanded to include full network monitoring, VDI management, and more, reflecting a growing reliance on Mindsight as a trusted IT partner.
Overcoming Challenges in Client Relationships

Building strong client relationships involves overcoming challenges that can hinder rapport and credibility. One common barrier is miscommunication or misunderstandings, which can arise due to differences in communication styles or cultural nuances. To address this, it is crucial to actively listen, clarify expectations, and adapt communication methods to suit the client’s preferences.
Managing Expectations
Another challenge is managing expectations effectively. Clients may have unrealistic expectations or need a clearer understanding of what can be achieved. Open and honest communication about project timelines, deliverables, and potential limitations can help set realistic expectations and build trust.
Dealing with Setbacks
In any professional relationship, setbacks are inevitable. Whether it is a missed deadline, unexpected issues, or other challenges, how you handle these setbacks can significantly impact your credibility and client relationships. It is crucial to take responsibility, communicate transparently, and offer proactive solutions when these situations arise. This approach demonstrates accountability and a commitment to resolving issues promptly.
Taking Responsibility
Taking responsibility for setbacks is the first step in addressing them effectively. Acknowledging your role in the issue shows that you are willing to confront challenges head-on and learn from them. This attitude fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within your team and organisation. It also reassures clients that you are committed to addressing the problem and preventing similar issues in the future.
Communicating Transparently
Transparent communication is essential when dealing with setbacks. This involves sharing information openly and honestly with the client. Explain the root cause of the issue, outline the steps being taken to address it, and provide updates on progress. This transparency fosters trust, reduces uncertainty, and shows a commitment to resolving the issue effectively.
For instance, if a project deadline is missed, inform the client immediately. Explain why the delay occurred, what you are doing to get back on track, and when they can expect the project to be completed. Providing this information helps manage the client’s expectations and shows that you are taking the issue seriously.
Offering Proactive Solutions
Beyond taking responsibility and communicating transparently, it is vital to offer proactive solutions to resolve the setback. This might involve reallocating resources, adjusting project timelines, or implementing new processes to prevent future issues. By presenting a clear plan of action, you demonstrate your commitment to rectifying the problem and improving future performance.
Rebuilding Trust After Setbacks
Rebuilding trust after a setback requires a strategic and thoughtful approach. The following strategies can help restore credibility and strengthen client relationships:
1. Acknowledging the Issue
Acknowledging the issue demonstrates humility and a commitment to honesty. It builds trust by showing that you are willing to confront challenges directly and learn from them. This approach fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within your team and organisation.
2. Sincere Apologies
Sincere apologies go beyond mere words; they convey genuine remorse and understanding of the impact of your actions. They validate the client’s feelings, humanise your interactions, and pave the way for rebuilding trust and repairing any damage caused by the mistake. An effective apology includes acknowledging the mistake, expressing regret, and outlining steps to prevent recurrence.
3. Transparent Communication
Transparent communication involves sharing information openly and honestly with the client. This includes explaining the root cause of the issue, outlining the steps being taken to address it, and providing updates on progress. Transparency fosters trust, reduces uncertainty, and shows a commitment to resolving the issue effectively.
4. Delivering on Promises
Delivering on promises is essential for building credibility and maintaining trust. It means consistently meeting or exceeding expectations, honouring commitments made to the client, and taking proactive steps to ensure future promises are realistic and achievable. Reliability and consistency in delivery build a solid foundation for long-term relationships.
5. Seeking Feedback
Seeking feedback actively demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and client satisfaction. It involves creating opportunities for open dialogue, actively listening to the client’s concerns and suggestions, and using feedback to make meaningful changes that enhance the client experience and strengthen the relationship. Regularly soliciting and acting on feedback shows clients that you value their input and are dedicated to meeting their needs.
6. Going the Extra Mile
Going the extra mile shows dedication and a willingness to exceed expectations. It involves offering personalised solutions, anticipating client needs, providing additional value through added services or resources, and demonstrating a genuine interest in the client’s success. This extra effort fosters loyalty, advocacy, and long-term partnerships.
For example, if a software update caused issues for a client, going the extra mile might involve providing additional support, offering training sessions, or implementing custom features that address their specific needs.
By actively addressing barriers to rapport and credibility and implementing strategies for rebuilding trust after setbacks, you can strengthen client relationships and foster long-term partnerships based on mutual respect and trust. These actions not only resolve immediate issues but also demonstrate your commitment to excellence and client satisfaction, paving the way for continued success and growth in your professional relationships.

Conclusion
Building rapport and credibility are crucial for effective communication and professional success. Rapport fosters trust, connection, and understanding, while credibility enhances your reputation and influence. You can strengthen rapport by actively listening, showing empathy, and being authentic.
Similarly, demonstrating expertise, reliability, and delivering on promises enhance credibility. Continuously developing these skills through practice, feedback, and learning from experiences is essential for sustained success in any personal or professional endeavour. Embrace opportunities to refine your rapport-building and credibility-establishing abilities, as they are fundamental to building strong relationships and achieving your goals.
In conclusion, building rapport and credibility is an ongoing process that requires commitment, consistency, and a genuine interest in your clients’ success. By mastering the techniques discussed in this manual, you can create strong, lasting relationships that not only enhance your professional reputation but also drive business success. Trust, understanding, and effective communication are the pillars of these relationships, and investing in them will yield significant returns in the form of loyal clients, positive outcomes, and sustainable growth.

Case Study: Building Rapport and Credibility
In a professional services context, such as accounting, building rapport and credibility is essential for establishing long-term client relationships. Consider a case study of a mid-sized accounting firm, Smith & Associates, specialising in providing financial advisory services to small businesses.
Smith & Associates adopts a client-centric approach focused on building strong rapport and credibility. They begin by assigning dedicated account managers to each client, ensuring personalised attention and continuity of service. These account managers not only possess deep expertise in accounting principles but also undergo training in interpersonal skills to effectively engage with clients.
To establish credibility, Smith & Associates prioritises transparency and reliability in their interactions. They maintain clear communication channels, providing clients with regular updates on their financial status, regulatory changes, and industry insights. Moreover, the firm invests in innovative technology to streamline processes and enhance data security, reassuring clients of their commitment to excellence and professionalism.
Through these efforts, Smith & Associates earns the trust and loyalty of their clients, becoming valued partners in their business growth journey. Clients appreciate the firm’s proactive approach, personalised service, and unwavering dedication to their success, solidifying Smith & Associates’ reputation as a trusted advisor in the accounting industry.

Exercise: Mock Client Meetings

Course Manual 3: Communication Skills
Professional services depend on effective communication to maintain smooth operations. Communication serves as a medium for ideas to generate connections and stimulate action. But it does more than just deliver information; it further strengthens bonds and raises one’s trust.
Think about it: when you are talking to someone, it is not just about the words you say, but also about how you say them. Communication is not just a skill; it is the foundation of success.
Picture yourself as a client seeking assistance. You would not only seek expertise; you would prefer lucidity as well as assurance in explanations. Herein lies the significance of effective communication—it instils experts with the ability to become trusted allies.
Dr. Deborah Tannen, a respected academic specialising in linguistics and communication, offers valuable insights into communication skills in the professional services context. Tannen emphasises the importance of clear and effective communication in building successful client relationships. She highlights the need for professionals in fields such as law, consulting, and accounting to understand the nuances of language and tailor their communication style to the specific needs and preferences of their clients.
According to Tannen, practitioners in the professional services sector must possess strong listening skills to accurately interpret client concerns and objectives. They should also be adept at articulating complex concepts in simple, accessible language, ensuring that clients fully comprehend their advice and recommendations.
Furthermore, Tannen underscores the significance of nonverbal communication, such as body language and tone of voice, in conveying professionalism and trustworthiness. Professionals must project confidence and empathy through their demeanour, fostering rapport and credibility with clients.
Overall, Tannen’s insights emphasise the integral role of effective communication skills in facilitating productive client interactions and driving success in the professional services sector.

Understanding Communication in Professional Services
In the world of professional services, communication is not just about sharing facts; it is a whole strategy for connecting deeply with clients. Instead of just listening passively, professionals need to actively engage with clients to understand what they really want and expect. This helps them personalise their communication to build trust and connection with each client.
Effective communication goes beyond words; it is also about building real relationships and making meaningful connections. Professionals who are great communicators pay attention to non-verbal signals like body language and tone of voice, which show empathy and understanding. They adjust how they communicate to match each client’s style, making sure their messages hit the mark.
Being a good communicator in professional services means showing empathy and understanding clients’ feelings. By recognising and dealing with what clients really need, professionals can create a supportive partnership. This all-around approach to communication not only makes clients happier but also builds strong, lasting relationships that lead to success for everyone involved.
Fundamentals of Effective Communication
Simplicity is key in the world of professional services. To build strong client relationships and provide exceptional service, effective communication is necessary. These basic principles guide professionals through the network of client interactions, ensuring clarity, efficiency, and professionalism every step of the way.
Clarity: Clear communication is vital. Clients need straightforward messages to make informed decisions and trust their service providers. Ambiguity can lead to misunderstandings and erode trust. So, professionals must speak, avoid jargon, and ensure their explanations match the client’s understanding level. Clear communication lays a solid foundation for beneficial client engagements.
Brevity: Time is precious in professional services. Clients appreciate concise communication that gets to the point. While details matter, being overly verbose can overwhelm you. Professionals should deliver key information succinctly, respecting the client’s time and attention. By being brief yet informative, they show professionalism and consideration for the client’s needs.
Tone: The tone sets the stage for client interactions. A positive tone fosters trust and encourages collaboration. Conversely, a negative tone can drive clients away. So, professionals must maintain a friendly demeanour, listen actively, and respond with empathy. A positive tone builds rapport and lays the groundwork for successful client relationships.
Active Listening Techniques
In professional settings, effective communication relies on active listening—a crucial skill that goes beyond simply hearing. It means fully engaging with the speaker, showing empathy, and striving to grasp their perspective.
• To improve active listening, start by giving your complete focus to the speaker. This shows respect and genuine interest. Maintain eye contact, nod to show you are listening, and use body language that signals attentiveness.
• Avoid jumping in with interruptions. Let the speaker express themselves freely. This demonstrates respect for their viewpoint and encourages open sharing. Hold back from cutting them off, patiently waiting until they finish speaking.
• Reflecting and clarifying key points can prevent misunderstandings. Paraphrasing shows you are engaged and encourages further elaboration. Seeking clarification when things are not clear demonstrates your commitment to clear communication and resolving misunderstandings promptly.

Expressing Ideas Clearly and Concisely
Exceptional professionals in professional services stand out by expressing ideas with clarity and brevity. It is not just about sharing facts; it is about structuring messages for easy understanding while capturing their essence. The first step towards clarity is organising thoughts before speaking or writing. Techniques like outlining key points, arranging messages logically, and highlighting valuable information streamline communication and make it impactful.
One way to achieve clarity is by outlining key points beforehand. This helps in identifying main themes and structuring messages accordingly. Organising thoughts logically ensures smooth communication flow and resonance with the audience. Logical structuring also prevents confusion, presenting each point cohesively.
Prioritising information is crucial too. In professional services, there is often a lot of data to manage. By prioritising based on relevance and importance, professionals keep their message focused and powerful. Key takeaways or action points are emphasised, ensuring they are noticed and acted upon.
Barriers to Effective Communication and How to Overcome Them
Several barriers can impede effective communication in professional services, including jargon, assumptions, and emotional barriers. Strategies to overcome these barriers include:

Technical Jargon:
• Simplify language by avoiding unnecessary technical terms.
• Use plain language that is accessible to clients from diverse backgrounds.
• Provide explanations or definitions for any specialised terms that are unavoidable.
Assumptions:
• Challenge assumptions by actively questioning and seeking clarification.
• Approach each interaction with an open mind, avoiding preconceived notions.
• Ask probing questions to validate or adjust assumptions about clients’ needs and preferences.
Emotional Barriers:
• Cultivate emotional intelligence to recognise and manage emotions during client interactions.
• Stay attuned to both your own emotions and those of your clients.
• Respond with empathy and compassion to address emotional concerns and build rapport.
• By addressing these barriers proactively and employing strategies such as simplifying language, challenging assumptions, and cultivating emotional intelligence, professionals can foster clear, effective communication in the realm of professional services.
Cross-Cultural Communication
Understanding Cultural Differences
The Importance of Cultural Awareness in Professional Communication
In today’s globalised world, cultural awareness has become a vital skill for professionals. In professional services, this is particularly crucial as it ensures that communication is effective and respectful, regardless of the cultural background of clients and colleagues. Cultural awareness involves understanding and appreciating the differences in customs, traditions, and communication styles that exist among various cultures. This understanding helps to prevent miscommunications and fosters a more inclusive and harmonious working environment.
Cultural awareness goes beyond merely recognising differences. It requires professionals to actively learn about and engage with other cultures. This can be achieved through cultural competence training, participating in multicultural events, or simply being open and curious about learning from others. By doing so, professionals can build stronger, more trusting relationships with clients and colleagues from diverse backgrounds.
Identifying and Respecting Diverse Communication Styles
Communication styles can vary significantly across cultures. For instance, some cultures may value direct and explicit communication, while others may prefer a more indirect and nuanced approach. Recognising these differences is the first step towards effective cross-cultural communication.
Professionals should strive to identify the preferred communication styles of their clients and colleagues. This can be done through observation, asking questions, and being sensitive to non-verbal cues. Once these styles are identified, it is essential to respect and adapt to them. For example, in a culture that values indirect communication, professionals should avoid being overly blunt and instead use more tactful language. Respecting diverse communication styles demonstrates cultural sensitivity and helps in building rapport and trust.
Adapting Communication Styles
Strategies for Adjusting Communication to Different Cultural Contexts
Adapting communication styles to suit diverse cultural contexts is a critical skill for professionals in any field. This involves being flexible and willing to modify your approach based on the cultural preferences of your audience. One effective strategy is to use a more formal tone and language when communicating with clients from cultures that value hierarchy and formality. Conversely, a more relaxed and informal approach might be more effective with clients from cultures that value egalitarianism and open communication.
Another strategy is to be mindful of non-verbal communication, which can vary between cultures. For instance, while maintaining eye contact is considered a sign of confidence in some cultures, it can be seen as disrespectful in others. Professionals should observe and adapt to these non-verbal cues to ensure their communication is respectful and effective.
Avoiding Cultural Misunderstandings and Fostering Inclusivity
To avoid cultural misunderstandings, professionals should avoid making assumptions about the preferences or behaviours of clients and colleagues based on their cultural background. Instead, they should approach each interaction with an open mind and a willingness to learn. Asking questions and seeking clarification when in doubt can prevent misunderstandings and demonstrate a genuine interest in understanding the other person’s perspective.
Fostering inclusivity involves creating an environment where all cultural perspectives are valued and respected. This can be achieved by encouraging open dialogue about cultural differences, providing diversity training, and implementing inclusive policies and practices. An inclusive environment not only enhances communication but also boosts morale and productivity by making everyone feel valued and respected.
Technology and Communication
Digital Communication Tools
Using Email, Video Conferencing, and Instant Messaging Effectively
Digital communication tools have revolutionised the way professionals interact with clients and colleagues. Email, video conferencing, and instant messaging are now essential components of professional communication. To use these tools effectively, professionals need to adhere to certain best practices.
When using email, it is important to be clear, concise, and professional. Emails should have a clear subject line, be well-structured, and free from jargon. For video conferencing, ensuring a professional appearance, good lighting, and a quiet environment is crucial. Active participation, such as nodding and using the chat function for comments, can enhance engagement. Instant messaging should be used for quick, informal communications, but still maintain a level of professionalism and respect.
Best Practices for Maintaining Professionalism in Digital Communication
Maintaining professionalism in digital communication involves being respectful, clear, and considerate. Professionals should avoid using slang or overly casual language, particularly with clients. Timely responses are also important, as they show respect for the other person’s time and foster trust.
Privacy and confidentiality should always be maintained, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Professionals should be aware of the security features of the digital tools they use and ensure that confidential information is protected.
Overcoming Challenges in Virtual Communication
Ensuring Clarity and Engagement in Virtual Meetings
Virtual meetings can pose challenges such as technical issues, distractions, and reduced engagement. To ensure clarity and engagement, it is important to prepare thoroughly, set clear agendas, and use engaging visuals. Encouraging participation by asking questions and using interactive features like polls can also enhance engagement.
Clear communication is crucial in virtual meetings. This includes speaking slowly and clearly, using visual aids to support your points, and summarising key takeaways at the end of the meeting. Regularly checking in with participants to ensure they are following along and addressing any questions or concerns promptly can help maintain clarity and engagement.
Strategies for Managing Remote Team Communications
Managing remote team communications requires a combination of technology and effective communication strategies. Regular check-ins, using collaboration tools, and setting clear expectations are key. It is also important to foster a sense of community by encouraging informal interactions and team-building activities.
Effective remote communication also involves being mindful of time zones and scheduling meetings at times that are convenient for all team members. Providing training on remote communication tools and practices can help ensure that all team members are comfortable and proficient in using these tools.
Conflict Resolution and Communication
Identifying Sources of Conflict
Common Communication-Related Conflicts in Professional Settings
Conflict in professional settings often arises from miscommunication, differing expectations, or cultural misunderstandings. Common sources of conflict include unclear instructions, ambiguous feedback, and perceived slights or disrespect. Recognising these potential sources of conflict early can help prevent escalation.
Recognising Signs of Miscommunication Leading to Conflict
Signs of miscommunication that may lead to conflict include repeated misunderstandings, frustration, and lack of engagement. Professionals should be alert to these signs and take steps to clarify communication and address any issues before they escalate into more serious conflicts.
Effective Conflict Resolution Strategies
Techniques for Addressing and Resolving Communication Conflicts
Effective conflict resolution involves using techniques such as active listening, empathy, and problem-solving. Professionals should approach conflicts with an open mind, seeking to understand the other person’s perspective and finding mutually acceptable solutions. Techniques such as summarising the other person’s points, asking open-ended questions, and collaboratively brainstorming solutions can be highly effective.
The Role of Mediation and Negotiation in Conflict Resolution
Mediation and negotiation are powerful tools for resolving conflicts. Mediation involves a neutral third party who helps facilitate a resolution, while negotiation involves the conflicting parties working together to find a mutually acceptable solution. Both approaches require clear communication, active listening, and a willingness to compromise. By using these techniques, professionals can resolve conflicts effectively and maintain positive working relationships.

Case Study
In the world of digital marketing, being proactive and creative are key, and GA Agency shines brightly as a top performer. Look at their partnership with a major online shopping site; it shows how good teamwork and clear communication can change everything.
The partnership between GA Agency and their client began with a specific need: to boost the platform’s online visibility and drive client engagement. Recognising GA Agency’s expertise in digital marketing, the client sought their assistance in devising a comprehensive strategy to achieve these goals.
GA Agency’s first task was to conduct a thorough assessment of the client’s existing digital presence and identify areas for improvement. Leveraging their deep understanding of market trends and consumer behaviour, GA Agency proposed a multi-faceted approach that encompassed search engine optimisation (SEO), social media marketing, and targeted advertising campaigns.
Impressed by GA Agency’s strategic insights and proactive approach, the client expanded the scope of their collaboration. What started as a focused project to enhance online visibility soon evolved into a long-term partnership aimed at driving sustained growth and profitability.
As the relationship matured, GA Agency continued to deliver exceptional results by leveraging innovative technologies and data-driven strategies. They implemented advanced analytics tools to track campaign performance, optimise marketing spend, and refine targeting strategies, ensuring maximum return on investment for the client.
One of the key milestones in the partnership was the successful launch of a highly targeted email marketing campaign, which resulted in a significant increase in client engagement and sales conversions. GA Agency’s meticulous attention to detail and unwavering commitment to excellence were instrumental in achieving this outcome.
Over the years, the partnership between GA Agency and their client has flourished, driven by a shared commitment to innovation and continuous improvement. GA Agency’s ability to adapt to evolving market dynamics and anticipate emerging trends has cemented its position as a trusted advisor and strategic partner to the client.
Conclusion
Effective communication is like the foundation of a strong building in professional services. It is not just a tool; it is what sets great professionals apart. Think of mastering communication skills as having a superpower. It helps you break down barriers, understand people better, and build lasting relationships.
When dealing with clients, effective communication holds everything together. By really listening, professionals can notice what clients need and how they feel. It is not just about talking; it is about showing you understand and care. It helps them grasp complicated ideas and processes. Professionals who can explain things clearly make it easier for clients to make decisions confidently. It is key to connecting with others. It is what builds trust and rapport between professionals and clients. When professionals show they understand and care, it creates a bond that goes beyond just business.
The case study of GA Agency’s partnership with a leading e-commerce platform highlights the critical role of effective communication and collaboration in driving success in the digital marketing landscape. By leveraging their expertise and embracing innovation, GA Agency has not only helped their client achieve their business objectives but has also forged a lasting and mutually beneficial partnership built on trust and shared success. So, let us embrace the power of communication and strive to be the best we can be in our professional journey.

Case Study
In the realm of professional services like advertising, effective communication skills are paramount for delivering successful campaigns and fostering client satisfaction. Consider the case of Creative Minds Agency (CMA), a boutique advertising firm known for its innovative campaigns.
CMA was tasked with developing a new advertising strategy for a multinational consumer goods corporation launching a revolutionary product. Recognising the importance of communication, CMA implemented a comprehensive approach to ensure clear and consistent messaging throughout the project.
Firstly, CMA conducted extensive research to understand the client’s brand, target audience, and market landscape. They then collaborated closely with the client, employing active listening and open dialogue to align their creative vision with the client’s objectives.
Throughout the campaign development process, CMA maintained transparent communication channels, providing regular updates, soliciting feedback, and addressing any concerns promptly. They leveraged various communication tools, including presentations, reports, and virtual meetings, to keep all stakeholders informed and engaged.
As a result of their effective communication skills, CMA delivered a compelling advertising campaign that exceeded the client’s expectations, driving brand awareness and consumer engagement. The client praised CMA for their professionalism, responsiveness, and ability to translate complex ideas into impactful messaging, solidifying CMA’s reputation as a trusted partner in the advertising industry.

Exercise: Mock Client Meetings

Course Manual 4: Ethics and Integrity
Introduction
Ethics and integrity are critical in the field of professional services. They play the role of guideposts that lead businesses to fair and dependable outcomes. Moreover, the presence of these ideologies creates reliability and confidence between the business and the clients. They are the foundational level that upholds morals, values, and ethics and are vital to developing mutual relationships built on trustworthiness and utmost respect. Professional connections become meaningless without these values. Therefore, the two strong foundational theories are the pillars that support professional relationships and solidify connections overall.

Dr. Laura P. Hartman, a respected academic specialising in business ethics, provides valuable insights into ethics and integrity in the professional services context. She emphasises that ethical behaviour is fundamental to maintaining trust and credibility in client relationships across various industries, including law, consulting, and accounting.
Hartman argues that professionals in these fields have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of their clients, prioritising honesty, transparency, and integrity in all interactions. This involves upholding ethical standards and legal regulations while navigating complex business environments and ethical dilemmas.
Moreover, Hartman stresses the importance of fostering a culture of ethical conduct within professional service firms. Leaders play a critical role in setting the tone for ethical behaviour, promoting accountability, and providing resources for ethical decision-making.
Hartman contends that adherence to ethical principles not only safeguards client trust but also contributes to long-term success and sustainability in the professional services industry. By prioritising ethics and integrity, professionals can uphold their professional obligations, mitigate risks, and enhance their reputation as trusted advisors in their respective fields.
The Importance of Ethics in Professional Services

Ethics in professional services refers to the principles and standards that guide behaviour and decision-making in the workplace. It is like a compass that helps people do the right thing, even when no one is watching.
Ethical behaviour is crucial for maintaining a good professional reputation and building client trust. When professionals act ethically, they show integrity and reliability, leading to long-lasting relationships with clients and a positive reputation in the industry.
For example, an accountant prioritising their client’s interests over personal gain, gains trust and loyalty. Similarly, a lawyer who upholds client confidentiality builds a powerful reputation for respecting privacy.
Ethical practices also lead to positive outcomes overall. Companies prioritising ethical conduct often see higher employee morale, better client satisfaction, and improved financial performance. Ethical behaviour benefits individuals and clients and contributes to a healthier and more trustworthy professional environment.
Maintaining Integrity in Client Relationships
Integrity in client interactions means honesty, trustworthiness, and doing what is right, even when no one is watching. It is about keeping promises, transparency, and treating clients respectfully and fairly. Integrity is vital because it builds trust and fosters long-lasting relationships. When clients trust you, they are more likely to stay loyal and recommend you to others. It is like the glue that holds a successful client-business relationship together, creating a positive reputation and mutual satisfaction.
Strategies for Maintaining Integrity:
a. Consistency in Actions and Promises
Maintaining integrity is crucial for building trust and credibility. Consistency in actions and promises is key; it shows reliability and dependability, whether in delivering services or meeting deadlines. Transparency in communications and operations is equally vital. Being open about processes, challenges, and successes fosters trust and encourages honest collaboration.
b. Transparency in Communications and Operations
Respecting client confidentiality and privacy is non-negotiable. Safeguarding sensitive information demonstrates respect for individuals and their trust in your organisation. Implementing robust security measures and adhering to legal regulations ensure data protection and privacy.
c. Respecting Client Confidentiality and Privacy
Regularly reviewing and updating internal policies and practices is essential to uphold integrity. Conducting ethical training for employees reinforces the values of honesty, accountability, and fairness. Encouraging a culture of integrity where ethical behaviour is rewarded and promptly addressing misconduct reinforces these principles throughout the organisation.
Real-Life Scenarios Highlighting Integrity in Professional Relationships.
In finance, integrity is often assumed to be a given, although history has shown that this is only sometimes the case, as seen in the cases of Enron and WorldCom. While compliance functions such as audits aim to gauge and uphold integrity, it boils down to the choices made by individuals and organisations.
CFO Selections, the executive search firm, prioritises integrity in business, and the tangible benefits are evident. Firstly, trust is paramount in business relationships. Clients and partners gravitate towards companies they perceive as trustworthy, fostering stronger, long-term connections. Moreover, integrity serves as a cornerstone of reputation management. It distinguishes your company in a competitive landscape, enhancing credibility and attracting stakeholders who align with ethical values.
Integrity is not just a moral virtue; it is also a strategic asset. It is widely recognised as a top leadership trait, shaping thought leadership initiatives and empowering teams to make a meaningful impact. Operating with integrity opens doors to new opportunities, as it builds a reputation that precedes you in business circles.
Introduction to Ethical Dilemmas in the Professional Services Environment
Navigating ethical dilemmas is like finding your way through a maze in the professional world. Imagine you are a superhero with a moral compass, facing challenges that test your integrity and values. In professional services, ethical dilemmas are like puzzle pieces that need careful handling to ensure fairness, honesty, and trust.

Common Ethical Dilemmas Faced by Professionals
One of the most common ethical challenges is conflicts of interest. Picture this: you are helping two clients who have opposing interests. How do you ensure fairness and avoid favouritism? It is like walking on a tightrope, balancing the needs of both parties without tipping the scales.
Then there is the issue of overcharging or underserving. It is like serving a plate of food—how much is too little and too much? Striking the right balance ensures that you are neither taking advantage of clients nor short-changing them.
Another situation is balancing client demands with ethical standards. Imagine a client asking you to bend the rules slightly. Do you prioritise their requests or stick firmly to ethical guidelines? It is like juggling multiple balls, ensuring you meet client expectations while upholding professional integrity.
To navigate these ethical mazes, professionals need a sturdy moral compass and a clear understanding of ethical principles. Transparency, honesty, and fairness are like guiding stars, helping you make decisions that align with your values and benefit everyone involved.
Ethical dilemmas are like riddles in the professional services landscape. By staying true to your values, being transparent, and finding the right balance, you can navigate these challenges with confidence and integrity, emerging as a trusted guardian of ethics in your field.
Frameworks and Strategies for Decision-Making in Complex Situations:
When faced with complex decisions, ethical decision-making models provide a clear path. These frameworks, like the practical or principle-centred approaches, help navigate moral dilemmas. Professional codes of conduct guide us by setting ethical standards for our fields. They act as compasses, ensuring our actions align with ethical principles.
Seeking counsel from peers or ethics boards is crucial. It offers fresh perspectives and ensures decisions consider diverse viewpoints. Peers can provide practical advice based on experience, while ethics boards offer specialised guidance, especially in intricate matters.
Collaboration enhances decision-making in complex situations. Discussing options with colleagues fosters collective wisdom, reduces blind spots, and promotes ethical reflection. Moreover, it strengthens professional relationships and builds trust within teams.
Ultimately, combining ethical decision-making models, professional codes, and peer input forms a robust yet fruitful strategy. It guides decision-making and upholds integrity, accountability, and trustworthiness in navigating complexities.
Building an Ethical Culture in the Workplace

Creating an ethical workplace starts with strong leadership. Leaders set the tone by demonstrating ethical behaviour and communicating clear expectations to their team. They inspire trust and respect, making employees more likely to follow ethical guidelines.
Training and resources are crucial for supporting ethical practices. Employees need to understand what is expected of them and have access to tools and guidance to make ethical decisions. Regular training sessions and resources like ethical guidelines, codes of conduct, and ethical decision-making frameworks can reinforce these principles.
Enforcing ethical behaviour involves setting clear consequences for violations. This could include disciplinary actions, such as warnings or even termination in severe cases. It is also essential to have a system in place for reporting ethical concerns safely and anonymously.
Handling violations should be done promptly and transparently, ensuring fairness and accountability. This could involve investigations, corrective actions, and opportunities for employees to learn from their mistakes and improve.
Building an ethical culture in the workplace requires a commitment from leadership, ongoing training and resources, and a robust system for enforcement and handling violations.
Ethics and Integrity in Leadership

The Role of Ethical Leadership
How Leaders Influence Organisational Ethics and Integrity
Ethical leadership is fundamental in shaping the ethical culture and integrity of an organisation. Leaders set the tone at the top, influencing the values, behaviours, and attitudes that permeate throughout the organisation. When leaders demonstrate ethical behaviour, they create a standard for others to follow, fostering an environment where integrity is valued and practised.
Leaders influence organisational ethics by:
1. Setting Clear Ethical Standards: Leaders articulate the ethical standards and expectations for the organisation. This involves developing a code of conduct, ethical policies, and clear guidelines for acceptable behaviour.
2. Leading by Example: Leaders who model ethical behaviour inspire their teams to act similarly. By demonstrating honesty, fairness, and respect in their decisions and actions, leaders set a powerful example for their employees.
3. Communicating Openly: Ethical leaders promote transparency by communicating openly with their teams about ethical issues and decisions. This openness encourages employees to voice concerns and seek guidance when faced with ethical dilemmas.
4. Creating a Supportive Environment: Leaders who foster an environment where ethical behaviour is recognised and rewarded build a culture of integrity. This includes providing resources and support for ethical decision-making and addressing unethical behaviour promptly and fairly.
Examples of Ethical Leadership in Professional Services
In the professional services sector, ethical leadership is critical due to the fiduciary responsibilities and trust placed in these professionals by their clients. Here are some examples:
• Law Firms: Ethical leadership in law firms involves upholding client confidentiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and ensuring that legal advice is provided with the utmost honesty and integrity. Leaders in law firms set the standard by prioritising ethical considerations over financial gain.
• Consulting Firms: Leaders in consulting firms influence organisational ethics by promoting transparency in client dealings, ensuring that advice is based on accurate data and sound analysis, and avoiding any practices that might compromise the client’s interests.
• Accounting Firms: In accounting, ethical leadership is demonstrated through adherence to regulatory standards, maintaining the accuracy and honesty of financial reporting, and ensuring independence and objectivity in audits.
Developing Ethical Leaders
Training Programmes and Resources for Ethical Leadership
Developing ethical leaders involves equipping them with the knowledge and skills to navigate complex ethical issues. Training programmes and resources play a crucial role in this development.
• Ethics Training: Regular ethics training sessions help leaders understand ethical principles and how to apply them in various situations. These programmes cover topics such as conflict of interest, confidentiality, and ethical decision-making frameworks.
• Workshops and Seminars: Interactive workshops and seminars on ethics allow leaders to engage in discussions, share experiences, and explore real-world scenarios. These platforms provide practical insights and enhance ethical awareness.
• Resources and Toolkits: Providing leaders with resources such as ethical guidelines, decision-making models, and case studies helps them make informed ethical decisions. These toolkits serve as valuable references in their day-to-day roles.
Mentorship and Role Modelling for Promoting Ethical Behaviour
Mentorship and role modelling are effective strategies for promoting ethical behaviour among leaders.
• Mentorship Programmes: Pairing emerging leaders with experienced mentors who exemplify ethical behaviour provides guidance and support. Mentors can share their experiences, offer advice on handling ethical dilemmas, and reinforce the importance of integrity.
• Role Modelling: Leaders who consistently demonstrate ethical behaviour influence their peers and subordinates. By making ethical decisions and behaving with integrity, they create a ripple effect that encourages others to follow suit.
Ethical Decision-Making in Practice
Decision-Making Frameworks
Utilising ethical frameworks is essential for making complex decisions. These frameworks provide a structured approach to evaluating the ethical implications of decisions.
• Consequentialist Approach: This approach focuses on the outcomes of a decision. Leaders consider the potential consequences for all stakeholders and choose the action that maximises positive outcomes and minimises harm.
• Deontological Approach: This approach is based on adherence to ethical principles and duties. Leaders following this framework prioritise actions that are inherently right, regardless of the consequences.

Case Studies of Ethical Decision-Making
Examining real-world examples of ethical dilemmas and resolutions provides valuable insights into ethical decision-making.
• High-Profile Ethical Breaches: Analysing cases such as Enron and WorldCom highlight the severe consequences of unethical behaviour. These case studies reveal the importance of transparency, accountability, and ethical leadership in preventing such breaches.
• Lessons Learned: From these cases, leaders learn the critical role of ethical culture, the need for robust internal controls, and the impact of ethical behaviour on an organisation’s reputation and sustainability.
Transparency and Accountability
Importance of Transparency
Transparency is vital in building trust with clients and stakeholders. When organisations operate transparently, they demonstrate honesty and openness, which are key to establishing and maintaining trust.
• Building Trust: Transparency in communication, decision-making, and operations reassures clients and stakeholders that the organisation acts in their best interests. It fosters a sense of reliability and confidence.
• Implementing Transparent Practices: Transparent practices include clear reporting, open communication channels, and regular updates on organisational activities. Organisations should ensure that information is accessible and understandable to all stakeholders.
Mechanisms for Accountability
Establishing accountability systems within organisations ensures that ethical standards are upheld and that there are consequences for unethical behaviour.
• Internal Audits: Regular internal audits help monitor compliance with ethical standards and identify areas for improvement. Audits provide an objective assessment of the organisation’s adherence to ethical practices.
• Ethical Oversight Committees: These committees oversee ethical conduct within the organisation. They review ethical concerns, investigate violations, and ensure that appropriate actions are taken. Ethical oversight committees play a crucial role in maintaining accountability and upholding integrity.
In conclusion, ethical leadership is the cornerstone of a trustworthy and sustainable organisation. By influencing organisational ethics, developing ethical leaders, utilising ethical decision-making frameworks, and ensuring transparency and accountability, organisations can foster a culture of integrity that benefits all stakeholders.
The Bottom Line
In wrapping up, let us revisit why ethics and integrity are crucial in professional services. They are like the compass guiding us towards fairness, honesty, and reliability. When we embody these values professionally, we create lasting bonds of trust with our clients, strengthening and enduring our relationships. The commitment to understanding clients’ needs also forms the foundation of enduring partnerships.
Embrace the practices we have talked about today. Communicate openly, prioritise honesty, and always keep your promises. These small yet powerful actions build the foundation of trust that clients cherish. Prioritising honesty means being straightforward in all your interactions. It is about being truthful about capabilities, limitations, and potential challenges.
But it does not end there. Ethical conduct requires continuous learning and vigilance. Stay updated with industry standards, seek feedback, and be open to self-improvement. Let us make ethical behaviour a habit, not just a checkbox.
Remember, it is not just about doing what is right; it is about being someone others can rely on. We elevate ourselves and contribute to a more trustworthy and sustainable business environment by weaving ethics into our professional fabric.
Together, let us strive for excellence through ethics!

Case Study
In 2015, the global accounting firm, PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), faced a significant ethical dilemma involving integrity and professional conduct. The case centred around the 2017 Academy Awards ceremony, where PwC was responsible for tabulating the voting results and ensuring the secrecy and accuracy of the winners’ envelopes.
During the ceremony, a PwC accountant mistakenly handed the presenters the wrong envelope for the Best Picture category, resulting in a highly publicised mix-up where the wrong film was initially announced as the winner. The error tarnished PwC’s reputation and raised questions about the firm’s adherence to ethical standards and protocols.
In response, PwC took swift and decisive action to address the situation and restore trust in its integrity. The firm issued a public apology, accepted full responsibility for the mistake, and launched an internal investigation to identify the root causes and implement corrective measures.
PwC also implemented rigorous reforms to its Oscars procedures, including additional safeguards and redundancies to prevent similar errors in the future. Furthermore, the firm reinforced its commitment to ethics and professionalism by providing enhanced training and oversight for its employees involved in high-profile events.
PwC’s handling of the incident demonstrated its dedication to ethical principles and accountability. By openly acknowledging its mistake, taking responsibility, and implementing corrective actions, PwC reaffirmed its commitment to integrity and strengthened its reputation as a trusted and dependable professional services provider in the accounting industry.

Exercise
Confidentiality and record safety are foundational in professional services like engineering and management consulting services, legal, accounting, scientific and environmental research services, architectural and surveying services, advertising, and market research services. These fields depend heavily on trust to ensure clean interactions between professionals and clients. Imagine consulting a professional service and not feeling steady within the confidentiality of your discussions or defensive of your touchy facts—it would surely disrupt the whole dynamic. Confidentiality ensures that non-public and sensitive subjects remain non-public, fostering a secure environment for clients to report their issues openly, but securely. Additionally, information safeguards against unauthorised access or misuse of valuable information are crucial in the current, interconnected, and virtual landscape. In these dynamic professional worlds, the assurance of confidentiality and robust records protection mechanisms build belief and permit clients to try to find help without apprehension, developing an extra effective and beneficial experience for everyone concerned. Dr. Ann Cavoukian, a respected academic specialising in privacy and data protection, emphasises the critical importance of confidentiality and data protection in the professional services context. Cavoukian asserts that trust is the cornerstone of client relationships in professions such as law, accounting, and consulting, and maintaining confidentiality is paramount to building and preserving that trust. She advocates for the implementation of robust data protection measures and adherence to strict confidentiality protocols to safeguard sensitive information entrusted to professionals. Cavoukian emphasises the principle of data minimisation, urging professionals to collect and retain only the data necessary for the fulfillment of their professional duties. Moreover, Cavoukian stresses the need for proactive measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits to mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorised access. She underscores that respecting client confidentiality not only demonstrates professionalism and integrity but also ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Overall, Cavoukian’s insights highlight the ethical and legal obligations of professionals to prioritise confidentiality and data protection in their service delivery, fostering trust and confidence in their clients and the broader community. Importance of Confidentiality in Professional Services Confidentiality in professional services plays a pivotal role in maintaining agreement, fostering sturdy relationships, and preventing reputational damage. Here is why it is so essential: Confidentiality assures clients that their sensitive information will remain stable and personal with the trusted professional. This creates a safe environment for them to report on and share critical information without fear of dissemination to non-approved audiences. When clients feel assured that their facts are safeguarded, they are likelier to expand a deeper reference to the professional. This agreement forms the inspiration for a long-lasting and fruitful relationship. Breaching confidentiality can have severe consequences. Imagine a professional services advisor leaking details about a high-profile client, disclosing brand strategies without consent. Such actions can lead to legal repercussions, damage the professional’s reputation, and result in clients seeking services elsewhere. Many professions have obligations to preserve confidentiality. Public Relations Specialists, for instance, are sure to manage the public image of companies and brands, which guarantees that conversations between them and their clients stay personal until authorised in any other case. Violating these obligations can have serious consequences and result in a lack of credibility. Professionals frequently address sensitive records, including personal budgets and company strategic advice. Keeping this information private respects clients’ privacy and protects them from building and maintaining a unique brand identity. Confidentiality is not only an expert courtesy but an essential issue of moral practice in many fields. Upholding confidentiality strengthens the integrity and reliability of the whole professional services sector. Understanding Data Protection Regulations Data safety rules, like GDPR, ensure private facts remain secure. Understanding these regulations is vital for experts in professional services. Other jurisdictions have such regulations, however, GDPR is mooted as the “toughest privacy and security law in the world.” As shared by GDPR.EU, “With the GDPR, Europe is signaling its firm stance on data privacy and security at a time when more people are entrusting their personal data with cloud services and breaches are a daily occurrence. The regulation itself is large, far-reaching, and light on specifics, making GDPR compliance a daunting prospect, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).” These guidelines inform agencies how to acquire, save, and use non-public information. Why does this matter? Well, imagine you are a client. You trust your trusted professionals with sensitive information, right? If they do not follow these regulations, precious data could get leaked, leading to significant problems and penalties. Plus, it damages the trust between you and your professional. Now, what if these regulations are not followed? It is important. Companies can face hefty fines or legal issues. The market could also lose faith in them, hurting their reputation and business. So, complying with data protection rules is not just about following the law. It is about respecting privacy, maintaining their information safe, and making sure they trust you. Best Practices for Ensuring Client Data Security Here is a simplified version: 1. Encryption is essential for shielding client information and data, specifically during transmission or whilst saved on digital and physical databases. By encrypting information, even though a person gains unauthorised admission, they may not be capable of accessing the base information without the decryption key. 2. Access manipulation limits who can get the right of entry to purchaser statistics to those who need it for their approved work. This minimises the danger of unauthorised access or leaks. Implementing role-primarily based access management (RBAC) guarantees that relevant personnel have the right of entry to the information and structures vital for their job obligations. 3. Regular audits are critical for keeping a sturdy security posture. These audits involve reviewing your encryption practices, getting the right of entry to controls, and overall security protocols to perceive any vulnerabilities or regions that need development. By undertaking audits often, you can stay proactive in addressing protection dangers before they become extreme. 4. Employee education is a key thing for record safety. Employees ought to recognise the significance of safeguarding purchaser data and be prepared with the understanding and abilities to do so effectively. Training must cover topics like recognising phishing emails, using robust passwords, and following safety protocols for managing and storing sensitive information. 5. Employee cognisance is critical in fostering a tradition of protection awareness. This knowledge is necessary for understanding the risks of data breaches and the capability effects for each business enterprise and its clients. Additionally, regularly speak about cybersecurity excellent practices, proportion actual international examples of breaches, and inspire personnel to record any suspicious interest immediately. Ensuring Client Trust through Confidentiality and Data Protection Maintaining confidentiality and information protection is essential for gaining and retaining purchaser consideration. When clients understand their statistics are safe and stable, they feel more assured about sharing sensitive details and running with your organisation. Here is why these matter: Firstly, it indicates that you respect their privacy and take their confidential information seriously. This can translate into a more potent relationship because clients feel valued and cared for. Secondly, it reduces the chance of statistics breaches and leaks, which are detrimental to your relationship and eroding of trust. Your practice demonstrates commitment to safeguarding purchaser facts by enforcing sturdy security features. To correctly communicate information security measures to clients, use easy language each person can apprehend. Explain the steps you take to guard their data, which includes encryption, stable servers, policies, practices, and audits. Provide clear instructions on how clients can get admission to, update, or delete their facts, empowering them to take manage. Thinks about the legislative and regulatory requirements within your own jurisdiction as minimum requirements here. Building a culture of agreement and security within the business enterprise includes training employees on information safety protocols and fostering an accountable mindset. Encourage open conversation about security issues and promote a culture of transparency. Regularly review and update your policies and practices against regulatory requirements to minimise potential threats. By prioritising confidentiality and data protection, sharing with clients, and cultivating a subculture of consideration internally, your agency can construct robust relationships and earn clients’ trust for the long haul. Ethical Considerations in Data Sharing In the realm of professional services, the management and sharing of client data are integral to operational success. However, these practices must be meticulously balanced with ethical considerations to safeguard client privacy and maintain trust. This section explores the complexities of data sharing, the ethical implications of data analytics, effective crisis management in data breaches, and the integration of confidentiality and data protection into daily operations. Evaluating the Necessity of Data Sharing for Operational Efficiency Data sharing can significantly enhance operational efficiency in professional services by enabling better decision-making, streamlined processes, and improved client services. However, professionals must carefully evaluate the necessity of sharing specific data. This involves assessing whether the operational benefits outweigh the potential risks to client privacy. For instance, law firms may need to share case details internally to provide comprehensive legal services, or accounting firms might require client financial information to offer tailored advice. In such cases, it is crucial to limit data sharing to what is strictly necessary, ensuring that only relevant information is disclosed to authorised personnel. Ensuring Informed Consent and Transparency in Data-Sharing Practices Transparency and informed consent are fundamental ethical principles in data sharing. Clients must be fully aware of how their data will be used and who will have access to it. This can be achieved through clear, concise privacy policies and regular communication with clients about data practices. Professionals should obtain explicit consent from clients before sharing their data, detailing the purpose, scope, and duration of data usage. This process not only complies with legal requirements but also builds trust by demonstrating respect for client autonomy and privacy. Managing Ethical Boundaries in Data Mining and Analytics Data analytics can provide valuable insights that drive business growth and enhance client services. However, it also raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding the scope of data mining and the potential for privacy invasion. Professionals must navigate these boundaries carefully, ensuring that data collection and analysis methods respect client privacy. Ethical data mining practices include anonymising data to protect client identities, minimising data collection to only what is necessary, and using data solely for the purposes outlined to clients. Additionally, professionals should regularly review and update their data analytics practices to align with evolving ethical standards and regulatory requirements. Avoiding Discriminatory Practices in Data Usage Another critical ethical consideration is the potential for data analytics to perpetuate or exacerbate discrimination. This can occur when data analysis unintentionally reflects or amplifies existing biases, leading to unfair treatment of certain groups. To avoid discriminatory practices, professionals should implement bias detection and mitigation strategies in their data analytics processes. This includes using diverse data sets, employing algorithmic fairness techniques, and regularly auditing outcomes to ensure they are equitable. By doing so, professionals can uphold ethical standards and promote inclusivity in their data practices. Immediate Response Strategies Steps to Take in the Event of a Data Breach Data breaches can have severe consequences for both clients and professional service firms. Immediate and effective response strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact. The first step is to contain the breach by identifying and isolating affected systems to prevent further data loss. Next, professionals should conduct a thorough investigation to understand the breach’s scope and origin. This involves collaborating with IT experts and forensic analysts to assess the damage and identify vulnerabilities. Documenting the incident comprehensively is essential for transparency and future prevention efforts. Communicating Breaches to Clients and Stakeholders Effectively Transparent communication is vital in the aftermath of a data breach. Clients and stakeholders should be promptly informed about the breach, its implications, and the steps being taken to address it. This communication should be clear, honest, and empathetic, acknowledging the severity of the situation and the firm’s commitment to resolving it. Providing clients with actionable advice on protecting their information, such as changing passwords or monitoring accounts, can help mitigate the breach’s impact. Maintaining open lines of communication throughout the resolution process also reassures clients and stakeholders of the firm’s dedication to their security and trust. Long-Term Recovery and Prevention Implementing Measures to Prevent Future Breaches Preventing future data breaches requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Professional service firms should implement robust security measures, such as advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular system updates. Additionally, conducting frequent security audits and vulnerability assessments can identify and address potential weaknesses. Employee training is another critical component of prevention. Staff should be educated on cybersecurity best practices, recognising phishing attempts, and responding to potential security threats. A well-informed workforce significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. Restoring Client Trust and Confidence Post-Breach Restoring client trust after a data breach is a long-term process that involves demonstrating a commitment to enhanced security and transparency. Firms should communicate the specific measures taken to prevent future incidents and provide regular updates on their progress. Offering complimentary services such as credit monitoring or identity theft protection can further reassure clients of the firm’s dedication to their security. Consistent, transparent communication and demonstrable improvements in data protection practices are key to rebuilding trust and confidence. Confidentiality Protocols in Client Interactions Best Practices for Maintaining Confidentiality During Client Meetings and Communications Maintaining confidentiality during client interactions is essential for building and preserving trust. Professionals should ensure that all discussions and communications with clients are conducted in secure environments, whether in person or virtually. This includes using private meeting rooms, secure communication channels, and encryption tools for sensitive information. Ensuring Confidentiality in Remote and Virtual Consultations With the increasing prevalence of remote work, ensuring confidentiality in virtual consultations is more important than ever. Professionals should use secure video conferencing platforms, implement strict access controls, and follow best practices for online security to protect client information during remote interactions. Implementing Robust Data Management Software Robust data management software is fundamental to maintaining data security. Professional service firms should invest in systems that offer comprehensive security features, including encryption, access controls, and regular updates. These systems should be integrated into daily operations to ensure consistent data protection. Regularly Updating Security Protocols to Address Emerging Threats The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging regularly. Professional service firms must stay ahead of these threats by regularly updating their security protocols and systems. This includes staying informed about the latest cybersecurity trends, implementing updates and patches promptly, and conducting ongoing training for employees. Trust, confidentiality, and data protection are crucial in all professional services. They are like the glue that holds strong client relationships together and builds a solid business reputation. Firstly, trust is the foundation. Clients need to feel confident that their information is safe and that you are reliable. Confidentiality means keeping sensitive data private and only sharing it with the right permissions, when necessary. Data protection involves safeguarding information from breaches or misuse. This includes using secure systems and following legal guidelines. To succeed, professionals must stay updated on data protection rules and adapt their practices accordingly. Learning is ongoing, and being proactive ensures you meet evolving requirements. Prioritising trust, confidentiality, and data protection benefits clients and strengthens your business overall.
1. Supplier Transparency: A company discovers that one of its suppliers engages in unethical labour practices. The dilemma: Should the company continue doing business with the supplier to maintain cost-effectiveness, or should it terminate the relationship to uphold ethical standards, risking disruptions to its supply chain and potential financial losses?
2. Competitive Intelligence: A company obtains confidential information about a competitor through questionable means. The dilemma: Should the company use the information to gain a competitive advantage, potentially violating ethical and legal boundaries, or should it refrain from using the information to maintain integrity and fairness in the marketplace?
3. Conflict of Interest: A business consultant is hired by two clients operating in the same industry. The dilemma: Should the consultant provide impartial advice to both clients, risking conflicts of interest and compromised integrity, or should the consultant decline one of the contracts to avoid ethical dilemmas, potentially losing valuable business opportunities?
4. Data Privacy and Security: A BUSINESS service provider discovers a security vulnerability in its software that could compromise client data. The dilemma: Should the provider disclose the vulnerability to its clients, risking damage to its reputation and potential legal repercussions, or should it attempt to address the issue internally without informing clients, potentially putting their data at risk?

Course Manual 5: Confidentiality and Data Protection
Introduction
Confidentiality and Data Protection – Insight



Balancing Client Privacy with Business Needs
Ethical Implications of Data Analytics
Crisis Management in Data Breaches

Integrating Confidentiality and Data Protection in Daily Operations
Secure Data Management Systems
Conclusion

Case Study
In 2017, the global law firm Mossack Fonseca faced a significant breach of confidentiality and data protection, commonly known as the Panama Papers leak. The case involved the unauthorised disclosure of millions of confidential documents detailing the firm’s offshore financial activities on behalf of clients worldwide.
The leak exposed sensitive information, including financial records, emails, and client communications, implicating numerous individuals, corporations, and government officials in tax evasion, money laundering, and other illicit activities. The breach not only tarnished Mossack Fonseca’s reputation but also triggered international investigations and legal proceedings, leading to significant financial and legal repercussions.
Mossack Fonseca’s failure to adequately protect client confidentiality and data highlights the severe consequences of lax data protection practices in the professional services industry. The case underscores the critical importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures, encryption protocols, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorised access or disclosure.
Moreover, the Panama Papers leak serves as a cautionary tale for professionals in law, accounting, and consulting, emphasising the ethical and legal obligations to uphold client confidentiality and data protection. It underscores the need for continuous vigilance, training, and compliance with data privacy regulations to mitigate the risk of data breaches and preserve trust in client relationships.
The Mossack Fonseca case underscores the high stakes involved in maintaining confidentiality and data protection in the professional services context, reinforcing the imperative for firms to prioritise cybersecurity and risk management as core components of their business practices.

Exercise

Course Manual 6: Managing Expectations
Introduction
Managing expectations in professional services ensures a more harmonious relationship with clients, enables more business growth, and fosters loyalty. It may lead to referrals, enhancing the expert’s recognition and increasing the enterprise. For experts, setting up and retaining engagements is another crucial pillar. This groundwork is the bedrock of successful client relationships, allowing open verbal exchange, effective collaboration, and long-term engagement.
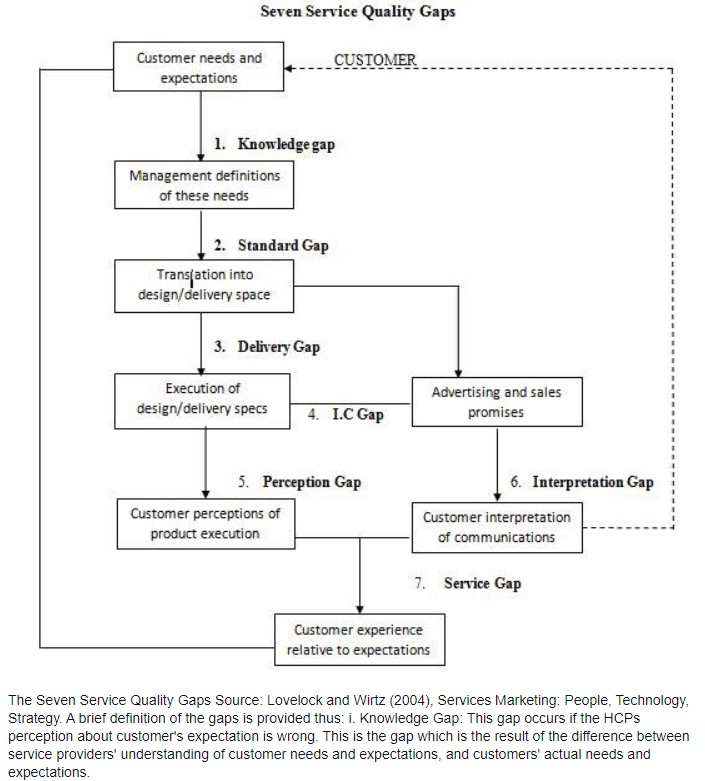
Dr. Christopher Lovelock, a respected academic in the field of service management, emphasises the critical importance of managing expectations in the professional services context. Lovelock argues that successful service delivery hinges not only on meeting client needs but also on aligning client expectations with realistic outcomes.
He emphasises the need for clear and transparent communication throughout the service engagement, from initial consultations to final delivery. By actively engaging clients in the process and setting realistic expectations regarding timelines, costs, and deliverables, professionals can avoid misunderstandings and dissatisfaction.
Moreover, Lovelock underscores the value of under-promising and over-delivering, advocating for a proactive approach to exceeding client expectations whenever possible. By consistently delivering high-quality service and demonstrating commitment to client satisfaction, professionals can foster trust and loyalty, leading to long-term client relationships and positive referrals.
Overall, Lovelock’s insights highlight the integral role of managing expectations in ensuring client satisfaction and success in the professional services industry. By prioritising transparency, communication, and proactive service delivery, professionals can effectively manage client expectations and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Managing expectations may be achieved through steady professional services, transparency, and moral practices. Additionally, maintaining those standards leads to extended client pride and retention. This method presents sensible strategies for experts to enhance their trustworthiness in the eyes of their clients.
Setting Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is significant for all professional services in effectively managing client relationships and having positive effects.
The importance of establishing doable and understood desires in any profession cannot be overstated. It allows for dealing with client expectations and notably builds trust and credibility. When clients have practical and achievable expectations, they are more likely to be satisfied with the services supplied and perceive the professional as trustworthy and reliable.
Conversely, unrealistic expectations can cause distrust and dissatisfaction. Clients who expect results beyond reality can also feel misled or upset, harming the relationship and business. Therefore, professional services must proactively control and set realistic expectations.
Several techniques can be employed to ensure realistic expectations are set:
1. Defining Project Scope: Professional service should define the scope of labour, which includes the services to be provided, deliverables, and any boundaries or exclusions. This allows clients to recognise what to anticipate and prevents misunderstandings afterwards.
2. Establishing Clear Timelines and Milestones: Setting practical timelines and milestones offers clients a roadmap for the project’s development. It permits higher monitoring of achievements and guarantees that both parties are aligned regarding the predicted timeline.
3. Communicating Limitations and Potential Challenges Upfront: Being obvious about ability challenges, such as project complexities or financial constraints, prepares clients for sensible eventualities. It additionally demonstrates honesty and professionalism, improving consumer agreement.
Aligning Client Expectations with Deliverables

In professional services, aligning client expectations with deliverables is crucial for successful consequences and retaining strong purchaser relationships. Understanding the nuances of patron expectations, the significance of alignment, and using effective strategies can notably impact purchaser delight and the general achievement of an undertaking or engagement.
Firstly, comprehending client expectations involves conducting thorough needs assessments. This entails open communication channels, feedback addressing concerns promptly, and delving into their requirements, such as goals and concerns. For professional service, this may include maintaining transparency, actively managing expectations, and ensuring consistent communication. It may also involve grasping financial objectives, compliance needs, and reporting preferences.
The importance of aligning expectations with deliverables must be balanced. Misaligned expectations can lead to misunderstandings, delays, dissatisfaction, or capability disputes. Clear alignment guarantees that both parties agree concerning venture scope, timelines, resources, and desired consequences. It fosters acceptance as true with transparency and duty at some point in the engagement.
To acquire this alignment, clarifying roles and responsibilities is crucial. Clearly defining who is chargeable for what tasks, selections, approvals, and communications prevents confusion and avoids assumptions. Professional services must outline their respective roles, knowledge, limitations, and the client’s responsibilities in contributing facts, presenting comments, and making selections for a better outcome.
Moreover, regular communiques and standing updates are pivotal in preserving alignment. Establishing a verbal exchange measure that fits the client’s preferences ensures ongoing talk, progress visibility, and opportunities to deal with rising issues or modifications promptly. Professional services can provide ordinary updates on milestones, build trust, and ensure client satisfaction throughout the project.
Finally, effective management of modifications is another important approach. Changes in mission scope, goals, or priorities are inevitable, but how they are managed can impact alignment significantly. In addition to that, proactively speaking about modifications, assessing their effect on timelines and assets, and collaboratively discussing answers with clients demonstrate adaptability, responsiveness, and commitment to turning in fees.
Strategies for Managing and Exceeding Expectations
Let us understand the pragmatic strategies which are extremely helpful to professionals. Like any other profession, managing and exceeding expectations is important for professional services to build robust client relationships and keep an aggressive area in their respective fields.
Here are strategies tailored for them:
Managing Expectations:

1. Clear Communication Channels: Establish obvious verbal exchange channels from the outset. Clearly define the scope of work, timelines, and deliverables. Use simple language to help certain clients comprehend complex prisons or financial concepts.
2. Feedback Management: Encourage open feedback and deal with it constructively. Regularly seek client input to ensure their expectations align with the venture’s progress. Use remarks as an opportunity to enhance and tailor your services.
3. Prompt Issue Resolution: Address issues promptly and transparently. If there are delays or unexpected challenges, communicate these to clients immediately, along with proposed solutions. Transparency builds trust and demonstrates your commitment to client satisfaction.
Strategies for Exceeding Expectations:
Going the Extra Mile: Strive to exceed expectations by supplying price-brought services. This could mean providing additional legal research or guidance beyond the initial scope for lawyers. Professional services could offer to identify potential risks associated with engineering projects and develop strategies to mitigate these risks effectively.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: They integrate sustainable practices and investigate environmental impacts to promote eco-friendly solutions and follow green construction standards.
Exceptional Quality and Service: Deliver exceptional quality and service consistently. Pay attention to detail, maintain accuracy in initiation to completion, and coordinate tasks, resources, schedules, and budgets to ensure successful outcomes. A focus on quality reflects professionalism and dedication to client success.
Showcasing Professionalism: Professionalism is crucial in setting up credibility and trustworthiness. This extends beyond technical understanding to include elements including punctuality, reliability, and moral conduct. Independent builders running with the tech company must adhere to excessive standards of professionalism, ensuring that all interactions with clients are respectful and effective.
This includes meeting closing dates, delivering on guarantees, and preserving a tremendous and solution-oriented attitude. Demonstrating professionalism also involves imparting thorough documentation, clean and concise reviews, and nicely structured venture outlines, which help clients apprehend the scope and development of the work being undertaken.
Consistently Delivering Exceptional Work: The closing degree of a tech company’s achievement is its potential to supply first-rate paintings constantly. This calls for a rigorous, high-quality assurance process to ensure all deliverables meet or exceed client expectations. Independent builders must be decided on primarily based on their information and music files regarding manufacturing great work. The company should offer them vital resources and help them excel in their roles.
Managing Client Expectations: Clear and practical assignment outlines are crucial for dealing with consumer expectations. At the undertaking’s outset, the tech corporation must collaborate closely with clients to define the undertaking’s scope, objectives, timeline, and budget. Providing certain project plans and timelines enables clients to apprehend what to expect at every degree of the assignment.
Regular updates and progress reviews are essential in keeping clients knowledgeable and engaged. This transparency enables constructive belief and allows for any necessary adjustments to be made in a timely way, ensuring that the challenge remains on target and meets the agreed-upon goals.

Ethical Communication Practices in Professional Services
Effective communication is the bedrock of professional services. It is not merely about conveying information but about building trust, managing expectations, and fostering long-term relationships. Ethical communication practices ensure that interactions with clients are honest, transparent, and proactive, leading to client satisfaction and business success. This document explores strategies for ensuring honest and transparent communication, addressing miscommunications, establishing performance metrics and accountability, and building long-term client relationships.
Ensuring Honest and Transparent Communication
The Importance of Honesty in Client Communications
Honesty is the cornerstone of ethical communication. In professional services, clients rely on their advisors for accurate, trustworthy information. Honesty in client communications builds credibility and trust, which are essential for maintaining strong, lasting relationships. When professionals are truthful about what they can deliver, they set realistic expectations, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings and disappointments.
Honesty also involves being upfront about potential challenges and limitations. Clients appreciate when their service providers are candid about what can and cannot be achieved, as it allows them to make informed decisions. This transparency helps in mitigating risks and preparing for potential setbacks, thereby fostering a collaborative, and trusting partnership.
Techniques for Maintaining Transparency While Managing Expectations
Maintaining transparency involves clear, open communication throughout the client engagement process. This can be achieved through several techniques:
1. Clear Initial Consultations: From the outset, professionals should provide a comprehensive overview of the services offered, including potential outcomes, timelines, and costs. This helps clients understand what to expect and aligns their expectations with what is feasible.
2. Regular Updates: Keeping clients informed about the progress of their projects is crucial. Regular updates through emails, reports, or meetings ensure that clients are aware of any developments, changes, or challenges. This ongoing communication helps maintain transparency and trust.
3. Open Dialogue: Encouraging clients to ask questions and express concerns fosters an open dialogue. Professionals should be responsive and address any issues promptly, demonstrating their commitment to the client’s satisfaction.
Addressing Miscommunications Proactively
Identifying Potential Communication Barriers
Miscommunications can arise from various barriers, such as language differences, cultural misunderstandings, or unclear messages. Identifying these barriers is the first step in addressing them:
• Language and Terminology: Using industry-specific jargon or technical language can confuse clients who are not familiar with these terms. Simplifying language and ensuring clarity can help prevent misunderstandings.
• Cultural Differences: Cultural norms and communication styles can vary significantly. Being aware of and sensitive to these differences is crucial for effective communication.
• Assumptions: Making assumptions about what the client knows or expects can lead to miscommunication. It is important to verify and clarify information to ensure mutual understanding.
Strategies for Clarifying Misunderstandings Before They Escalate
Proactively addressing potential misunderstandings involves several strategies:
1. Active Listening: Paying close attention to what the client is saying and confirming understanding by paraphrasing or summarising their points can prevent miscommunication.
2. Clarification Questions: Asking clarifying questions when something is unclear can help ensure that both parties are on the same page. This demonstrates attentiveness and a commitment to clear communication.
3. Documentation: Keeping detailed records of communications and agreements can serve as a reference to clarify any misunderstandings that may arise later. Providing clients with written summaries of discussions and decisions helps in maintaining clarity.
Performance Metrics and Accountability
Establishing Clear Performance Metrics
Performance metrics are essential for setting expectations and measuring success. In professional services, clear, measurable performance goals help manage client expectations and track progress.
• Defining Metrics: Metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Examples include project completion times, client satisfaction scores, and adherence to budget.
• Communicating Metrics: Clearly communicating these metrics to clients ensures that they understand how success will be measured. This transparency helps align their expectations with the firm’s capabilities.
Using Metrics to Manage Client Expectations and Track Progress
Using performance metrics to manage expectations involves regularly reviewing and discussing these metrics with clients. This ongoing dialogue helps ensure that both parties are aware of progress and any deviations from the plan. Regular performance reviews provide an opportunity to address any concerns and adjust strategies as needed, fostering a collaborative and transparent relationship.
Accountability Mechanisms in Professional Services
Implementing accountability systems ensures that professional services meet their quality standards and client expectations. These mechanisms include:
• Internal Audits: Regular internal audits assess compliance with established procedures and identify areas for improvement. These audits help maintain high standards of service quality.
• Performance Reviews: Conducting regular performance reviews with employees ensures that they are meeting their goals and adhering to ethical standards. These reviews also provide an opportunity for professional development and improvement.
• Client Feedback: Actively seeking client feedback and incorporating it into service improvements demonstrates a commitment to accountability and continuous improvement.
Building Long-Term Client Relationships

Strategies for Client Retention
Retaining clients is crucial for long-term business success. Strategies for maintaining client engagement post-project include:
1. Regular Check-ins: Staying connected with clients through regular check-ins, even after a project is completed, helps maintain the relationship and identify future opportunities for collaboration.
2. Personalised Communication: Tailoring communication to each client’s preferences and needs shows that the firm values their relationship. Personalised emails, updates, and follow-ups can strengthen client bonds.
3. Providing Value: Offering additional value through insights, resources, or complimentary services can enhance client loyalty. Demonstrating ongoing value encourages clients to return for future services.
Developing Loyalty Programmes and Follow-Up Services
Loyalty programmes and follow-up services can further strengthen client relationships:
• Loyalty Programmes: Implementing loyalty programmes that reward repeat clients with discounts, exclusive offers, or additional services can incentivise continued engagement.
• Follow-Up Services: Offering follow-up services, such as maintenance, updates, or ongoing support, ensures that clients continue to benefit from the firm’s expertise. This ongoing support fosters long-term loyalty and satisfaction.
Enhancing Client Trust Over Time
Building and maintaining trust requires consistently exceeding client expectations and leveraging feedback for continuous improvement.
• Exceeding Expectations: Consistently delivering high-quality services that exceed client expectations builds trust and reinforces the firm’s reputation for excellence.
• Leveraging Client Feedback: Regularly seeking and acting on client feedback demonstrates a commitment to improvement and responsiveness. Clients appreciate when their input is valued and used to enhance services.
In conclusion, ethical communication practices, effective performance metrics, accountability mechanisms, and strategies for building long-term client relationships are essential for success in professional services. By prioritising honesty, transparency, and proactive engagement, professionals can build trust, manage expectations, and foster lasting client relationships that drive business growth and success.
Final Word
In conclusion, professional services are the cornerstone of managing client’s expectations and building successful consumer relationships. Professionals can foster consideration by realistically outlining what can be accomplished, aligning purchaser expectations with deliverables, and enforcing techniques to exceed those expectations. Furthermore, trust-constructing is paramount in all the professional domains. Clients anticipate competence, transparency, reliability, successful project implementation and long-term sustainability.

Case Study
In the case of a digital marketing agency, Bright Digital Solutions (BDS), managing client expectations played a pivotal role in a successful campaign for a high-profile e-commerce client.
BDS was tasked with launching a new product line for the client within a tight timeframe to capitalise on seasonal trends. Recognising the importance of managing expectations, BDS conducted thorough consultations with the client to understand their goals, preferences, and constraints. During these discussions, BDS outlined realistic timelines, budget allocations, and performance metrics, setting clear expectations for the project.
Throughout the campaign, BDS provided regular updates to the client, highlighting progress, addressing any challenges, and soliciting feedback. By maintaining open lines of communication, BDS ensured that the client was informed and engaged at every stage of the process, mitigating surprises and misunderstandings.
Despite facing unexpected technical issues and supply chain disruptions, BDS proactively communicated these challenges to the client and presented alternative solutions to minimise delays and maintain project momentum.
The campaign exceeded the client’s expectations, surpassing key performance indicators and driving significant sales growth. The client praised BDS for their professionalism, transparency, and commitment to delivering results, highlighting the importance of managing expectations in fostering successful client relationships. This case demonstrates how proactive communication and realistic goal setting can lead to client satisfaction and project success in the professional services industry.

Exercise

Course Manual 7: Conflict Resolution
Introduction
Dr. John Paul Lederach, a prominent scholar in the field of conflict resolution, emphasises the importance of relationship-building and trust in resolving conflicts in the business context. He argues that traditional adversarial approaches often exacerbate tensions and hinder long-term collaboration. Instead, Lederach advocates for a transformative approach that focuses on understanding underlying interests and fostering mutual respect.
In the business environment, Lederach highlights the need for active listening and empathetic communication to uncover the root causes of conflicts. By creating a dialogue-oriented process, businesses can move beyond surface-level disputes to address deeper issues, such as misaligned goals or cultural differences. Lederach also stresses the importance of involving all stakeholders in the conflict resolution process to ensure that solutions are comprehensive and sustainable.
Furthermore, Lederach suggests that conflict resolution in business settings should be proactive rather than reactive. Establishing clear communication channels, setting mutual expectations, and creating joint problem-solving mechanisms can prevent conflicts from escalating. By fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement, businesses can not only resolve conflicts more effectively but also build stronger, more resilient partnerships.
Overall, Lederach’s insights underscore the significance of a holistic, relationship-centred approach to conflict resolution in the business context, aiming for long-term harmony and cooperation.
Prompt and meaningful conflict resolution in professional services delivers offerings civilly, reliably, and ethically. It encompasses the notion that specialists will act with the clients’ best interests at heart, preserve confidentiality, and offer accurate and sincere advice. It fosters open conversation, facilitates collaboration, and complements pride with the work undertaken.
When those involved in a conflict trust the mediator or each other, they are much more likely to be open about their worries, interact in meaningful dialogue, and decide to collectively useful answers.
However, conflict resolution in professional services must include strategies, policies, and processes to address and resolve disagreements and disputes between clients and provider vendors.
Effective conflict resolution is critical for preserving acceptance as true and ensuring persevering collaboration. Techniques consist of clean conversation, active listening, negotiation, and mediation. Professionals must remain unbiased, understand the underlying issues, and attempt mutually beneficial answers. Successful conflict resolution repairs and strengthens relationships and demonstrates a commitment to professionalism and purchaser pride, similarly, reinforcing agreement.
Identifying and Addressing Conflicts

Conflicts are an inevitable part of any organisational or social setting. Recognising unusual sources of dissent or ill-feeling is essential for effective resolution. Differences in expectations can emerge when parties have differing understanding or vision on matters, leading to misunderstandings and frustration.
Miscommunication, another common source, occurs when information is not shared correctly/precisely, inflicting confusion and inaccurate assumptions. Resource allocation issues, where individuals or groups compete for limited resources, can foster resentment and competition. Ethical dilemmas present conflicts when moral principles clash, requiring careful navigation to uphold integrity while addressing differing viewpoints.
Early detection and open communication are essential in mitigating conflicts earlier than they increase. Active listening is pivotal in ensuring every party feels heard and understood. By attentively listening, you can still become aware of underlying issues and emotions that may not immediately be apparent. Creating a secure environment for speaking similarly supports war resolution. When individuals feel steady and respected, they are much more likely to specify their issues clearly and constructively. This open trade fosters mutual understanding and collaborative problem-fixing, paving the manner for answers that fulfil all concerned events. Conflicts may be managed efficaciously through early detection and fostering open communique, preserving concord and productivity inside any setting.
Let us understand it better through a case study!

Case Studies
Brad and Frank, two integral professionals in management consulting services, faced a common dilemma – differing views on deadlines and priorities.
Acknowledging Differences with Empathy: Brad initiated a conversation using principles from “Difficult Conversations” to address the issue without confrontation. He started by acknowledging their differing perspectives on deadlines, paving the way for open dialogue.
Understanding Perspectives: Through their conversation, Brad learned that Frank prioritised potential sales over deadlines, believing it to be more beneficial for the company’s growth. This understanding was pivotal in finding a collaborative solution.
A Compromise for Success: Building on this understanding, Brad proposed a compromise: he would manage reports on Frank’s days but requested a two-hour notice and a share in commission from leads pursued during that time. This solution honoured Frank’s sales focus while ensuring timely reports for the team.
Leveraging Strengths for Collaboration: Brad and Frank resolved their conflict by valuing each team member’s strengths and perspectives. This led to timely reports and fostered a more collaborative and understanding work environment.
The Power of Constructive Dialogue: This story highlights the power of constructive dialogue and empathy in resolving workplace conflicts. By approaching differences with understanding and seeking collaborative solutions, teams can leverage individual strengths for collective success.
Conclusion: Navigating variations in perspectives and priorities is crucial in any group. By acknowledging expertise and valuing those variations, teams can foster a way of life of collaboration, creativity, and mutual respect, ultimately riding achievement and growth. Professionals can apply this case study to themselves in conflict resolution.
Techniques for Resolving Disputes
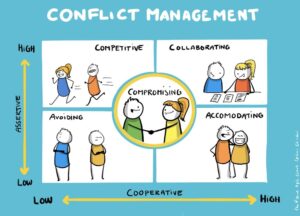
Collaborative Problem-Solving Approaches
1. Win-Win Negotiation Strategies
Win-win negotiation specialises in finding beneficial solutions for all parties concerned. It emphasises open verbal exchange and can benefit from brainstorming creative answers. The goal is to attain an agreement that satisfies each person’s wishes, fostering long-term cooperation and tremendous relationships.
2. Mediation and Arbitration Techniques
Mediation entails a neutral third celebration supporting disputants to attain a voluntary agreement. The mediator enables speaking and ability without implementing a decision. Arbitration, conversely, entails an impartial arbitrator making a binding choice after listening to arguments and evidence. Both techniques aim to solve conflicts correctly and fairly.
Leveraging the era of conflict resolution includes using online dispute resolution (ODR) structures and digital mediation practices. ODR systems facilitate resolving disputes via the Internet, imparting negotiation, mediation, and arbitration tools without physical presence. They enhance accessibility, reduce prices, and expedite the resolution manner.
Virtual mediation practices use video conferencing tools to conduct mediation periods remotely, allowing events to clear up conflicts successfully from special places. These practices increase flexibility, ensure convenience, and maintain the mediation process’s integrity while adapting to the digital age’s demands. Both methods exemplify how technology can streamline and improve conflict resolution.
Fairness and transparency are important in resolving disputes to gain trust and credibility. Establishing clear strategies and tips gives a structured framework, making the process predictable and understandable for all events. This transparency minimises misunderstandings and perceptions of bias. Ensuring impartiality and fairness includes treating all events similarly and without favouritism, fostering an experience of justice and fairness. When disputes are overseen impartially and transparently, it promotes recognition of the outcomes, reduces conflicts, and upholds the integrity of the resolution mechanism, contributing to an extra harmonious and simple society.
Turning Conflicts into Opportunities for Trust-Building

Conflicts, often seen as destructive, may be transformed into treasured opportunities for increase and agreement construction within a business enterprise. By transferring views on the battle, embracing positive comments, and fostering a superb culture, agencies can turn disputes into catalysts for development and stronger relationships.
Shifting Perspectives on Conflict
Viewing conflict as a catalyst for growth involves recognising that disagreements can highlight underlying issues and prompt necessary changes. Conflicts can stimulate innovation and improvement, driving the organisation forward when approached positively. Embracing constructive feedback is essential; it allows individuals to learn from their experiences and enhance their skills. Conflicts become valuable to organisational development by focusing on the potential benefits rather than the immediate discomfort.
Building Trust through Effective Resolution
Effective conflict resolution is rooted in honesty and integrity. Addressing conflicts transparently and ethically ensures that all parties feel heard and respected, which builds trust. Following up on resolutions is equally important. It shows a commitment to continuous improvement and accountability, reinforcing trust and demonstrating that the organisation values its members’ concerns. Learning from resolutions helps prevent similar conflicts in the future and strengthens the overall conflict management process.
Cultivating a Positive Organisational Culture around Conflict
A positive organisational culture around conflict encourages collaboration and teamwork. When crew contributors view conflict as a natural and constructive part of operating collectively, they are likelier to interact recklessly and cooperatively. Therefore, encouraging a culture where numerous critiques are valued fosters an environment where conflicts are resolved extra efficiently and smartly.
Moreover, celebrating successes in warfare resolution reinforces this advantageous approach. Acknowledging the worthwhile efforts to manage conflicts constructively not only motivates people around you but also proposes methods of disagreements with a problem-fixing attitude.
Transforming conflicts into opportunities for agreeing with constructing necessitates a fundamental shift in how we understand and technique disagreements. It begins with spotting conflicts no longer simply as barriers but as capability catalysts for fantastic change. This attitude shift is complemented by a steadfast determination to employ transparent and truthful resolution mechanisms. Open conversation, lively listening, and empathy play pivotal roles in this process, fostering surroundings where numerous viewpoints are valued and understood.
Moreover, cultivating a supportive organisational culture that values collaboration over opposition is critical. This involves creating spaces where people feel secure to express their worries, where positive comments are endorsed, and wherein conflicts are visible as mastering opportunities instead of threats. By embracing those strategies, groups can harness the transformative strength of conflicts to gas boom, innovation, and the development of strong, consider-primarily based relationships amongst crew participants.
Emotional Intelligence in Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is a crucial skill in professional services, where interactions with clients and colleagues are frequent and often intense. Emotional intelligence (EI) plays a pivotal role in managing and resolving conflicts effectively. This document explores the importance of understanding emotional triggers, building emotional resilience, applying effective negotiation techniques, and addressing conflicts in virtual teams, with a focus on professional services.
Understanding Emotional Triggers
Identifying and Managing Emotional Responses During Conflicts
Conflicts often trigger strong emotional responses, which can hinder effective resolution if not managed properly. In professional services, understanding these triggers is essential for maintaining professionalism and fostering positive outcomes. Common emotional triggers include perceived threats to self-esteem, unmet expectations, and miscommunications.
Professionals should develop self-awareness to identify their emotional triggers and recognise the physical and psychological signs of emotional arousal, such as increased heart rate, tension, or anxiety. By acknowledging these signs early, individuals can take steps to manage their emotions before they escalate.
Strategies for Maintaining Emotional Control and Empathy
Maintaining emotional control involves techniques such as deep breathing, taking breaks, and practising mindfulness. These strategies help professionals stay calm and composed, allowing them to respond to conflicts rationally rather than reactively.
Empathy is equally important in conflict resolution. It involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others, which fosters mutual respect and cooperation. Professionals can practise empathy by actively listening to the other party, validating their emotions, and showing genuine concern for their perspectives. This approach not only de-escalates conflicts but also builds stronger, more trusting relationships.
Building Emotional Resilience
Techniques for Developing Emotional Resilience in High-Stress Situations
Emotional resilience refers to the ability to adapt to and recover from stressful situations. In the context of conflict resolution, resilience enables professionals to handle disputes constructively and maintain their well-being.
Key techniques for building emotional resilience include:
1. Stress Management: Practising regular stress-relief activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies can enhance overall resilience.
2. Positive Thinking: Cultivating a positive mindset by focusing on solutions rather than problems helps professionals navigate conflicts more effectively.
3. Support Systems: Building a strong network of colleagues, mentors, and friends provides emotional support and valuable perspectives during challenging times.

The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Fostering Positive Relationships
Emotional intelligence is not only about managing one’s own emotions but also about understanding and influencing the emotions of others. In professional services, high EI facilitates better teamwork, client interactions, and conflict resolution.
Professionals with high EI are adept at recognising the emotional states of others and responding appropriately. This skill fosters an environment of trust and collaboration, which is essential for resolving conflicts amicably. By demonstrating empathy, active listening, and emotional regulation, professionals can build positive, enduring relationships with clients and colleagues.
Negotiation and Compromise
Effective Negotiation Techniques
Negotiation is a critical component of conflict resolution. Effective negotiation techniques help professionals reach agreements that satisfy all parties involved.
Approaches to Interest-Based Negotiation
Interest-based negotiation focuses on understanding the underlying interests and needs of both parties rather than their stated positions. This approach involves:
1. Exploring Interests: Identifying the fundamental needs and concerns driving each party’s position.
2. Generating Options: Brainstorming multiple solutions that address these underlying interests.
3. Evaluating Solutions: Assessing the feasibility and fairness of potential solutions to find a mutually acceptable outcome.
Interest-based negotiation encourages collaboration and creativity, leading to more sustainable and satisfactory resolutions.
Balancing Assertiveness and Empathy to Reach Mutually Beneficial Agreements
Balancing assertiveness and empathy are crucial for successful negotiations. Assertiveness involves clearly and confidently expressing one’s needs and boundaries, while empathy requires understanding and respecting the other party’s perspectives.
Professionals should strive to:
• Assert Their Needs: Clearly articulate their goals and limitations without aggression.
• Show Empathy: Demonstrate genuine understanding and consideration for the other party’s needs.
• Seek Win-Win Solutions: Focus on finding outcomes that benefit all parties, enhancing long-term relationships and cooperation.
Principles of Fair Compromise
Establishing Criteria for Fair and Equitable Compromises
A fair compromise involves finding a middle ground where both parties feel their interests have been adequately addressed. Establishing clear criteria for compromises ensures that resolutions are balanced and just.
Professionals should consider:
• Proportionality: Ensuring that concessions made by each party are proportionate to their needs and contributions.
• Reciprocity: Promoting a give-and-take approach where each party gains something of value.
• Transparency: Keeping the negotiation process open and honest to build trust and prevent misunderstandings.
Ensuring All Parties Feel Heard and Valued in the Negotiation Process
For compromises to be effective, all parties must feel respected and valued. This involves:
• Active Listening: Paying full attention to the other party’s concerns and feedback.
• Acknowledgement: Recognising and validating the other party’s viewpoints and emotions.
• Inclusive Decision-Making: Involving all relevant stakeholders in the negotiation process to ensure that solutions are comprehensive and inclusive.
Conflict Resolution in Virtual Teams
Addressing Conflicts in Remote Work Settings
The rise of remote work has introduced new challenges for conflict resolution. Virtual teams often face difficulties such as miscommunication, lack of non-verbal cues, and feelings of isolation.
Challenges Unique to Virtual Teams and How to Overcome Them
1. Miscommunication: Without face-to-face interactions, messages can be easily misinterpreted. Professionals should prioritise clear, concise communication and avoid relying solely on text-based messages.
2. Lack of Non-Verbal Cues: Non-verbal signals such as body language and facial expressions are absent in virtual settings. Using video calls can help restore some of these cues, enhancing understanding and empathy.
3. Isolation: Remote work can lead to feelings of disconnection and isolation. Regular virtual check-ins, team-building activities, and fostering a sense of community can mitigate these issues.
Best Practices for Resolving Conflicts in a Remote Environment
Effective conflict resolution in virtual teams requires:
• Scheduled Meetings: Setting regular virtual meetings to discuss ongoing issues and address conflicts promptly.
• Structured Communication: Using structured formats for meetings and discussions to ensure all voices are heard.
• Conflict Resolution Training: Providing team members with training on virtual conflict resolution techniques and tools.
Tools and Technologies for Virtual Conflict Resolution
Leveraging Technology to Facilitate Conflict Resolution in Distributed Teams
Technology plays a crucial role in resolving conflicts in virtual teams. Tools such as video conferencing platforms, collaborative software, and instant messaging apps facilitate communication and problem-solving.
1. Video Conferencing: Tools like Zoom or Microsoft Teams enable face-to-face interactions, enhancing empathy and understanding.
2. Collaborative Software: Platforms like Slack or Trello support real-time collaboration and transparent communication.
3. Instant Messaging: Apps such as WhatsApp or Slack allow for quick, informal communication to address issues as they arise.
Using Collaborative Tools to Enhance Communication and Understanding
Collaborative tools help bridge the gap between remote team members, fostering better communication and understanding. Features such as shared documents, real-time editing, and discussion forums ensure that all team members are aligned and informed.
The Bottom Line
Conflict resolution is a crucial skill for any professional service. Since we deal with humans, we must know how to explore key strategies, including active listening, empathetic communication, and collaborative hassle-fixing, which are fundamental to coping with conflicts effectively.
In addition, building acceptance is another significant pillar that demands consistency, transparency, and integrity, fostering effective and productive work surroundings. However, professionals must remember that continuous improvement is crucial in preserving these skills.
We hope you will actively apply these smart techniques as you return to your expert roles. Use the equipment and insights gained to deal with conflicts constructively and build more potent, accept-as-with-based relationships with your peers and clients. By fostering a trust-worthy culture of open verbal exchange and mutual admiration, you enhance your effectiveness and contribute to an extra harmonious and collaborative place of business.
Finally, gaining knowledge to strive for conflict resolution develops a more resilient and cohesive crew environment than ever before!

Case Study
In a notable case within the architectural industry, a mid-sized architectural firm, DesignInnovate, faced a significant conflict with a key client, a large property developer. The disagreement arose over the project timeline and scope changes. The client demanded expedited delivery and additional features without agreeing to the increased costs, leading to tension and stalled progress.
To resolve the conflict, DesignInnovate employed a structured conflict resolution approach. First, they organised a joint meeting with all stakeholders, including project managers, lead architects, and the client’s representatives. During this meeting, they facilitated open communication to clearly articulate each party’s concerns and expectations.
DesignInnovate’s team utilised active listening techniques to fully understand the client’s demands and constraints. They then proposed a phased approach to the project timeline, allowing for the incorporation of additional features without compromising on quality. This approach included regular check-ins and progress reports to keep the client informed and engaged.
The firm also suggested a revised budget that transparently detailed the costs associated with the scope changes, emphasising value and long-term benefits. By demonstrating flexibility and a commitment to the client’s vision, DesignInnovate was able to rebuild trust.
The conflict was resolved through a combination of empathetic communication, transparent planning, and collaborative problem-solving, resulting in a successful project completion that satisfied both parties.

Exercise 1: Role Reversal Negotiation
1. Divide participants into pairs, assigning each a conflicting role (e.g., supplier vs. client).
2. Each pair discusses a typical conflict scenario for 15 minutes.
3. After the discussion, participants switch roles and discuss the same scenario from the opposite perspective.
4. Reconvene as a group and have each pair share insights gained from the role reversal. Outcome: Participants develop a deeper understanding of the other party’s challenges and motivations, fostering empathy and collaborative solutions.
Exercise 2: Interest-Based Problem Solving
1. Present a conflict scenario where both parties have a fixed position (e.g., budget constraints vs. project scope).
2. Break participants into small groups, each representing one side of the conflict.
3. Each group identifies their underlying interests (e.g., financial stability, quality of work).
4. Groups then reconvene and share their interests, working together to brainstorm solutions that satisfy both sides. Outcome: Participants learn to identify and prioritise interests over positions, leading to creative and mutually beneficial conflict resolutions.
Exercise 3: Joint Goal Setting
1. Introduce a conflict scenario involving misaligned goals between two BUSINESS partners.
2. In pairs or small groups, have participants list their individual goals and concerns.
3. Facilitate a discussion to find common ground and establish shared goals that address both parties’ concerns.
4. Create a joint action plan with specific, measurable steps to achieve these goals, assigning responsibilities and setting deadlines. Outcome: Participants practice setting and working towards common objectives, enhancing cooperation, and reducing conflict likelihood through mutual accountability.

Course Manual 8: Risk Management
Risk management is important in professional services, which include engineering and management consulting services, legal, accounting, scientific and environmental research services, architectural and surveying services, advertising and market research services and others. It enables companies to become aware of, evaluate, and cope with potential threats that could affect their operations. By proactively managing risks, companies can prevent or reduce economic losses, felony problems, and damage to their reputation.
Dr. Robert S. Kaplan, a renowned expert in risk management and co-creator of the Balanced Scorecard, provides valuable insights into business risk management. He emphasises the importance of integrating risk management into the strategic planning process rather than treating it as a standalone activity. Kaplan argues that in the business context, risk management should be proactive, focusing on identifying potential risks early and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Kaplan suggests that companies should employ a comprehensive risk assessment framework that includes both internal and external risks. Internal risks could involve operational inefficiencies, financial instability, or compliance issues, while external risks might encompass market volatility, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory changes. By systematically evaluating these risks, businesses can prioritise them based on their potential impact and likelihood.
Furthermore, Kaplan highlights the role of communication and transparency in effective risk management. He advocates for regular risk reporting and open dialogue between departments and with business partners to ensure that everyone is aware of potential risks and their mitigation plans. This collaborative approach helps in building resilience and adaptability within business relationships.
In summary, Kaplan’s insights underscore the necessity of integrating risk management into the core strategy, employing a thorough risk assessment framework, and fostering open communication to navigate the complexities of business environments effectively.
Identifying Risks in Professional Services
Identifying risks in professional services is essential for preserving the integrity and success of the enterprise. These risks could be widely labelled as property or marketing-related issues or helping clients manage their assets.
However, financial dangers involve capability losses because of mismanagement of pricing, incorrect pricing techniques, costing and resourcing issues, or unforeseen economic downturns. Legal risks arise from non-compliance with laws and regulations, leading to penalties or complaints. For instance, misconduct services corporations may encounter legal dangers if they fail to satisfy regulatory standards or if their advice results in client losses.
Reputation risks affect the trust and perception of the organisation or client in the marketplace. Negative purchaser studies or scandals can significantly damage an organisation’s reputation. For instance, consulting a professional service might face reputation dangers if a high-profile client publicly criticises its recommendation or methodologies.
Operational risks encompass disruptions to the firm’s inner techniques or structures, which can include people, processes, systems, and external events. Specifically, professional services must seek to mitigate these operational risks, understanding that some risks are always likely to be present.
Moreover, these professional services face specific examples of risks like wrong cost-advantage analyses, criminal risks from affected person records breaches, recognition risks from publicised errors in strategic recommendations, and operational dangers from reliance on defective information analytics gear. Hence, identifying and mitigating those dangers is important to ensure sustained overall performance and client belief.
Mitigating Risks in Professional Services

Mitigating dangers in professional services is vital for preserving reputation, ensuring client satisfaction, and safeguarding monetary stability. Effective danger mitigation involves several techniques, including due diligence, contractual protections, coverage insurance, and compliance measures.
Conducting thorough due diligence is the foundation of threat mitigation. It includes complete background examinations and checks of capability clients, partners, and tasks. This system enables the picking out of any red flags or ability troubles early on. For instance, advising clients on compliance and litigation can prevent future payment defaults. Additionally, knowledge of clients’ particular wishes and expectations ensures that the provider company can meet or exceed them, for this reason minimising the danger of disputes or dissatisfaction.
Well-drafted contracts are crucial tools for managing some of these threats. They outline the scope of deliverables, timelines, fee terms, and responsibilities of each party. Including specific clauses for dispute resolution, indemnity, and obstacles of legal responsibility can offer criminal safety and make clear the approaches for addressing any problems. However, contracts must be reviewed to make certain they are complete and enforceable.
Furthermore, insurance acts as a protection net for professional services. Focusing on wills, trusts, property-making plans, and probate regulation, assisting clients in controlling their belongings and planning for the future. Adequate coverage insurance guarantees the company can manipulate unexpected activities without intense financial repercussions.
Adhering to relevant guidelines, regulations, and enterprise standards is vital. Establishing and retaining sturdy compliance programs facilitates keeping away from criminal consequences and protects the organisation’s popularity. Regular counselling and audits ensure all professionals recognise and cling to compliance requirements. This proactive method mitigates dangers and enhances the company’s credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of clients and regulators.

Case Study
LawFirm LLC faced a project whilst coping with sensitive purchaser facts. They identified risks like information breaches and confidentiality breaches. To manage those dangers, they implemented a sturdy threat control plan. This covered securing their IT structures with superior encryption, accomplishing everyday body of workers education on records privacy, and developing strict access controls. Additionally, they bought professional liability insurance to cover ability misconduct. By proactively handling risks, LawFirm LLC’s greater patron accepted as true, ensured compliance with felony requirements, and protected their popularity. This method not only minimised capability losses but also helped the usual service to be fine.
Strategies for Effective Risk Management
Effective risk management is vital for ensuring the steadiness and achievement of any organisation. Proactive change management, which involves waiting and making ready for capacity dangers earlier than they materialise, is vital as it allows companies to mitigate ability threats and capitalise on possibilities. This ahead-wondering technique enables reduced disruptions, reduced prices associated with unforeseen activities, and maintains an aggressive edge.

A complete control plan includes numerous key elements:
1. The first step systematically identifies capacity organisational risks. Techniques including brainstorming exercises, SWOT evaluation, and risk checklists are usually used to find internal and external risks.
2. Evaluate the probability and effect of potential risks. This includes studying every chance’s possibility and potential results at the corporation. Risk assessment equipment like danger matrices, failure mode and outcomes evaluation (FMEA), and situation analysis help prioritise risks based totally on severity.
3. Organisations must increase management techniques as soon as risks are assessed. This can consist of hazard avoidance, reduction, switch (e.g., through insurance), or acceptance. Developing contingency plans and implementing manipulative measures are important to mitigate the identified dangers effectively.
4. Continuous monitoring and normal evaluation of the threat management plan are critical to ensure its effectiveness. This includes monitoring recognised dangers, monitoring the effectiveness of mitigation techniques, and figuring out new risks as the organisational environment evolves. Regular audits and chance reporting mechanisms are critical components of this system.
Various tools and technology can be hired to streamline risk control. Risk control software programs, for example, can automate many aspects of the threat control system, from danger identification and assessment to mitigation tracking and reporting. Tools like ERM (Enterprise Risk Management) software, GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) systems, and undertaking control software with included hazard control modules are beneficial in improving efficiency and accuracy. Data analytics and synthetic intelligence also can offer predictive insights, helping corporations anticipate and prepare for dangers more efficaciously.
Implementing Risk Assessment in Professional Services
Implementing risk assessment in professional services is important for assessing threats, minimising their impact, and making sure of clean operations. To effectively integrate threat assessment into business processes, organisations should embed chance control techniques into their core activities.
This entails aligning chance evaluation with strategic making plans, selection-making, and operational workflows. By doing so, dangers are recognised early, bearing in mind proactive management and mitigation. Standard running tactics need to be developed to encompass threat checks at vital stages, ensuring that capability issues are taken into consideration and addressed before they boost.
The function of records analytics in risk evaluation cannot be overstated. Data analytics enhances the accuracy and performance of danger tests by leveraging huge datasets to perceive styles, traits, and anomalies that imply emerging risks. Predictive analytics, specifically, allows companies to forecast potential dangers based on historical facts and contemporary situations. This forward-looking approach allows more knowledgeable choice-making and aid allocation. Additionally, real-time information analytics can offer instantaneous insights, supporting agencies to reply swiftly to changing risk landscapes.

Continuous improvement in hazard evaluation practices is crucial for keeping their effectiveness. This entails frequently reviewing and updating hazard management frameworks and methodologies to reflect new insights, technology, and regulatory necessities. Organisations must adopt a comments loop where instructions learned from past hazard incidents are analysed and used to enhance destiny danger assessments. Benchmarking towards industry first-rate practices and incorporating innovations consisting of synthetic intelligence and machine-gaining knowledge can also pressure non-stop improvement.
Training and training for risk assessment teams are essential to building a robust chance control capability. Regular education applications ought to be conducted to ensure that crew contributors are well-versed in modern-day danger evaluation strategies and equipment. These programs should cover theoretical understanding and realistic applications, together with state-of-affairs-based exercises and simulations. Furthermore, fostering continuous knowledge of and improvement in the subculture allows the hazard evaluation team to stay agile and adept at coping with the evolving threat panorama. Investing in expert development and certifications can also increase the team’s expertise and credibility.
Integrating Technology into Risk Management in Professional Services
In the dynamic landscape of professional services, effective risk management is critical to maintaining operational integrity, safeguarding client trust, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Leveraging technology, particularly advanced analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI), has become increasingly essential in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the accuracy and efficiency of risk management processes but also strengthens the overall resilience of professional service firms.
The Role of Advanced Analytics and AI in Risk Management
Leveraging Predictive Analytics to Anticipate Potential Risks
Predictive analytics involves using historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on past patterns. In professional services, predictive analytics can be instrumental in anticipating potential risks before they materialise.
For instance, consulting firms can analyse project data to predict budget overruns, timeline delays, or client dissatisfaction. Legal firms might use predictive models to foresee case outcomes or identify clients at risk of non-compliance. By leveraging predictive analytics, firms can proactively address these issues, implement preventive measures, and allocate resources more effectively, thereby minimising potential disruptions and enhancing service delivery.
Using AI to Identify Patterns and Anomalies That Signal Emerging Threats
Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances risk management by identifying patterns and anomalies that may signal emerging threats. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data in real-time, uncovering insights that human analysis might miss.
In accounting and financial services, AI can detect unusual transaction patterns indicative of fraud or financial irregularities. In the legal sector, AI tools can analyse vast legal databases to highlight precedents or trends that could impact case strategies. By automating the detection of these anomalies, AI not only improves the speed and accuracy of risk identification but also allows professionals to focus on strategic decision-making and client engagement.
Cybersecurity Risk Management
Strategies for Protecting Sensitive Client Data from Cyber Threats
Cybersecurity is a paramount concern in professional services due to the sensitive nature of client data handled daily. Implementing robust cybersecurity strategies is essential to protect this data from breaches, hacks, and other cyber threats.
Key strategies include:
• Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable to unauthorised parties.
• Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to systems.
• Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities and ensures that security measures are up-to-date and effective.
Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Protocols to Prevent Data Breaches
Preventing data breaches requires a comprehensive approach that integrates technology, policies, and training. Professional service firms should develop and enforce cybersecurity protocols that cover all aspects of data handling and system access.
• Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorised personnel can access sensitive data.
• Incident Response Plans: Developing and regularly updating incident response plans enables firms to respond swiftly and effectively in the event of a security breach.
• Employee Training: Continuous training programs ensure that employees are aware of the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices, reducing the likelihood of human error leading to data breaches.
Enhancing Risk Communication and Reporting
Building a Risk-Aware Culture
Creating a risk-aware culture within a professional service firm involves fostering an environment where employees at all levels are vigilant about identifying and reporting potential risks.
Training Employees to Recognise and Report Potential Risks
Training programs should be designed to help employees recognise signs of potential risks, such as unusual client requests, discrepancies in financial records, or compliance concerns. Regular workshops and e-learning modules can reinforce the importance of risk awareness and provide practical guidelines for reporting.
Encouraging a Culture of Transparency and Open Communication About Risks
Encouraging transparency and open communication about risks ensures that potential issues are addressed promptly and effectively. Establishing clear channels for risk reporting, such as anonymous hotlines or dedicated email addresses, allows employees to report concerns without fear of retribution.
Effective Risk Reporting Systems
Developing Comprehensive Risk Reporting Frameworks
A robust risk reporting framework provides a structured approach to documenting, analysing, and addressing risks. This framework should include standardised templates and procedures for reporting distinct types of risks, ensuring consistency and comprehensiveness.
Utilising Risk Dashboards and Real-Time Reporting Tools to Keep Stakeholders Informed
Risk dashboards and real-time reporting tools offer visual representations of risk data, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the current risk landscape and make informed decisions. These tools can provide real-time updates on risk levels, highlight emerging threats, and track the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Navigating Regulatory Changes
Professional service firms must stay abreast of changing laws and regulations to ensure compliance and mitigate associated risks.
Staying Updated with Changing Laws and Regulations Affecting Professional Services
Regularly monitoring regulatory developments and participating in industry forums can help firms stay informed about new and upcoming regulations. Subscribing to legal and regulatory updates or engaging with regulatory consultants can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Implementing Compliance Programs to Ensure Adherence to Regulatory Requirements
Compliance programs should be comprehensive and integrated into the firm’s overall risk management strategy. These programs include policies, procedures, and training designed to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and mitigate compliance risks.
Conducting Regular Compliance Audits
Establishing Procedures for Internal and External Compliance Audits
Regular compliance audits, both internal and external, are essential for verifying that the firm’s practices align with regulatory standards. Internal audits provide ongoing monitoring, while external audits offer an objective assessment of compliance efforts.
Using Audit Findings to Improve Risk Management Practices and Mitigate Potential Regulatory Risks
Audit findings should be used to identify areas for improvement and implement corrective actions. By addressing audit recommendations promptly and thoroughly, firms can enhance their risk management practices and reduce the likelihood of regulatory breaches.
The Bottom Line
Concisely, risk management includes deploying comprehensive techniques encompassing preventative measures and responsive moves in every professional service. These smart techniques regularly include thorough history checks, non-stop education programs, and sturdy internal controls. In addition, by fostering a lifestyle of hazard recognition, corporations can highly prepare their groups to manage unexpected challenges and reduce the probability of career disruptions quite easily.

Case Study
In a significant case study, a prominent consulting firm, StrategyPlus, faced substantial risk management challenges while advising a multinational manufacturing client. The client was undergoing a major global expansion, which introduced risks related to supply chain disruptions, regulatory compliance, and financial volatility.
To address these risks, StrategyPlus implemented a comprehensive risk management strategy. First, they conducted a thorough risk assessment to identify potential internal and external threats. This included detailed analyses of the client’s supply chain vulnerabilities, regulatory landscapes in new markets, and financial exposure.
StrategyPlus developed a risk mitigation plan that focused on several key areas:
1. Supply Chain Resilience: They advised the client to diversify suppliers and establish contingency plans to manage potential disruptions. This included identifying alternative suppliers and creating buffer inventories.
2. Regulatory Compliance: The consulting firm provided a compliance roadmap tailored to each new market, ensuring that the client met local regulations and avoided legal pitfalls. This involved training for local staff and regular compliance audits.
3. Financial Stability: StrategyPlus helped the client implement robust financial risk management practices, such as hedging strategies to protect against currency fluctuations and financial stress testing to evaluate the impact of various economic scenarios.
By closely monitoring these areas and maintaining open communication channels, StrategyPlus enabled the client to proceed with their expansion confidently. The proactive risk management approach not only mitigated potential risks but also enhanced the client’s strategic decision-making capabilities, leading to a successful global expansion.

Exercise 1: Risk Identification Workshop
1. Scenario Setup: Present a hypothetical project (e.g., a large-scale IT implementation).
2. Group Work: Divide participants into small groups and provide them with categories such as operational, financial, regulatory, and strategic risks.
3. Identification: Each group lists potential risks within their assigned category.
4. Discussion: Reconvene and discuss the identified risks, encouraging each group to explain their reasoning and how they categorised the risks.
5. Prioritisation: As a whole group, prioritise the risks based on impact and likelihood. Outcome: Participants improve their risk identification skills and learn to categorise and prioritise risks systematically.
Exercise 2: Risk Mitigation Planning
1. Scenario Setup: Provide a list of risks identified from a previous exercise or a new project scenario.
2. Group Work: Assign each group a specific risk to focus on.
3. Mitigation Strategies: Each group develops a detailed mitigation plan for their assigned risk, including preventive measures and contingency plans.
4. Presentation: Groups present their plans to the entire group, explaining their strategies and rationale.
5. Feedback: Facilitate a discussion to provide feedback and suggestions for improvement. Outcome: Participants learn to create comprehensive risk mitigation plans and understand the importance of proactive planning.
Exercise 3: Risk Monitoring and Reporting
1. Scenario Setup: Assign a project with known risks and a timeline for monitoring.
2. Group Work: Each group is responsible for creating a risk monitoring plan, including key performance indicators (KPIs) and reporting schedules.
3. Simulation: Conduct a simulated project timeline where groups must respond to risk triggers and report their findings and actions taken.
4. Reporting: Groups present their monitoring results and adjustments made during the simulation.
5. Review: Discuss the effectiveness of the monitoring plans and the quality of reporting. Outcome: Participants gain experience in continuous risk monitoring, learn to use KPIs effectively, and improve their risk reporting skills.

Course Manual 9: Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in professional services provides reliable and high-quality services to clients. This practice includes systematic approaches and requirements designed to support experts and corporations. Quality assurance is vital in any domain as it upholds the integrity and credibility of professionals, complements purchaser delight, and mitigates the dangers of malpractice and professional negligence.
Dr. A. Parasuraman, a highly respected academic in the field of marketing and service quality, offers valuable insights into services quality assurance. He is renowned for his work on the SERVQUAL model, which identifies five key dimensions of service quality: tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. Parasuraman emphasises that understanding and managing these dimensions is crucial for ensuring high-quality service delivery.
Parasuraman argues that service quality assurance must start with a clear understanding of client expectations. He suggests that businesses should regularly collect and analyse client feedback to identify gaps between expected and perceived service. This client-centric approach helps organisations pinpoint areas needing improvement.
Furthermore, Parasuraman highlights the importance of employee training and empowerment in quality assurance. Employees must be equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to deliver exceptional service consistently. Empowering employees to make decisions can lead to quicker problem resolution and enhance overall service quality.
Parasuraman also advocates for the implementation of standardised processes and continuous improvement practices. By establishing clear service delivery standards and regularly reviewing performance against these standards, organisations can ensure consistency and identify opportunities for improvement.
In summary, Parasuraman’s insights underscore the importance of a structured, client-focused approach to service quality assurance, incorporating continuous feedback, employee training, and standardised processes to meet and exceed client expectations consistently.
The importance of the best guarantee for specialists lies in maintaining ethical requirements, ensuring compliance with regulations, and promoting continuous improvement in provider transport. It enables building consideration with clients, fosters expert boom, and enhances the general effectiveness of the enterprise.
Ensuring Quality in Professional Services
Quality in professional services refers to the competence, reliability, and ethical standards maintained by experts who turn in their respective services. It encompasses thoroughness in case studies, accuracy in documentation, timely communiques, and customised client care. Quality is critical in professional services because it, without delay, influences client outcomes, pride, and belief. High-quality professional services ensure compliance with legal standards, reduce the likelihood of mistakes, and enhance the standing of provider firms. This, in turn, fosters long-term client relationships and upholds the integrity of these interactions.
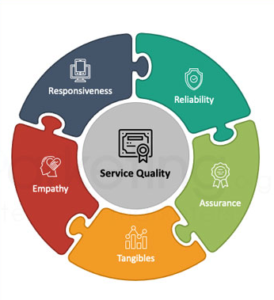
Building Trust through Quality
Consistent Excellence
Providing professional services constantly at a high degree reassures clients of the firm’s reputation. This unwavering dedication to excellence ensures that clients can rely upon your services to meet and exceed their expectations. It fosters long-term relationships, as clients experience security and the information that their needs can always be met with high-quality solutions. Moreover, this dedication to excellence enhances your business enterprise’s reputation, which is due to advantageous word-of-mouth referrals. By continuously delivering professional services, you construct a sturdy basis of trust and loyalty, which is important for maintaining a business boom. The ripple effect of keeping high requirements of excellence extends past client satisfaction, as it additionally motivates your team to uphold these standards, developing a way of life of pleasure and responsibility inside your organisation.
Transparent Processes
Communicating your methods, requirements, and processes establishes client credibility. Transparency demonstrates that your company operates with integrity and is committed to turning in offerings morally and responsibly. Clients recognise how matters are accomplished and are concerned with decision-making processes, which fosters more potent partnerships and mutual knowledge. Being open about your approaches reduces uncertainties and constructs self-assurance in your operations. This openness encourages clients to interact more deeply with your services and is a cornerstone of collaboration between both the organisation and the client.
Responsive Support
Offering prompt and effective support when problems arise displays your willpower to attain client satisfaction and preserve high professional requirements. Responsiveness demonstrates how you value your clients’ time and issues, leading to improved agreement, self-assurance, and potential to navigate demanding situations successfully. Quick and in a position to help ensure that issues are resolved earlier than they can improve, minimising disruptions to the client’s operations. This proactive method now needs to be the handiest to address immediate problems. However, it also indicates your dedication to long-term purchaser success. By prioritising responsive support, you show that you are dependable and attentive, reinforcing the client’s choice to choose your services. This care and attention to detail can reinforce client loyalty and encourage fantastic referrals, increasing business.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly updating and enhancing your services indicates a determination to stay current, adapt to converting needs, and preserve high fine standards. Continuous development demonstrates a proactive method to address demanding situations, embrace innovation, and deliver client fees. By constantly looking for ways to refine your offerings, you show clients that you are devoted to their evolving needs and invested in supplying first-class, valuable services. This dedication to innovation meets clients’ expectations and often exceeds them, putting your firm on a higher footing in a competitive marketplace. Continuous improvement fosters a subculture of excellence inside your team, encouraging creativity and problem-solving. This determination to evolve and enhance your offerings ensures that you remain relevant and valuable for your clients, driving longer-term success and client loyalty.

Key Elements of Quality Service Delivery
Quality assurance transport hinges on the following key elements: accuracy and reliability, timeliness and responsiveness, professionalism, and ethical standards. Accuracy and reliability ensure that services are introduced correctly and consistently, fostering belief and dependability. Timeliness and responsiveness cope with the need for prompt and efficient service, improving client pleasure by swiftly meeting expectations. Professionalism and ethical standards uphold the integrity and admiration of the carrier issuer, ensuring that interactions are conducted with courtesy, honesty, and duty.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Quality control in professional services ensures that the project meets established standards and client expectations. It involves systematic procedures for reviewing and enhancing the quality of peer reviews, audits, and performance evaluations to identify and correct errors in output documentation. Key factors encompass well-known running methods, client feedback, ongoing training, and advanced generation and tools. Implementing these measures facilitates holding exacting standards of accuracy, consistency, and professionalism, leading to extra client delight and acceptance as true.
Effective Quality Control Techniques
Effective quality control techniques are important for maintaining exacting standards in any corporation. Regular audits and opinions help perceive discrepancies and regions for development, ensuring compliance with established protocols. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) offer clear, step-by-step commands to maintain consistency and fine across all techniques. Checklists and documentation also decorate excellent control by imparting a systematic manner to affirm that each major step is finished successfully and that nothing is disregarded. Together, these strategies create a sturdy framework that helps continuous improvement, reduces errors, and ensures the shipping of brilliant services or products.
Role of Technology in Quality Control
Technology plays a pivotal position in modern control techniques. Software devoted to best management enables corporations to systematically music, examine, and enhance their services or products. It centralises facts, streamlines workflows, and complements team collaboration to improve performance and accuracy in identifying and addressing high-quality troubles. Automation, in addition, lowers human error, increasing the velocity of inspections and checks, and supplying real-time tracking of processes and methods.
Continuous Improvement in Professional Services
Continuous improvement in professional services is an ongoing attempt to enhance strategies, services, and consequences. It involves frequently assessing and refining practices for better performance, exceptional, and client pleasure. This mindset is critical because it guarantees variation to changing policies, technology, and purchaser needs. The benefits encompass elevated productivity, decreased expenses, more client satisfaction, and an aggressive area in a dynamic marketplace. Embracing continuous improvement fosters a tradition of studying, innovation, and excellence, positioning specialists to supply superior services and reap long-term fulfilment.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement includes numerous key strategies to enhance overall performance and meet evolving desires:
1. Feedback loops and consumer surveys gather insights without delay from stakeholders, figuring out areas for refinement and innovation.
2. Professional development and education empower groups with updated competencies and knowledge, fostering adaptability and increase.
3. Benchmarking and overall performance metrics offer quantifiable goals and comparisons, driving performance and excellence through fact-driven choice-making.
Together, those techniques create a dynamic cycle of studying, variation, and development, ensuring companies live aggressively and are conscious of converting environments.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Creating a lifestyle of continuous development entails encouraging innovation amongst group contributors and fostering a good environment. Rewarding fine and excellence further reinforces this lifestyle, motivating individuals to strive for the first-rate in their paintings.
Leadership plays a vital role in this manner by setting clear expectations, providing assets for development, and championing a mindset of boom and getting to know. By actively supporting and selling those values, agencies can cultivate a dynamic, forward-thinking culture targeted at persistent development and achievement.
Enhancing Client Communication in Quality Assurance
In the realm of professional services, ensuring quality assurance is pivotal for maintaining client trust and delivering exceptional service. Effective client communication is a cornerstone of this process, enabling firms to meet and exceed client expectations consistently. This comprehensive approach to communication encompasses clear strategies, the use of data analytics, and strong leadership commitment to quality.
Clear and Effective Communication Strategies
Techniques for Clear and Concise Client Communication
Clear and concise communication is essential in professional services to convey complex information efficiently. Techniques include:
1. Simplifying Technical Jargon: Translating technical terms into layperson’s language helps clients understand the services provided.
2. Structured Communication: Organising information logically, starting with the most critical points, ensures clarity.
3. Feedback Mechanisms: Encouraging client feedback and addressing it promptly helps refine communication practices.
Importance of Active Listening in Understanding Client Needs
Active listening is crucial for understanding client needs and building strong relationships. This involves:
1. Full Attention: Giving clients undivided attention during conversations.
2. Reflective Listening: Paraphrasing what the client has said to confirm understanding.
3. Non-Verbal Cues: Observing body language and tone to gauge client emotions and responses.
By practising active listening, professional service firms can tailor their services more precisely to meet client expectations.

Managing Client Expectations
Setting Realistic Expectations from the Outset
Establishing realistic expectations at the beginning of a project is fundamental to preventing misunderstandings and dissatisfaction. This can be achieved by:
1. Detailed Proposals: Providing comprehensive proposals that outline scope, timelines, costs, and deliverables.
2. Transparent Communication: Being honest about potential challenges and limitations.
3. Mutual Agreement: Ensuring both parties agree on the project’s objectives and deliverables.
Regular Updates and Transparency in Service Delivery
Maintaining regular updates and transparency throughout the service delivery process fosters trust and keeps clients informed. Effective methods include:
1. Progress Reports: Sending regular updates on project milestones and any changes in scope.
2. Open Channels: Establishing clear lines of communication for clients to voice concerns or ask questions.
3. Real-Time Dashboards: Using digital tools to provide clients with real-time access to project status.
This ongoing communication helps manage client expectations and addresses issues promptly, enhancing client satisfaction.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Quality Assurance
Using Data to Monitor Service Quality
Implementing data analytics is vital for tracking and improving service quality. This involves:
1. Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various touchpoints within the service delivery process.
2. Analysis Tools: Using analytics software to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
3. Performance Reviews: Regularly reviewing data to assess service quality and make informed decisions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Quality Assurance in Professional Services
Defining and monitoring KPIs is essential for maintaining high-quality standards. Key KPIs include:
1. Client Satisfaction Scores: Measuring client feedback and satisfaction levels.
2. Service Delivery Timeliness: Tracking adherence to project timelines.
3. Error Rates: Monitoring the frequency and severity of service errors or issues.
These KPIs provide a quantitative basis for evaluating and improving service quality.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Quality Management
Predictive analytics can foresee potential quality issues and enable proactive management. Steps include:
1. Historical Data Analysis: Using past performance data to predict future outcomes.
2. Risk Identification: Identifying potential risks and quality issues before they occur.
3. Proactive Measures: Implementing strategies to mitigate identified risks based on predictive insights.
By leveraging predictive analytics, firms can stay ahead of potential problems and maintain high service standards.
The Role of Leadership in Quality Assurance
Leadership Commitment to Quality
Leadership plays a crucial role in embedding quality assurance within an organisation. Key aspects include:
1. Setting Standards: Leaders must establish clear quality standards and expectations.
2. Resource Allocation: Providing the necessary resources and tools to meet quality objectives.
3. Leading by Example: Demonstrating commitment to quality through their actions and decisions.
Developing a Quality-Focused Leadership Culture
Creating a culture that prioritises quality requires consistent effort from leadership. This involves:
1. Quality Training: Regular training sessions to keep staff updated on quality standards and practices.
2. Open Dialogue: Encouraging open discussions about quality issues and solutions.
3. Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledging and rewarding employees who demonstrate excellence in quality assurance.
Training and Empowering Teams
Leadership’s Role in Continuous Training and Development
Continuous training is essential for maintaining high-quality standards. Leadership should:
1. Identify Training Needs: Regularly assess the skills and knowledge gaps within the team.
2. Provide Training Opportunities: Offer workshops, courses, and other learning opportunities.
3. Encourage Lifelong Learning: Foster a culture where continuous improvement and learning are valued.
Empowering Employees to Uphold and Improve Quality Standards
Empowering employees involves giving them the authority and tools to maintain and enhance quality. This can be achieved by:
1. Decision-Making Authority: Allowing employees to make decisions that impact service quality.
2. Access to Resources: Ensuring employees have access to the necessary resources and information.
3. Supportive Environment: Creating a work environment that encourages innovation and quality improvement.
Conclusion
Quality assurance in professional services is paramount. It is achieved via competence critiques, defining requirements, embracing client fulfilment, studying felony procedures, fortifying structural pillars, and advancing through studies – quality is a journey, not a destination.
Quality assurance guarantees in professional services are paramount because of their profound impact on clients and their outcomes. The article delves into the essential aspects of quality assurance, highlighting several key factors.
Firstly, ensuring accuracy and reliability in professional documentation and recommendations is critical. Errors or inconsistencies can jeopardise consumer trust. Secondly, keeping compliance with standards and moral guidelines is non-negotiable. Adhering to these standards now upholds expert integrity and mitigates risks.
Additionally, the article emphasises the importance of continuous development in professional services. Implementing feedback mechanisms, accomplishing everyday audits, and investing in ongoing education and improvement is crucial for fostering a tradition of first-rate. This way of life now advantages clients and enhances general operations’ effectiveness and efficiency.

Case Study
Background: GlobalConsult, a leading management consulting firm, faced challenges in maintaining consistent service quality across its international offices. Clients reported variability in service delivery, leading to concerns about the firm’s overall reliability and client satisfaction.
Implementation of Quality Assurance Program: To address these issues, GlobalConsult implemented a comprehensive Quality Assurance (QA) program. The program focused on three key areas: standardisation of processes, employee training, and client feedback mechanisms.
1. Standardisation of Processes: GlobalConsult developed a set of standardised procedures and best practices for project delivery. These standards were documented in a comprehensive manual accessible to all employees. Regular audits were conducted to ensure compliance with these standards across all offices.
2. Employee Training: The firm invested in extensive training programs for consultants at all levels. This included both initial onboarding and continuous professional development focused on the firm’s quality standards, client service skills, and industry-specific knowledge.
3. Client Feedback Mechanisms: To continuously improve service quality, GlobalConsult introduced a structured client feedback system. After each project, clients were asked to provide detailed feedback on various aspects of the service. This feedback was systematically analysed and used to identify areas for improvement.
Outcomes: The QA program led to significant improvements in service consistency and client satisfaction. The standardised processes ensured that clients received the same elevated level of service regardless of the office location. Enhanced training programs equipped consultants with the skills needed to meet client expectations effectively. The feedback system allowed for timely adjustments and continuous improvement.
Conclusion: GlobalConsult’s QA program successfully addressed service variability, leading to higher client satisfaction, and strengthening the firm’s reputation for reliability and excellence in service delivery.

Exercise 1: Process Standardisation Workshop
1. Scenario Setup: Select a common service provided by the firm (e.g., project management).
2. Group Work: Divide participants into small teams and assign each team a phase of the service process (e.g., initiation, planning, execution, closure).
3. Process Mapping: Each team maps out the detailed steps, tools, and best practices for their assigned phase.
4. Discussion: Teams present their process maps to the entire group. Facilitate a discussion to refine and integrate these maps into a comprehensive, standardised process.
5. Documentation: Compile the standardised process into a manual or guide for company-wide use. Outcome: Participants develop a thorough understanding of standardised processes and contribute to creating consistent service delivery guidelines.
Exercise 2: Quality Assurance Simulation
1. Scenario Setup: Create a realistic project scenario with potential quality issues (e.g., inconsistent client communications, missed deadlines).
2. Role Play: Assign roles to participants, such as project manager, QA specialist, and client.
3. Simulation: Run the project scenario, having participants identify and address quality issues using QA techniques such as audits, feedback loops, and corrective actions.
4. Debrief: After the simulation, discuss what quality issues were identified, how they were resolved, and what could be improved. Outcome: Participants gain firsthand experience with QA processes, enhancing their ability to identify and address quality issues in real projects.
Exercise 3: Client Feedback Analysis
1. Scenario Setup: Provide participants with anonymised client feedback data from previous projects.
2. Group Work: Divide participants into small groups and assign each group a set of feedback data.
3. Analysis: Each group analyses their feedback to identify common themes, strengths, and areas for improvement.
4. Presentation: Groups present their findings and suggest specific actions to improve service quality based on the feedback.

Course Manual 10: Client Empowerment
Client empowerment in professional services serves as a cornerstone for building, considering, and cultivating enduring relationships among providers and clients.
Dr. Richard L. Oliver, a renowned expert in service management and professor at Vanderbilt University, offers valuable insights into client empowerment in professional services. He emphasises that client empowerment is crucial for fostering a sense of ownership and partnership in the service delivery process. Dr. Oliver states, “Empowering clients transforms the service dynamic, allowing clients to actively participate in decision-making and service customisation. This leads to a more personalised and satisfactory service experience.”
According to Dr. Oliver, client empowerment involves several key elements: providing clients with access to relevant information, involving them in key decisions, and encouraging their feedback and input. This collaborative approach not only enhances client satisfaction but also drives service innovation, as clients contribute unique perspectives and insights.
Dr. Oliver also underscores the importance of setting clear expectations and maintaining open communication to avoid potential misunderstandings. He notes that while client empowerment can lead to more effective and tailored services, it requires a balanced approach where service providers guide and support clients without relinquishing their professional expertise.
In conclusion, Dr. Oliver asserts that client empowerment is a vital strategy for professional services, fostering stronger client relationships, enhancing service quality, and driving continuous improvement through collaborative engagement.
One of the essential aspects of client empowerment is expertise empowerment. This entails equipping clients with important data and insights applicable to their projects or desires. In fields like engineering and management consulting, this may imply teaching clients about technical approaches, enterprise tendencies, and first-rate practices. Criminal and accounting services involve explaining complex legal frameworks or economic concepts clearly and understandably. Similarly, clients benefit from information methodologies, statistics interpretation, and implications for choice-making in scientific research and environmental offerings.
Empowering Clients with Knowledge and Information

Importance of Client Empowerment
Client empowerment refers to giving clients the information, skills, and self-assurance to make knowledgeable selections about their lives or the services they receive. Knowledge is important in empowerment, permitting clients to recognise their alternatives and assert their rights. Empowering clients makes each party’s clients feel better on top of things in their conditions and can actively participate in choice-making, which is the main goal of better outcomes. Service providers also benefit by building agreements, fostering collaboration, and ensuring services meet clients’ needs. Client empowerment complements autonomy, improves outcomes, and strengthens relationships between clients and carrier carriers.
The Role of Information in Building Trust
Information plays a key role in constructing an agreement by increasing transparency. When businesses provide clear and exact facts, clients feel more confident and trusting. Informed clients tend to be happy with offerings as they recognise what to anticipate. Critical statistics for client empowerment include commercial and pricing information, project deliverables and scope, and overall performance metrics. Overall, transparency through information is critical for organising, agreeing with, and ensuring patron empowerment.
Educating Clients about the Services Provided

Comprehensive Service Education
When explaining offerings, readability is fundamental. Avoiding jargon and use of plain language enables clients to understand better. Use tools like visual aids, easy diagrams, and examples to make standards clean. Online resources such as movies, infographics, and FAQs also can be powerful for consumer education. Overall, the aim is to speak in a way everyone can without difficulty hold close, ensuring higher information and appreciation of the services provided.
Ongoing Communication and Updates
Ongoing conversations and updates are critical in client service. Regular progress reports and updates assist in keeping clients knowledgeable about the status of their initiatives or offerings. Email, phone calls, or committed client portals can do this. Feedback loops are similarly vital in training, permitting college students to recognise their strengths and areas for development. Educators can offer comments through assessments, discussions, and interactive classes, fostering continuous knowledge of and increase. Effective conversation and remarks mechanisms ensure transparency, collaboration, and hit effects in each professional service and training.
Leveraging Technology for Client Education
Digital platforms empower purchaser schooling by supplying online sources, webinars, and interactive resources. These resources enhance understanding, foster engagement, and facilitate clean admission to facts. For instance, interactive apps provide customised knowledge of reviews, even as webinars provide real-time discussions.
Building Client Confidence through Empowerment
The Connection between Knowledge and Confidence
When clients feel informed, they take advantage of a sense of management and self-belief. Knowing the information empowers them, decreasing uncertainty and tension. For example, a property owner who understands their coverage feels more assured during a claim process. Likewise, patients who study their health situations are more confident during medical discussions. This connection between knowledge and self-belief is profound. It suggests that sharing records is not information; it empowers people to navigate existence’s complexities with assurance and poise.
Strategies for Boosting Client Confidence
1. Tailor services to client wishes: Customise offerings to shape personal choices and requirements.
2. Foster active participation in decisions: Involve clients in choice-making methods to empower them and boost confidence.
3. Ensure smooth access to sources: Provide tools and data to aid clients effortlessly in their journey.
4. Personalise services: Show attentiveness by adapting services to clients’ specific situations, making their experience valued and understood.
5. Encourage client involvement: Empower clients by encouraging them to take an energetic position in shaping their experience.
6. Provide supportive assets: Offer additional help, including instructional materials or guidance, to lessen uncertainty and build belief.
Measuring and Enhancing Client Confidence
Assessing client satisfaction levels entails using tools like surveys, interviews, and feedback materials. These techniques help gauge purchaser pleasure and belief in your services or offerings. Continuous improvement and empowerment are accomplished via everyday education classes, supplying guide sources, and imparting personalised guidance.
These efforts empower clients in their decision-making procedures and movements, enhancing their basic enjoyment. Feedback from delighted clients who have benefited from your offerings can highlight how their confidence and empowerment have grown because of your assistance.
Their testimonials serve as treasured evidence of the effectiveness of your techniques in constructing agreements with and empowering clients to make informed selections. Through techniques, groups can create an effective surrounding in which clients feel confident and empowered in their interactions and selections.
Enhancing Client Participation in Service Design
In the competitive landscape of professional services, client participation in service design is critical for achieving high levels of client satisfaction and loyalty. Engaging clients in the service development process ensures that their specific needs and preferences are met, leading to more tailored and effective solutions. Here is how to enhance client participation in service design.
Collaborative Service Customisation
Involving Clients in Service Development
One of the most effective ways to tailor services to clients’ needs is to involve them directly in the service development process. This can be achieved through various means, such as joint workshops, design thinking sessions, and co-creation activities. These collaborative efforts allow clients to contribute their insights and preferences, ensuring that the final product aligns closely with their expectations.
For example, in management consulting, clients can be invited to participate in strategy sessions where they share their unique business challenges and goals. This involvement helps consultants design customised strategies that are more likely to succeed because they are rooted in the client’s actual needs and circumstances.
Feedback-Driven Improvements
Continuous improvement is essential in professional services. By systematically gathering and analysing client feedback, service providers can identify areas for enhancement and implement changes that drive better results. This feedback can be collected through regular check-ins, satisfaction surveys, and post-project reviews.
For instance, legal firms can hold quarterly feedback sessions with clients to discuss ongoing cases and gather suggestions on improving communication and service delivery. By acting on this feedback, legal professionals can enhance their service quality, leading to increased client trust and satisfaction.
Tools for Client Involvement

Surveys and Focus Groups
Structured surveys and focus groups are valuable tools for gaining detailed insights into client needs and preferences. Surveys can be distributed online, allowing clients to provide feedback at their convenience. Focus groups, on the other hand, offer a more interactive setting where clients can discuss their experiences and suggestions in depth.
In architectural services, for example, conducting focus groups with key stakeholders during the design phase can uncover specific functional requirements and aesthetic preferences. This direct input helps architects design buildings that better meet client expectations, enhancing the overall project success.
Beta Testing and Pilot Programs
Allowing clients to participate in beta testing and pilot programs is another effective way to involve them in service development. These programs enable clients to experience new services or features before they are fully implemented, providing valuable feedback that can be used to make final adjustments.
For instance, a software development firm might launch a beta version of a new application to a select group of clients. These clients can then provide feedback on usability, functionality, and overall satisfaction, allowing the firm to refine the product before its official release.
Developing Client Self-Service Capabilities
Empowering clients with self-service capabilities is a growing trend in professional services. It offers numerous benefits, including increased convenience for clients and reduced workload for service providers.
Empowering Clients with Self-Service Options
Client Portals
Creating secure online portals is a powerful way to enhance client empowerment. These portals provide clients with easy access to their account information, project updates, and relevant documents. Clients can track progress, manage their accounts, and even make payments through these portals, providing a seamless and convenient experience.
In the accounting sector, for example, a client portal can allow clients to upload financial documents, view their tax filings, and communicate directly with their accountants. This transparency and accessibility foster a stronger client-provider relationship and streamline service delivery.
Automated Support Tools
Implementing automated support tools, such as chatbots and AI-driven systems, can provide clients with immediate assistance and answers to common queries. These tools are available 24/7, ensuring that clients receive timely support even outside regular business hours.
In the legal industry, a chatbot can be used to answer frequently asked questions about legal processes, document requirements, and case statuses. This not only improves client satisfaction by providing instant support but also frees up valuable time for legal professionals to focus on more complex tasks.
Benefits of Self-Service
Increased Convenience
Self-service options offer clients the flexibility to resolve issues and obtain information on their own schedule. This convenience is particularly valuable for busy professionals who may not have time to contact service providers during standard business hours.
For instance, in engineering consulting, a client portal can allow clients to access project updates and technical documents whenever they need them, without having to wait for responses from the consulting team. This level of accessibility enhances the client experience and satisfaction.
Reduced Workload for Service Providers
By offloading routine queries and tasks to self-service platforms, service providers can free up their professional resources to focus on more complex and value-added activities. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the overall quality of service delivery.
In the field of environmental consulting, for example, automated systems can handle routine data collection and reporting, allowing consultants to dedicate more time to analysing data and developing strategic recommendations. This shift in focus leads to better client outcomes and stronger professional relationships.

Case Study: Successful Client Empowerment in Action
Client Overview
Our client is one of North America’s biggest superior carriers of fuel, lubricants, and chemical compounds to the Energy, Marine, Mining, and Industrial markets. Facing demanding situations, including immoderate turnover, inefficient approaches, and a loss of organisational structure, they sought to streamline operations and enhance average performance whilst containing expenses.
Business Challenges Faced
The consumer’s demanding situations have been multifaceted, inclusive of:
1. Resignation of a dedicated Accounting Manager leading to a lack of supervision and reduction in controls.
2. Unskilled assets and a lack of organisational shape affect typical efficiency.
3. Client gadget conversion from SAP to Sage, necessitating a seamless transition.
Approach to Virtual Accounting Talent
Our crew completed a complete evaluation of the consumer’s strategies and crew dynamics, figuring out key areas for improvement. We targeted streamlining methods, improving performance, and reallocating assets for strategic tasks. Our method included:
1. Lockbox Automation: Establishing a database for purchaser banking data to streamline transactions.
2. Improved Handling Time in Cash Posting: Reducing posting time from 2-plus days to identical-day posting.
3. Migration Success: Assisting with transitioning from SAP to Sage, ensuring smooth operations among structures.
4. Team Flexibility: Scaling resources primarily based on transaction volumes, ensuring well-timed invoice processing.
5. Completed Projects: Clearing backlog on Document Indexing, ensuring ordinary updates and efficiency in billing techniques.
Results and Achievements
Through our partnership, the client achieved large milestones and upgrades:
1. Cost Containment: Our solutions helped the patron reduce charges and reallocate assets effectively.
2. Efficiency Gains: Streamlined techniques brought about stepped-forward performance, with reduced handling times and faster transaction turnaround.
3. Successful System Migration: Smooth transition from SAP to Sage, minimising disruptions and ensuring continuity of operations.
4. Flexibility and Scalability: Our group’s potential to scale based on transaction volumes ensured steady overall performance, even during top intervals.
5. Clearing Backlogs: Addressing backlog troubles and organising green file indexing approaches.
6. Strategic Focus: Our solutions freed up time for the purchaser to be aware of strategic tasks and boom initiatives.
Outlook
Looking beforehand, we retain to assist the purchaser’s accounting wishes, supplying ongoing efficiency enhancements, scalability, and strategic steerage. Our partnership has advanced from crisis control to long-term strategic assistance, using organic increase and operational balance.
Tasks Managed
Our team manages a range of tasks for the patron, including billing, buybacks, and money owed payable. With a group of eleven participants, we deal with 2 hundred-2,500 volumes each month and ensure efficient and accurate accounting processes.
Conclusion
Our virtual accounting solutions have empowered our purchasers within the logistics enterprise to conquer demanding situations, enhance performance, and attain price financial savings. By leveraging our expertise, the patron has experienced tangible advantages and can now recognise strategic priorities for sustained growth and fulfilment.
The Bottom Line
Briefly, client empowerment is crucial in professional services because it fosters belief, complements collaboration, and results in better results. To empower clients, experts should be cognisant of teaching them their alternatives, supplying clear records about offerings, and regarding them in selection-making strategies. Building their self-assurance via energetic listening, clear communication, and ongoing support is also a key position. By empowering clients with understanding and sources, experts can create meaningful partnerships that result in extra knowledgeable picks and more pleasure for each person involved.
Furthermore, client education is another vital element. By offering clients complete information on processes, alternatives, and ability results, specialists permit them to make informed decisions. This transparency no longer fosters acceptance as true but results in more powerful collaboration and problem-solving. Empowered clients are extra engaged, happy, and likely to increase lengthy-term relationships with carrier providers. They are empowered to participate actively in decision-making, leading to greater success effects and mutual advantages.

Case Study: Deloitte’s Client Empowerment Initiative
Deloitte, one of the leading professional services firms, implemented a client empowerment initiative to enhance service delivery and client satisfaction. The initiative, called “Deloitte Client Connect,” aimed to involve clients more deeply in the consulting process, ensuring their needs and perspectives were integral to the service outcomes.
Background
Deloitte recognised that traditional consulting models often left clients feeling sidelined and disengaged. To address this, Deloitte launched Client Connect, a program designed to enhance transparency, collaboration, and client involvement.
Implementation
Deloitte provided clients with access to a digital platform that offered real-time project updates, data analytics, and collaborative tools. Clients were invited to participate in regular strategy meetings, decision-making processes, and feedback sessions. Deloitte consultants also conducted workshops to educate clients on relevant methodologies and industry trends, empowering them to make informed decisions.
Outcomes
The initiative led to a significant increase in client satisfaction and project success rates. Clients reported feeling more valued and informed, resulting in stronger trust and loyalty towards Deloitte. Furthermore, the collaborative approach fostered innovation, as client insights and feedback helped tailor solutions more closely to their specific needs.
Conclusion
Deloitte’s Client Connect demonstrates the positive impact of client empowerment in professional services. By involving clients as active partners, Deloitte not only improved service outcomes but also strengthened client relationships and trust, highlighting the effectiveness of a collaborative service model.

Exercise: Enhancing Client Empowerment in Professional Services
1. Form Teams: Divide participants into small teams of 3-4 members.
2. Client Scenario: Each team is assigned a client scenario. For example, a client in the financial sector seeking advisory services for a merger.
3. Identify Empowerment Opportunities:
o Brainstorm: List potential ways to involve the client in the service process. Consider information sharing, decision-making, feedback, and collaboration opportunities.
o Discussion Points:
– What information can be shared with the client to enhance transparency?
– How can the client be involved in key decisions?
– What methods can be used to gather and incorporate client feedback?
– How can the service process be adjusted to accommodate client collaboration?
4. Develop an Empowerment Plan:
o Action Items: Outline specific actions to implement client empowerment strategies.
o Roles and Responsibilities: Assign roles within the team to ensure each aspect of the plan is covered.
o Timeline: Create a timeline for implementing the empowerment strategies.
5. Presentations: Each team presents their empowerment plan to the group. Highlight the expected benefits for the client and the service provider.
6. Feedback and Discussion:
o Group Feedback: Other teams provide constructive feedback on the presented plans.
o Discussion: Facilitate a discussion on the potential challenges and solutions for implementing client empowerment strategies.

Course Manual 11: Transparency in Processes
Thomas H. Davenport on Transparency in Business Processes
Thomas H. Davenport, in his book Process Innovation, emphasises the crucial role of transparency in enhancing business processes. He explains that transparent processes are key to improving operational efficiency and fostering trust within organisations. Davenport asserts that transparency enables better analysis, standardisation, and continuous improvement. By leveraging information technology, companies can achieve higher transparency, ensuring accurate data flow and informed decision-making. This approach enhances internal communication and collaboration, fostering a more agile business environment. Transparent processes help identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement, driving competitive advantage and operational excellence.
Michael Hammer on Transparency in Business Processes
Michael Hammer, a pioneer in business process reengineering, underscores the importance of transparency for significant performance improvements. In his influential book Reengineering the Corporation, Hammer advocates for clear and open processes to eliminate inefficiencies and enhance communication across all organisational levels. He argues that transparency helps identify and eliminate redundant activities, align operations with strategic goals, and foster continuous improvement. Transparent processes enable higher accountability and trust, both internally and with external partners. Hammer’s approach focuses on radically redesigning business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in cost, quality, service, and speed. By adopting transparent processes, organisations can better manage resources, reduce waste, and respond more effectively to market changes, leading to sustained competitive advantage and stronger business relationships. For more insights, refer to Hammer’s work on business process reengineering in Reengineering the Corporation.
These perspectives from Davenport and Hammer underscore the importance of transparency in business processes, highlighting how it can drive efficiency, trust, and competitive advantage in organisations.
Transparency in professional services like engineering and management consulting services, legal and services accounting, scientific and environmental research services, architectural and surveying services, advertising and market research services, and others provides reliable and high-quality services to clients. It is crucial to build acceptance and ensure assembly expectations are met. Key regions to pay attention to include maintaining transparency, sharing specific statistics about services, and speaking techniques. Hence, clients recognise what to anticipate and accept it as true through consistent openness. By doing so, professional services can enhance client satisfaction and foster long-term relationships.
Significance of Transparency in Professional Services
Transparency in professional services means being open, sincere, and clear with clients. This includes clean communication regarding charges, tactics, and capacity outcomes. Transparent practices involve sharing all relevant statistics, being prematurely aware of barriers, and providing regular updates. For instance, a transparent legal professional explains their fees and informs the clients about the case’s progress. Conversely, non-obvious practices involve hidden prices, withholding valuable information, or failing to speak frequently. Transparency builds trust and guarantees clients understand what to expect, fostering better relationships and effective service delivery.
Benefits of Transparency
Transparency is a cornerstone of successful enterprises and relationships, supplying many benefits and contributing to long-term and superior results. Here are a few extra factors to expand on the advantages of transparency:
1. Improved Communication: Transparency fosters open verbal exchange channels. When facts flow freely, personnel feel more engaged and are informed about the business enterprise’s desires, techniques, and demanding situations. This leads to better teamwork, collaboration, and, overall, better productivity.
2. Enhanced Decision-Making: Transparent companies empower personnel in any respect degrees to make informed choices. When people have the right to access applicable facts and insights, they can make a meaningful contribution to choice-making tactics. This improves the best of choices and promotes responsibility and possession.
3. Attracts Talent: In the modern-day aggressive task marketplace, transparency can be a key thing in attracting top talent. Potential personnel are frequently drawn to establishments prioritising openness and honesty. It alerts a wholesome work subculture wherein contributions are recognised, and feedback is valued.
4. Risk Management: Transparent practices also play a critical position in chance control. By overtly addressing issues and challenges, businesses can proactively pick out and mitigate dangers before they increase. This proactive technique minimises potential damage and allows for the preservation of stability.
5. Client Loyalty: Transparent conversation with clients builds consideration and loyalty. Clients experience greater confidence in their alternatives whilst organisations are upfront about their merchandise, offerings, pricing, and rules. This leads to repeat commercial enterprise, high-quality reviews, and referrals.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have regulatory requirements concerning transparency and disclosure. Adhering to those requirements ensures criminal compliance and demonstrates integrity and accountable business practices.
7. Innovation: Transparency encourages a culture of innovation. When personnel feel comfortable sharing thoughts and feedback, innovation flourishes. Transparent enterprises often see extra creativity and problem-solving initiatives from their groups.
Maintaining Transparency in Professional Services
Setting Clear Expectations
Setting clear expectations is essential for fulfilment. From the beginning, everyone ought to realise what is anticipated. This avoids confusion and builds trust. To establish mutual expertise, first, speak and clearly. Use written agreements or checklists. Hold conferences every day to speak about progress and any issues.
Additionally, ask for reviews to ensure all are on the same page and repeat key factors to boost expertise. Encourage inquiries to clarify doubts. Set precise, achievable goals and cut-off dates, and by doing this, everyone knows their roles and responsibilities, which is the main goal of higher teamwork and consequences. Finally, clear expectations make the assignment smoother and more efficient.
Consistent Communication
Consistent conversation is key to clients’ happiness. You can schedule weekly or bi-weekly conferences to discuss progress and ensure smoother conversations through e-mail, messaging apps, and video calls. Always spark interest in responding to consumer queries and keep clients informed about any changes or troubles without delay. Encourage open talk and comments; be clear and concise in your messages. Maintain a friendly and professional tone. Consistent communication builds acceptance as true and guarantees that everybody is on the same web page and ends in successful venture effects.
Documentation and Reporting
Keeping designated information on strategies and decisions is critical. It helps tune progress, ensures transparency, and permits easy evaluation. You may share the documentation with clients to keep them informed and involved. With clear and concise facts, construct belief and professionalism, clients recognise the steps to take and why. Good documentation ends in better communique, smoother workflows, and stronger consumer relationships. Therefore, always maintain up-to-date and correct records to aid your endeavours and satisfy clients.
Handling Mistakes and Setbacks
Handling mistakes and setbacks includes honesty and proactive strategies. First, admit mistakes and delays openly. This builds belief and suggests duty. Next, address problems quickly. Identify the problem and create a plan to fix it. Communicate your plan truly to each worried person. Apologise if you want to and explain the steps taken to prevent destiny troubles. Stay high quality and aware of answers. Learn from errors and use them as opportunities for increase. Regularly assess progress and regulate your approach if essential. You can correctly deal with demanding situations and hold sturdy relationships by being transparent and proactive.
Communicating Processes and Methodologies to Clients
Simplifying Complex Information
To simplify complicated records, begin by breaking them into smaller steps. Use easy words and short sentences. Explain one concept at a time and use visuals like charts or diagrams to expose how matters work. Analogies can help, too, by comparing complicated ideas to acquainted ones.
Transparency in Methodology Selection

Choosing a technique is critical in studies. We choose precise methods because their quality suits our desires, facts, and constraints. For example, a survey is selected to collect broad opinions quickly. Alternative approaches, like interviews, should offer deeper insights but take extra time. Each method has strengths and weaknesses. Discussing those helps others apprehend our choices and agree with our outcomes. Exploring alternatives shows we considered other options and apprehended their capacity impacts. This transparency ensures our research is thorough and credible, permitting others to follow or reflect on our work correctly.
Involving Clients in the Process

Involving clients within the decision-making system most effectively fosters a partnership experience; however, it additionally brings tangible benefits to agencies. This collaborative approach transcends the traditional purchaser-provider courting, reworking it into a symbiotic alliance where mutual respect and information thrive.
When clients actively participate in discussions and contribute their thoughts, they convey a fresh perspective, which could lead to progressive solutions. Their insights often stem from a deep knowledge of their desires, possibilities, and pain points, which help refine products or services. Moreover, involving clients instils an experience of ownership and investment in the task or career, enhancing their commitment and satisfaction.
The feedback loop created via purchaser involvement will become a powerful tool for continuous improvement. Businesses can pinpoint regions for enhancement, pick out rising tendencies, and tailor offerings to higher healthy client expectations. This proactive method not only boosts client satisfaction but also strengthens the overall competitiveness of the business in a dynamic market landscape.
Furthermore, involving clients nurtures trust and loyalty. When clients feel heard and valued, they are more likely to expand long-term relationships with the commercial enterprise, becoming advocates who refer others and contribute to logo increase.
Building Trust through Openness
Openness in Client Interactions
In client interactions, openness is key. It is a method of being pleasant and open to any questions or worries they’ve. It also means being ready to share facts openly without preserving them again. This openness facilitates the construction of acceptance as true and fosters a nice relationship with clients. It shows how you price their entry and are transparent in your verbal exchange. Being approachable and willing to foster an environment where clients feel heard and respected leads to higher effects and more potent partnerships.
Ethical Considerations
Ensuring ethical requirements in conversation and movements is important for any organisation. It includes being straightforward, fair, and respectful in dealings with others. Building an environment of honesty and integrity in the enterprise fosters belief among employees, clients, and stakeholders. This way of life encourages transparency, responsibility, and accountable decision-making at all ranges. It additionally facilitates high-quality work surroundings where everybody feels valued and revered. Adhering to moral issues strengthens the corporation’s popularity and contributes to its long-term success and sustainability.
Long-term Relationship Building
Building a true loyal partnership fosters benefits from consistent transparency. Being open and honest with your client builds trust and strengthens your bond. Transparency means openly sharing your thoughts, feelings, and reviews without hiding or manipulating records. This openness creates a safe and supportive environment where both events can grow collectively. Communicating bravely, listening actively, and respecting each other’s obstacles are vital to cultivating a healthy and enduring relationship. By prioritising transparency, you lay the foundation for a strong, lasting connection built on acceptance as true with and mutual information.
Additional Topic Areas for Client Empowerment in Professional Services
Technology Integration for Enhanced Client Engagement
Implementing Client-Centric Technologies
Utilising CRM systems for personalised client interactions: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are indispensable tools for managing client relationships effectively. They help professional service providers keep detailed records of client interactions, preferences, and feedback. By utilising CRM systems, businesses can personalise their communication and tailor their services to meet individual client needs more accurately. This personalisation fosters stronger client relationships and enhances overall client satisfaction.
Adopting mobile applications to provide real-time updates and services: Mobile applications offer clients the convenience of accessing services and updates on the go. For instance, clients can track the progress of their projects, schedule appointments, and receive notifications about important milestones through a dedicated mobile app. This real-time access to information empowers clients by keeping them informed and engaged throughout the service delivery process.
Leveraging AI and Automation
Using AI-driven analytics to offer tailored service recommendations: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can analyse vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that might not be immediately apparent to humans. By leveraging AI-driven analytics, professional service providers can offer clients tailored recommendations that align with their specific needs and preferences. This not only enhances the quality of service but also demonstrates a deep understanding of the client’s unique requirements.
Automating routine tasks to provide faster and more efficient client services: Automation technology can streamline routine administrative tasks, such as scheduling, billing, and data entry. By automating these processes, service providers can reduce the time spent on manual tasks, allowing them to focus more on delivering value-added services. This efficiency translates to quicker service delivery and a better client experience.
Developing Strong Client Feedback Mechanisms
Structured Feedback Systems
Creating formal channels for continuous client feedback: Establishing formal feedback channels is crucial for understanding client needs and improving service quality. These channels can include online feedback forms, suggestion boxes, and dedicated email addresses where clients can share their thoughts and concerns. Continuous feedback helps service providers identify areas for improvement and adapt their services to better meet client expectations.
Conducting regular satisfaction surveys and follow-up interviews to gather detailed insights: Regular satisfaction surveys and follow-up interviews provide deeper insights into client experiences. Surveys can be designed to measure various aspects of service quality, such as responsiveness, professionalism, and overall satisfaction. Follow-up interviews offer an opportunity to explore feedback in more detail, uncovering specific issues that may not be captured in a survey. These insights are invaluable for driving continuous improvement.
Implementing Client Advisory Boards
Establishing advisory boards comprising key clients to guide service improvements: Client advisory boards are groups of key clients who provide strategic advice and feedback on service offerings. These boards can meet regularly to discuss service quality, share their perspectives, and suggest improvements. Involving clients in this way not only empowers them but also ensures that the services are aligned with their needs and expectations.
Engaging clients in strategic planning sessions to align services with their evolving needs: Strategic planning sessions that include client participation can help service providers stay ahead of emerging trends and changing client needs. These sessions allow clients to voice their opinions on the direction of service development and offer insights into future requirements. This collaborative approach helps in designing services that are proactive and responsive to client needs.
Building a Culture of Empowerment within the Organisation

Employee Training and Development
Providing training programs focused on client empowerment and engagement: Training programs that focus on client empowerment and engagement equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to deliver exceptional service. These programs can cover areas such as effective communication, problem-solving, and client relationship management. Well-trained employees are better prepared to meet client needs and foster a culture of empowerment.
Encouraging continuous professional development to enhance service delivery skills: Continuous professional development ensures that employees stay updated with the latest industry trends and best practices. Encouraging ongoing learning and development helps employees improve their skills and adapt to changing client demands. This commitment to professional growth enhances the overall quality of service delivery.
Promoting an Empowerment Mindset
Fostering a culture that values and acts upon client feedback: Creating a culture that values client feedback involves recognising the importance of client input and acting on it. This means not only collecting feedback but also implementing changes based on client suggestions. Such a culture demonstrates to clients that their opinions are valued, and that the organisation is committed to continuous improvement.
Recognising and rewarding employees who excel in client empowerment initiatives: Employee recognition programs that highlight achievements in client empowerment can motivate staff to prioritise client needs. Rewarding employees for their efforts in enhancing client satisfaction and engagement reinforces the importance of client empowerment within the organisation. This recognition can take the form of awards, bonuses, or public acknowledgment, fostering a positive and client-focused work environment.
Conclusion
Transparency is vital in professional services because it fosters agreement and knowledge. It entails clean verbal exchange and honesty, which are essential for building sturdy client relationships. By maintaining transparency, professionals ensure that clients are well-informed and might make informed selections. This results in higher collaboration and more effective results. Cultivating transparent patron relationships brings long-term success, satisfaction, and fantastic popularity. It is a foundation for mutual admiration and trust, growing a win-win scenario for both events.

Case Study: IBM’s Transparent Consulting Approach
Background
IBM, a global leader in IT and consulting services, recognised the need for greater transparency in its business processes to build stronger client relationships and improve service outcomes. The company launched the “Open Consulting” initiative to ensure transparency in its service delivery.
Implementation
IBM implemented several key strategies to enhance transparency:
1. Client Dashboards: IBM developed real-time dashboards that provided clients with comprehensive visibility into project progress, milestones, and resource allocation. These dashboards were accessible 24/7, allowing clients to monitor their projects closely.
2. Regular Updates: The company instituted a policy of regular updates and status reports. Consultants held weekly meetings with clients to discuss progress, challenges, and any changes in project scope or direction.
3. Open Communication Channels: IBM encouraged open communication by setting up dedicated channels for client feedback and inquiries. This ensured that clients could easily reach out to IBM consultants with questions or concerns.
4. Documentation and Transparency: All project documentation, including meeting minutes, decision logs, and financial reports, were shared with clients in real-time. This fostered a culture of openness and trust.
Outcomes
The Open Consulting initiative led to several positive outcomes:
• Increased Client Trust: Clients reported higher levels of trust and satisfaction due to the increased visibility and openness.
• Improved Project Efficiency: Transparency allowed for quicker identification and resolution of issues, leading to more efficient project execution.
• Stronger Relationships: The transparent approach strengthened client relationships, resulting in higher client retention and repeat business.
Conclusion
IBM’s Open Consulting initiative demonstrates the significant benefits of transparency in business processes. By providing clients with clear, real-time access to project information, IBM enhanced trust, improved efficiency, and strengthened client relationships, highlighting the value of transparency in professional services.

Exercise: Enhancing Transparency in Business Processes
1. Form Teams: Divide participants into small teams of 3-4 members.
2. Business Scenario: Assign each team a business scenario, such as a consulting firm working with a large corporate client on a digital transformation project.
3. Identify Transparency Gaps:
o Brainstorm: List potential areas where transparency is currently lacking in the scenario. Consider project reporting, communication channels, decision-making processes, and resource allocation.
o Discussion Points:
What information is critical for the client to have?
How can current processes be modified to enhance transparency?
What tools or technologies can support increased transparency?
4. Develop a Transparency Plan:
o Action Items: Outline specific actions to address the identified transparency gaps. This might include implementing real-time dashboards, setting up regular update meetings, and sharing detailed project documentation.
o Roles and Responsibilities: Assign roles within the team to ensure each aspect of the transparency plan is covered.
o Timeline: Create a timeline for implementing the transparency strategies.
5. Presentations: Each team presents their transparency plan to the group. Highlight the expected benefits for both the service provider and the client.
6. Feedback and Discussion:
o Group Feedback: Other teams provide constructive feedback on the presented plans.
o Discussion: Facilitate a discussion on potential challenges and solutions for implementing transparency strategies.

Course Manual 12: Feedback and Continuous Improvement
The Significance of Feedback in Professional Services
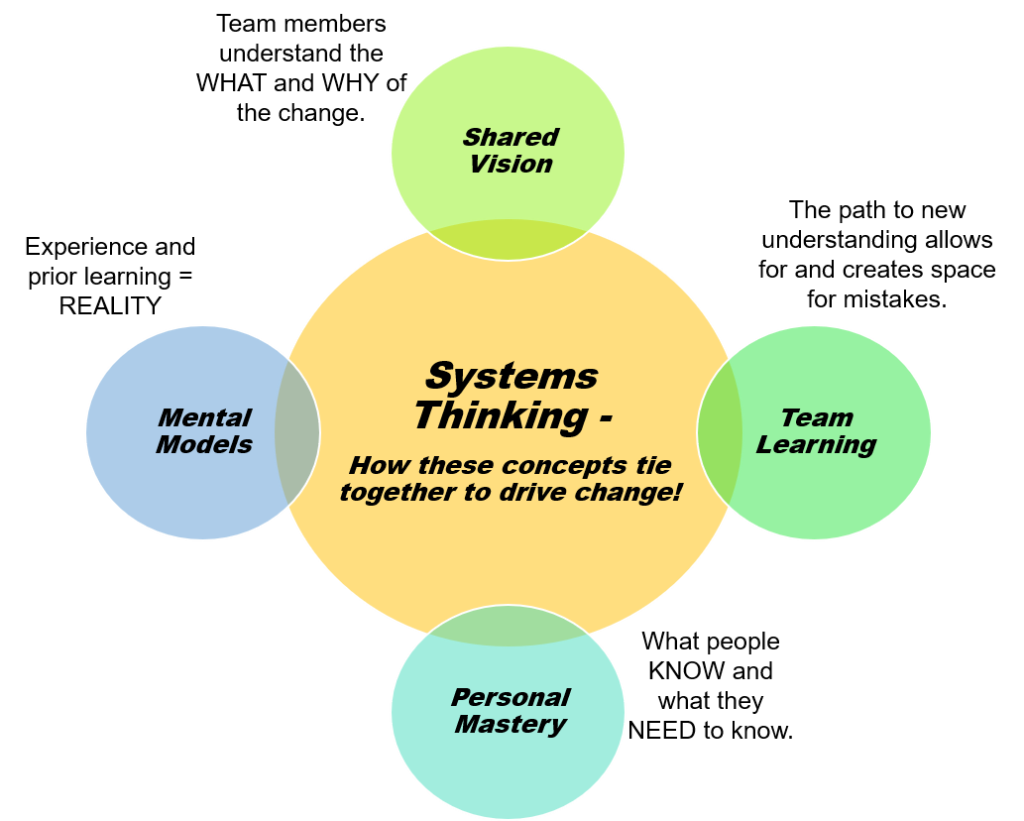
Definition and Importance
In professional services, feedback involves giving comments or suggestions about someone’s work or performance. It helps individuals understand what they are doing well and where they can improve. Feedback is essential for both personal and organisational growth. It aids individuals in learning and developing their skills. For organisations, feedback ensures that employees are on the right track and working effectively. This leads to better performance, high-quality services, and increased employee and client satisfaction. Feedback also fosters a culture of continuous development and open communication.
Impact on Client Satisfaction
Feedback is essential for understanding consumer desires and expectations. When clients share their thoughts, businesses can identify what is working well and what needs improvement. For example, if clients point out areas needing improvement, a firm can leverage these suggestions across all clients. Similarly, if clients praise a particular feature, the business can focus on enhancing it further. Feedback helps groups make informed decisions, leading to better service delivery. By listening to clients, organisations can adapt and provide services that meet or exceed expectations, increasing client satisfaction.
Building Trust through Feedback
Effective feedback builds trust by showing honesty and care. When feedback is clear and useful, it indicates appreciation and a desire to improve together. A transparent approach to sharing all relevant information builds confidence. Accountability means taking responsibility for actions and feedback, showing commitment and reliability. Together, transparency and accountability ensure that feedback is genuine and trustworthy. This creates a trusting environment where individuals feel valued and understood, knowing that feedback is given with their best interest at heart. Consistent, honest feedback fosters mutual respect and trust.
Strategies for Soliciting and Providing Feedback
Techniques for Soliciting Feedback
Gathering feedback is critical for development. Use methods like surveys, interviews, and suggestion boxes. Surveys can reach many people quickly. Interviews allow for detailed, personal insights, and suggestion boxes offer anonymous remarks. Always ask the right questions to get useful information, focus on specific areas, stay clear, and avoid leading questions. This ensures sincere and helpful responses. By regularly reviewing and acting on the feedback, professionals foster a collaborative and supportive environment, leading to great outcomes.
Best Practices for Providing Feedback
Applying models like SBI (Situation-Behaviour-Impact) or the Feedback Sandwich is critical when providing feedback. SBI helps by describing the situation, explaining the behaviour, and detailing the impact. The Feedback Sandwich starts with positive feedback, offers constructive criticism, and ends with more positive comments. Timeliness is important; provide feedback as soon as possible so it is relevant. Be specific about what you observed to avoid confusion. Show empathy to make the person feel understood and supported. These practices ensure feedback is clear, helpful, and encouraging, fostering growth and development.
Overcoming Barriers to Effective Feedback
Common barriers to effective feedback include fear of criticism and lack of time. To overcome these obstacles, start by creating a positive and constructive feedback environment. Encourage open communication and emphasise the importance of feedback for growth. Provide specific examples and focus on behaviours, not personalities. Schedule regular feedback sessions to prioritise giving and receiving feedback. Offer support and guidance for improvement rather than criticism. Addressing these barriers head-on and fostering a culture of feedback can create a more productive and supportive work environment.
Implementing Feedback for Continuous Improvement

Analysing and Interpreting Feedback
Analysing feedback involves looking for patterns and areas needing improvement. Separating actionable feedback (things you can act on) from non-actionable (things beyond control) is crucial. This helps focus efforts effectively. For instance, if many clients mention slow service, it is actionable and prompts faster service techniques. But it is non-actionable if someone dislikes a policy you cannot change. This distinction saves time and resources. By identifying trends and focusing on actionable feedback, groups can continuously improve and meet client needs better.
Developing Action Plans
To create action plans based on feedback, read the feedback for key insights. Identify areas for improvement or change. Then, set SMART goals:
1. Specific: Define clear objectives.
2. Measurable: Establish metrics to track progress.
3. Achievable: Ensure goals are realistic and feasible.
4. Relevant: Align goals with overall objectives.
5. Time-bound: Set deadlines for achievement.
For instance, if feedback suggests enhancing communication skills, a SMART goal could be “Increase weekly team communication by 20% within 3 months.” Regularly review progress and adjust as needed to stay on track.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress
Monitoring and evaluating progress through feedback implementation involves using various strategies to track and measure the impact of changes. One effective method is using surveys, where structured questions are presented to a sample group to gather feedback. Surveys provide quantitative data, making it easy to track trends and identify areas for improvement. Interviews, on the other hand, offer qualitative insights through open-ended questions, allowing for a deeper understanding of feedback. Additionally, observation entails witnessing actions and behaviours to assess progress and implementation.
A comparative analysis is widely used to determine the impact of changes resulting from feedback. This involves comparing data or metrics from before and after implementing feedback-driven changes. For example, if the feedback relates to client service, metrics like customer satisfaction scores or response times can be compared to gauge improvement. Similarly, metrics like production output or error rates can be compared if feedback relates to process efficiency.
Repetition of feedback processes involves regularly reviewing feedback, analysing trends, and adjusting, as necessary. This iterative process ensures that feedback is continuously incorporated into decision-making processes, leading to ongoing improvements and effective implementation. By leveraging these methods and iterative approaches, organisations can effectively monitor progress, measure impact, and optimise their feedback implementation strategies.
Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Leadership and Commitment
Leadership is crucial in fostering a culture of continuous improvement within an organisation. A strong leader sets the tone by encouraging innovation, embracing change, and supporting initiatives that drive progress. They inspire employees to strive for excellence, take calculated risks, and learn from failures to improve continuously.
Commitment from all levels of the organisation is equally important. When everyone is committed to the organisation’s goals and values, they work together towards common objectives. This commitment fosters teamwork, collaboration, and accountability, ensuring that everyone contributes their best efforts to achieve success.
Overall, effective leadership creates an environment where continuous improvement is valued and supported, and commitment from all levels ensures that this culture of improvement is ingrained within the organisation’s DNA, leading to sustained growth and success.
Encouraging a Growth Mindset

To foster a growth mindset among employees, praise effort, not just results. Encourage them to view challenges as opportunities to learn and grow. Provide regular feedback that focuses on progress rather than criticism. Offer training and development opportunities to support continuous learning.
A growth mindset can lead employees to embrace feedback by seeing it as an opportunity for improvement. For example, if someone receives feedback on a project, they may ask for specific areas to work on and actively seek ways to enhance their skills. This mindset fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Similarly, a growth mindset encourages continuous learning by motivating employees to seek new knowledge and skills. They may take on new projects or roles to expand their capabilities, understanding that challenges are opportunities for growth. Overall, this mindset drives innovation and success within the organisation.
Embedding Feedback into Organisational Processes
Embedding feedback mechanisms into regular workflows and performance reviews is essential for organisational growth. This can be achieved by incorporating feedback tools into daily operations, encouraging open communication channels, and emphasising a culture that values feedback. Additionally, regular training and development opportunities are crucial to enhance continuous improvement, as they empower employees to learn from feedback and apply it effectively. By integrating feedback into workflows and providing ongoing learning opportunities, organisations can create a culture of continuous improvement, leading to increased productivity, employee satisfaction, and overall success.
Leveraging Technology for Feedback and Improvement
Digital Tools for Gathering Feedback
In the digital age, leveraging technology to gather feedback has become increasingly important. Implementing digital tools such as online surveys, feedback apps, and client portals can streamline the feedback collection process, making it more efficient and accessible. These tools can provide real-time feedback, allowing organisations to respond promptly and effectively to client needs and concerns.
Online Surveys and Feedback Apps: Online surveys are a quick and efficient way to gather feedback from a large audience. Feedback apps can be integrated into client interactions, providing an easy and convenient way for clients to share their thoughts and experiences.
Client Portals: Client portals offer a centralised platform where clients can provide feedback, track progress, and access relevant information. These portals can enhance transparency and engagement by giving clients direct access to the feedback process.
Data Analytics for Feedback Analysis
Utilising data analytics to analyse feedback can provide valuable insights into client satisfaction and areas for improvement. Advanced analytics can identify patterns and trends in feedback data, helping organisations prioritise and address key issues.
Sentiment Analysis: Sentiment analysis tools can assess the tone and emotion in client feedback, providing a deeper understanding of client sentiment. This can help organisations identify areas of concern and take proactive measures to address them.
Dashboard Visualisation: Data visualisation tools can present feedback data in an easy-to-understand format, such as dashboards. These visual representations can help stakeholders quickly grasp key insights and make informed decisions based on feedback.
Developing a Feedback-Driven Culture
Encouraging Open Communication
Creating an environment that encourages open communication is essential for a feedback-driven culture. This involves fostering a safe space where employees and clients feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and concerns.
Town Hall Meetings and Forums: Regular town hall meetings and forums can provide opportunities for open dialogue and feedback. These sessions can help build a culture of transparency and trust, where feedback is valued and acted upon.
Anonymous Feedback Channels: Providing anonymous feedback channels can encourage more honest and candid feedback. This can be particularly useful for addressing sensitive issues that employees or clients may be hesitant to discuss openly.
Training and Development
 Investing in training and development is crucial for cultivating a feedback-driven culture. Providing employees with the skills and knowledge to give and receive feedback effectively can enhance their ability to contribute to continuous improvement.
Investing in training and development is crucial for cultivating a feedback-driven culture. Providing employees with the skills and knowledge to give and receive feedback effectively can enhance their ability to contribute to continuous improvement.
Feedback Training Workshops: Conducting workshops focused on feedback skills can help employees learn how to provide constructive feedback and how to use feedback for personal and professional growth.
Continuous Learning Opportunities: Offering continuous learning opportunities, such as online courses and seminars, can help employees stay updated on best practices for feedback and continuous improvement.

Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Case Study 1: Engineering Consultancy
An engineering consultancy firm implemented a structured feedback mechanism to gather client insights regularly. By using online surveys and client portals, the firm collected valuable feedback on project performance and client satisfaction. The feedback was analysed using data analytics tools, identifying key areas for improvement. The firm developed action plans based on the feedback, focusing on enhancing communication and project delivery. As a result, client satisfaction increased, and the firm gained a competitive edge in the market.
Case Study 2: Legal Services Firm
A legal services firm recognised the importance of feedback for continuous improvement. The firm established a feedback-driven culture by encouraging open communication and providing anonymous feedback channels. Regular town hall meetings and feedback training workshops were conducted to foster a culture of transparency and trust. The firm also used sentiment analysis tools to assess client feedback and identify areas of concern. By addressing these concerns proactively, the firm improved client relationships and enhanced service quality.
Case Study 3: Environmental Research Services
An environmental research services firm implemented digital tools for gathering and analysing feedback. The firm used online surveys and feedback apps to collect real-time feedback from clients. Data visualisation tools were used to present feedback data in an easy-to-understand format, helping stakeholders make informed decisions. The firm also developed a feedback-driven culture by encouraging open communication and providing continuous learning opportunities for employees. As a result, the firm achieved higher client satisfaction and improved research outcomes.
Additional Topic Areas for Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Feedback Mechanisms
Implementing Client-Centric Technologies:
Utilising CRM systems for personalised client interactions: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are indispensable tools for managing client relationships effectively. These systems help professional service providers maintain detailed records of client interactions, preferences, and feedback. By leveraging CRM systems, businesses can personalise their communication and tailor their services to meet individual client needs more accurately. This personalisation fosters stronger client relationships and enhances overall client satisfaction.
Adopting mobile applications to provide real-time updates and services: Mobile applications offer clients the convenience of accessing services and updates on the go. For instance, clients can track the progress of their projects, schedule appointments, and receive notifications about important milestones through a dedicated mobile app. This real-time access to information empowers clients by keeping them informed and engaged throughout the service delivery process.
Leveraging AI and Automation:
Using AI-driven analytics to offer tailored service recommendations: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can analyse vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that might not be immediately apparent to humans. By leveraging AI-driven analytics, professional service providers can offer clients tailored recommendations that align with their specific needs and preferences. This not only enhances the quality of service but also demonstrates a deep understanding of the client’s unique requirements.
Automating Routine Tasks: Automation can significantly enhance efficiency by handling routine tasks such as scheduling, reminders, and initial client queries. By automating these tasks, professional service providers can free up valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on more complex and value-added activities. This can lead to faster service delivery, reduced errors, and improved client satisfaction.
Developing Strong Client Feedback Mechanisms
Structured Feedback Systems:
Creating formal channels for continuous client feedback: Establishing formal feedback channels, such as dedicated email addresses, online feedback forms, and customer service hotlines, ensures that clients have multiple ways to share their thoughts and concerns. Regularly reviewing and responding to this feedback can help organisations address issues promptly and improve service quality.
Conducting regular satisfaction surveys and follow-up interviews to gather detailed insights: Regular satisfaction surveys and follow-up interviews provide deeper insights into client experiences and expectations. These tools can help organisations identify trends, understand client needs better, and make informed decisions to enhance service delivery.
Implementing Client Advisory Boards:
Establishing advisory boards comprising key clients to guide service improvements: Forming client advisory boards with key clients can provide valuable insights into service quality and areas for improvement. These boards can act as a sounding board for new ideas and initiatives, ensuring that services are aligned with client expectations and industry standards.
Engaging clients in strategic planning sessions to align services with their evolving needs: Involving clients in strategic planning sessions can help organisations understand their evolving needs and preferences. This collaborative approach ensures that services remain relevant and responsive to client demands, fostering long-term relationships and loyalty.
Building a Culture of Empowerment within the Organisation
Employee Training and Development:
Providing training programmes focused on client empowerment and engagement: Training programmes that focus on client empowerment and engagement can equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to build strong client relationships. These programmes can cover topics such as effective communication, active listening, and conflict resolution, ensuring that employees are well-prepared to handle client interactions.
Encouraging continuous professional development to enhance service delivery skills: Continuous professional development is essential for maintaining exacting standards of service delivery. By encouraging employees to participate in workshops, seminars, and certification courses, organisations can ensure that their teams stay updated with the latest industry trends and best practices.
Promoting an Empowerment Mindset:
Fostering a culture that values and acts upon client feedback: Creating a culture that values client feedback and takes it seriously can drive continuous improvement and innovation. Organisations should encourage employees to actively seek and act on client feedback, recognising and rewarding those who excel in this area.
Recognising and rewarding employees who excel in client empowerment initiatives: Recognising and rewarding employees who demonstrate a commitment to client empowerment can reinforce the importance of this approach. By celebrating successes and sharing best practices, organisations can motivate their teams to prioritise client empowerment and engagement.
Conclusion
Feedback and continuous improvement are essential for professional services to thrive in a competitive landscape. By leveraging structured feedback mechanisms, fostering a culture of open communication, and implementing iterative processes, organisations can enhance service quality, boost client satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge. Incorporating technology and promoting a culture of empowerment further strengthens these efforts, ensuring sustained growth and success.

Case Study: Accenture’s Feedback-Driven Improvement Program
Background
Accenture, a global professional services company, recognised the need for a systematic approach to leverage client feedback for continuous improvement. They launched the “Client Insight Initiative” to enhance service delivery and client satisfaction through structured feedback mechanisms.
Implementation
Accenture implemented several strategies to gather and utilise client feedback effectively:
1. Client Feedback Surveys: After key project milestones and upon project completion, Accenture conducted detailed client surveys to capture feedback on various aspects of the service provided, including project management, communication, and deliverables.
2. Regular Review Meetings: Monthly review meetings were established with clients to discuss ongoing project progress, address concerns, and gather real-time feedback. These meetings facilitated open dialogue and immediate action on feedback received.
3. Performance Metrics: Accenture developed a set of performance metrics based on client feedback. These metrics were used to measure service quality and identify areas needing improvement.
4. Feedback Analysis and Action Plans: The collected feedback was systematically analysed to identify common themes and areas for improvement. Action plans were developed to address these areas, with specific timelines and responsibilities assigned.
Outcomes
The Client Insight Initiative led to several positive outcomes:
• Enhanced Service Quality: By systematically incorporating client feedback, Accenture was able to make targeted improvements, leading to higher service quality.
• Increased Client Satisfaction: Clients appreciated the proactive approach to feedback, resulting in higher satisfaction and stronger relationships.
• Continuous Learning and Improvement: The initiative fostered a culture of continuous learning and improvement within Accenture, driving innovation and efficiency.
Conclusion
Accenture’s Client Insight Initiative demonstrates the power of structured feedback and continuous improvement in professional services. By actively involving clients in the feedback process and systematically acting on their insights, Accenture enhanced service delivery, strengthened client relationships, and maintained a competitive edge.

Exercise 1: Client Feedback Survey Design
Exercise 2: Feedback Review Meeting Simulation
Exercise 3: Continuous Improvement Action Plan
Project Studies
Project Study (Part 1) – Professional Services Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the Professional Services Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 2) – Administration and Finance Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the Administration and Finance Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 3) – Leadership Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the Leadership Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 4) – Human Resources (HR) Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the HR Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 5) – Information Technology (IT) Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the IT Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 6) – Sales and Marketing Team
After the completion of this workshop, the head of the Sales and Marketing Team, with the involvement of all key stakeholders, is to provide a detailed report on the implementation of Services Trust within their area of responsibility. This report should incorporate process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review elements. Your process should feature the following 12 areas:
01. Understanding Trust in Professional Services
02. Building Rapport and Credibility
03. Communication Skills
04. Ethics and Integrity
05. Confidentiality and Data Protection
06. Managing Expectations
07. Conflict Resolution
08. Risk Management
09. Quality Assurance
10. Client Empowerment
11. Transparency in Processes
12. Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Program Benefits
Management
- Profitability
- Business Adaptability
- Streamlined Operations
- Trust Development
- Change Management
- Problem Solving
- Improved Communication
- Remove Waste
- Project Management
- Refined Metrics
Human Resources
- Talent Retention
- Improved Culture
- Engaged Team
- Skilled Resources
- Employee Satisfaction
- Team Building
- Team Empowerment
- Embracing Change
- Skills Development
- Employer Branding
Marketing
- Client Management
- Client Retention
- Valuable Segments
- Client Targeting
- Service Quality
- Business Development
- Market Positioning
- Strategic Partnerships
- Sales Effectiveness
- Value Creation
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.
































