Transformational Leadership

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Transformational Leadership is provided by Dr. Keis Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Dr. Keis, is a globally recognized authority on behavioral assessment strategies and processes and an expert in leadership, purpose, and wellness. He has spent over three decades serving thousands of companies, associations, industry groups, and leaders in over 30 countries. He has been recognized as one of the top three Leadership Development consultants and boasts one of the Top Ten Coaching Processes globally by HR.com Lead 500 Awards.
Dr. Keis is a prolific content creator, having authored over 4 million words of content, including 4 books and a dozen assessments. Dr. Keis has conducted more than 3,000 presentations and 10,000 hours of coaching and consulting, earning him a reputation as a sought-after author, speaker, trainer, podcast host, and media guest.
Beyond his professional work, Dr. Keis is deeply committed to his community. He has served as director, chair, or president of several community groups and has consistently donated his expertise to youth events and initiatives. He is the 2023 recipient of the 4-H Canada Distinguished Alumni Award, further recognizing his commitment to leadership and service.
From his humble beginnings as a dairy farmer, to his achievements as a globally recognized expert in professional development, Dr. Keis is a shining example of how one can overcome personal obstacles, such as dyslexia, and make substantial contributions to global industries and societies. His story, expertise, and commitment to purpose-driven work make him an exemplary role model for aspiring professionals in any field.
To request further information about Dr. Keis through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Transformational Leadership
Unlock your leadership potential with our comprehensive 12-month program, derived from 44 years of rigorous research and previously the backbone of a 160-hour university course. Targeted at individuals across the leadership spectrum, from supervisors to CEOs, our program encompasses 12 principles and 60 skills within five crucial categories. As a participant, you will journey from self-awareness to self-mastery, refining your abilities in self-management, interpersonal communication, coaching, accountability, problem solving, team and consulting skills, and organizational development. Harness the power of our five proven online assessments to catalyze your personal and professional growth, and join a community of transformational leaders shaping the future.
Leaders undergo a remarkable transformation, mastering 60 transformational leadership skills across a year-long journey. Our course takes you deep into self-exploration, leveraging personal style indicators and values to enhance your leadership potential. Beyond individual skills, we highlight the art of teamwork, coaching, and organizational development, all geared towards crafting resilient, empathetic, and strategic leaders for our modern world.
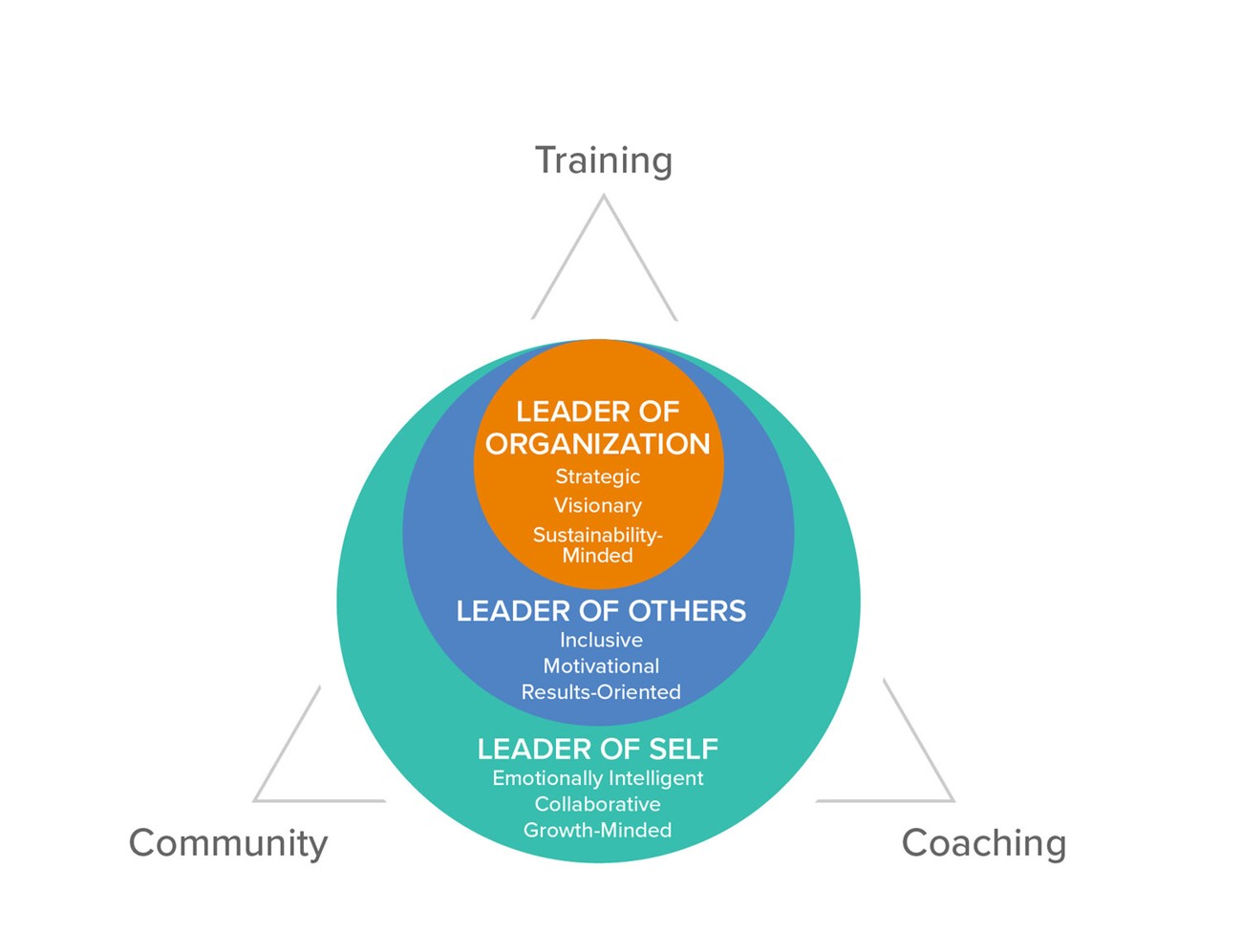
Source: Sr4 Partners
Transformational leadership is an approach to leadership that emphasizes a comprehensive and interconnected view of individuals and their roles within organizations and society as a whole. It goes beyond traditional leadership theories that focus solely on specific aspects of leadership, such as task-oriented or people-oriented approaches, and instead considers a broader perspective that takes into account the well-being of individuals, the organization, and the larger ecosystem in which it operates.
Transformational leadership recognizes that individuals are multifaceted beings with physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual dimensions. It acknowledges the importance of nurturing these different aspects of individuals to promote their personal growth and fulfillment, as well as their effectiveness as leaders. Moreover, transformational leadership recognizes the interconnectedness of individuals within teams, organizations, and the larger community or society, understanding that actions and decisions made in one area can have ripple effects elsewhere.
The concept of transformational leadership draws from various disciplines, including psychology, philosophy, systems thinking, and spirituality. It integrates elements of emotional intelligence, ethical decision-making, mindfulness, self-awareness, and the ability to inspire and empower others. It emphasizes the development of leaders who are not only competent in their technical skills but also possess qualities such as empathy, resilience, adaptability, and a long-term perspective.
The origins of transformational leadership can be traced back to the evolution of leadership theories and practices over time. It builds upon earlier approaches such as transformational leadership, servant leadership, and authentic leadership, which also recognized the importance of a more inclusive and value-based leadership style. However, transformational leadership takes this further by incorporating a broader perspective that encompasses the well-being and interconnectedness of individuals, organizations, and society.
It is worth noting that transformational leadership is not limited to a specific cultural or geographical origin. Instead, it has emerged as a response to the complex and interconnected challenges faced by leaders in various contexts, including businesses, nonprofit organizations, government, and community settings. Its principles and practices can be applied in diverse leadership contexts and are adaptable to different cultures and situations.
Overall, transformational leadership promotes a more integrative and compassionate approach to leadership that seeks to create positive and sustainable outcomes for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.

Source: www.linkedin.com
Why Transformational leadership is so effective
Transformational leadership is effective for several reasons:
Comprehensive Perspective
Transformational leadership takes into account the various dimensions of individuals and their interconnectedness with the larger system. This broader perspective allows leaders to understand the complex dynamics at play and make decisions that consider the well-being of all stakeholders involved. By considering the holistic picture, leaders can better identify and address root causes of issues rather than just treating symptoms.
Enhanced Well-being: Transformational leadership emphasizes the well-being and growth of individuals. By fostering a supportive and inclusive work environment, leaders can enhance employee satisfaction, engagement, and motivation. When employees feel valued and supported, they are more likely to be productive, creative, and committed to the organization’s goals.
Increased Resilience
Transformational leaders promote resilience by focusing on the development of individuals’ physical, emotional, and mental well-being. By encouraging self-care practices, stress management techniques, and promoting work-life balance, leaders help employees better cope with challenges and bounce back from setbacks. This resilience contributes to higher levels of performance and adaptability.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Transformational leadership emphasizes the importance of collaboration and teamwork. By fostering a culture of trust, open communication, and shared goals, leaders can create an environment where individuals feel empowered to contribute their unique skills and perspectives. This collaborative approach leads to more effective problem-solving, innovation, and synergy within teams.
Ethical and Values-Based Leadership
Transformational leadership emphasizes ethical decision-making and values-based actions. By aligning the organization’s mission and values with the leader’s actions, trust and credibility are established. This ethical foundation contributes to positive organizational culture, reputation, and stakeholder relationships.
Long-term Perspective
Transformational leadership encourages leaders to take a long-term view and consider the sustainable impact of their decisions. This perspective involves balancing short-term goals with the long-term consequences on the organization, its stakeholders, and the environment. By considering the broader implications, leaders can make choices that promote long-term success and create a positive legacy.
Adaptability and Change Management
Transformational leaders recognize the need for adaptability in a rapidly changing world. They encourage learning, personal growth, and continuous improvement among themselves and their teams. This adaptability helps organizations navigate uncertainty, embrace innovation, and respond effectively to evolving challenges and opportunities.
In summary, transformational leadership is effective because it incorporates a comprehensive perspective, promotes well-being, resilience, collaboration, ethical decision-making, and long-term thinking. By considering the interconnectedness of individuals and systems, transformational leaders create environments that support individuals’ growth and the organization’s success.
Transformational leaders
There are several notable leaders who promote transformational leadership in their approach and have made significant contributions to this field. Here are a few examples:
• Satya Nadella: Satya Nadella is the CEO of Microsoft and is known for his advocacy of a more transformational leadership style. Under his leadership, Microsoft has embraced a growth mindset, focusing on empathy, collaboration, and inclusivity. Nadella encourages a culture of continuous learning, personal growth, and well-being, which has helped transform Microsoft into a more innovative and customer-centric organization.
• Arianna Huffington: Arianna Huffington is the co-founder of The Huffington Post and the founder of Thrive Global, a company focused on promoting well-being and reducing stress and burnout. She is a vocal advocate of the importance of sleep, mindfulness, and self-care in leadership. Huffington emphasizes the need for leaders to prioritize their own well-being as well as the well-being of their teams to foster a more sustainable and successful work environment.
• Richard Branson: Richard Branson, the founder of the Virgin Group, is known for his transformational and people-centered leadership style. He emphasizes the importance of employee empowerment, work-life balance, and nurturing a positive company culture. Branson believes that putting employees first creates a positive ripple effect, leading to happier customers, higher productivity, and business success.
• Mary Barra: Mary Barra is the CEO of General Motors and has been recognized for her transformational leadership style. She promotes a collaborative and inclusive work environment, valuing diversity and teamwork. Barra encourages open communication, innovation, and ethical decision-making, while also prioritizing employee development and well-being.
• Dalai Lama: Although not a traditional corporate leader, the Dalai Lama, the spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhism, is often mentioned in discussions of transformational leadership due to his emphasis on compassion, mindfulness, and interconnectedness. His teachings highlight the importance of leading with values, promoting peace, and considering the broader impact of our actions on others and the world.
These are just a few examples of leaders who embrace and promote transformational leadership principles in their respective fields. They demonstrate that transformational leadership can be applied across industries and sectors, contributing to positive organizational cultures, employee well-being, and sustainable success.

Source: Entrepreneur
The Transformational Leadership Program is designed to empower individuals with a comprehensive and interconnected approach to leadership, enabling them to thrive in today’s complex and evolving world. By participating in this program, you will experience transformative personal and professional growth, gaining valuable skills and insights that will positively impact their lives and their leadership effectiveness.
By participating in our Transformational leadership program, individuals will unlock their full leadership potential, lead with authenticity, and make a positive impact in their organizations and communities. You will experience personal growth, enhanced well-being, and the ability to navigate complex challenges, ultimately becoming effective and influential leaders who create positive and sustainable outcomes.
Curriculum
Transformational Leadership – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Introduction and Leadership Principles
- Part 1 Month 2 Self-Management and Leadership Style
- Part 1 Month 3 Discovering Personal Values
- Part 1 Month 4 Stress Management and Health Practices
- Part 1 Month 5 Interpersonal Communication Skills (Part One)
- Part 1 Month 6 Interpersonal Communications Skills (Part Two)
- Part 1 Month 7 Coaching, Accountability and Problem Management Skills (Part One)
- Part 1 Month 8 Coaching, Accountability and Problem Management Skills (Part Two)
- Part 1 Month 9 Team and Consulting Skills (Part One)
- Part 1 Month 10 Team and Consulting Skills (Part Two)
- Part 1 Month 11 Versatility and Organizational Development
- Part 1 Month 12 Application of Transforming Leadership Skills
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Transformational Leadership corporate training program.
Transformational Leadership – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Introduction and Leadership Principles – Immerse yourself in the world of transformative leadership. Delve into the 12 essential principles, understand your leadership style, and learn about the 60 skills needed for transformational development. Self-assessment is just the beginning of this exciting leadership journey.
- Part 1 Month 2 Self-Management and Leadership Style – Enhance your self-management and leadership style through in-depth case studies. Understand the motivations of others, and discover what this means for your unique style. Learn to adjust your style for optimal engagement and job fit.
- Part 1 Month 3 Confirming your Beliefs and Discovering your Personal Purpose and Values – Knowing oneself deeply is critical to successful leadership. We will take you through a journey of self-discovery and confirmation of your beliefs and purpose and what do you truly value? Find out in this introspective module. Align your actions with your motivational values and get clarity on your life’s priorities and direction. Embrace mindfulness and emotional intelligence for a well-rounded leadership approach.
- Part 1 Month 4 Stress Management and Health Practices – Learn to navigate stress and maintain your health for sustainable leadership. Use our comprehensive Stress Indicator and Health Planner to develop your personal wellness plan. Find your equilibrium and enhance your resilience in stressful situations.
- Part 1 Month 5 Interpersonal Communication Skills (Part One) – Embark on the journey of honing your interpersonal communication skills. Learn to self-disclose appropriately, manage impressions effectively, and cultivate unbiased understanding of others. Practical exercises help you master these skills in real-life scenarios.
- Part 1 Month 6 Interpersonal Communications Skills (Part Two) – Dive deeper into the world of interpersonal communication. Develop your skills in questioning, listening, and responding. Practice assertiveness, confrontation, and positive challenging, all key to becoming a more effective and influential leader.
- Part 1 Month 7 Coaching, Accountability and Problem Management Skills (Part One) – Enhance your coaching abilities and learn how to foster accountability. Explore problem management techniques, set inspiring goals, and create a sense of ownership around problem-solving. Practice these skills to become an effective leader-coach.
- Part 1 Month 8 Coaching, Accountability and Problem Management Skills (Part Two) – Delve further into coaching and problem management. Learn to facilitate action planning, confront self-defeating behaviors, and share personal experiences to enlighten others. Develop referral skills to ensure everyone gets the help they need.
- Part 1 Month 9 Team and Consulting Skills (Part One) – Master the art of team development and consulting. Learn to assess needs, overcome resistance to change, foster team spirit, and align values for synergy. Practice these skills through a project that will bring transformative change.
- Part 1 Month 10 Team and Consulting Skills (Part Two) – Drive consensus within your team and implement strategies for achieving objectives. Evaluate the impact of your action plans, foster continuous learning, and install accountability systems. Learn how to lead your team towards continuous improvement.
- Part 1 Month 11 Versatility and Organizational Development – Expand your versatility in leadership roles and gain insight into organizational development. Learn to adapt to different styles, facilitate organizational development stages, and lead proactive responses for future success. Apply these skills in an off-the-grid project.
- Part 1 Month 12 Application of Transforming Leadership Skills – Put all your skills into practice in this final module. Review the principles and skills learned, celebrate your improvements, and identify areas for further work. Create a long-term personal leadership development plan based on your past year’s growth.
Methodology
Transformational Leadership
Becoming a transformational leader involves a journey of personal and professional development that integrates various aspects of leadership, well-being, and the ability to create positive change. During this program, you will unlock your leadership potential by participating in 12 comprehensive workshops backed by 44 years of rigorous research and experience.
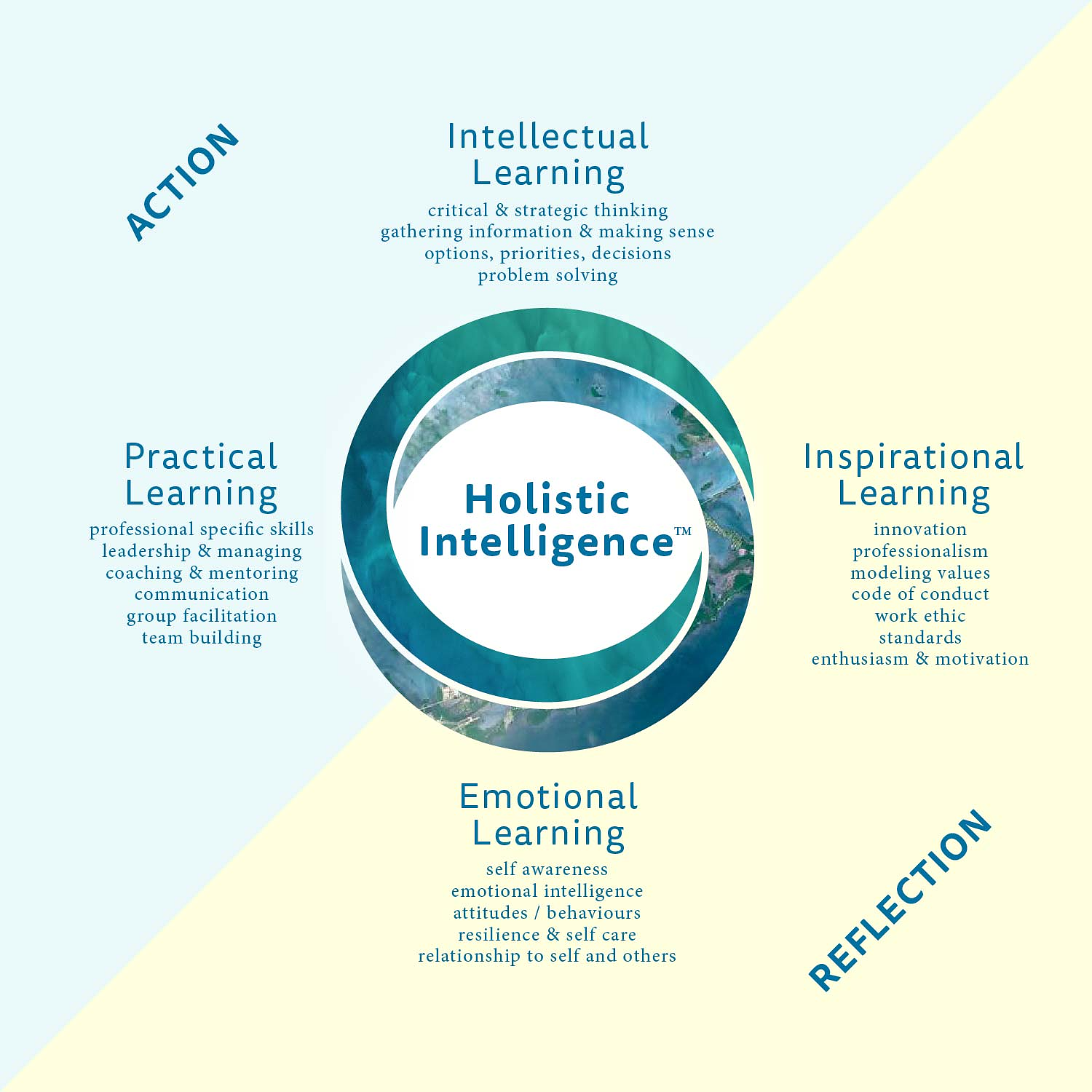
Source: Spirited Leaders
Targeted at individuals across the leadership spectrum, from supervisors to CEOs, our program encompasses 12 principles and 60 skills within five crucial categories. As a participant, you will journey from self-awareness to self-mastery, refining your abilities in self-management, interpersonal communication, coaching, accountability, problem solving, team and consulting skills, and organizational development. Harness the power of our five proven online assessments to catalyze your personal and professional growth, and join a community of transformational leaders shaping the future.
Leaders undergo a remarkable transformation, mastering 60 transformational leadership skills across a year-long journey. Our course takes you deep into self-exploration, leveraging personal style indicators and values to enhance your leadership potential. Beyond individual skills, we highlight the art of teamwork, coaching, and organizational development, all geared towards crafting resilient, empathetic, and strategic leaders for our modern world.
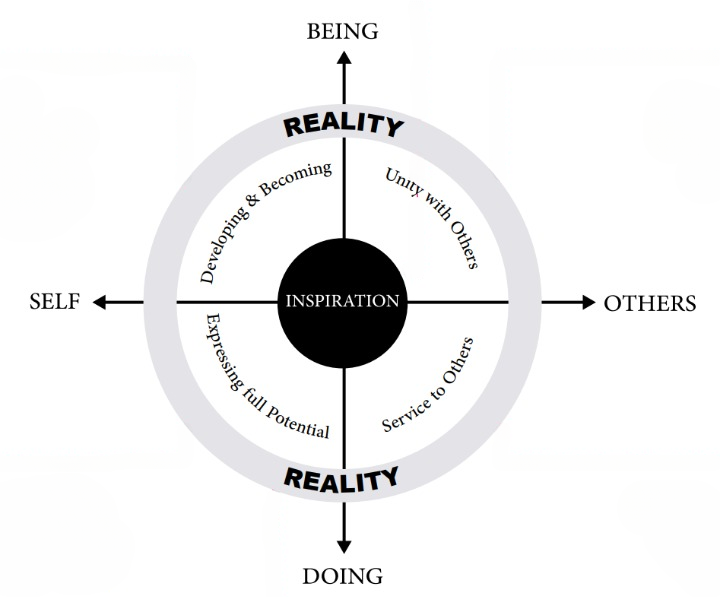
Source: www.holisticleadership.co.uk
Here are the stages involved in the transformational leadership process:
Self-Awareness
The first stage focuses on developing self-awareness, which is crucial for transformational leadership. It involves exploring your values, strengths, weaknesses, and leadership style. This stage may include self-reflection activities, assessments, feedback from others, and gaining insights into your beliefs, motivations, and behaviors as a leader.
The process of self-awareness involves various activities and practices:
• Reflection and introspection: Taking time for self-reflection to gain insights into one’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors as a leader.
• Seeking feedback: Actively seeking feedback from peers, mentors, and team members to gain different perspectives on strengths and areas for improvement.
• Assessments and tools: Utilizing self-assessment tools, personality assessments, or 360-degree feedback to gain a deeper understanding of one’s leadership style and preferences.
• Mindfulness and meditation: Engaging in mindfulness practices to develop present-moment awareness and observe thoughts and emotions without judgment.
• Journaling: Regularly journaling thoughts, experiences, and reflections to enhance self-reflection and insight.
• Coaching or mentoring: Engaging in coaching or mentoring relationships to receive guidance, support, and feedback on self-awareness and leadership development.
Mindset and Perspective Shift
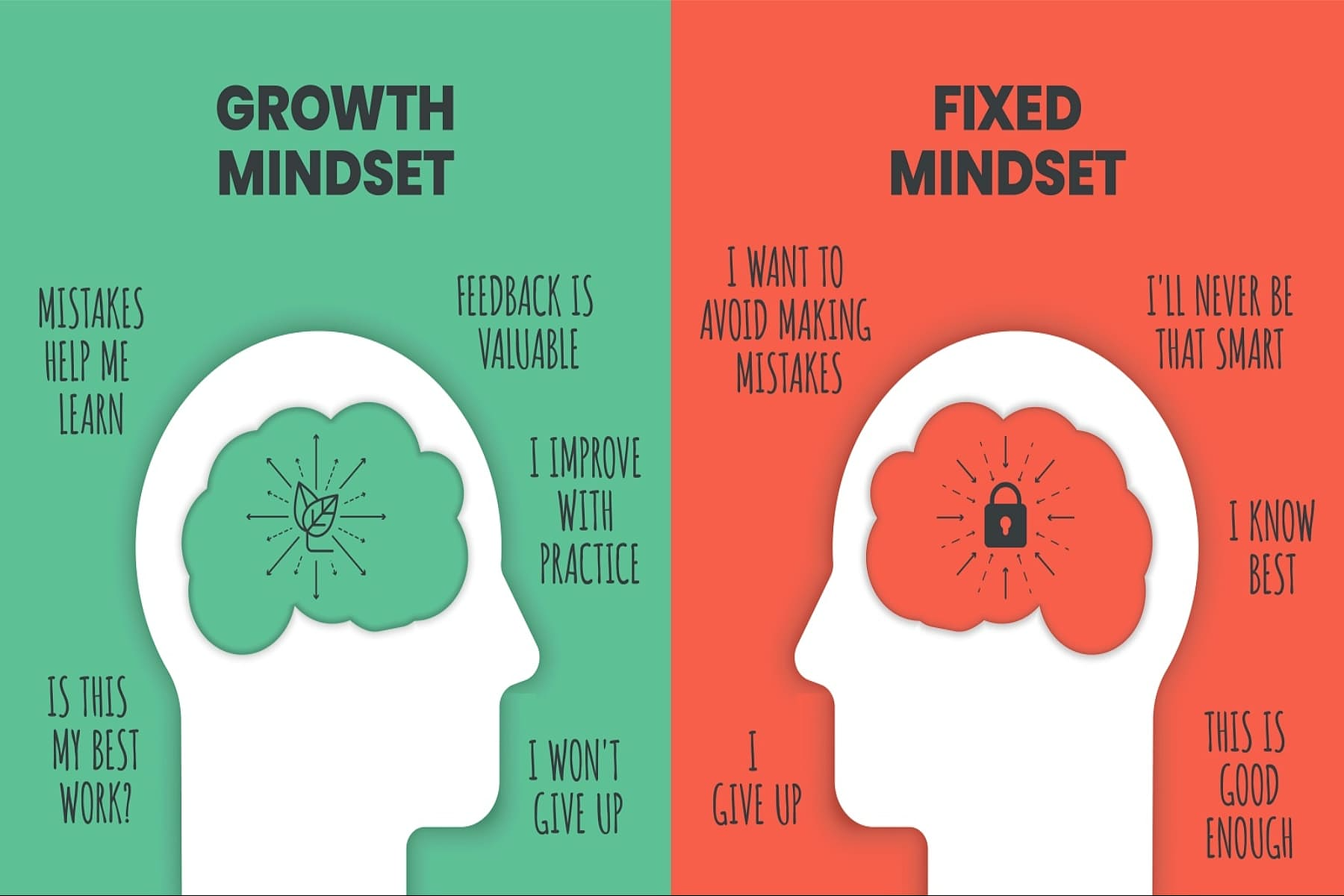
Source: Uprise Health
In this stage, you work on cultivating a transformational mindset and shifting your perspective. This involves expanding your awareness beyond your immediate concerns and considering the broader impact of your leadership on individuals, teams, organizations, and society. It includes embracing empathy, embracing diverse perspectives, and developing a systems thinking approach.
The process of Mindset and Perspective Shift involves:
• Learning and Exposure: Engaging in continuous learning to broaden knowledge and perspectives.
• Self-Reflection and Awareness: Reflecting on existing mindsets, biases, and assumptions to identify areas where a shift in perspective is needed. Developing self-awareness helps leaders recognize their own limitations and open themselves to new ideas.
• Empathy Development: Practicing empathy by actively listening to others, seeking to understand their perspectives, and putting oneself in their shoes. This involves valuing and respecting diverse opinions and fostering a culture of empathy within the organization.
• Challenging Assumptions: Actively questioning and challenging existing assumptions and beliefs to foster a more open and flexible mindset. This involves encouraging constructive dissent, promoting diverse viewpoints, and valuing critical thinking.
Well-being and Resilience
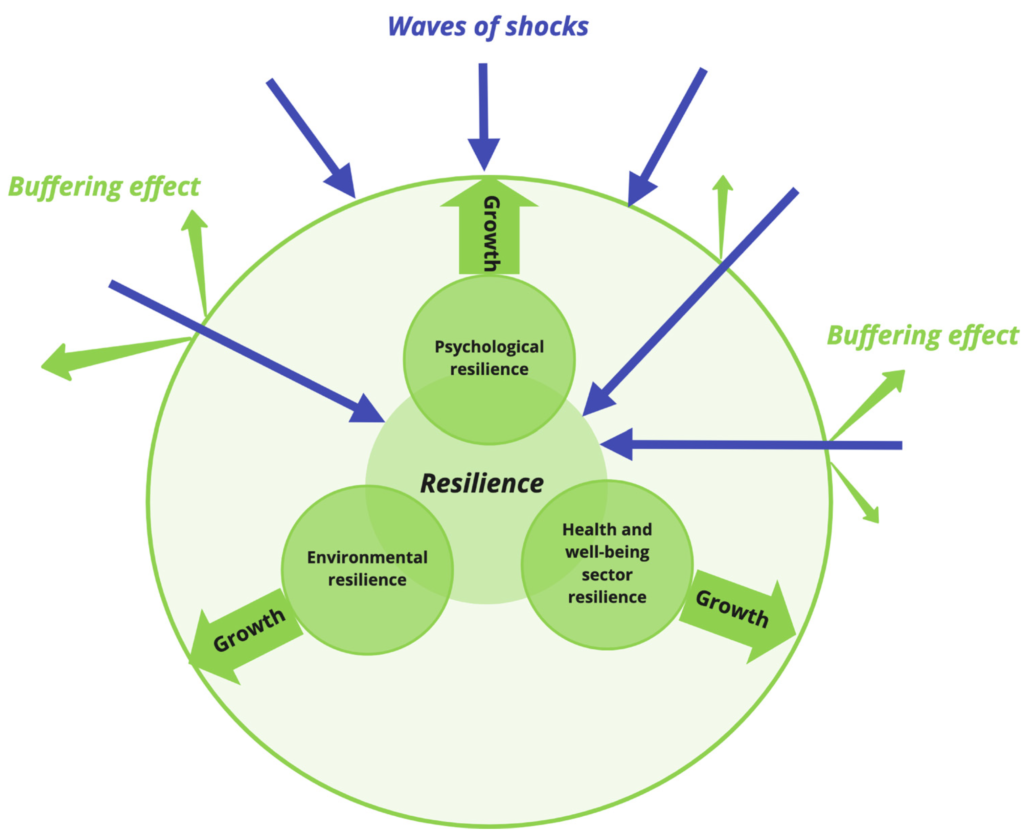
Source: MDPI
Transformational leaders recognize the importance of well-being and resilience in their own lives and the lives of their teams. This stage involves adopting practices that support physical, mental, and emotional well-being. It includes self-care, stress management techniques, work-life balance, and promoting a supportive work environment that fosters well-being and resilience.
The process of Well-being and Resilience involves:
• Self-Care Practices: Leaders engage in self-care activities that promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being. This includes exercise, proper nutrition, sufficient sleep, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation.
• Stress Awareness: Leaders develop awareness of their stress triggers and signs of burnout. They learn to recognize when stress levels are becoming overwhelming and take proactive steps to manage stress effectively.
• Boundary Setting: Leaders establish boundaries to maintain a healthy work-life balance. This includes setting clear expectations, delegating tasks, and creating time for personal activities and rejuvenation.
• Support Networks: Leaders build support networks that provide emotional support, guidance, and feedback. This can include mentors, coaches, peers, or a trusted circle of friends who provide a safe space for sharing challenges and seeking advice.
• Resilience Building: Leaders develop resilience through practices such as practicing gratitude, reframing challenges as learning opportunities, cultivating optimism, and seeking lessons from setbacks.
• Regular Reflection: Leaders engage in regular reflection to assess their well-being and identify areas for improvement. This can involve journaling, self-assessment tools, or feedback from trusted individuals to gain insights into personal well-being.
• Wellness Initiatives: Leaders promote well-being initiatives within their organization, such as wellness programs, flexible work arrangements, and resources for mental health support. They create a culture that values well-being and encourages employees to prioritize self-care.
Authentic Leadership

Authenticity is a cornerstone of transformational leadership. This stage focuses on aligning your actions and decisions with your values, beliefs, and personal identity. It involves embracing vulnerability, building trust, and leading with integrity. Authentic leaders create an environment where individuals feel safe to express themselves and contribute to the fullest.
The process of Authentic Leadership involves:
• Self-Reflection: Leaders engage in self-reflection to gain a deep understanding of their values, beliefs, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth. This introspective process helps leaders uncover their authentic selves and clarify their leadership identity.
• Values Exploration: Leaders identify and define their core values. This involves reflecting on what is most important to them and how those values shape their leadership approach and decision-making.
• Authentic Communication: Leaders practice authentic communication by expressing their thoughts, emotions, and ideas genuinely and transparently. They listen actively and engage in open and honest conversations, fostering trust and authenticity within their teams.
• Feedback and Reflection: Leaders actively seek feedback from trusted sources to gain insights into how their behavior and actions are perceived by others. They reflect on this feedback and make necessary adjustments to align their leadership style with their authentic self.
• Personal Growth and Development: Leaders continuously seek personal growth and development opportunities.
• Values Alignment: Leaders align their actions and decision-making with their identified values. They consistently evaluate whether their choices are congruent with their authentic selves and make adjustments when necessary.
• Leading by Example: Authentic leaders lead by example, modeling the behaviors, values, and attitudes they expect from others. They demonstrate consistency between their words and actions, gaining the trust and respect of their teams.
Relationship Building and Collaboration

Source: DaSh Factor
Transformational leaders understand the power of relationships and collaboration. This stage involves developing strong interpersonal skills, effective communication, and the ability to build and nurture relationships. It includes fostering a culture of collaboration, promoting teamwork, and leveraging the diverse strengths and perspectives of others.
The process of Relationship Building and Collaboration involves:
• Building Rapport: Leaders invest time and effort in building rapport with team members and stakeholders. This involves getting to know individuals on a personal level, showing genuine interest, and creating opportunities for informal interactions.
• Active Listening: Leaders practice active listening to demonstrate respect and understanding. They pay attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues, seeking to comprehend others’ perspectives and needs.
• Empathy and Emotional Intelligence: Leaders develop empathy and emotional intelligence to understand and connect with others on a deeper level. This involves recognizing and validating emotions, demonstrating empathy, and adapting communication styles to different individuals.
• Team-Building Activities: Leaders facilitate team-building activities to enhance relationships and collaboration. This can include team retreats, workshops, or shared experiences that promote trust, communication, and a sense of camaraderie.
• Effective Feedback: Leaders provide timely and constructive feedback to foster growth and development. They offer praise for achievements and provide guidance for improvement, creating a culture of continuous learning.
• Conflict Resolution Skills: Leaders develop skills in conflict resolution and manage disagreements or conflicts proactively. They encourage open dialogue, facilitate compromise, and find win-win solutions to promote positive relationships.
• Collaboration Platforms and Tools: Leaders leverage collaboration platforms and tools to facilitate effective communication and teamwork. This can include project management software, virtual meeting platforms, and shared document repositories.
• Recognition and Celebration: Leaders recognize and celebrate team achievements and milestones. This reinforces a sense of accomplishment, boosts morale, and strengthens the bonds among team members.
Vision and Purpose
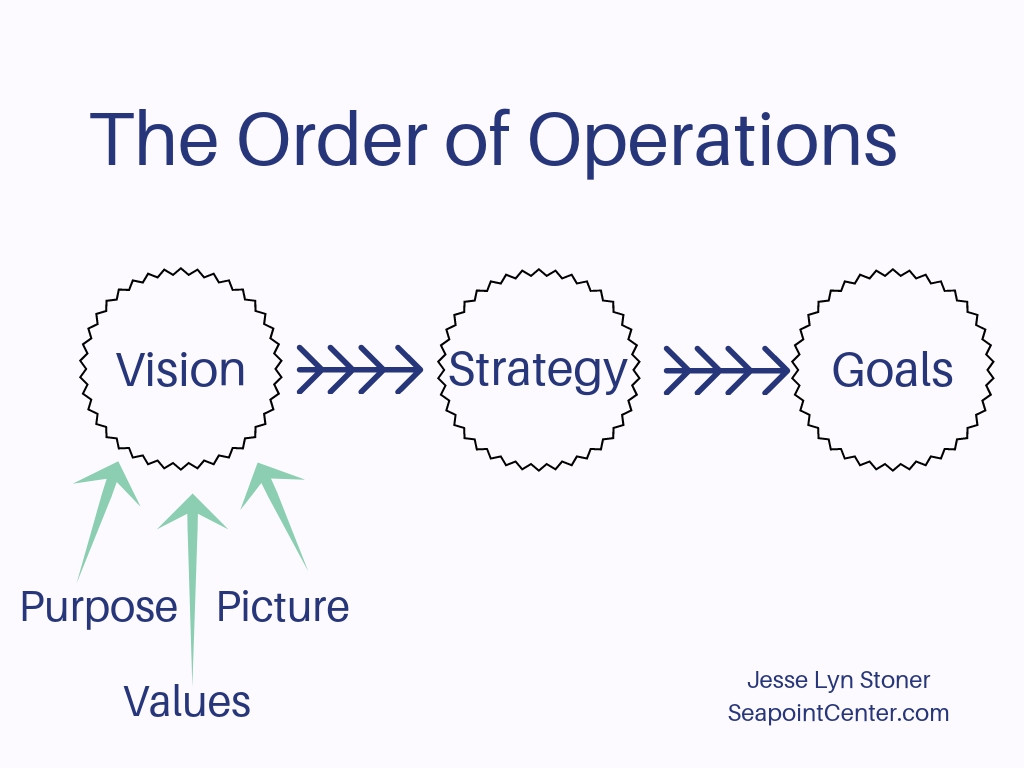
In this stage, you work on defining your leadership vision and purpose. It involves reflecting on your long-term aspirations as a leader and aligning them with the greater good. Developing a compelling vision and purpose provides direction, inspiration, and a sense of meaning to your leadership journey.
The process of Vision and Purpose involves:
• Defining the Vision: Leaders articulate a compelling vision that describes the desired future state of the organization. This involves envisioning the impact the organization aims to make and defining the overarching goals and aspirations.
• Purpose Identification: Leaders identify the purpose of the organization beyond financial success. They answer the question of why the organization exists, its contribution to society, and the value it brings to stakeholders.
• Stakeholder Engagement: Leaders engage stakeholders to gain insights and perspectives. This can include conducting surveys, focus groups, or interviews to understand stakeholders’ expectations, needs, and aspirations.
• Strategic Planning: Leaders align the vision and purpose with strategic planning. They translate the vision into actionable strategies and initiatives, setting goals, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress.
• Communication and Storytelling: Leaders effectively communicate the vision and purpose to inspire and engage others. They craft a compelling narrative, using storytelling techniques to connect emotionally with individuals and communicate the vision in a memorable way.
• Alignment and Integration: Leaders ensure alignment and integration of the vision and purpose throughout the organization. They cascade the vision to different levels, departments, and teams, ensuring that every individual understands how their work contributes to the larger purpose.
• Ongoing Evaluation and Adaptation: Leaders regularly evaluate the relevance and effectiveness of the vision and purpose. They seek feedback, monitor progress, and make adjustments as needed to ensure alignment with the evolving needs and aspirations of stakeholders.
Continuous Learning and Growth

Source: www.linkedin.com
Transformational leadership is an ongoing learning process. This stage emphasizes the importance of continuous learning, seeking feedback, and embracing personal and professional growth opportunities. It includes staying updated on industry trends, attending workshops, conferences, and pursuing further education to enhance your leadership capabilities.
The process of Continuous Learning and Growth involves:
• Learning Needs Assessment: Leaders assess their learning needs and identify areas for growth and development.
• Reading and Research: Leaders dedicate time to reading and research to stay informed about industry trends, and emerging practices.
• Networking and Collaboration: Leaders engage in networking and collaboration with peers and professionals in their field.
• Reflection and Integration: Leaders engage in reflective practices to integrate their learning into their leadership approach. They reflect on their experiences, identify lessons learned, and consider how to apply new knowledge and skills in their daily leadership practices.
Leading Positive Change

Source: Dr. Alan Zimmerman
Transformational leaders are catalysts for positive change. This stage focuses on developing the skills and strategies to lead change initiatives effectively. It involves understanding change dynamics, engaging stakeholders, and creating a shared vision for change. Transformational leaders inspire and empower others to embrace change and drive sustainable outcomes.
The process of Leading Positive Change involves:
• Vision and Strategy: Leaders articulate a clear vision for the desired change and develop a strategic plan to achieve it. This involves setting specific goals, defining key milestones, and outlining the steps required to implement the change.
• Change Management: Leaders apply change management principles and methodologies to effectively navigate the change process. They communicate the vision, create a sense of urgency, address resistance, and support individuals through the stages of change.
• Inspiring and Engaging Others: Leaders inspire and engage others by communicating the purpose and benefits of the change. They connect the change initiative to the organization’s vision and values, creating a compelling narrative that motivates and rallies individuals around the shared goal.
• Empowering Change Agents: Leaders empower change agents within the organization. They identify individuals who are passionate about the change, provide them with the necessary resources and authority, and support them in driving change at various levels.
• Communication and Transparency: Leaders communicate transparently throughout the change process. They provide regular updates, address concerns, and create opportunities for dialogue, ensuring that individuals are informed and involved in the decision-making process.
• Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Leaders embrace a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation during the change process. They monitor progress, gather feedback, and make adjustments as needed, recognizing that change is a dynamic and iterative process.
• Celebration and Recognition: Leaders celebrate milestones and achievements along the change journey. They acknowledge and recognize individuals and teams for their contributions, reinforcing a culture of positivity, resilience, and success.
Throughout these stages, it is important to note that the transformational leadership process is iterative, meaning that you may revisit and refine each stage as you progress in your leadership journey. Each stage builds upon the previous one, creating a well-rounded and comprehensive approach to leadership that considers the individual, the team, the organization, and the wider community.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Government
History
Governments have existed in various forms throughout human history. Ancient civilizations, such as those in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had established systems of governance. However, the modern concept of the government sector, characterized by a structured administrative apparatus, emerged during the Enlightenment period in the 17th and 18th centuries. This era saw the development of theories of governance, including social contract theory and the division of powers.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries led to the expansion of government intervention in economic and social affairs. Governments began to establish public services, regulate industries, and provide social welfare programs. The 20th century witnessed significant growth in the government sector, particularly during times of war and economic crises. The role of governments expanded further in areas such as infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and environmental protection.
Current Position
The current position of the government sector varies across countries, reflecting different political systems, ideologies, and levels of economic development. Generally, governments are responsible for maintaining law and order, providing public services, formulating and implementing policies, and representing the interests of their citizens.
In many developed countries, governments have established extensive welfare states, offering services like healthcare, education, social security, and unemployment benefits. These governments often engage in regulation and oversight of various sectors, such as finance, environment, labor, and consumer protection. Additionally, they play a role in diplomacy, defense, and maintaining relations with other nations.
The size and scope of the government sector can vary significantly. Some countries have larger public sectors with substantial involvement in the economy, while others emphasize smaller governments with a focus on free markets and limited intervention. The balance between private and public sectors is a subject of ongoing debate, influenced by political ideologies, economic conditions, and societal needs.
Future Outlook
The future outlook of the government sector is influenced by several factors and evolving trends. Here are a few key considerations:
• Technological Advancements: Governments are increasingly adopting digital technologies and data-driven approaches to enhance service delivery, improve efficiency, and promote transparency. This trend is likely to continue, with the potential for further automation, artificial intelligence applications, and the use of emerging technologies like blockchain.
• Governance Challenges: Governments face complex challenges such as climate change, cybersecurity threats, migration, inequality, and demographic shifts. Addressing these issues requires innovative policies, international cooperation, and effective governance frameworks. Governments will need to adapt and respond to these challenges to remain relevant and effective.
• Citizen Engagement and Participation: There is a growing emphasis on citizen engagement and participatory governance, facilitated by technology. Governments are exploring ways to involve citizens in decision-making processes, seek feedback, and improve accountability. This trend is likely to continue, promoting a more inclusive and responsive government sector.
• Public-Private Partnerships: Governments are increasingly collaborating with the private sector and civil society organizations to address complex problems and deliver public services. Public-private partnerships can leverage diverse expertise, resources, and innovation. This collaborative approach may become more prevalent in the future.
• Reshaping of Public Administration: The nature of public administration is evolving, with a focus on agility, adaptability, and evidence-based decision-making. Governments are adopting new organizational models, streamlining processes, and investing in capacity-building to enhance service delivery and responsiveness.
Overall, the government sector will continue to play a vital role in shaping societies, addressing challenges, and providing public goods and services. As the world evolves, governments will need to adapt to changing circumstances, embrace innovation, and foster effective governance to meet the needs and expectations of their citizens.
Automotive
History
The history of the automotive sector dates back to the late 19th century when Karl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler developed the first practical automobile designs. The industry quickly evolved with the introduction of mass production techniques by Henry Ford, who pioneered assembly line manufacturing in the early 20th century.
Throughout the 20th century, the automotive sector experienced significant growth and innovation. Advances in technology, such as the introduction of electric starters, automatic transmissions, and improved suspension systems, made cars more accessible and convenient. The industry also faced challenges and transformations during times of economic crises, global conflicts, and changing consumer preferences.
Current Position
The automotive sector is a crucial global industry that encompasses the production, sale, and maintenance of motor vehicles. It plays a significant role in economies worldwide, contributing to employment, innovation, and trade. Here are some key aspects of its current position:
• Production and Sales: Major automotive manufacturing countries include China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and South Korea. These countries have a significant share of global vehicle production. The sector is dominated by established multinational corporations, such as Toyota, Volkswagen Group, General Motors, Ford, and Hyundai-Kia.
• Technological Advancements: The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements. Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity due to concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability. Autonomous driving technologies, connectivity, and digitalization are also shaping the future of mobility.
• Shift towards Electric Vehicles: Governments and consumers worldwide are increasingly focused on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. This has led to a surge in the development and adoption of electric vehicles. Many countries have introduced regulations and incentives to promote EVs, and major automakers are investing heavily in electric vehicle technologies.
• Mobility Services and Shared Mobility: The concept of mobility is expanding beyond individual vehicle ownership. Ride-sharing services, car-sharing platforms, and other mobility-as-a-service models are gaining popularity in urban areas. This trend is driven by factors such as urbanization, changing consumer preferences, and advancements in digital technology.
Future Outlook
The automotive sector is poised for significant transformations in the coming years. Here are a few key factors that will shape its future outlook:
• Electric and Autonomous Vehicles: The shift towards electric vehicles is expected to continue, driven by advancements in battery technology, improved charging infrastructure, and government regulations promoting sustainable transportation. Autonomous driving technology is also evolving, and self-driving vehicles are likely to become more prevalent, offering enhanced safety and convenience.
• Connectivity and Digitalization: Vehicles are becoming increasingly connected, offering features like infotainment systems, advanced driver-assistance systems, and vehicle-to-vehicle communication. The integration of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing is expected to further enhance connectivity and enable new services and business models.
• Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: The automotive sector will continue to face pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Governments may introduce stricter emissions standards and incentives to promote sustainable practices. The development of alternative fuel sources and lightweight materials will also be important for reducing energy consumption and emissions.
• Mobility Solutions and Urbanization: With the growth of urban areas and changing mobility needs, the demand for integrated and multimodal transportation solutions is expected to increase. Public transportation systems, shared mobility services, and smart city initiatives will play a crucial role in shaping the future of urban mobility.
• Supply Chain and Manufacturing: The automotive industry will need to adapt its supply chain and manufacturing processes to accommodate changing technologies and consumer demands. The adoption of flexible production systems, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and increased collaboration with technology companies may become more prevalent.
Overall, the automotive sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and changing consumer behaviors. The future outlook is focused on electric and autonomous vehicles, connectivity, digitalization, and new mobility solutions. The industry’s ability to innovate and adapt to these changes will determine its long-term success.

Banking & Financial Services
History
The history of banking and financial services can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early forms of banking and lending emerged. However, the modern banking system as we know it today developed during the Renaissance period in Europe. The establishment of central banks, such as the Bank of England in 1694, marked significant milestones in the evolution of banking.
The 20th century witnessed the expansion and globalization of the banking and financial services sector. Technological advancements, including the advent of computers and the internet, transformed the way financial transactions are conducted. Financial institutions diversified their services, offering a wide range of products such as savings accounts, loans, insurance, investment management, and more.
Current Position
The banking and financial services sector plays a crucial role in the global economy, facilitating capital allocation, financial intermediation, and risk management. Here are some key aspects of its current position:
• Banking Institutions: The sector is dominated by a mix of large multinational banks, regional banks, and smaller community banks. These institutions provide a wide array of services, including deposit-taking, lending, investment banking, asset management, and wealth management.
• Regulation and Compliance: Following the global financial crisis in 2008, regulatory oversight of the banking and financial services sector has increased significantly. Regulatory bodies, such as the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and the Financial Stability Board, have implemented stricter regulations to enhance financial stability and protect consumers.
• Digital Transformation: Technological advancements have disrupted the traditional banking model, leading to the rise of digital banking services. Online banking, mobile banking apps, and financial technology (fintech) companies have gained prominence, offering convenient and innovative financial solutions to consumers and businesses.
• Financial Inclusion: Efforts are being made to improve financial inclusion, ensuring that individuals and businesses have access to basic financial services. Microfinance institutions and mobile banking platforms have played a significant role in expanding financial access in underserved regions and populations.
Future Outlook
The banking and financial services sector is undergoing rapid transformation driven by technological advancements, changing customer expectations, and regulatory requirements. Here are a few key considerations for its future outlook:
• Digitalization and Fintech: The sector will continue to embrace digitalization, leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and data analytics. Fintech companies will play an increasingly important role, disrupting traditional banking models and offering innovative financial products and services.
• Open Banking and Collaboration: Open banking, enabled by application programming interfaces (APIs), allows third-party developers to build applications and services around banking data. This promotes collaboration between traditional banks and fintech firms, leading to enhanced customer experiences and the development of new business models.
• Regulatory Environment: Regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve, with a focus on enhancing consumer protection, cybersecurity, and financial stability. Compliance requirements may become more stringent, necessitating increased investment in risk management, data privacy, and anti-money laundering measures.
• Sustainable Finance: The sector is witnessing a growing focus on sustainable finance, including environmentally friendly investments, social impact financing, and responsible lending practices. Banks and financial institutions are expected to integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into their decision-making processes.
• Personalized and Customer-Centric Services: With the increasing availability of data and advanced analytics, the sector will strive to offer more personalized and customer-centric services. Artificial intelligence and automation will enable tailored financial advice, customized product offerings, and improved customer experiences.
• Resilience and Risk Management: Strengthening resilience and risk management will be a priority, considering the potential impact of economic downturns, cybersecurity threats, and geopolitical uncertainties. Institutions will need to invest in robust risk assessment frameworks, cybersecurity measures, and business continuity plans.
Overall, the banking and financial services sector is poised for continued transformation driven by technology, regulatory changes, and evolving customer expectations. Adapting to these changes, embracing innovation, and prioritizing customer-centricity will be key to success in the future.

Manufacturing
History
The history of manufacturing can be traced back to ancient times when humans began crafting tools and goods using basic techniques. The Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century marked a significant turning point, introducing mechanization, mass production, and the factory system. This period saw the emergence of industries such as textiles, iron and steel, and machinery manufacturing.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, manufacturing evolved with advancements in technology, transportation, and globalization. The sector expanded into diverse areas, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. Countries with strong manufacturing capabilities experienced economic growth and industrialization.
Current Position
The manufacturing sector remains a critical component of the global economy, contributing to employment, productivity, and innovation. Here are some key aspects of its current position:
• Global Manufacturing Hubs: Manufacturing is dispersed globally, with different countries specializing in specific industries or products. China, the United States, Japan, Germany, and South Korea are among the leading manufacturing nations. However, emerging economies like India, Brazil, and Mexico are also gaining prominence in manufacturing.
• Technological Advancements: Technology has revolutionized manufacturing, leading to increased automation, robotics, and digitalization. The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), internet of things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics is enhancing efficiency, productivity, and customization in the sector.
• Supply Chains and Global Trade: Manufacturing relies on complex global supply chains, with components and raw materials sourced from different countries. Global trade and logistics networks play a crucial role in facilitating the movement of goods and materials. However, disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic and trade conflicts have highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains.
• Sustainable Manufacturing: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices, driven by environmental concerns and regulations. Manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly processes, energy-efficient technologies, and waste reduction measures. The circular economy concept, focused on recycling and reusing materials, is gaining traction in the sector.
Future Outlook
The manufacturing sector is poised for further transformation and adaptation to emerging trends. Here are a few key considerations for its future outlook:
• Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: The fourth industrial revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0, is characterized by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. Smart manufacturing systems, enabled by AI, IoT, and automation, will enhance productivity, customization, and flexibility. The use of real-time data analytics will enable predictive maintenance and optimized production.
• Reshoring and Regionalization: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to discussions about reshoring manufacturing operations and promoting regionalization. Companies may consider bringing production closer to their markets to reduce dependence on distant suppliers and mitigate risks.
• Customization and Personalization: Consumer preferences are shifting towards customized and personalized products. Manufacturing technologies like 3D printing and flexible production systems enable cost-effective customization. Manufacturers will need to adapt to meet individual customer needs and offer personalized experiences.
• Workforce Skills and Talent: Technological advancements will reshape the skills required in the manufacturing sector. There will be a growing demand for workers with expertise in digital technologies, data analytics, cybersecurity, and advanced automation. Upskilling and reskilling programs will be crucial to ensure a skilled workforce for the future.
• Sustainability and Circular Economy: Environmental sustainability will continue to be a key focus in manufacturing. Companies will be under pressure to reduce emissions, minimize waste, and adopt sustainable materials. The circular economy approach, emphasizing recycling and reuse, will gain further traction.
• Resilience and Risk Management: Manufacturers will need to enhance resilience and risk management strategies to mitigate disruptions. This includes diversifying supply chains, investing in cybersecurity measures, and adopting agile production processes to respond quickly to changing market demands.
Overall, the manufacturing sector is undergoing significant transformation with the integration of advanced technologies, sustainability considerations, and changing market dynamics. Adapting to these trends, fostering innovation, and investing in talent and sustainability will be crucial for the sector’s future success.
Technology
History
The history of the technology sector dates back to the development of early computing machines in the mid-20th century. The invention of the transistor and the subsequent development of integrated circuits paved the way for the emergence of modern electronics and computer technology. The technology sector experienced significant growth and innovation with the advent of personal computers, the internet, and the digital revolution.
Current Position
The technology sector, also known as the tech industry, is a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry that encompasses a wide range of businesses involved in the development, manufacturing, and distribution of technological products and services. Here are some key aspects of its current position:
• Dominance of Tech Giants: The sector is dominated by large multinational companies known as tech giants. Companies like Apple, Google (Alphabet Inc.), Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook have a significant influence on the global technology landscape. These companies operate across multiple sectors, including hardware, software, e-commerce, cloud computing, social media, and search engines.
• Innovation and Disruption: The technology sector is characterized by rapid innovation and disruption. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and quantum computing are transforming industries and shaping the way we live and work.
• Startups and Entrepreneurship: The technology sector has a thriving startup ecosystem, with many innovative startups and entrepreneurs driving technological advancements. Venture capital firms and incubators actively invest in promising startups, fostering innovation and driving industry growth.
• Digital Transformation: Businesses across various sectors are undergoing digital transformation, adopting technology to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve customer experiences. Cloud computing, data analytics, and automation are key components of this transformation.
Future Outlook
The technology sector is poised for continued growth and disruption in the future. Here are a few key considerations for its outlook:
• Artificial Intelligence and Automation: AI and automation technologies will continue to advance, transforming industries and job roles. AI will drive innovations in areas like autonomous vehicles, robotics, natural language processing, and personalized customer experiences. Automation will streamline processes and potentially reshape the workforce.
• Connectivity and 5G: The deployment of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable connectivity, unlocking new opportunities for industries such as autonomous vehicles, Internet of Things (IoT), and smart cities. The proliferation of connected devices will fuel data generation and drive the need for advanced data analytics.
• Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: As technology becomes more integrated into everyday life, the importance of cybersecurity and data privacy will continue to grow. The sector will focus on developing robust security measures and regulations to protect sensitive data and privacy rights.
• Sustainability and Green Tech: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable technologies and practices within the technology sector. The development of green tech solutions, such as renewable energy, energy-efficient devices, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes, will gain traction as companies and consumers prioritize environmental sustainability.
• Healthcare Technology: The intersection of technology and healthcare, often referred to as healthtech, is poised for significant growth. Telemedicine, wearable devices, health monitoring systems, and AI-powered diagnostics are transforming healthcare delivery and improving patient outcomes.
• Ethical and Social Considerations: As technology continues to shape society, there will be increased focus on ethical and social considerations. Issues such as data ethics, algorithmic bias, digital divide, and the impact of automation on jobs will require careful attention and regulation.
Overall, the technology sector is expected to drive innovation, disruption, and economic growth in the coming years. Advances in AI, connectivity, sustainability, and healthcare technology will play a pivotal role in shaping its future outlook.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

London, UK
London’s history is rich and spans over two millennia. Originally founded by the Romans in AD 43 as Londinium, it served as a strategic trading and transportation hub along the River Thames. The city grew and flourished during the Roman era but faced decline after their departure in the 5th century.
Throughout the medieval period, London gradually regained its importance, becoming the capital of England in the 12th century. It developed as a center of political power, trade, and culture. Landmarks like the Tower of London and Westminster Abbey were built during this time.
London faced various challenges over the centuries, including the devastating Great Fire of 1666 that destroyed much of the city. However, it was swiftly rebuilt under the guidance of renowned architect Sir Christopher Wren, leading to the construction of iconic buildings such as St. Paul’s Cathedral.
The city continued to expand and prosper during the British Empire’s height in the 18th and 19th centuries, becoming a global trading center. The Industrial Revolution brought rapid growth and urbanization, with the development of railways, factories, and a bustling port. London’s population exploded, and new districts emerged.
The 20th century brought further transformations. London endured the devastation of World War II during the Blitz, which led to extensive rebuilding and modernization efforts in the post-war era. The city experienced waves of immigration, contributing to its multicultural character and diverse communities.
In recent decades, London has solidified its status as a global financial hub, with the City of London at its heart. The city has undergone significant redevelopment, including the construction of modern skyscrapers like the Shard and the revitalization of areas such as the Docklands.
London’s cultural scene has also evolved over time, with the establishment of renowned museums, galleries, and theaters. The city has become a vibrant center for arts, fashion, music, and literature, attracting creative talent from around the world.
London makes a significant contribution to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the United Kingdom. Over the last decade or so London has contributed more than £12 billion each and every year (over and above what it has received in public expenditure) to the UK’s public finances. The city boasts one of the world’s largest and most diverse economies, serving as a major financial hub. It is home to numerous banks, insurance companies, and financial institutions, with the City of London, also known as the “Square Mile,” housing the London Stock Exchange. The financial sector is complemented by a strong professional services industry, including law firms, consultancies, and accounting firms. London’s economy extends beyond finance to sectors such as media, technology, creative arts, tourism, and retail.
In addition to its economic prowess, London is renowned for its vibrant and diverse cultural scene. The city’s multicultural identity attracts people from all corners of the globe. Visitors and residents alike can enjoy world-class museums, galleries, theaters, and music venues. Landmarks such as the British Museum, Tate Modern, National Gallery, and West End theaters exemplify the cultural richness found in London. The city plays host to various festivals, events, and celebrations that showcase its diverse heritage, including the vibrant Notting Hill Carnival, Diwali on the Square, Chinese New Year festivities, and the colorful Pride in London.
London’s economic strength and cultural offerings are intertwined, forming a symbiotic relationship. The city’s cultural attractions contribute to its thriving tourism industry, attracting visitors from around the world who spend money on accommodation, dining, shopping, and entertainment. This influx of tourism revenue bolsters the local economy and adds to London’s overall GDP. London’s contribution to the UK’s GDP is around 22%, highlighting its significance as an economic powerhouse within the country. However, it is important to note that economic contributions can vary over time due to changing economic conditions and global events.

Miami, FL
Miami’s history is a tale of transformation and growth, shaped by a combination of factors such as geography, immigration, and economic development. From its humble origins as a small settlement, Miami has evolved into a vibrant and cosmopolitan city.
The area now known as Miami has been inhabited by indigenous tribes for thousands of years. However, the modern history of Miami began in the late 19th century when a settlement was established at the mouth of the Miami River. It started as a trading post and farming community.
In the early 20th century, Miami experienced significant growth due to the extension of the Florida East Coast Railway and the real estate boom of the 1920s. The city’s tropical climate and beautiful beaches attracted tourists and real estate investors, leading to a rapid population increase.
Miami’s growth was further accelerated by waves of immigration. In the 1950s and 1960s, many Cuban exiles arrived in Miami, fleeing the political upheaval of the Cuban Revolution. This influx of immigrants transformed the city and led to the establishment of a vibrant Cuban community, particularly in the neighborhood of Little Havana.
Over the years, Miami’s economy diversified and expanded. It became a major center for trade and finance, with the Port of Miami playing a crucial role in international commerce. The city also developed a strong tourism industry, drawing visitors with its sunny climate, beaches, and vibrant nightlife.
In the latter part of the 20th century, Miami faced challenges such as racial tensions, crime, and urban decay. However, the city experienced a revival in the 1980s and 1990s, fueled by urban renewal efforts, investment in infrastructure, and a focus on attracting businesses and cultural events.
Miami’s proximity to Latin America and its multicultural population have played a significant role in its development. The city has become a hub for international trade, finance, and a gateway for business between the United States and Latin America. It has also become a center for the arts, with renowned institutions like the Adrienne Arsht Center for the Performing Arts and the Art Basel Miami Beach art fair.
Today, Miami is known for its thriving tourism industry, booming real estate market, diverse culinary scene, and as a global destination for art, music, and entertainment. The city continues to evolve and adapt, attracting residents and visitors from around the world who are drawn to its unique blend of cultures, beautiful coastline, and dynamic lifestyle.
Miami contributes to the economy through several key sectors and industries. Here are some of the ways in which Miami plays a significant role in economic growth:
• Tourism and Hospitality: Miami is renowned as a popular tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year. The city’s beautiful beaches, vibrant nightlife, cultural attractions, and events contribute to a thriving tourism industry. Tourists spend money on accommodations, dining, shopping, entertainment, and other activities, generating revenue and supporting businesses in the hospitality sector.
• International Trade: Miami serves as a major international trade hub, particularly for trade with Latin America and the Caribbean. The strategic location of the city, along with its robust transportation infrastructure and the Port of Miami, facilitates the movement of goods and services. The city’s trade connections contribute to import and export activities, logistics services, and the growth of businesses involved in international trade.
• Financial and Professional Services: Miami has a growing financial and professional services sector. The city is home to numerous banks, investment firms, accounting firms, law firms, and other financial institutions. Miami serves as a regional center for finance and provides a range of services to businesses and individuals, including banking, investment, wealth management, legal, and consulting services.
• Real Estate and Construction: Miami has experienced significant real estate development in recent years. The city’s booming real estate market attracts investors, developers, and construction companies. High-rise condominiums, luxury developments, and commercial properties contribute to the construction sector’s growth, creating jobs and economic activity.
• Creative and Entertainment Industries: Miami’s vibrant arts, entertainment, and creative industries play a role in the local economy. The city hosts major events, including film festivals, art shows, music festivals, and fashion events, attracting visitors, artists, and industry professionals. The creative sector contributes to job creation, tourism, and the overall cultural vibrancy of the city.
• Healthcare and Life Sciences: Miami has a robust healthcare sector, including renowned hospitals, medical research institutions, and biotechnology companies. The city is a center for medical tourism, attracting patients from around the world who seek specialized treatments and services. The healthcare and life sciences sector contribute to job creation, research and development, and economic growth.
The Miami Metropolitan Area has the highest GDP of all the metro areas in Florida with $344.9 billion in 2017. From 2023 to 2025, GDP is expected to grow at an annual rate of 1.8% led by real estate which is expected to contribute 20% of the growth.

Vancouver, BC
Vancouver’s history dates back thousands of years, with indigenous peoples, particularly the Coast Salish First Nations, inhabiting the area long before European settlement. The Vancouver area was home to indigenous communities for thousands of years. The Coast Salish peoples, including the Musqueam, Squamish, and Tsleil-Waututh First Nations, thrived in the region, relying on the land and sea for sustenance.
European exploration of the area began in the late 18th century, with British and Spanish expeditions mapping the Pacific Northwest. In 1792, Captain George Vancouver, an English naval officer, explored and surveyed the region’s coastline, giving his name to the area. The Hudson’s Bay Company established trading posts in the area in the early 19th century, facilitating the fur trade and interactions with indigenous peoples.
Vancouver was officially incorporated as a city in 1886. The Canadian Pacific Railway played a significant role in the city’s growth, as the railroad reached Vancouver in 1887, connecting it to the rest of Canada and facilitating trade and transportation. Vancouver experienced rapid economic growth in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, fueled by resource-based industries such as logging, fishing, and mining. The Klondike Gold Rush of 1896 further boosted Vancouver’s economy as the city became a gateway for prospectors traveling to the goldfields.
The hosting of the 1986 World Exposition, Expo 86, marked a turning point for Vancouver. The event spurred urban development, including the construction of iconic structures like the Canada Place convention center and the development of False Creek, which transformed former industrial lands into a thriving residential and recreational area. Vancouver has become known for its cultural diversity and welcoming attitude towards immigrants. Waves of immigration from Asia, Europe, and other parts of the world have shaped the city’s vibrant multicultural fabric.
Today, Vancouver is a bustling metropolitan city known for its stunning natural surroundings, diverse population, and thriving industries such as technology, film, tourism, and green initiatives. The city continues to evolve and adapt, facing challenges such as housing affordability and sustainability while embracing its role as a global hub for business, culture, and innovation.
Vancouver has a diverse and robust economy with several key sectors driving its growth. Here’s a brief overview of Vancouver’s economy:
1. Trade and Logistics: Vancouver is a major international trade hub, facilitated by the Port of Vancouver, Canada’s largest port. The port handles a significant volume of goods and commodities, supporting trade with Asia, the United States, and other regions. The transportation and logistics sector plays a crucial role in supporting this trade activity.
2. Real Estate and Construction: Vancouver has experienced a booming real estate market and significant construction activity. The city’s desirable location, high quality of life, and foreign investment have fueled the development of residential, commercial, and mixed-use properties. The real estate and construction sectors contribute to employment and economic growth.
3. Technology and Innovation: Vancouver has emerged as a thriving technology hub, attracting startups and established companies alike. The city’s strong talent pool, renowned universities, and supportive ecosystem have fostered growth in areas such as software development, biotechnology, video game development, and clean technology. The technology sector contributes to job creation, innovation, and economic diversification.
4. Film and Creative Industries: Vancouver has a vibrant film and creative sector, attracting major film and television productions. The city’s scenic landscapes, favorable filming incentives, and skilled workforce have made it a popular destination for the film industry. This sector supports job creation, tourism, and related industries such as visual effects and animation.
5. Tourism and Hospitality: Vancouver’s natural beauty, including mountains, forests, and ocean views, attracts tourists from around the world. The city offers a range of outdoor activities, cultural attractions, and a diverse culinary scene. The tourism and hospitality sectors contribute to employment and generate revenue through accommodations, dining, entertainment, and transportation services.
6. Financial and Professional Services: Vancouver has a growing financial and professional services sector. The city is home to numerous banks, investment firms, accounting firms, and law firms. It provides a range of financial services and expertise to local businesses and individuals.
7. Green Economy: Vancouver is committed to sustainability and has developed a green economy. The city focuses on renewable energy, green building practices, waste management, and public transportation. Vancouver’s efforts in sustainability contribute to the growth of green industries and position the city as a global leader in environmental initiatives.
These sectors, along with others such as healthcare, education, and manufacturing, contribute to Vancouver’s economy and make it an important economic center in Canada. Metro Vancouver has the third largest GDP of metropolitan regions in Canada, with a total estimated GDP of about $135.6 billion in 2017. The largest contributor to the region’s GDP was the finance, insurance and real estate sector.

Dallas, TX
Dallas, Texas, has a rich history and a thriving economy. Dallas was founded in 1841 as a trading post along the Trinity River. The city experienced rapid growth in the late 19th century as a major center for the cattle industry. Railroads played a crucial role in Dallas’ development, making it a transportation hub for the region. In the early 20th century, the discovery of oil in nearby regions further contributed to the city’s economic boom. Over time, Dallas has evolved into a diverse and cosmopolitan city, attracting businesses, immigrants, and a vibrant cultural scene.
Dallas has a robust and diversified economy, with various sectors contributing to its growth and prosperity. Financial services are a significant component of the city’s economy, with several national and regional banks, investment firms, and insurance companies headquartered there. Dallas is also a major center for telecommunications and technology, with companies specializing in software development, IT services, and data centers.
The healthcare industry is a significant driver of Dallas’ economy, with numerous hospitals, medical centers, and research institutions located in the city. Additionally, Dallas has a growing biotechnology sector that contributes to medical advancements. The manufacturing sector in Dallas produces a range of goods, including aerospace equipment, machinery, electronics, and consumer products. The city’s central location and transportation infrastructure make it an ideal hub for logistics and distribution centers.
Dallas has historical ties to the energy industry, particularly oil and gas. While not directly involved in oil production, the city serves as a major center for energy companies and related services. The retail sector is vibrant, with numerous shopping centers, upscale boutiques, and restaurants. Dallas also attracts tourists with its cultural attractions, sports events, and convention facilities, contributing to the hospitality and tourism industry.
The city’s arts and culture scene is thriving, with museums, theaters, galleries, and music venues. Dallas is known for its creative industries, including entertainment, design, and media, which contribute to its economic growth and cultural vibrancy.
Overall, Dallas’ dynamic and diverse economy has made it one of the largest and most influential cities in the United States. The city continues to attract businesses, residents, and visitors, contributing to its ongoing economic growth and prosperity.
As one of the largest cities in the country, Dallas has a robust and diverse economy that encompasses various sectors. The city’s economic output is driven by industries such as finance, telecommunications, healthcare, manufacturing, energy, retail, and hospitality, among others. The combined economic activities of businesses, residents, and visitors in Dallas contribute substantially to the overall GDP of the region and the nation as a whole. The Bureau of Economic Analysis states that the Dallas-Fort Worth- Arlington MSA GDP was $598.3 B in 2021.

Denver, CO
Denver, Colorado, has a fascinating history and a diverse and thriving economy. Denver was founded in 1858 during the Pikes Peak Gold Rush when gold was discovered in the South Platte River Valley. Initially, Denver served as a mining town and a supply hub for gold prospectors. The city grew rapidly as settlers flocked to the area in search of gold and opportunities. In 1870, Denver became the capital of the newly formed Colorado Territory and continued to expand as a trade and transportation center with the arrival of the railroad.
Denver’s economy is diverse and encompasses various sectors that contribute to its growth and prosperity. The city has a strong presence in the energy sector, particularly in oil, natural gas, and renewable energy. Denver serves as a regional hub for energy companies, with headquarters and operations related to extraction, production, and distribution of energy resources. The city also has a significant aerospace and defense industry, with major aerospace companies, defense contractors, and research institutions. This sector includes aircraft manufacturing, space systems, satellite operations, and defense-related technologies.
Denver has experienced growth in the technology sector, attracting startups, entrepreneurs, and established tech companies. The city fosters innovation and entrepreneurship, focusing on software development, cybersecurity, data analytics, and emerging technologies. As a regional center for financial services, Denver hosts a concentration of banks, investment firms, and insurance companies, providing a range of financial services to businesses and individuals.
The city’s robust healthcare and biotechnology industry is another key economic driver. Denver is home to numerous hospitals, medical centers, and research institutions, with a focus on medical technologies and pharmaceuticals. Denver’s proximity to the Rocky Mountains and its scenic beauty make it a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts and tourists. The city benefits from tourism and outdoor recreational activities, contributing to hospitality, accommodations, and dining services.
Denver has a vibrant arts and culture scene, with a strong presence of galleries, theaters, music venues, and museums. The creative industries encompass visual arts, performing arts, film, design, and media. These sectors, along with others such as manufacturing, education, and professional services, contribute to Denver’s diverse and thriving economy.
Denver’s strategic location, business-friendly environment, and quality of life have attracted a diverse range of industries. The city continues to foster economic growth, innovation, and entrepreneurship, positioning itself as a dynamic economic center in the Rocky Mountain region.
Denver makes a significant contribution to the GDP (Gross Domestic Product) of both Colorado and the United States. As one of the largest cities in the state and a regional economic hub, Denver’s diverse economy generates substantial economic output. The city’s key industries, including energy, aerospace, technology, finance, healthcare, tourism, and creative sectors, contribute to its GDP. In 2021, the real gross domestic product (GDP) amounted to 214.52 billion U.S. dollars.
Program Benefits
Technology
- Foster creativity
- Ensure compliance
- Enhance skills
- Improve experience
- Reduce footprint
- Streamline processes
- Ensure protection
- Drive advancements
- Embrace change
- Optimize processes
Management
- Nurture leaders
- Foster collaboration
- Retain talent
- Smooth transitions
- Data-driven decisions
- Drive improvement
- Resolve conflicts
- Promote inclusivity
- Enhance EQ
- Set direction
Operations
- Streamline operations
- Optimize logistics
- Ensure consistency
- Mitigate risks
- Decrease expenses
- Measure performance
- Eliminate variability
- Enhance satisfaction
- Promote responsibility
- Drive enhancements
Testimonials

Smith Gardens
“I have known Dr. Keis for over ten years and have sat on two volunteer boards together which has progressed into a close friendship. In fact, I have recommended Dr. Keis to sit on the board of an organization I co-founded several years ago. His leadership qualities are numerous bringing insight, wisdom, discernment, integrity with skilled communications where ever he goes. His over 300 podcasts have been an inspiration to many. One of his books changed my life and I was so impressed with the content that I have bought a number of cases of books to give to my friends and staff. As a business owner now with over 1,200 employees, I know firsthand how important people management and leadership are to run a successful organization. Dr. Keis is a wonderful person, and natural cheer-leader. He is passionate about making a difference in the lives of people he encounters. If you are looking for a distinguished individual for your alumni award Dr. Keis meets all the criteria and more.”
Mr. Smith,
Smith Gardens.
Chrysler
“Dr. Keis’s consulting services, coaching expertise, and ability to communicate effectively exceeded my expectations. Thank you very much for being the lead consultant for our national business process redesign project. Like the VP of Chrysler stated on tape, this was the best work he has ever seen, to help us move forward.”
S. J. Landry, National Manager,
Chrysler.

Southwest Credit Union Ltd
“We want to thank you, Dr. Keis, for the recent leadership development session held with my management team. The session accomplished my primary objectives in a very professional and non-threatening fashion. I highly recommend your process for all organizations, particularly ones that are trying to move to a more effective team approach.”
F. Townley-McKay, CEO,
Southwest Credit Union Ltd.

BC Career Develop Association
“From one of the evaluations of Dr. Keis’s presentation at our recent Career Development Conference, “I really like his interaction and experiential activities. Very well done.” Of the 40 workshops we offered, Dr. Keis received the most positive evaluations ranging from 85 to 97% approval rating.”
D. Brendon,
General Manager,
BC Career Develop Association.

Texas Woman’s University
“Dr. Keis is probably one of the best trainers in leadership development and assessments out there. His program represents outstanding value for money even if all you get out of it is your own self-development let alone the people you serve in your field. As a teacher and speaker who has taught around the world I give Dr. Keis 5 out of 5 stars for communication, interactive teaching and just being an incredible persuader!”
J. Michael, MA,
Senior Level Birkman Coach, Adjunct Instructor TWU.

Jazzthink Consulting
“I have chosen to use Dr. Keis’s learning and communication tools in my coaching and consulting practice for three reasons: the quality of thinking that has gone into their development; the ease of use in creating and interpreting the results; and the breadth and wisdom of the interpretive material. The tools are positive in their approach and profound in their impact. That is why I have chosen the Dr. Keis’s tools over the many others available in the marketplace.”
B. J. Fraser, Ph.D.
Founder, Jazzthink Consulting.

Abbotsford Chrysler
“We have made significant gains over the past year because of Dr. Keis and his onsite business consulting. On many occasions, his in-depth knowledge and understanding of business operations have challenged us to think beyond the average and ordinary. I have no hesitation recommending Dr. Keis to other businesses who may require such services.”
Paul Chiang, General Manager,
Abbotsford Chrysler.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.













