Change Resilience

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Change Resilience is provided by Ms. Aikerson Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Ms. Aikerson is a Certified Learning Provider (CLP) with Appleton Greene and a highly sought-after speaker, trainer, coach, and consultant. She has a remarkable ability to simplify complex concepts, designing programs that deliver immediate and lasting results. Her approach to learning is engaging, actionable, and impactful, ensuring participants walk away with practical strategies they can apply right away.
With extensive experience across a diverse range of industries—including Aviation, Government, Financial Services, Manufacturing, Consumer Goods, Pharmaceuticals, Consultancy, Insurance, Food & Beverage, Telecommunications, Transportation, and Construction—Ms. Aikerson helps organizations successfully navigate change and transformation. By integrating principles of human psychology, she equips leaders and employees with the tools they need to adapt, ensuring measurable improvements in key business metrics and performance outcomes.
Her impressive academic background includes a Change Management Certificate from Harvard University, an MBA from Northwestern University, and a degree in Electrical Engineering from Bradley University. She also holds multiple certifications, including Prosci ADKAR Change Management, DISC Personality Traits, Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), Emotional Intelligence, Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP), and Six Sigma (Green Belt), among others.
A dedicated leader in her field, Ms. Aikerson has served as chapter president for several professional organizations, including the National Technical Association (NTA), the Association for Women in Communications (AWC), and Tomorrow’s Scientists, Technicians, and Managers (TSTM).
Her passion for empowering individuals and organizations to thrive in change continues to make her an influential force in professional development and organizational success.
To request further information about Ms. Aikerson through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Change Resilience
Change will happen. The rapid pace of change is only accelerating. Organizations today must navigate an evolving landscape shaped by technological advancements, market disruptions, workforce shifts, and global events. The ability to adapt and thrive in the face of change is no longer just a competitive advantage; it is a necessity for long-term success. This is where change resilience becomes essential.
At its core, change resilience is the ability to effectively respond to change, recover from setbacks, and embrace new challenges with confidence. It is not about avoiding or resisting change, but rather about adapting to it with agility and optimism. While it is natural for individuals and teams to feel discomfort or hesitation when faced with uncertainty, organizations that cultivate a culture of resilience can minimize disruption, enhance employee engagement, and sustain high performance through transitions.
Why Change Resilience Matters
For many years, organizations viewed change as a single, isolated event—a restructuring, a new leadership team, a technology implementation, or a market shift that needed to be managed and stabilized before returning to business as usual. However, in today’s business environment, change is not an event—it is a constant. Disruptions happen frequently and often without warning. Whether these changes come from external factors outside of your organization or internal factors that you have yourself determined, organizations must navigate change continuously rather than reactively.
This perpetual state of change creates uncertainty and stress among employees, who are often expected to adapt quickly to new processes, tools, and structures. Many organizations fail to recognize the emotional and psychological impact of these shifts. Without the right support, employees experience resistance, anxiety, and even burnout. When change is introduced without a framework to guide employees through the transition, productivity dips, morale suffers, and overall performance declines.
Organizations that struggle with change resilience often face significant operational and cultural challenges. When employees resist change, they may exhibit low engagement, decreased motivation, and skepticism toward leadership. This reluctance often stems from uncertainty—employees worry about job security, the difficulty of learning new skills, or the fear of failure in a changing environment.

• Lower Employee Morale – Resistance to change often leads to frustration and disengagement. Employees who feel unsupported or uninformed during transitions may become disconnected from the organization’s vision.
• Poor Collaboration – Teamwork suffers when individuals hesitate to embrace new ways of working. Change-resistant teams may become siloed, avoiding cross-functional collaboration and reducing innovation.
• Decline in Customer Experience – Employees struggling to adapt to internal changes often struggle to maintain service quality for customers. Whether it is a new system implementation, a revised workflow, or an updated product offering, customers feel the effects when employees are unprepared.
• Decreased Organizational Performance – Productivity slows when employees are resistant to change. Instead of focusing on innovation and efficiency, they expend energy trying to maintain the status quo.
On the other hand, organizations that prioritize change resilience set themselves apart by empowering employees to see change as an opportunity rather than a threat. These organizations invest in strategies that help employees navigate uncertainty, manage stress, and adapt with confidence.
When teams are equipped with the right mindset and tools, they become more innovative, agile, and proactive. Employees in a resilient organization feel engaged, supported, and prepared for whatever shifts may come. Instead of resisting change, they develop the ability to embrace it, learn from it, and use it to drive success.
The benefits of change resilience extend beyond employees—it strengthens the entire organization. Businesses that foster a culture of adaptability experience:
• Higher employee engagement – When employees understand why change is happening and feel equipped to handle it, they remain motivated and committed to their work.
• Stronger teamwork and collaboration – Resilient teams embrace open communication, problem-solving, and knowledge-sharing, making transitions smoother.
• Improved business performance – Organizations that adapt quickly to change are more competitive, agile, and responsive to market demands.
By developing change resilience, organizations future-proof themselves against disruption. Change is not going away—the key to long-term success is learning how to manage it effectively.
What Can Change Resilience Help With?
Change resilience is a critical skill that enables individuals, teams, and organizations to navigate uncertainty, adapt to disruptions, and sustain high performance in an evolving world. By cultivating resilience, organizations can transform resistance into agility, innovation, and growth, ensuring they remain competitive and prepared for whatever comes next.
One of the biggest challenges organizations face during transitions is employee resistance. People naturally gravitate toward familiar routines and may struggle with uncertainty or fear of failure. Change resilience helps employees shift from a reactive mindset to a proactive one, allowing them to embrace change rather than resist it. This shift reduces stress, increases adaptability, and fosters a culture of openness to new ideas.
Beyond overcoming resistance, change resilience significantly improves employee well-being and engagement. Unmanaged change can lead to stress, burnout, and disengagement as employees struggle to keep up with new expectations. However, resilience equips employees with coping mechanisms that help them manage emotions, stay focused, and maintain a sense of control, even in uncertain situations. This leads to higher job satisfaction, improved morale, and greater overall engagement.
Leadership effectiveness also strengthens with change resilience. Resilient leaders are more adaptable, decisive, and empathetic during times of change. They can communicate effectively, inspire confidence, and provide clear direction, even when facing uncertainty. By modeling resilience, leaders help their teams navigate challenges more effectively, creating an environment of trust and stability within the organization.
For organizations as a whole, change resilience enhances organizational agility. Businesses that prioritize resilience are better able to adapt quickly to market shifts, industry disruptions, and competitive challenges. Instead of seeing change as a disruption, they anticipate and prepare for it, ensuring teams can pivot efficiently while maintaining momentum. This agility is essential for long-term sustainability and business growth.
Decision-making under pressure also improves when teams develop change resilience. Change often brings complex decisions with uncertain outcomes, which can create hesitation or panic. Resilient individuals and teams are better equipped to analyze situations objectively, manage stress, and make informed decisions without succumbing to fear. This ability to remain calm and solution-focused leads to better long-term results and stronger problem-solving capabilities.
Additionally, organizations that embrace resilience foster a culture of innovation and creativity. Instead of resisting new ideas, employees become more open to experimentation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. This mindset drives forward-thinking solutions, keeps businesses competitive, and positions organizations as industry leaders.
Another crucial benefit of change resilience is maintaining strong customer relationships. Customers notice when organizations struggle with change—whether through a disorganized product rollout, inconsistent service, or communication breakdowns. Change resilience ensures that customer service teams can adapt quickly, manage customer concerns effectively, and maintain service excellence during transitions, reinforcing customer trust and loyalty.
Additionally, change resilience helps minimize productivity disruptions. Every major change comes with an adjustment period, but resilient teams recover faster, shortening the productivity dip and maintaining efficiency. This allows organizations to avoid costly delays and performance setbacks, ensuring smoother transitions with less operational impact.
In the long run, developing change resilience helps create a future-ready workforce. The workforce of tomorrow requires continuous learning, adaptability, and problem-solving skills to thrive amid technological advancements and industry shifts. Resilience ensures that employees can handle evolving job roles, rapid changes, and shifting industry demands without hesitation.
Ultimately, change resilience drives long-term success. Organizations that embed resilience into their culture future-proof themselves against disruption, build stronger teams, and create an environment where change is embraced rather than feared. By investing in resilience today, businesses set themselves up for sustained growth, innovation, and adaptability in an ever-changing world.

Case Study
A compelling example of organizational change resilience is the transformation of Southwest Energy (SWN). Facing industry volatility and internal challenges, SWN recognized the need to cultivate a culture that could adeptly navigate change. To achieve this, they collaborated with the Center for Creative Leadership (CCL) to implement a comprehensive resilience-building program.
The initiative focused on two primary tracks: “Leading Change” and “Building a Culture of Resilience.” The “Leading Change” track equipped leaders with strategies to manage transitions effectively, emphasizing adaptive leadership and proactive communication. The “Building a Culture of Resilience” track aimed to embed resilience into the organizational fabric, encouraging employees at all levels to embrace change and view challenges as opportunities for growth.
As a result of this program, SWN experienced enhanced adaptability, improved employee engagement, and a strengthened capacity to manage industry fluctuations. This case underscores the importance of deliberate resilience development in fostering an organization’s ability to thrive amid change.
The Evolution of Change Resilience: Preparing for the Future
As the pace of change accelerates across industries, the need for change resilience is more critical than ever. Organizations that fail to develop adaptability risk falling behind in an increasingly dynamic and uncertain world. The future of change resilience development will be shaped by technological advancements, evolving workplace expectations, and a greater emphasis on human-centered leadership. Companies that proactively build resilience into their culture and operations will gain a competitive edge, ensuring their workforce remains engaged, agile, and prepared for the unknown.
1. The Role of Technology in Change Resilience
Technology will play a crucial role in enhancing resilience development, both in how organizations manage change and in how employees are trained to adapt. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and digital transformation tools will help organizations anticipate change before it happens. AI-driven data models will allow companies to identify trends, assess risks, and implement proactive strategies, reducing the shock of sudden disruptions.
In addition, virtual reality (VR) and simulation-based training will become more prevalent in resilience development. Employees will be able to practice adapting to different scenarios in a controlled, low-risk environment, improving their confidence and ability to handle real-world challenges. These tools will allow organizations to scale resilience training across teams, ensuring a consistent approach to managing change.
2. Psychological Safety and Emotional Intelligence
The future of change resilience will place a stronger emphasis on psychological safety and emotional intelligence. Organizations are beginning to recognize that employees cannot simply be forced to accept change—they need support, reassurance, and a sense of security during transitions.
Leaders will be expected to cultivate an environment where employees feel safe to voice concerns, experiment with new approaches, and embrace change without fear of failure. Emotional intelligence will become a core leadership competency, helping managers navigate team emotions, provide empathetic communication, and reduce resistance.
Workplace culture will also shift to prioritize mental and emotional well-being as part of resilience development. Organizations will invest more in stress management programs, mindfulness training, and personalized coaching to help employees stay emotionally balanced during periods of change.
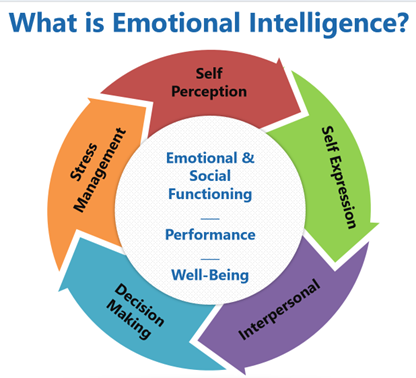
3. Adaptive Learning and Continuous Development
Traditional training methods will evolve into more dynamic, real-time learning experiences. Instead of one-time change management workshops, organizations will adopt continuous learning models that focus on building adaptability as an ongoing skill.
Microlearning platforms will allow employees to engage with bite-sized training modules that provide just-in-time learning—helping them build resilience as they experience change rather than after the fact. AI-driven coaching tools will personalize learning experiences, ensuring that each employee receives tailored support based on their unique challenges and responses to change.
4. A Shift in Leadership Mindset
Leadership development programs will increasingly emphasize adaptive leadership, equipping leaders with the ability to guide teams through change with clarity, transparency, and confidence. Instead of focusing on control and stability, future leaders will be trained to embrace uncertainty, encourage innovation, and foster a culture of agility.
Change-resilient organizations will also decentralize decision-making, empowering employees at all levels to contribute to change initiatives and take ownership of transitions. This will reduce resistance and create a more engaged, solution-focused workforce.
The Road Ahead
The future of change resilience development is clear: organizations must move beyond rigid change management approaches and instead build adaptability into their DNA. By leveraging technology, prioritizing emotional intelligence, embracing continuous learning, and shifting leadership mindsets, companies can equip their workforce with the tools needed to thrive in an ever-changing world.
In a future where change is constant, resilience will be the defining factor of success. Organizations that invest in developing it today will be the ones that lead tomorrow.
A Mindset Shift: From Resistance to Resilience
The good news is that change resilience is a skill that can be developed. It begins with a mindset shift—moving from resistance to acceptance, from uncertainty to adaptability. Instead of viewing change as something to fear, resilient teams anticipate it, prepare for it, and harness it as a tool for growth.
This program will provide you with the strategies and tools needed to build a workforce that is not just reactive, but proactive when faced with change. You will explore the psychology behind change, practical techniques to build resilience, and proven methods to foster a culture of adaptability across your organization.
By mastering these concepts, your organization can move beyond change resistance and create an environment where adaptability, resilience, and innovation thrive. Change is coming—the question is, will you be ready for it?
Curriculum
Change Resilience – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Change Psychology
- Part 1 Month 2 Change Resilience
- Part 1 Month 3 Team Personality
- Part 1 Month 4 Emotional Intelligence
- Part 1 Month 5 Effective Communication
- Part 1 Month 6 Present Well
- Part 1 Month 7 Write Well
- Part 1 Month 8 Team Building
- Part 1 Month 9 Celebrate Now
- Part 1 Month 10 Cultivate Feedback
- Part 1 Month 11 Sustained Inspiration
- Part 1 Month 12 Establish Growth
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Change Resilience corporate training program.
Change Resilience – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Change Psychology – Description: To create a Change Resilient organization, you must first understand what change is and how it impacts people. In this session you will get a working definition for change, learn the types of change we experience, and understand the various ways people respond to changes that impact them. We begin by exploring change. Change can be something we want and desire or something we don’t want. It can be planned or completely unexpected. Because we as people prefer it when we have control over our environments, all types of change induce a psychological response. This response will take one of several forms. You will understand specifically how this shows up in the workplace. It is important to understand that we can’t stop our response to change—we can only manage it. This requires understanding the difference between a healthy response to change and an unhealthy response to change. From this foundation you will learn more about change resistance. You will specifically learn how change and change psychology result in change resistance. We will explore what change resistance looks like and the stages people go through when faced with resistance to change. You will learn how to score change resistance. You can use this assessment to determine your own level of change resistance, the level of change resistance in another person, and the level of change resistance across your team or organization. Knowledge is power. You will no longer guess. Rather, you will have a firm understanding of what you face. Outcome: You will leave this session with a clear understanding of what change is, the psychology of change, and what to expect when you try to change something.
- Part 1 Month 2 Change Resilience – Description: This session will give you the foundational tools to create change resilience. While we will build on these tools with the sessions that follow, this framework will be the foundation upon which you build the rest of this program. Building change resilience begins with clarity. We will begin by exploring how to create this clarity. You will learn the critical boundaries that need to be set to create and sustain change resilience. You will understand the role culture plays, while taking a critical analysis of your own culture. Outcome: The identification of specific boundaries to support your organization as you realize change resilience.
- Part 1 Month 3 Team Personality – Understanding team personality dynamics is essential for effectively managing change and fostering a healthy organizational culture. In this session, you will explore different personality types and their predictable responses to change, gaining insights into how individuals process and adapt to new situations. Recognizing these responses allows leaders to anticipate challenges, tailor communication, and guide teams through transitions more effectively. You will learn techniques to identify personality styles within your team and develop strategies to manage them in a way that promotes collaboration and resilience. By understanding how different personalities react to change—whether with enthusiasm, hesitation, or resistance—you will be better equipped to support your team through uncertainty and ensure smoother transitions. By the end of this session, you will have practical tools to create and sustain organizational health by leveraging personality insights. You will learn how to balance diverse working styles, build stronger relationships, and foster a culture of adaptability, ultimately enhancing your team’s ability to navigate change successfully.
- Part 1 Month 4 Emotional Intelligence – Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a critical skill for navigating change and fostering a resilient, adaptive organization. In this session, you will explore how strong emotions often arise when change is introduced and learn strategies to manage these emotions effectively. Developing EI as an organizational norm allows for healthier communication, stronger relationships, and better decision-making under pressure. You will gain practical tools to recognize and regulate emotions—both your own and those of others—ensuring that emotional reactions do not derail progress or collaboration. Additionally, you will learn techniques to navigate emotional landmines, addressing conflicts and challenges with self-awareness, empathy, and composure. By the end of this session, you will have a deeper understanding of how to meet emotional challenges with intelligence, respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively, and create an emotionally resilient workplace where individuals feel heard, valued, and understood.
- Part 1 Month 5 Effective Communication – Effective communication is essential for clarity, collaboration, and trust within any organization. In this session, you will learn the definition of Effective Communication, explore common reasons why communication breaks down, and practice the Assertive Communication technique. Authenticity, truth, and integrity are critical, especially in difficult conversations, and this session will equip you with strategies to navigate them with confidence. Effective communication occurs when the message sent by the sender matches what the receiver understands. This involves three key components: verbal (actual words used), vocal (tone and inflection), and visual (body language). Since over half of communication is conveyed through body language, extra emphasis must be placed on verbal and vocal elements when communicating in non-visual formats such as emails or phone calls. A key focus of this session is Assertive Communication, which balances between passive and aggressive styles. Communication can be seen as a pendulum: being passive means not expressing needs clearly and expecting others to read between the lines, while being aggressive disregards others’ perspectives in favor of control. The worst combination, passive-aggressive communication, results in unclear expectations and unresolved tension. Assertive communication, by contrast, respects both parties—allowing individuals to courageously speak their truth while also creating space for others to do the same. By the end of this session, you will have actionable strategies to ensure consistent and effective communication across your organization. You will gain tools to enhance clarity, improve collaboration, and build stronger relationships through intentional and respectful communication practices.
- Part 1 Month 6 Present Well – Public speaking is one of the most common fears, yet mastering it is essential for effective leadership and communication. In this session, you will learn how to cultivate the courage to speak up with confidence and clarity, ensuring your message is well received and understood. You will explore techniques to overcome fear, refine your delivery, and engage your audience with impact. By the end of the session, you will have practical strategies to determine when and how to speak up effectively, as well as the skills to command a team or audience with clarity, authority, and presence.
- Part 1 Month 7 Write Well – Effective writing is a powerful tool for driving change and achieving desired outcomes. In this session, you will learn how writing style and nuance influence how messages are received and acted upon. Change resilience does not only occur through direct interaction but also in how written words are interpreted when no one is present to clarify intent. This session is not about grammar rules but about refining your writing style to ensure clarity, engagement, and impact. By the end, you will be equipped with the skills to write in a way that consistently aligns with and reinforces the results you seek to achieve.
- Part 1 Month 8 Team Building – Effective team building requires understanding the four key stages that all teams must go through before reaching high performance. In this session, you will explore the Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning stages, gaining insights into how to successfully navigate each phase. You will also learn strategies to resolve team conflicts and proactively prevent many common challenges. A strong foundation of trust is essential for team success, and you will discover how to cultivate it within your organization. Additionally, you will be introduced to the RACI framework, a powerful tool for clearly defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring alignment, accountability, and collaboration. By the end of this session, you will have a deeper understanding of team dynamics and the skills to guide your team toward sustained high performance.
- Part 1 Month 9 Celebrate Now – Celebration is not just an option—it is a crucial element in building change resilience within an organization. In this interactive session, you will explore why recognizing achievements and milestones fosters motivation, engagement, and adaptability. You will learn the key characteristics of an effective celebration approach and how to implement it consistently across your organization. The methodology emphasizes a proactive rather than reactive approach by intentionally identifying what to celebrate and how to celebrate it. By the end of the session, you will have a documented celebration strategy that can be applied repeatedly, ensuring that recognition becomes an integral part of your organizational culture.
- Part 1 Month 10 Cultivate Feedback – In this session, you will learn the importance of actively seeking and leveraging candid feedback from your employees. Many organizations operate under assumptions, whereas change-resilient organizations thrive by embracing the reality of truth. This session will equip you with the skills to foster an open feedback culture. You will develop a structured feedback tool to use at regular intervals, ensuring you gather honest input and apply it effectively to encourage even greater transparency. The methodology follows a two-step approach: LB (Liked Best)—asking what was effective or well-received, and NT (Next Time)—focusing on what could be improved in the future. This method intentionally avoids asking, “What did I do wrong?” and instead promotes constructive and forward-looking dialogue. Additionally, you will learn how to establish a formalized process for requesting and integrating feedback to strengthen engagement and continuous improvement within your organization.
- Part 1 Month 11 Sustained Inspiration – Description: You will learn how to inventory the progress you have made and sustain this progress over time. Many times organizations start strong, then taper off over time as new priorities surface. You will learn how to maintain the momentum you started. Outcome: Sustained inspiration from your team, even when new business priorities take center stage.Methodology: Proactively assess your progress at set intervals. Train your team at set intervals (say quarterly or annually) to refresh the training learned. Establish clear metrics to assess your team, with goals they must meet each evaluation period.
- Part 1 Month 12 Establish Growth – Description: You will learn how to maintain change resilience as your organization itself grows and changes. Outcome: A plan to handle new hires and employee changes over time. Methodology: Create and document a plan for new hires to get up to speed on all of this. Determine the “trigger” moments when it is time to implement this plan (new hires, reorganization, leadership change, merger/acquisition, etc.) – ensure this is an exhaustive list. This is all about the plan.
Methodology
Change Resilience
Organizations that successfully develop change resilience often rely on structured business processes, frameworks, and methodologies to navigate transitions effectively. These standardized approaches provide a clear path for organizations to manage change, reduce resistance, and enhance adaptability. Below are some of the most widely used methodologies and processes for building change resilience.
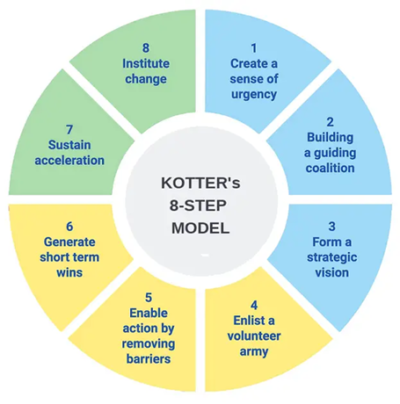
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
Developed by John Kotter, this model provides a structured approach to leading and sustaining change while fostering resilience within an organization.
Key Steps:
1. Create a Sense of Urgency – Communicate why change is necessary and mobilize employees around a shared vision.
2. Build a Guiding Coalition – Form a leadership team to drive change and lead by example.
3. Develop a Change Vision – Establish a clear vision and strategy to guide transformation.
4. Communicate the Vision – Reinforce the change message consistently to all stakeholders.
5. Empower Action – Remove obstacles and enable employees to take ownership of change.
6. Generate Short-Term Wins – Celebrate early successes to maintain momentum.
7. Sustain Acceleration – Use initial successes to drive further change efforts.
8. Anchor Changes in the Culture – Embed resilience into the organization’s culture to ensure long-term adaptability.
This model helps organizations proactively prepare for and navigate change, making resilience an embedded part of the business culture.
ADKAR Change Management Model
The ADKAR model, developed by Prosci, is widely used for managing change at both individual and organizational levels. It emphasizes a structured process for employees to personally transition through change, ensuring that they build resilience along the way.
Note: This program primarily draws on the ADKAR model as the foundation for managing and reinforcing organizational change.

ADKAR Stages:
• Awareness – Understanding why change is necessary.
• Desire – Creating personal motivation to support change.
• Knowledge – Learning new skills and behaviors needed for the transition.
• Ability – Developing the capability to implement change successfully.
• Reinforcement – Ensuring the change sticks and becomes part of daily operations.
This method ensures that employees not only accept change but also actively engage in making it successful, fostering resilience at every level of the organization.
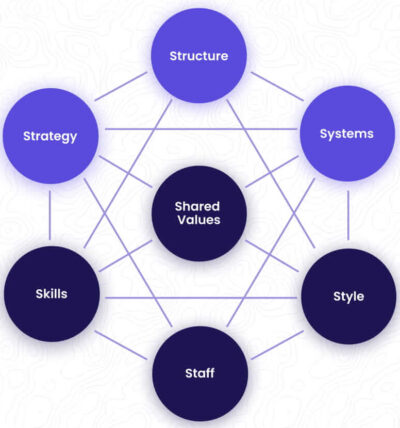
McKinsey 7S Framework
The 7S Framework, developed by McKinsey & Company, is a holistic model that helps organizations align their structure, strategy, and culture to ensure resilience in the face of change.
Key Elements:
• Strategy – The plan to adapt and remain competitive.
• Structure – The way the organization is organized to support change.
• Systems – The internal processes and workflows needed for successful adaptation.
• Shared Values – The cultural foundation that drives behavior during change.
• Style – The leadership approach and management style that supports resilience.
• Staff – The skills, training, and workforce readiness for change.
• Skills – The competencies needed to sustain change over time.
By addressing all seven elements, organizations build resilience not just in individuals but in their entire operational structure.
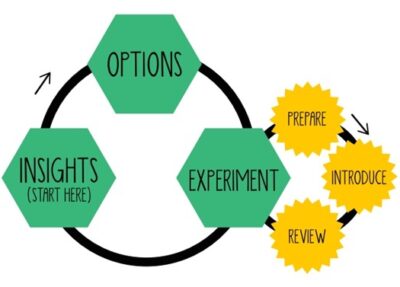
Lean Change Management
Lean Change Management takes an agile, iterative approach to resilience-building, emphasizing experimentation, feedback, and adaptability. It aligns well with organizations undergoing rapid transformation or digital change initiatives.
Core Components:
• Insights-Based Planning – Continuous assessment of organizational readiness.
• Small, Iterative Changes – Implementing and testing change in small increments.
• Stakeholder Engagement – Regular feedback loops to adapt strategies.
• Flexibility Over Rigidity – Adjusting strategies based on real-time data.
This approach helps organizations remain nimble and responsive, allowing them to pivot quickly without major disruption.
Psychological Safety Practices in Change Management
Beyond structured methodologies, resilience is also built through leadership behaviors and workplace culture. Leading organizations integrate psychological safety into their change management processes to ensure employees feel supported during transitions.
Key Strategies:
• Encouraging open dialogue and transparent communication about change.
• Establishing a feedback-rich culture where employees feel heard and valued.
• Providing stress management and resilience training to employees.
• Training leaders in supportive and empathetic behaviors to foster trust.
By prioritizing psychological safety, organizations reduce fear and uncertainty, making employees more receptive to change. Emotional intelligence as a formal focus area will be explored further in a later module of the program.
Agile and Scrum Methodologies for Change Resilience
Agile principles are widely used in software development, project management, and business transformations, making organizations more adaptive and resilient.
How Agile Builds Change Resilience:
• Iterative Adaptation – Teams work in short cycles, allowing for continuous improvement.
• Cross-Functional Collaboration – Employees from different departments work together to drive change.
• Customer Feedback Loops – Frequent adjustments based on user and stakeholder input.
• Decentralized Decision-Making – Employees have more control over how they implement change.
Scrum, a popular Agile framework, breaks down change into manageable sprints, allowing organizations to adapt faster and more efficiently.
Conclusion: The Future of Change Resilience Processes
As change continues to accelerate across industries, resilient organizations will rely on structured methodologies to stay ahead. Whether through traditional frameworks like Kotter’s 8-Step Model and ADKAR, or agile approaches such as Lean Change Management and Scrum, businesses that proactively invest in resilience development will thrive.
Future success will depend on embedding resilience into everyday business operations, prioritizing employee well-being, and creating a culture of continuous learning and adaptability. Organizations that embrace these principles will not only survive change—but lead it.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Aviation
The aviation industry is a cornerstone of the global economy, facilitating the movement of people and goods across vast distances. In 2016, it supported 65.5 million jobs worldwide and contributed approximately $2.7 trillion to the global GDP, accounting for 3.6% of the world’s economic activity.
ICAO.INT
In the United States, commercial aviation is particularly significant, driving 5% of the nation’s GDP, which equates to $1.45 trillion as of 2024. Each day, U.S. airlines operate over 27,000 flights, transporting 2.7 million passengers and 61,000 tons of cargo to and from numerous countries.
Looking ahead, the aviation sector is poised for substantial growth. Projections indicate that by 2036, the industry could directly support 15.5 million jobs and contribute $1.5 trillion to the world economy. When considering the broader impacts, including tourism, these figures could rise to 97.8 million jobs and $5.7 trillion in GDP.
Technological advancements are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of aviation. The development of electric and hybrid aircraft aims to reduce environmental impacts and operational costs. Companies are investing in research to bring electric aircraft into commercial service within the next decade, with some prototypes already having completed inaugural flights.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is another area of focus. Initiatives are underway to produce SAF from renewable sources, such as converting agricultural products like canola oil. For instance, Sydney Airport is exploring the conversion of domestic agricultural products into SAF, positioning itself at the forefront of this emerging industry.
The integration of advanced technologies is also transforming passenger experiences. Self-service options, such as online check-ins and electronic boarding passes, are streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency. The future promises further innovations, including more comprehensive self-service solutions and the potential for single-pilot commercial flights, although the latter remains a topic of debate due to safety considerations.
However, the industry faces challenges, notably supply chain disruptions affecting aircraft production. Despite high demand, manufacturers are grappling with delays due to parts shortages and labor constraints. The Farnborough International Airshow highlighted these issues, emphasizing the need for resilience in production processes to meet growing demands.
In summary, the aviation industry remains a vital component of the global economy, with promising prospects driven by technological advancements and a focus on sustainability. Addressing current challenges will be crucial to realizing its full potential in the coming years.

Government
The government sector plays a pivotal role in shaping national economies, influencing various aspects of society through its policies, expenditures, and regulatory frameworks. Quantifying its exact economic value is complex, as it encompasses a wide range of activities, from public services to infrastructure development. However, its impact is undeniably substantial, with government spending accounting for a significant portion of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in many countries. In the United States, for example, government consumption expenditures and gross investment contribute notably to the nation’s GDP.
In recent years, the government sector has been undergoing a transformation driven by technological advancements and a growing demand for efficient public services. The integration of digital technologies has become a cornerstone of modern governance, leading to innovations such as data-sharing programs and cloud migration. These initiatives aim to enhance transparency, improve data management, and facilitate better decision-making processes.
Looking ahead, several key trends are poised to shape the future of the government sector. One of the most significant developments is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Governments are increasingly adopting AI to enhance service delivery and operational efficiency. AI-powered systems are expected to enable proactive governance, allowing for real-time responses to citizen needs and more efficient resource allocation.
Another critical trend is the emphasis on sustainability initiatives. With the growing urgency of climate change, governments are prioritizing investments in sustainable infrastructure and renewable energy projects. Public spending is expected to rise in areas such as sustainable urban development and climate resilience, reflecting a commitment to environmental stewardship.
Public sector innovation is also transforming governance by placing citizens at the center of service design and delivery. Governments are leveraging technology to create more responsive and personalized services, which enhances public satisfaction and strengthens trust in institutions. This shift ensures that government services remain accessible, effective, and tailored to meet evolving societal needs.
Despite these advancements, the government sector faces significant challenges, particularly in managing public expenditures and ensuring fiscal sustainability. High public sector employment can sometimes lead to lower overall productivity, as resources may be diverted from more efficient private sector activities. Additionally, increasing public spending necessitated by crises and long-term investments raises concerns about managing public debt and maintaining financial stability.
In summary, the government sector remains a fundamental component of national economies, with its policies and expenditures playing a crucial role in shaping economic and social outcomes. As it navigates the complexities of the modern world, embracing technological advancements and sustainable practices will be essential in addressing current challenges and maximizing future opportunities.

Financial Services
The financial services industry is a cornerstone of the global economy, encompassing sectors such as banking, insurance, investment management, and real estate. In 2024, the industry was valued at approximately $33.54 trillion, accounting for about 31% of the world’s economy. Its vast influence extends across businesses and individuals, providing essential financial infrastructure and support for economic growth and stability.
In the United States, the financial services and insurance sectors play a significant role in national employment, with over 6.7 million people working in the industry as of mid-2024. The sector’s contributions extend beyond employment, driving economic development, investment, and consumer financial security.
Looking ahead, several key trends are set to shape the future of financial services. One of the most impactful developments is Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration. AI is revolutionizing financial services by enhancing customer interactions through chatbots and virtual assistants while optimizing back-office operations. Generative AI, in particular, is expected to transform financial planning and wealth management by providing personalized insights and automating complex tasks.
The rise of digital banking and remote services is another major shift. As online and mobile banking continue to gain traction, customers can perform most financial activities remotely. However, some functions, such as cash deposits and notarizations, still require in-person visits. This trend suggests a future where digital banking dominates, offering convenience while traditional branches become less common.
Regulatory evolution is also influencing the industry. Regulatory bodies are moving away from rigid, detailed rules and adopting more flexible oversight frameworks. This shift is aimed at reducing uncertainty and encouraging investment while ensuring compliance and financial stability.
With increased digitalization comes a heightened focus on cybersecurity and risk management. As financial institutions handle vast amounts of sensitive data, the rise of sophisticated scams, including those powered by generative AI, has led to significant financial losses. Banks and financial firms are investing heavily in advanced cybersecurity protocols and employee training to counter these evolving threats.
Another major trend shaping the industry is sustainable finance. There is a growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations in investment strategies and financial products. Institutions are integrating ESG criteria into their operations, reflecting a broader commitment to sustainability and responsible finance.
In summary, the financial services industry remains a dynamic and integral part of the global economy. To thrive in this rapidly evolving landscape, institutions must embrace technological advancements, adapt to regulatory changes, and prioritize cybersecurity and sustainability. These factors will be key in shaping the future of financial services and ensuring its continued growth and resilience.

Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is a cornerstone of the global economy, encompassing a vast array of sectors such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. In 2024, the global manufacturing market was valued at approximately $14.16 trillion, with projections indicating growth to $20.76 trillion by 2031. This reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9%, highlighting the sector’s continuous expansion and economic significance.
The United States plays a major role in this industry, accounting for 16.6% of the global manufacturing market share, with a market size of $2.24 trillion in 2023. Similarly, countries like Japan and Germany also hold substantial shares, emphasizing the industry’s global distribution and interconnected nature. Manufacturing remains a crucial driver of economic development, employment, and technological progress worldwide.
The industry is currently experiencing a transformative phase, often referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0. This evolution is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies aimed at enhancing efficiency, productivity, and adaptability. One major trend shaping the future of manufacturing is the development of smart factories, where cyber-physical systems and the Internet of Things (IoT) enable real-time monitoring and autonomous decision-making. These innovations improve efficiency and responsiveness in production environments.
Another key advancement is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI-driven analytics optimize production schedules, predict maintenance needs, and enhance quality control, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs. Additionally, sustainable manufacturing is gaining momentum, with an increasing emphasis on eco-friendly practices such as renewable energy integration, waste reduction, and the development of sustainable products. This shift is driven by both regulatory requirements and growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible manufacturing.
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is also revolutionizing the sector, enabling rapid prototyping and customized production while minimizing material waste. Meanwhile, digitalization and data analytics are transforming manufacturing operations by providing deeper insights into supply chain management, optimizing processes, and enhancing overall competitiveness.
Despite these advancements, the manufacturing sector faces several challenges, including supply chain disruptions, fluctuating energy costs, and geopolitical uncertainties. For example, high energy prices in certain regions, such as the UK, have impacted industrial competitiveness, highlighting the need for strategic energy management and cost control.
In summary, the manufacturing industry remains a vital component of the global economy. Ongoing technological innovations and a focus on sustainability are driving its evolution, and by embracing these trends, manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic market.

Consumer Goods
The consumer goods industry, which includes sectors such as food and beverage, household items, personal care, and apparel, is a vital pillar of the global economy. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately $14.5 trillion, with projections indicating growth to $20.8 trillion by 2031. This expansion reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9%, highlighting the industry’s continuous evolution and economic impact.
Among these sectors, the food and beverage industry remains the largest, accounting for $8.3 trillion in 2024. This dominance underscores the essential nature of these products and their consistent demand across global markets. As consumers prioritize convenience, quality, and sustainability, brands in this sector are continuously innovating to meet evolving preferences.
Looking ahead, several key trends are shaping the future of the consumer goods industry. One of the most significant is the shift toward sustainability and eco-friendly products. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing environmentally responsible goods, prompting brands to develop sustainable offerings and create transparent supply chains. Companies that integrate sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive edge as environmental consciousness continues to influence purchasing decisions.
Technological integration and artificial intelligence (AI) are also revolutionizing the industry. AI-driven innovations are transforming personalized marketing strategies, improving supply chain efficiency, and enhancing product development. In the beauty sector, for example, AI is enabling customized skincare solutions and virtual try-on experiences, offering a more tailored approach to consumer engagement.
Another major trend is the rise of personalization and consumer engagement. Brands are leveraging data analytics to provide personalized products and shopping experiences, fostering deeper consumer loyalty. Customization, from tailored marketing campaigns to unique product formulations, is becoming a crucial strategy for companies looking to differentiate themselves in a crowded market.
The growing emphasis on health and wellness is also reshaping the industry. Consumers are seeking products that promote well-being, leading to an increased demand for healthier options, natural ingredients, and transparent sourcing. Companies that align with this trend by offering nutritious food choices, clean-label beauty products, and wellness-focused innovations are well-positioned for future success.
Additionally, e-commerce expansion continues to redefine the consumer goods landscape. The shift toward online shopping has accelerated, prompting brands to invest in digital marketing strategies and robust e-commerce platforms. As consumers increasingly prefer the convenience of online shopping, businesses must optimize their digital presence to remain competitive.
Despite these opportunities, the industry faces challenges such as supply chain disruptions, fluctuating commodity prices, and evolving consumer preferences. Commodity prices are projected to remain elevated, posing cost management challenges for manufacturers. Navigating these uncertainties will require strategic planning and adaptability.
In summary, the consumer goods industry is experiencing rapid transformation driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and sustainability imperatives. Companies that embrace innovation, respond to shifting market demands, and proactively address industry challenges will be well-positioned to thrive in the evolving global marketplace.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Miami, FL
Miami, located in southeastern Florida, is a major center for finance, commerce, culture, and international trade. As of 2023, the Miami-Fort Lauderdale-West Palm Beach metropolitan area boasts a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of approximately $533.67 billion, underscoring its significant economic influence within the state and beyond.
The city’s economy is diverse, encompassing sectors such as banking, tourism, real estate, and international trade. Downtown Miami hosts one of the largest concentrations of international banks in the United States, reflecting its pivotal role in global finance. The Port of Miami stands as the world’s busiest cruise port, significantly contributing to the local economy through tourism and trade.
In terms of employment, the Miami metropolitan area had an unemployment rate of 2.2% as of May 2024, indicating a relatively strong job market. The financial services and insurance sectors are particularly prominent, employing over 6.7 million people nationwide as of mid-2024, with Miami being a significant contributor to this figure.
The real estate market in Miami has experienced notable growth, with luxury office space rents reaching record highs. Buildings like 830 Brickell have seen rents approaching $200 per square foot, driven by an influx of companies relocating from cities such as New York, attracted by Miami’s favorable tax environment and growing business opportunities.
Demographically, Miami is a majority-minority city, with a Hispanic and Latino population comprising 70.2% of its residents as of 2020. This cultural diversity enriches the city’s social fabric and contributes to its dynamic economic landscape.
In summary, Miami’s economy is robust and multifaceted, characterized by strong performance in finance, tourism, real estate, and international trade. Its strategic location, cultural diversity, and business-friendly environment continue to attract investment and talent, solidifying its status as a key economic hub in the United States.

Atlanta, GA
Atlanta, the capital city of Georgia, serves as a significant economic hub in the southeastern United States. As of 2023, the Atlanta metropolitan area’s real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was approximately $471.66 billion, reflecting its substantial contribution to both the state and national economies.
The city’s economy is diverse, encompassing key sectors such as finance, transportation, media, and technology. Atlanta is home to the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, which oversees the sixth district of the Federal Reserve System, underscoring the city’s importance in national financial operations.
Transportation plays a pivotal role in Atlanta’s economic landscape. Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport is recognized as the world’s busiest airport, facilitating both passenger travel and cargo transit. This status not only bolsters the city’s connectivity but also attracts businesses that rely on efficient logistics.
The city also boasts a significant corporate presence, with 31 Fortune 1000 companies headquartered in the metropolitan area. Notable corporations include The Home Depot, United Parcel Service (UPS), and The Coca-Cola Company. This concentration of major companies highlights Atlanta’s role as a center for corporate operations and its appeal to large businesses.
In terms of employment, the Atlanta metropolitan area has demonstrated resilience and growth. As of January 2025, the region reported an unemployment rate of 3.3%, indicating a robust job market. The professional and business services sector is a significant employer, reflecting the city’s diversified economic base.
The technology sector in Atlanta has seen notable expansion, earning the city the nickname “Silicon Peach.” As of 2013, Atlanta contained the fourth-largest concentration of IT jobs in the U.S., numbering over 85,000 positions. The city’s lower costs and educated workforce continue to attract technology companies, contributing to ongoing growth in this sector.
Media and entertainment also contribute significantly to Atlanta’s economy. The city has become a prominent center for film and television production, largely due to the Georgia Entertainment Industry Investment Act, which offers tax incentives to productions. In 2017, film and television production injected $9.5 billion into Georgia’s economy, with Atlanta garnering most of the projects.
In summary, Atlanta’s economy is robust and multifaceted, characterized by strengths in finance, transportation, corporate operations, technology, and media. Its strategic location, infrastructure, and business-friendly environment continue to attract investment and talent, solidifying its status as a key economic center in the United States.

New York
New York State stands as a formidable economic powerhouse within the United States, boasting a Gross State Product (GSP) of approximately $2.284 trillion in 2024, ranking third nationally behind California and Texas. If New York were an independent nation, it would position as the 10th largest economy globally by nominal GDP.
The state’s economic landscape is diverse, with significant contributions from finance, insurance, real estate, and professional services. In the third quarter of 2023, the finance and insurance sector alone generated a real GDP of $395.4 billion, underscoring its pivotal role in the state’s economy.
New York City, the state’s largest metropolis, is a central driver of this economic activity. In 2023, the city’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was approximately $1.286 trillion, with Manhattan accounting for $939 billion, or 73% of the city’s total GDP.
The city’s economy is multifaceted, encompassing sectors such as finance, healthcare, technology, and tourism. As of November 2023, New York City had total employment of over 4.75 million, with more than a quarter employed in education and health services. Manhattan alone accounted for more than half of the city’s jobs, with an average weekly wage of $2,590 in the second quarter of 2023, ranking fourth-highest among the nation’s 360 largest counties.
Despite its economic strengths, New York faces challenges, including income inequality and a higher unemployment rate compared to the national average. In October 2024, New York City’s unemployment rate stood at 5.4%, higher than the U.S. rate of 4.1%. The Bronx and Brooklyn experienced the highest unemployment rates within the city, at 6.9% and 5.7% respectively.
Recent developments have also highlighted the state’s fiscal dynamics. In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, New York’s legal marijuana industry is projected to generate $161.8 million in tax revenues, a significant increase from the $43.3 million collected in the previous year. This burgeoning sector is anticipated to contribute $248 million in the next fiscal year, reflecting the state’s efforts to diversify its revenue streams.
In summary, New York’s economy is robust and diverse, anchored by its significant contributions to finance, insurance, and real estate. While the state continues to leverage its strengths, it must also address ongoing challenges to ensure sustained economic prosperity.
Chicago, IL
Chicago, the largest city in Illinois, serves as a major economic hub in the United States. As of 2023, the Chicago-Naperville-Elgin metropolitan area reported a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of approximately $725.75 billion, underscoring its significant contribution to both the state and national economies.
The city’s economy is notably diverse, encompassing key sectors such as finance, manufacturing, real estate, and wholesale trade. In 2022, Chicago’s nominal GDP reached an estimated $822 billion, with substantial growth observed in manufacturing, real estate, and wholesale trade sectors. Specifically, the manufacturing sector expanded by over $11 billion during that year.
Chicago is home to a significant number of major corporations, including 31 Fortune 500 companies. Notable firms headquartered in the city include McDonald’s, United Airlines, and Blue Cross Blue Shield. This concentration of corporate headquarters highlights Chicago’s role as a central hub for business operations.
In terms of employment, the Chicago metropolitan area supports a substantial labor force. As of January 2025, the region reported an unemployment rate of 4.4%, reflecting a stable job market. The professional and business services sector is a significant employer, contributing to the city’s diversified economic base.
The city’s financial sector is particularly prominent, with Chicago serving as a major world financial center. It hosts the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago and is home to leading financial and futures exchanges, including the Chicago Stock Exchange, the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (the “Merc”). In 2017, Chicago exchanges traded 4.7 billion in derivatives, underscoring the city’s pivotal role in global finance.
Despite its economic strengths, Chicago faces challenges such as fluctuations in business activity. The Chicago Business Barometer, also known as the Chicago Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), has indicated periods of contraction in recent years. For instance, in October 2024, the index dropped to 41.6 from 46.6 the previous month, marking its lowest point in five months and remaining below the breakeven threshold of 50 for 11 consecutive months. This decline has been partly attributed to factors such as strikes affecting major manufacturers like Boeing, which have reduced production levels.
In summary, Chicago’s economy is robust and multifaceted, characterized by strengths in finance, manufacturing, real estate, and corporate operations. Its strategic location, diverse industrial base, and status as a transportation hub continue to attract investment and talent, solidifying its position as a key economic center in the United States.

Charlotte, NC
Charlotte, North Carolina, stands as a significant economic hub in the southeastern United States, with a diverse economy encompassing finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy sectors. As of 2023, the Charlotte-Concord-Gastonia metropolitan area’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was approximately $255.7 billion, reflecting its substantial contribution to both state and national economies.
The city’s prominence in the financial sector is notable, being the second-largest banking center in the United States after New York City. Charlotte is home to the headquarters of Bank of America, the nation’s second-largest financial institution by assets, and Truist Financial, the sixth-largest. Additionally, Wells Fargo maintains its East Coast operations in the city, further solidifying Charlotte’s status as a banking powerhouse.
In terms of employment, the Charlotte metropolitan area supports a robust labor market. As of December 2022, the region’s nonfarm employment increased by 4.6% year-over-year, adding approximately 58,500 jobs, which represents about 31.4% of the state’s total job growth during that period. The unemployment rate in the city stood at 3.7% in November 2022, slightly higher than the national average of 3.4%.
The healthcare sector is a major employer in the region, with Atrium Health leading as the largest employer, providing jobs to approximately 35,700 individuals. Other significant employers include Wells Fargo, Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools, and American Airlines, each contributing substantially to the local economy.
Manufacturing also plays a vital role in Charlotte’s economy. The city has seen growth in this sector, with a 1.9% increase in manufacturing employment as of December 2022, adding around 2,000 jobs. This expansion underscores the city’s diversified economic base and its capacity to attract and retain manufacturing enterprises.
The energy sector, particularly utilities, is another cornerstone of Charlotte’s economic landscape. Duke Energy, one of the largest utility companies in the United States, is headquartered in the city, highlighting its significance in the energy industry.
In summary, Charlotte’s economy is robust and multifaceted, characterized by strengths in finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy. Its strategic location, diverse industrial base, and business-friendly environment continue to attract investment and talent, solidifying its status as a key economic center in the United States.
Program Benefits
Information Technology
- System Stability
- Security Adaptability
- Incident Response
- Process Efficiency
- Scalable Solutions
- Technology Adoption
- Risk Mitigation
- Agile Development
- Data Protection
- Automation Readiness
Management
- Decision Agility
- Crisis Leadership
- Strategic Flexibility
- Risk Awareness
- Employee Trust
- Conflict Resolution
- Clear Communication
- Operational Stability
- Leadership Confidence
- Goal Alignment
Human Resources
- Talent Retention
- Workforce Adaptability
- Policy Flexibility
- Employee Engagement
- Cultural Alignment
- Conflict Management
- Onboarding Efficiency
- Skill Development
- Diversity Inclusion
- Crisis Support
Testimonials

UPS (United Parcel Service)
Background: As the result of Covid business shifts, a leading package delivery company faced mandated changes to their operations. Their peak season hiring process shifted to include a technology change and workforce reduction. This impacted operations and processes, yet they were at 0% change adoption. They hired our boutique change management firm to create and sustain change adoption for this mandated change.
Results: This client went from 0% to over 30% adoption as a result of our accelerated 2-month engagement.
Approach: We used a five-phase solution, which aligned outcomes with organizational goals. We trained the 1,000 employees in this department. We also trained and coached the top 25 executives.
Solution:
1. Phase One: The Change Process. Our team facilitated strategy day sessions with key stakeholders and evaluated relevant data, using our Baseline Assessment Process. Our deliverable established priorities, based on buy-in, and determined our engagement roadmap.
2. Phase Two: Train and Prepare the Leaders. We identified and overcame objections to foster needed senior level executive support. We built consensus while establishing accountability. Our deliverable addressed challenges, concerns, resistance, and solutions.
3. Phase Three: Train and Prepare the Employees. This department of 1,000 employees each learned our Five Distinctions of Leadership program. They practiced, with trainer feedback, how to apply it to their current change. As an example, one solution included a specific way to gain buy-in from change champions, while experiencing change resistance. Each participants received a guidebook, with the step-by-step training solutions.
4. Phase Four: Employee Implementation Coaching. We delivered one-on-one coaching to the top 25 executives, designed to support their role as leaders in driving employee adoption. This coaching addressed individual needs with real-time feedback.
5. Phase Five: Ongoing Monitoring. We assessed program success and obtained client feedback. This client went from 0% to over 30% adoption from our accelerated 2-month engagement, exceeding our target by over 20%. We set the stage to continue our Phase Five work.
Client Feedback:
“As a new executive in a company that historically promoted from within, I faced unique challenges as an outsider. Your training program addressed our change adoption challenges, even turning a key executive into our strongest advocate. We finally began to see adoption. Hiring you was the best decision I have made!” Danelle M.
“As a result of this engagement we have seen a shift not only in our leadership, but our entire department. Thank you, and your team, for the great results you helped us create. We truly shifted from change resistant to change resilient.” Dan H. and Tayo F.
“When we first met, I did not know what to expect. We mostly only used Accenture for change management. I knew we needed additional support that was nimble and quick to get change adoption. You were easy to work with, delivered the training results you promised, and even won over our leadership team. Our organization embraced this change. I look forward to our next engagement together.” Kelly P.
Eastex Credit Union
“We started working with Ms. Aikerson in 2016. Initially we hired her to train our leadership team. For years she helped us address numerous leadership topics through her highly interactive approach that ensured success with our diversity of personalities. Given her track record of delivering training results we expanded this work to include training our entire organization in 2020. For three years we hired Ms. Aikerson and her team to train our entire organization. During this time we went from an annual revenue of $29 million to $188 million – a significant increase! Our training work with Ms. Aikerson has resulted in the realization of our most critical results to success at a time of tremendous change.”
Team Member Quotes During Final Training Program (documented December 2022):
Shannon Hargroder (employee): “This training was spot on, I learned so much that will help me navigate this change. I learned to always treat others with kindness and work hard. The trainer was informative, enthusiastic, direct, and kind.”
Renee Will (VP): “This work has helped the management team and helped the employees. We communicate better and are now able to coach each other in a way that is working.”
Loretta Chatagnier (CEO): “As a result of the training we did with Ms. Aikerson and her team, our annual revenue is now at $188 million (we were at $29 million when started this training program). This is a significant increase! Our training work with Ms. Aikerson has resulted in the realization of our most critical results to success at a time of tremendous change.”

CDC (The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
“Ms. Aikerson became a CDC training vendor in January of 2015. During this time Ms. Aikerson and her team has consistently facilitated numerous training topics, helping our leaders and employees across multiple disciplines, to realize their goals and adapt to the changes this agency has faced, including during the Covid-19 global pandemic. Her training approach leverages adult learning techniques such that the materials are easy to understand and directly applicable to our day to day work. She incorporates real-world scenarios into her solutions so that we can be successful the first time. Her solutions invite you to want to immediately apply them so you can realize the benefits, results, and solutions you’ve always wanted. I highly recommend Ms. Aikerson’s training programs to anyone interested in creating real results and realizing true commitment from their teams to apply the training lessons learned.”

FEMA (The Federal Emergency Management Agency)
“I first hired Ms. Aikerson to train for us when I was the training director for OSHA (Occupational Health and Safety Administration). After meeting with her and introducing her to our other training decision makers I found her solution to our training needs very “cutting edge” and results oriented. We hired her to facilitate our big training event, where we flew in team members from across our region for the big event. Ms. Aikerson was a hit! I got continually feedback that her content was not only easy to apply and understand, but they also found her step-by-step approach made it almost impossible to not want to use that they learned immediately – the moment they returned to the office.
Based on this success when I left OSHA and transitioned to FEMA as their training director, I asked Ms. Aikerson to facilitate our key training programs there as well. As usual, she was a hit. Ms. Aikerson has taught our annual training programs for a few years now. I’ve personally attended just about every program she facilitated. She makes information come to life with her easy to follow steps and cutting edge content. After each of her programs there is a flurry of activity as everyone implements the specific steps Ms. Aikerson not only outlined, but helped us to practically understand within the context of our specific work challenges.
By design our agency must face continually change. Our ability to embrace this change and create immediate and sustained results is due, in part, to the great training we get from Ms. Aikerson.“
![]()
Delta Air Lines
“Having worked with Ms. Aikerson in the past on Change Management efforts, I knew I wanted to hire Ms. Aikerson when I transitioned into a new role and needed to do a global event with hundreds of Customer Service leaders. This multi-day event had to go off without a hitch. Not only was my name on the line, but my leadership was counting on these sessions to create tangible workplace results. First, Ms. Aikerson’s training program kept everyone’s attention—she made complex topics easy to understand and embrace. Second, Ms. Aikerson motivated action—one participant, in the middle of the training, took the microphone and wanted to explain the “ah-ha” moment he just experience and how it would make him a better leader. Third, Ms. Aikerson inspired everyone to create tangible results—her program literally walked people through what to do when they returned to the office, inspiring a results-oriented mindset. Some even engaged in a friendly competition to see who could realize the specific results first.
I give Ms. Aikerson’s programs my highest recommendation to anyone who must realize immediate training results.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.