Optimizing Sales – WDP1 (Challenges Identified)

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Optimizing Sales is provided by Mr. Monroe Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
If you would like to view the Client Information Hub (CIH) for this program, please Click Here
Learning Provider Profile

Mr. Monroe is a Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene. He has spent his career in High Tech sales and sales leadership positions. Hired straight out of University by AT&T, David was one of the first 100 employees hired by AT&T outside of the US. David then transitioned to software sales and was a founding member of the Nixdorf Optical Document Management team in Toronto, Canada, securing the first sales with the Canadian Federal Government and a leading Property and Casualty Insurance company prior to the acquisition of Nixdorf by Siemens. Having had considerable sales success in the Telecommunications and Imaging industries, David was recruited to join a leading Canadian Executive Recruitment firm where he specialized in placing Sales and Sales Leadership roles before returning to the Software industry where he has spent most of his career.
With a proven track record of sales success early in his career, Mr. Monroe transitioned to Sales Leadership and has spent the last 25+ years of his career building new sales teams or fixing broken sales organizations. With a passion for sales and building/fixing teams, David has been hired by the same CEO’s on multiple occasions which is a testament to his ability to deliver results in the most challenging scenarios.
Mr. Monroe’s proficiency in sales organization optimization has played a crucial role in the financial success of both start-up and mid-market high tech companies. David’s common-sense approach to sales success is rooted in the recognition that your sales team members are your most valuable commodity. Creating an environment that clearly lays out expectations, removes obstacles and marries the best sales strategies with new technological advancements has made his approach to sales optimization as critical today as it has been throughout his career.
With a strong focus on delivering consistent and reliable sales results, Mr. Monroe’s proven strategies create trust with other functional areas of an organization, the C-suite Executive Team and Board of Directors.
Mr. Monroe, as VP Sales, led Reward & Recognition start-up Cooleaf to #1,637 on the Fast 5000 privately held companies list in 2021. Cooleaf has since been acquired by ITA Group. As EVP & CRO at Awee (Cybersecurity Education start-up), he has been quoted in numerous publications in 2024 including LA Weekly, USA Today and MSN. Working throughout his career in North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Asia, Europe and the Middle East, Mr. Monroe’s approach has delivered consistent results around the world.
Recently, Mr. Monroe founded a boutique management consulting firm to bring his unique blend of sales experience, insights and perspective to a broader audience.
Education-wise, Mr. Monroe holds a Bachelor of Social Science from the University of Western Ontario.
With a solid foundation of experience, knowledge, and a results-driven approach, Mr. Monroe is well-equipped to contribute to the success of any sales organization.
MOST Analysis
Mission Statement
The objective of this workshop is to identify key challenges facing sales organizations today. A selection of identified challenges will be addressed, and the group will be asked to provide feedback on the topics covered and to add topics for group discussion that they want to bring to the group. This exercise will help to build a foundation for understanding the complexity of the sales process landscape as it exists today. It is understood that not all topics will apply to all organizations and by soliciting feedback and input from the group we are looking to expand our understanding and bring a collective strategy to address challenges identified by the group. Key areas to be covered include forecasting to ensure that it is seen as reliable, and everyone is speaking the same language. Onboarding needs to be a critical element of sustainable sales success that sets every new hire up for long term sales goal achievement. Everyone on the sales team must understand the foundation of daily sales activity that will lead to ongoing sales performance that meets or exceeds expectations. We will explore what your ICP looks like and ensure that it becomes the focal point of prospecting efforts. We will discuss the critical importance of preparing ahead of time for each prospect/client interaction. Never is this more important than before a first meeting. How do you handle unsolicited and wired RFP’s so that sales have a game plan and strategy to execute that gives them confidence about how and why they are investing their time in this activity. When a deal starts to go sideways or is delayed what do you do? We will identify a strategy to engage with a prospect on a high probability deal that looks to be slipping in the forecast to give us our best shot at getting the deal back on track.
Objectives
01. Current Challenges: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
02. Challenge Experiences: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
03. Challenge Impacts: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
04. Common Mistakes: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
05. Forecasting Model: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
06. Hiring/Onboarding: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
07. Daily Routines: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. 1 Month
08. Prospect Profile: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
09. RFP Strategy: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
10. Maintaining Trust: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
11. Deal(s) Slipping: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
12. Compensation Effectiveness: departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development. Time Allocated: 1 Month
Strategies
01. Current Challenges: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
02. Challenge Experiences: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
03. Challenge Impacts: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
04. Common Mistakes: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
05. Forecasting Model: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
06. Hiring/Onboarding: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
07. Daily Routines: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
08. Prospect Profile: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
09. RFP Strategy: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
10. Maintaining Trust: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
11. Deal(s) Slipping: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
12. Compensation Effectiveness: Each individual department head to undertake departmental SWOT analysis; strategy research & development.
Tasks
01. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Current Challenges.
02. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Challenge Experiences.
03. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Challenge Impacts.
04. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Common Mistakes.
05. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Forecasting Model.
06. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Hiring/Onboarding.
07. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Daily Routines.
08. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Prospect Profile.
09. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze RFP Strategy.
10. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Maintaining Trust.
11. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Deal(s) Slipping.
12. Create a task on your calendar, to be completed within the next month, to analyze Compensation Effectiveness.
Introduction
Sales methodologies have evolved significantly over the past century, shaped by shifts in market dynamics, consumer expectations, and technological innovation. This journey from transactional selling to relationship-focused approaches highlights the industry’s response to changing economic landscapes and growing buyer sophistication.
Foundations of Modern Sales (Early 20th Century)
Before industrialization, sales were simple, direct exchanges where small business owners handled all aspects of sales and operations themselves. The approach centered on meeting local demand without actively pursuing new customers. This changed with the Industrial Revolution, which ushered in mass production and required more structured sales operations to move higher product volumes to wider markets. Companies began forming dedicated sales divisions, although these roles were largely transactional, with sales representatives incentivized on commission and typically more loyal to the sale than to customer relationships.
Structured Techniques and Sales Theories (Mid-20th Century)
By the 1930s, companies were refining sales techniques to improve effectiveness. The release of Dale Carnegie’s How to Win Friends and Influence People in 1936 introduced the concept of relationship-based selling, where building customer rapport became a valuable strategy. Alongside this, methods like barrier selling emerged, encouraging manipulative tactics to close sales, often at the expense of customer trust. This approach eventually led to consumer protection laws, shaping a new ethical landscape. In the 1950s, formula selling methodologies like AIDA (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) brought structure to the sales process, guiding salespeople through predictable steps toward closing a sale.
Emergence of Consultative Sales Models (1960s – 1980s)
The mid-20th century saw a shift from high-pressure tactics to more customer-centric, consultative methods. In the late 1960s, Xerox pioneered needs-satisfaction selling, a technique focused on understanding and addressing customer needs rather than simply pushing products. This laid the groundwork for solution selling, a methodology that gained traction through the 1980s and 1990s. Solution selling encouraged salespeople to understand specific customer pain points and create long-term relationships based on addressing these issues. With the rise of the internet in the 1990s, salespeople faced a more informed consumer base and adapted by becoming advisors rather than information gatekeepers, helping customers navigate their purchasing journey.
Modern Sales Strategies and Technology Integration (2010-Present)
In recent years, methodologies such as The Challenger Sale, introduced by Matthew Dixon and Brent Adamson in 2011, have redefined sales success as the ability to reshape customer thinking. This approach emphasizes the role of salespeople as educators who provide valuable insights to challenge and expand customer perspectives. Technological advancements have further transformed sales practices, with CRM systems, data analytics, and AI-driven insights allowing sales teams to personalize interactions and optimize strategies. However, these tools have also introduced challenges related to data management and analysis overload.
Current Trends and the Customer-Centric Future
Today, sales methodologies increasingly prioritize customer experience and relationship management. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote selling, prompting teams to refine virtual engagement strategies to maintain rapport with clients despite physical distances. As we move forward, agile responses to technological advances and evolving buyer behaviors will continue to shape the sales landscape, underscoring the industry’s journey from a transactional approach to one that values trust, relationship-building, and customer satisfaction.
Identifying Challenges

This means that no matter how big your goal or journey is, you can achieve it if you just take the first step.
The first step in the Optimizing Sales journey is to bring together sales team members (Leaders and individual Contributors) to discuss and explore the challenges faced by B2B sales organizations and how these and other concerns may be impacting their organization and its achievement of sales goals and objectives. This first step will ultimately acknowledge that improvements and changes are required, and action should be taken to resolve the concern(s).
With a group brought together to debate and review potential challenges, we can better understand the impact of these concerns on individuals’ motivation and performance, which are both at the core of developing a high-performance sales team.
However, before you embark on the journey to implement a solution to solve the problem(s), you must first develop a clear and concise understanding of the details surrounding the identified concerns and get to the root cause. Putting those challenges in perspective against the broader marketplace is also critical. Ultimately, you want to,
• Understand the issues your sales organization faces today
• Compare and contrast them to behaviors and challenges that exist in the broader marketplace that your organization is part of
• Explore the impact these challenges have on the team members involved, with a laser-like focus on team effectiveness to meet and exceed sales targets
• Identify how these or similar challenges were identified and resolved in previous work experiences
• Debate and discuss amongst your colleagues the impact and importance of each identified issue/concern
• Start to explore how these challenges may be addressed to the benefit of the sales team and overall organization
This workshop aims to identify key challenges facing sales organizations today. A selection of identified challenges will be discussed, and the group will be asked to provide feedback on the topics covered and add topics for group discussion they want to bring to the group. This exercise will help build a foundation for understanding the complexity of the sales process landscape in your organization. It is understood that not all topics will apply to all organizations. By soliciting feedback and input from the group, we seek to expand our understanding and bring a collective knowledge of the specific challenges affecting your organization.
By breaking down the issues your sales organization faces and then discussing their impacts on sales performance, we will begin to chart a process to address and solve these concerns for your sales team. The goal is always to identify goals and objectives that will address the root causes of the problem areas to drive increased sales performance! At the core of this approach is identifying and understanding common mistakes that organizations make when identifying problem areas and addressing them. Identifying and discussing these common mistakes can help avoid the costly outcome created when “knee-jerk” responses are taken to complex problems. Often, these attempted “quick fixes” not only don’t resolve the underlying issues but may also exacerbate them and/or create a new set of concerns that must be addressed.
A critical thought process when beginning this journey as a sales team is to resist the “them vs. us” mentality that can arise with both sales leaders and individual contributors. Ultimately, it cannot be overstated that you win and lose AS A TEAM!
Human nature is often to try and find the easy answer, like “salespeople are lazy” or “our sales leaders don’t understand the challenges we face in the field,” when the actual situation is much more complex and nuanced.

The reality is that only as a team can a sales organization bring diverse perspectives and critical thinking skills together to truly make substantive and lasting changes to their organization.
Throughout this process, individual learners will better understand that many of the problems they face have been seen in other organizations they or other team members have worked for. It is beneficial to realize that these concerns are not insurmountable, and others have encountered and resolved them. This realization can inspire personal growth and motivate individuals to find process-based solutions to mitigate the identified challenges and maximize sales performance!
For instance, many organizations find their current forecasting methodology unreliable, and everyone takes a different approach to forecasting. At the heart of this topic is the need for a common forecasting language that is integrated into the CRM tool that your organization has chosen. A common language simply means that there are precise explanations of each step in the agreed forecasting methodology. Within each stage in the forecasting model, more granular steps need to be met before a deal can move on to the next stage.
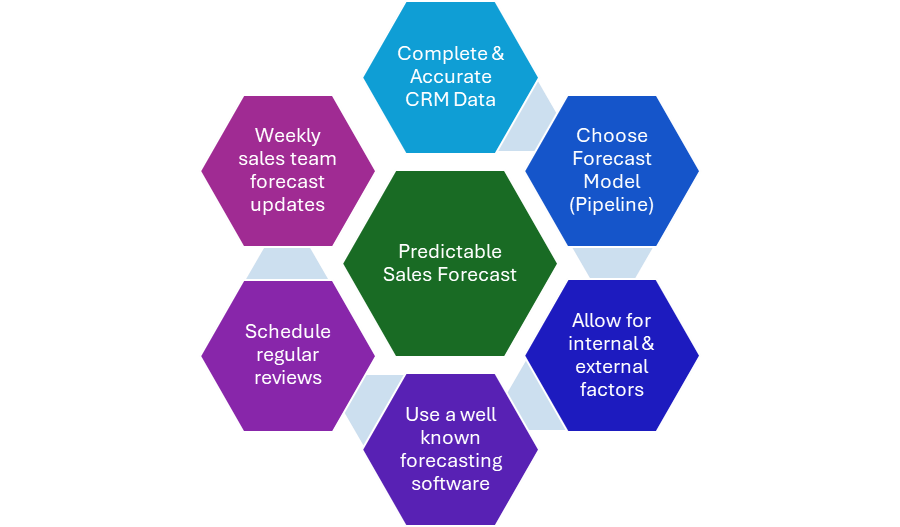
Figure 1 We flow – 2024
Once the forecasting model is built, there must be no exceptions in adherence to the model. Individual contributors and their sales leaders should play an active role in determining if/when a deal moves from one step to another within a stage and from one stage to the next. Taking this approach ensures that they understand what each other means when discussing sales pursuit progress, and decisions to move deals forward are not made in isolation but as a team.
Ultimately, the forecasting process’s goal is to create predictability in achieving revenue goals and, in doing so, build trust between individual contributors and sales leaders and between sales leadership and the rest of the executive leadership team and the Advisory Board or Board of Directors.
This process should start right at the onboarding stage. It is critical to set realistic expectations during onboarding and ensure that individuals get access to all the information and resources that will lead to their success. Onboarding is often an afterthought in the rush to get new headcount operational in the field. However, placing a new sales hire or leader in the field without the requisite contacts, tools, company/industry insights, and knowledge is a recipe for failure. A well-articulated onboarding plan should last several days to a week. A curriculum for this period needs to be developed and agreed to by sales leadership, as well as other areas of the organization that must play an active role in the success of the sales organization.
Remember, we win and lose as a team. That “team” is much broader than just the sales team and includes all company operational areas (Finance, Support, Product Development, Marketing, etc.). All areas should be involved, and content and instruction should be provided for new sales team members. Engaging critical clients in a new salesperson’s territory can also be beneficial in sharing their client journey experience with their organization.
This includes focusing on the daily routines necessary to deliver sustainable revenue results. Successful B2B salespeople must engage in three non-negotiable daily activities: prospecting for net new opportunities, nurturing deals through the sales forecasting stages, and closing the high-probability deals in the sales funnel. This might seem simplistic, but it can be overlooked.
This is also an area where sales leadership needs to resist becoming a micromanager. Guiding daily routines does not mean inspecting and interrogating adherence on an hourly/daily basis. As Steve Jobs once said,
In this context, that means giving people the leeway to finesse the desired daily routine in a way that works for them. You hired them because they demonstrated sustainable previous sales success. Start from the position that they know what they are doing and can interpret the objective successfully! They should be given the runway to “make it their own.”
The foundation of any successful B2B sales organization includes having a well-defined Ideal Client Profile (ICP). This becomes the foundation for your prospecting efforts. As mentioned earlier, prospecting must be critical to a salesperson’s daily routine. Although marketing carries a significant prospecting function for the organization and its goal of delivering an ongoing pipeline of “qualified leads,” B2B salespeople need to own this process and outcome. However, prospecting in the B2B world for salespeople must be more of a “quality vs. quantity” endeavor. The most crucial role of a B2B salesperson is to think strategically about their territory, prospects, target profiles in their ICP prospects, and how to engage them meaningfully.
Over the last 10+ years, there has been a significant shift to a prospecting-at-scale approach. This is often repetitive, mindless work that delivers little result for the time and effort invested. Sales is an effectiveness pursuit, not an efficiency pursuit. Successful salespeople know how to identify the right prospects and contacts. They can develop engagement strategies that highlight real value for their target contacts and create relationships that differentiate your solution value proposition in a way that engages people.
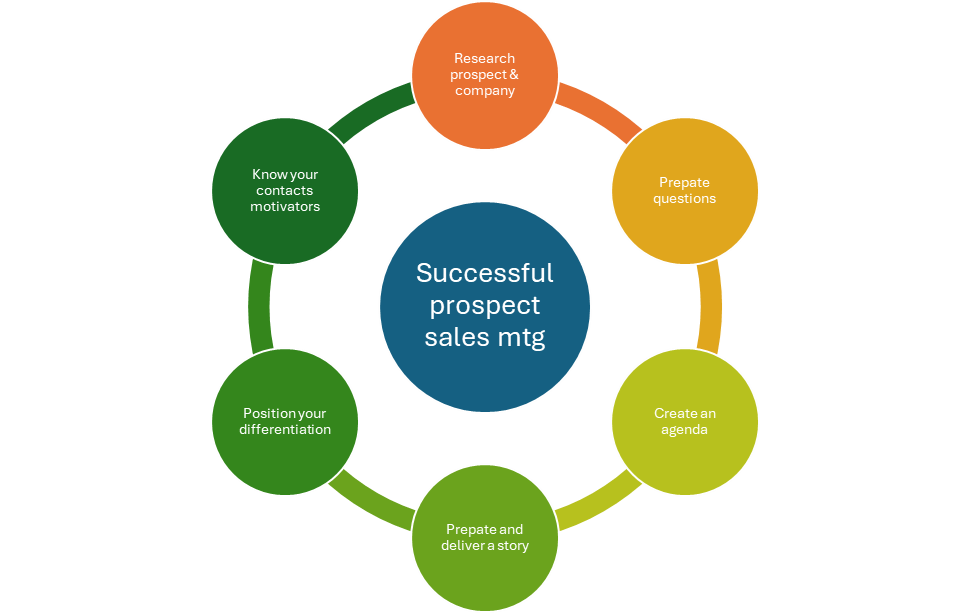
Once the organization determines its ICP and prospecting focuses on these target accounts, it is critical to get the most out of every contact with the prospect, starting with a well-thought-out first meeting strategy. The good news is that preparing for a first meeting is easier than ever. If your salespeople engage in the first meeting with a contact, they have cultivated themselves; they will understand the individual’s background, their professional priorities, and where the common ground is between them, you, and your value proposition. However, when qualified leads come in from marketing, it is critical to not “fly by the seat of your pants” and simply show up to a first meeting but invest the time and energy to research the individual, their organization, and the key goals and objectives of the senior leadership team well in advance of a meeting. This is easy to find in a publicly traded organization through the CEO’s goals and objectives in the Annual Report. For privately held organizations, a Google search of critical executives will bring up panels they may have participated in at trade shows, industry presentations they made, or press releases that outline vital topics of importance. With this critical research complete, you set yourself up for the first meeting success and achieving a Single Sales Objective (SSO) to secure a second meeting to develop the relationship.
OECHSLI – 2024
Trust between individual contributors and sales leadership is the foundation of any successful sales organization. This means that respect is a two-way street. When performance expectations are set, they should be fair and explained to all involved. An example of a surefire way to undermine trust is to ask for critical deal data to be input to the CRM by individual contributors and then ask sales team members about that same data. If you ask for it inputted into the CRM, as a sales leader, you should use the CRM to access the information you seek. Another common betrayal of trust is using one-on-one territory reviews as an interrogation vs. a collaborative team effort to build and execute effective critical account sales plans together.
Many organizations must go through a Request for Proposal (RFP) process when spending significant time and money to acquire a new tool or technology. Most successful sales organizations and salespeople know that it improves their chances of success if they find a way to help a prospect develop their RFP. When working on this strategy, you can ensure that many client requirements align with your value proposition. However, what do you do if you receive an unsolicited RFP? Many organizations and individuals consider these situations a potential waste of time.
Salespeople shy away from responding, but leadership wants all opportunities to “run to the ground.” These two perspectives are at odds and can cause friction, which does not help drive revenue.
We will review a strategy and approach to take advantage of unsolicited RFP’s and determine if there is a way to influence the client’s evaluation process before making a final decision about responding to the RFP. This approach can reduce friction between salespeople and sales leadership when approaching unsolicited RFPs with a strategy focused on “go-no go” decision points, the team can make an educated decision on the viability of creating an RFP response based on critical data points secured at the outset of the RFP process.
Lastly, we will discuss two of the biggest impediments to sales success: compensation and what to do when a high-probability deal starts to go sideways.
Compensation is the building block of any sales organization. Salespeople are “coin-operated”; if there is a disconnect between the compensation plan and its ability to engage salespeople meaningfully to achieve the agreed sales goals and objectives, this is a foundational issue that can undermine all the other good work and plans/strategies that have been put in place. Is compensation perceived as fair by both the organization and the sales team? Is it easy to understand for salespeople? What role do commission clawbacks play in your organization’s day-to-day world of sales compensation, and are commission payments tied closely to the moment of sales success?
When you consider the complexity of building a B2B sales organization, effectively differentiating your value proposition in the marketplace, engaging prospects, and nurturing relationships through the sales cycle, you may feel like you have already climbed Mount Everest before closing a deal. When your high probability deal(s) go sideways at the 11th hour, the results can be catastrophic for both the salesperson relying on that deal to make quota and the company relying on the revenue to meet quarterly or yearly revenue goals.
The first objective must always be to execute flawlessly throughout your sales cycles. However, we are all human, and we can all make mistakes. Having a plan to navigate the high-stakes environment associated with the potential loss of a high-probability deal is stressful for all involved.
In crisis management, talk is often about “getting ahead of the situation” as quickly as possible. This approach holds when dealing with a potential loss of a sale that you were counting on. Through the Optimizing Sales program, we will review what to do in these situations and equip you with a strategy to “get ahead of the situation” as quickly as possible, take back control of the problem as best as you can, and create an environment where you have the best possible chance of salvaging the deal/revenue at risk.

Case Study: HubSpot – Overcoming Sales Challenges with AI
Industry: SaaS (Software as a Service)
Revenue: $2.1 billion (2022)
Challenge: Scaling Sales Efficiency and Personalization with Rapid Growth
Background:
HubSpot, a leading CRM software company, experienced rapid growth in its early years. As the company expanded, it faced several challenges in managing its sales process at scale. HubSpot provides businesses with marketing, sales, and service software, but ironically, it struggled with sales inefficiencies as it scaled.
HubSpot’s sales challenges included:
• Inefficient Lead Management: As more leads pour in from their inbound marketing efforts, sales teams struggle to prioritize and manage these leads effectively.
• Lack of Personalization: Sales reps manually personalized outreach, which became unsustainable as the number of leads grew.
• Missed Cross-Sell Opportunities: With multiple products and service tiers, sales reps often fail to recognize opportunities to cross-sell or upsell existing customers.
• Declining Sales Productivity: As the volume of leads increased, the time required to move them through the funnel extended, reducing the sales team’s overall productivity.
Current Challenges:
1. Overwhelmed Sales Team Due to Lead Volume
HubSpot’s marketing engine was highly influential, generating many leads every month. However, the sales team struggled to keep up with the sheer volume of leads. Manually prioritizing, which led to following up first, was inefficient and often led to delays in outreach. The team didn’t have an automated system to identify high-quality leads versus those unlikely to convert.
Impact:
• Sales reps spent significant time on low-priority leads, reducing the time spent on high-quality prospects.
• A growing number of leads fell through the cracks, leading to lost revenue.
2. Inconsistent Personalization in Sales Outreach
HubSpot prided itself on a personalized sales experience, but personalizing each email or outreach effort became difficult as the company scaled. Sales reps couldn’t keep track of each prospect’s specific interests and engagement history in a scalable way, leading to generic outreach that failed to connect with prospects.
Impact:
• Decreased engagement rates with prospects.
• Reduced effectiveness of sales communications, leading to lower conversion rates.
3. Missed Cross-Sell and Upsell Opportunities
HubSpot offers multiple products, including CRM, marketing, sales, and service software. However, due to a lack of data integration across these products, sales reps didn’t always have the insights they needed to recommend the right complementary product to customers.
Impact:
• You missed opportunities to increase the average deal size through cross-selling and upselling.
• Lower customer lifetime value as customers were not aware of other HubSpot offerings that could benefit their business.
4. Declining Sales Productivity
With growing leads and a lack of efficient systems, HubSpot’s sales team found that closing deals took longer. Sales cycles grew longer, and reps spent more time managing administrative tasks rather than focusing on selling.
Impact:
• Longer sales cycles lead to delayed revenue recognition.
• Lower overall sales productivity, with fewer deals closed per sales rep.
AI-Driven Solutions:
To overcome these challenges, HubSpot implemented several AI-driven strategies that significantly optimized its sales operations:
1. Automated Lead Scoring with AI
HubSpot integrated AI-powered lead scoring into its CRM, allowing the system to automatically prioritize leads based on engagement data, company size, and likelihood to convert. This helped the sales team focus their efforts on high-quality leads.
Result:
• Sales reps could spend more time on high-value leads, increasing conversion rates.
• The lead response time dropped, ensuring prospects received timely follow-ups.
2. AI-Powered Personalization
Using AI, HubSpot was able to automate personalized outreach at scale. The system would analyze past interactions, content engagement, and customer behavior to craft customized messages tailored to each prospect’s needs.
Result:
• Engagement rates improved as prospects received more relevant and timely communication.
• Sales reps no longer had to spend time manually personalizing each outreach, allowing them to focus on selling.
3. Cross-Selling and Upselling with Predictive Analytics
HubSpot deployed AI to analyze customer data and predict which existing customers were most likely to benefit from additional products or service upgrades. This allowed sales reps to proactively recommend solutions aligned with the customer’s needs.
Result:
• Cross-sell and upsell rates increased, boosting customer lifetime value.
• The average deal size grew as customers adopted more HubSpot products.
4. Improved Sales Productivity with AI Automation
AI tools helped automate many of the administrative tasks that were bogging down HubSpot’s sales team. From scheduling follow-up emails to logging interactions in the CRM, AI reduced the manual workload on sales reps, freeing them to focus on high-impact activities.
Result:
• Sales cycles shortened as reps could move leads through the funnel faster.
• Sales productivity increased, with reps closing more deals in less time.
Results:
By leveraging AI-powered solutions, HubSpot was able to overcome its sales optimization challenges:
• Lead response time decreased by 40%, leading to higher conversion rates.
• Sales productivity increased by 30%, as sales reps spent more time selling and less on administrative tasks.
• Cross-sell and upsell revenue grew by 25%, increasing the average customer lifetime value.
• Sales cycle times were reduced by 20%, resulting in faster deal closures.
This case highlights how AI can streamline sales processes, enhance personalization, and increase productivity, all of which are critical in optimizing sales operations for fast-growing businesses like HubSpot.

Exercise: Sales Challenge Story Sharing
• The Challenge: What was the specific sales problem? (e.g., low lead conversion rates, unexpected competitor moves, customer churn, etc.)
• Impact: How did this challenge affect the team’s performance or morale?
• Action Taken: What steps did the team (or you personally) take to overcome or address the issue?
• Outcome: What was the result? Was the challenge resolved, or did it lead to a different approach?
• What common themes or challenges emerged across different stories?
• How might AI tools have been used to help resolve some of these challenges?
Executive Summary
Chapter 1: Current Challenges
Sales optimization is a fundamental priority for B2B organizations looking to enhance performance and boost revenue growth. However, before implementing any optimization strategies, it is crucial to identify the key challenges that sales teams face, which often act as obstacles to success. These challenges can stem from various sources, such as inefficient processes, poor team alignment, or external factors like shifting market conditions. To effectively address these issues, organizations must thoroughly examine pain points, roadblocks, and inefficiencies that hinder sales performance.
The sales optimization process begins with an open discussion that invites participants to share their experiences and learn from one another. This interactive approach allows sales professionals to explore the specific circumstances and challenges within their organizations. It also helps in recognizing the common themes affecting the broader B2B sales landscape, making you feel connected and part of a larger community. Whether it’s the struggle with customer acquisition, competition, or lead generation, identifying these issues provides a clearer picture of what is holding sales teams back.
One of the most prevalent challenges in B2B sales is customer acquisition and lead generation. Sales teams frequently grapple with identifying and engaging high-quality leads, and the complexities of the modern buying process only compound this issue. Today’s B2B buyers are well-informed and conduct extensive research before engaging with sales teams, making it harder to capture their attention. Moreover, competitive pressures and the sheer volume of options available to buyers intensify the difficulty of standing out in the market.
Technology, particularly AI and automation, offers a powerful solution to some of these challenges by streamlining the lead generation process and providing actionable insights into buyer behavior. This technological empowerment, when combined with strategic thinking and strong collaboration, can help you overcome even the most daunting obstacles. It’s a tool that can make you feel confident and capable. However, the effectiveness of these technologies depends heavily on the alignment between sales and marketing teams. Without proper collaboration and communication, even the best tools and strategies can fall short. For this reason, fostering cross-functional alignment is critical to ensuring a seamless lead handoff from marketing to sales and increasing conversion rates.
Another challenge in the B2B landscape is navigating the increasingly complex buyer journey. With multiple stakeholders involved in decision-making and extended sales cycles, sales teams must manage interactions effectively across different touchpoints. Personalization, consistency, and trust-building are critical elements in navigating these complexities, and using CRM systems and AI tools can help sales teams tailor their approach to each buyer’s specific needs.
Ultimately, overcoming these challenges requires a combination of strategic thinking, technological innovation, and strong collaboration between teams. This strategic engagement, when applied to the specific hurdles faced in the B2B sales process, can lead to the implementation of effective solutions that drive optimization, improve alignment, and achieve sustained growth. It’s your strategic thinking that will put you in control of the situation.

Chapter 2: Challenge Experiences
In the fast-paced world of B2B sales, each professional’s journey is unique and shaped by personal experiences, challenges, and successes. While common challenges such as customer acquisition, competition, and team dynamics are prevalent across industries, solutions often differ based on individual approaches, market conditions, and company strategies. The Sales Optimization program recognizes the value of these differences, encouraging an interactive environment where participants share their stories and experiences. This knowledge exchange fosters learning, helping others gain insights to tackle their sales challenges.
The program emphasizes the importance of collaboration, where participants understand that they are not alone when facing obstacles. By listening to how others have overcome challenges, such as lead generation or positioning against competitors, learners gain new strategies that can be adapted to their unique situations. Through shared stories, participants learn from their peers’ successes and failures, highlighting how diverse approaches can lead to effective problem-solving.
One of the program’s key strengths is its interactive nature, fostering a sense of community where participants are encouraged to discuss experiences from different industries and sales environments. Not everyone will face the same challenges, but this variability allows for a richer exchange of ideas. Learners benefit from hearing fresh perspectives, often discovering solutions they may not have considered. This open dialogue builds a support network among participants, creating a shared understanding essential for long-term success in B2B sales.
In Personalizing Customer Acquisition Strategies, participants discuss how to tailor their approach to identifying and nurturing leads. They recognize that the decision-making process often involves multiple stakeholders with different priorities. Personalizing acquisition strategies ensures that the communication and value propositions resonate with each decision-maker, increasing the likelihood of successful conversions.
Navigating Competitive Markets focuses on the challenges of standing out in crowded industries. Participants explore how companies can refine their value propositions, leverage AI and data analytics for competitive insights, and maintain market share while seeking new business opportunities. Through shared experiences, participants learn how to outmaneuver aggressive competitors by emphasizing value over cost and building long-term client relationships.
Finally, Overcoming Sales Team Dynamics delves into the internal challenges that can hinder team performance. Misaligned goals, poor communication, and conflicts within sales teams are common issues. By sharing experiences of managing these dynamics, participants learn how to foster collaboration, align goals, and create a positive team environment that drives individual and collective success.
In conclusion, the Sales Optimization program offers a valuable platform for B2B sales professionals to learn from one another. By embracing the diversity of experiences and fostering collaboration, the program empowers participants to develop new strategies for overcoming challenges, ultimately strengthening individual and organizational performance. The program equips sales teams with the tools and knowledge to achieve sustained success in competitive markets through shared wisdom and open dialogue, instilling a sense of confidence and capability.

Chapter 3: Challenge Impacts
At the outset of the sales optimization journey, the pivotal and primary step is the early identification of the challenges that impede performance, both at an industry-wide level and within your specific organization. These challenges, often concealed beneath the surface, can exert a significant influence on critical sales processes, including team morale, conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and overall revenue generation. While some obstacles are readily apparent, others may be deeply rooted in complex systems, making them harder to uncover but equally detrimental to sales performance.
Recognizing and understanding the root causes of these challenges is essential to driving meaningful improvement. Without this clarity, efforts to enhance sales processes may miss the mark. By thoroughly analyzing specific difficulties and their effects, sales teams can lay the foundation for a more granular, process-oriented approach to optimization. This foundational knowledge allows sales leaders to develop targeted solutions that directly address the most pressing pain points, ensuring that future interventions are effective and sustainable.
One of the most valuable outcomes of this initial phase is the ability to prioritize which challenges should be tackled first. Sales organizations often face multiple issues simultaneously, and determining where to begin can be daunting. However, by evaluating the impact of each challenge on performance metrics such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and deal sizes, sales leaders can focus on areas that will generate the most significant and immediate results.
Quantifying the negative impacts of sales challenges is critical for prioritization. For example, a drop in conversion rates might suggest a need to improve lead qualification, while rising customer acquisition costs could indicate inefficiencies in the sales funnel. These metrics provide a clear, data-driven picture of the toll these obstacles are taking on the organization, empowering sales leaders to make informed decisions about resource allocation.
However, addressing these challenges often requires more than internal changes within the sales team. It’s a team effort that involves collaboration with other departments, such as marketing, customer service, and operations, to resolve cross-functional issues. Sales leaders must build a strong case for organizational support by demonstrating how resolving sales challenges aligns with company-wide goals like increased profitability, improved customer satisfaction, or market expansion. Presenting data to support these claims is vital in securing the necessary buy-in and resources from key stakeholders.
The subsequent step in this journey involves the development of a clear action plan that delineates the steps required to address each challenge and assigns responsibilities across teams. This not only helps foster accountability but also ensures that all departments are in sync in their efforts to support sales optimization.
By identifying and quantifying the impact of challenges and building cross-departmental support, sales teams can create a clear path toward long-term, sustainable improvements. This approach empowers the organization to optimize performance, driving growth and ensuring the success of individual salespeople and the company.

Chapter 4: Common Mistakes
Sales optimization is crucial for improving performance and driving revenue growth, but many organizations make common mistakes that prevent them from achieving their full potential. These mistakes range from misaligned strategies and lack of communication to neglecting the use of data and focusing too heavily on short-term wins. While they may seem minor, these issues can severely impact both short-term results and long-term business success.
One of the most prevalent mistakes is the misalignment between sales and marketing teams. Despite their complementary roles, these two departments often operate in silos, leading to inefficiencies. Marketing focuses on lead generation and building brand awareness, while sales teams are responsible for converting those leads into paying customers. However, without proper alignment, the leads generated by marketing may not meet the qualifications that sales teams need. Sales may feel that the leads are of low quality, while marketing believes sales aren’t effectively nurturing the leads they provide. This disconnect not only results in wasted resources but also missed sales opportunities. It’s crucial for organizations to foster collaboration, as it’s the key to establishing shared goals and clearly defining what constitutes a qualified lead. Regular communication and data sharing between departments are crucial for ensuring alignment and maximizing revenue potential.
Another standard error is neglecting data-driven insights. In today’s digital age, sales teams can access vast amounts of data, including customer preferences, behavior patterns, and sales performance metrics. However, many organizations fail to leverage this data effectively, relying instead on outdated methods or intuition. Ignoring data-driven insights can lead to poor decision-making, inefficient targeting, and inaccurate sales forecasting. Using data analytics tools and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, sales teams can better understand customers, predict trends, and tailor their approaches to meet evolving customer needs. For example, analyzing historical sales data and customer behavior can provide insights into which leads are most likely to convert, allowing sales teams to prioritize their efforts more effectively. Predictive sales analytics can enhance performance by helping sales teams anticipate customer needs, predict sales cycles, and identify risks such as potential customer churn.
Lastly, sales teams frequently fall into the trap of prioritizing short-term gains over long-term relationships. While closing deals quickly may boost immediate revenue, this short-term focus often comes at the expense of building sustainable client relationships. A transactional approach can lead to decreased customer loyalty and missed opportunities for repeat business, upselling, and referrals. In contrast, long-term success in sales depends on nurturing relationships, building trust, and providing ongoing value to clients. Sales teams should focus on customer satisfaction and retention as key performance indicators (KPIs) rather than chasing immediate wins. Following up with clients, addressing concerns, and consistently offering solutions that meet their evolving needs are all essential to fostering long-term loyalty. The value of these long-term relationships cannot be overstated, as they are the foundation of a successful sales strategy.
Avoiding these common mistakes is essential for optimizing sales processes and achieving sustainable business growth. However, these changes cannot be implemented without strong leadership. By aligning sales and marketing, leveraging data-driven insights, and focusing on long-term relationships, companies can enhance their sales effectiveness and drive better results. Prioritizing collaboration, informed decision-making, and customer-centric strategies will lead to more robust performance in the short term and over the long haul. The leadership’s responsibility is to drive these changes and ensure that the entire organization is aligned toward these goals.

Chapter 5: Forecasting Model
Sales forecasting is vital to any successful sales organization, providing clear insights into future revenue, identifying potential gaps, and guiding critical strategic decisions. Despite its importance, many sales teams struggle with creating and managing effective forecasting models, often leading to inconsistent results, missed sales targets, and a lack of actionable insights. This problem arises mainly because each salesperson may have their interpretation of forecasting, which causes confusion and inaccurate forecasts.
The foundation of a reliable forecasting process lies in developing a structured, uniform model that ensures all team members use the same language when discussing deals in the sales pipeline. This shared understanding of the stages within the sales process, along with clear, measurable criteria for each stage, not only eliminates ambiguity and improves forecast accuracy but also fosters a sense of unity and collaboration among sales representatives, managers, and executives. This shared language enhances accountability and ensures that everyone evaluates deal progression consistently, strengthening the team’s bond.
One critical function of a forecasting model is categorizing and tracking deals as they move through the pipeline, using specific terminology for each stage and defining clear steps within those stages. For example, if a deal is marked as a “commit” deal, everyone should know what that term means and that the agreement meets specific criteria before progressing. This clarity prevents confusion and allows sales leaders to make well-informed decisions based on reliable data.
In addition to tracking deals, an effective forecasting model creates a repeatable and scalable process that can be applied throughout the organization. This process helps sales teams identify potential risks, allocate resources more efficiently, and adjust strategies based on the most accurate data. A well-designed forecasting model supports long-term success by enabling organizations to meet their revenue targets and respond quickly to changes in the market.
A critical part of establishing a reliable forecasting model is defining standardized stages within the sales pipeline. Each stage must have specific, measurable criteria to guide deal progression. These stages generally include prospecting, qualification, proposal, commitment/negotiation, and closing. By ensuring that every deal is categorized according to clearly defined benchmarks, organizations can reduce the risk of subjectivity and create more consistent, predictable forecasts.
Another essential aspect of modern sales forecasting is leveraging data and AI-driven analytics. AI and predictive models, by analyzing historical sales data, current market conditions, and customer behavior, can significantly enhance the accuracy of sales forecasts. These tools not only help organizations identify potential roadblocks and improve deal progression but also instill a sense of confidence and empowerment in sales teams, reducing uncertainty in the forecasting process and making them feel more informed and in control.
Furthermore, sales forecasts must align with the organization’s broader sales strategy. Whether focusing on market expansion, customer acquisition, or product launches, the forecasting model should reflect the company’s goals and inform strategic decisions such as resource allocation or pricing adjustments. This alignment is not just a formality, but a strategic imperative that ensures sales teams are positioned for success and that the forecast supports the organization’s long-term growth and sustainability. It makes the audience feel more strategic and goal-oriented, understanding that their work is directly contributing to the company’s success.
Creating and managing an effective forecasting model is critical to improving forecast accuracy, reducing ambiguity, and supporting the overall sales strategy. Organizations can build a scalable, repeatable process that drives long-term success by defining standardized stages, leveraging data, and aligning the forecast with strategic goals.

Chapter 6: Hiring/Onboarding
Hiring and onboarding, as the bedrock of a successful sales force, wield a profound influence on sales success. A well-oiled hiring process, coupled with a comprehensive onboarding journey, not only shapes a new salesperson’s effectiveness and long-term engagement but also serves as a beacon of inspiration for the entire team. Conversely, a lackluster experience in either phase can dampen their potential and organizational contributions. Most employees, particularly in sales, have experienced both effective and ineffective processes, which deeply influence their perceptions of the company and their ability to perform from day one.
The journey begins by identifying the qualities that define a great salesperson within the specific context of an organization and industry. Sales attract various personality types, but successful salespeople typically share specific vital attributes. By analyzing the performance of top sales representatives, companies can pinpoint the skills, behaviors, and mindsets that drive success. This analysis facilitates the creation of an ideal candidate profile, including essential qualities—such as solid communication skills, resilience, and problem-solving abilities—and desirable traits like industry-specific knowledge. Focusing recruitment efforts on these criteria increases the likelihood of hiring individuals who meet job requirements and thrive within the organizational environment.
Onboarding is equally crucial. Even the most skilled sales professionals will struggle to succeed without the necessary resources, knowledge, and support to navigate internal systems and understand company goals. A subpar onboarding experience can lead to miscommunication, wasted time, and missed opportunities. It’s important to note that a poor onboarding experience not only affects the new hire’s performance but also reflects poorly on the company’s brand, potentially deterring future candidates. For instance, if a new salesperson is expected to complete tasks such as updating forecasts or submitting reports without proper training or access to tools, their chances of success diminish significantly. By the time they acquire the essential information, they may have already faced setbacks, leading to frustration and disengagement.
As the architects of seamless hiring and onboarding processes, the audience’s role is pivotal. They must focus on creating effective frameworks that support individual success and the health of the broader sales team. This involves defining the ideal salesperson profile, which sets the groundwork for effective recruitment. Understanding the characteristics of top performers and articulating the skills and cultural fit required for success is vital, and it’s a responsibility that the audience is uniquely positioned to fulfill.
The hiring process should be streamlined to attract and retain top talent and provide a positive candidate experience that reflects well on the company’s brand. Leveraging technology, such as applicant tracking systems and video interviews, can streamline operations and provide a seamless experience for candidates. Clear job descriptions, structured interviews, effective communication, and feedback mechanisms are also crucial in reducing friction points throughout the recruitment journey. Engaging team members early in the hiring process can foster collaboration and ensure that selected candidates are a good fit for the team.
Once hired, effective onboarding programs must equip new sales hires with structured training, mentorship, and ongoing development opportunities. These ongoing development opportunities, such as continuous training and mentorship, are crucial in boosting employee morale and retention. Comprehensive training should cover company culture, sales processes, product knowledge, and internal tools, ensuring new hires feel confident and supported as they begin their roles. Organizations can promote integration and teamwork among new and existing employees by fostering a collaborative environment.
Investing in efficient hiring and effective onboarding processes is not just a choice, but a necessity for cultivating a successful sales force. Organizations that prioritize these elements are not just better positioned to achieve sales targets, but also to enhance employee engagement and foster a thriving sales culture that drives overall growth and success. The urgency and significance of these actions cannot be overstated.

Chapter 7: Daily Routines
In the dynamic world of B2B sales, trust is not just a buzzword, but the cornerstone of successful sales strategies. It’s more than just a belief in the resources provided or the fairness of compensation models. It’s about the daily dedication of salespeople to meet and exceed their goals, knowing that they will receive adequate support and rewards for their efforts. This trust empowers sales professionals to engage with their responsibilities purposefully and passionately, leading to significant results over time.
Collaboration is not just a buzzword in B2B sales, it’s a necessity. Sales leaders and individual contributors must align on the essential daily activities that drive sustainable success. This alignment ensures that salespeople are clear on their responsibilities and motivated to take ownership of their results. Every B2B salesperson should focus on three critical daily activities: prospecting, nurturing, and closing. Each component is vital in building a robust sales pipeline and achieving long-term growth.
Prospecting is not just a task for junior roles or the marketing team. It’s a core responsibility for every salesperson, vital to their success and the health of the sales pipeline. Effective prospecting lays the groundwork for meaningful relationships and long-term partnerships. It allows sales professionals to engage potential clients proactively, positioning themselves as valuable resources rather than mere sellers.
A key aspect of effective prospecting is the identification of Ideal Customer Profiles (ICPs). Sales professionals should conduct thorough research to understand their ICP deeply, analyzing attributes like industry, company size, pain points, and decision-making processes. This knowledge equips salespeople to tailor their outreach efforts, ensuring they resonate with potential clients’ specific needs and challenges.
Once prospects are identified, the next phase is nurturing, a stage that requires patience and persistence. It’s not just about keeping prospects warm; it’s about actively engaging them with tailored communication that adds value to their experience. By providing unique insights and maintaining effective communication, we can reinforce our role as trusted advisors, leading to stronger relationships and higher conversion rates.
The final phase, closing, is a collaborative effort that requires active participation from individual contributors and sales leaders. It’s not just the end of the process but a crucial stage that can make or break a deal. Successful closings rely on open communication and trust, enabling salespeople to approach the process confidently. A collaborative closing process allows for aligning sales strategies with the prospect’s needs, facilitating the effective handling of objections and concerns.
The overarching theme of this course manual is the importance of trust and collaboration in B2B sales. When organizations prioritize these elements, they cultivate a culture where sales teams feel supported, empowered, and inspired. This drives immediate results and lays the groundwork for sustainable growth and long-term success in an ever-evolving sales landscape.

Chapter 8: Prospect Profile
In the dynamic world of B2B sales, prospecting at scale has transformed significantly over the last decade. Early adopters of mass outreach strategies initially leveraged technology to reach a broad audience, achieving notable success quickly. However, as the marketplace matured, prospects became more discerning and skeptical of insincere outreach efforts. Today’s buyers often perceive mass campaigns as intrusive, especially when they fail to comply with local spam and privacy regulations.
For organizations looking to expand their market reach, it’s essential to recognize that while technology can facilitate broad outreach, it does not guarantee success. Missteps in adhering to legislation can lead to wasted resources and potential legal issues, damaging an organization’s credibility. As such, sales teams must transition from a broad, indiscriminate approach to a more strategic and thoughtful methodology.
A key strategy in refining outreach efforts is developing an Ideal Client Profile (ICP). This is a detailed description of the type of client that is most likely to benefit from your product or service. Every organization has clients whose characteristics align with their product offerings, and by analyzing these successful engagements, sales teams can identify patterns that define their best prospects. This introspective process allows for creating a targeted profile that serves as a foundation for all new outreach efforts.
Instead of sending generic messages to hundreds or thousands of contacts, a refined prospecting strategy focuses on targeted outreach to specific decision-makers within ICP companies. This involves crafting messages that resonate with these prospects’ unique goals and challenges. By examining annual reports and industry presentations, sales professionals can uncover insights that align with their value propositions, tailoring communications to foster genuine connections. This personalized approach enhances the likelihood of engagement and leads to meaningful conversations that can convert prospects into clients.
Optimizing sales through effective prospect profiling necessitates a nuanced understanding of past successes and current market dynamics. As regulations continue influencing outreach practices, the emphasis must shift toward sincere, targeted communication rather than mass messaging. This evolution results in a more focused, efficient, and effective sales strategy that enhances the organization’s overall success, making the audience feel informed and prepared.
The landscape of B2B prospecting has experienced a significant shift from mass outreach to targeted engagement, driven by advancements in technology, changing client expectations, and a demand for authentic communication in a saturated market. Historical mass outreach tactics, once embraced, led to low engagement rates and negative brand perceptions. In contrast, targeted engagement allows businesses to gather and analyze vast amounts of data about potential clients, enabling more personalized and relevant outreach strategies.
The rise of Account-Based Marketing (ABM) emphasizes building relationships with key stakeholders within specific target accounts, enhancing engagement, and increasing conversion likelihood. Moreover, introducing privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA has heightened awareness of ethical marketing practices, pushing organizations to navigate legal requirements more diligently.
The benefits of targeted engagement are substantial, resulting in higher engagement rates, improved conversion rates, and stronger relationships between sales representatives and prospects. This evolution reflects a broader shift in how businesses approach sales in the digital age, reinforcing the importance of personalized communication and ethical practices. Ultimately, organizations that embrace these changes will be better positioned for sustained growth and success in an increasingly competitive landscape, reassuring the audience about the effectiveness of the strategy.

Chapter 9: RFP Strategy
In the competitive landscape of B2B sales, responding to Requests for Proposals (RFPs) poses a significant challenge for sales professionals, especially when faced with unsolicited RFPs. Often perceived as an uphill battle—akin to fitting a round peg into a square hole—salespeople can instinctively view these unsolicited proposals as a waste of time and resources. This mindset can lead to an ingrained belief within organizations that pursuing unsolicited RFPs is not worth the effort, ultimately hindering their ability to capitalize on potential revenue opportunities.
However, unsolicited RFPs can offer unique opportunities to expand market reach and engage with prospects who might not have initially considered a company’s solutions. By reframing the perception of these proposals from burdensome to strategic engagement opportunities, sales teams can unlock new pathways to success. This transformation requires a robust RFP strategy that empowers sales professionals to assess each RFP on its merits, determining whether it warrants a thoughtful response.
Navigating unsolicited RFPs involves understanding the intricacies of the buying process and leveraging the RFP response format to influence decision-making. A well-structured strategy enables sales teams to identify critical decision points throughout the RFP lifecycle, aiding resource allocation and increasing the chances of success by aligning proposals with the prospect’s needs.
A vital component of a successful sales strategy is the assessment of unsolicited RFPs based on specific criteria. Sales teams must evaluate alignment with the company’s strengths, potential profitability, and the strategic importance of the prospect. For instance, the first step involves assessing whether the RFP specifies needs that align with the company’s solutions, ensuring a close match that enhances the likelihood of delivering a compelling proposal. Furthermore, evaluating the team’s expertise, experience, and resource availability is essential to confirm that they can adequately meet the project’s requirements.
Potential profitability is another crucial factor in deciding whether to pursue an RFP. Analyzing the budget outlined in the RFP against the company’s pricing model and considering the long-term value of potential partnerships can help gauge the project’s financial viability. Additionally, understanding the prospect’s market influence and strategic goals further aids in evaluating the merits of the RFP.
Organizations should develop a structured framework for go/no-go decisions to streamline the decision-making process. This includes establishing clear evaluation criteria, assessing the competitive landscape (such as the number of competitors, their strengths, and weaknesses), evaluating existing relationships with the prospect (like past interactions, feedback, or partnerships), and analyzing resource allocation. Creating a go/no-go matrix allows teams to score RFPs based on predefined criteria, ensuring a consistent approach to evaluating opportunities.
Ultimately, sales teams can effectively influence the buying process by employing these strategies and fostering ongoing communication with prospects throughout the evaluation process. This continuous dialogue not only keeps the prospect engaged but also allows the sales team to understand their evolving needs and concerns. Crafting compelling proposals that address client needs while highlighting unique value propositions can significantly enhance the likelihood of securing contracts. By transforming the approach to unsolicited RFPs, organizations can unlock new pathways for growth and success, driving incremental revenue and establishing long-term partnerships that enhance their competitive edge in the marketplace.

Chapter 10: Maintaining Trust
In the dynamic realm of B2B sales, trust is a foundational element for optimizing performance and fostering long-term relationships. It is crucial for collaboration between sales leaders and their teams and for building rapport with prospects. When trust is established, sales teams engage more openly in discussions, share insights, and work together towards common objectives, improving morale, accountability, and performance.
Trust in sales is multifaceted, rooted in reliability, transparency, and mutual respect. Sales leaders who nurture trust within their teams empower their members to take calculated risks, make independent decisions, and innovate in customer engagement. Similarly, when sales professionals approach prospects with sincerity and integrity, they create a conducive environment for meaningful dialogue. This openness allows clients to express their pain points, enabling sales teams to tailor their solutions more effectively.
However, maintaining trust requires ongoing effort and commitment. It is not a one-time achievement but a continuous process that evolves with each interaction. Trust differentiates successful salespeople from the competition in a market saturated with options and information. Those who consistently deliver on their promises, diligently follow up, and provide exceptional service establish themselves as reliable partners, enhancing their credibility and encouraging repeat business. Trust also plays a crucial role in overcoming market challenges, such as high turnover rates and shifting team dynamics, by fostering a culture of transparency and accountability and prioritizing communication and feedback.
The journey to maintaining trust is fraught with challenges, including high turnover rates, shifting team dynamics, and external market pressures. Organizations must adopt strategies to reinforce trust at all levels, which involves fostering a culture of transparency and accountability and prioritizing communication and feedback.
Trust among sales team members is essential for creating a high-performing, collaborative environment. Key strategies to build and maintain trust include:
• Open Communication: Encouraging transparent dialogue through regular check-ins, team meetings, and one-on-one sessions helps team members feel valued and heard.
• Shared Goals: Establishing clear, measurable objectives that align with the organization’s vision fosters unity and commitment among team members. Involving them in the goal-setting process enhances their sense of ownership.
• Team-Building Activities: Engaging in structured and informal activities allows team members to connect outside work tasks, promoting camaraderie and trust.
• Leadership Modeling Trustworthiness: Leaders play a pivotal role in building and maintaining trust within sales teams. They must exemplify honesty, consistency, and reliability to set a positive example for their teams. By recognizing and rewarding trustworthy behavior, leaders can reinforce a culture of trust, thereby enhancing team performance and fostering long-term relationships.
• Creating a Supportive Environment: Leaders should prioritize the well-being of their team members by providing resources for professional growth and fostering psychological safety.
Building trust with prospects is integral to sales and can significantly influence closing rates and long-term client relationships. Techniques to establish trust include:
• Building Rapport: Creating genuine connections through shared interests and personalized conversations fosters comfort and openness.
• Active Listening: Demonstrating attentiveness and understanding through reflective listening and nonverbal cues enhances trust.
• Understanding Client Needs: Thoroughly researching and asking insightful questions is crucial in building trust with prospects. This approach positions the salesperson as a trusted advisor rather than just a vendor, thereby enhancing the likelihood of closing deals and fostering long-term client relationships.
• Demonstrating Expertise: Sharing valuable insights and resources establishes credibility and positions the salesperson as a knowledgeable resource.
• Follow-Through and Transparency: Prompt follow-ups and honest communication about product capabilities help to maintain trust and foster loyalty.
The shift to remote work has introduced new challenges and opportunities for maintaining trust. Key aspects include:
• Challenges of Trust: Physical distance and limited face-to-face interactions can hinder rapport and connection, leading to potential feelings of isolation.
• Opportunities for Building Trust Remotely: Technology can enhance collaboration and transparency, creating a culture of accountability.
• Best Practices for Virtual Communication: Prioritizing regular communication through stand-ups, open-door policies, and video conferencing promotes engagement.
• Regular Check-Ins: Scheduled one-on-ones and informal interactions help strengthen relationships and maintain team morale.
• Leveraging Technology: Utilizing collaboration tools fosters seamless communication and project management.
Trust is an ongoing commitment vital to the success of B2B sales organizations. By focusing on trust at all levels—within teams and with prospects—sales leaders can effectively navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace and achieve lasting success.

Chapter 11: Deal(s) Slipping
In the competitive landscape of B2B sales, the pressure to achieve revenue goals is immense, making it critical for sales organizations to manage committed deals within the sales funnel effectively. One of the most detrimental occurrences in this environment is deal slippage, a situation where deals, which were expected to close within a specific timeframe, begin to falter, often moving into later months or quarters. This situation poses significant challenges for the sales team and executive management, as it can rapidly erode trust and jeopardize long-term business success.
When committed deals slip, they raise immediate concerns about the robustness of the sales process. Executives depend on accurate sales forecasts to make strategic decisions regarding resource allocation and hiring. If sales teams are perceived to be overpromising and underdelivering, skepticism about future forecasts can emerge, leading to a breakdown in communication and trust. This erosion of trust fosters a toxic environment where sales professionals may hesitate to share accurate updates for fear of repercussions, ultimately exacerbating the issue of deal slippage.
Deal slippage’s impact extends beyond immediate financial concerns; it can significantly affect company culture and employee morale. A culture defined by mistrust can stifle creativity and motivation among sales teams, leading to decreased productivity and a disengaged workforce. Such an environment can also permeate other departments, hindering cross-functional collaboration and the organization’s ability to respond to market changes effectively.
Financially, deal slippage jeopardizes revenue targets. Organizations risk missing critical quarterly or annual revenue goals when numerous deals shift out of their expected timeframes. This can result in cash flow issues, affecting the company’s ability to invest in growth initiatives such as product development, market expansion, or talent acquisition. Additionally, consistent deal slippage can damage the organization’s reputation among investors and stakeholders, leading to diminished confidence in leadership and potential challenges in acquiring new clients.
Organizations must prioritize open communication and alignment between sales leadership and salespeople to address these challenges. By implementing a common forecasting language, we can reduce instances of deal slippage, creating a shared understanding of what constitutes a committed deal. Regular check-ins, collaborative goal-setting, and structured feedback can promote transparency and cooperation, making everyone feel included and valued in the process.
Engaging key executives in the buying process is another critical strategy. By identifying the right stakeholders and building strong relationships, we can help maintain momentum, especially when high-probability deals are slipping. By asking thoughtful questions that uncover strategic goals and challenges, sales leaders can gain insights into deal viability and alignment with customer needs, empowering them to make influential decisions.
The effective management of deal slippage is vital for sustaining trust between sales teams and executive management, ultimately driving revenue growth and long-term success. By creating a resilient sales culture that thrives in a challenging market, we can prioritize open communication, align goals, and engage with key decision-makers. Addressing the complexities of deal slippage proactively will enhance sales performance and secure a prosperous future for the business, reassuring the audience and instilling confidence in our strategies.

Chapter 12: Compensation Effectiveness
In the sales world, the phrase “salespeople are coin-operated” aptly captures compensation’s vital role in motivating sales professionals. While monetary incentives are significant motivators, it is essential to recognize that financial rewards do not solely drive salespeople. Instead, compensation is a powerful catalyst that encourages salespeople to tackle the complexities and challenges inherent in their roles, promoting resilience, strategic thinking, and persistent effort. The prospect of achieving high earnings can propel sales professionals to engage fully in the tasks necessary for success.
However, the relationship between compensation and sales effectiveness is nuanced. Organizations often struggle to design compensation plans that incentivize desired behaviors and outcomes. A poorly constructed plan can lead to confusion, frustration, and disengagement among sales teams, ultimately undermining revenue objectives. Yet, when organizations succeed in aligning compensation strategies with the activities they want to promote, they foster an environment where salespeople feel empowered, confident, and in control of their success.
Effective compensation plans must be structured to encourage the right behaviors. A mentor once illustrated this by explaining how a successful discovery call should leave a salesperson with a clear understanding of their potential earnings—essentially, a ‘ballpark’ estimate of their commission from closing a deal. In this context, a ‘ballpark’ estimate refers to a rough but fairly accurate calculation or figure. This clarity reinforces the link between effort and reward. It can detract from their focus and motivation if salespeople find it challenging to determine their potential earnings due to an overly complex compensation structure. When compensation becomes an obstacle, it stifles essential behaviors like relationship-building and meaningful engagement with prospects.
To optimize compensation effectiveness, organizations should offer attractive financial rewards and create a transparent and easily understandable compensation framework. This transparency not only helps align salespeople’s efforts with the organization’s objectives but also reassures them of the fairness of the system, cultivating a culture where individuals are inspired and committed to pursuing personal and collective success.
In addition to monetary incentives, non-monetary rewards motivate sales teams. These can include recognition programs, opportunities for professional development, and flexible work arrangements. By acknowledging individual achievements and investing in their growth, organizations can foster a sense of value and appreciation among sales professionals, leading to increased loyalty and long-term engagement.
Furthermore, understanding that different salespeople are motivated by various factors is essential for designing effective incentive programs. Organizations can enhance their strategies by soliciting feedback and conducting surveys to understand their teams’ preferences better. Open communication channels between management and sales teams, such as regular team meetings, one-on-one check-ins, and anonymous suggestion boxes, can provide insights into the unique drivers of motivation and inform the design of incentive structures.
Finally, organizations must regularly evaluate and adapt their compensation plans to remain effective and aligned with business goals. This involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), fostering a culture of accountability, and conducting periodic reviews to ensure the compensation structure remains relevant.
Aligning compensation with desired outcomes is a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to optimize sales performance. By addressing common pitfalls such as complexity and misalignment with company goals and ensuring clear communication and ongoing feedback, organizations can create compensation strategies that motivate sales teams and contribute to achieving broader business objectives. A well-designed compensation plan is a transformative tool, empowering sales teams and driving organizational growth.
Curriculum
Optimizing Sales – WDP1 – Challenges Identified
- Current Challenges
- Challenge Experiences
- Challenge Impacts
- Common Mistakes
- Forecasting Model
- Hiring/Onboarding
- Daily Routines
- Prospect Profile
- RFP Strategy
- Maintaining Trust
- Deal(s) Slipping
- Compensation Effectiveness
Distance Learning
Introduction
Welcome to Appleton Greene and thank you for enrolling on the Optimizing Sales corporate training program. You will be learning through our unique facilitation via distance-learning method, which will enable you to practically implement everything that you learn academically. The methods and materials used in your program have been designed and developed to ensure that you derive the maximum benefits and enjoyment possible. We hope that you find the program challenging and fun to do. However, if you have never been a distance-learner before, you may be experiencing some trepidation at the task before you. So we will get you started by giving you some basic information and guidance on how you can make the best use of the modules, how you should manage the materials and what you should be doing as you work through them. This guide is designed to point you in the right direction and help you to become an effective distance-learner. Take a few hours or so to study this guide and your guide to tutorial support for students, while making notes, before you start to study in earnest.
Study environment
You will need to locate a quiet and private place to study, preferably a room where you can easily be isolated from external disturbances or distractions. Make sure the room is well-lit and incorporates a relaxed, pleasant feel. If you can spoil yourself within your study environment, you will have much more of a chance to ensure that you are always in the right frame of mind when you do devote time to study. For example, a nice fire, the ability to play soft soothing background music, soft but effective lighting, perhaps a nice view if possible and a good size desk with a comfortable chair. Make sure that your family know when you are studying and understand your study rules. Your study environment is very important. The ideal situation, if at all possible, is to have a separate study, which can be devoted to you. If this is not possible then you will need to pay a lot more attention to developing and managing your study schedule, because it will affect other people as well as yourself. The better your study environment, the more productive you will be.
Study tools & rules
Try and make sure that your study tools are sufficient and in good working order. You will need to have access to a computer, scanner and printer, with access to the internet. You will need a very comfortable chair, which supports your lower back, and you will need a good filing system. It can be very frustrating if you are spending valuable study time trying to fix study tools that are unreliable, or unsuitable for the task. Make sure that your study tools are up to date. You will also need to consider some study rules. Some of these rules will apply to you and will be intended to help you to be more disciplined about when and how you study. This distance-learning guide will help you and after you have read it you can put some thought into what your study rules should be. You will also need to negotiate some study rules for your family, friends or anyone who lives with you. They too will need to be disciplined in order to ensure that they can support you while you study. It is important to ensure that your family and friends are an integral part of your study team. Having their support and encouragement can prove to be a crucial contribution to your successful completion of the program. Involve them in as much as you can.
Successful distance-learning
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes or workshops, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. But unlike traditional internal training courses, it is the student’s responsibility, with a distance-learning program, to ensure that they manage their own study contribution. This requires strong self-discipline and self-motivation skills and there must be a clear will to succeed. Those students who are used to managing themselves, are good at managing others and who enjoy working in isolation, are more likely to be good distance-learners. It is also important to be aware of the main reasons why you are studying and of the main objectives that you are hoping to achieve as a result. You will need to remind yourself of these objectives at times when you need to motivate yourself. Never lose sight of your long-term goals and your short-term objectives. There is nobody available here to pamper you, or to look after you, or to spoon-feed you with information, so you will need to find ways to encourage and appreciate yourself while you are studying. Make sure that you chart your study progress, so that you can be sure of your achievements and re-evaluate your goals and objectives regularly.
Self-assessment
Appleton Greene training programs are in all cases post-graduate programs. Consequently, you should already have obtained a business-related degree and be an experienced learner. You should therefore already be aware of your study strengths and weaknesses. For example, which time of the day are you at your most productive? Are you a lark or an owl? What study methods do you respond to the most? Are you a consistent learner? How do you discipline yourself? How do you ensure that you enjoy yourself while studying? It is important to understand yourself as a learner and so some self-assessment early on will be necessary if you are to apply yourself correctly. Perform a SWOT analysis on yourself as a student. List your internal strengths and weaknesses as a student and your external opportunities and threats. This will help you later on when you are creating a study plan. You can then incorporate features within your study plan that can ensure that you are playing to your strengths, while compensating for your weaknesses. You can also ensure that you make the most of your opportunities, while avoiding the potential threats to your success.
Accepting responsibility as a student
Training programs invariably require a significant investment, both in terms of what they cost and in the time that you need to contribute to study and the responsibility for successful completion of training programs rests entirely with the student. This is never more apparent than when a student is learning via distance-learning. Accepting responsibility as a student is an important step towards ensuring that you can successfully complete your training program. It is easy to instantly blame other people or factors when things go wrong. But the fact of the matter is that if a failure is your failure, then you have the power to do something about it, it is entirely in your own hands. If it is always someone else’s failure, then you are powerless to do anything about it. All students study in entirely different ways, this is because we are all individuals and what is right for one student, is not necessarily right for another. In order to succeed, you will have to accept personal responsibility for finding a way to plan, implement and manage a personal study plan that works for you. If you do not succeed, you only have yourself to blame.
Planning
By far the most critical contribution to stress, is the feeling of not being in control. In the absence of planning we tend to be reactive and can stumble from pillar to post in the hope that things will turn out fine in the end. Invariably they don’t! In order to be in control, we need to have firm ideas about how and when we want to do things. We also need to consider as many possible eventualities as we can, so that we are prepared for them when they happen. Prescriptive Change, is far easier to manage and control, than Emergent Change. The same is true with distance-learning. It is much easier and much more enjoyable, if you feel that you are in control and that things are going to plan. Even when things do go wrong, you are prepared for them and can act accordingly without any unnecessary stress. It is important therefore that you do take time to plan your studies properly.
Management
Once you have developed a clear study plan, it is of equal importance to ensure that you manage the implementation of it. Most of us usually enjoy planning, but it is usually during implementation when things go wrong. Targets are not met and we do not understand why. Sometimes we do not even know if targets are being met. It is not enough for us to conclude that the study plan just failed. If it is failing, you will need to understand what you can do about it. Similarly if your study plan is succeeding, it is still important to understand why, so that you can improve upon your success. You therefore need to have guidelines for self-assessment so that you can be consistent with performance improvement throughout the program. If you manage things correctly, then your performance should constantly improve throughout the program.
Study objectives & tasks
The first place to start is developing your program objectives. These should feature your reasons for undertaking the training program in order of priority. Keep them succinct and to the point in order to avoid confusion. Do not just write the first things that come into your head because they are likely to be too similar to each other. Make a list of possible departmental headings, such as: Customer Service; E-business; Finance; Globalization; Human Resources; Technology; Legal; Management; Marketing and Production. Then brainstorm for ideas by listing as many things that you want to achieve under each heading and later re-arrange these things in order of priority. Finally, select the top item from each department heading and choose these as your program objectives. Try and restrict yourself to five because it will enable you to focus clearly. It is likely that the other things that you listed will be achieved if each of the top objectives are achieved. If this does not prove to be the case, then simply work through the process again.
Study forecast
As a guide, the Appleton Greene Optimizing Sales corporate training program should take 12-18 months to complete, depending upon your availability and current commitments. The reason why there is such a variance in time estimates is because every student is an individual, with differing productivity levels and different commitments. These differentiations are then exaggerated by the fact that this is a distance-learning program, which incorporates the practical integration of academic theory as an as a part of the training program. Consequently all of the project studies are real, which means that important decisions and compromises need to be made. You will want to get things right and will need to be patient with your expectations in order to ensure that they are. We would always recommend that you are prudent with your own task and time forecasts, but you still need to develop them and have a clear indication of what are realistic expectations in your case. With reference to your time planning: consider the time that you can realistically dedicate towards study with the program every week; calculate how long it should take you to complete the program, using the guidelines featured here; then break the program down into logical modules and allocate a suitable proportion of time to each of them, these will be your milestones; you can create a time plan by using a spreadsheet on your computer, or a personal organizer such as MS Outlook, you could also use a financial forecasting software; break your time forecasts down into manageable chunks of time, the more specific you can be, the more productive and accurate your time management will be; finally, use formulas where possible to do your time calculations for you, because this will help later on when your forecasts need to change in line with actual performance. With reference to your task planning: refer to your list of tasks that need to be undertaken in order to achieve your program objectives; with reference to your time plan, calculate when each task should be implemented; remember that you are not estimating when your objectives will be achieved, but when you will need to focus upon implementing the corresponding tasks; you also need to ensure that each task is implemented in conjunction with the associated training modules which are relevant; then break each single task down into a list of specific to do’s, say approximately ten to do’s for each task and enter these into your study plan; once again you could use MS Outlook to incorporate both your time and task planning and this could constitute your study plan; you could also use a project management software like MS Project. You should now have a clear and realistic forecast detailing when you can expect to be able to do something about undertaking the tasks to achieve your program objectives.
Performance management
It is one thing to develop your study forecast, it is quite another to monitor your progress. Ultimately it is less important whether you achieve your original study forecast and more important that you update it so that it constantly remains realistic in line with your performance. As you begin to work through the program, you will begin to have more of an idea about your own personal performance and productivity levels as a distance-learner. Once you have completed your first study module, you should re-evaluate your study forecast for both time and tasks, so that they reflect your actual performance level achieved. In order to achieve this you must first time yourself while training by using an alarm clock. Set the alarm for hourly intervals and make a note of how far you have come within that time. You can then make a note of your actual performance on your study plan and then compare your performance against your forecast. Then consider the reasons that have contributed towards your performance level, whether they are positive or negative and make a considered adjustment to your future forecasts as a result. Given time, you should start achieving your forecasts regularly.
With reference to time management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual time taken in your study plan; consider your successes with time-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; consider your failures with time-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future time planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to time planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your time expectations. You need to be consistent with your time management, otherwise you will never complete your studies. This will either be because you are not contributing enough time to your studies, or you will become less efficient with the time that you do allocate to your studies. Remember, if you are not in control of your studies, they can just become yet another cause of stress for you.
With reference to your task management: time yourself while you are studying and make a note of the actual tasks that you have undertaken in your study plan; consider your successes with task-efficiency and the reasons for the success in each case; take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; consider your failures with task-efficiency and the reasons for the failures in each case and take this into consideration when reviewing future task planning; re-evaluate your study forecast in relation to task planning for the remainder of your training program to ensure that you continue to be realistic about your task expectations. You need to be consistent with your task management, otherwise you will never know whether you are achieving your program objectives or not.
Keeping in touch
You will have access to qualified and experienced professors and tutors who are responsible for providing tutorial support for your particular training program. So don’t be shy about letting them know how you are getting on. We keep electronic records of all tutorial support emails so that professors and tutors can review previous correspondence before considering an individual response. It also means that there is a record of all communications between you and your professors and tutors and this helps to avoid any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation. If you have a problem relating to the program, share it with them via email. It is likely that they have come across the same problem before and are usually able to make helpful suggestions and steer you in the right direction. To learn more about when and how to use tutorial support, please refer to the Tutorial Support section of this student information guide. This will help you to ensure that you are making the most of tutorial support that is available to you and will ultimately contribute towards your success and enjoyment with your training program.
Work colleagues and family
You should certainly discuss your program study progress with your colleagues, friends and your family. Appleton Greene training programs are very practical. They require you to seek information from other people, to plan, develop and implement processes with other people and to achieve feedback from other people in relation to viability and productivity. You will therefore have plenty of opportunities to test your ideas and enlist the views of others. People tend to be sympathetic towards distance-learners, so don’t bottle it all up in yourself. Get out there and share it! It is also likely that your family and colleagues are going to benefit from your labors with the program, so they are likely to be much more interested in being involved than you might think. Be bold about delegating work to those who might benefit themselves. This is a great way to achieve understanding and commitment from people who you may later rely upon for process implementation. Share your experiences with your friends and family.
Making it relevant
The key to successful learning is to make it relevant to your own individual circumstances. At all times you should be trying to make bridges between the content of the program and your own situation. Whether you achieve this through quiet reflection or through interactive discussion with your colleagues, client partners or your family, remember that it is the most important and rewarding aspect of translating your studies into real self-improvement. You should be clear about how you want the program to benefit you. This involves setting clear study objectives in relation to the content of the course in terms of understanding, concepts, completing research or reviewing activities and relating the content of the modules to your own situation. Your objectives may understandably change as you work through the program, in which case you should enter the revised objectives on your study plan so that you have a permanent reminder of what you are trying to achieve, when and why.
Distance-learning check-list
Prepare your study environment, your study tools and rules.
Undertake detailed self-assessment in terms of your ability as a learner.
Create a format for your study plan.
Consider your study objectives and tasks.
Create a study forecast.
Assess your study performance.
Re-evaluate your study forecast.
Be consistent when managing your study plan.
Use your Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) for tutorial support.
Make sure you keep in touch with those around you.
Tutorial Support
Programs
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. They are implemented over a sustainable period of time and professional support is consistently provided by qualified learning providers and specialist consultants.
Support available
You will have a designated Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and an Accredited Consultant and we encourage you to communicate with them as much as possible. In all cases tutorial support is provided online because we can then keep a record of all communications to ensure that tutorial support remains consistent. You would also be forwarding your work to the tutorial support unit for evaluation and assessment. You will receive individual feedback on all of the work that you undertake on a one-to-one basis, together with specific recommendations for anything that may need to be changed in order to achieve a pass with merit or a pass with distinction and you then have as many opportunities as you may need to re-submit project studies until they meet with the required standard. Consequently the only reason that you should really fail (CLP) is if you do not do the work. It makes no difference to us whether a student takes 12 months or 18 months to complete the program, what matters is that in all cases the same quality standard will have been achieved.
Support Process
Please forward all of your future emails to the designated (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit email address that has been provided and please do not duplicate or copy your emails to other AGC email accounts as this will just cause unnecessary administration. Please note that emails are always answered as quickly as possible but you will need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general tutorial support emails during busy periods, because emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. You will also need to allow a period of up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Please therefore kindly allow for this within your time planning. All communications are managed online via email because it enables tutorial service support managers to review other communications which have been received before responding and it ensures that there is a copy of all communications retained on file for future reference. All communications will be stored within your personal (CLP) study file here at Appleton Greene throughout your designated study period. If you need any assistance or clarification at any time, please do not hesitate to contact us by forwarding an email and remember that we are here to help. If you have any questions, please list and number your questions succinctly and you can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each and every query.
Time Management
It takes approximately 1 Year to complete the Optimizing Sales corporate training program, incorporating 12 x 6-hour monthly workshops. Each student will also need to contribute approximately 4 hours per week over 1 Year of their personal time. Students can study from home or work at their own pace and are responsible for managing their own study plan. There are no formal examinations and students are evaluated and assessed based upon their project study submissions, together with the quality of their internal analysis and supporting documents. They can contribute more time towards study when they have the time to do so and can contribute less time when they are busy. All students tend to be in full time employment while studying and the Optimizing Sales program is purposely designed to accommodate this, so there is plenty of flexibility in terms of time management. It makes no difference to us at Appleton Greene, whether individuals take 12-18 months to complete this program. What matters is that in all cases the same standard of quality will have been achieved with the standard and bespoke programs that have been developed.
Distance Learning Guide
The distance learning guide should be your first port of call when starting your training program. It will help you when you are planning how and when to study, how to create the right environment and how to establish the right frame of mind. If you can lay the foundations properly during the planning stage, then it will contribute to your enjoyment and productivity while training later. The guide helps to change your lifestyle in order to accommodate time for study and to cultivate good study habits. It helps you to chart your progress so that you can measure your performance and achieve your goals. It explains the tools that you will need for study and how to make them work. It also explains how to translate academic theory into practical reality. Spend some time now working through your distance learning guide and make sure that you have firm foundations in place so that you can make the most of your distance learning program. There is no requirement for you to attend training workshops or classes at Appleton Greene offices. The entire program is undertaken online, program course manuals and project studies are administered via the Appleton Greene web site and via email, so you are able to study at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office as long as you have a computer and access to the internet.
How To Study
The how to study guide provides students with a clear understanding of the Appleton Greene facilitation via distance learning training methods and enables students to obtain a clear overview of the training program content. It enables students to understand the step-by-step training methods used by Appleton Greene and how course manuals are integrated with project studies. It explains the research and development that is required and the need to provide evidence and references to support your statements. It also enables students to understand precisely what will be required of them in order to achieve a pass with merit and a pass with distinction for individual project studies and provides useful guidance on how to be innovative and creative when developing your Unique Program Proposition (UPP).
Tutorial Support
Tutorial support for the Appleton Greene Optimizing Sales corporate training program is provided online either through the Appleton Greene Client Support Portal (CSP), or via email. All tutorial support requests are facilitated by a designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). They are responsible for deciding which professor or tutor is the most appropriate option relating to the support required and then the tutorial support request is forwarded onto them. Once the professor or tutor has completed the tutorial support request and answered any questions that have been asked, this communication is then returned to the student via email by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM). This enables all tutorial support, between students, professors and tutors, to be facilitated by the designated Program Administration Manager (PAM) efficiently and securely through the email account. You will therefore need to allow a period of up to 20 business days for responses to general support queries and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because all tutorial support requests are answered strictly within the order in which they are received. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Consequently you need to put some thought into the management of your tutorial support procedure in order to ensure that your study plan is feasible and to obtain the maximum possible benefit from tutorial support during your period of study. Please retain copies of your tutorial support emails for future reference. Please ensure that ALL of your tutorial support emails are set out using the format as suggested within your guide to tutorial support. Your tutorial support emails need to be referenced clearly to the specific part of the course manual or project study which you are working on at any given time. You also need to list and number any questions that you would like to ask, up to a maximum of five questions within each tutorial support email. Remember the more specific you can be with your questions the more specific your answers will be too and this will help you to avoid any unnecessary misunderstanding, misinterpretation, or duplication. The guide to tutorial support is intended to help you to understand how and when to use support in order to ensure that you get the most out of your training program. Appleton Greene training programs are designed to enable you to do things for yourself. They provide you with a structure or a framework and we use tutorial support to facilitate students while they practically implement what they learn. In other words, we are enabling students to do things for themselves. The benefits of distance learning via facilitation are considerable and are much more sustainable in the long-term than traditional short-term knowledge sharing programs. Consequently you should learn how and when to use tutorial support so that you can maximize the benefits from your learning experience with Appleton Greene. This guide describes the purpose of each training function and how to use them and how to use tutorial support in relation to each aspect of the training program. It also provides useful tips and guidance with regard to best practice.
Tutorial Support Tips
Students are often unsure about how and when to use tutorial support with Appleton Greene. This Tip List will help you to understand more about how to achieve the most from using tutorial support. Refer to it regularly to ensure that you are continuing to use the service properly. Tutorial support is critical to the success of your training experience, but it is important to understand when and how to use it in order to maximize the benefit that you receive. It is no coincidence that those students who succeed are those that learn how to be positive, proactive and productive when using tutorial support.
Be positive and friendly with your tutorial support emails
Remember that if you forward an email to the tutorial support unit, you are dealing with real people. “Do unto others as you would expect others to do unto you”. If you are positive, complimentary and generally friendly in your emails, you will generate a similar response in return. This will be more enjoyable, productive and rewarding for you in the long-term.
Think about the impression that you want to create
Every time that you communicate, you create an impression, which can be either positive or negative, so put some thought into the impression that you want to create. Remember that copies of all tutorial support emails are stored electronically and tutors will always refer to prior correspondence before responding to any current emails. Over a period of time, a general opinion will be arrived at in relation to your character, attitude and ability. Try to manage your own frustrations, mood swings and temperament professionally, without involving the tutorial support team. Demonstrating frustration or a lack of patience is a weakness and will be interpreted as such. The good thing about communicating in writing, is that you will have the time to consider your content carefully, you can review it and proof-read it before sending your email to Appleton Greene and this should help you to communicate more professionally, consistently and to avoid any unnecessary knee-jerk reactions to individual situations as and when they may arise. Please also remember that the CLP Tutorial Support Unit will not just be responsible for evaluating and assessing the quality of your work, they will also be responsible for providing recommendations to other learning providers and to client contacts within the Appleton Greene global client network, so do be in control of your own emotions and try to create a good impression.
Remember that quality is preferred to quantity
Please remember that when you send an email to the tutorial support team, you are not using Twitter or Text Messaging. Try not to forward an email every time that you have a thought. This will not prove to be productive either for you or for the tutorial support team. Take time to prepare your communications properly, as if you were writing a professional letter to a business colleague and make a list of queries that you are likely to have and then incorporate them within one email, say once every month, so that the tutorial support team can understand more about context, application and your methodology for study. Get yourself into a consistent routine with your tutorial support requests and use the tutorial support template provided with ALL of your emails. The (CLP) Tutorial Support Unit will not spoon-feed you with information. They need to be able to evaluate and assess your tutorial support requests carefully and professionally.
Be specific about your questions in order to receive specific answers
Try not to write essays by thinking as you are writing tutorial support emails. The tutorial support unit can be unclear about what in fact you are asking, or what you are looking to achieve. Be specific about asking questions that you want answers to. Number your questions. You will then receive specific answers to each and every question. This is the main purpose of tutorial support via email.
Keep a record of your tutorial support emails
It is important that you keep a record of all tutorial support emails that are forwarded to you. You can then refer to them when necessary and it avoids any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Individual training workshops or telephone support
Please be advised that Appleton Greene does not provide separate or individual tutorial support meetings, workshops, or provide telephone support for individual students. Appleton Greene is an equal opportunities learning and service provider and we are therefore understandably bound to treat all students equally. We cannot therefore broker special financial or study arrangements with individual students regardless of the circumstances. All tutorial support is provided online and this enables Appleton Greene to keep a record of all communications between students, professors and tutors on file for future reference, in accordance with our quality management procedure and your terms and conditions of enrolment. All tutorial support is provided online via email because it enables us to have time to consider support content carefully, it ensures that you receive a considered and detailed response to your queries. You can number questions that you would like to ask, which relate to things that you do not understand or where clarification may be required. You can then be sure of receiving specific answers to each individual query. You will also then have a record of these communications and of all tutorial support, which has been provided to you. This makes tutorial support administration more productive by avoiding any unnecessary duplication, misunderstanding, or misinterpretation.
Tutorial Support Email Format
You should use this tutorial support format if you need to request clarification or assistance while studying with your training program. Please note that ALL of your tutorial support request emails should use the same format. You should therefore set up a standard email template, which you can then use as and when you need to. Emails that are forwarded to Appleton Greene, which do not use the following format, may be rejected and returned to you by the (CLP) Program Administration Manager. A detailed response will then be forwarded to you via email usually within 20 business days of receipt for general support queries and 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies. This does not include weekends or public holidays. Your tutorial support request, together with the corresponding TSU reply, will then be saved and stored within your electronic TSU file at Appleton Greene for future reference.
Subject line of your email
Please insert: Appleton Greene (CLP) Tutorial Support Request: (Your Full Name) (Date), within the subject line of your email.
Main body of your email
Please insert:
1. Appleton Greene Certified Learning Provider (CLP) Tutorial Support Request
2. Your Full Name
3. Date of TS request
4. Preferred email address
5. Backup email address
6. Course manual page name or number (reference)
7. Project study page name or number (reference)
Subject of enquiry
Please insert a maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Briefly outline the subject matter of your inquiry, or what your questions relate to.
Question 1
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 3
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 4
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Question 5
Maximum of 50 words (please be succinct)
Please note that a maximum of 5 questions is permitted with each individual tutorial support request email.
Procedure
* List the questions that you want to ask first, then re-arrange them in order of priority. Make sure that you reference them, where necessary, to the course manuals or project studies.
* Make sure that you are specific about your questions and number them. Try to plan the content within your emails to make sure that it is relevant.
* Make sure that your tutorial support emails are set out correctly, using the Tutorial Support Email Format provided here.
* Save a copy of your email and incorporate the date sent after the subject title. Keep your tutorial support emails within the same file and in date order for easy reference.
* Allow up to 20 business days for a response to general tutorial support emails and up to 30 business days for the evaluation and assessment of project studies, because detailed individual responses will be made in all cases and tutorial support emails are answered strictly within the order in which they are received.
* Emails can and do get lost. So if you have not received a reply within the appropriate time, forward another copy or a reminder to the tutorial support unit to be sure that it has been received but do not forward reminders unless the appropriate time has elapsed.
* When you receive a reply, save it immediately featuring the date of receipt after the subject heading for easy reference. In most cases the tutorial support unit replies to your questions individually, so you will have a record of the questions that you asked as well as the answers offered. With project studies however, separate emails are usually forwarded by the tutorial support unit, so do keep a record of your own original emails as well.
* Remember to be positive and friendly in your emails. You are dealing with real people who will respond to the same things that you respond to.
* Try not to repeat questions that have already been asked in previous emails. If this happens the tutorial support unit will probably just refer you to the appropriate answers that have already been provided within previous emails.
* If you lose your tutorial support email records you can write to Appleton Greene to receive a copy of your tutorial support file, but a separate administration charge may be levied for this service.
How To Study
Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can help you to plan a task list for getting started so that you can be clear about your direction and your priorities in relation to your training program. It is also a good way to introduce yourself to the tutorial support team.
Planning your study environment
Your study conditions are of great importance and will have a direct effect on how much you enjoy your training program. Consider how much space you will have, whether it is comfortable and private and whether you are likely to be disturbed. The study tools and facilities at your disposal are also important to the success of your distance-learning experience. Your tutorial support unit can help with useful tips and guidance, regardless of your starting position. It is important to get this right before you start working on your training program.
Planning your program objectives
It is important that you have a clear list of study objectives, in order of priority, before you start working on your training program. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance here to ensure that your study objectives have been afforded due consideration and priority.
Planning how and when to study
Distance-learners are freed from the necessity of attending regular classes, since they can study in their own way, at their own pace and for their own purposes. This approach is designed to let you study efficiently away from the traditional classroom environment. It is important however, that you plan how and when to study, so that you are making the most of your natural attributes, strengths and opportunities. Your tutorial support unit can offer assistance and useful tips to ensure that you are playing to your strengths.
Planning your study tasks
You should have a clear understanding of the study tasks that you should be undertaking and the priority associated with each task. These tasks should also be integrated with your program objectives. The distance learning guide and the guide to tutorial support for students should help you here, but if you need any clarification or assistance, please contact your tutorial support unit.
Planning your time
You will need to allocate specific times during your calendar when you intend to study if you are to have a realistic chance of completing your program on time. You are responsible for planning and managing your own study time, so it is important that you are successful with this. Your tutorial support unit can help you with this if your time plan is not working.
Keeping in touch
Consistency is the key here. If you communicate too frequently in short bursts, or too infrequently with no pattern, then your management ability with your studies will be questioned, both by you and by your tutorial support unit. It is obvious when a student is in control and when one is not and this will depend how able you are at sticking with your study plan. Inconsistency invariably leads to in-completion.
Charting your progress
Your tutorial support team can help you to chart your own study progress. Refer to your distance learning guide for further details.
Making it work
To succeed, all that you will need to do is apply yourself to undertaking your training program and interpreting it correctly. Success or failure lies in your hands and your hands alone, so be sure that you have a strategy for making it work. Your Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and Accredited Consultant can guide you through the process of program planning, development and implementation.
Reading methods
Interpretation is often unique to the individual but it can be improved and even quantified by implementing consistent interpretation methods. Interpretation can be affected by outside interference such as family members, TV, or the Internet, or simply by other thoughts which are demanding priority in our minds. One thing that can improve our productivity is using recognized reading methods. This helps us to focus and to be more structured when reading information for reasons of importance, rather than relaxation.
Speed reading
When reading through course manuals for the first time, subconsciously set your reading speed to be just fast enough that you cannot dwell on individual words or tables. With practice, you should be able to read an A4 sheet of paper in one minute. You will not achieve much in the way of a detailed understanding, but your brain will retain a useful overview. This overview will be important later on and will enable you to keep individual issues in perspective with a more generic picture because speed reading appeals to the memory part of the brain. Do not worry about what you do or do not remember at this stage.
Content reading
Once you have speed read everything, you can then start work in earnest. You now need to read a particular section of your course manual thoroughly, by making detailed notes while you read. This process is called Content Reading and it will help to consolidate your understanding and interpretation of the information that has been provided.
Making structured notes on the course manuals
When you are content reading, you should be making detailed notes, which are both structured and informative. Make these notes in a MS Word document on your computer, because you can then amend and update these as and when you deem it to be necessary. List your notes under three headings: 1. Interpretation – 2. Questions – 3. Tasks. The purpose of the 1st section is to clarify your interpretation by writing it down. The purpose of the 2nd section is to list any questions that the issue raises for you. The purpose of the 3rd section is to list any tasks that you should undertake as a result. Anyone who has graduated with a business-related degree should already be familiar with this process.
Organizing structured notes separately
You should then transfer your notes to a separate study notebook, preferably one that enables easy referencing, such as a MS Word Document, a MS Excel Spreadsheet, a MS Access Database, or a personal organizer on your cell phone. Transferring your notes allows you to have the opportunity of cross-checking and verifying them, which assists considerably with understanding and interpretation. You will also find that the better you are at doing this, the more chance you will have of ensuring that you achieve your study objectives.
Question your understanding
Do challenge your understanding. Explain things to yourself in your own words by writing things down.
Clarifying your understanding
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your understanding.
Question your interpretation
Do challenge your interpretation. Qualify your interpretation by writing it down.
Clarifying your interpretation
If you are at all unsure, forward an email to your tutorial support unit and they will help to clarify your interpretation.
Qualification Requirements
The student will need to successfully complete the project study and all of the exercises relating to the Optimizing Sales corporate training program, achieving a pass with merit or distinction in each case, in order to qualify as an Accredited Optimizing Sales Specialist (AOSS). All monthly workshops need to be tried and tested within your company. These project studies can be completed in your own time and at your own pace and in the comfort of your own home or office. There are no formal examinations, assessment is based upon the successful completion of the project studies. They are called project studies because, unlike case studies, these projects are not theoretical, they incorporate real program processes that need to be properly researched and developed. The project studies assist us in measuring your understanding and interpretation of the training program and enable us to assess qualification merits. All of the project studies are based entirely upon the content within the training program and they enable you to integrate what you have learnt into your corporate training practice.
Optimizing Sales – Grading Contribution
Project Study – Grading Contribution
Customer Service – 10%
E-business – 05%
Finance – 10%
Globalization – 10%
Human Resources – 10%
Information Technology – 10%
Legal – 05%
Management – 10%
Marketing – 10%
Production – 10%
Education – 05%
Logistics – 05%
TOTAL GRADING – 100%
Qualification grades
A mark of 90% = Pass with Distinction.
A mark of 75% = Pass with Merit.
A mark of less than 75% = Fail.
If you fail to achieve a mark of 75% with a project study, you will receive detailed feedback from the Certified Learning Provider (CLP) and/or Accredited Consultant, together with a list of tasks which you will need to complete, in order to ensure that your project study meets with the minimum quality standard that is required by Appleton Greene. You can then re-submit your project study for further evaluation and assessment. Indeed you can re-submit as many drafts of your project studies as you need to, until such a time as they eventually meet with the required standard by Appleton Greene, so you need not worry about this, it is all part of the learning process.
When marking project studies, Appleton Greene is looking for sufficient evidence of the following:
Pass with merit
A satisfactory level of program understanding
A satisfactory level of program interpretation
A satisfactory level of project study content presentation
A satisfactory level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
A satisfactory level of the practical integration of academic theory
Pass with distinction
An exceptional level of program understanding
An exceptional level of program interpretation
An exceptional level of project study content presentation
An exceptional level of Unique Program Proposition (UPP) quality
An exceptional level of the practical integration of academic theory
Preliminary Analysis
Websites
Here are two websites that provide valuable insights into overcoming sales challenges and fostering a collaborative environment for sharing sales strategies:
Close.com offers guides and resources on sales strategies, customer acquisition, and overcoming common sales obstacles. It emphasizes the importance of using tools and techniques to drive sales efficiency.
https://www.close.com/blog/customer-acquisition
Single Grain – This marketing and sales strategy blog includes case studies on successful sales strategies. It addresses obstacles like competition and market positioning while focusing on data-driven solutions for overcoming sales barriers.
https://www.singlegrain.com/casestudies/lead-generation-case-study/
These resources can help sales teams reflect on their challenges and share solutions within their organizations.

Books
Here are five insightful books that cover sales challenges and strategies for overcoming obstacles, including team dynamics, customer acquisition, lead generation, and more:
“The Challenger Sale: Taking Control of the Customer Conversation” by Matthew Dixon and Brent Adamson
This book explains how successful sales reps challenge customers’ assumptions and teach them new perspectives, addressing sales challenges like customer hesitation, lead generation, and competitive positioning.
“New Sales. Simplified.: The Essential Handbook for Prospecting and New Business Development” by Mike Weinberg
Focused on overcoming challenges in prospecting and new business generation, Weinberg provides strategies and practical steps to improve the sales process and secure more business.
“SPIN Selling” by Neil Rackham
This book is a classic in sales methodology. It introduces the SPIN technique (Situation, Problem, Implication, Need-Payoff) to address complex sales challenges and improve closing rates.
“Sales EQ: How Ultra High Performers Leverage Sales-Specific Emotional Intelligence to Close the Complex Deal” by Jeb Blount
This book covers how emotional intelligence is crucial in overcoming sales challenges such as long sales cycles and difficult customer relationships, offering strategies to handle team dynamics and boost performance.
“The Ultimate Sales Machine: Turbocharge Your Business with Relentless Focus on 12 Key Strategies” by Chet Holmes
Holmes outlines 12 strategies to improve sales effectiveness, covering lead generation, customer acquisition, and overcoming team-related challenges. His approach is practical and action-oriented, making it ideal for sales teams looking to optimize their performance.
These books will help sales professionals reflect on their challenges and provide proven strategies for overcoming them.

Articles
Here are four insightful articles that address various sales challenges and provide strategies for overcoming them:
“19 Top Sales Challenges in 2024 and Beyond (With Proven Solutions)”
This article explores the major challenges that sales teams face today, such as personalization, increasing competition, and longer sales cycles. It offers actionable solutions, including CRM and AI tools for better customer insights and lead management. Read More.
“How To Tackle B2B Sales Challenges in 2024”
Focused on the evolving landscape of B2B sales, this article covers challenges such as integrating marketing and sales efforts, handling longer sales cycles, and the importance of in-person networking in a digital era. Read More.
“6 Customer Acquisition Challenges (And How To Overcome Them!)”
This article highlights customer acquisition difficulties like competition, shifting consumer behavior, and the challenge of generating high-quality leads. It provides strategies such as improving differentiation, using customer data analytics, and focusing on personalized experiences. Read More.
“Dynamics 365 Sales: Customer Success Stories”
This post outlines how companies in various industries, such as finance and manufacturing, have successfully used CRM tools like Microsoft Dynamics 365 to streamline their sales processes, manage leads, and build stronger client relationships. Read More.
These resources will help you reflect on common sales challenges and identify strategies for overcoming obstacles in areas such as lead generation, customer acquisition, and sales team dynamics.
Course Manuals 1-12
Course Manual 1: Current Challenges
The sales optimization program is a strategy and a crucial initiative for any B2B organization aiming to boost its performance and drive revenue growth. Before delving into optimization strategies, it’s vital to acknowledge and tackle the current challenges that sales teams face. This is the starting point of our journey—exploring the specific pain points, roadblocks, and hurdles hindering sales success. Understanding these challenges allows teams to put their unique circumstances into perspective while drawing on collective experiences to learn from one another. The sales optimization program starts with an interactive discussion about common challenges in the B2B sales world, enabling individuals to share stories and learn from diverse perspectives.
While no two organizations face the same circumstances, it’s important to recognize that many challenges in B2B sales have shared roots. By openly discussing these challenges, sales teams can foster a more comprehensive understanding of what’s holding them back. Whether the challenges revolve around customer acquisition, competition, or pricing issues, the goal is to dissect these obstacles and analyze their impact in general and in the specific context of each participant’s organization. This open discussion will help sales teams identify the obstacles that need immediate attention and recognize areas where improvements can make the most significant difference.
The B2B sales landscape continually evolves, and keeping up with its pace can be daunting. External market conditions, technological advancements, buyer behavior shifts, and competitive pressures often add layers of complexity. Additionally, internal factors such as inefficient sales processes, misalignment between sales and marketing, or lack of data-driven decision-making further complicate the efforts to optimize sales. By sharing experiences, sales professionals can better understand how these challenges manifest in different settings and learn strategies that others have found successful.
Participants in this program are encouraged to bring in insights from their current roles, past experiences, and industry best practices to enrich the discussion. The goal is not just to identify challenges but to understand their implications and determine actionable steps toward overcoming them. While each organization may face distinct obstacles, there is immense value in pooling knowledge to find standard solutions. Whether it’s addressing challenges like lead qualification, customer retention, or adapting to changing buyer expectations, the discussion is designed to empower sales teams to chart a more informed path toward optimization.
Customer Acquisition and Lead Generation Challenges
One of the most significant and persistent challenges in B2B sales is the acquisition of high-quality leads. While the volume of leads is essential, the true measure of success lies in generating leads that convert into loyal customers. Sales teams often struggle to identify and engage the right prospects, those who show interest, fit the ideal customer profile and possess the potential for long-term value. This process of identifying and engaging the right prospects is what we refer to as ‘lead qualification ‘. With intense competition and the sheer volume of available options in the marketplace, cutting through the noise to capture the attention of these prospects can be daunting.
One of the primary reasons lead generation remains a challenge is the increasing complexity of the B2B buying process. Today’s buyers are more informed than ever, conducting extensive research before engaging with a sales team. This shift has pressured sales and marketing teams to rethink their strategies, ensuring they reach prospects earlier in their decision-making process. While still in use, traditional outbound tactics like cold calling or email blasts are often less effective in this modern landscape. Instead, there’s a growing emphasis on inbound marketing strategies, where companies create valuable content that attracts potential leads organically, such as through blogs, webinars, and social media. However, many organizations fail to ensure these efforts translate into actionable sales opportunities.
Another critical factor in overcoming lead generation challenges is the strategic use of technology, particularly AI and automation tools. AI can significantly enhance the lead generation process by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns in customer behavior, and predicting which prospects are most likely to convert. Machine learning algorithms can analyze the characteristics of a company’s most successful customers and find similar prospects that align with that profile. AI can also help prioritize leads, enabling sales teams to focus on high-value opportunities rather than spending time on leads with low conversion potential. Furthermore, automation tools can handle repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails or scheduling appointments, freeing sales professionals to concentrate on relationship-building and closing deals. This technological advancement is a game-changer in the B2B sales landscape, offering new opportunities and strategies for success.
However, one of the most critical and often overlooked elements of lead generation success is the alignment between sales and marketing teams. These two functions must work in harmony for a lead generation strategy to work effectively. Marketing teams are typically responsible for generating interest and awareness, while sales teams focus on converting that interest into closed deals. When there’s a disconnect between these functions—unclear messaging, poorly defined lead qualification criteria, or a lack of shared goals—the process breaks down, resulting in lost opportunities. Therefore, it’s not just a suggestion, but a necessity for organizations to invest in creating seamless communication between sales and marketing, ensuring they continuously share data, insights, and feedback to refine their lead-generation efforts. This collaboration is not just beneficial, but essential for success.
Additionally, the competition in the B2B space presents another layer of difficulty in customer acquisition. Buyers today are not only evaluating one or two companies—they are likely researching numerous vendors and comparing prices, features, and long-term value. Companies must offer more than just a superior product or service; they must demonstrate value throughout the buyer’s journey. This means offering personalized content, engaging through multiple channels, and providing a solution that aligns with the prospect’s unique challenges and objectives.
Attracting and generating quality leads in B2B sales requires not just technology, but strategic thinking. Companies that can effectively leverage these elements are better positioned to turn prospects into long-term, high-value customers and overcome the inherent challenges of customer acquisition in today’s competitive landscape. It’s not just about having the right tools, but about knowing how to use them strategically.
Navigating Complex Buyer Journeys
The B2B buying journey, also known as the customer’s purchasing process, has evolved into a more intricate process, with sales cycles extending longer, decision-making becoming more decentralized, and prospects demanding greater personalization throughout the experience. Unlike traditional sales approaches, where a single decision-maker could greenlight a purchase, today’s B2B transactions often involve multiple stakeholders across various departments. This increased complexity poses significant challenges for sales teams, requiring them to adopt more sophisticated strategies to manage interactions and guide prospects toward a final purchase decision.
1. Multiple Stakeholders and Decision Makers
One of the primary difficulties in navigating the B2B buying process is managing multiple stakeholders, each with distinct roles, priorities, and concerns. In larger organizations, the buying committee often includes representatives from various departments such as procurement, IT, finance, and even legal. Each of these stakeholders has a say in the final decision, and often, their concerns differ widely. For example, while the end-user may prioritize functionality and ease of use, the procurement department may focus on price, and IT might be concerned with integration and security.
Sales teams must address all these diverse needs and tailor their approach to each stakeholder, ensuring that the product or solution resonates across the organization. This means building relationships and delivering targeted messaging that speaks to the specific interests of each decision-maker. However, coordinating communication with multiple parties, often over a lengthy sales cycle, can be complex and requires careful planning and organization.
2. Lengthier Sales Cycles and Multi-Touch Interactions
In B2B sales, the path to purchase is rarely linear. Prospects often engage in multiple touchpoints with a company before making a decision. These interactions occur across various channels—email, phone calls, product demonstrations, social media, webinars, and in-person meetings. Sales teams must ensure consistency and continuity across these channels, as a disjointed experience can easily deter potential buyers. Additionally, these interactions don’t always progress smoothly from one stage to the next. Buyers may pause to conduct further research, seek approval from additional stakeholders, or prioritize other business needs, which can stretch out the sales cycle.
The length of the sales cycle itself adds another layer of difficulty. Unlike B2C sales, where decisions are often made relatively quickly, B2B purchases—especially those involving higher-value products or services—take time. Prospects must evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI), review case studies, request demos, and perhaps even conduct pilot programs before committing to a purchase. This extended process means that sales teams must maintain engagement over the long term while ensuring that interest doesn’t wane during the decision-making period.
3. Heightened Expectations for Personalization
In today’s business environment, B2B buyers expect the same level of personalization that they receive in their B2C interactions. They want tailored content, personalized communication, and a buying experience that addresses their unique challenges and goals. This shift means that a one-size-fits-all sales approach is no longer effective. Sales teams must leverage data-driven insights to craft individualized messaging and proposals that align with each buyer’s pain points.
Personalization can be achieved through customer relationship management (CRM) systems and artificial intelligence (AI) tools that provide detailed insights into buyer behavior, preferences, and needs. By analyzing data, sales teams can segment their audience more effectively and provide customized recommendations that resonate with each prospect. However, this level of personalization requires a robust infrastructure and a deep understanding of each buyer’s journey, making it a challenging yet essential part of the sales process.
4. Building Trust and Credibility
Trust and credibility are paramount in a complex B2B buying journey. Buyers are increasingly risk-averse, especially with large-scale purchases, and need reassurance that they are making the right decision. Sales teams must present their solution as the best option and establish themselves as trusted advisors. This means providing value beyond the product by offering insights, industry knowledge, and practical solutions that help the buyer address broader business challenges.
One key strategy for building trust is thought leadership and content marketing. Sales teams can leverage whitepapers, case studies, testimonials, and market research to demonstrate their expertise and credibility. Additionally, they must maintain transparency throughout the process, offering clear communication about pricing, timelines, and deliverables. Consistency, follow-through, and responsiveness are crucial to building the long-term relationships necessary for navigating the complexities of B2B sales.
Strategies for Streamlining the Process
To successfully navigate these complex buyer journeys, sales teams can implement several strategies:
Account-Based Selling (ABS): This approach focuses on identifying key accounts and tailoring the sales strategy to each account’s specific needs, addressing the multiple stakeholders involved in the decision-making process.
Sales and Marketing Alignment: Ensuring that both sales and marketing teams are aligned is critical for providing a seamless experience across all touchpoints. Marketing should provide sales with insights into buyer behavior, and sales should relay feedback to refine marketing campaigns.
Leveraging Technology: Sales teams can utilize CRM systems, AI, and automation tools to manage and track interactions across multiple channels, providing a cohesive experience while reducing manual efforts. These technologies can also help identify high-intent leads and predict the next steps in the buyer journey.
Continuous Engagement: Sales teams must stay in front of prospects throughout the extended sales cycle, providing value at each interaction. This can be done through nurturing campaigns, regular follow-ups, and delivering content that keeps the conversation moving forward.
By understanding and addressing the complexities of the modern B2B buying journey, sales teams can better manage their interactions, build stronger relationships, and ultimately close more deals despite the challenges.
Sales Process Efficiency and Team Alignment
In any B2B organization, optimizing the sales process is key to driving consistent growth and achieving revenue goals. However, internal inefficiencies and misalignments between departments—particularly between sales, marketing, and customer success—can significantly impede a company’s ability to sell effectively. These breakdowns often lead to lost opportunities, decreased productivity, and lower sales performance. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach to streamlining sales processes, improving time management, leveraging data, and fostering cross-functional team alignment.
1. Time Management and Prioritization of Sales Activities
Sales teams often struggle with managing their time efficiently. With many tasks such as lead follow-ups, meetings, administrative duties, and prospecting, it’s easy for sales reps to become overwhelmed. Ineffective time management leads to missed opportunities, slower deal cycles, and reduced productivity. One of the common culprits behind poor time management is the lack of prioritization—sales reps may not be clear on which prospects to focus their attention on or spend too much time on non-revenue-generating activities.
To overcome this, organizations need to implement tools and practices that help salespeople prioritize high-value activities. This often involves setting clear goals, implementing structured workflows, and using CRM systems effectively to track tasks and progress. Time-blocking strategies, where salespeople allocate specific periods for prospecting, meetings, and administrative tasks, can also help streamline day-to-day operations. Sales leaders must also encourage delegating or automating low-value tasks, allowing sales reps to focus on revenue-driving activities like closing deals and nurturing relationships.
2. CRM Usage and Data Tracking
A well-implemented Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is the backbone of a high-performing sales team. CRMs provide a centralized platform to manage customer interactions, track the sales pipeline, monitor key metrics, and store vital data about prospects and customers. However, inefficient use of CRM tools is a common challenge that hinders sales process efficiency. Some teams may struggle with data entry; others may not fully utilize CRM features, or, worse, sales teams may not adopt the CRM due to its perceived complexity or time-consuming nature.
For a CRM system to be effective, there must be a consistent and disciplined approach to data entry, ensuring that all relevant information is captured accurately and promptly. Automating certain tasks within the CRM—such as lead scoring, follow-up reminders, or email campaigns—can also increase efficiency. Training and adoption are key; sales teams need to be educated on maximizing the CRM’s capabilities, and leadership should foster a culture that values data-driven decision-making. CRM data should also be used proactively, not just for tracking past interactions but for forecasting, identifying bottlenecks in the sales cycle, and providing insights that can guide the sales strategy.
3. Cross-Functional Alignment: Sales, Marketing, and Customer Success
One of the most critical factors in sales success is the alignment between sales, marketing, and customer success teams. When these departments operate in silos, it can create a disjointed experience for the customer and lead to inefficiencies in the sales process. For example, marketing may generate leads that are not adequately qualified, leading to wasted time and effort by sales teams. Conversely, sales teams may not provide sufficient feedback to marketing about which leads are converting, leading to ineffective marketing strategies. Similarly, if customer success teams are not aligned with sales, it can result in a poor handoff of new clients, damaging customer retention and satisfaction.
To address this, organizations need to create open lines of communication between these departments, fostering a collaborative culture where data and insights are shared freely. Regular alignment meetings can help ensure that marketing generates leads that meet sales criteria, while sales can provide marketing feedback about the leads’ quality. Customer success teams should be looped in early to ensure a smooth transition once a deal is closed, helping to maintain continuity in the customer journey. This cross-functional collaboration also allows for a more unified messaging and value proposition, ensuring the customer receives consistent communication throughout their engagement with the company.
4. The Role of Technology in Enhancing Efficiency
The right technology can significantly enhance the efficiency of sales processes by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and providing deeper insights into performance. Beyond CRM systems, there are a variety of tools that can help streamline sales operations. For example, sales engagement platforms can automate follow-up emails, schedule meetings, and track customer interactions, allowing sales reps to focus on higher-value activities. Data analytics tools can provide sales teams with insights into which prospects are most likely to convert and identify areas where the sales process can be improved.
AI and machine learning are playing an increasing role in enhancing sales process efficiency. AI-driven tools can analyze customer data to identify patterns, predict buyer behavior, and recommend the next best actions. These tools can also help with lead scoring, identifying which prospects are ready to move to the next stage of the sales funnel. By leveraging these technologies, sales teams can operate more efficiently and focus on the highest-impact activities.
5. Continuous Process Improvement
Sales process optimization is not a one-time activity. Continuous monitoring and improvement are required to adapt to changes in the market, customer behavior, and organizational priorities. Sales leaders should regularly review performance metrics, such as conversion rates, average deal size, and sales cycle length, to identify areas for improvement. Incorporating feedback from the sales team is also critical, as they interact with customers daily and can provide valuable insights into what’s working and what’s not.
Implementing a culture of continuous improvement can lead to incremental gains that, over time, significantly enhance sales performance. Sales teams should also embrace agile methodologies, be open to experimenting with new strategies, tools, and processes, and quickly iterate based on the results.
Improving sales process efficiency and fostering alignment between teams is essential for driving success in B2B sales. Sales teams can operate more effectively and achieve better results by streamlining workflows, effectively using technology, and promoting cross-functional collaboration. Organizations prioritizing efficiency and alignment in today’s competitive environment are better positioned to respond to challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and drive sustained growth.
Sales optimization is crucial for any B2B organization striving for growth and improved performance. However, recognizing and addressing sales teams’ specific challenges is the first step toward achieving optimization. Teams can better contextualize their unique obstacles by facilitating open discussions about customer acquisition, lead generation, buyer journey complexities, and internal inefficiencies. These conversations help prioritize the most pressing challenges and foster collaboration and shared learning. Ultimately, understanding the root causes of these challenges allows organizations to implement strategies that streamline processes, align teams, and improve overall sales outcomes.

Case Study: Salesforce – Optimizing Sales for B2B Performance and Growth
Background:
Despite being a sales-driven organization, Salesforce, a global leader in customer relationship management (CRM) software, has faced challenges in optimizing its sales processes. Like many B2B companies, Salesforce experienced inefficiencies in lead generation, gaps in alignment between sales and marketing teams, and a need for more personalized engagement with increasingly complex buyer journeys. With growing competition in the SaaS space and more informed buyers, Salesforce recognized the need to optimize its internal sales processes to maintain growth and drive revenue performance.
Challenge 1: Inefficient Lead Generation and Qualification
Salesforce’s primary challenge was the inefficiency in its lead generation and qualification process. Sales teams were receiving a large volume of leads from marketing, but many were poorly qualified, leading to wasted time and effort chasing prospects that weren’t ready to convert. Additionally, there was a lack of real-time insight into which leads had the highest potential to turn into high-value customers, resulting in missed opportunities.
Challenge 2: Misalignment Between Sales and Marketing
The misalignment between Salesforce’s sales and marketing departments exacerbated the lead generation problem. Marketing was focused on driving volume, but the sales team needed more targeted, high-quality leads. The two departments were not fully aligned on what constituted a qualified lead, leading to frustrations and finger-pointing. Additionally, Salesforce’s marketing campaigns weren’t tailored enough to the diverse needs of different segments, resulting in generic outreach that didn’t resonate with many potential customers.
Challenge 3: Complex Buyer Journeys and Stakeholder Engagement
Salesforce also faced the challenge of navigating increasingly complex buyer journeys. In larger enterprise deals, multiple stakeholders from different departments—such as IT, finance, and operations—were involved in the decision-making process. These stakeholders had varying priorities, and managing communication with them across a long sales cycle required a more personalized and consistent approach. The sales team struggled with keeping the momentum going and ensuring that their outreach addressed the specific pain points of each stakeholder.
Strategy: Sales Process Optimization
Salesforce embarked on a sales optimization initiative that began with identifying and addressing the root causes of inefficiency in their processes. This initiative included several key steps:
Cross-Functional Alignment: Salesforce hosted a series of workshops and open discussions between its sales and marketing teams to break down silos and build alignment. These sessions focused on refining the definition of a qualified lead, developing shared goals, and establishing seamless communication protocols. Salesforce adopted a more data-driven approach to ensure that marketing delivered leads that met specific criteria aligned with the sales team’s needs.
Leveraging AI and Automation for Lead Scoring: Salesforce integrated its AI-powered tool, Einstein, to enhance lead scoring and prioritization. Einstein used machine learning algorithms to analyze past customer interactions, website behavior, and CRM data to identify which leads were most likely to convert. This allowed the sales team to focus on the most promising leads, saving time and increasing conversion rates. Additionally, automation tools were employed to handle repetitive tasks such as sending follow-up emails, allowing sales reps to focus on high-value activities like relationship building and closing deals.
Personalizing the Buyer Journey: Salesforce utilized its CRM platform to personalize buyer engagement. By tracking interactions and capturing data at every touchpoint, Salesforce’s sales team could provide highly personalized communication tailored to each stakeholder’s needs. For example, while IT stakeholders were concerned with integration and security, finance departments were focused on cost and ROI. The CRM system allowed Salesforce to create tailored messaging and content for each organizational stakeholder, ensuring that all pain points were addressed in a targeted way.
Ongoing Process Improvements: The optimization initiative was not a one-time fix. Salesforce is committed to continuous process improvement by regularly analyzing sales performance data, customer feedback, and team insights. They implemented a culture of iterative improvement, allowing them to stay agile and adapt to new challenges as they arose. They also ensured that feedback from sales was regularly shared with marketing, allowing for continuous refinement of lead-generation strategies and campaigns.
Results:
Salesforce’s sales optimization efforts resulted in significant improvements in both lead quality and conversion rates. AI-driven lead scoring increased the sales team’s efficiency, as reps could now focus on high-potential leads. The alignment between sales and marketing reduced friction and improved collaboration, ensuring marketing campaigns were more effectively tailored to the target audience. Additionally, personalized buyer engagement allowed Salesforce to close more deals with complex enterprise customers, driving revenue growth.
Key Outcomes:
• A 20% increase in conversion rates by focusing on high-quality leads.
• A 15% reduction in sales cycle length due to better-qualified leads and more personalized engagement.
• Improved cross-departmental collaboration, resulting in better overall sales performance.
• Enhanced customer satisfaction due to more targeted communication and personalized buyer journeys.
Conclusion:
Salesforce’s sales optimization journey highlights the importance of addressing the root causes of inefficiency before implementing optimization strategies. By aligning sales and marketing, leveraging AI and automation tools, and personalizing the buyer experience, Salesforce overcame its challenges and improved sales performance. This case study underscores the value of cross-functional collaboration and the need for continuous process improvements in a fast-evolving B2B sales environment.

Exercise: Identifying and Addressing Sales Challenges
• Each person should take 2 minutes to reflect on a key challenge their sales team faces in customer acquisition or lead generation.
• Share these challenges with your partner, explaining why they are significant roadblocks to success.
• Together, discuss the root causes of these challenges. Are they due to inefficient processes, lack of alignment between teams, or external factors (e.g., market competition, buyer complexity)?
• How do these challenges impact your sales performance or conversion rates?
• Brainstorm potential solutions to these challenges. Consider how technology, such as AI or CRM tools, or improving cross-functional collaboration between sales and marketing could help address the issues.
• Discuss any strategies that have worked in the past or propose new ideas you haven’t yet tried.
• Each pair will summarize their discussion, focusing on the main challenge identified and a potential solution or strategy to address it.
• Be prepared to share your findings with the larger group in the next session.

Course Manual 2: Challenge Experiences
In the dynamic world of B2B sales, every professional’s journey is unique and shaped by individual experiences, challenges, and victories. While many challenges are common across industries, the solutions often vary depending on personal approach, market conditions, and organizational strategies. The Sales Optimization program acknowledges this diversity by fostering an interactive and collaborative environment, encouraging participants to share their personal stories and experiences. This program’s strength lies in its ability to tap into the collective wisdom of its participants, offering a platform where shared experiences become valuable lessons for others.
The program’s design is grounded in the belief that challenges can feel less daunting when we realize we are not alone in facing them by listening to how others have overcome obstacles, whether in customer acquisition, lead generation, competition, or product positioning, learners can gain new insights and strategies to tackle their roadblocks. No two journeys in sales are identical, but every story has the potential to inspire, inform, and empower others facing similar challenges.
The real power of this program lies in its interactive nature. Not every participant will have encountered every challenge being discussed. This variability is an asset, allowing for a rich exchange of experiences. Some learners may offer fresh perspectives or introduce new challenges that haven’t been considered before, adding to the depth of collective knowledge. Through open dialogue, learners not only address their immediate sales hurdles but also build a network of support and shared understanding, essential for long-term success in the B2B space.
To maximize the benefits of this collaborative learning approach, the program encourages learners to engage with three key subtopics: Personalizing Customer Acquisition Strategies, Navigating Competitive Markets, and Overcoming Sales Team Dynamics.
Personalizing Customer Acquisition Strategies
Customer acquisition is the backbone of any successful B2B sales operation, but it is also one of the most challenging aspects of the sales process. Unlike B2C, where sales are often volume-driven, B2B sales typically involve longer sales cycles, multiple decision-makers, and higher stakes. The complexity of identifying, reaching, and nurturing suitable leads requires more than a one-size-fits-all approach. This subtopic focuses on how salespeople can personalize their customer acquisition strategies to fit the unique needs of their target audience, their specific product or service, and the nuances of the industry in which they operate.
One of the most significant hurdles in customer acquisition is identifying suitable leads. Salespeople are tasked with finding prospects who need the product or service and can make purchasing decisions. This process can be highly variable, depending on the product, industry, and target market. Personalizing this stage involves tailoring lead-generation efforts based on detailed customer profiles and specific pain points that the product or service can solve.
For example, some participants may share how they’ve leveraged AI tools to mine data from social media platforms, industry reports, or competitor analyses to identify prospects interested in similar products. Others may discuss how focusing on specific industries or verticals has helped them streamline the lead identification process by aligning their product offerings more closely with the prospects’ needs. This tailored approach improves lead quality and increases the likelihood of successful conversions.
B2B sales are relationship-driven, requiring a deep understanding of the prospect’s needs, challenges, and business goals. Once potential leads have been identified, nurturing those relationships becomes critical. The challenge often lies in engaging prospects in a way that feels authentic and valuable, not just as a part of a sales pipeline. Personalizing this nurturing process can dramatically improve the chances of closing deals, as prospects respond more positively to approaches that demonstrate a genuine understanding of their business.
Participants might share how they’ve used personalized emails, tailored content, or customized product demonstrations to engage prospects in the interactive session. For instance, sending industry-specific case studies or insights tailored to a prospect’s particular business challenge can make a significant impact. This level of personalization shows that the salesperson has taken the time to understand the prospect’s needs, which helps to build trust and establish a long-term relationship.
Some participants may also mention the importance of timing and frequency in lead nurturing. Knowing when to follow up, how often to reach out, and which communication channels work best for specific industries can all be elements of a personalized acquisition strategy. By sharing their experiences, learners can learn how others have effectively managed these variables to keep prospects engaged without overwhelming them.
In B2B sales, the decision-making process often involves multiple stakeholders with varying priorities and concerns. Each decision-maker may have a different perspective on the product or service, requiring salespeople to adjust their approach accordingly. Personalizing customer acquisition strategies means recognizing these differing needs and tailoring communication and value propositions to each stakeholder’s role within the company.
For example, the approach used to convince a CFO might focus on ROI and financial benefits, while the approach for a CTO might emphasize technical features and integration capabilities. Participants can share how they’ve segmented their messaging for different personas within the same organization, ensuring that each stakeholder sees the value from their perspective. This can lead to more effective conversations and, ultimately, a higher likelihood of converting leads into customers.
Personalizing customer acquisition is as much about learning from failures as it is about celebrating successes. Not every approach will work in every situation, and part of the value in this subtopic is the opportunity to reflect on past experiences—good and bad. Participants are encouraged to share stories of strategies that didn’t yield the expected results and how they adjusted their approach. This allows for collective learning, where others can avoid similar pitfalls and refine their strategies.
For example, a participant might share how an overly generic approach to customer acquisition failed to resonate with a highly specialized market, prompting a shift toward more tailored outreach efforts. Conversely, success stories of how personalization led to breakthroughs in previously unresponsive prospects can inspire others.
Personalizing customer acquisition strategies in B2B sales is not just about understanding the product and the market; it’s about deeply understanding the customer. By sharing personal experiences, tips, and lessons learned, participants can help each other refine their approaches, leading to better identification of high-quality leads, more meaningful engagement, and, ultimately, higher conversion rates. This subtopic within the Sales Optimization program provides a valuable platform for learners to exchange knowledge, expand their skill sets, and develop more effective customer acquisition strategies tailored to the complexities of B2B sales.
Navigating Competitive Markets
In the ever-evolving world of B2B sales, competition is a constant, and navigating crowded markets can be one of the most daunting challenges for sales professionals. With numerous players offering similar products or services, companies must find ways to differentiate themselves, capture attention, and sustain long-term relationships with clients. Success in this arena hinges on a company’s ability to showcase the superiority of its offerings and position itself as a strategic partner that understands and addresses the unique needs of its clients. The strategies shared in this subtopic revolve around how to outmaneuver competitors, refine value propositions, and leverage cutting-edge tools like AI and data analytics to stay ahead.
At the heart of competitive B2B markets is the need for clear differentiation. Many companies struggle to differentiate themselves in industries where products and services seem increasingly commoditized. Positioning a product or service as a superior option requires a deep understanding of the competition and the customer. In this subtopic, participants share insights into how they have positioned their offerings to stand out despite the noise in crowded markets.
For instance, participants might discuss strategies such as crafting a unique value proposition beyond product features, highlighting areas such as customer service, ease of integration, or long-term value. Others may focus on how they’ve used storytelling to convey their brand’s mission, values, and commitment to solving customer pain points, making the offer more emotionally resonant. By showcasing how they differentiate themselves, participants provide real-world examples of what works in highly competitive environments.
A common challenge discussed may include navigating price wars and avoiding the race to the bottom. Learners can explore tactics for emphasizing value over cost, demonstrating how their solution can deliver better long-term ROI, even if the upfront costs are higher. By positioning themselves as a premium option rather than a commodity, companies can shift the conversation from price to value, which is often a winning strategy in B2B sales.
In today’s B2B landscape, data-driven decision-making is critical to staying competitive. AI and data analytics are increasingly used to gain deeper insights into market trends, customer preferences, and competitor activity. Sales teams that leverage these technologies have a significant advantage, as they can quickly adapt to market changes, anticipate competitor moves, and better understand their performance in real-time.
Participants delve into the tools and techniques they’ve employed to outsmart competitors by harnessing AI and data analytics. For instance, participants might share how they use AI to gather and analyze competitor pricing models, identify gaps in competitors’ product offerings, or monitor shifts in customer preferences. AI tools can also provide predictive analytics that helps sales teams forecast market trends and make more informed decisions about where to allocate resources, allowing them to stay one step ahead of competitors.
Some participants may also discuss how they’ve used AI-driven insights to personalize marketing efforts, ensuring that their messaging and outreach are more aligned with their target audience’s specific needs and pain points. This can be a significant advantage in competitive markets, where prospects may be bombarded with similar offers from multiple companies. By tailoring their approach based on AI insights, companies can stand out as more relevant and responsive to the prospect’s needs.
In competitive B2B markets, maintaining market share while pursuing new business can feel like a balancing act. The challenge is to defend existing clients from aggressive competitors and find growth opportunities. Participants in this subtopic share stories of how they’ve successfully defended their market share while expanding into new business opportunities.
For example, some learners may discuss how they’ve reinforced relationships with existing clients by going beyond the traditional sales model and positioning themselves as long-term partners who provide ongoing value. This could involve offering additional services, consulting, or proactive problem-solving that keeps competitors at bay. Others may share experiences of upselling and cross-selling within their existing client base, thereby increasing the customer’s lifetime value and making it more difficult for competitors to lure them away.
When it comes to winning new business in a crowded market, participants will explore strategies they’ve used to open doors with new clients. This might include developing targeted campaigns that focus on niche markets where competition is less intense or finding ways to tap into underserved segments. Others may discuss the importance of agility and the ability to quickly pivot in response to changing market conditions, seizing opportunities where competitors are slow to act.
In any competitive market, there will be times when competitors become aggressive, whether through pricing tactics, marketing campaigns, or direct customer poaching. In this subtopic, participants discuss their experiences facing these situations head-on and share strategies for not just surviving but thriving in the face of such challenges.
Some participants may share how they’ve responded to competitors who slash prices or offer steep discounts. Rather than engage in a price war, they may have shifted focus to their product’s additional value, emphasizing quality, service, and long-term benefits. Others may discuss how they’ve combated aggressive marketing campaigns from competitors by doubling down on customer relationships, reinforcing brand loyalty, and offering exceptional customer support as a differentiator.
Additionally, participants might share stories of times when competitors have attempted to lure away their key clients and how they’ve successfully retained those clients through proactive engagement, personalized service, and tailored solutions that meet the client’s evolving needs.
Navigating competitive markets is no easy task, but through shared stories and experiences, sales professionals can gain a wealth of strategies and insights to help them stay ahead of the curve. From refining positioning and leveraging AI for competitive insights to maintaining market share and facing aggressive competitors, this topic offers participants practical, real-world tools to overcome the challenges they face in crowded B2B landscapes. By learning from each other, they can sharpen their competitive edge and find new ways to succeed, regardless of the intensity of the market competition.
Overcoming Sales Team Dynamics
Sales teams are critical to the success of any B2B organization, as they drive revenue and serve as the primary connection between a company and its customers. However, even the most skilled and motivated sales teams can struggle to perform when internal dynamics become strained. Issues such as misaligned goals, poor communication, conflicts between team members, and differences in experience or skill levels can significantly impact performance and morale. Addressing these challenges is essential to creating a high-performing sales team that works together efficiently and effectively. In this subtopic, participants share their experiences navigating team dynamics, offering valuable insights into overcoming internal obstacles and fostering a collaborative, high-functioning sales environment.
One of the most common challenges sales teams face is the misalignment of goals—whether between individual team members, departments, or between the team and the larger organizational strategy. When salespeople operate under different assumptions or priorities, it can lead to confusion, missed targets, and frustration.
Participants in this subtopic can share how they’ve overcome goal misalignment by creating a shared vision for the team. Some may discuss their efforts to involve salespeople in goal-setting, ensuring that individual objectives are clearly tied to broader organizational goals. This sense of shared purpose can increase motivation and buy-in, as everyone understands how their contributions directly impact the company’s success.
For example, a participant might describe how they’ve instituted regular strategy meetings where the sales team and management review progress, align on upcoming targets, and ensure everyone is on the same page. Others may talk about the importance of transparency, where key metrics and performance indicators are shared openly across the team so that each member knows how their efforts contribute to the overall success. By aligning on both short-term objectives and long-term strategy, sales teams can operate more cohesively and effectively.
Communication breakdowns are another significant challenge within sales teams. Miscommunication, lack of information sharing, or siloed working environments can confuse and prevent team members from collaborating effectively. In B2B sales, where deals often require coordination across multiple departments (such as marketing, product, and customer support), transparent and open communication is vital for success.
Participants explore how they’ve improved communication within their teams. Some may share experiences of implementing regular team check-ins or debriefs where everyone discusses their progress, shares insights, and flags any issues. These regular touchpoints can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure all team members are aligned on current priorities and objectives.
Others may focus on how they’ve used technology to enhance communication. Tools like CRM systems, team collaboration platforms (such as Slack or Microsoft Teams), and shared dashboards can facilitate better information flow, ensuring everyone can access the same data and updates. By leveraging technology to create a more transparent and collaborative work environment, sales teams can avoid communication breakdowns and maintain better coordination.
Conflict within sales teams is inevitable, especially when strong personalities are involved, or team members have differing opinions on how to approach deals or handle customers. Additionally, varying experience levels or differences in selling styles can sometimes create tension. However, if managed effectively, conflict can lead to growth, as it often brings underlying issues to the surface, allowing the team to address them constructively.
Participants share stories of how they’ve managed conflict within their teams. For example, some may discuss the importance of establishing clear roles and responsibilities to prevent confusion or competition among team members. Others might discuss how they’ve created a culture of open feedback, where team members are encouraged to share their concerns or frustrations in a constructive manner rather than allowing conflicts to fester.
In some cases, formal conflict resolution strategies, such as mediation or peer-to-peer coaching, can be practical tools. Participants who have implemented these strategies may share how they helped resolve disputes by fostering open dialogue and understanding. For instance, encouraging team members to understand each other’s perspectives and focus on shared goals can help resolve conflicts and strengthen relationships within the team.
Collaboration is critical to a successful sales team, particularly in B2B sales, where closing deals often requires input from multiple team members with different areas of expertise. However, fostering a truly collaborative team environment can be challenging, especially in competitive sales environments where individual performance metrics can create a sense of rivalry.
Participants discuss how they’ve fostered collaboration within their teams in this subtopic. Some may share strategies for creating a more collaborative culture, such as team-based incentives that reward collective achievements rather than individual sales performance. By focusing on team-wide success, companies can encourage collaboration and create an environment where team members support each other in achieving shared goals.
Others may discuss how they’ve fostered knowledge-sharing within their teams. For example, setting up regular peer-to-peer learning sessions where more experienced salespeople mentor newer team members can be a highly effective way to enhance collaboration and ensure that best practices are shared across the team. This approach improves team cohesion and helps bridge skill gaps, ensuring that everyone is performing at their best.
Additionally, participants might share their experiences with creating cross-functional collaboration between the sales team and other departments, such as marketing or customer service. In B2B sales, where understanding the customer’s journey is crucial, cross-departmental collaboration can provide sales teams with valuable insights and tools to close deals more effectively.
Finally, morale is a critical factor in the performance of any sales team. High-pressure sales environments can lead to burnout and disengagement if team members don’t feel supported or appreciated. In this subtopic, participants explore how they’ve boosted team morale and created a positive work environment that encourages engagement and motivation.
Some participants may share how they’ve celebrated team successes, from small wins to significant achievements, creating a culture where accomplishments are recognized and rewarded. Others might discuss how they’ve implemented initiatives to promote work-life balance, ensuring team members stay motivated and avoid burnout.
By sharing their experiences in overcoming team dynamics, managing conflict, and enhancing collaboration, participants provide valuable insights that can help others build stronger, more cohesive sales teams. Through this exchange of ideas, learners can develop fresh approaches to improving communication, fostering collaboration, and creating a supportive environment that drives individual and collective success.
Overcoming sales team dynamics is crucial for maintaining high performance in B2B sales. Whether aligning goals, improving communication, managing conflict, or boosting collaboration, sales teams must address internal challenges to function as a cohesive unit. By sharing personal stories and experiences, participants in this subtopic gain valuable insights into the best practices for fostering a positive team environment, ultimately leading to better sales outcomes and higher team morale.
The Sales Optimization program creates a unique platform for B2B sales professionals to share their diverse journeys, offering valuable insights into overcoming the everyday challenges of the sales world. Through the interactive exchange of personal experiences, participants gain fresh perspectives on customer acquisition, navigating competitive markets, and enhancing team dynamics. This collaborative environment empowers learners to develop new strategies, fostering a deeper understanding of how to adapt approaches for success in a competitive landscape. By embracing collective wisdom, the program strengthens individual and organizational growth, paving the way for sustained success.

Case Study: IBM – Personalizing Customer Acquisition and Navigating Complex Sales Environments
Background: IBM is a global technology company that offers a wide range of B2B solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and IT infrastructure services. IBM operates in highly competitive markets, facing challenges from established technology companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, particularly in the cloud computing and AI sectors. As a business focused on enterprise-level clients, IBM needed to continuously refine its customer acquisition strategies and adapt to the unique dynamics of a competitive and rapidly evolving industry.
Challenges: IBM encountered multiple challenges in its pursuit of growth:
Customer Acquisition in Highly Complex Sales Cycles: Selling enterprise technology solutions requires navigating long, complex sales cycles. With multiple decision-makers involved, IBM had to tailor its approach to address the specific needs of each stakeholder, from technical teams to C-suite executives. This made customer acquisition both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Differentiating in a Competitive Market: The technology landscape is highly competitive, particularly in cloud computing and AI services. Competitors like AWS and Microsoft Azure often had a head start in cloud market share, making it difficult for IBM to stand out. To differentiate from its competitors, IBM needed to emphasize its unique strengths, including its AI capabilities and hybrid cloud solutions.
Internal Sales Team Coordination: With teams spread across the globe and serving diverse industries, IBM faced challenges in aligning its sales teams on common goals and ensuring consistency in delivering value propositions. Misalignment across regions and product lines resulted in inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
Solutions Implemented:
Personalizing Customer Acquisition Strategies: IBM adopted a highly personalized approach to customer acquisition to engage enterprise clients better, each with distinct needs and complex decision-making processes.
Industry-Specific Solutions: IBM segmented its customer base by industry, tailoring its offerings to sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail. This allowed IBM to present highly relevant solutions that addressed industry-specific challenges, such as regulatory compliance in finance or AI-driven diagnostics in healthcare.
Collaborative Selling: IBM engaged in collaborative selling, working closely with clients to co-create solutions that met their unique business needs. By involving clients in the development process, IBM could build trust and demonstrate that its solutions were not just off-the-shelf products but bespoke offerings tailored to the client’s business challenges.
AI-Powered Insights for Lead Generation: IBM leveraged its AI platform, Watson, to analyze vast datasets, providing its sales teams real-time insights into potential clients’ needs and market conditions. This allowed IBM to identify high-quality leads more effectively and tailor its outreach to align with the customer’s business priorities. AI-powered insights enabled IBM to anticipate client needs before formal inquiries, enhancing their ability to offer solutions proactively.
Navigating Competitive Markets: In an industry dominated by major players, IBM’s strategy emphasized its unique strengths and showcased its competitive advantages.
Hybrid Cloud Strategy: IBM positioned itself as a leader in hybrid cloud solutions to differentiate from competitors. While AWS and Microsoft Azure focused on public cloud services, IBM emphasized hybrid cloud flexibility, allowing clients to integrate their existing on-premise infrastructure with cloud services. This strategy resonated with clients who needed a more tailored, secure, and flexible approach to cloud adoption, particularly in regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
Building Strategic Partnerships: IBM formed strategic partnerships with key industry players to strengthen its competitive positioning. For example, its partnerships with companies like Red Hat (which IBM acquired) and SAP allowed IBM to integrate additional technologies into its ecosystem, offering clients more comprehensive solutions that its competitors could not easily replicate.
Thought Leadership and Innovation: IBM consistently positioned itself as a thought leader in AI and cloud innovation, publishing white papers, hosting conferences, and providing extensive industry reports. This helped IBM build credibility and trust among clients, reinforcing its role as a partner always ahead of industry trends and innovations.
Optimizing Sales Team Dynamics: IBM recognized the need for better coordination and alignment within its global salesforce to deliver personalized solutions to clients effectively.
Cross-Functional Teams: IBM created cross-functional teams of experts from various departments, including sales, technical consulting, and customer support. This helped ensure clients received comprehensive and seamless support throughout the sales cycle, from initial discussions to post-sale implementation. It also facilitated better communication and knowledge-sharing within the salesforce, aligning everyone on a common goal.
Sales Enablement Tools: IBM invested in advanced sales enablement tools to support its teams. These tools provided real-time access to market data, competitor insights, and customer profiles, making sales teams more informed and responsive. By integrating AI-driven analytics into its sales process, IBM effectively equipped its teams with the insights to personalize pitches and proposals.
Sales Training and Development: IBM introduced a robust training and development program to upskill its sales teams. This training emphasized consultative selling, where sales professionals advise clients, helping them solve complex business challenges rather than pushing products. The training also focused on collaboration, conflict resolution, and team dynamics, ensuring that IBM’s salesforce worked cohesively across different regions and business units.
Results: IBM’s approach to personalizing customer acquisition, navigating competitive markets, and optimizing sales team dynamics yielded significant results:
Increased Market Share in Hybrid Cloud: IBM’s focus on hybrid cloud solutions allowed the company to discover a unique market position. By offering flexible cloud integration options, IBM captured clients who were hesitant to fully transition to the public cloud, helping the company grow its market share in this competitive segment.
Enhanced Client Relationships and Higher Conversion Rates: Through personalized, industry-specific solutions and collaborative selling, IBM improved client relationships, resulting in higher conversion rates. Clients saw IBM as a strategic partner rather than just a vendor, leading to long-term engagements and higher customer loyalty.
Improved Sales Team Efficiency and Global Alignment: The introduction of cross-functional teams and advanced sales tools helped streamline the sales process, improving efficiency and reducing internal friction. IBM’s sales teams became more aligned on goals, and communication between regions and departments improved, leading to faster decision-making and better collaboration on complex deals.
Conclusion: IBM’s success in personalizing customer acquisition strategies, navigating competitive markets, and optimizing its sales team dynamics demonstrates how a company can thrive in a challenging and competitive B2B environment. By focusing on industry-specific solutions, leveraging AI-powered insights, and emphasizing internal and client collaboration, IBM has maintained its position as a leader in the technology sector. The company’s ability to continuously adapt to market conditions and align its global salesforce ensures its long-term success and growth.

Exercise: Sharing Experiences in B2B Sales
• Flip chart or whiteboard
• Markers
• Notepads and pens for participants (optional)
• Personalizing customer acquisition strategies
• Navigating competitive markets
• Overcoming sales team dynamics
• How did the approach or solution in the story differ from others they have heard?
• What insights can be gained from this experience?
• How could these strategies be adapted to their sales environment or industry?
• A unique challenge or strategy shared within the group.
• New insights or solutions that can be applied across different sales environments.
• A common theme or lesson that emerged from the discussion.
• How can they continue to share knowledge and collaborate with peers to overcome future challenges?
• What action steps can they take to apply the insights gained today?

Course Manual 3: Challenge Impacts
In the journey toward sales optimization, the first and most critical step is identifying the challenges that hinder performance within the broader industry and your organization. These challenges often significantly impact your sales organization, influencing everything from team morale to revenue generation. However, many of these issues tend to “hide in plain sight,” undermining various aspects of the sales process and obscuring opportunities for growth and improvement.
The importance of identifying and understanding the root causes of these challenges cannot be overstated. Without clearly recognizing these obstacles’ detrimental impact on your sales organization, efforts to address them can fall short or miss the mark entirely. By analyzing the specific challenges and understanding their effects on performance, we lay the groundwork for a more granular, process-oriented approach to improvement. This foundational knowledge becomes the basis for developing targeted solutions in subsequent workshops, ensuring that the strategies implemented directly address the pain points most impactful to your team’s success.

One of the most significant outcomes of this initial discovery phase is the ability to prioritize which challenges should be addressed first. Sales organizations often manage multiple issues simultaneously, making it difficult to know where to start. However, by evaluating the negative impact each challenge has on performance, teams can begin to identify the areas where intervention will generate the most meaningful results. This path forward not only clarifies sales teams but also helps sales leaders communicate their needs to the broader organization.
A key aspect of sales optimization is gaining the support of other organizational stakeholders—departments such as marketing, operations, and customer service—to help resolve the identified challenges. This stage of the process enables sales leaders to quantify what additional resources, tools, or structural changes will be required to address the challenges successfully. As these insights take shape, sales teams move closer to realizing a more optimized and efficient sales process, driving individual and organizational success.
Identifying Hidden Challenges and Their Root Causes
In any sales organization, the most visible challenges tend to dominate discussions—missed sales targets, low conversion rates, and declining win rates- all standard metrics that signal when things are not going well. However, while these challenges are apparent and demand attention, there are often more profound, hidden obstacles that significantly impact sales performance. These hidden challenges are more difficult to detect because they exist beneath the surface, entrenched in the daily processes, behaviors, and systems that the sales team relies on. Left unaddressed, these issues can create long-term inefficiencies and erode the effectiveness of the entire sales organization.
The first step in addressing these hidden challenges is recognizing that they exist. This requires sales leaders to move beyond the apparent metrics and take a more holistic view of the sales process, looking for potential bottlenecks, misalignments, and inefficiencies that may not be immediately apparent. These hidden challenges are often related to factors such as poor communication between teams, unclear sales processes, outdated tools or technologies, or misaligned goals between sales and other departments. These underlying issues can go unnoticed without systematic exploration, causing sales performance to plateau or decline without an apparent reason.
To identify hidden challenges, sales leaders can adopt several methods:
1. Process Audits and Mapping
Conducting a thorough sales process audit can help identify inefficiencies or bottlenecks that may not be visible at first glance. This involves breaking down each step of the sales journey, from lead generation to closing, and analyzing where deals are getting stuck or slowing down. By mapping out the entire process, it becomes easier to spot areas where things are not flowing as efficiently as they should be, such as excessive time spent on manual tasks or unnecessary steps in the approval process.
2. Data and Performance Analytics
While top-level metrics like revenue and win rates provide a snapshot of sales success, digging deeper into data can uncover patterns and anomalies that suggest deeper issues. For instance, a lead increase without a corresponding increase in closed deals might indicate a problem with lead qualification or follow-up processes. Conversely, consistently high-performing sales reps might rely on ad-hoc methods that have not been codified into formal processes, leaving room for improvement across the rest of the team. Sales analytics can reveal where sales are being lost and where efficiencies are breaking down, giving teams a clearer picture of the hidden challenges.
3. Team Feedback and Interviews
Often, the people closest to the problem are those on the front lines—sales reps, account managers, and customer service teams. Regularly gathering feedback from these teams through surveys, interviews, or workshops can uncover hidden challenges that might not be evident from the data alone. For example, a sales team might struggle with overly complex pricing structures, misaligned marketing messages, or insufficient support from other departments, all of which can create friction in the sales process. Encouraging open communication about these challenges is essential for identifying problems that might otherwise remain hidden.
4. Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Sales do not operate in a vacuum; many hidden challenges in the sales process result from poor coordination between sales and other departments, such as marketing, operations, or customer service. For instance, misaligned messaging between sales and marketing can lead to confusion among prospects and lower conversion rates. At the same time, a lack of support from customer service can erode customer trust and harm the brand’s reputation. Engaging other departments in the diagnostic process allows sales leaders to identify cross-functional challenges affecting performance and opens the door to more collaborative solutions.
5. Technology and Tools Assessment
Sometimes, hidden challenges stem from outdated or ineffective tools and technologies not optimized for current sales processes. Sales teams might be relying on outdated CRM systems that don’t provide the insights or flexibility they need or lack the automation tools necessary to streamline routine tasks. Assessing the current sales technology stack can help identify areas where modern tools—such as AI-powered analytics, automated workflows, or improved customer engagement platforms—can improve efficiency and reduce the burden on the sales team.
By identifying overt and hidden challenges and understanding their root causes, sales leaders can take a more proactive approach to optimization. These root causes often hold the key to sustainable, long-term improvements, as they allow teams to address the systemic issues dragging down performance. Once these challenges are uncovered and analyzed, the organization can move forward with targeted interventions in future workshops, ensuring that solutions are developed with a clear understanding of what needs to be fixed at a granular level.
Quantifying the Impact of Sales Challenges on Performance
Once sales challenges have been identified, the next crucial step is quantifying their impact on the organization’s performance. Understanding how these obstacles affect vital sales metrics—such as conversion rates, average deal size, and customer acquisition costs—is essential for prioritizing which challenges to address first. By assigning measurable data to each challenge, sales leaders can translate complex problems into actionable insights, enabling them to make informed decisions about where to focus their efforts for maximum impact.
Quantifying the impact of sales challenges requires a data-driven approach. While qualitative insights provide valuable context, it’s through precise metrics that sales teams can truly grasp the magnitude of these issues. This step highlights the financial and operational toll that specific challenges impose. It offers a roadmap for improvement, enabling leaders to allocate resources where they can make the most significant difference.
Steps to Quantify the Impact of Sales Challenges:
1. Analyzing Conversion Rates
Conversion rate is a critical metric that reflects the percentage of leads or prospects who move through each stage of the sales funnel and eventually become customers. A drop in conversion rates can indicate several underlying issues, such as poorly qualified leads, ineffective sales messaging, or lack of timely follow-up. By analyzing the impact of specific challenges on conversion rates, sales leaders can identify where prospects are dropping off and why. For instance, if leads generated by marketing are not converting into opportunities, it could point to a misalignment between the sales and marketing teams or issues in the lead qualification process. Understanding where conversions are lost and returning them to specific challenges allows for a more targeted response.
2. Evaluating Average Deal Size
The average deal size is another critical metric that can be affected by hidden sales challenges. Suppose the average deal size has been shrinking over time. In that case, it may be an indication that sales teams are struggling with negotiating value, customers perceive less value in the offerings, or discounting is being used excessively to close deals. This could be symptomatic of broader issues, such as weak value propositions, poor competitive positioning, or ineffective benefits communication. By examining how specific challenges correlate with changes in deal size, sales leaders can determine whether these problems affect the overall profitability of the sales organization. A smaller average deal size can lead to revenue shortfalls even if the sales volume remains consistent, making it a crucial area to address.
3. Assessing Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) measures the total expense incurred in acquiring a new customer, including marketing, sales efforts, and associated administrative costs. A rising CAC can clearly indicate inefficiencies within the sales process. Challenges such as poorly qualified leads, elongated sales cycles, or high churn rates can significantly inflate CAC, making it more expensive to bring in new customers. By quantifying the impact of these challenges on CAC, sales leaders can identify areas where costs are spiraling out of control and need to be reeled in. For example, if CAC has increased significantly without a corresponding rise in customer lifetime value (CLV), this could suggest that the organization is investing too much in acquiring low-quality leads or failing to retain valuable customers. Quantifying CAC allows leaders to balance the cost of acquisition with the potential long-term value of each customer.
4. Measuring Sales Cycle Length
The length of the sales cycle—the time it takes for a lead to convert into a paying customer—is another key performance indicator that can reveal the impact of sales challenges. A prolonged sales cycle can indicate inefficiencies in lead nurturing, decision-making delays, or inadequate follow-up by the sales team. For example, suppose deals are getting delayed at the negotiation stage. In that case, this may point to challenges with pricing flexibility, product customization, or even a lack of alignment between customer needs and the solutions being offered. By quantifying the impact of specific challenges on the sales cycle length, sales leaders can focus on streamlining processes, improving communication, and eliminating bottlenecks that slow down the closing of deals.
5. Tracking Churn and Retention Rates
Customer churn rate—the percentage of customers who stop doing business with a company over a given period—is a crucial indicator of how well a company retains its customers. High churn rates can result from poor customer experiences, ineffective follow-up after the sale, or unmet expectations set during the sales process. By measuring churn and understanding its contributing factors, sales leaders can assess the financial impact of losing customers and determine how much revenue is being lost due to specific challenges. Reducing churn by addressing underlying sales process issues can have a substantial positive effect on the bottom line. Conversely, high customer retention rates are a strong indicator of successful customer relationship management and sales follow-through, and they should be tracked alongside churn to provide a more complete picture.
6. Calculating Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost represents the revenue or growth potential lost when resources are inefficiently allocated to low-priority areas or when challenges prevent teams from pursuing high-value opportunities. For example, if sales reps spend excessive time chasing unqualified leads or managing administrative tasks, the organization loses out on more profitable activities. By quantifying opportunity costs, sales leaders can better understand the trade-offs associated with various challenges and make informed decisions about resource allocation. Reducing opportunity costs by addressing inefficiencies can lead to improved sales performance and a higher return on investment (ROI) for sales activities.
Once the impact of each challenge has been quantified across these various metrics, the next step is to prioritize which issues to address first. Sales teams can rank challenges based on the magnitude of their impact on performance metrics like revenue, profitability, and efficiency. For example, suppose a particular challenge significantly drives up CAC or elongates the sales cycle. In that case, it may need to be tackled as a priority because of the immediate financial consequences. On the other hand, challenges with a more moderate impact can be addressed later as part of a longer-term strategy.
By quantifying the impact of sales challenges, sales leaders can make data-driven decisions that lead to more efficient processes, higher performance, and, ultimately, greater profitability. Prioritizing challenges based on their measurable impact ensures that resources are allocated where they will deliver the most meaningful results for both individual salespeople and the organization as a whole.
Building a Case for Organizational Support
Addressing the challenges that impede sales performance often requires more than internal adjustments within the sales team. Many issues that hinder sales success—such as misaligned messaging, inefficient processes, or inadequate tools—are rooted in broader organizational dynamics and require collaboration across departments. To resolve these challenges, sales leaders must effectively build a case for organizational support, securing the necessary resources and involvement from other teams such as marketing, product development, operations, customer service, and IT. This process is critical because it ensures that the solutions to address sales challenges are sustainable and supported by the entire organization.
Building a solid case for organizational support involves demonstrating the broader impacts of sales challenges and clearly articulating how solving these issues will benefit the entire business, not just the sales department. Sales leaders must present a compelling narrative that ties sales performance to overall business goals, emphasizing how improved sales outcomes can drive growth, profitability, and market competitiveness. When done effectively, this approach helps secure buy-in from key stakeholders and ensures that other departments understand their role in addressing sales challenges.
Critical Strategies for Building a Case for Organizational Support
1. Link Sales Challenges to Company-Wide Goals
The most effective way to gain organizational support is to show how resolving sales challenges aligns with the company’s broader goals. Every business has strategic objectives: increasing market share, improving profitability, expanding into new markets, or enhancing customer satisfaction. Sales leaders should demonstrate how their team’s specific challenges are impeding progress toward these goals. For example, if lead conversion rates are low due to misaligned messaging between marketing and sales, this can prevent the company from reaching revenue targets. By framing sales challenges regarding their impact on overarching business goals, sales leaders clarify that addressing these issues is not just a sales priority but a company-wide imperative.
2. Use Data to Quantify the Impact
Numbers speak volumes when it comes to building a support case. Sales leaders should quantify the negative impact of the identified challenges on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as revenue, customer acquisition costs, sales cycle length, and churn rates. For example, if outdated technology is slowing down the sales process, it can be shown how much time is wasted, how many deals are lost, or how customer acquisition costs are inflated. By providing complex data, sales leaders make a more compelling argument for why resources are needed to address these issues. Data-driven insights help stakeholders in other departments see the tangible benefits of investing in the right tools, training, or process improvements.
3. Demonstrate Cross-Departmental Benefits
Many sales challenges have ripple effects that extend beyond the sales department, affecting other business areas. For example, poor communication between sales and customer service may lead to inconsistent customer experiences, which can damage the company’s reputation and increase churn. Similarly, if sales and marketing are misaligned, marketing resources may be wasted on campaigns that don’t generate qualified leads. Sales leaders should highlight these cross-departmental impacts, showing how resolving sales challenges can improve sales performance, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall brand perception. By demonstrating the benefits to other departments, sales leaders can secure their collaboration and support in addressing the challenges.
4. Present a Clear Action Plan with Defined Roles
Once the challenges have been identified and their impacts quantified, sales leaders should present a clear, actionable plan for addressing them. This plan should outline specific steps that need to be taken, timelines for implementation, and, most importantly, the roles and responsibilities of other departments. For example, marketing may need to work with sales to align messaging and develop more targeted lead-generation strategies, or IT might need to implement new sales enablement tools. By defining the contributions required from each department, sales leaders create a sense of ownership and accountability across the organization. Additionally, providing a roadmap helps other departments understand how their involvement fits into the bigger picture and what outcomes they can expect from their contributions.
5. Foster Collaborative Problem-Solving
Building a case for organizational support is not just about making demands—it’s about fostering collaboration and working together to solve the identified challenges. Sales leaders should actively engage stakeholders from other departments in problem-solving, inviting them to share their perspectives and contribute ideas. This approach helps build stronger relationships and ensures that the solutions developed are holistic and address the root causes of the challenges. By involving other departments early in the process, sales leaders increase the likelihood of securing their ongoing support and commitment.
6. Communicate the Long-Term Value of Change
Sales challenges often require long-term solutions involving significant investments in new tools, training, or process changes. To gain organizational support for these initiatives, sales leaders must communicate the long-term value of resolving these issues. For example, investing in a more advanced CRM system may require upfront costs. Still, it can significantly improve sales efficiency, customer insights, and lead tracking, resulting in higher revenue and reduced churn over time. Similarly, aligning sales and marketing efforts may require time and resources initially, but it can lead to more effective campaigns, better-qualified leads, and, ultimately, more tremendous sales success. Sales leaders should articulate these changes’ return on investment (ROI), emphasizing how short-term investments will yield long-term benefits for the company.
7. Leverage Executive Sponsorship
Gaining executive sponsorship can be a powerful way to build momentum and secure organizational support for addressing sales challenges. Sales leaders should aim to engage senior executives early in the process, presenting the business case for why resolving these issues is critical to the company’s success. When executives are on board, they can help champion the cause, influence other departments, and ensure the necessary resources are allocated. Executive sponsorship can also help overcome resistance to change by signaling that addressing sales challenges is a top priority for the company’s leadership.
Building a case for organizational support is essential to resolving the complex, cross-functional challenges that hinder sales performance. By linking sales challenges to broader company goals, using data to quantify the impact, and demonstrating the cross-departmental benefits of resolving these issues, sales leaders can secure the resources and collaboration they need from other teams. With a clear action plan and solid executive sponsorship, sales leaders can foster a collaborative approach to problem-solving, ensuring that the entire organization works together to optimize sales performance and drive long-term business success.
In the journey toward optimizing sales, the initial and most crucial step is identifying challenges that impede performance, both industry-wide and within your organization. These obstacles, often hidden beneath the surface, affect key areas of the sales process, such as conversion rates, customer acquisition, and overall revenue generation. Recognizing and understanding the root causes of these challenges is essential to creating targeted solutions that will improve sales efficiency and outcomes.
By analyzing and quantifying the impact of these challenges, sales leaders gain the clarity needed to prioritize issues and allocate resources effectively. Moreover, building a case for organizational support—demonstrating the broader benefits of resolving these challenges—ensures that the necessary tools, processes, and cross-departmental collaboration are secured to achieve sustainable improvements. This approach empowers sales teams and aligns the entire organization around common goals, driving both individual and business success.

Case Study: Microsoft’s Sales Optimization and Process Transformation
Background: Microsoft, a global leader in software, services, and hardware, faced significant sales challenges as it transitioned from a product-based to a cloud-based service model with its Azure platform and Office 365 offerings. The shift to cloud services required Microsoft’s sales teams to adopt new approaches. Still, the organization struggled with inefficiencies in sales, inconsistent customer acquisition strategies, and rising customer churn rates. Microsoft realized that its traditional sales methods were not optimized for the subscription-based business model and sought to optimize its sales processes to remain competitive in the growing cloud market.
As part of this transformation, Microsoft embarked on a sales optimization journey, focusing on identifying hidden challenges, understanding their root causes, and implementing targeted solutions to enable its sales organization to adapt to the cloud services landscape.
Challenge Identification: During the initial phase of this journey, Microsoft identified several key challenges that were impacting sales performance:
Misaligned Sales and Product Strategies: The sales teams were still primarily focused on selling on-premise software, while the company’s strategic direction had shifted toward cloud services. This misalignment meant that sales reps lacked the tools, training, or messaging to sell cloud solutions effectively.
High Customer Churn Rates: Microsoft experienced higher-than-expected churn rates in its Office 365 subscriptions. While the company was acquiring new customers, retaining them was becoming increasingly complex, especially in the face of stiff competition from other cloud service providers like Google and Amazon.
Long and Complex Sales Cycles: Selling cloud services requires longer sales cycles, with complex decision-making processes involving multiple stakeholders at the customer’s organization. Sales reps were often ill-prepared to navigate these complexities, resulting in prolonged sales cycles and lost opportunities.
Lack of Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Microsoft’s sales, marketing, and product development teams were not effectively collaborating, leading to inconsistent messaging and missed opportunities. The sales team often received unqualified leads from marketing, resulting in lower conversion rates and wasted resources.
Root Cause Analysis: To understand these challenges better, Microsoft conducted a root cause analysis and uncovered several underlying issues:
Outdated Sales Training and Tools: Many of Microsoft’s sales reps were not trained to sell cloud-based solutions. They lacked the knowledge and resources to effectively communicate the benefits of Microsoft’s cloud offerings to customers, especially compared to competitors.
Disconnected Customer Data: Sales reps were working with fragmented customer data, making it difficult to personalize interactions and build long-term relationships. The absence of a unified customer relationship management (CRM) system meant that sales, marketing, and customer service teams were not aligned on customer needs and preferences.
Inefficient Lead Management: Marketing generated a large volume of leads, but without a clear lead qualification process, many of these leads were not ready to buy, leading to frustration among sales teams and low conversion rates.
Quantifying the Impact: Once these challenges were identified, Microsoft’s sales leadership quantified the impact on key performance indicators:
High Customer Churn: The analysis revealed that reducing churn by even 5% could significantly increase overall customer lifetime value (CLV), leading to an additional $100 million in annual revenue from cloud services alone.
Prolonged Sales Cycles: Microsoft estimated that shortening the sales cycle by 20% could lead to a 10% increase in overall sales volume, enabling the company to close more deals in a shorter amount of time.
Lower Conversion Rates: Microsoft projected that it could increase conversion rates by 15% by improving lead qualification processes and better aligning sales and marketing efforts, resulting in a substantial boost to revenue.
Building a Case for Organizational Support: Addressing these challenges required collaboration across multiple departments within Microsoft, including sales, marketing, customer service, and product development. To secure organizational support, Microsoft’s sales leadership built a compelling case by demonstrating the financial impact of resolving these issues. They showed that improving customer retention, reducing the sales cycle length, and increasing conversion rates could generate significant revenue growth.
Microsoft emphasized the importance of aligning sales strategies with the company’s cloud-based goals and demonstrating to stakeholders how cross-departmental collaboration could improve sales efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Action Plan and Implementation: Microsoft developed a comprehensive action plan to address its sales challenges, focusing on the following key initiatives:
Cloud-Specific Sales Training: Microsoft revamped its sales training programs to ensure all sales reps were fully equipped to sell cloud solutions like Azure and Office 365. The training focused on educating reps about the cloud’s benefits, how to address customer concerns, and how to differentiate Microsoft’s offerings from competitors.
Unified CRM and Customer Data: Microsoft implemented its Dynamics 365 CRM system to unify customer data across sales, marketing, and customer service teams. This enabled sales reps to access real-time customer insights, track customer interactions, and personalize their sales approach based on customer needs and preferences.
Lead Scoring and Qualification: The company introduced a more robust lead scoring system that enabled marketing to pass only high-quality, well-qualified leads to the sales team. This ensured that sales reps focused on prospects with the highest likelihood of conversion, reducing wasted time and resources.
Sales and Marketing Alignment: Microsoft created a shared set of goals and metrics for the sales and marketing teams to ensure better alignment. Regular cross-functional meetings were implemented to review performance, share feedback, and adjust strategies based on market trends and customer insights.
Customer Success Initiatives: To reduce churn, Microsoft introduced a customer success team dedicated to helping customers maximize the value of their cloud subscriptions. This team provided ongoing support and resources to customers, ensuring they understood how to fully leverage Microsoft’s cloud offerings, which helped improve customer satisfaction and retention.
Results: Within 18 months of implementing these changes, Microsoft saw dramatic improvements in its sales performance and customer retention:
Customer churn rates decreased by 8%, leading to higher customer lifetime value (CLV) and a significant increase in recurring revenue from cloud services.
Sales cycles were shortened by 15%, allowing Microsoft to close deals faster and more efficiently. This contributed to a 12% increase in overall sales volume.
Lead conversion rates improved by 20%, resulting in a higher percentage of qualified leads being turned into paying customers.
Sales and marketing alignment improved, leading to more cohesive messaging and a smoother customer journey from initial interest to purchase.
Customer satisfaction and retention improved due to the success of the customer success team, which provided ongoing value to cloud customers and reduced the likelihood of churn.
Conclusion: Microsoft’s journey toward sales optimization is a prime example of how identifying hidden challenges, understanding their root causes, and implementing targeted solutions can significantly improve sales performance. By aligning sales strategies with organizational goals, leveraging data-driven insights, and fostering cross-departmental collaboration, Microsoft successfully transitioned to a cloud-focused sales model, driving growth and ensuring long-term success in a highly competitive market.

Exercise: Identifying and Prioritizing Sales Challenges
• Conversion rates
• Customer acquisition costs
• Team morale
• Sales cycle length
• Cross-departmental collaboration (e.g., sales and marketing alignment)
• Decreased conversion rates
• Longer sales cycles
• Increased customer acquisition costs
• Lower deal sizes or revenue
• Reduced team productivity or morale

Course Manual 4: Common Mistakes
Sales optimization is critical to improving sales performance by refining strategies, enhancing techniques, and utilizing data to drive better results. However, in the pursuit of optimization, sales teams and organizations often fall into common pitfalls that hinder their ability to reach maximum potential. These mistakes can range from misaligned strategies to poor execution, and while they may seem small, they can significantly affect revenue growth and overall business success.
Understanding and avoiding these common mistakes is essential for any sales team striving to optimize its efforts. Often, these errors stem from a lack of clear objectives, miscommunication between sales and marketing teams, or failure to leverage modern technology. Businesses may invest heavily in sales training, tools, and marketing campaigns, yet without the proper execution and alignment, these investments can fail to yield the desired results. Additionally, sales teams sometimes overlook the importance of building strong, long-term relationships with clients in favor of short-term gains, which can harm customer loyalty and limit future growth opportunities.
By recognizing these common mistakes, sales leaders can proactively address weaknesses within their processes and improve both short-term results and long-term sustainability. This involves assessing current strategies and workflows and adopting a continuous learning and improvement mindset. Below are three key subtopics that explore some of the most frequent mistakes made during sales optimization and how to avoid them.
Misalignment Between Sales and Marketing
One of the most prevalent and damaging mistakes in sales optimization is the misalignment between sales and marketing teams. Despite their interconnected roles, these two departments often work in isolation, hindering the overall effectiveness of a company’s revenue-generating strategies. While marketing focuses on building brand awareness, generating leads, and crafting messaging that resonates with potential customers, the sales team is responsible for converting those leads into paying clients. When these two functions are not aligned, it can lead to poor-quality leads, missed sales opportunities, and wasted resources, undermining the company’s growth objectives.
The misalignment between sales and marketing usually stems from differing goals and priorities. Marketing teams are often incentivized to bring in many leads, focusing on top-of-the-funnel activities like content creation, digital advertising, and social media campaigns. Their success metrics may center around traffic, lead generation, or campaign engagement. On the other hand, sales teams are tasked with closing deals, moving leads through the funnel, and generating revenue. Their metrics revolve around conversion rates, deal sizes, and revenue growth.
The gap between these departments can grow without clear communication and shared goals. Marketing may believe they deliver qualified leads, only to have the sales team disregard them as poor quality or too early in the buying journey. Conversely, sales may feel that marketing isn’t providing enough support to nurture leads through the consideration phase, leaving them to fend for themselves when converting prospects. This lack of cohesion results in wasted efforts, with both teams often blaming each other for missed targets and lost revenue opportunities.
Misalignment between sales and marketing has several detrimental consequences. First, it diminishes the overall quality of leads entering the sales funnel. When marketing is not fully aware of what constitutes a qualified lead for the sales team, they may focus on volume over quality, resulting in an influx of leads not ready to purchase. This leads to frustration for sales, as they waste valuable time trying to convert leads with little potential to close.
Second, it leads to inefficiencies in the sales process. Without a collaborative strategy, sales teams may not have access to the critical information they need to engage with leads effectively. Marketing teams often have valuable insights into a lead’s behavior—content they’ve consumed, their interactions with the brand, and their position in the buying journey—which can help sales tailor their approach. If this data is not shared correctly, sales reps are left to guess how to approach the best lead, which can result in missed opportunities.
Lastly, misalignment leads to wasted resources. A lack of synchronization often means that marketing dollars are spent on campaigns that don’t yield the intended results while sales teams struggle to hit their targets with unqualified or poorly nurtured leads. This inefficiency can severely affect the company’s return on investment (ROI) for marketing and sales initiatives.
To avoid the pitfalls of misalignment, companies need to foster collaboration between sales and marketing, ensuring that both teams are working toward the same goals. Here are some key strategies for achieving this alignment:
1. Define Shared Objectives: One of the first steps in aligning sales and marketing is establishing shared goals. Both teams should collaborate on defining what success looks like and what metrics matter most. Instead of marketing focusing purely on lead volume and sales on revenue, both teams should align on metrics like qualified leads, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs. This ensures that everyone is working toward the same outcome.
2. Agree on Lead Qualification Criteria: Both sales and marketing must have a clear, agreed-upon definition of what constitutes a “qualified” lead. This could be based on demographic data (e.g., company size, industry) or behavioral signals (e.g., specific actions taken on the website, engagement with content). A formal service-level agreement (SLA) between sales and marketing can help outline the expectations for both teams regarding lead generation and nurturing.
3. Enhance Data Sharing and Communication: Seamless data flow between sales and marketing is essential for effective alignment. CRM and marketing automation systems should be integrated to ensure both teams can see the same data. Marketing should see which leads are converting into customers, while sales should have access to insights on how leads engage with marketing content. Regular meetings or check-ins between the two teams are critical for ongoing communication. This fosters a culture of collaboration and ensures that both teams stay informed on progress and challenges.
4. Implement a Feedback Loop: A feedback loop between sales and marketing is essential for continuous improvement. Sales teams should provide feedback on the quality of leads from marketing and offer insights into what messaging resonates with prospects. Similarly, marketing should share performance data on campaigns and lead nurturing efforts with sales. This iterative feedback process helps both teams refine their strategies and better understand what is working and what needs to be adjusted.
Achieving alignment between sales and marketing is critical to optimizing sales efforts. By setting shared goals, defining lead qualification criteria, improving data sharing, and fostering continuous communication, companies can avoid the costly mistakes of siloed operations and maximize their potential for revenue growth.
Neglecting Data-Driven Insights
In today’s increasingly digital world, one of the most costly mistakes sales teams make is neglecting to leverage data-driven insights to inform their strategies. Modern sales environments generate abundant data, from customer preferences and behaviors to sales performance metrics and market trends. Yet, many organizations still fail to use this valuable data to optimize their sales processes. Instead, they continue to rely on outdated methods, gut feelings, or intuition-based decisions that can lead to missed opportunities, inefficient practices, and suboptimal performance.
Sales strategies based on assumptions or intuition may have worked in the past, but in today’s competitive and data-driven marketplace, they are no longer enough to maintain an edge. When sales teams neglect data, they risk making decisions that do not reflect the current realities of their customer base, market trends, or internal performance. For instance, without data, a sales team may overinvest in a product that no longer resonates with customers or allocate resources to the wrong market segments, wasting time and money.
Additionally, ignoring data can lead to inaccurate sales forecasting. Many organizations rely on manual processes or outdated systems to predict future sales. However, these methods often fail to account for the dynamic nature of the market, customer behavior, and external factors that can influence sales outcomes. As a result, sales teams may either overestimate or underestimate their performance, leading to missed revenue targets or resource misallocation.
Another consequence of neglecting data-driven insights is the inability to identify patterns in customer behavior. Data can reveal critical insights about buying patterns, preferences, and pain points, which can be used to tailor the sales approach to meet customer needs. Without this information, sales teams may struggle to engage with prospects in a way that resonates, potentially losing deals to more data-savvy competitors.
Leveraging data-driven insights offers several advantages that can significantly improve the effectiveness of sales teams. Here are some key benefits:
1. Improved Customer Targeting: By analyzing customer data, sales teams can segment their audience more effectively and identify the highest-value prospects. Data allows sales teams to understand their best customers, what motivates them to buy, what challenges they face, and how they prefer to be engaged. This level of understanding enables more personalized and effective sales outreach, which increases the chances of closing deals and building long-term relationships.
2. More Accurate Sales Forecasting: Data analytics enables sales teams to forecast future sales more accurately. By analyzing historical sales data, current market trends, and customer behavior patterns, businesses can predict potential outcomes more reliably. This helps sales managers allocate resources more effectively, set realistic goals, and adjust strategies in response to market changes. Accurate forecasting also allows organizations to manage inventory, staffing, and cash flow more efficiently.
3. Enhanced Performance Tracking: Data-driven insights help sales teams monitor their performance more effectively. Sales performance metrics—win rates, deal velocity, and conversion rates—can be tracked in real-time using customer relationship management (CRM) tools and analytics platforms. By regularly reviewing these metrics, sales managers can identify areas for improvement, recognize top performers, and adjust their strategies to ensure the team continually improves.
4. Informed Decision-Making: Data-driven insights remove much guesswork from sales decision-making. Sales leaders can use data to evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies, campaigns, or approaches and make informed decisions about where to invest their time and resources. For example, a sales team may analyze data to determine which marketing campaigns generate the most qualified leads or which products perform well in specific markets. This allows them to focus their efforts where they are most likely to yield results.
5. Predictive Sales Analytics: One of the most potent applications of data-driven sales is predictive analytics. Predictive sales analytics use historical data, machine learning algorithms, and statistical modeling to forecast future sales outcomes and trends. By analyzing patterns in customer behavior, sales teams can anticipate which leads are most likely to convert when a customer might be ready to make a purchase or which accounts are at risk of churning. This foresight allows sales teams to be more proactive, ensuring they are in the right place at the right time to close deals and retain clients.
Organizations must take a strategic approach to implementation to effectively harness the power of data. Here are critical steps for incorporating data-driven insights into sales optimization:
1. Invest in the Right Tools: The foundation of a data-driven sales strategy is having the right technology in place. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems, sales analytics platforms, and marketing automation tools are essential for collecting, organizing, and analyzing data. These tools provide real-time insights that can help sales teams track leads, monitor performance, and make data-backed decisions. Integrating these tools with other business systems, such as marketing platforms or inventory management, can further enhance the effectiveness of data-driven sales strategies.
2. Train Sales Teams on Data Usage: Technology alone is insufficient; sales teams must be trained to interpret and use data effectively. Salespeople should understand how to read reports, interpret analytics, and apply insights to everyday activities. Training programs should emphasize the importance of data in guiding decision-making, customer engagement, and forecasting.
3. Create a Data-Driven Culture: For data-driven insights to be efficient, organizations must foster a culture prioritizing data in decision-making processes. This means encouraging all departments, not just sales, to leverage data and collaborate on insights. Regular meetings to review data trends, share insights, and adjust strategies can help instill this culture.
4. Continuously Refine Strategies: Data-driven sales strategies are not static. Sales teams must continuously analyze new data, assess performance, and refine their strategy based on the insights they uncover. This iterative approach ensures that the sales process remains agile and responsive to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
Neglecting data-driven insights is a critical mistake in sales optimization. By embracing data and using it to inform strategies, sales teams can improve targeting, forecasting, and performance, ultimately driving better results for the organization. Data should be at the heart of any modern sales strategy, enabling businesses to adapt, innovate, and thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Focusing on Short-Term Gains Over Long-Term Relationships
One of the most common and costly mistakes sales teams make is prioritizing short-term wins over building sustainable, long-term relationships with clients. In the pressure to meet quarterly targets or generate immediate revenue, salespeople often focus heavily on closing deals quickly, which can offer short-term financial gains but neglect the larger picture of customer loyalty and retention. This short-sighted approach can hinder long-term business growth and reduce the potential for recurring revenue and valuable customer referrals.
The allure of quick wins in sales is understandable. Closing a deal brings immediate recognition and adds to revenue targets, but it can come at the expense of building meaningful connections with clients. When sales teams focus on rapidly pushing leads through the pipeline without considering the long-term value of the relationship, they risk several negative consequences:
1. Decreased Customer Loyalty: When the focus is on closing deals without nurturing the relationship, customers may feel undervalued or ignored once the sale is completed. This often results in a lack of trust and diminished loyalty. Customers who don’t feel valued will likely switch to a competitor offering a more personalized and consistent experience in the long run.
2. Missed Opportunities for Upselling and Cross-Selling: A short-term focus on making the sale can prevent sales teams from exploring other opportunities to meet the client’s broader needs. When a relationship is built solely on closing a deal, there’s little room for upselling or cross-selling additional products or services that may benefit the client. A deeper relationship built on trust allows sales teams to identify ongoing needs and propose additional solutions over time.
3. Reduced Repeat Business: Customers treated as quick wins are less likely to return for future purchases. Repeat business is one of the most valuable sources of revenue for any company because it’s far more cost-effective to sell to an existing customer than to acquire a new one. If customers feel that their needs are not met post-sale or disconnected from the company, the likelihood of returning for future purchases diminishes significantly.
4. Lost Referral Opportunities: Happy, satisfied customers are one of the best sources of new business through word-of-mouth referrals. However, if the relationship is transactional and focused only on closing the deal, customers are unlikely to refer others. Building long-term relationships encourages customers to speak positively about their experience, which can lead to valuable referrals and increased brand reputation.
In contrast to a short-term, transactional approach, long-term success in sales depends heavily on cultivating lasting relationships beyond the initial sale. Building trust, providing consistent value, and maintaining open lines of communication with customers ensures that they return for future business and recommend your services to others. Here are some reasons why long-term relationship building is critical to sales optimization:
1. Trust is the Foundation of Long-Term Sales: Trust is critical to any business relationship. When salespeople prioritize building trust with clients over time, it creates a foundation for ongoing business. Clients who trust their sales representatives are more likely to consult them for future purchases and view them as partners rather than just vendors. Trust leads to stronger customer loyalty and long-term business relationships.
2. Customer Retention is More Profitable than Acquisition: Acquiring new customers is often more expensive than retaining existing ones. Sales teams that invest in building long-term relationships with their clients enjoy repeat business and benefit from a higher lifetime value of each customer. Retention strategies, such as consistent follow-up, personalized communication, and offering solutions that evolve with the client’s needs, help maintain a solid client base and drive recurring revenue.
3. Opportunities for Growth and Expansion: A strong relationship with a customer opens the door to growth opportunities that may not be immediately apparent during the initial sale. Clients whose needs evolve may require new products, services, or solutions your company can provide. Sales teams maintaining close relationships can anticipate these needs and position themselves as the go-to partner for solving new challenges.
4. Word-of-mouth and Referrals: Customer referrals are among the most powerful drivers of business growth. Satisfied customers who feel valued and well-served are more likely to refer others to your company. Long-term relationships foster this kind of advocacy, as clients with positive, lasting experiences with your brand are more inclined to recommend your services to their peers and networks. This helps sales teams expand their reach without relying solely on traditional lead-generation methods.
To avoid focusing solely on short-term gains, sales teams must shift their mindset and strategies toward building strong, long-lasting client relationships. Here are some practical ways to do so:
1. Focus on Customer Satisfaction and Retention: One of the most important key performance indicators (KPIs) for sales teams should be customer satisfaction and retention, not just closed deals. This means following up after the sale, checking in regularly to ensure the customer’s needs are met, and promptly addressing any issues or concerns. Sales teams should actively seek customer feedback to ensure they are happy with the service or product and continuously look for ways to add value.
2. Provide Ongoing Value: Building long-term relationships requires sales teams to move beyond just selling a product or service. Instead, they should aim to become trusted advisors who provide ongoing value to the customer. This could mean offering expert advice, sharing industry insights, or helping clients solve problems beyond the sale’s original scope. By becoming a valuable resource, sales teams can strengthen the relationship and position themselves as indispensable to the customer.
3. Personalize the Experience: Every customer is unique, and sales teams should tailor their approach accordingly. Personalization can range from understanding the customer’s needs and preferences to offering customized solutions uniquely suited to their business. Personalizing communication and consistently showing the customer that you understand their challenges and goals fosters a deeper connection and a sense of trust.
4. Maintain Open Communication: Consistent and open communication is critical to building solid relationships. Sales teams should ensure they are readily available to their customers, providing updates, checking in regularly, and offering assistance when needed. A proactive approach, where the sales team reaches out to provide value even when not trying to make a sale, helps solidify long-term relationships.
While short-term wins may provide immediate satisfaction and revenue, long-term relationships are far more valuable for sustainable business growth. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, retention, and ongoing value, sales teams can retain clients and create a strong network of loyal customers who will return for future business and refer others. This shift from a transactional mindset to a relationship-focused approach is crucial for optimizing sales and driving long-term success.
Sales optimization is essential for improving performance and driving sustainable growth. Still, common mistakes—such as misaligned strategies, neglecting data, and focusing on short-term gains—can severely limit success. By recognizing and addressing these pitfalls, organizations can streamline their sales processes, enhance collaboration between sales and marketing, leverage data-driven insights, and foster long-term client relationships. Prioritizing customer satisfaction, refining strategies through continuous learning, and building trust are critical to ensuring immediate results and long-term sustainability. Successful sales optimization requires a commitment to alignment, informed decision-making, and nurturing valuable customer relationships.

Case Study: Coca-Cola – Sales Optimization Through Data-Driven Insights and Alignment of Sales and Marketing
Background:
One of the largest beverage companies globally, Coca-Cola faced challenges maintaining its market dominance amidst changing consumer preferences and increasing competition. The company had a massive global salesforce but lacked a unified, data-driven approach to optimize its sales processes. Coca-Cola needed to enhance collaboration between its sales and marketing teams and better leverage the growing amount of consumer data to improve targeting, optimize campaigns, and drive revenue growth.
The company identified three main issues: misalignment between its sales and marketing functions, underutilization of customer data for decision-making, and overemphasizing short-term sales wins at the expense of long-term customer relationships. Coca-Cola embarked on a comprehensive sales optimization initiative to address these issues and improve market performance.
Challenge 1: Misalignment Between Sales and Marketing
Coca-Cola’s marketing department operated separately from the sales teams, with both functions focusing on their objectives. The marketing team was tasked with building brand awareness and running promotions, while the sales teams concentrated on closing deals with retailers and distributors. This siloed approach led to inconsistent strategies and missed opportunities, as the messaging and campaigns that marketing created were often not aligned with the needs of the sales teams on the ground.
Marketing focused on mass campaigns and product promotions, but the sales teams felt the leads generated did not align with their regional or account-specific needs. In some cases, sales teams found it challenging to convert these leads into actual retail placements or orders because the marketing initiatives did not account for the specific needs of regional retailers or varying consumer preferences.
Challenge 2: Neglecting Data-Driven Insights
Despite Coca-Cola’s extensive consumer reach and large amounts of available data, the company was not using data effectively to drive sales decisions. The sales teams relied on traditional sales forecasting methods and personal relationships with retailers to push products. Still, this approach lacked precision and did not allow for a more strategic allocation of resources. Additionally, marketing campaigns were created with broad assumptions about customer preferences without diving deep into data analytics that could provide a more granular understanding of customer behavior.
The company recognized that failing to leverage data-driven insights resulted in missed opportunities to improve market targeting, product placement, and promotional effectiveness. Coca-Cola needed to build a more data-centric sales culture to maximize the value of its consumer and market data.
Challenge 3: Focusing on Short-Term Wins Over Long-Term Relationships
Coca-Cola’s sales approach focused heavily on driving short-term revenue through promotional deals with retailers and distributors. While this strategy helped achieve immediate sales boosts, it often led to inconsistent sales performance and did not foster long-term relationships with key retail partners. Retailers and distributors expected more from Coca-Cola than discounts and promotions; they wanted to work with the company to develop collaborative strategies to drive long-term category growth.
This short-term focus also hindered the company’s ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences. Coca-Cola often focused on pushing its core product lines without considering how to evolve its offerings to meet emerging health and wellness trends or region-specific demands.
Solution 1: Aligning Sales and Marketing
To address the misalignment between sales and marketing, Coca-Cola developed a collaborative framework that integrated the two functions more closely. The company implemented a “one team” strategy where marketing and sales shared objectives, ensuring both departments worked toward common goals. Coca-Cola introduced joint planning sessions where sales and marketing worked together to craft campaigns tailored to specific regions and retailer needs, making the campaigns more relevant and actionable for the sales teams.
Marketing and sales teams also aligned their performance metrics. Instead of marketing focusing solely on brand awareness and sales on immediate orders, they both tracked metrics like product placement success, in-store promotional effectiveness, and long-term sales growth. This alignment allowed marketing to create campaigns that better supported the sales team’s efforts and ensured that the sales team could convert marketing leads more effectively.
Solution 2: Leveraging Data-Driven Insights
Coca-Cola invested heavily in technology and data analytics to turn its vast consumer data into actionable insights. The company implemented advanced analytics tools that allowed the marketing and sales teams better to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns. This data-driven approach enabled Coca-Cola to segment its customer base more effectively and personalize its marketing efforts for specific markets.
The sales teams were provided real-time insights into product performance at the regional and store levels, enabling them to make more informed decisions about which products to promote to retailers. Additionally, Coca-Cola used predictive analytics to forecast demand, optimize product distribution, and improve sales forecasting accuracy. This helped the company allocate resources more strategically, ensuring the right products were in the right stores at the right time.
The data insights also empowered Coca-Cola’s sales teams to offer retailers more tailored solutions. Instead of pushing products, sales reps could present data-backed strategies to retailers, demonstrating how specific product assortments or promotions could drive overall category growth, fostering stronger, long-term partnerships.
Solution 3: Focusing on Long-Term Relationships
Coca-Cola shifted its focus from short-term promotional gains to building long-term, value-driven relationships with its retail partners. The sales team began to engage retailers in more strategic discussions about category management rather than just pitching individual promotions or products. By offering data-backed insights and collaborative planning, Coca-Cola positioned itself as a partner that could help retailers grow their beverage categories over time.
This long-term relationship focus was supported by a customer-centric approach to sales, where the key performance indicators (KPIs) were adjusted to emphasize customer satisfaction and partnership success. Sales teams were evaluated on immediate sales and their ability to build long-term, sustainable business with retailers and distributors.
Coca-Cola also began offering retailers more personalized marketing support, including region-specific promotions and product assortments designed to meet local consumer demand. This helped the company build stronger relationships with its retail partners, resulting in increased shelf space, better product visibility, and higher sales over time.
Results
Coca-Cola’s sales optimization efforts delivered significant improvements across several key areas. The alignment between sales and marketing resulted in more cohesive campaigns that resonated better with retailers and distributors, leading to increased product placements and higher conversion rates. The collaboration between sales and marketing also allowed the company to tailor its efforts to specific markets, improving the relevance of its offerings and strengthening relationships with retail partners.
The company’s use of data-driven insights transformed its sales operations, enabling Coca-Cola to make more informed decisions, improve sales forecasting accuracy, and enhance its targeting strategies. This data-centric approach also helped the sales team identify new opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, driving additional revenue growth.
Finally, Coca-Cola’s focus on long-term relationships improved retailer satisfaction, stronger partnerships, and increased loyalty. Retailers valued Coca-Cola’s collaborative approach and its ability to provide data-backed strategies that supported category growth. This shift in focus helped Coca-Cola maintain its market leadership position and secure long-term growth in a competitive beverage market.
Conclusion
Coca-Cola’s case demonstrates the importance of aligning sales and marketing, leveraging data-driven insights, and focusing on long-term relationships for successful sales optimization. By addressing these common challenges, Coca-Cola was able to streamline its sales processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable revenue growth. The company’s experience highlights how a more integrated and data-driven approach to sales can lead to more robust performance and long-term success.

Exercise: Identifying and Solving Sales Optimization Mistakes
• Identify one common mistake (misalignment, data neglect, or short-term focus) your team is experiencing.
• Work together to develop a concrete solution. For example, if you identified misalignment, brainstorm ways to improve communication and collaboration between your teams (e.g., regular alignment meetings and shared KPIs).

Course Manual 5: Forecasting Model
Forecasting is critical to any successful sales organization, providing visibility into future revenue, identifying potential shortfalls, and guiding strategic decisions. However, despite its importance, creating and managing an effective forecasting model is often misunderstood or inconsistently applied within many sales teams. With as many interpretations of forecasting as there are salespeople, organizations frequently struggle with inconsistent results, missed targets, and a lack of actionable insights.
At the heart of these challenges lies the need for a structured, uniform forecasting model that ensures all team members speak the same language when discussing deals in the pipeline. A common understanding of the stages in the sales process—along with specific, clearly defined criteria for each stage—creates a more predictable and reliable forecasting process. By developing this shared language, sales teams can improve accuracy, increase accountability, and foster better collaboration between sales representatives, managers, and executives.
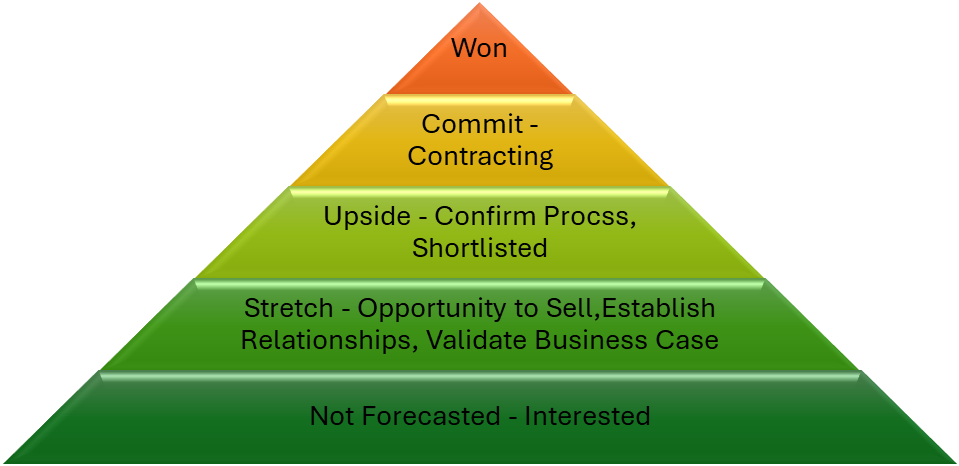
One key goal of a forecasting model is to categorize and track deals as they progress through the pipeline. This means having specific terminology for each stage of the sales process and defining granular steps within each stage. For example, if a deal is labeled as a “commit” deal, everyone in the organization should clearly understand what that means. A forecasting model ensures that each deal is appropriately categorized, preventing confusion and enabling leaders to make informed decisions based on consistent data.
A robust forecasting model tracks deals and creates a repeatable and scalable process that can be applied across the organization. It allows sales teams to efficiently identify potential risks, allocate resources, and adjust strategies based on the most accurate data. This lays the foundation for long-term success, enabling organizations to meet their revenue targets and swiftly respond to market dynamics.
Defining Forecasting Stages and Dealing with Progression
A fundamental aspect of creating a reliable forecasting model is establishing clear, standardized stages within the sales pipeline. This process involves outlining each stage, from the initial engagement with a prospect to the final close, ensuring that every sales team member understands and agrees on the criteria defining where a deal is in its lifecycle. Salespeople may interpret deal statuses differently without clear definitions, leading to confusion, inaccurate forecasts, and a lack of accountability.
Each stage in the sales pipeline must reflect a distinct phase in the buyer’s journey, with measurable criteria that act as benchmarks to guide the movement of deals from one stage to the next. Standardizing these stages helps eliminate subjectivity, ensuring that everyone understands the precise meaning when a salesperson categorizes a deal at a specific stage. This standardization is crucial for building a forecasting model that is both transparent and reliable.
For instance, if one salesperson categorizes a deal as “committed” based on their subjective feeling that the deal will close, while another salesperson applies stricter criteria—such as a signed proposal or a verbal confirmation—the forecast will become inconsistent and difficult to manage. Standardized stages ensure that every deal is judged by the same criteria, creating consistency and allowing for more accurate forecasting.
Here’s a breakdown of typical sales pipeline stages, each with its measurable criteria that guide deal progression:
Prospecting (Initial Contact):
The sales team identifies potential customers in this first stage and begins outreach. For a deal to be categorized here, the organization typically requires specific actions, such as a discovery call, qualification discussion, or a first engagement where the prospect shows interest. Metrics such as the number of leads contacted or qualified can be used to measure progress at this stage.
Qualification:
This stage involves determining whether a prospect has the potential to become a viable customer based on factors such as budget, authority, need, and timing (BANT). Criteria for this stage might include a detailed conversation with the prospect about their pain points, needs, and alignment with the company’s solution. A deal cannot progress beyond this stage until the customer has met certain qualification benchmarks, like confirming interest in moving forward or demonstrating alignment with the business’s product or service offering.
Proposal/Value Proposition:
Here, the sales team presents a tailored proposal or solution to the prospect, clearly demonstrating the value of the offering. This stage is marked by presenting product or service specifics, pricing, and deal terms. A measurable action, such as delivering a formal proposal or getting a verbal indication of interest, is required for the deal to proceed. This stage often includes follow-up presentations, Q&A sessions, and discussions with decision-makers on the prospect’s side.
Commitment/Negotiation:
In the commitment stage, the customer signals that they are seriously considering purchasing. This stage often involves negotiations on pricing, terms, or contract details. The criteria for progressing beyond this stage could include formal agreement to terms, legal reviews, or signing a letter of intent (LOI). Sales teams need a clear and measurable signal, such as a signed contract or an agreement on the deal’s framework, before moving to the final stage.
Closing:
The closing stage is where the deal is finalized. To move a deal into this stage, the team must secure the formal purchase agreement, confirm payment terms, and ensure the delivery timeline is agreed upon. Deals categorized in this stage should be finished, with only administrative steps left to finalize the transaction. The metrics at this stage may involve collecting signatures on contracts or confirming the order fulfillment process has begun.
Defining the specific, measurable criteria that must be met before a deal can advance to the next stage is essential for each stage. These criteria act as checkpoints, ensuring an agreement meets the conditions before moving forward. For example, a deal cannot move from “Qualification” to “Proposal” until the prospect has demonstrated interest and has the authority to make purchasing decisions.
This approach helps avoid over-optimism, where deals are prematurely moved into later stages, inflating the sales forecast. By adhering to these criteria, sales leaders can ensure that every agreement is accurately categorized and that the forecast reflects the actual status of deals within the pipeline.
Developing a universal language for deal stages ensures that salespeople, managers, and executives are all on the same page. Everyone understands exactly what it means when a deal is in the “Negotiation” stage versus the “Qualification” stage. This clarity leads to better communication, improved collaboration, and more accurate forecasts. It also fosters greater accountability within the team, as each salesperson must meet the defined criteria before advancing deals in the pipeline.
Additionally, this universal language provides a foundation for better coaching and performance management. Sales managers can more easily identify where individual team members may need additional support or training based on where their deals are stalling in the pipeline.
Establishing clear, standardized forecasting stages and defining measurable criteria for deal progression is critical in creating a reliable and scalable sales forecasting process. By building a forecasting model with transparency and consistency, sales teams can improve forecast accuracy, reduce ambiguity, and align their efforts with the organization’s broader sales goals. This approach ultimately leads to more informed decision-making, better resource allocation, and greater confidence to meet revenue targets.
Using Data to Enhance Forecast Accuracy
In today’s data-driven sales environment, organizations have access to vast amounts of information that can significantly improve the accuracy of their sales forecasts. Integrating data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive models allows sales teams to generate more precise, actionable forecasts by analyzing historical trends, current market conditions, and customer behaviors. This subtopic explores the types of data critical for accurate forecasting, the role of AI and predictive analytics, and how these tools help identify potential roadblocks to ensure sales forecasts are grounded in a realistic understanding of future outcomes.
Data is the foundation upon which accurate sales forecasts are built. Traditional forecasting often relied on gut instinct or qualitative insights from salespeople. While these inputs are valuable, they are inherently subjective and prone to bias. By incorporating data into the forecasting process, organizations can develop more objective, evidence-based forecasts that reduce uncertainty and improve decision-making.
Several key types of data are essential to sales forecasting:
1. Historical Sales Data:
Analyzing past sales performance is critical to understanding future trends. Historical sales data reveals patterns related to sales cycles, seasonal fluctuations, average deal size, and sales team performance. By identifying which factors contributed to previous successes or failures, businesses can set more accurate expectations for future performance. For instance, if a particular quarter consistently performs better due to seasonal demand, historical data can adjust the forecast accordingly.
2. Current Market Conditions:
Forecasts must account for external factors impacting sales, such as economic changes, industry trends, or competitor behavior. Real-time data on market conditions, customer sentiment, and industry benchmarks help adjust sales forecasts to align with the current business environment. For example, if economic indicators suggest a downturn, the sales forecast may need to be adjusted downward to reflect reduced customer spending.
3. Customer and Buyer Behavior Data:
Understanding how customers move through the buyer’s journey is essential for predicting the likelihood of deal closure. Analyzing customer behaviors, such as website visits, engagement with marketing materials, response to sales outreach, and interactions with the sales team, provides valuable insights into buyer intent. Data-driven insights into how customers make purchasing decisions allow sales teams to prioritize deals and focus their efforts on high-probability opportunities.
4. Sales Activity Data:
Tracking key sales activities, such as the number of calls made, meetings held, proposals sent, and follow-ups completed, provides insight into the sales team’s performance and pipeline health. This data helps identify potential bottlenecks in the sales process, such as deals stalling in specific stages and can inform adjustments to the sales strategy to drive deals forward.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics have revolutionized sales forecasting accuracy by enabling organizations to process and analyze large volumes of data quickly and efficiently. These technologies allow sales teams to move beyond historical data and subjective inputs, providing real-time insights and forward-looking predictions based on patterns and trends.
1. Predicting Deal Outcomes:
AI-driven models can analyze the attributes of deals in the pipeline and compare them with historical data to assess the likelihood of closure. By looking at variables such as deal size, industry, sales rep activity, and customer engagement, AI models can assign probability scores to each deal, helping sales teams focus on high-likelihood opportunities. This approach reduces the risk of overestimating or underestimating potential sales outcomes.
2. Forecasting Revenue Timelines:
Predictive analytics can provide insights into when deals are likely to close by analyzing factors such as the typical sales cycle length, buyer behaviors, and external conditions. By understanding the pace at which deals progress through the pipeline and identifying potential delays, sales leaders can more accurately predict when revenue will be realized. This allows for more precise financial planning and resource allocation.
3. Identifying Potential Roadblocks:
AI can also help identify patterns or trends that indicate potential obstacles in the sales process. For example, if deals in a particular industry or region consistently stall at the same stage, predictive analytics can flag this as a risk. Sales leaders can then investigate the underlying causes, such as pricing issues, product misalignment, or competition, and adjust the sales strategy. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and ensures the forecast reflects a more realistic outlook.
One of the primary benefits of using data to enhance sales forecasts is reducing uncertainty. Sales forecasting is inherently probabilistic, but organizations can shift from speculative forecasts to models grounded in evidence by relying on data. This approach reduces the likelihood of large forecast variances and allows for more accurate planning.
Key ways data reduces uncertainty include:
Weighted Pipelines:
Sales teams can use data to assign weighted probabilities to deals based on their pipeline status and historical likelihood of closing. This ensures that not all deals are treated equally in the forecast and helps set more realistic expectations for future revenue.
Scenario Planning:
Data allows organizations to run different forecasting scenarios, such as best-case, worst-case, and most-likely outcomes. By incorporating variables like changes in market conditions or internal performance, sales leaders can prepare for various possible outcomes and adjust strategies accordingly. This flexibility is essential in volatile industries or economic environments.
Real-Time Adjustments:
Modern sales forecasting tools, powered by AI and data analytics, allow for real-time updates to forecasts based on new information. As new data becomes available, such as changes in buyer behavior or updated market conditions, forecasts can be adjusted dynamically. This ensures that sales leaders always work with the most accurate and up-to-date information, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
Incorporating data into the sales forecasting process is critical for improving accuracy, reducing uncertainty, and making more informed strategic decisions. By leveraging historical sales data, current market conditions, and customer behaviors and using AI-powered predictive analytics, sales teams can move beyond traditional, subjective forecasting methods. This data-driven approach helps identify patterns, predict potential roadblocks, and provide realistic projections for deal closures and revenue generation. Ultimately, using data to enhance forecast accuracy enables organizations to allocate resources better, set achievable targets, and respond more effectively to changing business environments.
Aligning Sales Forecasting with Sales Strategy
Sales forecasting plays a pivotal role in driving business success, but to be truly effective, it must be tightly aligned with the broader sales strategy of the organization. A forecasting model isolated from the overall sales goals will likely lead to misalignment between revenue expectations and strategic objectives, making it harder for teams to execute effectively. This subtopic explores the importance of ensuring sales forecasts harmonize with broader sales goals, such as market expansion, customer acquisition, and new product launches, and how these forecasts can inform critical decision-making processes. By integrating forecasting into the strategic framework of the business, organizations are better equipped to allocate resources, adjust pricing strategies, and position their teams for long-term success.
Sales forecasting should be viewed as a strategic tool that predicts revenue and guides the direction of the sales organization. By aligning the forecasting model with key sales goals—such as expanding into new markets, acquiring new customers, or launching new products—businesses can ensure that their forecasts support the company’s broader vision and objectives.
1. Market Expansion:
When an organization is focused on expanding into new markets, whether geographic or demographic, the sales forecast should reflect the potential impact of these efforts. For example, a company entering a new region may need to adjust its projections based on market size, competition, and local economic conditions. The forecasting model must incorporate assumptions about market penetration rates, sales cycle length in the new market, and customer acquisition cost. By factoring in these variables, the forecast becomes a realistic representation of the growth potential in the new market. It helps ensure that the sales strategy is geared toward achieving that expansion.
2. Customer Acquisition:
If customer acquisition is a key strategic priority, the sales forecast must account for the efforts and investments required to attract new customers. This may involve analyzing historical customer acquisition costs (CAC), conversion rates, and lead sources. A well-aligned forecasting model will help the sales team set realistic targets for new customer acquisition while identifying the resources needed to achieve those targets, such as marketing budgets, sales personnel, or technology investments. Furthermore, forecasts can provide insights into the customers that offer the most value, enabling the sales strategy to prioritize high-quality leads and optimize acquisition efforts.
3. Product Launches:
New product launches require a careful balance of forecasting and strategy alignment. When a business introduces a new product, the forecast must consider the learning curve associated with selling the product, the potential demand, and any cannibalization of existing product lines. The sales forecast should incorporate expected sales volumes for the new product, adjustments to sales cycles, and how the product fits into the existing customer base. By aligning the forecasting model with the product launch strategy, businesses can ensure that they are adequately prepared for the rollout and that the sales team is equipped to meet revenue targets associated with the new offering.
Sales forecasts are critical in informing various strategic decisions across the organization. When aligned with the overall sales strategy, forecasts can provide valuable insights into where and how resources should be allocated, whether pricing strategies need adjustment, and how to position the sales team for maximum impact.
1. Resource Allocation:
A well-aligned sales forecast allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively. For example, suppose the estimates indicate that specific markets or customer segments will experience significant growth. In that case, management can allocate additional resources, such as hiring more sales personnel, increasing marketing budgets, or investing in localized campaigns. Conversely, if the forecast shows a downturn in a particular region or product line, resources can be reallocated to more promising areas, minimizing risk and optimizing performance. This approach ensures that the organization consistently focuses on the most lucrative opportunities and that resources are not wasted on low-priority initiatives.
2. Pricing Adjustments:
Sales forecasts also provide critical insights into pricing strategy. For example, if the forecast predicts strong demand for a product or service, the company may increase prices to maximize profit margins. On the other hand, if the forecast suggests a potential downturn or increased competition, the business may need to adjust pricing to remain competitive. By incorporating pricing scenarios into the forecasting model, companies can better understand the impact of different pricing strategies on overall revenue and profitability. This approach allows organizations to make proactive adjustments rather than react to market conditions afterward.
3. Sales Team Positioning:
Forecasts can help sales leaders decide to position their teams for success. For instance, if the forecast indicates that a particular region or customer segment will experience strong growth, management may focus additional sales efforts, reassigning existing team members or hiring new personnel. Similarly, if the forecast identifies a specific product line or service offering expected to outperform others, the sales team can be trained and incentivized to prioritize that offering. This strategic positioning ensures that sales teams are aligned with the company’s revenue goals and are focused on the most impactful opportunities.
One of the most powerful benefits of aligning sales forecasting with the overall sales strategy is the creation of a feedback loop between the two. As sales forecasts provide insights into the likelihood of achieving specific sales goals, they also offer valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the current sales strategy.
For example, suppose a forecast shows that the sales team is consistently missing targets in certain pipeline stages or within specific market segments. In that case, this information can signal a need to reevaluate the sales approach. Perhaps the sales strategy must be adjusted to align with market conditions, customer preferences, or product positioning. Using the forecasting model as a real-time feedback tool, businesses can continually refine their sales strategy to ensure long-term success.
Additionally, this feedback loop helps organizations remain agile and responsive to changes in the business environment. If external factors such as economic shifts, new competitors, or changes in customer behavior impact the forecast, companies can quickly adjust their strategy to address these challenges. This proactive approach allows for better risk management and enables businesses to stay on track toward achieving their broader goals.
Aligning sales forecasting with the overall sales strategy is essential for driving long-term growth and ensuring sales teams work toward the company’s broader objectives. Organizations can make informed decisions about resource allocation, pricing, and sales team positioning by integrating forecasting into the strategic framework. This alignment improves forecast accuracy and enables businesses to be more agile and responsive to market dynamics. Ultimately, a forecasting model that supports broader sales goals positions the organization for sustained success in a competitive landscape.
Sales forecasting is essential to any organization’s success, providing the necessary visibility into future revenue and guiding strategic decision-making. However, many sales teams face challenges in creating and managing effective forecasting models, often leading to inconsistent results and missed targets. To overcome these issues, establishing a structured, standardized forecasting process is critical to ensure consistency across the sales team. Organizations can enhance forecast accuracy, improve collaboration, and foster accountability by defining clear stages within the sales pipeline and using specific, measurable criteria for each stage.
Additionally, leveraging data and AI-driven analytics to refine forecasting models reduces uncertainty and enhances decision-making. Aligning sales forecasts with broader sales strategies, such as market expansion, customer acquisition, and product launches, enables businesses to allocate resources more effectively and respond proactively to changing market dynamics. A well-aligned forecasting model helps teams meet revenue targets and supports long-term growth and sustainability by creating a more predictable, scalable, and agile sales process. Ultimately, a robust forecasting model becomes a strategic asset, ensuring organizations can confidently navigate complex business environments.

Case Study: Cisco – Transforming Sales Forecasting with AI and Data-Driven Models
Background: Cisco Systems, a global leader in networking and telecommunications technology, faced significant challenges in accurately forecasting sales due to the complexity and size of its operations. Cisco serves diverse industries and has a broad portfolio of products and services. As the company expanded its offerings, managing and predicting sales across multiple regions, industries, and product lines became increasingly difficult. Despite its vast customer base and global reach, Cisco struggled with forecasting accuracy, missed revenue targets, and inefficient resource allocation.
In addition to these challenges, Cisco’s sales teams had different interpretations of how deals should progress through the pipeline. This led to a lack of consistency in forecasting across the company, making it difficult for leadership to have a clear and accurate view of future revenue. With the growing complexity of their business, Cisco recognized the need for a more structured, uniform sales forecasting model that could improve accuracy, accountability, and decision-making.
The Problem: Cisco’s existing forecasting model relied heavily on manual data entry and subjective inputs from sales teams. Sales representatives across different regions and divisions had varied definitions of deal stages, which caused inconsistency in forecasting. This lack of standardization resulted in over-optimistic forecasts, where deals were moved too quickly through the pipeline without meeting key benchmarks, and under-estimated forecasts, where deals with high potential were neglected.
Leadership faced challenges in determining which deals were likely to close and when. The lack of a unified forecasting system led to inconsistent revenue predictions, making it difficult for the company to plan effectively, allocate resources, and respond to market dynamics. Cisco needed to overhaul its sales forecasting process to create a standardized, data-driven model that could scale with the organization and its global sales operations.
The Solution: Cisco turned to artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to transform its sales forecasting process. By leveraging advanced data analytics tools and AI-driven forecasting models, Cisco was able to overhaul its forecasting approach. The key components of this transformation included:
Standardizing Sales Pipeline Stages: Cisco redefined its sales pipeline stages to create a uniform system that could be applied across all regions and product lines. Each stage was clearly defined with measurable criteria that a deal had to meet before progressing. This eliminated ambiguity and ensured all sales teams followed the same process when categorizing and advancing deals.
For example, before deals could be moved to the next phase, such as budget approval, decision-maker engagement, and a clear understanding of customer needs, Cisco implemented specific requirements for each stage. This created a universal language that improved communication and collaboration across global sales teams.
AI-Driven Forecasting Models: Cisco introduced AI-powered predictive models to enhance the accuracy of its sales forecasts. The AI tools analyzed vast historical data, including deal attributes, past sales performance, customer interactions, and external market conditions. By identifying patterns in this data, the AI system could predict the likelihood of deal closures and assign probabilities to each deal in the pipeline.
AI also helped Cisco to forecast timelines more accurately by analyzing the typical length of sales cycles for different products and regions. This allowed the company to predict when deals would close, enabling better resource allocation and financial planning.
Data-Driven Insights and Real-Time Adjustments: Cisco integrated real-time data analytics into its forecasting process. Sales teams had access to dashboards that displayed the pipeline’s health, key performance indicators (KPIs), and potential risks. AI-driven insights helped sales leaders identify deals that were stalling or at risk and allowed them to take corrective action early in the sales process.
Real-time adjustments to the forecast became possible as AI continually updated predictions based on new data, such as changes in customer behavior, economic conditions, or internal sales activities. This dynamic approach to forecasting allowed Cisco to stay agile and responsive to market changes.
Alignment with Strategic Goals: Cisco’s new forecasting model was aligned with its broader strategic goals, such as expanding its cloud-based services and entering new markets. The AI-powered forecasts provided insights into how these strategic initiatives would impact future revenue, allowing leadership to make more informed decisions on where to focus resources.
Cisco used the forecasting data to prioritize high-growth areas and allocate sales resources to the most promising opportunities. For example, during a major cloud services expansion, the company used its AI tools to forecast potential demand across different industries, ensuring that its sales teams aligned with its overall growth strategy.
The Results: Cisco’s transformation of its sales forecasting process delivered several key benefits:
Increased Forecast Accuracy: Cisco significantly improved forecast accuracy, reducing forecast variances by over 25%. AI-driven insights enabled sales teams to predict deal closures more accurately and adjust forecasts in real-time based on new data.
Improved Sales Team Accountability: With a standardized pipeline and clear criteria for deal progression, sales reps were held accountable for ensuring that deals met specific benchmarks before moving to the next stage. This reduced over-optimistic forecasts and increased the overall quality of deals in the pipeline.
Better Resource Allocation: Cisco was able to allocate resources more effectively by focusing on high-probability deals and areas with the highest growth potential. This resulted in higher win rates and improved conversion rates across its global sales operations.
Scalability and Flexibility: The AI-powered forecasting model was scalable and adaptable to new markets and product launches. Cisco could adjust its forecasts dynamically, allowing the company to remain competitive and agile in a rapidly changing market.
Strategic Alignment: By aligning sales forecasting with broader company goals, Cisco ensured that its sales teams worked toward its strategic objectives. This allowed Cisco to make more informed decisions on product development, market expansion, and customer acquisition strategies.
Conclusion: Cisco’s adoption of AI-driven sales forecasting transformed its ability to predict revenue, allocate resources efficiently, and align sales efforts with broader company goals. By standardizing pipeline stages, leveraging AI and data analytics, and integrating real-time forecasting adjustments, Cisco improved forecast accuracy, increased accountability across sales teams, and supported its long-term growth objectives. This case study demonstrates the value of using data and AI to create a scalable, accurate, and strategic sales forecasting model.

Exercise: Building a Unified Sales Forecasting Model
• Flipcharts or whiteboards
• Markers
• Sticky notes or index cards
• Access to past sales data (optional)
• Qualification Stage: The customer has the budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT criteria).
• Proposal Stage: A formal proposal has been submitted, and pricing discussions are underway.
• How would this forecasting model help identify potential risks in the sales pipeline?
• What key metrics or data (e.g., historical performance, current market trends) would help improve forecast accuracy?
• How can this forecasting model inform strategic decisions such as resource allocation or pricing adjustments?

Course Manual 6: Hiring/Onboarding
Emphasizing the importance of a smooth hiring process and a comprehensive onboarding experience is crucial. These steps set the tone for a new salesperson’s success and long-term engagement. A poor experience in either step can undermine everything a new hire tries to accomplish. Most employees, especially in sales, have experienced both the highs of an effective process and the frustrations of a poorly managed one. These experiences shape their perception of the company and their ability to contribute effectively from day one.
The process begins with identifying what makes a great salesperson in your organization and industry. Sales is a profession that attracts diverse personality types, but success is usually built on critical attributes. By examining your best-performing salespeople, you can quantify the skills, behaviors, and mindsets that drive their success. This exercise helps create an ideal candidate profile that includes both “must-have” qualities (e.g., strong communication skills, resilience, problem-solving) and “nice-to-haves” (e.g., industry-specific knowledge or particular sales experience). By focusing recruitment efforts on these criteria, you ensure the right people are in the right roles, increasing the likelihood of hiring individuals who can thrive in your specific environment.
Onboarding is just as important. Even the most talented sales professionals will struggle to succeed if they lack the resources and knowledge to navigate internal systems, understand company goals, or feel supported in their new role. A poor onboarding experience can have a significant impact on a new salesperson’s success, potentially leading to wasted time, miscommunication, and missed opportunities. For example, suppose a new salesperson is expected to update forecasts, submit reports, or deliver presentations without being adequately trained or given access to the right tools. In that case, they may fail to meet expectations through no fault of their own. Often, when they receive the critical information they need, valuable time has been lost, and frustration has set in.
Ensuring seamless hiring and onboarding is crucial not only for individual success but also for the long-term health of the sales team and the broader organization. With the right people in the right roles and a robust support system from the outset, businesses are better positioned to achieve their sales targets and grow.
Building the Ideal Salesperson Profile
Defining the ideal salesperson profile is a strategic process that sets the foundation for effective hiring in any organization. Sales is a complex and dynamic field, requiring individuals who possess specific skills, the right mindset, and cultural fit to thrive in a particular business environment. Building this profile is critical to recruiting and retaining high-performing salespeople who can drive the organization toward its growth objectives. This understanding empowers you, as a professional, to confidently navigate the hiring process.

Creating the ideal salesperson profile begins with a deep analysis of the characteristics that make current top performers successful. This involves evaluating both tangible and intangible qualities that contribute to their achievements. Tangible qualities might include specific skills, industry knowledge, and measurable outcomes like sales quotas met or exceeded. Intangible qualities often involve traits like resilience, adaptability, and emotional intelligence, which play a significant role in navigating the complexities of sales.
Steps to Building the Ideal Salesperson Profile
1. Analyze Top Performers:
Start by examining the current sales team, specifically the top performers who consistently meet or exceed their targets. This involves looking beyond just numbers and diving into the behaviors, habits, and personal characteristics that set them apart. Questions to consider include:
• What specific actions do they take in their sales process that lead to success?
• How do they handle customer objections or rejections?
• What personality traits enable them to build strong relationships with clients?
• How well do they collaborate with other departments (e.g., marketing, customer service) within the organization?
By answering these questions, companies can identify common traits among successful salespeople.
2. Identify Key Skills and Attributes:
Once top performers are analyzed, the next step is identifying the core skills and attributes that define them. These may include:
• Communication Skills: The ability to convey complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
• Problem-Solving Abilities: Strong salespeople are often natural problem-solvers who can quickly assess a client’s pain points and provide tailored solutions.
• Resilience: Sales can be a field full of rejection, and resilience is critical to bouncing back from setbacks without losing motivation.
• Emotional Intelligence: High emotional intelligence allows salespeople to connect with clients on a deeper level, understand their needs and concerns, and adjust their approach accordingly.
• Adaptability: With shifting markets, product updates, and evolving client expectations, sales professionals must be flexible and able to pivot strategies quickly.
Identifying these must-have skills helps form the foundation of the ideal salesperson profile.
3. Consider Cultural Fit:
Cultural fit is just as important as skills and experience. A salesperson might be highly skilled, but their potential may not be fully realized if they do not align with the organization’s values or working style. To assess cultural fit, companies should:
• Evaluate how well the salesperson collaborates with team members.
• Consider their attitude toward feedback and continuous learning.
• Determine whether their personal goals align with the company’s long-term vision.
Salespeople who align with the company culture are more likely to integrate well into the team and contribute to a positive work environment.
4. Create a Hiring Blueprint:
With a clear understanding of the traits, skills, and cultural attributes that define a successful salesperson in the organization, a hiring blueprint can be developed. This blueprint serves as a guide for recruitment efforts and should outline the “must-haves” and “nice-to-haves” in a candidate. The blueprint typically includes:
• Core competencies (e.g., communication, negotiation, closing skills).
• Behavioral traits (e.g., resilience, initiative, emotional intelligence).
• Specific experience or industry knowledge, where applicable.
• Indicators of cultural alignment (e.g., teamwork, adaptability).
By formalizing these criteria, hiring managers can more easily assess potential candidates, ensuring they meet the skill requirements and have the right mindset and personality for the role.
5. Leverage Data and Technology:
In modern sales hiring, companies can leverage AI and data analytics tools to identify patterns among top performers. These tools can analyze vast amounts of data, including sales metrics, CRM activity, and customer feedback, to highlight what top performers do differently. Based on historical data, predictive analytics can help anticipate which candidates are most likely to succeed. This modern approach to hiring provides reassurance and confidence in your recruitment decisions.
A well-defined salesperson profile improves the hiring process by creating clarity and focus. It helps:
• Reduce turnover: Organizations can reduce turnover, which is often high in sales positions, by hiring candidates who align with both the role and the company culture.
• Increase productivity: When the right individuals are hired, they are more likely to ramp up quickly and contribute effectively, leading to increased productivity.
• Strengthen team dynamics: Hiring salespeople who fit well within the team and company culture enhances collaboration and morale, which is critical for long-term success.
Building the ideal salesperson profile involves more than just identifying good salespeople—it involves finding those who will excel within your unique organizational context. By focusing on the right mix of skills, traits, and cultural fit, businesses can create a blueprint that leads to more effective hiring and stronger sales performance.
Streamlining the Hiring Process
A streamlined hiring process is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent, especially in competitive fields like sales. When candidates have a positive experience from initial contact to a job offer, they are more likely to accept and feel motivated to join the organization. Additionally, a smooth and efficient hiring process reflects well on the company’s brand and culture, signaling candidates that the organization values their time and effort. Here’s how companies can streamline their hiring process to create a more efficient, transparent, and positive candidate experience.
1. Define Clear Job Descriptions:
A well-defined job description is the foundation of a successful hiring process. It should clearly outline the role’s responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications. By providing potential candidates with a detailed understanding of the position, you set clear expectations from the outset. This not only attracts suitable candidates but also minimizes the time spent reviewing unqualified applications. Moreover, incorporating company culture and values elements into the job description can help attract candidates who align with the organization’s ethos.
2. Utilize Technology and Automation:
Leveraging technology can significantly enhance the efficiency of the hiring process. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) can help manage resumes, track candidates through different stages of the recruitment process, and automate communication, such as interview scheduling and follow-up messages. Moreover, online assessment tools can evaluate candidates’ skills early, ensuring that only qualified individuals advance to interviews. Video interview platforms can also expedite initial interviews, allowing hiring managers to assess candidates’ communication skills and cultural fit without needing in-person meetings.
3. Establish a Structured Interview Process:
A structured interview process enhances the consistency and fairness of hiring decisions. Interviewers can evaluate candidates based on the same criteria by using a standardized set of questions that align with the ideal salesperson profile. This reduces bias and ensures that all candidates are assessed fairly. Additionally, incorporating a panel interview format can provide diverse perspectives on the candidates, making the evaluation process more comprehensive.
4. Improve Communication and Feedback:
Clear and timely communication is vital throughout the hiring process. Companies should keep candidates informed about their application status and next steps. Regular updates can be automated through an ATS, but personalized communication can also be employed when significant decisions are made (e.g., moving a candidate to the next stage). Regardless of the outcome, providing constructive feedback to candidates fosters goodwill and can enhance the employer’s reputation. Candidates who feel respected and informed are more likely to view the hiring process positively, even if they are not ultimately selected.
5. Reduce Friction Points:
Identifying and minimizing friction points in the hiring process is essential for creating a seamless experience. Common friction points include overly lengthy application forms, multiple rounds of interviews without a clear purpose, and delayed decision-making. Companies can streamline application processes by limiting the required fields and allowing candidates to upload their resumes directly. Additionally, setting clear timelines for each stage of the interview process and adhering to them can help avoid delays and uncertainties that may frustrate candidates.
6. Involve Team Members Early:
Involving relevant team members early in the hiring process can help align expectations and foster a sense of ownership in the recruitment effort. Collaborating with team members in crafting job descriptions, assessing candidates, and participating in interviews ensures that the selected candidates possess the right skills and fit well within the team dynamics. This collective approach can also enhance the candidate experience, as candidates may appreciate the involvement of future colleagues in the decision-making process.
7. Create a Positive Candidate Experience:
From the first interaction to the final offer, it is important to ensure that candidates have a positive experience. This includes respecting their interview time, providing a welcoming environment, and demonstrating genuine interest in their backgrounds and aspirations. Small gestures, such as sending a thank-you note after interviews or providing candidates with insights about the company culture and team dynamics, can leave a lasting impression and make candidates feel valued.
8. Gather Candidate Feedback:
After the hiring process concludes, gathering feedback from candidates—whether they were hired or not—can provide valuable insights into the candidate experience. Surveys can be used to assess candidates’ impressions of the recruitment process, what worked well, and what could be improved. This feedback can inform future hiring strategies, allowing the organization to refine its processes and address identified weaknesses continually.
By streamlining the hiring process, organizations can ensure they attract top talent and create a positive experience for candidates. This approach increases the likelihood of hiring the right individuals and fosters a strong employer brand that can set a company apart in the competitive job market. A well-structured and efficient hiring process ultimately leads to more effective recruitment outcomes and a more engaged and motivated sales team.
Effective Sales Onboarding
A robust onboarding program is critical to setting new sales hires up for success. Effective onboarding goes beyond mere orientation; it is a comprehensive training process that equips new employees with the knowledge, skills, and resources necessary to excel. The goal is to help new sales hires feel confident and competent as they start their journey, ensuring they can contribute meaningfully to the organization from the outset. Here are the essential elements of an effective sales onboarding program.
1. Structured Training Programs:
A well-structured training program is the backbone of effective onboarding. This should include a combination of formal training sessions, workshops, and self-paced learning modules that cover key areas such as:
Company Orientation: New hires should be introduced to the company’s mission, vision, values, and culture. Understanding the organizational context helps them align their personal goals with the company’s.
Sales Process Training: New employees must be well-versed in the company’s sales process, including lead generation, qualification, pitching, handling objections, and closing deals. This training should incorporate real-life scenarios and role-playing to help them practice and internalize the process.
Product Knowledge: Comprehensive knowledge of the company’s products or services is essential for effective selling. Training should cover product features, benefits, and differentiators, as well as how they meet target customers’ needs. Providing access to product demos and documentation can enhance understanding.
2. Familiarization with Internal Tools and Systems:
Sales representatives rely on various tools and systems to manage their work effectively. As part of the onboarding process, new hires should receive training on:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Familiarity with the CRM is vital for tracking interactions, managing leads, and analyzing sales performance. New hires should learn to navigate the system, input data, and utilize its features to enhance workflow.
Sales Enablement Tools: Tools that assist in lead generation, marketing automation, and analytics are essential. Training should cover using these tools effectively to streamline sales efforts and improve productivity.
Reporting and Forecasting Tools: Understanding how to generate reports and forecasts is crucial for evaluating performance and predicting future sales. New hires should learn how to interpret data to inform their strategies.
3. Mentorship and Support:
Mentorship plays a vital role in the onboarding process. Pairing new hires with experienced sales team members can give them the guidance and support they need to navigate their new roles. Key components include:
Buddy System: Assigning a mentor or buddy can help new hires acclimate to the company culture and expectations. This relationship offers a safe space for asking questions, seeking advice, and learning from real-world experiences.
Regular Check-Ins: Scheduled check-ins with managers and mentors allow for ongoing support and feedback. These meetings provide an opportunity to discuss challenges, celebrate achievements, and set short-term goals.
4. Alignment with Company Goals and Expectations:
Effective onboarding ensures new hires understand how their roles contribute to the broader company objectives. This alignment is crucial for motivation and performance. Key strategies include:
Goal Setting: In the early days of onboarding, managers should work with new hires to establish clear, measurable goals aligned with team and company objectives. These goals should be realistic and achievable, providing a roadmap for success.
Understanding KPIs: New sales hires should be aware of the key performance indicators (KPIs) used to evaluate their success. Understanding what metrics they are being measured against helps set clear expectations and encourages accountability.
5. Creating a Collaborative Environment:
Onboarding should foster community and collaboration among new hires and existing team members. This can be achieved by:
Team Integration Activities: Hosting social events or team-building exercises helps new hires feel welcomed and integrated into the team. Building relationships with colleagues can enhance collaboration and create a supportive work environment.
Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Introducing new hires to other departments, such as marketing, product development, and customer service, allows them to understand how their roles intersect with others. This holistic view of the organization can foster collaboration and improve overall performance.
6. Ongoing Training and Development:
Onboarding should not be viewed as a one-time event but as the beginning of a continuous learning journey. Effective sales onboarding programs include:
Regular Training Updates: Providing ongoing training opportunities ensures that sales hires remain current with industry trends, new products, and changes in the sales process. This could include quarterly workshops, online courses, or access to industry conferences.
Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing mechanisms for new hires to provide feedback on their onboarding experience can inform improvements. Surveys and discussions can help identify gaps in training and support, leading to a more effective onboarding process.
Effective sales onboarding is a multifaceted process that lays the groundwork for new hires to thrive. Companies can ensure that new sales representatives hit the ground running by focusing on structured training, familiarization with tools, mentorship, alignment with company goals, and ongoing development. A comprehensive onboarding program improves individual performance and contributes to team cohesion and organizational success, ultimately driving sales growth and fostering a positive workplace culture.
Hiring and onboarding are pivotal to cultivating a successful sales force. A streamlined and efficient hiring process and a well-structured onboarding program can significantly enhance a new salesperson’s ability to contribute effectively and remain engaged in their role. When organizations invest the time and resources to identify key attributes of top performers and create an ideal candidate profile, they set the stage for successful recruitment. Furthermore, effective onboarding equips new hires with the necessary tools and knowledge and fosters a sense of belonging and alignment with the company’s goals.
Conversely, a poorly executed hiring or onboarding process can lead to frustration, wasted time, and missed opportunities, undermining the potential contributions of new salespeople as most sales employees can attest, their experiences—whether positive or negative—shape their perceptions of the company and influence their long-term engagement.
Ultimately, by prioritizing a seamless hiring experience and a comprehensive onboarding program, organizations position themselves to achieve their sales objectives and promote a thriving sales culture. Investing in these processes enhances individual performance and strengthens the entire sales team, driving overall organizational growth and success.

Case Study: Zocdoc’s Innovative Hiring and Onboarding Approach
Company Overview: Zocdoc is a health technology company that connects patients with healthcare providers through an online platform. Founded in 2007, Zocdoc’s mission is to improve healthcare access and streamline the patient experience. As the company expanded its services and scaled its operations, it recognized the importance of an effective hiring and onboarding process, especially within its sales department.
Challenges: Zocdoc faced challenges maintaining its customer-centric culture while rapidly growing its sales team. With increasing competition in the healthcare technology sector, Zocdoc needed to hire talented sales representatives quickly without compromising quality. The company understood that an efficient hiring process, followed by a thorough onboarding experience, was critical to the success of new hires and their long-term engagement with the company.
Identifying Ideal Salesperson Qualities: Zocdoc analyzed its top-performing sales representatives to create a strong sales team and determine the attributes that contributed to their success. The evaluation highlighted several key traits, including:
Empathy: Successful salespeople at Zocdoc demonstrated a deep understanding of patient and provider needs, allowing them to build strong relationships and effectively address concerns.
Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to think critically and provide tailored solutions was essential for navigating the complexities of healthcare sales.
Strong Communication Skills: Effective communication was crucial for conveying product value and understanding customer feedback.
Cultural Fit: Zocdoc emphasized the importance of aligning with its core values, which focus on integrity, teamwork, and a commitment to improving healthcare.
By analyzing these traits, Zocdoc developed an ideal candidate profile that guided its hiring process.
Streamlining the Hiring Process: To enhance its hiring process, Zocdoc implemented several strategic initiatives:
Clear and Engaging Job Descriptions: Zocdoc crafted job descriptions that outlined the skills and experiences required and highlighted the company culture and mission. This approach helped attract candidates who resonated with Zocdoc’s values.
Innovative Assessment Techniques: Zocdoc incorporated unique assessment methods, such as simulation exercises and real-world scenarios, to evaluate candidates’ skills in action. This allowed hiring managers to gauge how candidates would handle actual sales situations.
Team-Based Interview Panels: The company established diverse interview panels comprising current sales team members and cross-functional colleagues. This collaboration ensured that candidates were evaluated from multiple perspectives, fostering inclusivity in the hiring process.
Leveraging Data and Analytics: Zocdoc used data analytics to track hiring metrics, such as time to hire and candidate quality, allowing them to identify areas for improvement in their recruitment strategies.
Effective Onboarding Program: Zocdoc recognized that effective onboarding was crucial for new sales hires to succeed in a fast-paced environment. The company developed a comprehensive onboarding program that included:
Structured Orientation: New hires participated in an orientation program introducing them to Zocdoc’s mission, values, and product offerings. This foundational training helped align new employees with the company’s goals.
Mentorship Pairing: Each new salesperson was paired with an experienced mentor who provided guidance, support, and insights into the sales process. This mentorship relationship helped new hires navigate challenges and build confidence.
Hands-On Training: Zocdoc implemented a hands-on training approach, allowing new hires to engage in role-playing exercises and real customer interactions early in their onboarding process. This practical experience facilitated quicker adaptation to their roles.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Zocdoc established regular check-ins between new hires and their managers to discuss progress, address challenges, and set goals. This ongoing feedback loop encouraged continuous development and alignment with performance expectations.
Results: Zocdoc’s strategic approach to hiring and onboarding yielded several positive outcomes:
Increased Employee Satisfaction: New sales hires reported high job satisfaction and engagement levels, attributing their positive experiences to the structured onboarding process and mentor support.
Reduced Turnover Rates: Zocdoc experienced lower turnover rates among new sales hires compared to previous years by focusing on cultural fit and providing adequate support during onboarding.
Enhanced Sales Performance: The combination of targeted hiring and comprehensive onboarding contributed to improved sales metrics, with new hires achieving their sales targets more quickly and effectively.
Conclusion: Zocdoc’s case highlights the critical importance of effective hiring and onboarding processes in shaping a successful sales force. By identifying the ideal salesperson profile, streamlining the hiring process, and implementing a robust onboarding program, Zocdoc has positioned itself for sustained growth and success in the competitive healthcare technology market. This holistic approach enhances individual performance and strengthens the organization as a whole, driving overall business outcomes and reinforcing Zocdoc’s commitment to improving healthcare access and experiences.

Exercise: Reflecting on Hiring and Onboarding Processes
• Think back to when you were hired for a sales position.
• Consider the hiring and onboarding processes you experienced. Was it efficient and positive, or was it disorganized and frustrating?
• What aspects of the hiring process stood out to you (positive or negative)?
• How did onboarding impact your initial performance and engagement in your new role?
• Were any specific resources, training, or support you felt were lacking during your onboarding?
• Based on your experiences, list the key qualities that you believe are essential for a successful salesperson.
• Consider personal attributes (e.g., resilience, communication skills) and professional skills (e.g., product knowledge, problem-solving abilities).
• For each quality, briefly explain why you think it is essential in the sales context.
• Must-Have Qualities: These are critical attributes that a candidate must possess to succeed.
• Nice-to-Have Qualities: Additional traits can enhance a candidate’s effectiveness but are not strictly required.
• The current issue(s) with the onboarding process.
• Suggested improvements and how they would benefit new sales hires and the organization.
• Any potential challenges in implementing these changes and how they might be addressed.
• Conclude by summarizing your insights on the importance of hiring and onboarding in shaping a successful sales force.
• Consider how your experiences and suggestions could apply to an organization’s future hiring and onboarding processes.

Course Manual 7: Daily Routines
In B2B sales, success hinges not only on strategy and execution but also on a bedrock of trust between sales leaders and their teams. This trust is multifaceted; it encompasses confidence in the resources provided, the fairness and effectiveness of compensation models, and the daily dedication of salespeople to meet and exceed their goals. When salespeople trust that they will be adequately supported and rewarded for their efforts, they are empowered to execute their responsibilities with purpose and passion. This empowerment, fostered by trust and collaboration, is at the heart of this dynamic relationship, understanding that success is often built on seemingly minor daily actions that yield significant results when compounded over time.
A critical component of fostering this trust is aligning on the essential daily activities that contribute to sustainable success. Both sales leaders and individual contributors must agree on what actions are necessary to thrive in a competitive landscape. This collaboration is crucial, as it ensures that salespeople are aware of their responsibilities and motivated to take ownership of their results. There are three vital daily activities that every B2B salesperson should engage in: prospecting, nurturing, and closing. These activities, when performed with dedication and commitment, are pivotal in building a robust sales pipeline and achieving long-term growth.
Prospecting: Taking Ownership of the Pipeline
Prospecting is often mistakenly viewed as a task suited primarily for junior sales roles or solely the marketing team’s responsibility. This perception significantly undervalues the importance of prospecting as a fundamental pillar of the sales process. In reality, every salesperson—regardless of their level—must embrace prospecting as a core responsibility that is integral to their success and the overall health of the sales pipeline. By doing so, they empower themselves to generate leads and create new opportunities, which are crucial for sustaining growth and achieving targets.
Prospecting is about more than just identifying potential clients; it’s about laying the groundwork for meaningful relationships and long-term partnerships. In the B2B landscape, where competition is fierce, and customer loyalty can be elusive, proactive prospecting enables sales professionals to engage with potential clients before entering the sales funnel. This proactive approach positions salespeople as valuable resources rather than just sellers, creating a favorable environment for initial conversations.
A key aspect of effective prospecting involves researching and identifying Ideal Customer Profiles (ICPs). An ICP is a detailed description of the type of customer who would benefit the most from your product or service. Sales professionals should take the time each day to understand their ICP deeply, analyzing key attributes such as industry, company size, pain points, and decision-making processes. This knowledge equips salespeople with the insights necessary to tailor their outreach efforts, ensuring they resonate with the specific needs and challenges potential clients face.
By conducting thorough research, sales professionals can prioritize their outreach efforts based on the likelihood of a successful conversion. This targeted approach maximizes efficiency and demonstrates a commitment to understanding the prospect’s business, fostering a sense of trust right from the outset.
Once potential targets have been identified, the next step is to reach out to key decision-makers with personalized messaging. This is where many salespeople falter; they often rely on generic templates or one-size-fits-all communications that fail to engage prospects effectively. Instead, successful prospecting hinges on crafting messages that leverage unique insights and perspectives relevant to each prospect’s situation.
Personalized messaging can take various forms, such as referencing recent company achievements, addressing known challenges within the industry, or proposing solutions that align with the prospect’s goals. For instance, if a prospect’s industry is facing a specific challenge, a salesperson can craft a message that acknowledges this challenge and proposes a solution. By demonstrating a genuine understanding of the prospect’s needs and offering valuable insights, sales professionals can differentiate themselves from competitors, making it more likely that their outreach will resonate and elicit a positive response.
Building rapport is an essential component of successful prospecting. Effective outreach goes beyond simply delivering a sales pitch; it involves establishing a connection with the prospect that lays the foundation for a lasting relationship. This can be achieved by focusing on how the salesperson’s product or service can help the prospect achieve their objectives. By doing so, salespeople can foster trust and demonstrate their role as strategic partners rather than mere vendors.
This rapport-building process is essential, especially in B2B sales, where decision-making often involves multiple stakeholders and lengthy timelines. When prospects feel that a salesperson genuinely understands their challenges and is invested in their success, they are more likely to engage in further discussions and ultimately consider the proposed solutions.
By consistently dedicating time to prospecting daily, sales professionals can ensure a steady stream of potential clients entering the sales funnel. This proactive approach mitigates the risk of a dry pipeline and allows for better forecasting and resource allocation. When salespeople own the prospecting process, they take control of their success and contribute to the organization’s overall growth.
Prospecting should be viewed as a fundamental responsibility for every salesperson, transcending junior roles and marketing functions. By embracing this mindset, engaging in thorough research, crafting personalized messaging, and fostering rapport, sales professionals can take ownership of their pipelines. This proactive approach is essential for sustaining long-term success in the competitive B2B landscape, ensuring that salespeople continually add value and build relationships that lead to fruitful partnerships.
Nurturing: Building Long-Term Relationships
Once a prospect has been identified through the prospecting phase, the next crucial step is nurturing—an essential process that focuses on building and maintaining long-term relationships. This stage often demands significant patience and persistence, as establishing meaningful connections can require numerous interactions—sometimes exceeding eight touches—before a productive conversation occurs. This reality underscores the importance of strategic nurturing in the sales process.
Nurturing goes beyond maintaining contact with prospects; it involves actively engaging them through tailored communication that adds value to their experience. In the B2B landscape, where buyers often conduct extensive research and comparison before making decisions, nurturing becomes vital in differentiating a salesperson from competitors. This phase is not just about keeping prospects warm; it’s about reinforcing the relationship through consistent engagement, relevant insights, and personalized content that aligns with the prospect’s needs and interests.
Sales professionals must understand that multiple touchpoints are often necessary before a prospect is ready to engage in a conversation. This highlights the need for a well-planned outreach strategy incorporating various communication forms. These include emails, phone calls, social media interactions, webinars, and in-person meetings. Each touchpoint should be thoughtfully executed to ensure it adds value to the prospect’s journey.
For instance, a salesperson might follow up a cold email with a relevant article or case study that addresses a specific challenge faced by the prospect’s industry. This approach keeps the conversation flowing and demonstrates the salesperson’s commitment to providing insights that matter.
In the nurturing phase, salespeople must prioritize bringing insights that prospects are unlikely to receive from other sources. This is where adopting a Challenger-based approach becomes particularly compelling. Instead of simply responding to a prospect’s needs, a Challenger salesperson proactively shares new perspectives that can challenge the prospect’s current thinking and decision-making processes.
By doing so, sales professionals can position themselves as thought leaders and trusted advisors rather than mere sellers. This differentiation is crucial in building a lasting relationship, as prospects are more likely to engage with individuals who offer valuable insights and solutions tailored to their specific challenges. Providing unique content, such as white papers, industry reports, or expert analysis, can significantly enhance the nurturing process.
Effective communication is the backbone of nurturing. Salespeople must cultivate strong listening skills, enabling them to understand and empathize with the prospect’s needs, challenges, and goals. This active listening allows sales professionals to tailor their messaging and outreach strategies accordingly. When prospects feel heard and understood, they are more likely to trust the salesperson and engage in meaningful conversations.
Regular check-ins and updates also play a vital role in maintaining the relationship. Salespeople should schedule follow-ups focusing not solely on selling but on understanding how the prospect’s situation has evolved. This ongoing dialogue helps reinforce the connection and keeps the salesperson top-of-mind when the prospect is ready to decide.
Through consistent nurturing, salespeople can effectively reinforce their role as trusted advisors. This is achieved by demonstrating reliability, delivering on promises, and consistently providing value. When prospects view a salesperson as a partner invested in their success, they are more likely to consider their solutions when making a purchasing decision.
Moreover, this nurturing process can lead to referrals and recommendations, as satisfied prospects are often willing to share their positive experiences with colleagues or industry peers. Building a reputation as a reliable and insightful resource can significantly enhance a salesperson’s credibility and visibility in their market.
Nurturing is a critical phase in the sales process that involves building long-term relationships through persistent and thoughtful engagement. Salespeople can foster deeper connections with prospects by recognizing the importance of multiple touchpoints, providing unique insights, and maintaining effective communication. This ongoing nurturing keeps conversations alive and solidifies the salesperson’s position as a trusted advisor, ultimately leading to stronger relationships and higher conversion rates. In the competitive landscape of B2B sales, nurturing effectively can be the differentiating factor that drives sustainable success and growth.
Closing: Collaborative Execution
Closing deals is often perceived as the final and most critical step in the sales process. Still, it is essential to recognize that successful closures are not solely the salesperson’s responsibility. Rather, closing is a collaborative effort that requires active participation from individual contributors and sales leaders. This collaboration is pivotal, as it helps create a cohesive sales strategy that aligns with the prospect’s unique needs while harnessing the sales team’s collective strengths.
A foundation of trust and open communication is at the heart of a successful closing process. Trust between the sales leader and the individual contributor is vital, as it enables salespeople to feel empowered and supported in their efforts. When salespeople trust that their leaders will provide the necessary guidance, resources, and encouragement, they can confidently approach the closing phase.
Effective communication is equally essential. Sales leaders should be accessible and approachable, fostering an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their insights, challenges, and successes. Regular check-ins and strategy discussions can enhance this communication, allowing for real-time feedback and adjustments to the sales approach. By maintaining a continuous dialogue, both parties can align on the best strategies to employ during the closing phase.
A collaborative approach to closing involves jointly developing and executing a comprehensive sales plan. This plan should outline the key objectives, strategies, and tactics during the closing process. Sales leaders can leverage their experience and insights to help individual contributors identify potential roadblocks and devise strategies to overcome them.
Involving the sales team in the planning process also fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. When salespeople contribute to developing the sales plan, they are more likely to invest in its success and be motivated to execute it effectively. Additionally, this collaborative approach allows for the pooling of diverse perspectives, ensuring that the sales strategy is well-rounded and adaptable to the prospect’s specific needs.
One critical advantage of a collaborative closing process is the ability to align the sales approach with the prospect’s needs. By working together, sales leaders and individual contributors can analyze the prospect’s pain points, goals, and preferences to tailor their messaging and solutions accordingly. This alignment is crucial, as prospects are more likely to engage positively when they feel their needs are being understood and addressed.
Moreover, collaboration allows for a more strategic approach to handling objections and concerns the prospect raises. Sales leaders can share their insights on potential objections based on past experiences, while individual contributors can provide valuable context regarding the prospect’s current relationship. This collaborative problem-solving approach enables the sales team to respond effectively to objections, reinforcing the prospect’s trust in the salesperson and the organization.
When salespeople feel supported by their leaders during the closing process, they are more likely to engage confidently with prospects. This confidence is critical, as it influences how salespeople communicate and negotiate during closing discussions. A confident salesperson can effectively convey the solution’s value, address concerns, and inspire trust in the prospect.
Sales leaders can enhance this confidence by providing coaching, role-playing scenarios, and constructive feedback. This support helps salespeople refine their closing techniques and reinforces the notion that they are not alone in this critical phase of the sales process. The result is a more empowered sales force capable of successfully navigating complex negotiations and closing deals.
Closing deals is a collaborative endeavor that thrives on trust, communication, and shared responsibility. Organizations can optimize their closing efforts and drive successful outcomes by fostering a culture of collaboration between sales leaders and individual contributors. Through developing a well-defined sales plan, alignment with prospect needs, and ongoing support, sales teams can confidently navigate the closing process.
In the competitive world of B2B sales, success is built on more than just strategic planning and execution; it fundamentally relies on a bedrock of trust between sales leaders and their teams. This trust fosters an environment where salespeople feel supported, valued, and empowered to excel. By cultivating this trust, organizations can ensure that their sales teams are motivated to engage in the essential daily activities of prospecting, nurturing, and closing.
Prospecting allows sales professionals to take ownership of their pipelines, establishing meaningful relationships with potential clients from the outset. Nurturing extends these relationships, ensuring ongoing engagement and reinforcing the salesperson’s role as a trusted advisor. Closing, viewed as a collaborative effort, enables sales leaders and individual contributors to align their strategies with prospect needs, fostering a cohesive approach that enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Ultimately, when organizations prioritize trust and collaboration within their sales processes, they create a culture where the collective efforts of their teams can flourish. This drives immediate results and lays the groundwork for sustainable growth and long-term success in the ever-evolving landscape of B2B sales.

Case Study: Salesforce’s Approach to Building Trust and Collaboration in B2B Sales
Background
Salesforce, a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform, has achieved significant success in the B2B sales landscape by fostering a culture of trust and collaboration between sales leaders and their teams. With its comprehensive suite of cloud-based solutions, Salesforce effectively helps organizations manage customer relationships, sales processes, and marketing strategies. The company recognizes that its sales success is not solely based on effective strategy or execution; it hinges on building strong relationships with its sales teams and clients.
Building Trust
At Salesforce, trust is considered a cornerstone of its organizational culture. The company emphasizes transparency, accountability, and open communication, creating an environment where sales professionals feel valued and empowered. This trust is nurtured through several key initiatives:
• Resource Allocation: Salesforce invests heavily in resources to support its sales teams, including training programs, advanced analytics, and AI-driven tools. This investment allows salespeople to access the latest technology and insights, enabling them to perform their roles more effectively.
• Fair Compensation Models: The company has established compensation models that reward individual performance and team collaboration. This approach encourages sales professionals to work together rather than compete against each other, reinforcing the idea that success is a shared goal.
• Ongoing Support and Mentorship: Salesforce promotes a culture of mentorship, where experienced sales leaders provide guidance and support to less experienced team members. This helps newer employees develop their skills and fosters a sense of community and collaboration.
Daily Activities: Prospecting, Nurturing, and Closing
Salesforce understands that daily activities are vital for sustainable success. The company encourages its sales teams to focus on three core areas: prospecting, nurturing, and closing.
Prospecting: Salesforce emphasizes identifying Ideal Customer Profiles (ICPs). Sales professionals are trained to analyze various attributes, such as industry, company size, and pain points. This targeted approach enables them to effectively tailor their outreach efforts, ensuring they connect with the right prospects.
Example: Salesforce utilizes data analytics to help salespeople identify potential leads that fit their ICPs. By leveraging their platform, sales teams can analyze market trends and customer data to identify organizations that would benefit most from their solutions.
Nurturing: Salesforce prioritizes nurturing relationships with prospects by encouraging personalized and meaningful communication. The sales team engages with potential clients through various touchpoints, including tailored emails, webinars, and content sharing, to provide insights and value throughout the buyer’s journey.
Example: The company runs targeted email campaigns that provide prospects with educational content, such as case studies and industry reports, demonstrating how Salesforce solutions can address specific challenges. This approach helps to build rapport and trust over time.
Closing: Salesforce’s closing phase is characterized by collaboration between sales leaders and individual contributors. Sales professionals are encouraged to seek feedback from their leaders on sales strategies and participate in team discussions about best practices and objection handling.
Example: Salesforce employs a collaborative closing strategy, where sales teams gather to discuss ongoing deals, share insights, and collectively strategize on overcoming obstacles. This approach empowers individual contributors and ensures alignment with the prospect’s needs.
Results
Salesforce’s commitment to trust and collaboration has yielded impressive results:
• Increased Sales Performance: The company’s focus on building a supportive environment has led to higher sales performance and productivity among its teams.
• Enhanced Customer Relationships: Salesforce has seen increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting in a strong retention rate, by nurturing long-term relationships with clients.
• Sustainable Growth: Salesforce’s collaborative culture allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to market changes, ensuring the company remains a leader in B2B sales.
Conclusion
Salesforce’s case study illustrates how a strong foundation of trust and collaboration can significantly impact B2B sales success. By prioritizing resource allocation, fair compensation, and ongoing support, the company empowers its sales teams to effectively engage in prospecting, nurturing, and closing. This holistic approach drives immediate results and lays the groundwork for sustainable growth in a competitive landscape, demonstrating that success in B2B sales is built on trust and teamwork.

Exercise: Building Trust in B2B Sales
• Discuss what trust means in the context of B2B sales.
• What specific ways can trust be built between sales leaders and individual contributors?
• Share examples of how trust (or lack thereof) has affected sales performance in your experiences.
• Identify the three critical daily activities for B2B sales success: prospecting, nurturing, and closing.
• Why it is essential.
• Specific actions that can be taken to improve effectiveness in each area.
• How collaboration between sales leaders and team members can enhance these activities.
• A unique insight or takeaway from the discussion.
• A specific action plan for how they can implement these insights in their own sales processes.

Course Manual 8: Prospect Profile
In the ever-evolving landscape of B2B sales, the concept of prospecting at scale has undergone significant transformation. A decade ago, early adopters of mass outreach strategies enjoyed considerable success as they quickly leveraged technology to reach a broad audience. However, the initial wins are no longer easily replicable; the marketplace has matured, becoming increasingly wary of insincere outreach efforts. Today’s prospects are more informed and discerning, often viewing mass outreach campaigns as intrusive, especially when they do not comply with local legislation surrounding spam and privacy.
As businesses seek to expand their market reach, it is imperative to recognize that while technology facilitates reaching prospects at scale, it does not guarantee success. Missteps in adhering to local legislation can lead to wasted resources and potential legal troubles, undermining an organization’s credibility. Therefore, it becomes crucial for sales teams to shift from a broad, indiscriminate approach to a more thoughtful and strategic methodology.
One of the most effective ways to refine this approach is by analyzing past successes to develop an Ideal Client Profile (ICP). Regardless of age or experience, every organization has encountered customers whose attributes align with their product offerings. By evaluating these successful engagements, sales teams can identify patterns that define their best prospects. This introspection allows for creating a targeted profile that serves as a foundation for all new outreach efforts.
Instead of sending generic messages to hundreds or thousands of contacts, a refined prospecting strategy focuses on targeted outreach to specific decision-makers within ICP companies. This entails crafting messages that resonate with these prospects’ unique goals and challenges. Sales professionals can delve into annual reports and industry presentations to uncover insights that align with their value propositions, tailoring their communications accordingly. This personalized approach increases the likelihood of engagement and fosters a more genuine connection, ultimately leading to meaningful conversations that can convert prospects into clients.
Optimizing sales through effective prospect profiling requires a nuanced understanding of past successes and current market dynamics. As legislation continues to shape outreach practices, the emphasis must be on sincere, targeted communication rather than mass messaging. The result is a more focused, efficient, and effective sales strategy that enhances the organization’s overall success.
“Those who do not know history are doomed to repeat it.” Edmund Burke
The Evolution of Prospecting: From Mass Outreach to Targeted Engagement
The landscape of B2B prospecting has experienced significant shifts over the past decade, moving from a paradigm dominated by mass outreach tactics to one that prioritizes targeted engagement. Advancements in technology drive this evolution, empowering sales professionals with the tools to understand and meet the changing expectations of potential clients, and the necessity for more authentic communication in a saturated marketplace.
In the early days of digital marketing and sales, organizations embraced the concept of mass outreach with open arms. Sales teams relied heavily on cold calling, bulk emailing, and broad advertising campaigns. The rationale was straightforward: reaching as many potential clients as possible would naturally yield more leads. The technology at the time allowed businesses to automate these processes, making it easy to send out thousands of emails or make numerous calls with minimal effort.
However, this approach often led to low engagement rates and high unsubscribe or rejection rates. Prospective clients began to view such outreach as intrusive and impersonal, usually resulting in a negative perception of brands. As the market became increasingly saturated with messages vying for attention, the effectiveness of mass outreach dwindled, prompting a need for a more sophisticated approach.
The shift towards targeted engagement can be attributed to several key factors:
Advancements in Technology:
Modern technology has enabled businesses to gather and analyze vast data about their prospects. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, data analytics tools, and AI-driven insights allow sales teams to better understand potential clients’ behaviors, preferences, and pain points. This wealth of information empowers organizations to segment their audience based on specific criteria, leading to more personalized and relevant outreach strategies.
Changing Market Expectations:
Today’s buyers are more informed and empowered than in previous years. They conduct extensive research before engaging with a sales representative, making it crucial for businesses to provide value right from the first point of contact. Prospects expect tailored messages that speak directly to their needs and challenges rather than generic pitches. Understanding and meeting these market expectations is key to successful targeted engagement.
The Rise of Account-Based Marketing (ABM):
Account-based marketing has gained traction as a strategic approach that focuses on targeting specific accounts rather than a broad audience. ABM emphasizes building relationships with key stakeholders within target organizations, allowing sales teams to create customized marketing campaigns that resonate with each prospect’s unique context. This method increases engagement and enhances the likelihood of conversion, as it demonstrates a commitment to understanding and meeting the specific needs of potential clients.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations:
The introduction of privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, has heightened awareness of ethical marketing practices. Organizations must now navigate legal requirements while crafting their outreach strategies. This has led to a greater emphasis on consent-based marketing, where prospective clients are likelier to engage with brands that respect their privacy and communicate transparently.
The transition from mass outreach to targeted engagement offers numerous benefits for B2B sales teams:
Higher Engagement Rates: Personalized messaging that resonates with specific audiences leads to increased open rates, response rates, and, ultimately, more meaningful conversations.
Improved Conversion Rates: By focusing on ideal client profiles and addressing their pain points, sales teams can effectively guide prospects through the sales funnel, resulting in higher conversion rates.
Stronger Relationships: Targeted engagement fosters genuine connections between sales representatives and prospects. By clearly understanding the client’s business and challenges, sales teams can position themselves as trusted advisors rather than mere vendors.
Prospecting’s evolution from mass outreach to targeted engagement reflects a broader shift in how businesses approach sales in a digital age. Organizations can create more effective and meaningful outreach strategies by leveraging technology, understanding market expectations, and embracing ethical practices. This transformation enhances sales performance and builds long-term relationships with clients, setting the stage for sustained growth and success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Navigating Legal Considerations in Outreach Campaigns
In the digital communication age, businesses increasingly rely on outreach campaigns to connect with potential clients. However, as the marketing and sales landscape evolves, so too do the legal considerations that govern these practices. Understanding local legislation regarding outreach, including spam laws and privacy regulations, is not merely a compliance requirement; it is a critical factor that can protect organizations and enhance their reputations.
Spam Laws and Regulations:
Most countries have enacted laws to regulate unsolicited communications, commonly called spam laws. In the United States, the CAN-SPAM Act mandates that commercial emails must include an explicit opt-out mechanism and provide accurate information about the sender and subject matter. Similarly, the Australian Spam Act imposes strict guidelines for sending commercial electronic messages.
Non-compliance with these laws can result in significant penalties, fines, and legal action. For example, organizations violating the CAN-SPAM Act may face fines of up to $43,280 per violation, emphasizing the financial implications of failing to adhere to legal standards.
Privacy Regulations:
Privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S., have transformed how organizations collect, store, and utilize customer data. These laws grant individuals greater control over their personal information and impose strict requirements on businesses that handle such data.
Under the GDPR, businesses must obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their data for marketing purposes. Similarly, the CCPA requires organizations to inform consumers about the data collected and allows them to opt out of its sale. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines and reputational damage.
Compliance as a Protective Measure
Avoiding Legal Consequences:
Ensuring compliance with local laws can protect organizations from the risk of legal action. By adhering to established guidelines, businesses can avoid costly penalties and the potential for litigation stemming from non-compliance. Furthermore, maintaining legal compliance fosters a culture of accountability within the organization, reducing the likelihood of inadvertent violations.
Enhancing Reputation and Trust:
Compliance with spam laws and privacy regulations protects organizations legally and enhances their reputations. In an era where consumers are increasingly concerned about data privacy and security, demonstrating a commitment to ethical marketing practices can bolster brand trust. Prospects are more likely to engage with companies that respect their privacy and comply with legal standards, ultimately leading to stronger relationships and increased customer loyalty.
Building a Responsible Brand Image:
Organizations prioritizing compliance can position themselves as responsible and trustworthy industry entities. This proactive approach to outreach demonstrates a commitment to ethical practices, setting a positive example for competitors and contributing to a healthier marketplace overall. As consumers become more discerning, they are likely to favor brands that demonstrate a commitment to ethical behavior, further enhancing the importance of compliance.
Best Practices for Compliance in Outreach Campaigns
Educate Your Team:
Provide training and resources for your sales and marketing teams to ensure they understand the legal landscape surrounding outreach. This education should include an overview of relevant laws, non-compliance implications, and best practices for conducting outreach ethically.
Implement Consent Mechanisms:
Incorporate explicit opt-in mechanisms into your outreach strategies. This ensures that prospects have consented to receive communications, aligning with legal requirements and fostering a positive relationship with potential clients.
Maintain Transparency:
Communicate to prospects how their data will be used and who will access it. Transparency builds trust and ensures potential clients feel comfortable engaging with your organization.
Regularly Review and Update Practices:
Laws and regulations continually evolve, and organizations must stay informed about changes that may impact their outreach strategies. Regular audits of marketing practices can help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing compliance.
Navigating legal considerations in outreach campaigns is essential for organizations looking to succeed in today’s complex regulatory environment. By understanding and adhering to local legislation regarding spam laws and privacy regulations, businesses can protect themselves from legal repercussions while enhancing their reputations. As trust and transparency become increasingly vital in the eyes of consumers, compliance emerges as a strategic advantage, fostering long-term relationships and driving sustainable growth.
Building and Utilizing Your Ideal Client Profile (ICP)
Creating an Ideal Client Profile (ICP) is crucial for any organization seeking to optimize its sales and marketing efforts. An ICP is a detailed description of the perfect customer that a business aims to attract based on analyzing past successes and identifying key attributes that define ideal prospects. By focusing on these characteristics, organizations can tailor their outreach strategies to engage effectively with their target audience, ultimately increasing conversion rates and fostering long-term relationships.
Analyzing Historical Success:
The foundation of an effective ICP lies in a thorough analysis of previous clients who have brought the most value to the organization. This process begins by collecting data on past customers, including demographic information, industry sectors, company size, purchasing behavior, and engagement history. Sales and marketing teams should identify common traits among these successful clients, such as revenue size, geographic location, and specific challenges they faced that the organization was able to solve.
Tools such as CRM systems and sales analytics platforms can facilitate this data collection process. By extracting insights from this data, organizations can identify patterns that highlight the attributes of their best customers, laying the groundwork for the ICP.
Identifying Key Attributes:
Once the data has been gathered, the next step is to define the key attributes that characterize the ideal client. These attributes may include:
Demographics: Age, gender, education level, and geographic location can inform targeting strategies.
Firmographics: Attributes related to companies, such as industry, company size, and revenue, provide insight into the organizational context of ideal prospects.
Behavioral Characteristics: Understanding how past clients interacted with the brand, including their buying habits and engagement levels, can reveal critical insights into what motivates them to make purchasing decisions.
Challenges and Pain Points: Identifying common challenges faced by successful clients allows organizations to tailor their messaging and value propositions to address these specific needs.
Segmenting the ICP:
After identifying the key attributes, organizations can segment their ICP into specific categories based on shared characteristics. This segmentation enables more granular targeting and allows sales and marketing teams to create tailored outreach strategies that resonate with different target audience segments. For example, a business may develop distinct messaging for small businesses versus large enterprises or clients in different industries with unique challenges.
Crafting Personalized Messaging:
With a well-defined ICP, sales and marketing teams can craft personalized messaging that speaks directly to ideal prospects’ pain points and objectives. This messaging should highlight how the organization’s solutions address specific challenges and add value to the prospect’s business. By speaking the language of the ICP, organizations can significantly enhance their chances of engagement and conversion.
Optimizing Lead Generation Efforts:
Understanding the ICP allows businesses to optimize their lead-generation strategies. By attracting leads that fit the ideal client profile, organizations can allocate their resources more efficiently and reduce the time spent pursuing leads that are unlikely to convert. This targeted approach enhances lead quality and streamlines the sales process, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates.
Enhancing Customer Retention:
The insights gained from an ICP can also inform customer retention strategies. By understanding the attributes that define ideal clients, organizations can identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling tailored solutions that meet their evolving needs. Additionally, by nurturing relationships with existing clients who fit the ICP, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to long-term success.
Continuous Iteration and Improvement:
Building and utilizing an ICP is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing refinement and adjustment. As market conditions change and organizations gather more data on their customers, it’s essential to revisit and update the ICP regularly. By continuously analyzing data and adjusting the ICP accordingly, businesses can remain agile and responsive to customer needs and preferences shifts.
Building and utilizing an Ideal Client Profile is a strategic necessity for organizations looking to optimize their outreach efforts and drive sales success. By leveraging data analysis to identify key attributes of past successes, businesses can create a well-defined ICP that informs tailored outreach strategies. This targeted approach enhances engagement and conversion rates and fosters long-term relationships with clients, positioning organizations for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. In an era where personalized communication is paramount, an effective ICP is a powerful tool for aligning marketing and sales efforts with the target audience’s needs.
The evolution of prospecting in B2B sales underscores a significant shift from mass outreach to targeted engagement strategies. While early adopters of broad outreach benefited from less competition and greater technology efficiency, today’s marketplace demands a more nuanced and thoughtful approach. Prospects are increasingly discerning, favoring personalized communications that resonate with their needs and challenges.
As organizations strive to expand their market reach, they must recognize the importance of complying with local legislation regarding spam and privacy, as non-compliance can lead to legal repercussions and reputational damage. By focusing on developing an Ideal Client Profile (ICP) based on historical successes, businesses can refine their outreach efforts to connect meaningfully with the right decision-makers.
The ability to craft tailored messages and optimize engagement strategies enhances the likelihood of conversion and fosters long-term client relationships built on trust and value. Ultimately, embracing this strategic evolution in prospecting will position organizations for sustained growth in an increasingly competitive landscape, ensuring they remain relevant and effective in addressing the needs of today’s informed buyers.

Case Study: LinkedIn’s Transformation to Targeted Engagement
Background
LinkedIn, launched in 2003, quickly became the leading professional networking platform. Initially, LinkedIn used mass outreach strategies to grow its user base and promote its premium subscription services. However, as the platform evolved and the B2B landscape became more competitive, LinkedIn recognized the need to pivot toward a more targeted and strategic approach to reach its audience effectively.
The Shift in Strategy
• Recognizing the Need for Change: LinkedIn noticed that many users viewed mass messaging as spam, especially as more businesses began leveraging the platform for sales outreach. As the marketplace matured, it became clear that a one-size-fits-all approach was no longer effective. This prompted LinkedIn to reevaluate its outreach strategies and prioritize personalized communication.
• Developing the Ideal Client Profile (ICP): LinkedIn analyzed the characteristics of its most engaged users to refine its outreach efforts, mainly focusing on premium subscribers and advertisers. By assessing user data—such as industry, job title, engagement levels, and purchasing behaviors—LinkedIn was able to identify key attributes that defined its Ideal Client Profiles (ICPs). This analysis served as the foundation for more targeted marketing initiatives.
• Implementing Account-Based Marketing (ABM): With a clear understanding of its ICPs, LinkedIn adopted an Account-Based Marketing strategy. This approach focused on engaging specific high-value accounts rather than broad outreach campaigns. The marketing and sales teams collaborated closely to design customized campaigns tailored to key stakeholders in these accounts.
Key Implementation Tactics
• Data-Driven Insights: LinkedIn leveraged its data analytics tools to gain insights into user behavior and preferences. By analyzing interactions, engagement metrics, and content consumption patterns, LinkedIn was able to develop targeted messaging that resonated with its audience.
• Personalized Outreach Efforts: Instead of sending generic promotional messages, LinkedIn emphasized personalized outreach. Sales and marketing teams crafted tailored messages that spoke directly to specific decision-makers pain points and goals. This included referencing industry trends or relevant content that addressed the target audience’s needs.
• Value-Added Content and Engagement: LinkedIn enhanced its content strategy by providing high-quality, industry-specific resources that offered valuable insights. Webinars, whitepapers, and thought leadership articles were shared to educate and engage potential clients. By positioning itself as a knowledgeable partner, LinkedIn fostered deeper connections with prospects.
Results and Impact
• Higher Engagement Rates: Following the implementation of targeted engagement strategies, LinkedIn saw a significant increase in engagement rates across its marketing campaigns. Personalized messages generated higher open and response rates than previous mass outreach efforts, leading to more meaningful interactions.
• Improved Conversion Rates: The shift to targeted outreach improved conversion rates for premium subscriptions and advertising solutions. By addressing the unique needs of its ICPs, LinkedIn successfully guided prospects through the sales funnel, ultimately leading to higher sales and revenue.
• Stronger Client Relationships: LinkedIn’s commitment to providing personalized communication and valuable content fostered stronger client relationships. Users appreciated the tailored support and resources, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
• Enhanced Brand Reputation: LinkedIn strengthened its brand reputation by prioritizing ethical marketing practices and respecting user privacy. Clients viewed LinkedIn as a trusted partner, enhancing the company’s credibility in the professional networking space.
Conclusion
LinkedIn’s transformation from mass outreach to targeted engagement illustrates how organizations can adapt to the changing dynamics of B2B sales. LinkedIn successfully navigated the complexities of an increasingly discerning marketplace by developing Ideal Client Profiles and embracing Account-Based Marketing strategies. This case study highlights the importance of leveraging data-driven insights, personalizing communication, and providing value to clients to drive sustainable growth and success. As B2B buyers continue to seek tailored experiences, LinkedIn’s evolution serves as a testament to the necessity for businesses to remain agile and responsive to the needs of today’s informed professionals.

Exercise: Developing an Ideal Client Profile (ICP)
• Whiteboard or flip chart
• Markers
• Sticky notes
• Pens and paper
• Industry sector
• Company size
• Geographic location
• Pain points
• Buying behavior
• Decision-making structure
• What are the common characteristics among their successful clients?
• What unique challenges do these clients face that their product/service addresses?
• How can this ICP guide their outreach efforts?
• How did defining the ICP help you think differently about your outreach efforts?
• What insights did you gain from other groups that could enhance your approach to prospecting?
• How can understanding regulations and ethical marketing practices influence your outreach strategy?

Course Manual 9: RFP Strategy
In the competitive landscape of B2B sales, responding to Requests for Proposals (RFPs) is a critical yet often daunting task for sales professionals. Salespeople frequently encounter unsolicited RFPs, which can be perceived as an uphill battle—akin to fitting a round peg into a square hole. When an RFP does not align with a salesperson’s solution or value proposition, the instinct is often to view it as a waste of time and resources. This perspective can lead to an ingrained belief within organizations that unsolicited RFPs are not worth pursuing, ultimately hampering their ability to capitalize on potential revenue opportunities.
However, unsolicited RFPs can present unique opportunities to expand market reach and engage with prospects who may not have initially considered a company’s solution. By shifting the mindset from viewing these proposals as burdensome to seeing them as opportunities for strategic engagement, sales teams can begin to unlock new pathways to success. This transformation starts with a robust RFP strategy that empowers sales professionals to assess each RFP on its merits, determining whether it warrants a thoughtful response.
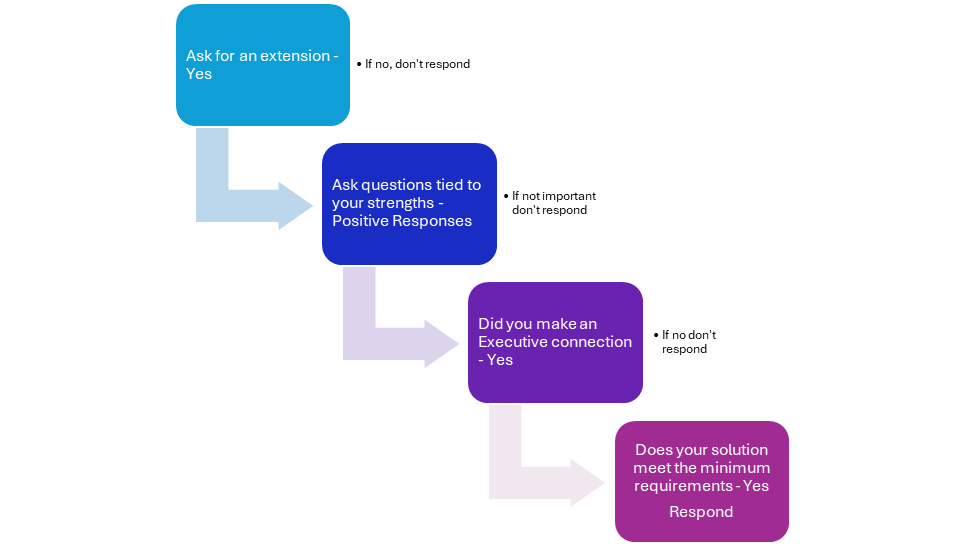
The key to navigating unsolicited RFPs lies in understanding the intricacies of the buying process and leveraging the RFP response format to influence it. A well-structured strategy allows sales teams to identify critical decision points throughout the RFP lifecycle. This approach not only aids in determining whether to invest resources in crafting a response but also increases the chances of success by aligning the proposal more closely with the prospect’s needs.
Assessing RFPs on Their Merits
While evaluating unsolicited Requests for Proposals (RFPs) is pivotal to a successful sales strategy, it’s important to note that not all RFPs are worth pursuing. The ability to discern which RFPs are worth pursuing can significantly impact a sales team’s efficiency and overall success. A well-defined assessment process enables sales professionals to identify viable opportunities while conserving resources and effort for the most promising leads. However, pursuing an RFP that doesn’t align with your strengths or stretches your resources too thin can jeopardize existing commitments and lead to subpar performance. This section will outline key criteria for assessing the merits of unsolicited RFPs, including alignment with the company’s strengths, potential profitability, and the strategic importance of the prospect.
1. Alignment with Company Strengths
The first step in evaluating an RFP is to assess its alignment with the company’s core competencies and strengths. This involves a thorough analysis of the following:
Product Fit: Does the RFP specify needs that align with your company’s solutions? A close match increases the likelihood of delivering a compelling proposal that resonates with the prospect’s requirements.
Expertise and Experience: Consider whether your team possesses the necessary expertise and track record to execute the project outlined in the RFP confidently. Highlighting relevant experience can be a significant advantage during the evaluation process.
Resource Availability: Assess whether your organization has the bandwidth—both in terms of personnel and financial resources—to commit to fulfilling the project if awarded. Taking on an RFP that stretches your resources too thin can jeopardize existing commitments and lead to subpar performance.
2. Potential Profitability
Profitability is a crucial factor in deciding whether to pursue an RFP. Evaluating the financial aspects of the opportunity will help determine its potential return on investment (ROI):
Budget Alignment: Analyze the budget outlined in the RFP. Is the scope of work being proposed realistic? Understanding whether the budget aligns with your pricing structure will help assess the project is worth pursuing.
Long-term Value: Consider the potential for long-term partnerships or additional projects with the prospect. An RFP may initially seem less lucrative, but it could be worth pursuing if it opens the door to future opportunities or leads to higher-value contracts. This long-term perspective can instill a sense of optimism and strategic planning in your sales team.
Competitive Landscape: Investigate the competitive environment surrounding the RFP. Who are the other bidders? If your company has a strong competitive edge, such as unique offerings or established relationships, it may enhance the project’s profitability potential.
3. Strategic Importance of the Prospect
Understanding the strategic significance of the prospect is key to evaluating an RFP’s merits. This involves assessing factors such as:
Market Influence: Does the prospect hold a significant position in the industry? Winning an RFP from a well-known company can enhance your brand’s visibility and credibility, potentially leading to further opportunities in that sector.
Alignment with Business Goals: Consider how the project aligns with your organization’s strategic objectives. Does it fit within your target market or sector focus? Aligning with your strategic vision can ensure that your efforts contribute to long-term growth.
Relationship Potential: Evaluate existing relationships with the prospect. If there is a pre-existing connection or positive interactions, the likelihood of success in responding to the RFP increases. Building on established trust can also smooth the negotiation process.
To implement an effective assessment strategy, sales teams can develop a standardized RFP evaluation matrix. This matrix can include criteria such as alignment with strengths, potential profitability, and strategic importance, allowing teams to score each RFP based on these factors. By quantifying the assessment process, sales professionals can clearly understand which opportunities warrant further investment. This systematic approach can instill a sense of organization and control in your sales team.
A systematic approach to assessing unsolicited RFPs ultimately empowers sales teams to make informed decisions. By identifying viable opportunities and prioritizing efforts accordingly, organizations can optimize their sales strategies, reduce wasted resources, and increase their chances of securing valuable contracts.
Influencing the Buying Process
Once a sales team decides to respond to an unsolicited RFP, the next critical step is to influence the buying process through their response effectively. This involves crafting proposals that do more than merely satisfy the client’s stated requirements; it requires a strategic approach that shapes the prospect’s perceptions, priorities, and decision-making criteria. Here are several key tactics that sales teams can employ to achieve this goal:
1. Understand the Prospect’s Needs and Pain Points
Before crafting the response, it’s essential to have a deep understanding of the prospect’s specific needs and challenges. This understanding can be gleaned from the RFP itself, but additional research—such as reviewing the prospect’s website, industry reports, and news articles—can provide valuable insights. By pinpointing the prospect’s pain points, sales teams can tailor their proposals to address these issues directly, showcasing how their solutions provide effective remedies. This empathetic approach can make the prospect feel understood and valued.
2. Highlight Unique Value Propositions
To stand out in a crowded field of competitors, sales teams should focus on their unique value propositions (UVPs). These distinctive benefits and features set their solutions apart from the competition. When crafting the response:
Articulate Benefits Clearly: Use language that resonates with the prospect’s objectives. Instead of merely listing features, translate these features into tangible benefits that align with the prospect’s goals. For instance, if your solution is faster than the competition, highlight how this speed can save the prospect time and money. If your solution is more user-friendly, emphasize how it can improve the prospect’s employees’ productivity.
Use Case Studies and Testimonials: Include relevant case studies or client testimonials that demonstrate the successful application of your solution in similar contexts. This social proof can effectively build credibility and trust, reinforcing your offering’s unique advantages.
3. Create a Compelling Narrative
A well-crafted narrative can significantly enhance the proposal’s impact. This narrative should tell a story that connects the prospect’s needs to your solution:
Position Your Company as a Partner: Frame your organization as a strategic partner rather than just a vendor. Emphasize your commitment to understanding their challenges and working collaboratively to achieve their objectives.
Visual Storytelling: Utilize visuals, such as infographics and charts, to illustrate key points and enhance understanding. Visuals can simplify complex information and make the proposal more engaging.
4. Address Evaluation Criteria Proactively
RFPs often come with specific evaluation criteria that the prospect will use to assess proposals. Proactively addressing these criteria within your response can demonstrate alignment and improve the chances of being viewed favorably:
Explicitly Link Features to Criteria: For each evaluation criterion, clearly link your solution’s features to the prospect’s needs. This shows that you understand what they are looking for and have tailored your offering to meet those expectations.
Provide Transparent Pricing: Include clear pricing structures and justifications for costs. Transparency in pricing can help to build trust and prevent potential objections related to budget concerns later in the process.
5. Anticipate Objections and Provide Reassurances
Understanding and addressing potential objections in advance can help mitigate concerns the prospect may have about your proposal:
Preemptive Solutions: If there are common objections related to your offering or industry, proactively address these within your response. Offer reassurances and solutions to mitigate these concerns before they become points of contention.
Offer Flexible Options: Various options or customizable solutions can help address different stakeholder needs, showing your willingness to adapt to the prospect’s requirements.
6. Foster Ongoing Communication
Influencing the buying process doesn’t end with submitting the RFP response. Engaging with the prospect throughout the evaluation process can help reinforce your position:
Follow-Up Strategically: After submitting the proposal, follow up with the prospect to address any questions or concerns they may have. This continued engagement demonstrates commitment and can provide opportunities to clarify your offerings further.
Leverage Existing Relationships: If your company has previously interacted with the prospect, use those relationships to facilitate conversations and gather feedback. Personal connections can significantly enhance your influence in the buying process.
By employing these tactics, sales teams can craft RFP responses that meet client requirements and actively shape the buying process. Effectively influencing the prospect’s perceptions and priorities increases the likelihood of securing the contract, turning unsolicited RFPs into valuable business opportunities. Ultimately, the goal is to position your solutions as the most compelling choice, leading to long-term partnerships and increased revenue.
Identifying “Go/No-Go” Decision Points
The “go/no-go” decision-making process is crucial to responding to RFPs, particularly unsolicited ones. Effectively identifying critical decision points can significantly enhance a sales team’s efficiency by allowing them to focus on proposals with the highest potential for success. A structured framework for assessing whether to proceed with an RFP response helps organizations maximize their resources while minimizing wasted effort on pursuits unlikely to result in a win. Below, we outline a comprehensive framework to aid sales teams in making these pivotal decisions.

1. Establish Clear Evaluation Criteria
To streamline the decision-making process, sales teams should develop a set of clear evaluation criteria. These criteria should be based on quantitative and qualitative factors reflecting the organization’s strategic objectives. Some common criteria to consider include:
Alignment with Business Objectives: Does the RFP align with your company’s strategic goals and priorities? If the project does not fit within your strategic framework, it may be best to refrain from pursuing it.
Budget and Pricing Structure: Evaluate the budget outlined in the RFP against your pricing model. If the budget is significantly lower than your expected costs, this could signal a potential mismatch in expectations.
Scope of Work: Assess whether the scope of work aligns with your organization’s capabilities. If the requirements are outside your expertise or resources, declining may be prudent.
2. Assess Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive environment surrounding the RFP is essential for making informed go/no-go decisions. Factors to evaluate include:
Competitive Advantages: Analyze your organization’s strengths and competitors. If your offering has unique advantages likely to appeal to the prospect, it may be worth pursuing the RFP.
Competitor Engagement: Consider the other companies competing for the same RFP. If the competition includes well-established players with solid relationships, the chances of success may diminish, suggesting a potential “no-go.”
Market Positioning: Evaluate how your solution is perceived in the market relative to competitors. If you lack credibility in the area the RFP addresses, this might influence your decision to engage.
3. Evaluate Relationship Dynamics
Existing relationships with the prospect can significantly influence go/no-go decisions. Consider the following factors:
Prior Interactions: If your organization has a history of positive engagements with the prospect, this relationship could enhance the likelihood of success. Conversely, a history of negative interactions might warrant a “no-go” decision.
Decision-Making Structure: Understand who is involved in the decision-making process and their familiarity with your company. This could be a positive indicator if critical stakeholders have previously expressed interest in your solutions.
Influence of Internal Advocates: Assess whether there are internal champions within the prospect’s organization who can advocate for your proposal. Their support can increase your chances of winning the RFP.
4. Analyze Resource Allocation
A practical consideration in the go/no-go decision-making process is allocating resources required to respond to the RFP. Important aspects to evaluate include:
Time Commitment: Consider how much time your team would need to dedicate to crafting the proposal. If responding to the RFP would detract from other critical projects or opportunities, it may not be worth pursuing.
Team Availability: Assess whether your team has the expertise and availability to respond effectively. If key personnel are already committed to other priorities, it could hinder your ability to deliver a strong proposal.
Cost of Participation: Calculate the estimated costs of responding to the RFP, including labor, materials, and potential travel. If the projected costs outweigh the potential benefits, a “no-go” decision may be advisable.
5. Create a Decision-Making Process
To ensure consistency in evaluating RFPs, organizations should formalize the decision-making process by:
Developing a Go/No-Go Matrix: Create a scoring matrix incorporating the established evaluation criteria. Each RFP can be scored based on these criteria to determine its viability. This matrix serves as a visual aid for decision-makers, facilitating informed discussions.
Involving Key Stakeholders: Ensure that relevant team members, such as sales, marketing, and technical experts, are involved in the decision-making process. Their diverse perspectives can contribute to a well-rounded evaluation.
Setting Thresholds for Decision Making: Define specific thresholds for what constitutes a “go” or “no-go.” For example, an RFP must score above a certain threshold to warrant further investment. This clarity helps streamline decision-making.
Identifying go/no-go decision points is a fundamental aspect of an effective RFP strategy. By establishing clear criteria, assessing competitive dynamics, evaluating relationships, analyzing resource allocation, and formalizing the decision-making process, sales teams can optimize their responses to RFPs. This strategic approach allows organizations to focus on the most promising opportunities, increasing the likelihood of success and driving incremental revenue growth. Ultimately, a well-defined go/no-go process is a critical tool for maximizing the efficiency of sales efforts and ensuring that resources are allocated where they can yield the greatest return.
In the dynamic world of B2B sales, the approach to unsolicited Requests for Proposals (RFPs) can significantly impact an organization’s growth and success. While many sales professionals may instinctively view these unsolicited RFPs as obstacles, they represent valuable opportunities to engage with potential clients and expand their market presence. By adopting a strategic mindset and implementing a robust RFP strategy, sales teams can evaluate each proposal’s merits, align responses with the prospect’s needs, and ultimately influence the buying process.
Through systematic assessment of RFPs—considering factors such as alignment with company strengths, potential profitability, and strategic importance—sales teams can make informed go/no-go decisions that maximize resource allocation and focus efforts on the most promising leads. Crafting compelling proposals that highlight unique value propositions and address client concerns positions a company favorably and fosters relationships that can lead to long-term partnerships.
Ultimately, by transforming the perception of unsolicited RFPs and developing a well-defined strategy to navigate them, sales organizations can unlock new pathways to success, driving incremental revenue and enhancing their competitive edge in the marketplace.

Case Study: Cisco Systems and Unsolicited RFPs
Background
Cisco Systems, a global leader in networking technology and IT solutions, frequently encounters unsolicited Requests for Proposals (RFPs) from organizations seeking to enhance their networking capabilities. Given Cisco’s extensive range of products and services, the challenge lies in determining which unsolicited RFPs to pursue and how to structure responses that resonate with potential clients while aligning with the company’s strengths.
The Challenge
In the early 2010s, Cisco faced a common challenge in the B2B landscape: many sales professionals viewed unsolicited RFPs as a time-consuming burden rather than an opportunity. The prevalent mindset within the organization was that responding to these proposals often led to wasted resources, especially when the requirements seemed misaligned with Cisco’s solutions. This attitude was detrimental, resulting in the company missing out on significant revenue opportunities and partnerships with potential clients.
Strategic Shift
Recognizing the need for change, Cisco initiated a strategic transformation in approaching unsolicited RFPs. The sales leadership emphasized reframing unsolicited RFPs as strategic engagement opportunities rather than obstacles. This cultural shift was complemented by the development of a robust RFP strategy that involved several key components:
Assessment Framework: Cisco developed a standardized RFP evaluation matrix to assess unsolicited proposals. This matrix included criteria such as alignment with Cisco’s core competencies, potential profitability, and the prospect’s strategic importance. By quantifying the assessment process, sales teams could prioritize RFPs that warranted a thoughtful response.
Understanding Prospect Needs: Sales teams were trained to conduct thorough research on prospective clients to understand their needs, pain points, and market positions. This deep understanding allowed Cisco to tailor responses more effectively and propose solutions that addressed each prospect’s unique challenges.
Highlighting Unique Value Propositions: Cisco focused on articulating its unique value propositions (UVPs) in each proposal. This involved showcasing relevant case studies and testimonials from similar industries, thus reinforcing the credibility of Cisco’s solutions.
Continuous Engagement: To effectively influence the buying process, Cisco encouraged sales teams to communicate with prospects throughout the evaluation stage. This included strategic follow-ups after submitting proposals to address questions and reinforce the company’s commitment to the prospect’s success.
Implementation and Results
Implementing this strategy led to a notable improvement in Cisco’s ability to secure contracts from unsolicited RFPs. Key outcomes included:
Increased Win Rates: Cisco improved its win rates for unsolicited proposals by using the RFP evaluation matrix. The matrix helped the sales team identify which RFPs aligned closely with the company’s strengths and capabilities.
Enhanced Resource Allocation: The structured approach allowed Cisco to allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that high-potential RFPs received the necessary attention while minimizing wasted efforts on proposals deemed unlikely to succeed.
Strengthened Client Relationships: Focusing on understanding client needs and maintaining ongoing communication fostered stronger relationships with prospects. Many of these relationships resulted in long-term partnerships and further opportunities for collaboration.
Revenue Growth: The strategic shift enhanced Cisco’s reputation in the market and contributed to significant incremental revenue growth. The company successfully converted numerous unsolicited RFPs into valuable contracts, further solidifying its position as a leader in the networking industry.
Conclusion
Cisco’s experience with unsolicited RFPs illustrates the importance of a strategic approach in B2B sales. By shifting the organizational mindset from viewing unsolicited proposals as burdens to recognizing them as opportunities for engagement, Cisco effectively transformed its RFP process. Implementing a systematic assessment framework, an emphasis on understanding client needs, and ongoing communication contributed to improved win rates and stronger client relationships. This case study is a compelling example for other organizations navigating the complexities of unsolicited RFPs, demonstrating that a proactive and strategic approach can unlock new avenues for growth and success in a competitive marketplace.

Exercise: Reframing Unsolicited RFPs
• Take a few minutes to write down your feelings and thoughts about unsolicited RFPs. Do you view them as burdensome? Why or why not?
• Consider any previous experiences you’ve had with unsolicited RFPs. What were the outcomes, and how did you feel during the process?
• Market Expansion
• Relationship building
• New revenue streams
• Alignment with Company Strengths: Does the RFP align with what your company does well? List specific strengths that match the RFP requirements.
• Potential Profitability: Based on the budget outlined, do you believe this project is financially viable? Explain your reasoning.
• Strategic Importance: Consider the prospect’s market influence. How could winning this RFP enhance your company’s credibility or future opportunities?
• Alignment with strengths
• Profitability potential
• Strategic importance
• Resource availability
• Steps to pursue the RFP if it’s a “go” (e.g., team meetings, research, proposal development).
• Reasons for declining the RFP if it’s a “no-go” (e.g., misalignment with strategy, lack of resources).
• Reflect on what you learned from this exercise and how you can apply these insights to future unsolicited RFPs.

Course Manual 10: Maintaining Trust
Maintaining trust is a cornerstone of effective sales optimization in the fast-paced world of B2B sales, where relationships often dictate success. Trust between sales leaders and their teams and between salespeople and their prospects is essential for fostering collaboration, open communication, and long-term loyalty. When trust is established, sales teams are more likely to discuss challenges honestly, share insights, and work together towards common goals. This trust-based environment enhances team morale and leads to improved performance and accountability.
The dynamics of trust in sales are multifaceted. At its core, trust is built on reliability, transparency, and mutual respect. Sales leaders who cultivate trust within their teams empower their salespeople to take calculated risks, make decisions autonomously, and innovate in their approach to customer engagement. This empowerment instills a sense of confidence and capability in sales professionals, enabling them to create an atmosphere conducive to meaningful dialogue. Clients are more inclined to share their pain points, enabling salespeople to tailor their solutions effectively.
Moreover, maintaining trust requires continuous effort. It’s not a one-time achievement but a persistent commitment that evolves with each interaction. Trust becomes a distinguishing factor in an era where customers have access to abundant information and options. Salespeople who consistently deliver on their promises, follow up diligently and provide exceptional service stand out in a crowded marketplace. They build a reputation for reliability that enhances their credibility and encourages repeat business and referrals.
However, maintaining trust is not without challenges. High turnover rates, shifting team dynamics, and external market pressures can strain relationships. For instance, when a team member leaves, it can disrupt the trust and collaboration within the team. In such cases, it’s important to communicate openly about the changes and reassure the team about the continuity of trust. Organizations must implement strategies that reinforce trust at every level to navigate these complexities. This involves fostering a culture of transparency and accountability and prioritizing communication and feedback.
By maintaining trust within their teams and clients, sales organizations can create a robust foundation for sustainable success. Trust drives performance and cultivates resilience, allowing sales teams to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Building Trust Within Sales Teams
Trust among sales team members is essential for creating a high-performing, collaborative environment that drives success. Trust is the bedrock of effective teamwork, and when team members feel secure in their relationships, they are more likely to share ideas, support each other, and engage in productive conflict. This subtopic explores several critical strategies for building and maintaining trust within sales teams.
1. Open Communication
Open and transparent communication is crucial for building trust within a sales team. Sales leaders should encourage an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns. Regular check-ins, team meetings, and one-on-one sessions provide opportunities for open dialogue. During these interactions, listening and validating team members’ perspectives is essential.
Implementing tools like anonymous feedback platforms can also help team members express themselves without fear of repercussions. This encourages candid discussions about challenges, successes, and areas for improvement. By fostering a culture where communication is prioritized, team members are more likely to feel heard and valued, strengthening trust.
2. Shared Goals
Establishing shared goals is another powerful way to foster trust within a sales team. When team members work together toward common objectives, they develop a sense of unity and collaboration. These goals should be clear, measurable, and aligned with the organization’s overall vision.
To create shared goals, leaders can involve team members in goal-setting, ensuring everyone has a voice in defining the targets. This inclusivity enhances commitment and reinforces the idea that each member plays a vital role in achieving success. Celebrating milestones together through formal recognition or informal gatherings further solidifies the bond of trust as team members experience collective achievement.
3. Team-Building Activities
Engaging in team-building activities is an effective strategy for fostering trust among sales team members. These structured or informal activities provide opportunities for team members to interact in a non-work setting, allowing them to build relationships based on camaraderie and mutual respect.
Activities range from team retreats and workshops to simple social gatherings or virtual team-building exercises. The key is to create an environment where team members can connect, have fun, and get to know each other on a personal level. These experiences can break down barriers and foster a sense of belonging, essential for trust.
4. Leadership Modeling Trustworthiness
Leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing and maintaining trust within sales teams. Leaders must model trustworthiness through their actions and behaviors. This includes being honest, consistent, and reliable in their commitments. When leaders demonstrate transparency in their decision-making processes and acknowledge their mistakes, they set an example for their team members.
Moreover, leaders should promote a culture of trust by recognizing and rewarding trustworthy behavior within the team. This could involve celebrating individuals who demonstrate collaboration, integrity, and accountability. By reinforcing these values, leaders cultivate an atmosphere where trust can thrive.
5. Creating a Supportive Environment
A supportive environment is vital for building trust within sales teams. Leaders should prioritize the well-being of their team members, offering assistance and resources to help them succeed. This includes providing ongoing training and development opportunities and encouraging professional growth.
Additionally, fostering a sense of psychological safety is crucial. Psychological safety refers to an environment where team members feel comfortable taking risks, sharing ideas, and expressing their concerns without fear of negative repercussions. Leaders can enhance trust and foster a high-performing sales team by promoting a supportive culture where individuals can thrive.
Building trust within sales teams is an ongoing process that requires intentionality and commitment from all members, especially leadership. Organizations can cultivate a culture of trust that enhances collaboration and drives performance by prioritizing open communication, establishing shared goals, engaging in team-building activities, modeling trustworthiness, and creating a supportive environment. Ultimately, a trusted sales team is more resilient, innovative, and equipped to meet the challenges of an ever-evolving marketplace.
Establishing Trust with Prospects
Building trust with prospects is a fundamental component of the sales process that can significantly impact the likelihood of closing deals and nurturing long-term client relationships. Trust fosters a sense of safety and confidence in the buyer, making them more willing to engage with sales professionals and consider their offerings. This subtopic delves into practical techniques for establishing trust with prospects, emphasizing the importance of rapport, active listening, transparency, and follow-through.
1. Building Rapport
Building rapport is the first step toward establishing trust with prospects. Rapport involves creating a genuine connection and making prospects feel comfortable and understood. Sales professionals can build rapport by finding common ground with potential clients. This can be achieved through personalizing conversations based on shared interests or experiences, such as discussing a recent industry event or a shared hobby, thus humanizing the sales process.
Compelling small talk can serve as an icebreaker, making prospects feel more at ease. Asking open-ended questions about their business challenges, goals, or industry trends can also help create a sense of camaraderie. The goal is to demonstrate empathy and interest in their needs beyond just making a sale. Trust is cultivated more naturally when prospects feel valued as individuals rather than just potential transactions.
2. Active Listening
Active listening is a crucial skill in establishing trust with prospects. This involves not just hearing but truly understanding what a prospect is communicating. Sales professionals should practice attentive listening, demonstrating that they are fully engaged in the conversation. This can be achieved through techniques such as:
• Reflective Listening: Paraphrasing what the prospect has said to confirm understanding and show that their input is valued.
• Nonverbal Cues: Maintaining eye contact, nodding, and encouraging gestures to signal attentiveness.
• Avoiding Interruptions: Allowing prospects to finish their thoughts before responding shows respect and fosters an open dialogue.
By actively listening, sales professionals can uncover valuable insights about a prospect’s needs, concerns, and pain points. This understanding enables them to tailor their solutions effectively, further building trust and credibility.
3. Understanding Client Needs
Understanding client needs is pivotal in establishing trust. Sales professionals must develop this understanding thorough research and preparation before engaging with prospects. This includes learning about the prospect’s industry, market position, and their specific challenges.
During conversations, sales professionals should ask insightful questions, encouraging prospects to articulate their needs and priorities. This demonstrates a genuine interest in finding the right solution and positions the salesperson as a trusted advisor rather than a mere vendor.
Once the salesperson clearly understands the prospect’s needs, they can present tailored solutions that directly address those challenges. This personalized approach fosters a sense of trust, as prospects feel that the salesperson is invested in their success rather than simply pushing a product.
4. Demonstrating Expertise
Demonstrating expertise is another crucial element in building trust with prospects. Sales professionals should position themselves as knowledgeable resources by providing valuable insights and information relevant to the prospect’s industry and challenges. This could include sharing industry trends, best practices, or case studies that showcase how similar clients have successfully addressed their issues.
To showcase their expertise, sales professionals can also leverage thought leadership content, such as whitepapers, webinars, or articles. By sharing valuable resources, they reinforce their credibility and demonstrate a commitment to helping the prospect succeed.
5. Follow-Through and Transparency
Follow-through and transparency are essential in nurturing long-term client relationships and maintaining trust. After initial conversations, sales professionals should promptly follow up with additional information, answers to questions, or next steps. This demonstrates reliability and respect for the prospect’s time and interest.
Moreover, transparency is critical throughout the sales process. Sales professionals should be honest about what their products or services can deliver, including any limitations. Setting realistic expectations helps prevent misunderstandings and builds trust over time.
When challenges arise, being upfront about potential issues and proactively addressing them further solidifies the trust between the salesperson and the prospect. By fostering a transparent relationship, sales professionals can enhance client loyalty and increase the likelihood of repeat business.
Establishing trust with prospects is a vital aspect of the sales process that requires intentionality and skill. Sales professionals can cultivate strong, trust-based relationships with potential clients by building rapport, practicing active listening, understanding client needs, demonstrating expertise, and maintaining follow-through and transparency. These relationships facilitate successful sales outcomes and lay the groundwork for long-term partnerships that benefit both parties. In an increasingly competitive marketplace, the ability to establish and nurture trust is a crucial differentiator for successful sales teams.
Managing Trust in a Remote Work Environment
In recent years, the shift to remote work has transformed how sales teams operate, presenting challenges and opportunities for managing trust. As sales professionals navigate virtual interactions, maintaining trust becomes essential for fostering collaboration, engagement, and productivity. This subtopic explores the dynamics of trust in remote sales settings and offers best practices to ensure that team members remain connected and committed.
1. Challenges of Trust in a Remote Setting
Maintaining trust in a remote work environment can be challenging due to physical distance and limited face-to-face interactions. The lack of in-person cues, such as body language and non-verbal communication, can hinder the development of rapport and connection among team members. Additionally, remote work may lead to feelings of isolation and disengagement, making it difficult for individuals to build and maintain trust.
Moreover, the flexibility of remote work can sometimes blur the lines between personal and professional boundaries, potentially leading to misunderstandings or miscommunications. Without regular in-person contact, it can also be more challenging to gauge team members’ morale and well-being, which can impact overall trust levels within the team.
2. Opportunities for Building Trust Remotely
Despite these challenges, remote work offers unique opportunities to build and manage trust. Technology reliance can enhance communication and collaboration, allowing teams to connect across geographical boundaries. By leveraging digital tools, sales leaders can create an environment where trust can thrive.
For instance, remote work can encourage greater transparency, as sales professionals often have to provide regular updates and progress reports. This culture of accountability can foster trust when team members are open about their challenges and successes. Additionally, remote work allows for more flexible scheduling, enabling team members to balance work and personal commitments and improving job satisfaction and trust.
3. Best Practices for Virtual Communication
Effective virtual communication is vital for building trust in remote sales teams. Sales leaders should prioritize regular, structured communication to keep team members informed and engaged. This can include:
Daily or Weekly Stand-ups are brief meetings to share updates, discuss priorities, and address any challenges. These meetings foster accountability and reinforce a sense of belonging within the team.
Virtual Open-Door Policies: Encouraging team members to reach out with questions or concerns creates a supportive atmosphere. Leaders should be approachable and available for one-on-one conversations as needed.
Utilizing Video Conferencing: Video calls can enhance personal connections and facilitate better communication than traditional phone calls or emails. Seeing colleagues’ facial expressions can improve understanding and rapport.
4. Regular Check-Ins
Regular check-ins are crucial for maintaining trust in a remote work environment. Sales leaders should implement scheduled one-on-one meetings with team members to discuss progress, goals, and any challenges they may face. These check-ins provide an opportunity to offer support, guidance, and feedback while reinforcing the leader’s commitment to the team’s success.
In addition to formal meetings, informal check-ins can be beneficial. Encouraging casual conversations among team members can strengthen relationships and build camaraderie. Creating dedicated time for social interactions, such as virtual coffee breaks or team-building activities, helps maintain connections in a remote setting.
5. Leveraging Technology for Collaboration
Technology is pivotal in facilitating collaboration and enhancing trust in remote sales teams. Organizations should invest in collaboration tools that support seamless communication and project management. Popular platforms include:
Project Management Tools: Tools like Trello, Asana, or Monday.com enable team members to track tasks, set deadlines, and collaborate on projects in real-time, fostering transparency and accountability.
Messaging Applications: Instant messaging tools, such as Slack or Microsoft Teams, provide a quick way for team members to communicate, share updates, and ask questions, promoting continuous engagement.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems allow sales teams to share customer information and insights, ensuring everyone is on the same page and fostering collaboration in pursuing leads.
6. Ensuring Engagement and Connection
To keep team members connected and engaged in a remote work environment, leaders should prioritize initiatives that promote team cohesion. This includes recognizing achievements, celebrating milestones, and encouraging peer-to-peer recognition. When team members feel appreciated and valued, trust is reinforced.
Additionally, leaders should be proactive in gauging team morale and well-being. Regularly seeking feedback through surveys or informal check-ins can help identify areas for improvement and foster a culture of open communication.
Managing trust in a remote work environment presents unique challenges and opportunities for sales teams. By implementing best practices for virtual communication, conducting regular check-ins, leveraging technology for collaboration, and prioritizing engagement, sales leaders can cultivate a strong culture of trust among team members. In a distributed workforce, trust enhances collaboration and productivity and fosters resilience, enabling sales teams to thrive in an increasingly digital landscape. Maintaining confidence in remote settings is essential for driving performance and achieving long-term success in sales.
In the competitive landscape of B2B sales, maintaining trust emerges as a critical element for optimizing performance and achieving sustainable success. Trust acts as the foundation for collaboration between sales leaders and their teams and between salespeople and prospects. When trust is firmly established, it enhances open communication, fosters accountability, and encourages honest discussions about challenges and opportunities. This dynamic leads to improved morale, stronger teamwork, and, ultimately, higher sales performance.
Building trust within sales teams requires intentional strategies, including promoting open communication, establishing shared goals, and engaging in team-building activities. Leaders play a pivotal role by modeling trustworthiness and creating a supportive environment that prioritizes the well-being and development of team members. Simultaneously, establishing trust with prospects hinges on rapport-building, active listening, understanding client needs, and demonstrating expertise. Follow-through and transparency further solidify these relationships, paving the way for long-term partnerships.
The shift to remote work has introduced unique challenges and opportunities in managing trust. Sales leaders must adapt their strategies to ensure effective virtual communication, regular check-ins, and the leveraging of technology to facilitate collaboration. By prioritizing engagement and connection, organizations can cultivate a culture of trust that empowers their teams to thrive in a distributed workforce.
Ultimately, trust is not merely a byproduct of effective sales practices but an ongoing commitment that underpins every interaction. By maintaining trust at all levels, sales organizations can navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace and position themselves for lasting success.

Case Study: Cisco Systems’ Approach to Trust in B2B Sales
Background
Cisco Systems, founded in 1984, is a multinational technology conglomerate specializing in networking hardware, telecommunications equipment, and high-technology services and products. As a leader in the technology sector, Cisco recognizes that trust is a fundamental element in B2B sales, impacting both internal team dynamics and external client relationships. The company has developed comprehensive strategies to build and maintain trust, which is crucial for its success in a competitive market.
The Importance of Trust
For Cisco, trust is essential for fostering collaboration among sales teams and building strong client relationships. The company understands that when trust is established, teams engage in open dialogue, share insights, and work collaboratively toward shared objectives. This trust-based culture enhances morale, accountability, and overall performance, enabling Cisco to adapt effectively to the fast-paced technology landscape.
Building Trust Within Sales Teams
Open Communication: Cisco promotes a culture of open communication, where team members feel safe expressing their thoughts and ideas. Regular meetings, town halls, and team huddles are standard practices that encourage transparency. Cisco uses tools like Webex for video conferencing, facilitating real-time discussions, and keeping remote team members engaged.
Shared Goals: Cisco emphasizes the importance of shared goals within its sales teams. Sales leaders work collaboratively with team members to set clear, measurable objectives that align with the company’s vision. This collective approach fosters unity and enhances commitment to achieving targets.
Team-Building Activities: Cisco organizes formal and informal team-building activities to build trust and camaraderie among sales team members. These include workshops, offsite retreats, and social events that help strengthen relationships and create a positive team culture.
Leadership Modeling Trustworthiness: Cisco’s leadership is committed to modeling trustworthiness. Leaders demonstrate integrity by being transparent about decision-making processes and acknowledging their mistakes. This approach encourages team members to emulate these behaviors, fostering a culture of accountability.
Creating a Supportive Environment: Cisco prioritizes the well-being of its employees by providing resources for professional development and mental health support. This commitment helps team members feel valued, strengthening trust within the organization.
Establishing Trust with Prospects
Building trust with prospects is integral to Cisco’s sales strategy. The company employs several effective techniques to foster strong relationships with potential clients:
Building Rapport: Cisco’s sales representatives focus on creating genuine connections with prospects by personalizing their interactions. They take the time to understand each client’s unique challenges and objectives, fostering an atmosphere of comfort and openness.
Active Listening: Cisco emphasizes active listening as a critical skill for its sales team. Representatives are trained to engage in reflective listening, ensuring they fully comprehend a prospect’s needs and concerns. This attentiveness builds respect and trust in the relationship.
Understanding Client Needs: Cisco’s sales professionals conduct thorough research on potential clients to position themselves as trusted advisors. They build credibility and rapport with prospects by asking insightful questions and tailoring their solutions to address specific challenges.
Demonstrating Expertise: Cisco leverages its extensive portfolio of case studies, whitepapers, and thought leadership content to establish credibility. The company reinforces its position as a knowledgeable resource in the technology sector by sharing valuable insights and best practices.
Follow-Through and Transparency: Cisco sales representatives prioritize prompt follow-ups after initial meetings, providing additional information, or addressing questions. This proactive communication, combined with transparency about product capabilities, fosters trust and encourages loyalty among prospects.
Managing Trust in a Remote Work Environment
The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated a shift to remote work for Cisco, presenting challenges and opportunities in maintaining trust. The company adopted several strategies to navigate this transition effectively:
Virtual Communication: Cisco adapted its communication practices by leveraging its Webex platform for team meetings and client interactions. This technology facilitated personal connections, helping to maintain strong relationships during physical distancing.
Regular Check-Ins: Scheduled one-on-one meetings between sales managers and team members became a staple practice, allowing for personalized support and feedback. Cisco also encouraged informal virtual gatherings, such as coffee chats, to strengthen team morale and engagement.
Leveraging Technology: Cisco utilized its technology solutions to foster collaboration among remote teams. Tools like Cisco Sales Connect enable team members to share real-time insights and updates, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
Cisco’s commitment to building and maintaining trust has been instrumental in its success in the B2B sales landscape. The company has cultivated a culture of collaboration, transparency, and integrity by focusing on trust within teams and with prospects. This approach enhances team performance and fosters long-lasting relationships with clients, positioning Cisco for sustained growth in a competitive market. Trust remains a vital component of Cisco’s strategy, enabling the company to navigate the complexities of the modern sales environment and achieve lasting success.

Exercise: Exploring Trust in B2B Sales
• Discuss why trust is a foundational element in B2B sales. How does it impact collaboration among sales teams and rapport with prospects?
• Share personal experiences where trust played a crucial role in a sales situation, either positively or negatively.
• Identify critical strategies for fostering trust among team members. Which methods do you think are most effective, and why?
• Discuss any specific team-building activities you have found successful in promoting trust and collaboration within your teams.
• Talk about techniques you’ve used or observed that effectively establish trust with prospects.
• Share an example of a situation where building rapport or demonstrating expertise helped close a deal.
• Reflect on the challenges of maintaining trust in a remote work setting. How have you adapted your approach to foster trust among team members?
• Discuss the tools or practices you use to ensure effective communication and connection in a remote environment.

Course Manual 11: Deal(s) Slipping
In the fast-paced environment of B2B sales, the stakes are high, and the pressure to meet revenue goals is relentless. One of the most detrimental phenomena that can occur is the slipping of committed deals within the sales funnel. These are the deals that sales teams are confident will close within a specific timeframe, typically in the contracting phase. When they begin to slip into subsequent months or quarters, it creates significant challenges for the sales team and executive management. This breakdown of commitment can rapidly erode trust between the sales organization and leadership, jeopardizing the business’s long-term success.
When deals that have been publicly committed to by the sales team start to falter, it raises red flags. It signals to executive management that the sales process may not be as robust as previously believed, potentially leading to missed revenue goals critical for the organization’s overall strategy. This scenario is particularly concerning when the organization has set ambitious targets that rely on these anticipated deals. Hence, understanding why deals slip and taking proactive measures to mitigate this risk is essential.
The first step in addressing deal slippage is fostering a culture of open communication and alignment between sales leadership and salespeople. Both parties must be in lockstep regarding the status of high-probability deals. A common forecasting language, as emphasized in the earlier Sales Optimization training program modules, can significantly reduce deal slippage instances. However, it is crucial to recognize that while such a framework can mitigate risks, it cannot entirely eliminate them. Therefore, swift and strategic action becomes imperative when signs of slippage emerge. Your active participation in this communication is crucial for our collective success.
Sales leadership plays a pivotal role in actively managing these high-stakes deals. This involves spending quality time in the field, building relationships with key clients, understanding their specific buying processes, and ensuring that the solutions being offered align with their needs. Your proactive engagement with these individuals at pivotal moments can provide crucial insights into the proposed solution’s implementation plans and expected outcomes, empowering you to steer these deals toward success.
By asking thought-provoking questions, such as, “Assume it is 18 months from now, and you have implemented the chosen solution. What is different in your organization?” sales leaders can gauge the readiness and alignment of the prospect’s organization with the proposed value proposition. The answers to this question can illuminate whether a viable deal is still within reach and highlight areas where further engagement may be needed.
The Impact of Deal Slippage on Trust and Revenue Goals
Understanding the effects of deal slippage is crucial for fostering a healthy sales culture and ensuring long-term success. When deals that were expected to close begin to falter, it affects immediate revenue projections and has far-reaching implications for the trust and morale within the organization. By being informed about these effects, you can better prepare and navigate through these challenges.
A foundation of trust between sales teams and executive management lies at the core of any successful sales organization. When committed deals slip, it raises questions about the integrity of the sales forecasting process and the reliability of the sales team’s assessments. Executives rely on sales forecasts to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, hiring, and strategic planning. If they perceive that sales teams are frequently overpromising and underdelivering, it can lead to skepticism about the accuracy of future forecasts.
This erosion of trust can create a toxic environment where salespeople feel pressured to inflate deal expectations to meet aggressive targets. Conversely, executives may become overly cautious, second-guess sales team inputs, and implement stricter oversight measures. Such dynamics can lead to a breakdown in communication, where sales professionals hesitate to share accurate updates for fear of repercussions, further exacerbating the issue of deal slippage.
Deal slippage’s repercussions extend beyond individual transactions; they can significantly impact the overall company culture. A culture characterized by mistrust and anxiety can stifle creativity and motivation among sales teams. When salespeople feel their contributions are undervalued or scrutinized, morale and productivity can decrease. A disengaged sales force is less likely to pursue innovative strategies or nurture client relationships, which is essential for long-term success. Moreover, the hostile atmosphere can permeate other departments, as teams that rely on sales performance, such as marketing and customer support, may also feel the ripple effects. Cross-functional collaboration suffers when trust is compromised, leading to a disjointed approach to achieving organizational goals. This lack of synergy can hinder the company’s ability to respond to market changes and seize growth opportunities.
From a financial perspective, the immediate impact of deal slippage is clear: it jeopardizes revenue targets. When a significant number of deals move out of the expected timeframe, it can lead to missed quarterly or annual revenue goals. This affects the sales department’s performance metrics and can result in a cascading effect on the organization’s overall financial health. Cash flow issues may hinder the company’s ability to invest in new initiatives or support existing operations. Furthermore, missing revenue targets can seriously affect the organization’s reputation. Investors and stakeholders closely monitor sales performance, and consistent slippage can lead to losing confidence in the company’s leadership. This skepticism may result in reduced investment, lower stock prices, or even challenges acquiring new clients who question the organization’s reliability.
Deal slippage profoundly impacts trust and revenue goals. It erodes confidence between sales teams and executive management and creates a negative ripple effect on company culture and morale. The implications extend beyond immediate financial losses, affecting the organization’s long-term growth trajectory and overall success. Addressing the root causes of deal slippage and fostering an environment of open communication and collaboration is essential for building trust and achieving sustainable revenue growth.
Strategies for Aligning Sales Leadership and Salespeople
Achieving alignment between sales leadership and salespeople is crucial for optimizing sales performance and reducing the risk of deal slippage. When both parties work in harmony, it fosters a culture of trust, accountability, and shared objectives. Here, we explore effective strategies to cultivate this alignment, focusing on communication, shared goals, and implementing a common forecasting language.
1. Prioritize Open Communication
Open and transparent communication is the cornerstone of alignment between sales leaders and their teams. Sales leaders should create an environment where salespeople feel comfortable sharing insights about their prospects, potential roadblocks, and market dynamics. Regular check-ins, team meetings, and one-on-one conversations can facilitate this dialogue.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish structured feedback mechanisms to ensure salespeople can voice their concerns and suggestions. This could involve anonymous surveys, suggestion boxes, or regular team morale and engagement pulse checks.
Active Listening: Sales leaders should practice active listening and demonstrate that they value input from their team. By acknowledging concerns and responding to feedback, leaders can build rapport and foster a culture of collaboration.
Cross-functional communication: Encourage collaboration between sales and other departments, such as marketing and customer support. Regular inter-departmental meetings can help ensure everyone is aligned on goals and messaging, reducing friction and improving overall performance.
2. Establish Shared Goals and Incentives
Aligning sales leadership and salespeople around common objectives is essential for driving collective success. Establishing shared goals helps create a unified vision that motivates the entire team to work together toward common targets.
SMART Goals: Develop Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals shared across the sales team and leadership. These goals should reflect both individual performance metrics and broader organizational objectives.
Collaborative Goal Setting: Involve salespeople in the goal-setting process. By allowing them to contribute to their expected goals, they will feel a greater sense of ownership and accountability, enhancing motivation and engagement.
Incentive Alignment: Create incentive structures that reward collaborative efforts rather than individual accomplishments. For example, consider team bonuses for achieving collective sales targets, which will encourage cooperation and teamwork.
3. Implement a Common Forecasting Language
A common forecasting language is vital for aligning expectations and reducing deal slippage. It creates a shared understanding of a “committed” deal and establishes clear criteria for evaluating deal progress.
Standardized Definitions: Develop standardized definitions for various stages of the sales funnel, including what it means for a deal to be “committed,” “likely to close,” or “slipped.” This consistency ensures that sales leadership and salespeople are on the same page when discussing deal status.
Training and Resources: Provide sales teams with training and resources on how to assess and report their deals accurately. This may include workshops on effective forecasting techniques, utilizing CRM systems, and understanding key performance indicators.
Regular Reviews and Adjustments: Schedule regular forecasting reviews, during which sales leaders and teams meet to discuss deal statuses. This collaborative approach allows for real-time adjustments and ensures that any potential slippage is identified and addressed promptly.
4. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Encouraging a continuous improvement mindset can help maintain alignment and adapt to changing market conditions. Both sales leadership and salespeople should be committed to ongoing learning and development.
Performance Reviews: Implement regular performance reviews that focus on individual accomplishments as well as team dynamics and collaboration. Use these reviews to discuss lessons learned from successes and failures, emphasizing a growth mindset.
Skill Development: Invest in ongoing training and development opportunities for sales teams, focusing on negotiation skills, relationship-building techniques, and advanced sales strategies. Empowering salespeople with new skills enhances their effectiveness and fosters a sense of investment from leadership.
Celebrate Wins Together: Recognize and celebrate team achievements, both large and small. This reinforces a sense of unity and encourages continued collaboration and alignment between sales leadership and their teams.
Organizations can effectively align sales leadership and salespeople by prioritizing open communication, establishing shared goals, implementing a common forecasting language, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. This alignment is essential for optimizing sales performance and mitigating the risks associated with deal slippage, ultimately contributing to sustained revenue growth and organizational success.
Engaging Key Executives: Best Practices for Maintaining Momentum
Engaging key executives during the buying process is crucial for maintaining momentum in sales, especially when high-probability deals show signs of slipping. By fostering strong relationships with decision-makers and understanding their unique perspectives, sales leaders and teams can navigate complex sales cycles more effectively. Here, we outline best practices for engaging key executives, identifying the right stakeholders, building meaningful relationships, and asking insightful questions to clarify deal viability.
1. Identifying the Right Stakeholders
Understanding the key stakeholders within a potential client’s organization is essential for effective engagement. Not all executives have the same influence or interest in a particular solution, so identifying the right individuals is critical.
Mapping the Organization: Begin by mapping the prospect’s organizational structure. This includes identifying decision-makers, influencers, and users of the proposed solution. Utilize tools such as LinkedIn, company websites, and networking to gather information about key players’ roles and responsibilities.
Understanding Influence: Recognize the difference between economic buyers (those who control budgets) and technical buyers (those who evaluate the product’s fit). Engaging both types is important, as the economic buyer ultimately approves expenditures while the technical buyer influences the evaluation process.
Leveraging Existing Relationships: If possible, leverage existing relationships within the organization. This could be through previous engagements, referrals, or mutual connections. A warm introduction can significantly enhance credibility and facilitate smoother conversations.
2. Significance of Relationship-Building
Building solid relationships with key executives is foundational to maintaining momentum throughout the sales process. Trust and rapport can significantly affect how executives perceive the value of a solution.
Personalized Engagement: Tailor your approach to each executive’s communication style, preferences, and interests. Understand what matters most to them—ROI, operational efficiency, or competitive advantage—and frame discussions around these priorities.
Consistent Communication: Regular, meaningful communication helps keep the lines open and reinforces the relationship. This can include sharing relevant insights, market trends, or updates on product developments that may interest the executive.
Face-to-Face Interactions: Whenever possible, prioritize face-to-face meetings, whether in person or virtual. These interactions allow for a deeper connection, enabling sales teams to read nonverbal cues and engage in more dynamic discussions.
3. Asking Insightful Questions
The types of questions asked during engagements with key executives can greatly influence the direction of the sales process. Thoughtful, open-ended questions can clarify deal viability and alignment with customer needs.
Understanding Goals and Challenges: Start by asking questions that uncover the executive’s strategic goals and challenges. For instance, “What are your top priorities for the upcoming year?” or “What obstacles are you encountering in achieving those goals?” This helps you understand how your solution can align with their objectives.
Clarifying Implementation and Outcomes: To assess the deal’s viability, pose questions that delve into the executive’s vision for implementation and expected outcomes. For example, “Assuming we move forward with this solution, what changes do you anticipate in your organization?” This encourages the executive to articulate their expectations and assess whether they align with your offering.
Addressing Concerns and Hesitations: Encourage executives to express any reservations. Asking, “Are there any concerns you have regarding our solution or its implementation?” opens the floor for dialogue and demonstrates your willingness to address potential barriers.
4. Maintaining Follow-Up and Accountability
Once initial engagements have occurred, maintaining follow-up and accountability is essential for keeping the momentum going.
Setting Clear Next Steps: After meetings, summarize the key takeaways and outline actionable next steps. This could involve scheduling follow-up meetings, providing additional information, or involving other stakeholders. Clear next steps ensure that the engagement does not lose momentum.
Regular Check-Ins: Establish a cadence for regular check-ins with key executives. This can help you stay informed about any changes in their priorities or challenges, allowing you to adjust your approach accordingly.
Showcasing Value: Continuously demonstrate the value of your solution by sharing relevant case studies, success stories, or metrics that reflect how similar organizations have benefited. This ongoing reinforcement helps keep the solution top-of-mind and encourages decision-makers to move forward.
By following these best practices for engaging key executives, sales teams can maintain momentum in the buying process and strengthen their relationships with crucial stakeholders. This proactive approach clarifies deal viability and aligns solutions with customer needs, ultimately leading to more successful sales outcomes.
In the high-stakes world of B2B sales, deal slippage poses a significant threat to revenue goals and the trust between sales organizations and executive management. When committed deals falter, they raise red flags that can erode confidence in the sales process, disrupt company culture, and jeopardize long-term success. As organizations set ambitious targets reliant on these anticipated deals, it becomes imperative to understand the root causes of deal slippage and take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Fostering a culture of open communication and alignment between sales leadership and sales teams is vital for addressing these challenges. Implementing a common forecasting language, encouraging regular check-ins, and establishing shared goals can create a cohesive approach that minimizes the likelihood of deal slippage. Moreover, engaging with key executives in the buying process is essential for maintaining momentum. By identifying the right stakeholders, building strong relationships, and asking insightful questions, sales teams can better align their solutions with customer needs and clarify deal viability.
Ultimately, organizations that prioritize these strategies will enhance their sales performance and cultivate a resilient culture that can withstand market pressures. By addressing the complexities of deal slippage head-on, businesses can foster trust, achieve revenue goals, and secure a successful future.

Case Study: SAP SE
Background
SAP SE, a global leader in enterprise software, faced significant challenges with deal slippage as it navigated the complexities of the B2B sales landscape. Known for its comprehensive ERP solutions, SAP aimed to streamline its sales process to meet aggressive revenue targets while managing a diverse client base. Despite its strong market position, SAP’s sales teams experienced frequent deal slippage, particularly as clients evaluated multiple software options and faced internal decision-making challenges. This case study explores how SAP identified and addressed the root causes of deal slippage, ultimately enhancing its sales performance and organizational culture.
Challenges Faced
As SAP expanded its offerings and customer base, several critical challenges related to deal slippage emerged:
Complex Decision-Making Processes: SAP’s clients often had intricate decision-making processes involving multiple stakeholders from various departments. This complexity led to delays and uncertainty, causing committed deals to slip beyond their expected closing dates.
Inconsistent Communication: Communication gaps between sales teams and internal stakeholders hindered effective deal management. Sales representatives often struggled to receive timely updates on client feedback and requirements, leading to misalignment in expectations.
Revenue Forecasting Discrepancies: The frequent slippage of committed deals created significant discrepancies in revenue forecasting. Executives relied on accurate sales projections for strategic planning, and when deals did not close as anticipated, it disrupted financial planning and resource allocation.
Strategic Response
To address these challenges, SAP implemented a comprehensive strategy focusing on improving deal management, enhancing communication, and fostering collaboration among teams:
Streamlined Sales Processes: SAP revised its sales processes to simplify the sales cycle. By implementing a more structured approach with defined stages for deal progression, sales representatives could manage their pipelines more effectively. This clarity helped identify potential slippage earlier and allowed for proactive measures.
Investment in Training Programs: SAP invested in extensive training programs for its sales teams, focusing on negotiation skills, consultative selling techniques, and understanding the intricacies of client businesses. Empowering sales professionals with the skills needed to navigate complex sales conversations contributed to increased deal closures.
Enhanced Collaboration Tools: SAP introduced advanced collaboration tools to facilitate communication among sales, technical, and executive teams. These tools allowed for real-time updates on deal statuses and client interactions, ensuring everyone involved had access to the latest information. Improved visibility helped to maintain alignment and address potential issues quickly.
Focus on Executive Engagement: SAP emphasized engaging with key executives within client organizations. Sales teams were trained to identify decision-makers and build relationships with them. By asking strategic questions to understand client goals and pain points, sales representatives could tailor their proposals to meet specific needs.
Implementation of Regular Deal Reviews: SAP instituted regular deal review meetings where sales leaders and teams would evaluate the status of high-priority deals. These meetings encouraged open discussion about potential roadblocks and strategies to keep deals on track. By fostering a culture of accountability, the company ensured that sales representatives felt supported in their efforts.
Results
Through these initiatives, SAP experienced significant improvements in sales performance and organizational culture:
Reduced Deal Slippage: SAP saw a noticeable reduction in deal slippage by streamlining sales processes and enhancing communication. Sales teams became more proactive in managing their pipelines and addressing challenges before they escalated.
Improved Revenue Forecasting: Implementing structured processes and enhanced collaboration led to more accurate revenue forecasts. Executives gained confidence in the sales team’s projections, enabling better strategic planning and resource allocation.
Strengthened Trust and Collaboration: Improved communication and regular deal reviews fostered a culture of trust and collaboration between sales teams and leadership. Sales representatives felt empowered to share updates and seek support when needed.
Sustained Revenue Growth: With reduced deal slippage and enhanced alignment with client needs, SAP achieved sustained revenue growth, reinforcing its position as a leader in the enterprise software market.
Conclusion
The SAP case illustrates the importance of effectively managing deal slippage in the B2B sales environment. SAP successfully addressed the challenges associated with deal slippage by streamlining sales processes, investing in training, and fostering collaboration through enhanced communication tools. This proactive approach not only improved sales performance but also cultivated a resilient organizational culture that could adapt to the complexities of the market, ultimately contributing to the company’s ongoing success.

Exercise: Addressing Deal Slippage in B2B Sales
• Whiteboard or flip chart
• Markers
• Sticky notes
• Briefly introduce the topic of deal slippage and its importance in B2B sales.
• Explain how deal slippage can impact trust, company culture, and revenue targets.
• Highlight the objectives of the exercise.
• Internal factors (e.g., communication breakdowns, misalignment between sales and leadership)
• External factors (e.g., market changes, client decision-making processes)
• Use sticky notes to write down each cause (one per note).
• Each group will share their top three causes with the larger group.
• Enhancing communication and collaboration between sales and leadership.
• Implementing a common forecasting language.
• Establishing regular check-ins and feedback mechanisms.
• Engaging key executives early in the sales process.
• Use a whiteboard or flip chart to list these strategies.
• Each group should aim to identify three actionable solutions.
• Summarize the key takeaways from the exercise, emphasizing the importance of addressing deal slippage proactively.
• Encourage participants to consider how they can implement the discussed strategies within their teams and organizations.
• Optionally, provide handouts or resources for further reading on managing deal slippage in B2B sales.

Course Manual 12: Compensation Effectiveness
In the realm of sales, the adage “salespeople are coin-operated” encapsulates the fundamental truth that compensation plays a pivotal role in motivating sales professionals. While it is essential to recognize that monetary incentives do not solely drive salespeople, financial compensation often ranks among their top motivators. The complexity and challenges inherent in sales require resilience, strategic thinking, and persistent effort. Consequently, the prospect of earning an executive-level income is a powerful catalyst that propels salespeople to engage in the arduous tasks essential for achieving success.
However, the relationship between compensation and sales effectiveness is not always straightforward. Organizations frequently encounter challenges in structuring compensation plans that incentivize desired behaviors and outcomes. A well-designed compensation plan, on the other hand, can empower sales teams, fostering an environment where they feel confident and in control, ultimately leading to enhanced revenue objectives.
A mentor once vividly illustrated the pivotal role of a well-structured compensation plan in the sales process. He emphasized that when a salesperson embarks on a discovery call with a new prospect, they enter a phase of exploration, seeking to understand the prospect’s needs and how their solutions can address specific challenges. A successful discovery call often perfectly aligns the prospect’s objectives and the company’s value proposition. In such cases, a salesperson should leave the meeting with a clear sense of potential earnings—an estimate of the commission they could earn from closing a deal with that client. This ‘ballpark’ figure serves as a powerful motivational tool, reinforcing the connection between the salesperson’s efforts and potential financial rewards.
This “ballpark” figure is a motivational tool, reinforcing the connection between the salesperson’s efforts and potential financial rewards. However, if the salesperson struggles to gauge their potential earnings, the overly complex compensation structure can detract from their motivation and focus. When compensation becomes an obstacle rather than a motivator, it stifles the behaviors organizations seek to encourage—such as building relationships, engaging in meaningful conversations, and ultimately closing deals.
In exploring the effectiveness of compensation in sales optimization, it becomes clear that organizations must offer attractive financial rewards and create a transparent and understandable compensation framework. This approach will help align salespeople’s efforts with the organization’s goals, fostering an atmosphere where they are inspired to pursue individual and collective success.
The Role of Incentives in Sales Motivation
In the competitive sales landscape, incentives play a crucial role in fostering motivation and driving performance among salespeople. These incentives, whether monetary or non-monetary, are powerful tools that can influence sales professionals’ behaviors and motivate them to achieve their targets.
Monetary incentives, often perceived as the primary motivators, include commissions, bonuses, and profit-sharing arrangements. These financial rewards are tangible and directly linked to sales performance, providing clear and immediate benefits for achieving targets. Here are some key considerations regarding monetary incentives:
Commission Structures: Different commission structures can significantly impact sales behavior. For instance, a straight commission plan may drive aggressive selling but could lead to short-term thinking, as salespeople might prioritize immediate sales over long-term customer relationships. Conversely, a base salary with bonuses for reaching targets can encourage a balance between meeting quotas and nurturing client relationships.
Performance Bonuses: Bonuses tied to specific metrics—such as exceeding quarterly targets or acquiring new clients—can motivate salespeople to push their limits. Structuring bonuses to reward sales volume and customer satisfaction or retention can create a more holistic approach to performance.
Tiered Compensation: Implementing tiered commission rates—where salespeople earn higher percentages for exceeding sales thresholds—can incentivize them to strive for more ambitious goals. This approach can drive high performers to continue their momentum while offering lower performers a path to improvement.
While monetary incentives are essential, non-monetary rewards also play a crucial role in motivating sales teams. These include recognition programs, career advancement opportunities, and personalized incentives tailored to individual preferences. Here are some examples of effective non-monetary incentives:
Recognition and Praise: Regular recognition of achievements—whether through formal awards, public acknowledgments, or simple expressions of appreciation—can significantly boost morale and motivation. Salespeople often thrive on acknowledgment from their peers and leadership, reinforcing their value within the organization.
Professional Development Opportunities: Providing access to training, workshops, or mentorship programs can motivate salespeople to enhance their skills and career prospects. By investing in their development, organizations demonstrate a commitment to their sales teams, fostering loyalty and long-term engagement.
Flexible Work Arrangements: Offering flexibility in work hours or remote work options can be a powerful incentive for many sales professionals. Balancing personal and professional commitments can enhance job satisfaction and motivate individuals to perform at their best.
Understanding that not all salespeople are motivated by the same factors is crucial for developing effective incentive programs. Individual motivations can vary based on personal goals, career aspirations, and life circumstances. Organizations can enhance the effectiveness of their incentive plans by:
Conducting Surveys and Feedback: Regularly soliciting feedback from sales teams regarding their motivations and preferences can provide valuable insights. Surveys can help identify what rewards resonate most with individuals, allowing for more personalized incentive strategies.
Creating a Culture of Communication: Fostering open communication between management and sales teams is key. This approach can help leaders understand the unique drivers of their salespeople, making them feel heard and understood. Regular check-ins, performance reviews, and informal conversations can uncover insights that inform incentive design.
Adapting Incentives Over Time: As individual motivations and market conditions evolve, so should incentive plans. Regularly reviewing and adjusting compensation structures to reflect changing needs and expectations can help maintain engagement and motivation among sales teams. This adaptability reassures the audience of the organization’s responsiveness and commitment to its success.
Incentives, both monetary and non-monetary, play a vital role in motivating salespeople and driving performance. By understanding the diverse motivations of their sales teams and tailoring incentives accordingly, organizations can create a more engaged and high-performing sales force. The right incentive strategies not only enhance individual performance but also contribute to the organization’s overall success by aligning sales efforts with business goals.
Aligning Compensation with Desired Outcomes
Designing compensation plans that effectively promote the right behaviors and results is crucial for maximizing sales performance and driving organizational success. A well-structured compensation plan aligns salespeople’s interests with the broader goals of the organization, ensuring that their efforts contribute directly to desired outcomes. Here are key strategies for aligning compensation with these outcomes.
1. Define Clear Performance Metrics
Organizations must establish clear and measurable performance metrics that directly correlate with sales objectives to align compensation with desired outcomes. This clarity is vital for guiding salesperson behavior and performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identifying relevant KPIs, such as revenue targets, customer acquisition rates, and retention metrics, provides a framework for assessing performance. Salespeople should know these metrics and understand how their contributions impact the organization’s success.
Realistic Goals: Setting achievable yet challenging goals helps maintain motivation and focus. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure that salespeople clearly understand what is expected of them.
2. Establish Transparent Compensation Structures
Transparency in compensation structures fosters trust and motivation among sales teams. Salespeople must clearly understand how their earnings are calculated and how their performance translates into compensation.
Clear Communication: Detailed documentation and explanations of compensation plans ensure that salespeople comprehend the link between their efforts and their rewards. This includes outlining commission rates, bonus eligibility criteria, and any tiered structures in place.
Regular Updates: Keeping sales teams informed about any changes to compensation plans and how those changes relate to performance metrics helps maintain alignment and engagement. Transparency fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among salespeople.
3. Incorporate a Mix of Incentives
A well-rounded compensation plan incorporates both monetary and non-monetary incentives to motivate salespeople. This blend ensures that various aspects of performance are recognized and rewarded.
Monetary Rewards: As discussed earlier, commissions, bonuses, and profit-sharing arrangements are crucial for sales compensation. These rewards should be linked to key performance metrics to drive specific behaviors.
Non-Monetary Rewards: Recognizing accomplishments through awards, public acknowledgment, or career advancement opportunities reinforces the importance of contributions beyond sales figures. Integrating non-monetary incentives can also enhance team collaboration and loyalty.
4. Foster a Culture of Accountability
Creating a culture of accountability encourages salespeople to take ownership of their performance and aligns their efforts with organizational goals. The compensation plan should support this culture.
Regular Performance Reviews: Conducting frequent performance reviews allows for ongoing feedback and discussions about individual progress toward goals. These reviews can help identify areas for improvement and reinforce the importance of achieving desired outcomes.
Peer Accountability: Encouraging collaboration and accountability among team members can drive performance. Implementing team-based incentives that reward collective achievements fosters a sense of camaraderie and motivates individuals to support each other in reaching common goals.
5. Adapt Compensation Plans to Evolving Business Needs
Business environments are dynamic, and compensation plans must be flexible to adapt to changing circumstances. Regularly reviewing and adjusting compensation structures ensures continued alignment with desired outcomes.
Market Analysis: Conducting periodic assessments of industry standards and competitor compensation practices can help organizations remain competitive in attracting and retaining top talent. Adjusting compensation plans based on market trends can also enhance motivation.
Feedback Mechanisms: Soliciting feedback from sales teams about the effectiveness of current compensation plans can provide valuable insights. This input can guide adjustments to ensure the compensation structure remains relevant and motivating.
Aligning compensation with desired outcomes is a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to optimize sales performance. By defining clear performance metrics, establishing transparent compensation structures, incorporating a mix of incentives, fostering a culture of accountability, and adapting plans to evolving business needs, organizations can create an environment where salespeople are motivated to achieve their goals. Ultimately, a well-aligned compensation plan not only enhances individual performance but also drives the organization’s overall success by ensuring that sales efforts are focused on the right behaviors and outcomes.
Overcoming Compensation Plan Pitfalls
An effective compensation plan motivates sales teams and drives organizational success. However, many organizations encounter common challenges that can undermine the effectiveness of these plans. This section will address these pitfalls—such as complexity, misalignment with company goals, and lack of communication—and provide insights on identifying and rectifying them.
1. Complexity in Compensation Plans
One of the most significant challenges organizations face is the complexity of their compensation structures. Overly complicated plans can confuse salespeople and lead to frustration, disengagement, and, ultimately, reduced performance.
Identification of Complexity: Organizations should assess their compensation plans for areas of unnecessary complexity. This can include convoluted commission structures, multiple tiers of bonuses, or intricate qualification criteria. Engaging sales teams in this evaluation process can provide insights into which elements are unclear or overly complicated.
Simplification Strategies: Simplifying compensation plans can significantly enhance clarity and motivation. Organizations can consider consolidating commission rates, standardizing bonus qualifications, and eliminating unnecessary tiers. A streamlined plan not only helps salespeople understand their earnings potential but also reduces administrative burdens.
2. Misalignment with Company Goals
Compensation plans not aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives can lead to misdirected efforts. When salespeople are incentivized to prioritize activities that do not contribute to the company’s goals, overall performance can suffer.
Assessment of Alignment: Organizations must regularly review their compensation plans against current business objectives to identify misalignment. This can involve examining how compensation metrics correlate with strategic goals, such as customer retention, market expansion, or product focus.
Strategies for Alignment: Organizations should recalibrate their compensation structures to reflect desired outcomes once misalignment is identified. For instance, if a company focuses on long-term customer relationships, compensation plans should reward immediate sales, customer satisfaction, and retention metrics.
3. Lack of Communication
Poor communication regarding compensation plans can create confusion and mistrust among sales teams. When salespeople do not understand how their compensation is structured or how it relates to their performance, it can lead to disengagement and decreased motivation.
Establishing Clear Communication Channels: Organizations must prioritize open lines of communication regarding compensation plans. This includes providing detailed documentation that explains how compensation works and regular updates about any changes or adjustments.
Training and Support: Training sessions or workshops can ensure sales teams fully understand the compensation plan. A forum for questions and discussions allows salespeople to clarify doubts, fostering a better understanding of how their efforts translate into earnings.
4. Inadequate Feedback Mechanisms
A lack of feedback mechanisms can hinder the effectiveness of compensation plans. Organizations that do not solicit input from sales teams regarding the effectiveness of compensation structures risk perpetuating issues that could be resolved.
Implementing Feedback Loops: Regularly seeking feedback from salespeople on the compensation plan is crucial for identifying pain points. Organizations can use surveys, one-on-one meetings, or team discussions to gather insights on how the plan is perceived and its impact on motivation.
Adapting Based on Feedback: Once feedback is collected, organizations must be willing to adjust their compensation plans accordingly. This demonstrates to sales teams that their input is valued and encourages ongoing engagement with the compensation structure.
5. Failure to Monitor and Evaluate Effectiveness
Organizations often overlook the importance of monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of their compensation plans over time. Without regular assessments, companies may fail to identify emerging issues or trends requiring adjustment.
Establishing Key Metrics for Evaluation: Organizations should define key metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of compensation plans. This can include turnover rates, sales performance against targets, and employee satisfaction with the compensation structure.
Regular Review and Adjustment: Conducting periodic reviews of compensation plans allows organizations to stay responsive to changing business needs and market conditions. This proactive approach ensures that compensation structures remain effective and motivating.
Overcoming the common pitfalls of compensation plans is essential for enhancing their overall effectiveness. By addressing complexity, ensuring alignment with company goals, fostering clear communication, implementing feedback mechanisms, and regularly monitoring performance, organizations can create a compensation strategy that motivates sales teams and drives the achievement of strategic objectives. A well-designed compensation plan can transform the sales function into a high-performing engine contributing to organizational success.
In the sales world, compensation is crucial in motivating sales professionals and driving performance. While financial incentives are often primary motivators, it’s essential to recognize that the complexities of the sales environment require a multifaceted approach to compensation. The adage “salespeople are coin-operated” highlights the importance of well-structured compensation plans that align with organizational goals and foster desired behaviors.
However, many organizations encounter challenges such as complexity, misalignment with company objectives, and inadequate communication, which can undermine the effectiveness of these plans. To address these pitfalls, organizations must focus on defining clear performance metrics, establishing transparent compensation structures, and creating a culture of communication and accountability. Moreover, regular feedback and continuous monitoring are vital for ensuring that compensation strategies remain relevant and motivating.
Ultimately, organizations can empower their sales teams by overcoming these challenges, designing effective compensation plans, enhancing individual performance, and driving overall success. A thoughtfully structured compensation strategy not only incentivizes salespeople but also aligns their efforts with the broader objectives of the business, transforming sales into a high-performing engine for organizational growth.

Case Study: Sales Team Process Improvement – Intangent (An Argano Company)
The Problem:
Intangent faced a significant challenge when it lost its exclusive partnership with IBM’s Sales Performance Management (SPM) team. This loss led to a noticeable decline in sales, with no new business opportunities on the horizon. The company recognized the urgent need to revamp its approach and reestablish itself in the competitive landscape.
The Approach:
To address these challenges, Intangent made a strategic decision to bring in a new sales leader who could overhaul the sales strategy. This leader undertook a comprehensive review of all sales processes, identifying key areas for improvement. Through this audit, the team developed a targeted Sales Process Improvement Plan, designed to drive growth and reinvigorate client acquisition efforts.
Key Success Factors:
The success of Intangent’s transformation can be attributed to a few crucial initiatives:
1. Building Trust within the Sales Team:
• Compensation structures were fine-tuned to ensure fairness and motivation across the team. This change, coupled with clearly defined sales territories, helped each team member understand their specific role and responsibilities.
• A strong emphasis was placed on using the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system effectively. This commitment fostered a data-driven approach, allowing team members to track leads and sales more accurately.
2. Enhancing Prospecting Strategies:
• The new approach focused on identifying and actively engaging potential partners, particularly those who could provide strategic value in the SPM sector. By nurturing these relationships, Intangent broadened its client base and unlocked new avenues for growth.
• Partnerships were strengthened by offering introductions to new clients, ensuring that each partner saw tangible value in collaborating with Intangent.
3. Addressing Common Pitfalls:
• The leadership team identified and eliminated several common issues that hindered sales growth. For instance, they reduced micromanagement, allowing the sales team to focus more on high-impact strategic tasks.
• Forecasting complexity was minimized by establishing a common language for sales predictions, which led to clearer expectations and more accurate goal-setting. Sales leadership also prioritized supporting field sales, enabling team members to operate with greater autonomy and effectiveness.
4. Sales Process Improvement Game Plan:
• Intangent implemented a detailed game plan that began with identifying challenges and addressing common mistakes. Specific focus areas included:
– Maintaining trust with the sales team and focusing on fair compensation.
– Overhauling the forecasting process to better align with organizational goals.
– Building effective strategies to respond to Request for Proposals (RFPs) and introducing structured onboarding for new team members.
• To ensure consistent progress, daily routines and activities were established, keeping the sales team aligned with the company’s overarching objectives.
Results:
The outcomes of these initiatives were both rapid and impressive. Within a year, Intangent achieved an 80% increase in overall revenue, driven primarily by a 300% surge in new client (or “new logo”) revenue. This turnaround validated the effectiveness of the revamped sales processes and the strategic improvements introduced by the new leadership.
Success Metrics:
Intangent’s success can be further illustrated through specific metrics:
• The team successfully onboarded four new SPM partners, broadening its influence and client base.
• The entire sales team was restructured to align with a new go-to-market strategy, ensuring that individual roles matched the company’s updated goals.
• Peer-to-peer collaboration was fostered among SPM partners, promoting knowledge-sharing and mutual growth.
• Strategic events were organized to elevate Intangent’s standing within both the SPM partner and client communities, solidifying its reputation and market position.

Exercise
Project Studies
Project Study (Part 1) – Customer Service
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 2) – E-Business
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 3) – Finance
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 4) – Globalization
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 5) – Human Resources
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 6) – Information Technology
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 7) – Legal
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Project Study (Part 8) – Management
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 9) – Marketing
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 10) – Production
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 11) – Logistics
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.

Project Study (Part 12) – Education
The Head of this Department is to provide a detailed report relating to the Challenges Identified process that has been implemented within their department, together with all key stakeholders, as a result of conducting this workshop, incorporating process: planning; development; implementation; management; and review. Your process should feature the following 12 parts:
01. Current Challenges
02. Challenge Experiences
03. Challenge Impacts
04. Common Mistakes
05. Forecasting Model
06. Hiring/Onboarding
07. Daily Routines
08. Prospect Profile
09. RFP Strategy
10. Maintaining Trust
11. Deal(s) Slipping
12. Compensation Effectiveness
Please include the results of the initial evaluation and assessment.
Program Benefits
Management
- Fundamentals Focus
- Effective Reviews
- Field Focus
- Avoid Mistakes
- Increase Wins
- Be Proactive
- Eliminate Poaching
- RFP Strategy
- Leader Teamwork
- Common Language
Human Resources
- Foster Culture
- Onboarding Effectively
- Hiring Well
- Sustainable Routines
- Team Building
- Competitive Knowledge
- Deliver Insights
- Action Focus
- Integrate Events
- Meeting Preparation
Finance
- Increase Revenue
- Save Deals
- Realistic Goals
- Commission Reliability
- Clear Accelerators
- Forecasting Accuracy
- Aligned Compensation
- ICP Focus
- Be Prepared
- Simplify Compensation
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.