Strategic Business Growth

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Strategic Business Growth is provided by Ms. Viswanath Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 48 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.


Personal Profile
Ms. Viswanath is a Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene and has over 20 years of industry experience helping Silicon Valley companies scale and grow. Her initial education was a BS in Nutritional Biochemistry from UC Berkeley and an MPH from UNC Chapel Hill. After some initial work in the medical field, she pivoted to technology where she has been aggressively helping companies with their go-to-market strategy, business development, product management, fundraising, and growth.
In 2020, she started her own consulting company, Viswanath Consulting, LLC which advises early and mid-stage companies on strategic growth, becoming profitable, and succeeding in the marketplace. She also advises and has helped over a dozen technology companies in the Plug & Play accelerator in Silicon Valley design their strategic growth plan and launch and scale successful products.
Though her work has primarily been in cities in the United States, such as San Francisco, Los Angeles, Seattle, New York, and Miami, she has also worked with companies in Europe and Asia during her tenure.
To request further information about Ms. Viswanath through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Strategic Business Growth
Is your company stagnant in its growth? Is there a process for continuous innovation and improvement? Do leadership and employees have a growth mindset and the tools to implement a strategic growth plan? Is revenue and profit stagnant from quarter to quarter, year to year? Is your organization struggling to find ways for unique differentiation as competitors come into the market? Is there a systematic approach to plan growth strategies?
Through my decades of helping Silicon Valley companies scale and grow, I have encountered numerous challenges and found effective mechanisms to face these challenges. Companies often struggle to adopt a mindset of continuous innovation and thus are stagnant in the marketplace. Their revenues and profit margins do not grow from quarter to quarter. Company leadership and employees are frustrated that their companies aren’t raising increased growth rounds of funding or improving their stock prices.
In assisting each company as a strategic growth advisor, I’ve adopted tools and methodologies that companies can implement to disrupt their current practices. Leadership and employees can embrace new ways of thinking which can lead their actions into better outcomes. The company itself can explore and compare alternate pathways in the marketplace to improve the legitimacy or value of its products and thus increase bottom-line profitability.
As a company struggling with growth, ask yourself these questions.
1. Are there processes in place for continuous innovation and improvement?
2. How often and with what tools are growth strategies evaluated?
3. How can leadership or employees change their mindset to embrace growth?
4. How can bottom-line revenues and profit increase in time?
5. How do digital transformation and data analytics assist with business growth?
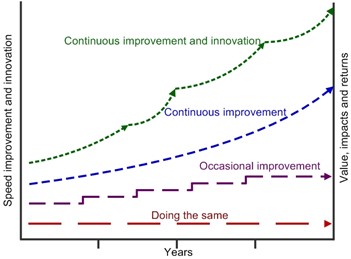
Continuous Innovation and Improvement
Companies both in technology and other areas such as life science or banking are under pressure from internal and external forces to be a leader in their marketplace sector. In becoming a leader and then maintaining a leadership position in the market, a company must first have a differentiated product offering but then evolve that product offering as needed over time to add continuous value to the customer. To evolve the product offering over time, companies must have a culture of innovation and improvement.
A culture of innovation and improvement within a company celebrates new ideas that are fostered internally. As leadership or employees realize new opportunities, they are encouraged to share those ideas. The company embraces ongoing evaluation of current practices for improved product development, marketing, product management, and marketplace growth strategies.
Evaluating Growth Strategies
For a company to achieve higher revenues and profitability, it needs to create more value for the customers it already has or be able to obtain new customers. Though an initial product may become successful in the marketplace, it will often face competitive challenges and stagnate if there aren’t improvements to the product or new channels of adoption. If your company isn’t growing, you may benefit greatly from the proper tools to assess avenues for expansion frequently.
Assessing growth channels will allow your company to constantly re-evaluate its product offerings in the competitive landscape and assess where there may be opportunities. At times, there may be product features that can be adjusted to have a greater impact. Other times, additional features may need to be added or new marketing avenues explored to reach new customers.
With the proper tools to evaluate growth strategies, your company can evaluate the pros and cons of pursuing different avenues and decide which best will help your company. There may be obvious differentiators to product development or engineering or channeling marketplace forces to give your offerings a continuous leading edge.
Mindset Shift
Leadership and employees who embrace change are more likely to help a company adapt and maintain its leading edge in the marketplace. An optimal company mindset starts when anyone is hired to work for a company by choosing the right people who embrace growth and change. In leadership training and management practices, tools and strategies can be taught that encourage employees to foster innovation, embrace change, and feel the tremendous impact of their contributions.
A company philosophy must also resonate among all internal staff that rewards creativity, strategic thinking, and flexibility. These traits, when innate in the working culture of an organization, can foster innovative thinking and novel ideas that can add value to a product or market. If your organization does not celebrate leaders and staff who constantly strive to think of how processes or strategies in place can be improved, then you may genuinely benefit from tools that will help your staff adopt the right mindset.
Increase Revenue and Profit
The result of any meaningful program implementation should be that the bottom-line financial picture of a company has improved. Any company that is struggling to grow its revenue or profitability and that is not able to show a track record of improving market shares is going to struggle. Thus, the adaptation of a meaningful growth strategy program that teaches big-picture thinking, as well as how to evaluate the details that matter will make a significant difference.
The principles and methodologies taught in this course have been tested with many of my technology clients over the last few decades. Every client has improved their customer traction, revenue, and unit economics anywhere from 20%-40%. We will use the same techniques that have worked for my technology companies and help you learn the right techniques to evaluate and adopt strategies for market penetration into new areas and expand the reach of product offerings.
When measuring success based on fiscal accomplishment, it is easy to know whether the time and expense of adopting new procedures are worthwhile. The metrics for success will be calculated all the way through the 24-month-long training segments of this program and eventually computed by looking at the actual financial metrics of your organization.
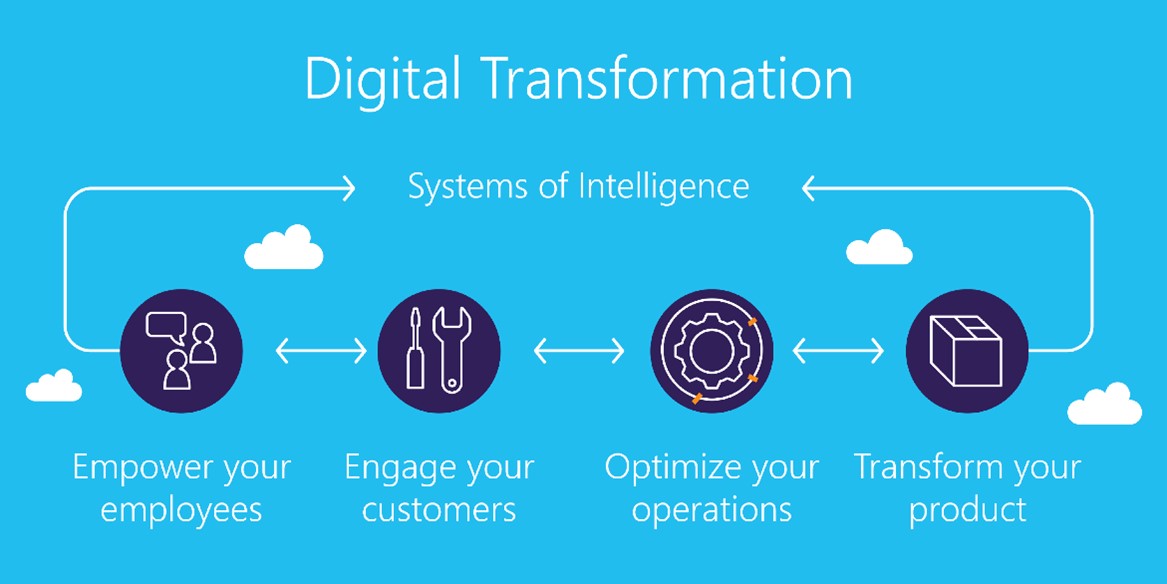
Digital Transformation and Data Analytics
At a time when the world is becoming increasingly digitally connected and dependent, business success also depends on adopting the latest technological advancements. Using AI, machine learning, and advanced data analytics tools, companies can get real-time information on how their products or services perform in the marketplace and have the tools to act on this data. Without this timely information, your business can fall behind quickly.
Thus, understanding how the latest technology can apply to your business growth strategy is critical. Once you learn how other businesses are using the latest tools to their advantage, you can decide which tools will benefit your business the most as well. Real-time analytics and the application of these analytics will be necessary for designing and implementing successful growth strategies.
Your company’s managers and employees will appreciate knowing how their efforts are affecting the actual growth in revenue of your product and services and understand where there may be inefficiencies. Time can be wasted in staff time in moving product development, management, or marketing in one direction when the data may tell you that a pivot is necessary. Time saved is money saved. All of this will affect the bottom-line revenue and profitability of your business.
Outcomes- What will Your Company Achieve as a result of this Course?
The outcomes of this course will be many and resonate through every aspect of your business.
First, a culture of continuous innovation and improvement will be established. This culture will lay the groundwork for all other aspects of strategic growth that your business will undertake. Leadership and employees will thrive in this culture and the direction of the business will leap forward in a manner that embraces change.
Second, your company will have the tools to evaluate growth strategies. Whether it may be enhancements to your product, marketing to new segments of customers, or a complete pivot in the direction of product development or distribution, avenues for growth need to be understood and evaluated properly. This course will give you the necessary and specific tools to evaluate growth channels.
Third, your staff will embrace a mindset shift. Company employees will have the tools and frame of mind to constantly evaluate their work with a critical eye, express their thoughts where there can be improvements, and strive for maximized output for efficiency. This growth mindset will directly impact the company’s strategic growth plan and include all company staff in planning and implementing influential strategies for growth.
Fourth, the revenue and profit from your products and services will grow from quarter to quarter, year to year. Ultimately, the numbers speak for itself. Showing that your financial bottom line is trending upward will be critical to securing more funding if you are growing or improving your stock price if your company is public. It is critical to show fiscal success in your company’s public and private profile.
Lastly, your company will embrace and implement the latest data analytics tools and use best practices for digital transformation. In today’s rapidly changing business environment, your company needs to embrace the technology that will keep it cutting-edge in terms of understanding the competitive landscape, how your products or services are performing, and abreast of real-time information.
Curriculum
Strategic Business Growth – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Introduction
- Part 1 Month 2 Informed Decision-Making
- Part 1 Month 3 Cultivating Culture
- Part 1 Month 4 Growth Strategies
- Part 1 Month 5 Growth-Oriented Mindset
- Part 1 Month 6 Driving Revenue
- Part 1 Month 7 Process Mapping
- Part 1 Month 8 Customer-Centric Design
- Part 1 Month 9 Managing Risks
- Part 1 Month 10 Process Standardization
- Part 1 Month 11 Methodologies
- Part 1 Month 12 Data-Driven Decisions
Strategic Business Growth – Part 2- Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Change Management
- Part 2 Month 2 Digital Transformation
- Part 2 Month 3 Fostering Innovation
- Part 2 Month 4 KPIs
- Part 2 Month 5 Growth Initiatives
- Part 2 Month 6 Resource Allocation
- Part 2 Month 7 Market Reach
- Part 2 Month 8 Scaling Operations
- Part 2 Month 9 Strategic Partnerships
- Part 2 Month 10 Sustainable Innovation
- Part 2 Month 11 Growth Resilience
- Part 2 Month 12 Capstone Project
Strategic Business Growth – Part 3- Year 3
- Part 3 Month 1 Market Analysis and Trends
- Part 3 Month 2 Global Expansion Strategies
- Part 3 Month 3 Innovation Ecosystems
- Part 3 Month 4 Data-Driven Marketing
- Part 3 Month 5 Strategic Pricing and Revenue Optimization
- Part 3 Month 6 Organizational Agility
- Part 3 Month 7 Customer-Centric Excellence
- Part 3 Month 8 Partnerships and M&A
- Part 3 Month 9 Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Part 3 Month 10 Strategic Crisis Management
- Part 3 Month 11 Scaling Innovation
- Part 3 Month 12 Strategic Growth Leadership
Strategic Business Growth – Part 4- Year 4
- Part 4 Month 1 Data Security and Privacy Compliance
- Part 4 Month 2 Agile Project Management
- Part 4 Month 3 Customer Retention and Loyalty
- Part 4 Month 4 Strategic HR Management
- Part 4 Month 5 Advanced Financial Modeling
- Part 4 Month 6 Supply Chain Optimization
- Part 4 Month 7 Customer-Centric Technology
- Part 4 Month 8 Brand Building and Reputation Management
- Part 4 Month 9 Strategic Environmental Sustainability
- Part 4 Month 10 Innovation Measurement and ROI
- Part 4 Month 11 Strategic Growth Analytics
- Part 4 Month 12 Strategic Leadership Excellence
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Strategic Business Growth corporate training program.
Strategic Business Growth – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Introduction – Objective: Introduce the fundamental concepts of strategic growth and process improvement/ Process: Understand the symbiotic relationship between strategic growth and process improvement. Explore case studies showcasing the impact of aligning growth strategies with optimized processes. Intended Result: Participants will comprehend the foundational principles of integrating strategic growth with process improvement.
- Part 1 Month 2 Informed Decision-Making – Objective: Equip participants with comprehensive strategic analysis tools. Process: Delve into methodologies like SWOT, Pestle, Porter’s 5 Forces, and Value Chain. Apply these tools to assess the business environment, identify potential avenues for growth, and align strategies accordingly. Intended Result: Participants will develop the analytical skills to evaluate current strategies, recognize growth opportunities, and make informed decisions.
- Part 1 Month 3 Cultivating Culture – Objective: Establish an organizational culture that prioritizes continuous innovation and improvement. Process: Explore the concept of continuous innovation, focusing on the importance of fostering an environment that encourages creative thinking, idea sharing, and iterative improvement. Intended Result: Participants will create a culture where innovation thrives, leading to ongoing enhancements across processes and strategies.
- Part 1 Month 4 Growth Strategies – Objective: Develop expertise in evaluating and selecting growth strategies. Process: Study methods for assessing growth channels, optimizing product features, and exploring diverse marketing avenues. Use tools to critically analyze expansion opportunities and adapt strategies. Intended Result: Participants will master the art of assessing growth strategies, enabling confident decision-making and strategic direction.
- Part 1 Month 5 Growth-Oriented Mindset – Objective: Foster a growth-oriented mindset within leadership and teams. Process: Examine leadership techniques that encourage adaptability, innovation, and change. Explore strategies to instill a mindset that embraces challenges and supports growth. Intended Result: Participants will embody a proactive mindset that aligns with the organization’s growth objectives.
- Part 1 Month 6 Driving Revenue – Objective: Equip participants with strategies for sustainable revenue and profit growth. Process: Explore techniques to create enhanced value for existing and new customers. Examine avenues for expansion and learn how to optimize revenue and profitability. Intended Result: Participants will master methods to drive financial growth, increase revenue, and boost profitability.
- Part 1 Month 7 Process Mapping – Objective: Develop skills in process mapping and optimization. Process: Understand various process mapping techniques, such as flowcharts and swimlane diagrams. Apply these tools to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Intended Result: Participants will become adept at visualizing processes, identifying optimization opportunities, and driving efficiency gains.
- Part 1 Month 8 Customer-Centric Design – Objective: Incorporate customer-centric design principles into process improvement. Process: Explore Design Thinking concepts, emphasizing empathy, ideation, and iteration. Apply these principles to enhance customer experiences and drive innovation. Intended Result: Participants will integrate customer-centricity into process improvement, leading to enhanced user experiences and innovative solutions.
- Part 1 Month 9 Managing Risks – Objective: Develop Strategies for identifying and mitigating risks during growth initiatives. Process: Study the Prosci ADKAR model to manage change effectively. Learn how to identify potential risks, create mitigation plans, and ensure smooth implementation. Intended Result: Participants will acquire the skills to manage risks associated with growth initiatives, ensuring successful outcomes.
- Part 1 Month 10 Process Standardization – Objective: Standardize processes and create effective documentation. Process: Understand the significance of process standardization and learn techniques to create clear and comprehensive process documentation. Intended Result: Participants will master process standardization, ensuring consistency, replicability, and facilitating ongoing improvement.
- Part 1 Month 11 Methodologies – Objective: Gain proficiency in Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen Methodologies. Process: Explore the processes of Lean for waste reduction, Six Sigma for quality enhancement, and Kaizen for continuous improvement. Apply these methodologies to streamline processes and drive efficiency. Intended Result: Participants will become skilled in using Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen to optimize processes and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
- Part 1 Month 12 Data-Driven Decision – Objective: Harness the power of data analytics for strategic decision-making. Process: Learn the importance of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data. Apply data insights to make informed decisions aligned with growth strategies. Intended Result: Participants will become proficient in utilizing data-driven insights to drive effective decision-making and strategic alignment.
Strategic Business Growth – Part 2- Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Change Management – Objective: Develop change management strategies for growth initiatives. Process: Study the Prosci ADKAR model and understand how to navigate resistance and facilitate successful change adoption. Apply change management principles to growth-focused transformations. Intended Result: Participants will master change management techniques, ensuring the seamless adoption of growth-driven changes.
- Part 2 Month 2 Digital Transformation – Objective: Integrate digital transformation into process improvement efforts. Process: Explore the role of automation, AI, and digital tools in process improvement and growth. Understand how to align technological advancements with strategic growth objectives. Intended Result: Participants will grasp how digital transformation complements process improvement efforts, amplifying growth outcomes.
- Part 2 Month 3 Fostering Innovation – Objective: Integrate innovation practices into process improvement strategies. Process: Discover methods to infuse innovation into process improvement efforts. Explore techniques to foster creative thinking, ideation, and the implementation of innovative solutions. Intended Result: Participants will acquire skills to infuse innovation into process improvement initiatives, leading to enhanced outcomes.
- Part 2 Month 4 KPIs – Objective: Learn to measure success using KPIs aligned with growth goals. Process: Understand the significance of setting relevant KPIs and monitoring progress. Learn how to align KPIs with strategic growth objectives and track improvements. Intended Result: Participants will master the art of using KPIs to measure the success of process improvements and their alignment with growth strategies.
- Part 2 Month 5 Growth Initiatives – Objective: Develop leadership skills for effective guidance during growth. Process: Explore leadership strategies to inspire teams, drive change, and align processes with growth objectives. Learn how effective leadership contributes to the successful implementation of growth initiatives. Intended Result: Participants will acquire leadership skills critical for steering growth initiatives and fostering an environment of success.
- Part 2 Month 6 Resource Allocation – Objective: Understand strategic resource allocation for effective growth. Process: Learn methods to allocate resources effectively to support growth initiatives. Explore techniques for optimizing resource allocation to maximize impact and drive growth. Intended Result: Participants will gain expertise in resource allocation strategies that enhance growth outcomes.
- Part 2 Month 7 Market Reach – Objective: Explore strategies for expanding market reach and targeting diverse customer segments. Process: Study methods for reaching new customers and markets. Learn techniques for tailoring products and services to different customer groups to achieve growth. Intended Result: Participants will acquire skills to extend market reach, diversify customer segments, and target new opportunities.
- Part 2 Month 8 Scaling Operations – Objective: Learn to scale operations to accommodate sustained growth. Process: Understand the challenges of scaling operations and explore strategies to handle increased demand efficiently. Study how process improvement supports scalability while maintaining quality. Intended Result: Participants will master techniques to scale operations smoothly and maintain quality standards while accommodating growth.
- Part 2 Month 9 Strategic Partnerships – Objective: Understand the role of strategic partnerships in driving growth. Process: Explore the benefits of collaborations and strategic partnerships in expanding market reach, leveraging expertise, and fostering innovation. Learn strategies for identifying, forming, and nurturing impactful partnerships. Intended Result: Participants will learn to establish and manage strategic partnerships that contribute to business growth.
- Part 2 Month 10 Sustainable Innovation – Objective: Develop sustainable innovation strategies for continuous growth. Process: Study methods for sustaining innovation efforts over time. Understand how to integrate innovation into the organization’s culture and strategies to ensure continuous growth. Intended Result: Participants will master sustainable innovation practices that foster consistent long-term growth.
- Part 2 Month 11 Growth Resilience – Objective: Develop strategies for managing growth during challenging times. Process: Explore how to navigate growth challenges and crises while maintaining strategic momentum. Learn how process improvement can enhance organizational resilience. Intended Result: Participants will acquire skills to manage growth in adverse conditions and adapt strategies during unexpected challenges.
- Part 2 Month 12 Capstone Project – Objective: Apply all learned concepts to create and execute a comprehensive growth strategy. Process: Collaborate on a practical project to design, implement, and monitor a growth strategy using methodologies from the course. Present the finalized growth plan and its implementation approach. Intended Result: Participants will synthesize their learnings into a practical strategic growth plan, ready for execution, ensuring the organization’s trajectory of sustained growth and innovation. Upon successful completion of this 24-module course, participants will possess and in-depth understanding of the integration of strategic growth and process improvement. They will be equipped with a comprehensive toolkit of methodologies, strategies, and skills to foster innovation, evaluate growth strategies, optimize processes, and navigate growth challenges effectively. The course empowers individuals and organizations to create a culture of continuous improvement, embrace change, and achieve sustainable long-term growth in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Strategic Business Growth – Part 3- Year 3
- Part 3 Month 1 Market Analysis and Trends – Objective: Develop skills in market analysis and trend forecasting. Process: Explore methods to analyze market trends, customer behavior, and competitive landscapes. Learn how to use data to anticipate market shifts and identify growth opportunities. Intended Result: Participants will gain the ability to make data-driven decisions and position their organizations strategically in evolving markets.
- Part 3 Month 2 Global Expansion Strategies – Objective: Understand the complexities of global expansion. Process: Study various international market entry strategies, risk assessment, and localization techniques. Learn how to adapt business models for global growth. Intended Result: Participants will be equipped to expand their organizations into new global markets while mitigating risks and optimizing growth potential.
- Part 3 Month 3 Innovation Ecosystems – Objective: Explore innovation ecosystems and open innovation. Process: Understand how to collaborate with external partners, startups, and research institutions to drive innovation. Learn how to create an ecosystem that supports continuous growth. Intended Result: Participants will develop strategies to foster innovation through external partnerships, accelerating growth and product development.
- Part 3 Month 4 Data-Driven Marketing – Objective: Harness the power of data in marketing strategies. Process: Dive into advanced data analytics for marketing, including customer segmentation, personalized marketing, and predictive analytics. Learn how data can drive marketing efficiency and effectiveness. Intended Result: Participants will be able to create data-driven marketing campaigns that target specific customer segments and maximize ROI.
- Part 3 Month 5 Strategic Pricing and Revenue Optimization – Objective: Develop pricing strategies for revenue growth. Process: Explore pricing models, value-based pricing, and dynamic pricing strategies. Learn how to optimize pricing to maximize revenue and profitability. Intended Result: Participants will acquire the skills to set strategic prices that drive revenue growth and maintain competitiveness.
- Part 3 Month 6 Organizational Agility – Objective: Foster organizational agility for rapid adaptation. Process: Study agile methodologies and how they can be applied beyond software development. Learn how to create an agile culture that embraces change and innovation. Intended Result: Participants will lead organizations that can pivot quickly in response to market changes, ensuring sustained growth.
- Part 3 Month 7 Customer-Centric Excellence – Objective: Cultivate a customer-centric culture for growth. Process: Explore customer journey mapping, feedback loops, and service design. Learn how to prioritize customer needs and deliver exceptional experiences. Intended Result: Participants will transform their organizations into customer-centric entities, driving customer loyalty and sustainable growth.
- Part 3 Month 8 Strategic Partnerships and M&A – Objective: Master the art of strategic partnerships and mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Process: Study the processes of identifying, evaluating, and negotiating partnerships and M&A deals. Learn how to integrate acquired companies effectively. Intended Result: Participants will be skilled in forming strategic alliances and executing M&A activities that fuel growth and innovation.
- Part 3 Month 9 Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) – Objective: Integrate sustainability and CSR into growth strategies. Process: Explore sustainable business practices, ethical considerations, and CSR frameworks. Learn how sustainability can enhance brand reputation and drive growth. Intended Result: Participants will develop strategies for sustainable growth that align with environmental and social responsibility.
- Part 3 Month 10 Strategic Crisis Management – Objective: Prepare for and manage crises effectively. Process: Study crisis management frameworks, risk assessment, and crisis communication. Learn how to navigate and recover from unexpected setbacks. Intended Result: Participants will develop crisis management strategies that safeguard growth objectives during challenging times.
- Part 3 Month 11 Scaling Innovation – Objective: Scale innovative ideas and technologies. Process: Explore techniques for scaling innovation, including incubators, accelerators, and corporate venture capital. Learn how to nurture innovation at scale. Intended Result: Participants will be able to scale innovation initiatives, driving continuous growth and competitive advantage.
- Part 3 Month 12 Strategic Growth Leadership – Objective: Hone leadership skills for strategic growth. Process: Delve into advanced leadership concepts, including transformational leadership, change management, and resilience-building. Learn how to inspire and lead teams to achieve strategic growth objectives. Intended Result: Participants will become strategic growth leaders capable of guiding organizations through complex growth initiatives successfully. Upon successful completion of this 24-module course, participants will have acquired an extensive toolkit of strategies and skills to lead their organizations through strategic growth, process improvement, and innovation. They will be well-prepared to navigate the ever-evolving business landscape, drive sustainable growth, and position their organizations for long-term success.
Strategic Business Growth – Part 4- Year 4
- Part 4 Month 1 Data Security and Privacy Compliance – Objective: Ensure data security and compliance in a digital age. Process: Explore data protection regulations, cybersecurity strategies, and privacy compliance frameworks. Learn how to safeguard customer data and maintain trust. Intended Result: Participants will develop strategies to protect data, ensure compliance, and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders.
- Part 4 Month 2 Agile Project Management – Objective: Apply agile principles to project management. Process: Study agile project management methodologies like Scrum and Kanban. Learn how to apply agile techniques to accelerate project delivery and innovation. Intended Result: Participants will become proficient in agile project management, enhancing project efficiency and adaptability.
- Part 4 Month 3 Customer Retention and Loyalty – Objective: Build customer loyalty for sustained growth. Process: Explore customer retention strategies, loyalty programs, and relationship marketing. Learn how to create long-term customer relationships that drive growth. Intended Result: Participants will develop customer retention strategies that boost loyalty and contribute to ongoing growth.
- Part 4 Month 4 Strategic HR Management – Objective: Align human resources with strategic growth objectives. Process: Study HR strategies for talent acquisition, development, and retention. Learn how to build a high-performance workforce that drives growth. Intended Result: Participants will develop HR strategies that align with organizational growth goals and enhance workforce capabilities.
- Part 4 Month 5 Advanced Financial Modeling – Objective: Master financial modeling for strategic planning. Process: Explore advanced financial modeling techniques for scenario analysis, forecasting, and budgeting. Learn how to use financial data to support growth strategies. Intended Result: Participants will become proficient in advanced financial modeling to support informed strategic decisions.
- Part 4 Month 6 Supply Chain Optimization – Objective: Optimize the supply chain for growth and efficiency. Process: Study supply chain management strategies, logistics optimization, and demand forecasting. Learn how to streamline the supply chain to support growth. Intended Result: Participants will acquire skills to optimize the supply chain, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Part 4 Month 7 Customer-Centric Technology – Objective: Leverage technology for enhanced customer experiences. Process: Explore customer-centric technologies such as CRM systems, chatbots, and personalization engines. Learn how to use technology to deliver exceptional customer experiences. Intended Result: Participants will harness customer-centric technologies to improve customer interactions and drive growth.
- Part 4 Month 8 Brand Building and Reputation Management – Objective: Strengthen brand identity and reputation. Process: Study brand building strategies, reputation management, and crisis communication. Learn how to protect and enhance your organization’s brand. Intended Result: Participants will develop strategies to build a strong brand and manage reputation effectively.
- Part 4 Month 9 Strategic Environmental Sustainability – Objective: Integrate environmental sustainability into growth strategies. Process: Explore sustainable business practices, green innovation, and carbon footprint reduction. Learn how to align sustainability with strategic growth. Intended Result: Participants will develop sustainability strategies that support growth while minimizing environmental impact.
- Part 4 Month 10 Innovation Measurement and ROI – Objective: Measure the impact and ROI of innovation efforts. Process: Explore key performance indicators (KPIs) for innovation, innovation metrics, and ROI assessment. Learn how to measure and communicate the value of innovation. Intended Result: Participants will be able to measure and maximize the return on investment in innovation initiatives.
- Part 4 Month 11 Strategic Growth Analytics – Objective: Utilize analytics for strategic growth. Process: Study advanced analytics techniques, including predictive analytics and machine learning. Learn how to leverage data for strategic decision-making and growth. Intended Result: Participants will become proficient in using advanced analytics to drive strategic growth.
- Part 4 Month 12 Strategic Leadership Excellence – Cultivate strategic leadership excellence. Process: Delve into advanced leadership concepts, including strategic thinking, global leadership, and ethical leadership. Learn how to lead with vision and integrity in the pursuit of growth. Intended Result: Participants will become strategic leaders who inspire and guide their organizations to sustained growth and success. With these additional 12 modules, your comprehensive course now consists of 48 modules, offering a deep and thorough exploration of strategic business growth, process improvement, and related topics. Participants will gain extensive knowledge and skills to lead their organizations effectively in a competitive and ever-changing business landscape.
Methodology
Strategic Business Growth
Methodology: Navigating Strategic Growth through Integrated Processes
This comprehensive methodology is structured to guide participants through an immersive journey, strategically designed to synergize growth aspirations with process refinement. The methodology unfolds in a series of interlinked segments, each aligned with specific modules of the course, forming a harmonious orchestration of insights, strategies, and tools.
Months 1-2: Establishing Strategic Foundations
Case Studies: Strategic Alignment Impact
The methodology commences with a collection of illuminating case studies showcasing the transformative impact of harmonizing growth strategies with process optimization. These real-world narratives serve as foundational pillars, emphasizing the symbiotic relationship between strategic vision and operational excellence.
Strategic Analysis Frameworks: Unveiling Growth Avenues
Participants are immersed in strategic analysis methodologies, including SWOT, PESTLE, Porter’s 5 Forces, and Value Chain. Through in-depth exploration, participants dissect the business environment, unravel growth possibilities, and architect strategies that align seamlessly with identified opportunities.
Months 3-5: Cultivating Growth Mindsets
Fostering a Culture of Continuous Innovation
In this segment, participants delve into the realm of continuous innovation, understanding the significance of nurturing environments that foster creative thinking, ideation, and iterative improvement. The module instills the importance of embracing change and challenges, sowing seeds for an innovative culture that resonates across the organization.
Leadership Techniques for Growth Nurturance
This section explores leadership dynamics that drive adaptability, innovation, and change acceptance. Participants uncover strategies to instill a growth-centric mindset across leadership and teams. The module empowers participants to orchestrate growth-aligned leadership, propelling organizations forward.
Months 6-10: Amplifying Value and Enhancing Processes
Amplifying Customer Value and Financial Metrics
Participants journey into techniques that elevate customer engagement and optimize revenue and profitability. By sculpting strategies that enhance value for existing and new customers, participants equip themselves with tools to fuel sustained financial ascension.
Process Enhancement and Design Thinking
The methodology introduces participants to diverse process mapping techniques and Design Thinking concepts. Participants dissect bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and inefficacies. Infusing empathy and ideation, they ingrain customer-centric innovation into evolving processes.
Insights Driven Decision-Making
This segment deepens participants’ understanding of data-driven decision-making. Participants collect, analyze, and visualize data to unlock insights that inform strategic choices aligned with growth objectives. The module accentuates the role of data as a compass in the growth journey.
Crafting Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen Excellence
In this segment, participants journey through the tenets of Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen methodologies. By embracing these transformative frameworks, participants streamline processes, boost quality, and infuse perpetual improvement into organizational DNA.
Months 11-15: Innovation Integration and Change Navigation
Infusing Innovation into Process Evolution
The methodology unveils techniques to interlace innovation into process enhancement. Participants foster creative thinking, ideation, and the application of innovative solutions within evolving processes, nurturing adaptive systems that resonate with modern business dynamics.
Embracing Digital Transformation for Growth
Participants delve into the realm of digital transformation, amplifying process enhancement through automation, AI, and advanced tools. By harnessing these digital levers, participants drive process evolution that resonates with technological advancement, heightening efficiency and innovation.
Navigating Change Resilience for Growth
Navigating change forms a pivotal element. Participants navigate the Prosci ADKAR model, mastering change management strategies. Simultaneously, participants comprehend the significance of process standardization, crafting lucid and comprehensive process documentation for sustained evolution.
Months 16-20: Leadership Resources and Market Expansion
Leadership Symphony: Guiding Growth Pathways
Unraveling leadership dynamics, participants explore strategies to galvanize teams, drive change, and harmonize processes with growth blueprints. Effective leadership emerges as a cornerstone, facilitating successful growth strategy implementation.
Resource Allocation: Orchestrating Impactful Growth
Participants traverse techniques to allocate resources in resonance with growth objectives. By mastering resource orchestration, participants amplify impact, ensuring optimal resource deployment that fuels strategic growth pursuits.
Diversifying Markets: Expanding Horizons
Understanding diverse market penetration and customer diversification strategies, participants embark on journeys to extend market reach, harness new customer segments, and penetrate untapped markets, catalyzing expansive growth.
Scaling Excellence: Process Evolution for Scaling Operations
The methodology delves into the challenges and strategies of scaling operations while preserving quality. Participants emerge as scaling virtuosos, adept at orchestrating operations that harmoniously scale, nurturing quality, and sustaining growth.
Months 21-24: Partnerships, Sustainability, and Implementation
Strategic Partnerships: Catalysts for Amplified Growth
Exploring the integral role of strategic partnerships, participants navigate the intricacies of partnership creation, fostering, and leveraging. This segment equips participants with the tools to craft alliances that catalyze accelerated growth.
Sustaining Innovation: Enduring Growth Momentum
Understanding methods to sustain innovation efforts over time, participants integrate innovation into organizational culture. They unearth strategies to ensure continuous growth, nurturing a culture of perpetual evolution.
Navigating Challenges: Resilience in Growth Contexts
Participants explore methodologies to navigate growth challenges and crises while maintaining strategic momentum. They learn how process improvement bolsters organizational resilience, ensuring strategic blueprints remain robust.
Implementing Growth: Project Collaboration
Culminating the methodology, participants collaboratively design, implement, and monitor a growth strategy. Presenting the finalized growth plan and its implementation approach, participants emerge as architects of strategic growth, ready to orchestrate triumph.
Conclusion
The methodologies discussed intricately thread the diverse modules of the course, creating a unified tapestry of knowledge, strategies, and tools. Through this integrative approach, participants are guided towards a holistic comprehension of the symphony that unites strategic growth and process refinement. Armed with this profound insight, participants become adept architects of growth, sculpting a dynamic future for their organizations within the ever-evolving business landscape
Methodology: Mastering Advanced Strategic Growth Integration
This comprehensive methodology builds upon the foundations established in the initial 24 modules. It further guides participants through an immersive journey, strategically designed to synergize advanced growth strategies with process refinement. Just as before, the methodology unfolds in a series of interlinked segments, each aligned with specific modules of the course.
Months 25-26: Building on Strategic Foundations
Case Studies: Advanced Strategic Integration
• These advanced case studies delve into complex scenarios showcasing the transformative impact of deeply integrated growth strategies and process optimization. They challenge participants to think critically and adapt these strategies to their own organizations.
Strategic Scenario Planning
• Participants learn to anticipate and plan for a range of strategic scenarios, incorporating insights from the case studies. They gain tools and frameworks to develop adaptable strategies that thrive in dynamic environments.
Months 27-29: Cultivating Advanced Growth Mindsets
Innovation Ecosystems
• Participants explore the intricacies of innovation ecosystems, from open innovation models to collaboration with startups. They learn to create and nurture environments where innovation thrives.
Advanced Leadership for Growth
• Building on the leadership concepts introduced earlier, this segment delves into advanced leadership practices, including leading through ambiguity and change, fostering intrapreneurship, and aligning leadership with complex growth strategies.
Months 30-34: Optimizing Processes for Complex Growth
Advanced Process Optimization Techniques
• Participants delve into advanced process optimization methodologies, including Total Quality Management (TQM), Theory of Constraints (TOC), and Business Process Reengineering (BPR). They learn to identify hidden bottlenecks and optimize processes for maximum efficiency.
Innovative Process Design
• Building on previous process design principles, this segment explores innovative process design concepts such as agile processes, self-organizing teams, and design for scalability.
Advanced Data-Driven Decision-Making
• Participants take a deep dive into advanced data analytics, including predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics, and big data management. They learn how to use these tools to make complex, data-informed decisions that drive growth.
Months 35-39: Orchestrating Growth Across Complex Ecosystems
Strategic Mergers and Acquisitions
• Participants explore the intricacies of mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances as growth strategies. They learn to evaluate potential partners, negotiate deals, and integrate organizations effectively.
Global Expansion Strategies
• This segment focuses on global expansion, covering international market entry strategies, localization, and managing cultural diversity in global teams.
Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability
• Participants examine strategies to build resilient and sustainable supply chains in a global context, taking into account geopolitical factors, environmental considerations, and emerging technologies.
Months 40-44: Leading Innovation at Scale
Scaling Innovation
• Participants learn how to scale innovation efforts across large organizations, addressing challenges related to culture, resource allocation, and alignment with strategic goals.
Innovation Measurement and ROI at Scale
• This module focuses on measuring the impact and return on investment (ROI) of innovation efforts in complex organizational structures, using advanced metrics and balanced scorecards.
Advanced Strategic Growth Analytics
• Building on previous analytics modules, this segment delves into advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning, AI-driven decision support, and sentiment analysis for market insights.
Months 45-48: Mastery and Implementation of Advanced Growth Strategies
Strategic Portfolio Management
• Participants explore advanced portfolio management techniques for optimizing resource allocation across a diverse range of growth initiatives.
Strategic Crisis Management and Resilience
• This module equips participants with advanced crisis management strategies, ensuring the organization’s strategic momentum is maintained during challenging times.
Capstone Project: Advanced Growth Strategy Implementation
• Culminating the methodology, participants apply their advanced knowledge to collaboratively design, implement, and monitor a complex growth strategy. They present a comprehensive plan ready for execution, demonstrating mastery of advanced strategic growth integration.
Conclusion This methodology, interwoven with the course modules, guides participants toward a profound mastery of advanced strategic growth integration. It equips them with the knowledge, strategies, and tools needed to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape successfully. Armed with this expertise, participants become adept architects of advanced growth, shaping the dynamic future of their organizations within the ever-evolving business environment.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Technology
History of the Technology Industry
The history of the technology industry is a tale of innovation, disruption, and transformation that has shaped the modern world. It traces its roots back to the mid-20th century when the first computers were developed for scientific and military purposes. The advent of the integrated circuit in the late 1950s laid the foundation for the semiconductor industry, enabling the rapid growth of computing power.
The 1970s saw the birth of personal computers, with companies like Apple and Microsoft leading the charge. The 1980s and 1990s witnessed the rise of the internet, transforming communication and commerce. The dot-com boom and subsequent bust in the late 1990s and early 2000s highlighted the industry’s potential for rapid growth and volatility.
The early 2000s marked the emergence of mobile technology, with the launch of smartphones that combined computing, communication, and entertainment in a single device. This paved the way for companies like Apple, Google, and Samsung to become industry giants. The mid-2000s saw the rise of social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube, further shaping the way people interact and share information.
Current Position of the Technology Industry
As of now, the technology industry is a powerhouse of innovation, influencing every aspect of modern life. It encompasses a diverse range of sectors, including hardware, software, telecommunications, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and more. The industry’s leaders such as Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, Google (now Alphabet), and Facebook (now Meta), have become some of the world’s most valuable and influential companies.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way that businesses operate, offering scalable and flexible solutions for storage, processing, and collaboration. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into various applications, from personalized recommendations to autonomous vehicles. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects everyday objects to the internet, enabling smart homes, industrial automation, and more.
E-commerce has seen exponential growth, especially accelerated by the Covid-19 pandemic, with companies like Amazon reshaping retail and logistics. The gig economy has emerged, driven by platforms like Uber, Lyft, and Airbnb, changing the nature of work and employment. Renewable energy and sustainability have gained prominence, with technology playing a vital role in addressing environmental challenges.
Future Outlook of the Technology Industry
Looking ahead, the technology industry is poised for continued evolution and disruption. Here are some key trends and projections for the future.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Automation: AI will continue to advance, with applications in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. Automation will reshape industries, leading to efficiency gains but also raising questions about job displacement.
2. 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster communication and pave the way for innovations like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and augmented reality.
3. Biotechnology and HealthTech: The convergence of technology and healthcare will lead to breakthroughs in personalized medicine, genomics, and telehealth, improving patient outcomes and access to care.
4. Sustainability and Green Tech: Technology will play a crucial role in addressing climate change, with innovations in renewable energy, carbon capture, and sustainable practices across industries.
5. Ethics and Regulation: As technology becomes more integrated into society, concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and ethical AI will drive the need for robust regulations and standards.
6. Space Exploration and Beyond: The technology industry will contribute to advancements in space exploration, satellite technology, and potentially commercial space travel.
7. Human-Computer Interaction: Interfaces like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) will become more immersive and integrated into daily life, transforming entertainment, education, and work.
8. Global Connectivity: Efforts will continue to bridge the digital divide, providing internet access to underserved regions and populations around the world.
9. Diversity and Inclusion: The industry will focus on promoting diversity and inclusion to ensure that technological advancements benefit various perspectives and backgrounds.
10. Innovation Ecosystems: Startups and small companies will play a significant role in driving innovation, supported by venture capital, accelerators, and collaborative ecosystems.
In conclusion, the history of the technology industry is one of continuous innovation and transformation, shaping the world we live in today. The current position of the industry is marked by its pervasive influence on every aspect of modern life, from communication to commerce, and from healthcare to entertainment. The future outlook is filled with promise, as technological advancements continue to reshape industries, address global challenges, and create new possibilities for a more connected and sustainable world. However, with these opportunities come the responsibilities of ethical considerations, regulatory frameworks, and a commitment to harnessing technology for the betterment of humanity.
Healthcare
History of the Healthcare Industry:
The history of the healthcare industry is a journey through medical breakthroughs, evolving practices, and the quest for improved patient care. It has its origins in ancient civilizations where traditional healers and herbal remedies were common. The formalization of medical practices began in ancient Greece and Rome, with Hippocrates often referred to as the “father of medicine.”
The Renaissance period brought advancements in anatomy and medical knowledge, laying the foundation for modern medical science. The 19th century saw the rise of hospitals and medical schools, as well as significant developments in surgical techniques and the understanding of infectious diseases. The discovery of antibiotics in the early 20th century revolutionized treatment by enabling the effective management of bacterial infections.
The latter half of the 20th century witnessed the development of medical imaging technologies, such as X-rays and MRIs, enabling more accurate diagnoses. The digital age brought electronic health records (EHRs) and telemedicine, transforming the way healthcare information is stored and accessed.
Current Position of the Healthcare Industry:
Today, the healthcare industry is a complex ecosystem encompassing medical care, research, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, digital health, and more. It is characterized by advances in medical science, improved patient outcomes, and a growing focus on preventive and personalized medicine.
Medical research has led to breakthroughs in understanding diseases at the molecular level, enabling the development of targeted therapies and precision medicine. The adoption of electronic health records has streamlined patient information management and improved communication among healthcare providers. Telemedicine has gained prominence, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing remote consultations and expanding access to care.
Pharmaceutical companies continue to develop innovative drugs to treat a wide range of conditions, including chronic diseases, cancer, and rare disorders. Medical device manufacturers are producing cutting-edge technologies like wearable health trackers, implantable devices, and robotic surgical tools. Digital health startups are revolutionizing patient engagement, health monitoring, and wellness through mobile apps, wearable devices, and virtual health platforms.
The healthcare industry has also witnessed a shift towards value-based care, where the emphasis is on improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. Population health management focuses on preventative measures and proactive interventions to keep communities healthier.
Future Outlook of the Healthcare Industry:
Looking ahead, the healthcare industry is poised for transformative changes driven by technological innovation, changing demographics, and evolving healthcare models. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Digital Health and Telemedicine: Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring will continue to grow, improving access to care, reducing healthcare costs, and enabling virtual consultations and diagnostics.
2. Precision Medicine and Genomics: Advances in genomics will drive personalized treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles, leading to more effective therapies with fewer side effects.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics: AI will play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases, predicting outbreaks, and analyzing vast amounts of medical data for insights that improve patient care.
4. Medical Robotics and Automation: Surgical robots and automation will enhance precision and reduce invasiveness in procedures, leading to shorter recovery times and better patient outcomes.
5. Value-Based Care and Population Health: The industry will continue to shift towards outcomes-based models, focusing on preventative care and improving the health of communities.
6. Drug Development and Biotechnology: Biotech innovations will lead to more targeted therapies, gene editing, and regenerative medicine approaches for treating diseases.
7. Global Health Preparedness: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic will drive international collaboration and investment in pandemic preparedness, vaccine development, and rapid response systems.
8. Aging Population and Chronic Disease Management: As populations age, there will be increased focus on managing chronic conditions and developing innovative solutions for elder care.
9. Healthcare Data Security and Privacy: With the digitization of healthcare, ensuring the security and privacy of patient data will remain a significant challenge and priority.
10. Mental Health and Wellness: The industry will place greater emphasis on addressing mental health concerns, leveraging technology for virtual therapy, mindfulness apps, and early intervention.
In conclusion, the history of the healthcare industry reflects a journey from ancient healing practices to cutting-edge medical technologies. The current position of the industry showcases a blend of medical breakthroughs, technological advancements, and a focus on patient-centered care. The future outlook promises transformative changes driven by digital health innovations, personalized treatments, and a shift towards value-based care. The healthcare industry’s role in addressing global health challenges, fostering collaboration, and embracing innovation will shape the way healthcare is delivered and experienced in the years to come.

Sustainability
History of the Sustainability Industry:
The history of the sustainability industry is a story of increasing awareness about environmental and social issues, leading to a global movement towards responsible practices. While concepts of sustainability can be traced back to ancient civilizations’ respect for nature, the modern sustainability movement gained momentum in the late 20th century.
The 1960s and 1970s marked the beginning of environmental activism, driven by concerns about pollution, resource depletion, and the impact of industrialization. The first Earth Day in 1970 brought together millions of people to raise awareness about environmental challenges. The 1980s saw the emergence of concepts like “sustainable development,” emphasizing the need to balance economic growth with environmental protection.
In the 1990s, global agreements like the Kyoto Protocol aimed to address climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Corporate social responsibility gained traction, pushing companies to consider their environmental and social impacts. The 21st century witnessed a growing emphasis on sustainability across industries, as the world faced urgent challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and social inequality.
Current Position of the Sustainability Industry:
Today, the sustainability industry encompasses a wide range of sectors, including renewable energy, circular economy practices, green building, responsible supply chains, and social impact initiatives. It reflects a shift in mindset towards balancing economic growth with environmental protection and social well-being.
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power have gained prominence as alternatives to fossil fuels. Companies are adopting sustainable practices to reduce their carbon footprint and transition to cleaner energy sources. The circular economy model encourages the reduction, reuse, and recycling of resources, minimizing waste and environmental impact.
Green building standards prioritize energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and reduced water usage in construction. Responsible supply chain management focuses on ethical sourcing, fair labor practices, and reducing negative environmental impacts throughout the production process.
The sustainability industry has also led to the rise of impact investing and socially responsible investment funds, where financial decisions consider both financial returns and positive social and environmental outcomes. This integration of financial goals with sustainability goals is reshaping the investment landscape.
Future Outlook of the Sustainability Industry:
Looking ahead, the sustainability industry is poised for significant growth and influence as global challenges like climate change, resource scarcity, and social inequality become more urgent. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Renewable Energy Expansion: The transition to renewable energy will continue, with advancements in energy storage, grid integration, and innovations in clean energy technologies.
2. Circular Economy Evolution: The circular economy model will gain traction, fostering innovative approaches to resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable consumption patterns.
3. Climate Mitigation and Adaptation: Efforts to address climate change will intensify, with a focus on mitigation through emissions reduction and adaptation to the impacts of a changing climate.
4. Sustainable Transportation: The transportation sector will see advancements in electric vehicles, public transit systems, and alternative fuels to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
5. Biodiversity Conservation: Conservation and restoration of ecosystems will be essential to combat biodiversity loss and protect critical habitats.
6. Sustainable Agriculture: Agricultural practices will prioritize regenerative farming, organic methods, and technologies that increase food production while minimizing environmental impact.
7. Green Technology Innovation: Sustainable technology solutions will continue to emerge, from energy-efficient appliances to smart cities with reduced energy consumption and enhanced urban planning.
8. Social Equity and Inclusion: The sustainability industry will increasingly address social inequalities, focusing on diversity, equity, and inclusion in both corporate practices and community initiatives.
9. Policy and Regulation: Governments and international bodies will play a key role in driving sustainability through regulations, incentives, and global agreements.
10. Consumer Awareness and Activism: Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products and services will push companies to adopt more responsible practices.
In conclusion, the history of the sustainability industry reflects a journey from environmental activism to a global movement encompassing environmental protection, responsible business practices, and social well-being. The current position of the industry demonstrates a broad spectrum of sectors and initiatives focused on addressing pressing global challenges. The future outlook is promising, as the industry is poised to play a pivotal role in advancing renewable energy, circular economy practices, climate resilience, and social equity. The integration of sustainability principles into various sectors and the collective effort to create a more sustainable and equitable world will shape the industry’s impact in the years to come.

Finance
History of the Finance Industry:
The history of the finance industry is a journey through the evolution of financial systems, instruments, and institutions that have shaped economies and societies. Its roots can be traced back to ancient civilizations where barter and commodity-based exchange systems were used for trade. As economies grew more complex, the need for standardized mediums of exchange led to the emergence of early forms of currency.
In medieval Europe, the first banking institutions appeared, offering services like money lending and safekeeping of valuable assets. The Renaissance period witnessed the rise of international trade and the birth of modern banking practices, with institutions like the Medici Bank paving the way for the development of credit and financial intermediation.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries spurred economic growth and the creation of stock markets, where shares of companies were traded. The 20th century saw the establishment of central banks to regulate monetary policy and stabilize economies. The advent of computers in the latter half of the century revolutionized financial operations, leading to electronic trading, online banking, and complex financial derivatives.
Current Position of the Finance Industry:
Today, the finance industry encompasses a wide range of sectors, including banking, investment, insurance, asset management, fintech, and more. It plays a crucial role in facilitating economic activities, managing risk, and allocating capital efficiently. The industry is characterized by increasing globalization, technological advancements, and regulatory oversight.
Traditional banking services offer a variety of financial products, from savings accounts to loans and mortgages. Investment banks facilitate capital raising and mergers and acquisitions for corporations. Asset management companies oversee investment portfolios on behalf of individuals and institutions. Insurance companies provide coverage for risks ranging from health to property.
The emergence of financial technology (fintech) has disrupted the industry by offering innovative digital solutions for payments, lending, investment, and personal finance management. Peer-to-peer lending platforms, robo-advisors, and mobile payment apps are reshaping customer experiences and enhancing accessibility.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology have introduced new possibilities for decentralized financial systems and digital assets, while also raising regulatory and security challenges. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are gaining prominence, with investors and financial institutions incorporating sustainability criteria into their decision-making.
Future Outlook of the Finance Industry:
Looking ahead, the finance industry is poised for further transformation driven by technology, regulatory changes, and evolving customer expectations. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Digital Transformation: The industry will continue to embrace digital technologies, leading to more efficient processes, personalized customer experiences, and greater accessibility to financial services.
2. Fintech Innovation: Fintech startups will drive innovation in payments, lending, wealth management, and other financial services, challenging traditional business models.
3. Blockchain and Digital Assets: Continued development of blockchain technology will impact areas like cross-border payments, supply chain finance, and asset tokenization.
4. Sustainable Finance: ESG considerations will become integral to investment decisions, encouraging companies to adopt responsible practices and meet sustainability goals.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Stricter regulations will be implemented to address financial stability, consumer protection, data privacy, and emerging risks in the digital space.
6. Financial Inclusion: Efforts will focus on expanding access to financial services for underserved populations through digital channels and innovative banking models.
7. Data Analytics and AI: Advanced data analytics and AI will enable better risk assessment, fraud detection, customer profiling, and personalized financial advice.
8. Open Banking: Open banking initiatives will promote data sharing among financial institutions, leading to more seamless financial experiences and product innovation.
9. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: As digitalization increases, the industry will invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect customer data and prevent cyber threats.
10. Global Collaboration: International cooperation will be vital to address challenges like cross-border transactions, regulatory harmonization, and the regulation of emerging technologies.
In conclusion, the history of the finance industry reflects a progression from basic exchange systems to complex financial instruments and digital innovations. The current position of the industry showcases a diverse landscape of traditional institutions, fintech disruptors, and evolving customer preferences. The future outlook is marked by digital transformation, sustainability considerations, and regulatory shifts that will shape the industry’s role in facilitating economic growth, managing risk, and enhancing financial well-being on a global scale.

Transportation
History of the Transportation Industry:
The history of the transportation industry is a tale of human ingenuity, technological advancements, and the evolution of mobility that has connected the world and transformed societies. From early forms of travel to modern innovations, the transportation industry’s journey spans millennia.
The earliest modes of transportation involved human and animal power, such as walking, horse-drawn carts, and boats. The ancient Romans constructed an extensive network of roads that facilitated trade and military movements. The invention of the wheel revolutionized transportation, enabling the development of carts and chariots.
The industrial revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant turning point, with the introduction of steam-powered locomotives and steamships. The 20th century witnessed the rise of the automobile and the airplane, reshaping the way people and goods moved across long distances. Mass production techniques made cars more accessible, while commercial aviation transformed global travel.
Current Position of the Transportation Industry:
Today, the transportation industry is a complex and interconnected system that encompasses various modes of travel, including road, rail, air, sea, and space transportation. It plays a vital role in the global economy, enabling the movement of goods, people, and ideas. The industry has evolved to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world, driven by technology, sustainability concerns, and urbanization.
The road transportation sector includes cars, trucks, buses, and bicycles, while rail transportation continues to be a crucial mode for moving goods efficiently. Commercial aviation has made international travel accessible to millions, while maritime transportation handles the majority of global trade. The emergence of ride-sharing services, electric vehicles, and autonomous technology has revolutionized urban mobility.
The transportation industry is also grappling with environmental challenges, such as emissions and congestion. Efforts to reduce carbon footprints have led to the development of electric vehicles, sustainable aviation fuels, and innovations in public transit.
Future Outlook of the Transportation Industry:
Looking ahead, the transportation industry’s future is marked by its potential to shape global connectivity, sustainability, and urban mobility. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Electrification and Green Technology: The transportation industry will continue to move towards electrification and sustainable energy sources to reduce emissions and environmental impact.
2. Autonomous and Connected Vehicles: Advances in autonomous technology and vehicle connectivity will transform the way people travel, enhancing safety and efficiency.
3. Urban Mobility Solutions: The rise of urbanization will drive innovation in public transit, micro-mobility options, and smart city initiatives to address congestion and improve mobility.
4. High-Speed Rail and Hyperloop: Investments in high-speed rail and hyperloop technology will revolutionize long-distance travel, connecting cities faster than ever before.
5. Aerospace Innovation: The aerospace sector will continue to develop supersonic and hypersonic flight technology, making global travel even faster.
6. Sustainable Aviation: The aviation industry will focus on sustainable aviation fuels, improved aircraft design, and efficiency measures to reduce its carbon footprint.
7. Digital Platforms: Transportation will become more integrated with digital platforms, enabling seamless travel planning, ticketing, and information sharing.
8. Space Tourism: The space transportation industry will evolve, making space tourism and commercial space travel a reality.
9. Last-Mile Delivery Solutions: Innovations in last-mile delivery will improve efficiency and reduce emissions in urban areas.
10. Infrastructure Investment: Governments and private sectors will invest in upgrading and expanding transportation infrastructure to support growing demand.
In conclusion, the history of the transportation industry reflects a journey from early forms of mobility to the interconnected and innovative systems of today. The current position of the industry showcases its role in global trade, connectivity, and urbanization. The future outlook is marked by the potential to shape sustainable, efficient, and interconnected transportation systems that address environmental concerns and enhance mobility for all. As technology continues to advance, the transportation industry will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the way people and goods move across the world.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

San Francisco Bay Area
History of the San Francisco Bay Area:
The history of the San Francisco Bay Area is a tale of exploration, innovation, and cultural diversity that has shaped the region into a global hub of technology, culture, and economic activity. The area’s history predates European colonization, with Native American tribes such as the Ohlone residing in the region for thousands of years.
European exploration began in the 18th century, leading to the establishment of Spanish missions and settlements. The California Gold Rush of 1848 sparked a massive influx of people seeking fortune, transforming San Francisco into a bustling port city and a gateway to the West. The completion of the Transcontinental Railroad in 1869 further accelerated the area’s growth and connectivity.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of industries such as shipping, manufacturing, and agriculture, establishing the Bay Area as an economic powerhouse. The devastating 1906 earthquake and subsequent rebuilding marked a period of resilience and innovation, with the introduction of new building standards and urban planning.
During World War II, the region played a crucial role in wartime industries and military logistics. The post-war years saw the emergence of the Bay Area as a center for technology and innovation, with the establishment of companies like Hewlett-Packard and the birth of Silicon Valley.
Current Position of the San Francisco Bay Area:
Today, the San Francisco Bay Area is a vibrant and diverse region known for its technological innovation, cultural richness, and economic significance. It comprises cities like San Francisco, San Jose, Oakland, and numerous smaller communities. The Bay Area is home to some of the world’s most influential technology companies, cultural institutions, and research universities.
Silicon Valley, located in the southern part of the Bay Area, is synonymous with the tech industry. It is home to tech giants like Apple, Google (Alphabet), Facebook (Meta), and many startups that have revolutionized communication, information technology, and entrepreneurship. The Bay Area’s cultural scene is equally vibrant, with world-renowned museums, theaters, music venues, and diverse culinary offerings.
The region’s economy is driven by technology, finance, biotechnology, healthcare, and tourism. The Bay Area’s innovation ecosystem thrives due to its concentration of venture capital, research institutions, and a highly skilled workforce. The presence of renowned universities like Stanford and UC Berkeley contributes to the continuous flow of talent and ideas.
However, the Bay Area also faces challenges related to housing affordability, income inequality, and transportation congestion. The high cost of living has led to debates about equitable access to economic opportunities and quality of life.
Future Outlook of the San Francisco Bay Area:
Looking ahead, the San Francisco Bay Area’s future is characterized by its potential to drive innovation, address social challenges, and shape global trends. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Technology Innovation: The Bay Area will continue to be a global center for technological innovation, with advancements in AI, biotechnology, clean energy, and other emerging fields.
2. Sustainability and Green Initiatives: The region will prioritize sustainability efforts, transitioning towards renewable energy, green infrastructure, and eco-friendly urban planning.
3. Diversity and Inclusion: The Bay Area will strive to address income inequality, housing affordability, and social disparities, ensuring a more inclusive and equitable future for all residents.
4. Remote Work and Digital Connectivity: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated remote work and digital connectivity trends, potentially shaping the Bay Area’s workforce dynamics and urban planning.
5. Transportation and Infrastructure: Investments in public transportation, smart mobility solutions, and infrastructure improvements will be essential to address traffic congestion and support economic growth.
6. Education and Research: Collaborations between universities, research institutions, and tech companies will drive scientific breakthroughs and advancements in various fields.
7. Cultural Resilience: The Bay Area’s rich cultural scene will continue to evolve, with initiatives that celebrate diversity, support the arts, and foster community engagement.
8. Healthcare Innovation: Biotechnology and healthcare sectors will drive advancements in personalized medicine, medical technology, and disease prevention.
9. Housing and Urban Planning: Efforts to address housing affordability will shape urban planning, encouraging sustainable development and community-focused initiatives.
10. Global Influence: The Bay Area will maintain its global influence through technology, culture, and entrepreneurship, shaping trends that resonate worldwide.
In conclusion, the history of the San Francisco Bay Area reflects a journey from exploration to technological innovation, cultural diversity, and economic prominence. The current position of the region showcases its leadership in technology, culture, and research. The future outlook is marked by the Bay Area’s potential to drive innovation, address social challenges, and shape global trends in areas such as sustainability, diversity, and technology. While facing challenges, the region’s history of resilience and forward-thinking suggests that it will continue to be a beacon of innovation and inspiration.

Los Angeles Greater Area
History of the Los Angeles Greater Area:
The history of the Los Angeles Greater Area is a narrative of exploration, cultural diversity, and growth that has transformed the region into a global hub of entertainment, innovation, and urban development. The area’s history is deeply rooted in the indigenous cultures that inhabited the region for thousands of years before European colonization.
Spanish colonization in the 18th century brought missions and settlements to the area. The city of Los Angeles was founded in 1781 as a Spanish pueblo. The 19th century saw California become part of the United States and the region’s economy diversify, with agriculture, oil, and transportation becoming significant industries.
The early 20th century marked the growth of the film industry in Hollywood, catapulting the area to global prominence as the entertainment capital of the world. The construction of infrastructure like the Pacific Electric Red Car system and the development of suburban communities contributed to the region’s urbanization and population growth.
The mid-20th century saw social and cultural movements, including civil rights activism and the rise of music and art scenes. The expansion of the aerospace industry during World War II and the post-war years further boosted the region’s economy.
Current Position of the Los Angeles Greater Area:
Today, the Los Angeles Greater Area is a dynamic and diverse region known for its entertainment industry, cultural richness, and economic significance. It comprises the city of Los Angeles, surrounding suburbs, and neighboring counties. The area is a global leader in entertainment, fashion, technology, and aerospace.
The entertainment industry remains a cornerstone of the region’s identity, with Hollywood serving as the epicenter of film, television, and music production. The Greater Los Angeles Area is also home to major tech companies, creative studios, and renowned universities. The diverse population contributes to a rich cultural scene, with museums, theaters, art galleries, and culinary offerings reflecting a wide range of influences.
The region’s economy spans multiple sectors, including entertainment, technology, healthcare, aerospace, tourism, and trade. The Port of Los Angeles is one of the busiest in the world, facilitating global commerce. The area’s cultural diversity and international connections make it a hub for international trade and cultural exchange.
However, the region also faces challenges related to housing affordability, traffic congestion, and environmental sustainability. Urban sprawl and income disparities have led to debates about equitable development and quality of life for residents.
Future Outlook of the Los Angeles Greater Area:
Looking ahead, the Los Angeles Greater Area’s future is marked by its potential to continue driving innovation, addressing social issues, and shaping global trends. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Entertainment Evolution: The entertainment industry will continue to evolve with advancements in virtual reality, streaming platforms, and interactive experiences.
2. Sustainability and Green Initiatives: The region will prioritize sustainable urban planning, renewable energy adoption, and efforts to combat climate change.
3. Technology Hub: The Los Angeles Greater Area will further develop as a technology hub, fostering innovation in areas like digital media, artificial intelligence, and biotech.
4. Transportation and Infrastructure: Investments in public transit, smart mobility solutions, and infrastructure improvements will be essential to alleviate traffic congestion and reduce emissions.
5. Cultural Resilience: The area’s cultural diversity will remain a source of strength, with initiatives that celebrate heritage, promote inclusivity, and support the arts.
6. Housing and Urban Development: Addressing housing affordability will be a priority, with urban planning focusing on mixed-use developments and community-centered initiatives.
7. Health and Wellness: Healthcare and wellness industries will continue to grow, with innovations in telemedicine, medical technology, and wellness services.
8. Education and Research: Collaborations between universities, research institutions, and industries will drive advancements in various fields, including technology and the arts.
9. Tourism and Hospitality: The region will adapt its tourism industry to changing travel trends and preferences, while also promoting sustainable tourism practices.
10. Social Equity and Inclusion: Efforts to address income inequality and provide equal opportunities for all residents will shape policies and initiatives in the coming years.
In conclusion, the history of the Los Angeles Greater Area reflects a journey from indigenous cultures to cultural diversity, entertainment prominence, and economic growth. The current position of the region showcases its global influence in entertainment, technology, and culture. The future outlook is marked by the potential to drive innovation, address social challenges, and shape trends in sustainability, technology, and diversity. While facing challenges, the area’s history of adaptability and creativity suggests that it will continue to be a dynamic and influential region on the global stage.
Seattle
History of the Seattle Area:
The history of the Seattle area is a tale of exploration, entrepreneurship, and technological innovation that has transformed the region from a small logging outpost into a global hub of technology, trade, and culture. The area’s history is deeply connected to the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest, including tribes like the Duwamish and Suquamish.
The arrival of European settlers in the mid-19th century marked the beginning of significant changes for the region. The establishment of the Denny Party in 1851 led to the founding of the city of Seattle on the shores of Puget Sound. The timber industry played a crucial role in the area’s early economy, with logging and shipbuilding contributing to its growth.
The late 19th century saw the Klondike Gold Rush of 1897, which turned Seattle into a major supply hub for prospectors heading to the Yukon. The development of the Great Northern Railway solidified Seattle’s position as a gateway to the Pacific.
The 20th century brought industrialization and urban growth, with the emergence of industries like aerospace and technology. Companies like Boeing and Microsoft would come to define the region’s identity as a center of innovation and ingenuity.
Current Position of the Seattle Area:
Today, the Seattle area is a thriving and diverse region known for its technological prowess, natural beauty, and vibrant cultural scene. The area encompasses the city of Seattle and its surrounding suburbs, situated between the Puget Sound and the Cascade Range. It is home to leading tech companies, educational institutions, and a mix of industries.
Seattle’s reputation as a technology hub is rooted in the presence of companies like Microsoft and Amazon. The region’s technology sector has driven economic growth and innovation, attracting talent and investment from around the world. The area’s cultural scene is equally dynamic, with a strong arts community, music festivals, museums, and a love for the outdoors.
The local economy is characterized by a mix of technology, healthcare, education, trade, and tourism. The Port of Seattle serves as a gateway for international trade, while the University of Washington and other research institutions contribute to scientific advancements.
However, the Seattle area also faces challenges related to housing affordability, homelessness, and transportation congestion. Rapid growth has strained housing availability and contributed to debates about equitable development.
Future Outlook of the Seattle Area:
Looking ahead, the Seattle area’s future is marked by its potential to continue driving technological innovation, addressing social issues, and shaping global trends. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Technology Innovation: The Seattle area will remain a global center for technology innovation, with continued growth in cloud computing, AI, biotech, and other emerging fields.
2. Sustainability and Green Initiatives: The region will prioritize sustainability efforts, transitioning to renewable energy, green infrastructure, and eco-friendly urban planning.
3. Urban Planning and Transportation: Investments in public transportation, smart mobility solutions, and urban planning will be vital to manage growth and reduce traffic congestion.
4. Arts and Culture: The cultural scene will continue to thrive, with an emphasis on inclusivity, public art, and community engagement.
5. Education and Research: Collaboration between universities, research institutions, and tech companies will drive scientific breakthroughs and advancements.
6. Health and Wellness: Biotechnology and healthcare sectors will continue to grow, with innovations in medical technology, telehealth, and wellness services.
7. Housing Solutions: The region will focus on addressing housing affordability through innovative housing projects and policies.
8. Social Equity: Efforts to address homelessness, income inequality, and social disparities will shape policies and community initiatives.
9. Global Connectivity: The Seattle area will maintain its global connectivity through trade, technology partnerships, and cultural exchange.
10. Outdoor Lifestyle: The region’s appreciation for outdoor activities and natural beauty will continue to play a significant role in the local culture and identity.
In conclusion, the history of the Seattle area reflects a journey from exploration to technological leadership, cultural vibrancy, and economic growth. The current position of the region showcases its global influence in technology, culture, and innovation. The future outlook is marked by the potential to drive technological advancements, address social challenges, and shape trends in sustainability, diversity, and technology. While facing challenges, the area’s history of resilience and innovation suggests that it will continue to be a dynamic and influential region on the global stage.
New York
History of the New York Area:
The history of the New York area is a narrative of exploration, immigration, and cultural dynamism that has shaped the region into a global epicenter of finance, culture, and innovation. The area’s history dates back to the indigenous peoples who inhabited the land before European colonization.
In the early 17th century, Dutch settlers established the colony of New Netherland, with New Amsterdam (now New York City) as its capital. The English later seized control and renamed it New York. The region played a crucial role in the American Revolutionary War, serving as a center of political and military activity.
The 19th century brought significant growth and transformation, with the construction of the Erie Canal connecting New York City to the Great Lakes and spurring economic development. The city’s Ellis Island became a gateway for millions of immigrants arriving in search of opportunity and a new life.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries marked the rise of the New York Stock Exchange and the financial district as a global financial hub. The city’s cultural scene flourished with the Harlem Renaissance, showcasing African American art, literature, and music.
Current Position of the New York Area:
Today, the New York area is a bustling and diverse region known for its financial power, cultural richness, and global influence. The area includes New York City and its surrounding boroughs, as well as parts of New Jersey and Long Island. It is a center for finance, arts, media, technology, and international trade.
New York City is renowned for its iconic landmarks, museums, theaters, and diverse neighborhoods. The city’s financial district is home to Wall Street, where the world’s largest financial institutions operate. The area’s cultural scene is equally vibrant, with Broadway, Times Square, and numerous art galleries attracting visitors from around the world.
The region’s economy is driven by finance, technology, healthcare, tourism, and media. The New York metropolitan area is a global gateway, with major airports and ports facilitating international trade and connectivity. Renowned universities and research institutions contribute to the area’s intellectual and scientific advancements.
However, the New York area also faces challenges related to housing affordability, transportation congestion, and social inequality. Sky-high real estate prices and income disparities have raised concerns about equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Future Outlook of the New York Area:
Looking ahead, the New York area’s future is marked by its potential to continue shaping global finance, culture, and innovation, while also addressing social challenges and environmental concerns. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. Financial Leadership: The New York area will maintain its role as a global financial hub, with Wall Street remaining at the forefront of international finance.
2. Cultural Vibrancy: The city’s cultural scene will continue to flourish, with investments in the arts, diverse communities, and creative industries.
3. Sustainability Initiatives: The region will prioritize sustainability efforts, transitioning to renewable energy, green building practices, and sustainable transportation solutions.
4. Technology and Innovation: Investments in technology and innovation will drive advancements in areas like fintech, biotech, and digital media.
5. Transportation Upgrades: Improvements in public transportation, smart mobility solutions, and urban planning will be crucial to address traffic congestion and pollution.
6. Education and Research: Collaboration between universities, research institutions, and industries will foster scientific breakthroughs and technological advancements.
7. Social Equity: Efforts to address income inequality, affordable housing, and social disparities will shape policies and community initiatives.
8. Global Connectivity: The New York area will maintain its global connectivity through international trade, cultural exchange, and diplomatic relations.
9. Healthcare Innovation: The region will continue to advance in healthcare, with innovations in medical technology, telehealth, and disease prevention.
10. Community Resilience: Community-driven initiatives and partnerships will enhance resilience in the face of challenges like climate change and economic shifts.
In conclusion, the history of the New York area reflects a journey from exploration to global influence, financial leadership, and cultural richness. The current position of the region showcases its iconic landmarks, economic power, and cultural diversity. The future outlook is marked by the area’s potential to continue shaping global trends, addressing social challenges, and driving innovation in areas such as sustainability, technology, and social equity. While facing challenges, the New York area’s history of resilience and adaptability suggests that it will continue to be a dynamic and influential region on the world stage.

Miami
History of the Miami Area:
The history of the Miami area is a tale of exploration, cultural diversity, and transformation that has shaped the region into a global hub of international trade, tourism, and cultural fusion. The area’s history is deeply connected to the indigenous peoples of the Tequesta tribe who inhabited the land for thousands of years.
The arrival of European explorers in the 16th century brought Spanish colonization and attempts to establish settlements. However, it wasn’t until the late 19th century that the city of Miami was officially incorporated. The completion of the Florida East Coast Railway in the early 20th century facilitated growth and transportation, contributing to the city’s development as a regional center.
The mid-20th century saw Miami become a hotspot for tourism and a gateway for Latin American immigration. The city’s cultural scene was enriched by influences from various cultures, leading to the vibrant and diverse environment that characterizes Miami today.
Current Position of the Miami Area:
Today, the Miami area is a vibrant and multicultural region known for its international influence, tourism, and economic significance. The area encompasses the city of Miami and its surrounding communities, extending to Miami Beach and other coastal areas. It serves as a hub for finance, trade, culture, and international relations.
Miami’s cultural diversity is reflected in its neighborhoods, cuisine, arts, and music. The city’s status as a melting pot of cultures has led to a vibrant fusion of traditions from Latin America, the Caribbean, and beyond. The area’s renowned Art Deco architecture, white-sand beaches, and vibrant nightlife attract visitors from around the world.
The region’s economy is driven by international trade, finance, tourism, real estate, and the creative industries. The Port of Miami is one of the busiest cruise ship ports in the world, and Miami International Airport facilitates global connectivity. The city’s status as a financial and cultural hub has attracted international businesses, entrepreneurs, and investors.
However, the Miami area also faces challenges related to climate change, affordable housing, and social inequality. Sea-level rise and extreme weather events have raised concerns about the region’s vulnerability to the effects of climate change.
Future Outlook of the Miami Area:
Looking ahead, the Miami area’s future is marked by its potential to continue thriving as a global gateway while addressing environmental and social challenges. Here are some key trends and projections for the future:
1. International Trade and Relations: Miami will maintain its status as a global trade hub, facilitating commerce between North and South America and serving as a center for international relations.
2. Tourism and Hospitality: The region’s appeal as a tourist destination will continue to attract visitors, with investments in sustainable tourism practices and innovative hospitality offerings.
3. Climate Resilience: The Miami area will focus on climate resilience measures, such as infrastructure improvements, flood management, and sustainable urban planning.
4. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Investments in technology, startups, and innovation will contribute to the growth of Miami’s tech ecosystem and creative industries.
5. Cultural Enrichment: The city’s multicultural identity will be celebrated through art, festivals, and community initiatives that promote understanding and unity.
6. Affordable Housing Solutions: Efforts to address affordable housing challenges will be critical to ensure a diverse and equitable community.
7. Health and Wellness: The region will invest in healthcare infrastructure, wellness services, and medical innovation to support the well-being of residents and visitors.
8. Education and Workforce Development: Collaborations between educational institutions and industries will prepare the workforce for future challenges and opportunities.
9. Sustainability Initiatives: The Miami area will lead in sustainability efforts, emphasizing renewable energy adoption, green building practices, and sustainable transportation.
10. Cultural Diplomacy: Miami’s unique cultural blend will continue to foster connections with Latin America, the Caribbean, and other regions, promoting cultural diplomacy and economic ties.
In conclusion, the history of the Miami area reflects a journey from exploration to cultural fusion, international significance, and economic growth. The current position of the region showcases its vibrant multiculturalism, economic importance, and global appeal. The future outlook is marked by the potential to continue thriving as an international hub while addressing challenges related to climate change, social equity, and sustainability. While facing these challenges, the Miami area’s history of adaptability and diversity suggests that it will continue to be a dynamic and influential region with a unique global perspective.
Program Benefits
Marketing
- Strategic Planning
- Market Analysis
- Customer Segmentation
- Product Innovation
- Competitive Edge
- Brand Positioning
- Marketing Channels
- Customer Acquisition
- Campaign Optimization
- Market Expansion
Operations
- Process Mapping
- Efficiency Gains
- Lean Implementation
- Six Sigma Techniques
- Kaizen Mindset
- Resource Allocation
- Automation Strategies
- Quality Enhancement
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Workflow Streamlining
Human Resources
- Change Management
- Growth Mindset
- Leadership Agility
- Culture of Innovation
- Employee Engagement
- Strategic Alignment
- Performance Metrics
- Talent Development
- Decision-Making
- Resilience Building
Testimonials

Plug & Play
“Having Ms. Viswanath as a business advisor to the companies in our ecosystem has been invaluable. Her decades of experience helping start-ups grow and scale translates to her ability to delve into any company’s issues and help them grow. This has helped our companies develop strategic roadmaps, scale anywhere from 25-75%, and increase productivity and profit margins by up to 100%. The tools she has implemented are used consistently and essential to growth.”

UNC Health
“Using the tools and methodologies Ms. Viswanath has taught us, our hospital system has increased productivity and bottom-line profits. Some processes needed to be streamlined and our growth strategy for drawing in new customers had to be reassessed. Ms. Viswanath worked closely with us to redefine our goals and form a reasonable plan of action to reach the goals. The knowledge we gained has helped shape our future direction.”

TiE Global – Achievement
“The mission of TiE is to foster entrepreneurship through mentoring, networking, education, funding, and incubation throughout the world. At TiE Global, Ms. Viswanath crafted strategic initiatives spanning marketing, fundraising, and product/program development. She collaborated with hundreds of entrepreneurs/executives globally to implement new ideas from concept to roll-out. >100 chapters with >100,000 members adopted the products and initiatives she implemented worldwide. She built a global ecosystem of startups and investors.”

ActiveScaler – Achievement
“ActiveScaler is launching and scaling innovative mobility products. ActiveScaler acquired Tagsi Inc. (a company which Ms. Viswanath founded) to expand its ride-share services to specialized niche markets of seniors, children, and special needs. Ms. Viswanth worked closely with the CEO & the COO to create and implement a strategic business development plan, creatively solve problems, and create mission & service-driven growth of mobility products. She managed a global cross-functional team of 50 to scale Tagsi’s innovative rideshare worth $5M. She oversaw operations, product management, business development, and strategy. This led to product management of a sophisticated transportation platform that could be used for >1 million rides/ year.
Ms. Viswanath also applied successfully for TNC licenses in the US and Asia and negotiated partnerships with taxi companies in the US and Asia. She leveraged market & user data, analytics, and financial modeling to deliver insights; and address challenges and competition while improving quality, customer satisfaction, and financial performance. This resulted in $10 million in cost savings for ten Central Bay area school districts and the potential to generate >$30 million in revenue. It also resulted in the efficient use of Series A funds to optimize revenue and minimize capital waste to help with Series B fundraising.”

Utavi
“Utavi empowers investments in private assets through compliant and secure capital flows between investors and assets. She assisted CEO to develop initial concept vision and product roadmap. She oversaw biz operations and sales with small business customers. She produced >$1M in first-year revenue for Utavi, enabling the company to raise Series A of $3M and to grow the engineering and operations team by 40 persons.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.