Revenue Operations (RevOps)

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Revenue Operations (RevOps) is provided by Mr. Anderson Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Anderson is a Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene, and he has extensive experience in Revenue Operations Leadership in the sales, marketing, and customer success functions. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Business Management with a focus in both Marketing and Communication Studies. During his 30+ year career, Mr. Anderson has transformed Revenue Operations in the software-as-a-service (SaaS), manufacturing, life sciences, and professional services sectors. He has had commercial experience within the following countries: the United States of America, Europe, and Australia, or more specifically within the following cities: New York City, San Franciso (Silicon Valley), Boston, Barcelona, London, and Ballarat. His achievements include Inaugural President’s Club and Mentor of the Year for the Sales Xceleration group of Fractional VPs of Sales, 15 years as CRO, and principal consultant, helping businesses and leaders achieve consistent and predictable growth. His service skills incorporate growth strategy, revenue operations process improvement, cross-functional integration and change management, executive coaching, sales leadership development, and team building.
To request further information about Mr. Anderson through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Revenue Operations (RevOps)
About This Program
The Revenue Operations (RevOps) program is a process for building the GTM Strategies, Processes, and Execution foundations that lead to reliable and profitable revenue growth. Many organizations have tremendous insight into the technologies, knowledge base, and scope of products and services they offer and the market that is currently available to serve. Over time, the market shifts, and buying preferences change. The structures initially put in place for developing, producing, and maintaining products and the clients who will buy them become less effective. The reasons most organizations need help to grow consistently over time are first having enough cash and then adjusting assumptions made when the executive team put the initial strategy in place. Initial assumptions are typically validated and adjusted by measuring past performance, then changing the approach when past performance doesn’t deliver expected results.
When adopting and executing a Revenue Operations (RevOps) function, organizations can proactively move into markets and recover and maintain consistent growth in developed markets with greater confidence and capacity to adjust quickly. RevOps allows organizations to better utilize past performance and real-time insights on what is occurring today and work with a more accurate prediction of future performance. When implementing a RevOps function process, organizations experience continuous improvement and consistency in productivity and profitability across all revenue-generating functions. These improvements appear early in the RevOps implementation process and continue to increase throughout the organization’s life.
The Imperative for Profitable Growth
Attaining and then maintaining consistency in revenue growth is challenging for any business. Slow and steady, rapid scale-up, or recovering from stagnation and decline all share the same core challenges, changing over time. Canned methodologies and principles older than 5 to 7 years do not work in the current global, data-driven, fast-moving economy. The old models for new businesses of Fail Fast and Fail Forward no longer provide the longevity needed to reverse burn rates, and the established business model of Market Entry, Growth, Cash Cow, and Decline is not sustainable in a world seeking sustainability.
A study published by Shopify in April of 2022 shows the failure rate of new US-based businesses over five years at 48.4%. What are the most common factors? Lack of financing and running out of cash. Global averages mirror this report, with almost 20% failing in their first year and over 30% in 2 years.
Also, a 2019 (pre-pandemic) study by Forbes puts the failure rate of acquisitions much higher: at 70% to 90%. The most cited reason is the lack of alignment between organizational goals, objectives, and processes.
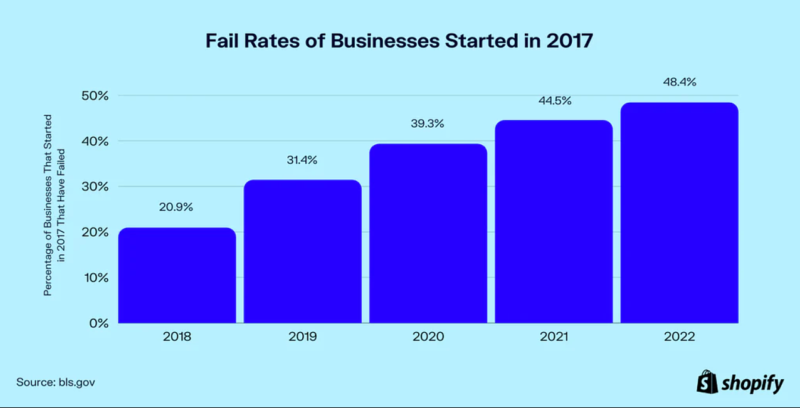
Figure 1: Rates of failure for US businesses formed in 2017.
What are the root causes of business failure?
First, new organizations struggle to validate and then acquire market share quickly. They need more cash or access to investors willing to take greater risks. For those that survive the first few critical years or become acquired, the same challenges appear for organizations with long-term market presence: Functional misalignment with Vision. As a new or established business starts to grow differently than they have in the past, a range of common themes appear that threaten or slow the potential initially seen at the start of the business journey:
Recognize any of these symptoms?
• Functional silos develop that limit alignment to overall organization goals.
• Processes and policies put in place for risk aversion and cost efficiency lead to stoic adherence to old procedures and productivity stagnation.
• Talent that produced fantastic results at early stages cannot transition to delivering effective results in the larger operation structures.
• Leadership loses visibility into actual execution at the ‘get it done’ level as more people perform more and more specific functions.
• Incomplete, inaccurate, and overly cleansed data is delivered by behaviors favoring position protection over goal achievement.

Gradually, growth slows as the product becomes misaligned with market preferences, and the execution of work becomes further misaligned with the overall strategy. The cycle starts with a slowdown in market engagement, followed by a lack of visibility into execution, declines in team engagement and productivity, and finally, employee churn, productivity stagnation, and financial loss.
The result: Leadership becomes firefighters, addressing many symptoms while lacking visibility into the causes, so the issues causing the initial decline to worsen. At some point, the pain of a complete organization restructure must be implemented with a “do or die” mandate.
Addressing these challenges when they exist, or better, preventing them from occurring, requires a proven set of strategies, processes, and execution methods that will work for your business.
From strategy creation to tactical execution, we will assemble the tools your business needs and the learning to maintain them for optimal performance. We will build a RevOps function that satisfies your business’s unique Vision – the unique WHY.
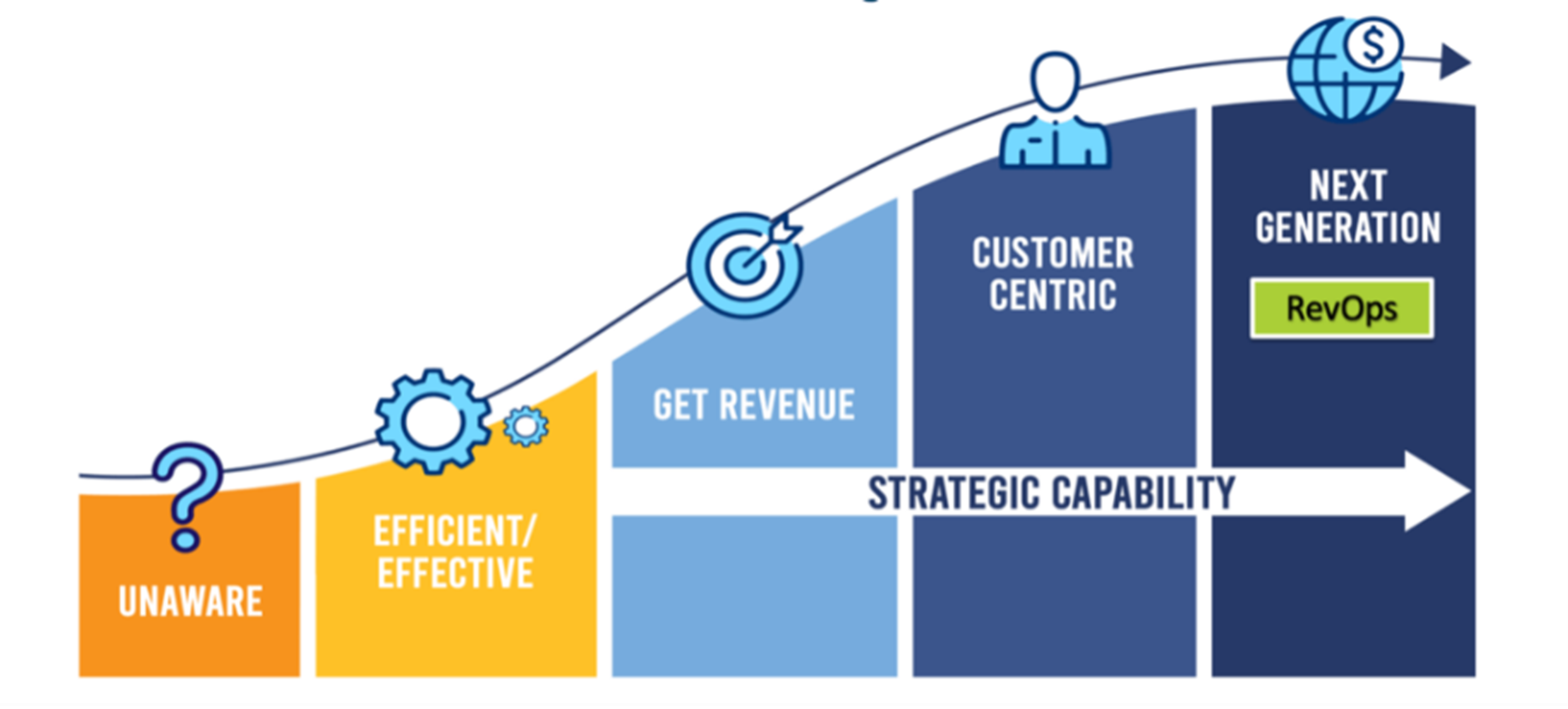
Figure 2: The marketing operations maturity model, introduced by Dr. Debbie Qaqish, Leads to RevOps, not decline.
Each set of processes and methods build on each other and provide your operating groups and individual team members the clarity of Vision needed for each person to do their part in generating revenue more consistently and in alignment with their colleagues.
5 Critical Success Factors for Adopting a Revenue Operations Function
1. Quickly Achieve and Maintain profitability
Introducing a new product or service requires fast and positive results to establish viability and longevity in the market. Profitability is the most important measure of potential in both the immediate and long term. Even if losses decrease over time, more than simply generating revenue at a loss is needed. Investors often expect early losses in a new venture, though that early investment comes with expectations for a significant and quick return.
Confidence in a strong return on the investment comes from both early and consistent validation of a viable and profitable product over time and an outlook indicating growth rate will accelerate. A solid Revenue Operations (RevOps) function provides that confidence with more reliable and predictable forecasts based on more accurate, real-time, and actionable data. The consistent focus of
RevOps brings both reliable growth and unprecedented visibility into the changes needed to achieve, accelerate, and maintain it. A high-performing RevOps function is the best-proven path to delivering the results investors and the boardroom demand.
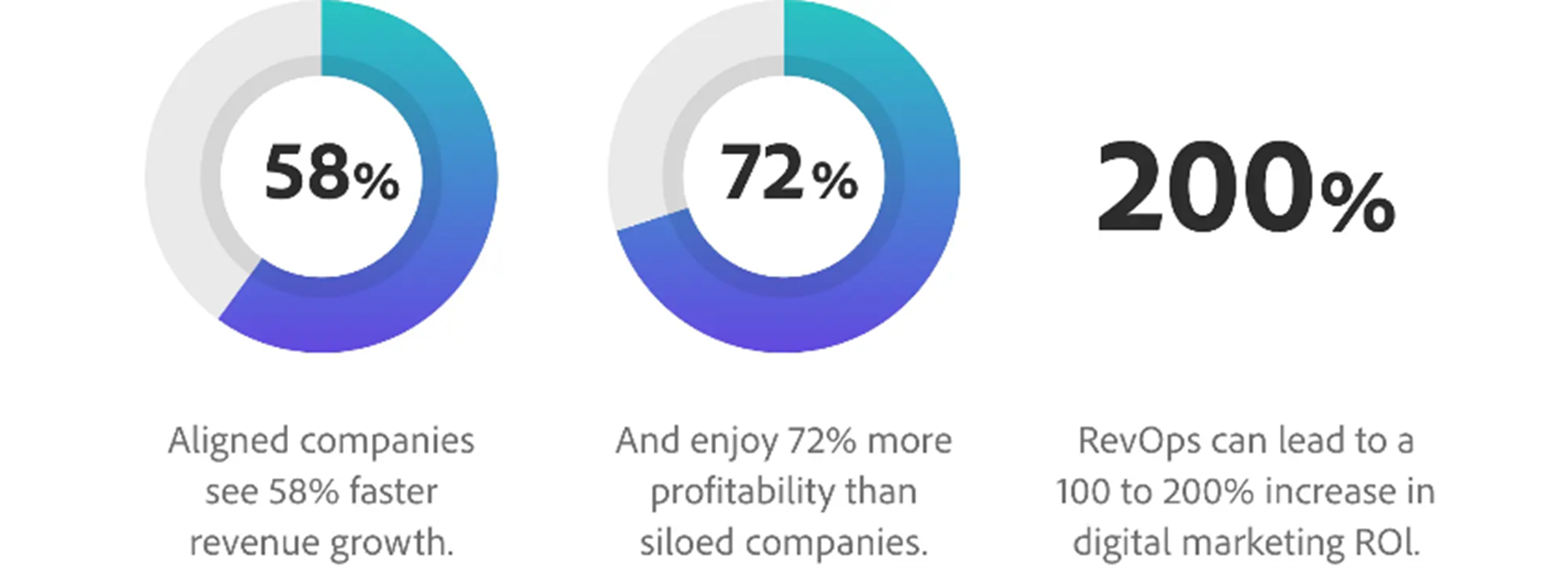
Figure 3: Studies by LSA Global and Boston Consulting Group, consolidated by Adobe Experience Cloud, demonstrate the value of alignment through RevOps.
2. Maximize Productivity of People and Resources
Enhance profitability with the most efficient and effective deployment of resources. A fast-growing organization’s rapidly changing environment requires agility and structure, with a balance between these competing forces.
Agility is essential to make necessary changes quickly. A rapidly growing organization must eliminate ineffective execution methods while adopting improved practices quickly.
The structure is needed to generate reliable data and insights as you overcome obstacles. The system is critical for clarifying what changes need to make, why, and what results to expect from those changes.

A vital RevOps function balances agility and structure, keeping people, tools, and resources optimized for productivity and aligned and engaged on corporate objectives. The result is continuous productivity improvement, delivering resilience in the market and long-term, reliable, and profitable growth.
3. Acquire and Retain Market Share
Validation of product viability is dependent on first acquiring and then retaining paying customers. There is no longer a case for one-and-done transactions. Even the one-time purchase still requires satisfaction with the product to attract new buyers, which may need to be improved to maintain a growth trajectory over time.
A strong RevOps organization monitors and manages the entire customer journey over the long term, from initial awareness to satisfaction, and then loops back to additional understanding of new ways the organization can deliver value to that same client. Integrating and aligning the functions of Marketing, Sales, and Customer Success is the only way to accurately assemble complete insights into the customer journey and understand changing customer needs over time. RevOps integration is critical for the organization to maintain the innovation required to retain and grow its market position.
4. Attract and Retain Talent
Solid and effective human-to-human interactions drive growth. Regardless of the communication method, the actions, behaviors, and decision-making at the personal level drive growth and organizations forward. This truth is most important in the client-facing functions of RevOps. RevOps talent engages with human behavior and assesses the data and insights from those interactions to decide on the best following action. When people know what to do, how to do it, and why doing it that way is essential, decision-making stays aligned with corporate objectives, and people are more engaged by knowing their work is valued and practical.
A vital RevOps function provides clear direction, alignment of skills to objectives, and the path for professional growth that people need to be satisfied with their work. A strong RevOps function is critical for attracting and retaining talent through the rapidly changing environment of human interactions in a high-growth organization.
5. Retain Alignment to Mission and Core Values
Achieving and maintaining profitable growth requires alignment with the organization’s mission with behaviors aligned with Core Values. When this fails, talent becomes dissatisfied, attention to market needs and customer satisfaction declines, productivity drops, and profits shrink.
A vital RevOps function, as Zappos implemented as part of their legendary Delivering WOW Through Service culture alignment program, provides leadership real-time and actional insights into revenue-generating execution activities and behaviors. Without an aligned RevOps function, this crucial visibility is diminished over time as the organization adds more people, with each new hire doing more distinct work than in earlier stages of the company. RevOps provides the structure needed to retain this critical visibility by providing the real-time insights and supporting data required to specifically identify who and what is moving off-track and the flexibility to make corrections quickly before misalignment with Mission and Core Values can spread through the organization.
Curriculum
Revenue Operations (RevOps) – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Organization Vision
- Part 1 Month 2 Go-To-Market Strategy
- Part 1 Month 3 Market Position
- Part 1 Month 4 Processes
- Part 1 Month 5 Team Structure
- Part 1 Month 6 Process Automation
- Part 1 Month 7 Metrics & KPIs
- Part 1 Month 8 Execution Structure
- Part 1 Month 9 Execution with People
- Part 1 Month 10 Execution with Data
- Part 1 Month 11 Growth Obstacles
- Part 1 Month 12 Re-Calibration
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Revenue Operations (RevOps) corporate training program.
Revenue Operations (RevOps) – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Organization Vision – The result of this session will be a clear long-term vision for the entire organization. This Vision (the Why) supports the foundational strategy (the How), which outlines the journey from where you are now to where your Vision directs you. The strategy we create will support a revenue generation map with clearly defined and measurable milestones that each group, team, and person can use to keep the Vision clear and stay true to the Vision even when the path forward must change due to unforeseen obstacles.
- Part 1 Month 2 Go-To-Market Strategy – In Session Number 2, you will learn to create and implement more reliable methods of building and maintaining the Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy and avoid the pitfalls of diluting your core. In addition, you will learn the skills and tactics for keeping GTM strategy aligned with the market, the RevOps functions of marketing, sales, and customer success, and to the other business functions, and most importantly, the core overall vision, even in the face of rapid and unpredictable change.
- Part 1 Month 3 Market Position – Building on the foundations built in sessions 1 and 2, we will continue to refine Vision and strategy in session three as we address defining and tuning the GTM strategy. You will receive the tools you need to apply the best methods for generating and constantly adjusting Competitive Positioning as well as Unique Value and Unique Selling propositions to keep your organization aligned with the market and how to deliver products that address actual market needs in ways your competition does not. At the end of this session, you will have an aligned GTM strategy that incorporates all RevOps functions and the knowledge and tools to remain differentiated and valued by your target customer base.
- Part 1 Month 4 Processes – In session 4, we address establishing processes with clear, measurable steps for executing strategy and deliver critical insights into what part of the strategy needs to be adjusted: Processes with the flexibility required to maintain consistent growth.
- Part 1 Month 5 Team Structure – In sessions 1-4, you learned how to establish and maintain alignment at the functional levels. In session 5, we will learn how to identify, align, and motivate the human resources necessary to accelerate strategy execution and connect those resources flexibly. You will define the human elements of roles and responsibilities, the skills needed to effectively meet obligations, role alignment, and goals for each seat, team, and function of the RevOps business unit. The workshop results in a clear understanding of the roles needed to execute the processes established in the prior session, maintaining alignment of active roles to goals and providing channels for professional growth for people as the organization grows, accelerating growth.
- Part 1 Month 6 Process Automation – In this session, we will build and refine your RevOps tech stack to optimize RevOps productivity. You will learn how to identify, assemble, implement, maintain, and stay current with the tech stack optimized toward the unique needs of your business. Without needing additional consultants and advisors, your team will know how to leverage customization and integration for cross-functional process automation and set up and maintain optimal user-tool interactions that improve productivity, reduce client acquisition and retention costs, and automate KPI measurement and reporting.
- Part 1 Month 7 Metrics & KPIs – In this workshop, you will learn how to set up and manage the Predictable Growth Formula for your business, establish the baseline measurements needed to ensure consistent, long-term profitability, and when to modify which metrics to use and which to change without compromising data consistency and integrity.
- Part 1 Month 8 Execution Structure – A well-planned and structured RevOps organization propels an organization through this stage quickly and with minimal disruption. This structure is the critical time to test and affirm that the strategy is sound, assumptions remain valid, processes are supportive, and tools and people remain aligned and moving in the same direction. In this workshop, you will learn how to set up and maintain efficient structures of execution that support and maintain alignment with overall strategy, from the function level to teams and individuals on teams. This workshop’s outcome is your organization’s ongoing capacity to make proactive and real-time decisions throughout the RevOps function that accelerates growth.
- Part 1 Month 9 Execution with People – In this critical workshop, you will learn the principles of “Right Person, Right Seat” and how to measure and implement this crucial decision-making process and lead individuals toward their best possible contributor role. You will also learn how to utilize compensation and incentive plans to encourage the behaviors that drive growth and how to assess the critical ‘soft- skills’ necessary for success in creative, selling, and service roles. You will set up onboarding and offboarding processes to ensure faster ramp-up times and define the training requirements and what needs to be ‘part of the package’ for new hires. This workshop will clarify how leadership can identify which groups, teams, and people are on or off track, how to get the right people back on track, and how to find, motivate, improve, and retain the human resources that power growth.
- Part 1 Month 10 Execution with Data – In this workshop, you will learn how to assemble and analyze the data generated from the day-to-day execution of strategy and processes from all team members and gain real-time insights on what can be changed – in the moment and over time – to improve results immediately and in the future.
- Part 1 Month 11 Growth Obstacles – In this workshop, you will create a clear and consistent framework for quickly identifying and resolving the barriers to growth, implement Issue Management Planning, and establish a system to Identify, Prioritize, and Solve (IPS) issues based on priority and level of impact. The result of this workshop will be faster, more effective issue resolution at the causal level and sustaining growth and productivity as best as possible through any market transition. If you must change everything, you will have the tools to do that quickly and minimize the impact on revenue and profitability.
- Part 1 Month 12 Re-Calibration – In this final workshop, you will exercise your active use cases to apply the learnings of this course. You will learn your business’s most effective change management practices and how to identify what to recalibrate as conditions change over time. You will identify obstacles, how data points to the cause and desired change in data, how people are part of the cause and the resolution, which execution processes to add or change, and the impact of those changes on processes, RevOps strategy, and overall strategy.
Methodology
Revenue Operations (RevOps)
Achieving consistent growth in a rapidly changing world
This course leverages a primary framework of Strategy, Process, and Execution – in this order – with supporting methods within each of these three essential elements of growth. Our research has found it essential to lay a foundation for growth that is at once clear and measurable while also allowing for rapid changes necessary to adapt to adjustments in the market. The pace of technological advances and global economic, political, and other influences have rendered one-time ‘digital transformation’ or restructuring efforts incapable of supporting a long-term growth trajectory. The methods applied throughout this primary framework of this course allow organizations to consistently adjust growth strategy without the financial and productivity costs that more disruptive change requires.
The Strategy element
On the journey to consistent growth, strategy is the desired destination. To achieve more predictable growth, leadership must have a clear vision for the future that is clear and adopted throughout the organization, as well as visibility into how well the vision is understood and acted on.
Through guided discussion using proven tools, participants will adopt and learn how to maintain a customized Vision Planning method that includes core objectives over a 10-year timeframe, communicating that plan to the organization, and aligning the plan with the go-to-market strategy, obstacle management, and functional execution.

The Process element
Strategy is the destination, and the Process is how the organization will reach the destination. Participants will learn and utilize the aKPI method for actionable measures of success and the Predictable Growth Formula, a set of the 12 key elements that determine long-term growth. Combining these two methods, participants will be guided through creating a view of the entire road map – rather than step-by-step instructions – from the starting point to the desired strategic destination to attain a clear view of the RevOps structure, human skills and mindsets, activities, and technologies needed to reach the destination most productively and profitably.
The Execution element
Execution is the tactics employed to navigate the process road map, which gets you to the Strategy destination. Participants will learn how to leverage the fundamentals of Agile project management best to streamline and accelerate activity. In addition, we will deploy the Most Important Goal (MIG) and pKPI system for keeping people and tools aligned to the most productive activities while providing leadership with real-time visibility to where everyone is on the map and whether each person and function is on track toward the destination defined in the strategy.
The Imperative
The combined methods deployed throughout this program, when configured to the unique requirements of your business, have consistently proven to transform organizations and leaders, providing a clearer path to long-term, sustainable, and profitable growth.
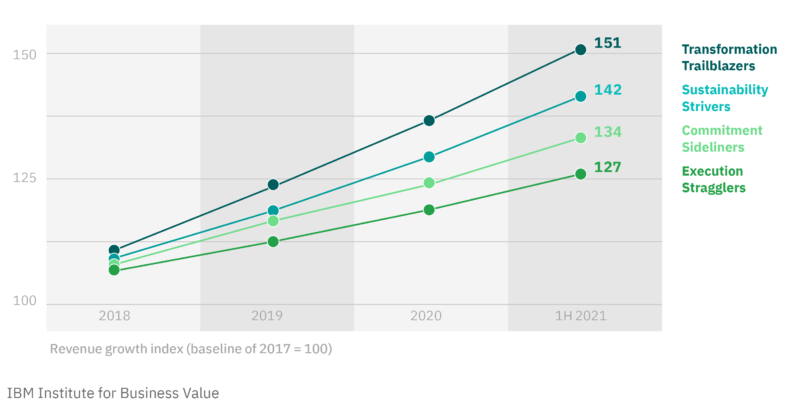
As this chart produced from a study by IBM indicate, “Transformational Trailblazers” outperform organizations with a lower commitment to the changes that drive sustainable growth.
Each of the three core elements, Strategy Process, and Execution, supports and informs the other. With the consistent application of the methods and tools provided in this course, Organizations and leaders can sustainably accelerate growth by implementing the changes necessary, based on relevant data and real-time insights, without the pains of constant restructuring.

Case Study
Consider the application of Revenue Operations principles to Amazon’s current meteoric growth. Founded in 1994, Amazon IPO’d at $18 per share in 1997. Focusing on a 10-year strategy that was based on providing a model by relentless process execution, learning through execution, and revising processes to match current market trends, Amazon’s success with books validated a strategy based on providing value to the consumer, first, and building processes and execution methods around consumer satisfaction that rapidly changed as adoption of online purchasing by consumers began to gin traction in the late 1990’s.
Remaining focused on acquisitions that aligned first with Amazon’s Consumer first strategy, the firm expanded beyond books in 1998, gathered more insights from execution in new markets, applied those insights to improve processes, and updated short term strategies to target additional verticals that were aligned with Amazon’s Vision. The magic happened when Amazon stayed true to their core vision and strategy and invest profits from prior successes into new acquisitions that would fuel even greater consumer value in the future, such as one-click ordering, AWS, Prime and Prime Music.
This example is Revenue Operations thinking and execution, before the strategic function of Revenue Operations was a defined function. Amazon did not have to re-structure, re-organize, or experience significant pain with each new acquisition. Strategy was enhanced rather than being scrapped and re-defined. New processes were learned from acquisitions, with the relevant elements applied to other groups, so execution on strategic objectives could continue to advance in a consistently improving manner.
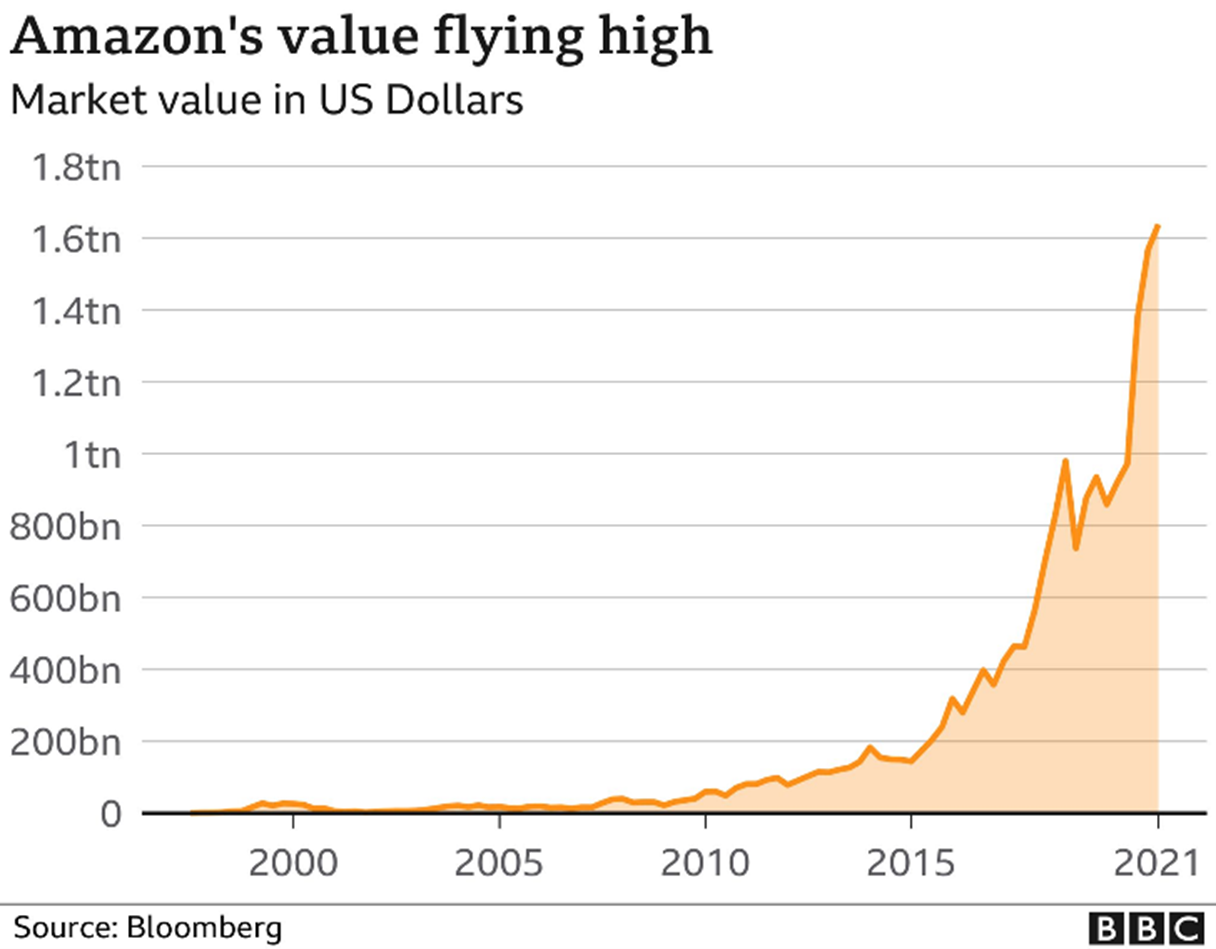
It is also important to note that Amazon’s strategy did not, and still does not incorporate a ‘maximize shareholder value’ component. The organization remains true to its core mission of providing value to consumers, and in doing so, performance is delivered from the Revenue Operation top line to the shareholder’s bottom line.
By following a Revenue Operations mindset: Strategy first, then processes that point the organization in that strategic direction, then execution of those processes to test, measure, and refine next steps, that led to Amazon’s $1 Trillion market capitalization value in 2018 – less than 25 years after founding.
Program Content
Session 1: Organization Vision and Strategy
Many leadership teams have a clear vision of what to accomplish but need more traction when executing that Vision over time. As teams grow and individuals become more specialized in their functions, the executive team’s Vision becomes diluted at the execution level – the layers between top leadership and those executing the tasks needed to realize the Vision, the more obscure the Vision becomes at the execution level. The result is that leadership slowly and steadily loses critical insights into the organization’s alignment with the Vision. Hence, decision-making at the leadership level loses efficacy, slows, and becomes less and less effective over time. For revenue generation, the result is missed goals, delays, and cost overruns.
Consistent growth starts with first knowing what you are growing toward. Which direction do you start walking on a journey of 10,000 kilometers? Consider the case of Apple. When Steve Jobs took on the CEO mantel at Apple for the second time (Having learned much from his initial failure to grow the business), the organization had been struggling to find a viable market for Apple’s powerful and unique technology. Jobs refocused Apple’s technology development team: From how the product functioned to what that technology would deliver to consumers. He realigned the Apple team on what kind of company Apple would be, based on the vision of how consumers would fee l about Apple products and Apple as a company. The vision statement for Apple today remains the same: “To make the best products on earth and to leave the world better than we found it.” To do that, Job’s focused the team on what Apple would look like in 1 year, 3 years, 5 years. The team shifted product design, not just function, to evoke the feeling consumers would have when they owned an Apple product – A feeling aligned with Apple’s vision. The emphasis was, and remains What will Apple be?
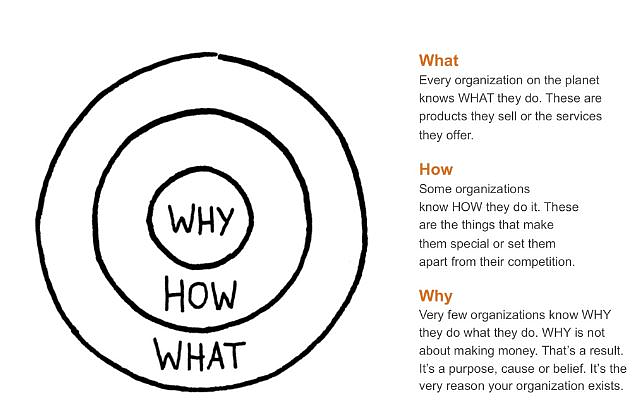
Clarity of Vision is the foundation for your organization and what it will strive to be along the journey. Strategy is the road map of How you will be that way, starting with where you are now and moving toward the direction of what you will be. A Why without an associated How is simply a dream. The How element transforms the idea into reality – supported and shaped by what the organization does.
In the first session, we will address the foundation of the business: WHY do you exist, and HOW do you do that? You will answer the critical questions on the Vision and how you plan to bring that Vision to life AND maintain it over the long term. We will work together to ensure that the foundation upon which everything you do is strong, clear, and powerful.
The result of this session will be a clear long-term vision for the entire organization. This Vision (the Why) supports the foundational strategy (the How), which outlines the journey from where you are now to where your Vision directs you. The strategy we create will support a revenue generation map with clearly defined and measurable milestones that each group, team, and person can use to keep the Vision clear and stay true to the Vision even when the path forward must change due to unforeseen obstacles.
Session 2: Revenue Operations and Go-To-Market Strategy
When organizations begin to grow, revenue creation and profitability rates often decline. The decline is a gradual process stemming from a progressive increase in the lack of alignment among the revenue-generating functions of Marketing, Sales, and Customer Success. As these teams grow to satisfy the demand for more tactical execution, misalignment increases. The symptoms appear first on the balance sheet, with these functions slowly delivering less to the bottom line. The signs show in the numbers: missed sales targets, decreasing ARR, and competitive pricing pressure.

For example, in 1996, Levi Strauss was larger than Nike. Then, between 1996 and 2001, sales revenues dropped to half what they were in 1996. The cause? Growth for growth’s sake and based on prior successes outside the core product line and their Vision. Levi’s has since turned this around by following a simple, RevOps-focused mantra of “Grow the core, expand for more.” Levi’s has returned to solid, consistent growth by addressing the most common and hidden cause of inconsistency in revenue growth: Lack of alignment in the revenue-generating functions to the overall Vision for the organization.
In Session Number 2, you will learn to create and implement more reliable methods of building and maintaining the Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy and avoid the pitfalls of diluting your core. In addition, you will learn the skills and tactics for keeping GTM strategy aligned with the market, the RevOps functions of marketing, sales, and customer success, and to the other business functions, and most importantly, the core overall vision, even in the face of rapid and unpredictable change.
Session 3: Market Position and Differentiation
GTM structure and maintaining a leadership position in a constantly changing market as the business grows is critical for attaining consistency in revenue growth, regardless of whether you see your target market as finite or ever-expanding. Many organizations struggle to maintain a market leadership position from a lack of consistent measurement and clarity on product offering alignment to shifts in market demand and changes in buying processes and patterns. All of these must remain aligned with the changing market.
Often, the best initial approach to establishing a differentiated position in the market is not always the most significant financial opportunity – it is the most strategically important. When Jeff Bezos set out to disrupt the consumer retail segment, he didn’t start with the most significant part of fast-moving consumer goods; he started with books. Why? The channel structure from publisher to consumer was antiquated, complex, and laden with complex distribution structures. The publishing sector provided a target that would validate Amazon’s model quickly and profitably while simultaneously revealing both inaccurate assumptions and unforeseen advantages of the model. Each new market that came afterward: Computer games, CDs, and DVDs, followed by durable consumer goods, like Shoes from Zappos, followed the lessons learned from prior successes. Amazon does not differentiate on inexpensive and easy for consumers to buy (even though these are positive benefits); they differentiate in the market on total value to the consumer. Sector after sector, Amazon stunned traditional market analysts by utilizing profits from these early projects to fund long-term investments into new sectors – 100% aligned with Amazon’s Mission “…to be Earth’s most customer-centric company, Earth’s best employer, and Earth’s safest place to work.”
Building on the foundations built in sessions 1 and 2, we will continue to refine Vision and strategy in session three as we address defining and tuning the GTM strategy. You will receive the tools you need to apply the best methods for generating and constantly adjusting Competitive Positioning as well as Unique Value and Unique Selling propositions to keep your organization aligned with the market and how to deliver products that address actual market needs in ways your competition does not. At the end of this session, you will have an aligned GTM strategy that incorporates all RevOps functions and the knowledge and tools to remain differentiated and valued by your target customer base.
Session 4: Processes
Once we have clarity of Vision and tools or building and maintaining alignment around it, and then who in the market will benefit from that Vision and how to reach them with value propositions that communicate that benefit, then we can address how to establish clear tactical steps necessary to drive vision implementation through to consistent execution.
Processes are the essential guideposts on our journey through growth. They are the most effective source of direction available to the organization, and each team member needs to stay on track toward goals and align with Vision. It is the measures derived from consistent process execution that provides the data necessary to make better decisions.

However, the processes can neither stagnate nor be inconsistent to work effectively. We must know what we want the Processes to deliver in value before establishing, adhering to, and measuring the results of processes designed to provide that. So how do you create compelling, flexible Processes when an organization enters growth mode, and team members and leaders need to do what they have never done before? At the same time, we can only know what is working and what needs to be changed if we have consistent means for measuring actual work results.
The challenge most organizations face with creating and implementing processes is that the process becomes a fixed set of directions, locking people and tools into set activities that rarely change. This practice prevents people from staying aligned with their Vision and each other. The result is an ongoing decline in productivity and stagnation in growth.
The key to establishing effective processes is to use them as the entire road map, showing all the options to get from here to there, not just a fixed set of ‘turn left, turn right’ directions. Also, different functions and members of your team are operating on other parts of the map, and all are heading to the same destination but from different locations and starting points. Processes must be specific enough for individuals to stay ‘on the map’ while staying aligned with who else is on the map, doing what, and in what relative position.
Effective processes for RevOps functions of marketing, Sales, and customer success provide each part a clear direction and deliver insights from everyone’s progress to other people in other organization functions. The increased transparency and insights that other organization functions gain and measurable data from consistently executed processes provide the leadership with the insights needed to make effective, informed, and rapid course corrections when barriers appear. They are the pavement on which alignment and consistency in growth achieve a smooth ride.
In session 4, we address establishing processes with clear, measurable steps for executing strategy and deliver critical insights into what part of the strategy needs to be adjusted: Processes with the flexibility required to maintain consistent growth.
Session 5: Team Structure
RevOps functions are client-facing. Each of the three organizational parts of RevOps focuses on engaging the market, encouraging and guiding buyers toward purchase decisions, and retaining and expanding relationships with the people who choose to start and then maintain relationships with the business. The human resources of the RevOps function are the critical catalyst between the company and the people outside the business who buy.
With a clear vision, market alignment, and definitions of required activity, the next logical step would be hiring the people who can do those things, and you’re ready to scale. Not so fast. To avoid the common misalignment with the Vision identified earlier, we must first understand the skills needed to execute the processes and how those who execute them interact. Where is collaboration, transfer of ownership, and specialization necessary? Do you need a strong digital marketing function and a small sales team of closing experts? How robust should your customer success function be? We will address ensuring ‘right person – right seat’ alignment in session 9, but first, we need to understand what seats we need and how they relate to one another.

3M’s organizational structure supports its mission of innovation. The system supports a culture focused on research and fostering entrepreneurial spirit among its staff. The support functions at 3M processes provide researchers the support they need to bring their ideas to market, with groups centered around specific market focus areas, such as consumer, industrial, and healthcare. The structure supports 3M’s unrivaled record of providing innovative solutions to consumers and other businesses – but #M did not start this way. 3M began as a mining operation focused on mining corundum to manufacture sandpaper. Unfortunately, what they thought was corundum was a different, lower-grade mineral, so the founders pivoted, found new uses for the material they owned, and refocused their team on finding new ways of using other commonly available materials that were otherwise underutilized. They created a structure of innovation that allowed the organization to thrive as a constant member of the Fortune 500 list from the inception of that list.
Without a well-defined structure for what functions focus on what work, organizations like 3M would have remained focused on making sandpaper and failed. Optimizing organization structure to maximize productivity and team engagement is critical for aligning with the ever-changing market and buyer preferences. However, constant changes in organizational structure confuse people hired to execute specific tasks and a lack of alignment between organizational goals and execution-level operations. At the same time, remaining in a rigid structure in an ever-changing market slows productivity and profitability and stagnates growth potential for individuals in those execution roles. Finding the balance between the demand for flexibility and stability requires having a clearly defined structure that connects but does not bind functional expertise. It so is based on both organizational goals as well as market conditions.
In sessions 1-4, you learned how to establish and maintain alignment at the functional levels. In session 5, we will learn how to identify, align, and motivate the human resources necessary to accelerate strategy execution and connect those resources flexibly. You will define the human elements of roles and responsibilities, the skills needed to effectively meet obligations, role alignment, and goals for each seat, team, and function of the RevOps business unit. The workshop results in a clear understanding of the roles needed to execute the processes established in the prior session, maintaining alignment of active roles to goals and providing channels for professional growth for people as the organization grows, accelerating growth.
Session 6: Process Automation and Tech Stack
Continuous technological advances offer seemingly limitless opportunities to leverage tools to do work that once required human tactical execution. The productivity benefits are immense, as are the number of options for tools to streamline human activity and information management. At the same time, every business has core processes at a macro-functional level that appear similar from a high-level view. However, every company is different from another, and leadership must customize the structure and execution processes within each core function to fit the organization’s Vision. Over time, organizations adopt core tools to help manage process execution. New systems can lead to having multiple systems unique to specific functions that don’t integrate with other functions tools or the opposite extreme of central tools that managers cannot effectively customize to satisfy the needs of each part. Both scenarios reduce RevOps productivity and profitability. When there are too many or not the right tools in play, the benefits of technology often have the reverse impact of their intended use, becoming a productivity drain and a source of confusion, enabling functional silos that stifle creativity and alignment.

In a classic example of a technology provider stagnated by tech, Orange Marketing worked with Isos Technology to optimize the Isos sales and marketing tech stack, as published in this case study. Isos is a productivity solutions provider, and in 2019 growth began to stagnate. Isos had brought in and implemented all the best-in-class tools for different teams, but RevOps productivity had hit a common barrier to growth. Orange, a B2B SaaS growth strategy firm, quickly got to work in consolidating the Isos tech stack, simplifying processes, cross-functional information sharing, and automating many manual processes. In just four months, sales at Isos took off, increasing quarter over quarter for the past five months with a 30% increase in closed won deals.
In this session, we will build and refine your RevOps tech stack to optimize RevOps productivity. You will learn how to identify, assemble, implement, maintain, and stay current with the tech stack optimized toward the unique needs of your business. Without needing additional consultants and advisors, your team will know how to leverage customization and integration for cross-functional process automation and set up and maintain optimal user-tool interactions that improve productivity, reduce client acquisition and retention costs, and automate KPI measurement and reporting.
Session 7: Metrics and KPIs
Establishing consistency in revenue growth while maximizing profitability requires measuring resource allocation. Measuring prior results against the actions that generated them – both process and execution measures – is essential to determine which activities and investments delivered as expected and which need to be revised to maintain a growth trajectory in the future – in short, looking back, then turning around and using those insights to see forward with more clarity.
In environments with constant change, particularly in revenue-generating functions, reliable and consistent measurements are critical for guiding execution today to achieve desired results. If the metrics in place are not measuring relevant data points, insights into changes needed are inaccurate, slowing growth and reducing profitability. The challenge is getting consistent measurements over time in an environment of constant change.
Default metrics that come with your CRM or other data visualization tools may not provide the insights relevant to your business. More importantly, how key RevOps metrics are measured must be adjusted to fit the unique nature of your business. For example, does measuring velocity from a first impression or first contact makes sense? If your company innovates quickly, and the first impression was four iterations ago, did momentum begin with the first, now invalid impression, or the new version V4 that incited action? How do the two very different impressions impact the conversion rate? To which impression is the deal attributed? Does it then make sense to re-invigorate all those old V1 impressions?
In this workshop, you will learn how to set up and manage the Predictable Growth Formula for your business, establish the baseline measurements needed to ensure consistent, long-term profitability, and when to modify which metrics to use and which to change without compromising data consistency and integrity.

You also will establish the core RevOps KPIs for your business, including CAC, conversion ratios, value, volume, velocity, activity optimization, cycle time, onboarding factors of success, retention, and satisfaction, as well as the supporting metrics that drive consistent achievement of core goals that are relevant for your business.
Session 8: Execution Structure
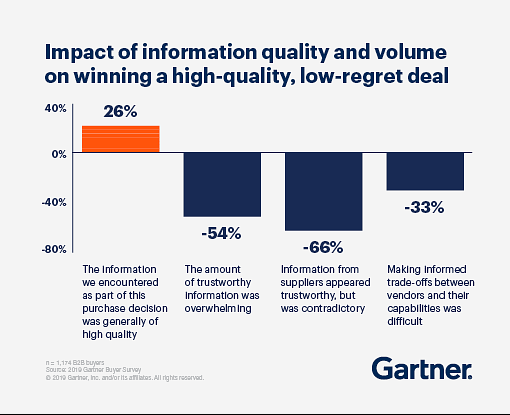
The business, business unit, or product team can execute confidently with the foundation for profitable and consistent revenue generation. The organization is at the business development stage when learning is at its peak. At this stage, insights on crucial profitability measures, such as market intelligence, competitive position, and product differentiation flood in, challenging any assumptions made during the strategic planning and core process development processes. The temptation is to rapidly change what is being executed on the tactical level using these new insights. This chart from a Gartner study reveals the impact of using too much information too fast. In that environment, deal close rates decline as more information is applied.
Still, leveraging large amounts of market intelligence, performance data, and other insights is critical for guiding the next steps for team members and accelerating engagement with the market. The impact of human behavior on results is at its peak.
Leadership must implement needed changes quickly. However, the challenge now is guiding and adjusting execution behaviors in an evolving market as your business expands.
Changes must align with Vision and Goals, maintain data integrity and consistency, and apply these changes through each topic covered in sessions 3 through 7. At this stage, most organizations stall, or projects lose traction in the market. Changes must align with the core operation, or the organization drifts off-track.
Using the Apple example again: When Apple’s Board released Steve Jobs as CEO in 1985, the new team brought in a suite of professional managers – all experienced and expert in their function, and they failed miserably. Why? Each functional leader brought their ideas on running their part and could not align with Apple’s core values. Further, according to an interview with Jobs, they were great managers but did not know how to do the work, so execution failed. When Jobs returned and replaced the team with people who knew how to execute in an aligned and values-focused way, Apple began to scale.
A well-planned and structured RevOps organization propels an organization through this stage quickly and with minimal disruption. This structure is the critical time to test and affirm that the strategy is sound, assumptions remain valid, processes are supportive, and tools and people remain aligned and moving in the same direction. In this workshop, you will learn how to set up and maintain efficient structures of execution that support and maintain alignment with overall strategy, from the function level to teams and individuals on teams. This workshop’s outcome is your organization’s ongoing capacity to make proactive and real-time decisions throughout the RevOps function that accelerates growth.
Session 9: Execution with People
The revenue-generating functions rely on human-to-human interactions to achieve results. This truth is challenging for the more fact-based processes of other business functions, such as finance, engineering, and production, and the “Yes or No” rules these teams operate in. The intensely human-to-human elements of RevOps make maintaining creativity, mindsets, and related behavioral factors more crucial than these already are for the rest of the organization.
In this critical workshop, you will learn the principles of “Right Person, Right Seat” and how to measure and implement this crucial decision-making process and lead individuals toward their best possible contributor role. You will also learn how to utilize compensation and incentive plans to encourage the behaviors that drive growth and how to assess the critical ‘soft- skills’ necessary for success in creative, selling, and service roles. You will set up onboarding and offboarding processes to ensure faster ramp-up times and define the training requirements and what needs to be ‘part of the package’ for new hires. This workshop will clarify how leadership can identify which groups, teams, and people are on or off track, how to get the right people back on track, and how to find, motivate, improve, and retain the human resources that power growth.
Session 10: Execution with Data
Revenue is most often measured by looking at prior performance, assessing whether the performance was sufficient to meet goals, and then making any changes necessary to improve performance to plan. Preliminary performance analysis is essential; however, the reactive nature slows innovation and effective and consistent GTM execution. According to ongoing annual research by Gartner that includes Sales Forecast Accuracy, only 45% of companies believe their sales forecasts are reliable, and more than half blame bad data. Revenue generation rarely occurs in real-time, in that actions taken today generate realized revenue in the future. For example, an online retailer requires marketing to drive buyers to the site and incite a purchase in an organization with a “same moment” sales cycle time, such as Amazon and other online purchasing tools.
Accurate historical and real-time data combined with the proper analysis tools and methods convert the clarity of hindsight to more precise forecasting and strategy adjustments. Clear and valid insight from RevOps into what is most likely to occur in the short and long term is another critical RevOps function that every other part of the business needs to be able to deliver and support a consistent growth rate. However, constant market evolution and human behavior influence challenge the capacity to generate the consistent data needed to manage processes, behaviors, and forecasts more accurately.
In this workshop, you will learn how to assemble and analyze the data generated from the day-to-day execution of strategy and processes from all team members and gain real-time insights on what can be changed – in the moment and over time – to improve results immediately and in the future.
You will learn the importance of creating transparency in the RevOps function and how to set up relevant reporting and dashboards that ‘tell the story’ RevOps data must provide to leadership and the entire organization. You will learn to assess the data for better, more proactive decision-making that accelerates growth and profitability. The results of this workshop are clarity on the specific causes of on-track and off-track results, accuracy in forecasting, improved and proactive planning and resource alignment, and more engaged and productive team members.
Session 11: Managing Obstacles to Growth.
What do you do when unexpected events challenge everything you know about your business? Technology advances, new and nimble competitive entrants in the market, and global economic, social, environmental, and political events. All these and more have, do, and will continue to threaten even the most successful business models. In 2000, Blockbuster Video had the opportunity to purchase Netflix for just $50M, and they declined. Blockbuster was technologically disrupted out of business ten years later. EU business losses due to Russia’s war on Ukraine have topped $100B. Global economic output was cut by over $8.5 Trillion during the COVID pandemic. According to the Sales Management Association and a study by Sales Xceleration, over 90% of sales processes, cycle times, and prospect contact methods were made obsolete almost overnight by the COVID pandemic, and those pre-COVID methods have yet to return as effective today.
How do you prepare to survive a meteor strike on your business?
Over the past ten sessions, you will have built a solid foundation for sustained growth. The GTM strategy will roll out with improved consistency, visibility into successes to amplify, and areas to improve. The processes, measures, and execution systems will be flexible and reliable in an ever-changing market. You are now prepared to plan for and address obstacles to growth as they arise, whether the barrier is small slow changes in the market or a meteor strike. Keeping an open mind to seeing obstacles at the earliest possible stage is now critical to sustaining and accelerating growth across all business functions.
Identifying barriers to growth is tantamount to the RevOps function, as this function leads revenue growth for the organization and is the first to experience the impacts of competitive activity and the economic, social, political, and environmental events that jeopardize growth.
In this workshop, you will create a clear and consistent framework for quickly identifying and resolving the barriers to growth, implement Issue Management Planning, and establish a system to Identify, Prioritize, and Solve (IPS) issues based on priority and level of impact. The result of this workshop will be faster, more effective issue resolution at the causal level and sustaining growth and productivity as best as possible through any market transition. If you must change everything, you will have the tools to do that quickly and minimize the impact on revenue and profitability.
Session 12: Re-Calibration
The key to establishing and maintaining reliable growth and profitability lies in a standard of clarity of the strategies, consistent application of the processes, and measured and optimized execution of these guideposts and milestones.
In this final workshop, you will exercise your active use cases to apply the learnings of this course. You will learn your business’s most effective change management practices and how to identify what to recalibrate as conditions change over time. You will identify obstacles, how data points to the cause and desired change in data, how people are part of the cause and the resolution, which execution processes to add or change, and the impact of those changes on processes, RevOps strategy, and overall strategy.
The result of the workshop is end-to-end clarity on establishing and maintaining consistent growth over the long term. Congratulations!
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Software as a Service (SaaS)
Background
The historical global transitions from first agrarian to manufacturing, then manufacturing to information-based economies, are well documented. The drive toward economy-of-scale production in the manufacturing sector required tools that automate production to reduce production time and the costs of human labor. Automated production systems operate on software and execution by tools, and the people interacting with them generate information, which is used to improve the productivity of machines and humans. More information, more options for productivity.
This transformation in manufacturing has driven the need to optimize the software that, in turn, optimizes machine and human productivity.
This transition occurred at the same time as global economies began increasing their service-based economies, supporting humans who now had more free time and disposable income. Tools were quickly developed to help automate service delivery, and rates of development of Software as a Service, or SaaS, accelerated. Overall, the SaaS sector has never had a year of decline – declines in growth rates, yes, but not a decline in growth overall.
SaaS, then, has been the answer to the need to optimize the productivity of humans and machines. So, SaaS tools have been developed to improve every economic sector we see in the world today.
Current State
The inevitable migration from “Software as a Service” to focusing on delivering service along with the primary product, both physical or service-based products, is well underway and accelerating. As products in all categories become commoditized over time, the need to differentiate how a similar product or service is delivered to the buyer increases, and that differentiation comes in the form of services. Consider the case of IBM. Originally a computer systems manufacturer, IBM led the transition to automation of once manual systems to information generating systems, then information processing systems. As the development of new software that drives systems began accelerating in the late 1980s and to today, IBM could not keep pace with a focus on systems development— hence the migration from system provider to systems integrator and today as a leading information services advisory service. Today, every seller of tools, products, or services, from cybersecurity services to jeans to grain, adds services to their offering to enhance market position and compete globally.
How, then, do we optimize the value that SaaS providers deliver?
The imperative for SaaS firms, or firms incorporating SaaS offerings to enhance core competencies, is to maintain relevance in a rapidly changing and commoditizing market profitably. The emphasis must shift from the Software as the product to how the software is provided – the Service.
The Outlook
SaaS as a sector is projected to see slowing growth rates as better service delivery methods are deployed. When delivering everything from wheat to jeans to cybersecurity incorporates a SaaS solution, SaaS will no longer be a distinct market sector and cannot be measured as it is today. SaaS tools have become as essential to existence as the plow was in the agrarian age. Consider the rapid advances in Artificial Intelligence, which provides data and emotion-based intelligence.
Global organizations of all types must consider the sustainability of the products and services they offer the market, from raw materials extraction to initial consumption and then re-use. AI is disrupting the once rapidly expanding platform-based SaaS market, requiring SaaS-based organizations and tools to adopt and accelerate how services are provided with their tools and rapidly migrate away from how their tools are delivered. The sector must migrate away from user-managed delivery through the limitations of controlled web apps and platforms to more self-service and intuitive tools with content delivered to users in real-time and generative AI form.
This is the driving imperative for SaaS-based firms to adopt Revenue Operations methods. At present, there is no more effective and efficient way to understand market needs for the delivery of goods and services and to consistently and quickly modify how these are being delivered.

Manufacturing – Consumer Goods
Background
Production of both durable and fast-moving consumer products transitioned from hand-made production to mass production through the industrial era, focusing on the economies of scale that lower total cost per unit and so maximize profitability. Consumer goods production has remined in this state for over a century, leveraging technology and expanding materials and labor sourcing from local to global in order to achieve ever-improving cost reduction. The drive toward constantly improved cost reduction has been based on consumer demand and the desire to reach a larger market with lower cost goods.
Globalization of production of consumer goods has now expand to the limits of the of the planet, and there are few, if any remaining ‘new’ resources manufactures can tap to reduce costs of both materials and labor.
Current State
Access to information via the internet and social media have provided consumers awareness of the finite nature of material and labor resources. Consumers recognize the low cost of products carry hidden costs that were hidden in the past. Natural resource depletion, abuse of human labor resources, and the impact of production waste make the headlines of news and other information resources, and there is now global awareness that the search for ever decreasing costs from ‘new’ untapped resources is over. Consumers demand products that have less negative impact on the environment and on the people and communities in which products are made. The era of optimism on an ever-expanding source of cheaper materials and labor is over.
Sustainable and ethical production has become an imperative if brands are to survive long term. This shift requires manufactures to re-thing material and labor sourcing, consumption of natural resources that go into the products, as well as the waste that is created in the production process. This shift requires re-tooling factories, implementing more ethical and higher paid labor policies, and trimming the supply chain to reduce waste in the distribution of materials and goods.
Further, consumers of more durable products demand greater transparency and circularity of the materials incorporated into the products they buy. Multiple studies show the percentage of consumers that care about sustainability of the products they purchase have risen from a fraction of a percent in 2000 to over 70% today. Questions to manufacturers on where consumers can recycle everything used electronic devices, denim jeans, or empty toothpaste tubes have increased from a fraction of a percent of inquires up to 8% of all inquiries received by some manufacturers. Consumers demand more sustainable packaging and less of it.
Manufacturers must re-think, re-tool, and re-configure everything from sourcing traceability to distribution, and post consumption recycling in order to retain the hard-won consumer loyalty developed over decades.
The Outlook
The rise of the information age and transition into the coming age of human, material, and environmental balance demands a change in the way manufactures think. This transition is more significant that the transition from hand-crafted to mass produced goods, and the transition is underway now. Manufacturing must adopt greater supply chain transparency and traceable post consumption circularity. These consumers driven imperatives will control sales volumes, and therefor production volume and capabilities going forward. Manufacturers of consumer goods must shift perspective from ever decreasing costs to ever increasing sustainability and transparency. Firms like Apple are already leading this transition with their commitment to be 100% carbon neutral by 2030, while increasing both brand loyalty and growth.
This is the imperative for adopting a Revenue Operations function. A function focused on ever-increasing alignment to market demand, with as much advance insight as possible to allow for better product design, production re-tooling, and packaging is the best way to gather, utilize, and implement changes in production that are based both on data and measurable consumer sentiment.

Professional Services
Background
The professional services sector has been led by the demand for intellect-based subject matter expertise to facilitate more profitable trade. As production of goods accelerated, the need to analyze and then optimize better resource utilization drove an increased need for specialists in trade data processing. Accounting, legal, and engineering services rapidly expanded as mass production and global trade expanded in the industrial age. The transition to the information age further enhanced the need for more and more specific subject matter expertise in the manufacturing sector at the same time as consumers became more affluent, and so able to pay others to do intellect-based work on their behalf. The professional services sector – those providing intellect-based product to other businesses – expand to fill this increased need for information processing and reporting, allowing producers of both physical products as well as service-based software tools to focus on their core deliverables. The case of IBM transitioning from a machine-based provider to an advisory firm focused on optimizing the insights that machines and data processing tools provide highlights the market-driven demand for more professional services while consuming less of the increasingly expensive physical resources over time.
Current State
The ever-increasing complexity of regulatory hurdles to global expansion, associated tax and trade policies, increasing competitive and technology advancement pressure, as well as the need to constantly drive down the cost per unit of physical goods while simultaneously becoming more sustainable and transparent, has fueled an explosion of hyperspecializing in the professional services sector. The need for short term expertise as organizations re-tool and restructure has driving a rapid rise in the ‘Gig Economy’ of subject matter experts delivering human intellect and talent-based services that organizations need to advance while remaining focused on their core deliverables and minimize long term costs associated with full time employment of those subject matter experts.
This transition to more outsourced subject matter expertise is the inevitable outcome for producers of physical and software-based products needing to continuously drive down cost per unit while pulling back from the once ‘limitless’ supply of lower cost resources available from global expansion. The boundaries of global expansion and lower costs resources have been reached, including service resources Costs for these resources can now only increase, or increase productive in-service delivery by adopting better tools, processes, and methodologies in order to provide more with the same, or fewer resources.
The Outlook
Subject matter expertise is no longer a differentiating vlaue for service providers. The amount of information available to end-users has exponentially increased year over year as product and services providers publish more and more insights in order to differentiate from competitors, and so buying patterns for services have changed in the same way buying patterns for physical goods has changed.
The influence of AI based knowledge collection and dissemination will soon render individual intellect based subject matter expertise obsolete, driven by consumer and buyer demand for increased transparency and value-based contributions of their providers.
The increase in total value-add vs. the incremental reduction in cost per unit decision making of the past will rely more and more in emotional intelligence about a topic, rather than fact-based intellect on a topic. This shift will be driven by the constant increase in available facts and AI based collection and dissemination of those facts.
The Rev Ops imperative for professional services providers is to access the data and human insights that only a the a solid strategic RevOps function can deliver and apply emotion-based intellect to that data to deliver insights into more sustainable and transparent practices – this is the value-add advantage over the incremental cost-based contributions professional services providers have delivered in the past.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

New York City, NY
Background
Originally founded by Dutch settlers in the early 1700’s who bargained with the local native population for land in order to establish a trading post on North America, The New York City area is now the most densely populated metropolitan statistical area in the USA, with a combined statistical area population of well over 23 million in 2023 and increasing annually. The geographic area is the largest urbanized area in the world.
The region is the center of multiple industries, including finance, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, life sciences, trade, publishing, real estate, fashion, entertainment, and manufacturing. It is the most important financial, diplomatic, and media center in the world.
Current State
NYC has a proud history of recovering quickly from a wide range of severe economic impacts, from absorbing heavy immigration early in the 1900s to terrorism attacks, and the US epicenter of the COVID pandemic, New York roars back, stronger, improved, and growing.
The technology sector began expanding in the Metro zone alongside Silicon Valley’s rise in the late 1980s and has continued to expand to serve the wide range of sectors prominent in the region and host locations for all the top 10 technology firms. NYC hosts locations for the USA’s top technology firms (Apple, Alphabet, Google, Amazon, Facebook, and more than 12,000 tech firms based in the post-pandemic New York of 2022.
Outlook
Despite post-pandemic migration fears, people from all over the USA and the world are moving to New York, with all five boroughs showing increases in population in 2023. The New York-based technology-dependent sectors of finance, healthcare and life sciences, entertainment and publishing, media, and manufacturing continue to expand even as remote work for NYC-based firms continues to expand.
NYC’s unique combination of volume of market sectors and the size and strength of the firms in those sectors that are based in the great metropolitan zone drive innovation. The availability and proximity of wide-ranging perspectives, human and intellectual resources, financial, technology and production assets spawn opportunities at a pace and volume unmatched by any other metropolitan zone on the planet.
Business based in this area thrive when they tap into the region’s well educated and diverse workforce, broad industry base, and dynamic financial services as a hub for businesses with globally distributed operations, New York will continue to thrive as a global strategically and financially important location.

San Francisco, CA (Silicon Valley and the Bay Area)
Background
California’s Bay Area metropolitan zone encompasses 9 counties that surround the San Francisco Bay, centered around Silicon Valley to the south and San Francisco and Oakland to the north. In 2020, population in the region was just under 8 million people, and growing, even though the Covid pandemic. The area is only recently developed by global standards, having begun experiencing population expansion during California’s’ Gold Rush, which began in 1849 and lasted nearly a decade. Trade Barrons also developed during this time, capitalizing on the gold rush and California’s abundance of natural, agricultural, and mineral resources. The Bay Area experienced additional marginal growth and trade as the canal system that provides water to inland farming led to increased trade centered on ports in the San Francisco Bay. Corruption from “The Robber Barons” of the early 1900’s and lack of new resources to be exploited led to a decline in California’s population growth rate up until the late 1950’s, when military and Space Race investments in Research and Development as well as Air Force and Naval Base installations brought both technology and trade to the region, particularly in the South Bay, now known as Silicon Valley
The so called ‘tech boom’ that started in the south bay continues to this day, and has spread around the entire 9 county region, with housing demand for tech workers expanding the Federal statistical area to 14 counties.
Current State
Rapid immigration to the Bay Area from all over the world, fueled by opportunities in the tech sector and California’s liberal immigration policies for skilled workers, has led to both rapid expansion of the tech sector and the industries that support it, including construction, finance, and professional services. Limited space for new housing has caused urban sprawl, with most flat spaces covered with industrial parks, commerce, and housing, while retaining the vistas provided by development restrictions on the surrounding hillsides. The ongoing rapid expansion from the late 50’s onward has led to high housing and other costs of living, traffic congestion, and increased regulation to protect increasingly stressed natural resources, including open space and water.
This environment has led to a culture of high-risk investments in a start-up fueled economy. Some investments reap huge rewards, others marginal, but the majority still fail at the same rate as global average business failure rates. It is the huge successes that continue to fuel technology investment and innovation. Firms such as 3-Com, Cisco, and others led the communications technology boom of the 90’s that led to breakthroughs in personal communication devices, spawning Apple’s meteoric growth, and the founding and rapid expansion of Alphabet (Google), and global social media giants like Meta (Facebook, Instagram), and X (formerly Twitter). Business infrastructure and pharma innovations also thrived in this period, including SalesForce, Oracle, and the rise of pharma firms like Gilead, born from addressing immunotherapy solutions to tackle the AIDS epidemic that decimated the area from the late 1980s into the 1990s.
The Outlook
Even with some of the highest costs of housing and overall living expenses on the planet the Bay area remains a magnet for innovators from all over the world. Business leaders and investors remain attracted to the entrepreneurial spirit, well education workforce with a strong work ethic, and hyper-innovation speeds that dominate ‘standard business practices’ in the area.
Businesses operating in the region can leverage a string Rev Ops function to consistently produce Revenue Efficiency in was that are not achievable in other regions due to the Bay Area’s density of innovative, emotionally intelligent, and entrepreneurial minded workforce.

Barcelona, Spain
Background
As the seat of Catalan culture and history, the Barcelona metropolitan zone enjoys long history of innovation, pluralism, trade, and culture. With defined independence of the principality dating back to the 1st century AD, Barcelona’s geographic position combines cultural influences from Northern Africa, Spain, France, and Italy, that have persisted in the region’s pluralistic society today. Catalonia’s history as an independent ‘city state’ for many centuries, complete with the alliances and power shifts of European city states through the first and second millennia AD, has carried through to the prominence of the region today as a global center for innovation, creativity, and integration of the influences from the surrounding region. Barcelona’s economic influence has spread well beyond the Catalan region, with dependance on the region’s economic productivity felt throughout Spain, southern France and parts of Italy.
Current State
The fifth largest economic zone in Europe, Barcelona’s 4 million plus population are also among the most productive. Strong presence in the chemical, pharmaceutical, automotive, electronics, and appliances markets have underpinned the regions strong economic output. The region is known for recovering quickly from the economic downturns experienced in the rest of Europe due largely to the ‘necessity’ based nature of the industries that thrive in the area, all bolstered by the more than 19 million tourists Barcelona attracts from around the world.
The strong manufacturing sector developed in the region over the past half century has brought the expected, and planned growth in ancillary markets such as SaaS development and professional services. Through the COVID pandemic of 2020-2021, the Barcelona region became a hub for digital nomads, which fueled Barcelona’s current boom as the fastest growing and most successful a tech hub in Europe. No coincidence that the rich culture of Barcelona draws, and then supports and encourages innovative entrepreneurs from all over the EMEA region Europe to base in Barcelona and leverage the tremendous innovative and creative spirit that has thrived in Barcelona for centuries.
It is important to note that this spirit has also fueled the region’s desire for autonomy, and more influence on how their economic strength is utilized by the central Spanish government. The idea of separation from Spain has made the region both a political powerhouse that wields tremendous power over the direction of Spanish politics, as well as a target for the rising tide of Spanish Nationalism. While the current political state has brought increased uncertainty and risk to businesses in the region, there have not yet been any manifestations of this increased risk measurable by business flight or reduced investment in the region.
In addition, Spain’s autonomous region of Catalonia has stepped up to the challenge. The recent growth in the region has spurred stronger communication and transportation links with the surrounding areas of Tarragon, Girona, and Valencia, further expanding Barcelona’s economic growth and position as the premier center of commerce in the region.
The Outlook
As the 5th largest metropolitan area in the European Union (after Paris, the Ruhr region, Madrid, and Milan) Barcelona’s courtship of technology innovators will continue to drive growth, capital investment, and innovation in the region. Firms in the region will be able to continue to leverage ability to design, build, and market products and services by leveraging the significant, well-planned infrastructure, as well as Barcelona’s cultural and creative appeal which draws talent to the region from all over the world.
The political risks associated with the region are tempered by both Spain’s string economic position within the EU, as well as Barcelona’s own strong economy and geographic position. Therefore, any large changes in the political environment would have temporary downside, which should recover quickly once a stable path forward is determined.
Implementing a Revenue Operations function in the region would enhance an organization’s capacity to generate revenue more efficiently in Barcelona’s unique and string position as a global center for innovation and commerce.
Program Benefits
Department 1
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
Department 2
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
Department 3
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
- Two Words
Testimonials

Testimonial 1
Content here…

Testimonial 2
Content here…

Testimonial 3
Content here…

Testimonial 4
Content here…

Testimonial 5
Content here…
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.