Revenue Growth
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Revenue Growth is provided by Mr. Hawkey Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Hawkey is an approved Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene. Mr. Hawkey is the founder of a successful Technology Consulting firm, and author of “Small Business Market Domination Strategies.” He brings to Appleton over 30 years of successful sales and marketing leadership expertise and operational experience. He is an esteemed business leader and strategist with an effective history of building new and rebuilding existing revenue growth teams made of sales, marketing, and operations for technology, manufacturing, and consulting services companies. Mr. Hawkey has consistently delivered against challenging revenue goals, especially when facing complex business problems, and is personally accountable for more than $1B in commerce sold.
Mr. Hawkey has a distinguished track record of successfully developing strategic revenue growth programs that have transformed companies ‘ market abilities. He has done this by leveraging his strategic planning skills shaped by his many years of customer engagement experience and comprehensive expertise in management, sales, partnerships, finance, and marketing. He has established a past performance of reliably making commitments that have helped companies secure investments, increase profitability, establish, and expand key partnerships, deliver new revenue streams, dominate new markets, and exceed growth initiatives.
After years of working in major value-added corporations, followed by years of running a business, Mr. Hawkey has recently been engaged with select high-potential companies as a Chief Revenue Officer (CRO) charged with building a revenue engine. In this role, he is keenly focused on acting on proven strategies to grow revenue, applying best practice coaching, reviving sales, advancing customer acquisition standards, establishing engaging and creative content, and driving new partnership development.
To request further information about Mr. Hawkey through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary

Revenue Growth
History
Over the past few decades, selling to B2B customers has changed dramatically. Through the early 1990s, the primary role of a salesperson was to be the company’s voice charged with targeting specific businesses in assigned geo-territories to build relationships and promote their products or services. Salespeople were authorized to disseminate product information highlighting its features and benefits that prospective buyers would use to solve their problems. Salespeople were considered the best source of product knowledge while developing needed buyer relationships. Salespeople held significant power over the buyer as the primary source of information. In this early process, marketing’s role supported sales, supplying product benefits and positioning qualities that helped customers understand differences and value.
Everything changed for buyers in 1993 with the introduction of the Internet and the World Wide Web. The web provided businesses a way to reach more buyers worldwide while enabling buyers to discover more product options almost instantly. The buying process also changed as technology continued to evolve, providing more access for buyers. Buyers became increasingly empowered as they now had product information at their fingertips, allowing them to start and advance a buying journey before engaging directly with a company representative.
By the late 1990s, we witnessed explosive digital transformation as most B2B companies invested heavily in innovative (through digital resources on social media, videos, blogs, websites, etc.) technology options and creative ways to introduce their products to more and more buyers. The internet became their new salesperson for providing product information, ratings, and user forums, which helps support a quick and efficient buying process. Access to an unlimited trove of product information without attending endless meetings or needing to talk to many salespeople is liberating for buyers.
The critical role of prospecting for a salesperson slowly began to be replaced by online digital content and social media. Knowing more about “the buyer,” where they shop, whom they listen to, and what they value in a relationship emerged as the critical path to attracting business. The internet forever altered the B2B buying process and introduced a new challenge to selling companies: the need to know who the buyer is. For the first time in business history, we are working with multiple generations in the workforce. Each generation values different things in a relationship and how those values affect a buying decision. For example, the younger generation of buyers has certain expectations that differ from older buyers, and it is critical to understand these nuances to work with them effectively and influence their decisions.

Current Position
Today, younger generations have become a growing force involved in decisions to purchase products and services both in growing businesses and as business owners. Being aware of who your client is is critical to advancing a sale. It requires that sellers become students of their customers and obtain the awareness of everyone involved with purchasing decisions.
For years, the conventional B2B sales process was usually initiated by a salesperson seeking to understand potential opportunities, and it followed a seller-centric sales process that led the customer (i.e., Discovery and Creating Interest; Educating: Qualifying and Closing the Sale.) through a structured sales process that met the seller’s timeframe.
Today, the buying process has become buyer-centric, exposing traditional sales processes that do not match the buyer’s journey. Most buyers start their journey performing product option due diligence by navigating digital resources on social media, videos, blogs, websites, etc., before engaging with a company’s sales team. This is especially true now as younger generational buyers grew up on the web, searching forums, reading blogs, evaluating Yelp reviews, Googling everything, and tweeting brands. Younger buyers decide about you and your products/services based on your digital presence or lack thereof. Unlike older generations, face-to-face meetings are unnecessary to build trust and will only support the relationship or impression they’ve already established from their online experience. Young buyers place a higher value on virtual content.
The new sales process that has emerged requires a collaborative effort from marketing and sales to learn and understand more about buyers and how they buy. To be effective, they must engage buyers on social networks and in other venues where buyers shop to establish trust and build relationships. This proactive engagement through social networking will produce tangible results and, eventually, a loyal buyer. Additionally, buyers want to learn about the salesperson and the salesperson’s company before they entertain advances from sales representatives. They want to be prepared with facts supported by influencing factors. Once engagement starts, the buyers expect the sales team to provide added value through credible information and supporting references from sources they trust.

Future Outlook
Sustainable revenue growth moving forward requires a superior awareness and focus on who is buying, understanding their buying process, and schemes needed to get them to consider your solutions. The emergence of a joint team charged with generating revenue that consists of sales, marketing, and operations support resources working as one unit, focused on the same revenue goal, is required to meet the buyers’ needs. Companies focused on growing revenue must understand how to connect with clients where they shop, nurture them, and engage with value creations that support a prospect’s purchasing challenges well, outperform their competitors, and dominate their markets.
Finding new customers is the fuel for any successful business. As customers implement tactics to create a buying process without engaging salespeople, it is incumbent on the selling team to ensure that the formula is not static and is tested. Companies must connect, engage, and nurture prospects digitally, offering their product and company information and altering their sales force purpose to be a buying facilitator and value formation organization.
A salesperson was responsible for finding and convincing prospects to engage in past generations. As we have already stated, in today’s modern buying environment, younger buyers don’t want or need a salesperson to feed product information already, as they can and will access enormous quantities of digital product information and reference material for companies they are considering using. Product companies must implement a demand-generation process encouraging prospects to stay engaged through continuous nurturing and social influencers.
This allows a company’s sales force to elevate its role and become more valuable to the buyer by focusing on being an influential asset that aligns buying and selling organizations around a mutually beneficial solution.
Successful companies will pivot from the traditional sales role of soliciting opportunities to concentrating more on understanding their prospect’s business and organization needs to help them through the decision process. Adding value to the decision/buying process is the new expectation. Value to the buyer is compelling information that provides accurate and worthy results and should position you (and your company) as an expert or authority that can be trusted.
Value to the buyer is compelling information that provides accurate and worthy results and should position you (and your company) as an expert or authority that can be trusted. The new generation of buyers is challenging traditions and conventions, helping B2B Sales organizations reassess their focus and work to deliver a better experience for the buyers. Salespeople have had and will continue to have tremendous value to business buyers. If they can adjust their process, provide substance, and deliver accurate results, they will be asked to be a big part of the buying process for many years.

Case Studies
Companies that adopt a structured revenue growth program often experience positive results. Implementing a structured revenue growth program provides several benefits that can contribute to the overall success of a company, including:
1. By implementing a structured program, companies can focus their sales and marketing efforts on specific revenue goals and align their teams toward achieving them. This alignment helps to reduce inefficiencies, maximize resources, and enhance overall productivity.
2. A structured revenue growth program often involves tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to gain insights into the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts. This data-driven approach enables companies to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their strategies for better results.
3. A structured program encourages coordination and collaboration between sales, marketing, and other departments involved in revenue generation. This collaboration ensures a cohesive approach, reduces silos, and enhances the overall effectiveness of revenue growth initiatives.
4. A structured revenue growth program often emphasizes a customer-centric approach, focusing on understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points. By aligning sales and marketing strategies with customer expectations, companies can deliver more targeted and impactful messaging, which leads to better customer engagement and higher conversion rates.
5. Implementing a structured program allows companies to establish scalable and consistent processes for revenue growth initiatives. This scalability enables companies to adapt to changing market conditions, increase efficiency, and replicate successful strategies for sustainable growth.
6. A structured program encourages ongoing evaluation and optimization of sales and marketing strategies. Companies that embrace continuous improvement can identify areas for enhancement, test new approaches, and adapt their tactics to achieve better results over time.
Here are a few examples of companies that have adopted structured revenue growth programs and have seen positive results:
1. HubSpot, a leading marketing and sales software company, has implemented a structured revenue growth program focused on inbound marketing and sales alignment. Their program includes comprehensive training for sales and marketing teams, well-defined processes, data-driven decision-making, and continuous improvement. This approach has helped HubSpot consistently achieve substantial revenue growth year after year.
2. Salesforce, a global customer relationship management (CRM) software leader, has a well-established revenue growth program driven by its “Ohana” culture. They strongly focus on customer success, data-driven decision-making, and alignment between sales, marketing, and customer success teams. Salesforce’s structured program has contributed to its consistent growth and market dominance.
3. A multinational software company, Adobe, has implemented a revenue acceleration program aligning its sales and marketing efforts. They have a robust lead management process, strong team collaboration, and a focus on customer experience and personalization. Adobe’s revenue growth program has helped them maintain a strong market position and drive consistent revenue growth.
4. Shopify, an e-commerce platform, has a structured revenue growth program focusing on customer acquisition, optimizing the sales funnel, and enhancing customer retention. They have implemented data-driven strategies, marketing automation, and a robust customer support system. Shopify’s revenue growth program has contributed to its rapid expansion and success in the e-commerce industry.
5. Slack, a popular collaboration and communication software provider, has a structured revenue growth program centered around improving customer onboarding, increasing product adoption, and fueling customer expansion. They prioritize customer success, offer personalized support, and leverage data analytics to drive revenue growth. Slack’s revenue growth program has significantly impacted its successful market penetration and customer retention.
These companies have embraced structured revenue growth programs and have consistently achieved positive results through their focused strategies, alignment between teams, customer-centric approach, and continuous improvement efforts. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of revenue growth programs can vary depending on the unique circumstances and execution of each company’s specific program.
While the effectiveness of a structured revenue growth program can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the execution of the program, it provides a framework for companies to drive revenue growth systematically and strategically. By implementing such a program, companies can improve their sales and marketing efforts, enhance customer engagement, and achieve revenue goals more effectively.
Curriculum
Revenue Growth – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Revenue Strategy
- Part 1 Month 2 Organization Plan
- Part 1 Month 3 Product Marketing
- Part 1 Month 4 Marketing Communications
- Part 1 Month 5 Content Strategy
- Part 1 Month 6 Lead Generation
- Part 1 Month 7 Value Selling
- Part 1 Month 8 Account Management
- Part 1 Month 9 Channel Strategy
- Part 1 Month 10 Revenue Enablement
- Part 1 Month 11 Customer Success
- Part 1 Month 12 Rev Ops
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Revenue Growth corporate training program.
Revenue Growth – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Revenue Strategy – Revenue strategy refers to the overall plan and approach that an organization implements to generate revenue and maximize its financial performance. It involves setting goals, defining tactics, and making strategic decisions to optimize revenue generation across various channels and aspects of the business. The objective of revenue strategy planning is to develop a comprehensive and structured approach to drive revenue growth and profitability. It encompasses analyzing market dynamics, understanding customer behavior and preferences, assessing the competitive landscape, and identifying opportunities to capture and maximize revenue. Revenue strategy planning objectives should include: 1. Revenue Growth: The primary goal of revenue strategy planning is to drive revenue growth by identifying new sources of revenue, exploring expansion opportunities, and optimizing existing revenue streams. This may involve identifying new target markets, developing new products or services, launching innovative pricing models, or enhancing sales and marketing strategies. 2. Profitability Enhancement: Revenue strategy planning aims to improve profitability by increasing revenues while managing costs effectively. This involves identifying strategies to increase the average transaction value, improve pricing strategies, optimize pricing of different products or services, and implement measures to reduce cost inefficiencies. 3. Market Positioning and Differentiation: Revenue strategy planning also focuses on positioning the organization in the market and differentiating its products or services from competitors. This may involve leveraging unique selling propositions, enhancing product features, improving customer experience, and building a strong brand identity to attract and retain customers. 4. Customer Acquisition and Retention: A key objective of revenue strategy planning is to acquire new customers and retain existing ones. This includes developing strategies to target specific customer segments effectively, implementing effective marketing and sales tactics, and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty through personalized experiences and exceptional service. 5. Optimal Pricing and Revenue Optimization: Revenue strategy planning involves developing pricing models and strategies that optimize revenue and profit margins. This may include conducting market research, analyzing customer value perception, understanding price elasticity, implementing dynamic pricing models, and utilizing revenue management techniques to optimize pricing decisions. 6. Channel Optimization: Revenue strategy planning considers the various channels through which the organization generates revenue, such as direct sales, indirect sales, online platforms, partnerships, and distribution networks. The objective is to optimize channel mix, invest in the most effective channels, and align sales and distribution strategies to maximize revenue generation. Overall, the objective of revenue strategy planning is to drive sustainable and profitable revenue growth by aligning business goals, market opportunities, customer needs, pricing strategies, and sales and marketing efforts. It involves a comprehensive, data-driven approach to optimize revenue streams and maximize financial performance.
- Part 1 Month 2 Organization Plan – Creating a revenue growth organization requires careful planning and strategic execution. The objective of this class is to establish requirements and plans to recruit and hire the best resources available, and ensure a methodology is followed when the organization grows. A sales and marketing organization that is structured to drive revenue growth should have the following characteristics: 1. Alignment: Sales and marketing teams should be closely aligned and have a shared understanding of the overall revenue goals and objectives. This alignment ensures that both teams are working together towards the same revenue targets. 2. Collaboration: Collaboration and communication between sales and marketing should be encouraged and fostered. Regular meetings and cross-functional collaboration should take place to share insights, align strategies, and coordinate efforts. 3. Targeted Marketing: Marketing efforts should be focused on identifying and targeting the right audience for the product or service. This involves conducting market research, developing buyer personas, and tailoring marketing messages and campaigns to resonate with the target audience. 4. Lead Generation: A strong lead generation process should be in place to ensure a steady flow of qualified leads into the sales pipeline. Marketing efforts should be focused on generating high-quality leads that have a higher likelihood of converting into customers. 5. Seamless Sales Process: The sales process should be streamlined and efficient, enabling sales teams to effectively engage with prospects, address their needs, and close deals. Sales enablement tools and technology can be leveraged to automate manual tasks, provide sales reps with relevant information, and track progress. 6. Customer-Centric Approach: The sales and marketing organization should have a deep understanding of the customer’s needs, pain points, and desired outcomes. Marketing campaigns and sales conversations should focus on showcasing the value of the product or service in solving customer problems and meeting their goals. 7. Data-Driven Decision Making: Sales and marketing organizations should leverage data and analytics to make informed decisions. This includes tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, and using data to identify areas for improvement in the sales process. 8. Continuous Improvement: A culture of continuous improvement should be fostered within the organization. This involves regularly evaluating and optimizing sales and marketing strategies, learning from successes and failures, and implementing changes based on data and insights. 9. Customer Retention: Revenue growth is not only about acquiring new customers but also retaining existing ones. Sales and marketing efforts should focus on nurturing customer relationships, providing excellent customer service, and identifying upsell or cross-sell opportunities. 10. Measurement and Accountability: Clear metrics and targets should be established to measure the success of sales and marketing efforts. Regular performance tracking and reporting should be conducted to monitor progress towards revenue goals and hold teams accountable. By having a sales and marketing organization that is aligned, collaborative, customer-focused, data-driven, and continuously improving, businesses can drive revenue growth effectively and efficiently.
- Part 1 Month 3 Product Marketing – The objectives of product marketing to support revenue growth plans include: 1. Product Positioning and Differentiation: Establish a clear and compelling product positioning that differentiates the offering from competitors and aligns with the target market’s needs and preferences. The objective is to create a strong market position that drives customer engagement and generates revenue. 2. Pricing and Packaging Strategy: Collaborate with pricing teams to develop optimal pricing models and packaging strategies for the product. These strategies should be designed to maximize revenue and profitability while considering competitive dynamics and customer value perception. The objective is to establish pricing that supports revenue growth while meeting customer expectations and market conditions. 5. Customer Retention and Expansion: Develop customer retention and expansion strategies to drive revenue growth from existing customers. This involves understanding customer needs, delivering exceptional customer experiences, and identifying opportunities for upselling, cross-selling, and renewal. The objective is to maximize customer lifetime value and foster long-term customer relationships that contribute to revenue growth. 6. Competitive Analysis and Strategy: Conduct ongoing competitive analysis to stay informed about the market landscape, monitor competitor activities, and identify areas for differentiation. Use this analysis to inform product development, marketing messaging, and sales strategies that position the product as superior and drive revenue growth. 7. Market Insights and Feedback: Gather market insights, customer feedback, and industry trends to inform product enhancements, go-to-market strategies, and revenue growth initiatives. This involves continuously monitoring customer needs, market dynamics, and emerging technologies to identify opportunities for product optimization and expansion. 8. Collaboration with Cross-functional Teams: Collaborate closely with cross-functional teams, such as product management, sales, and marketing, to align efforts, share insights, and collectively drive revenue growth. By fostering collaboration, the objective is to ensure a unified approach to product marketing that supports revenue goals and promotes overall business success. 9. Metrics and Analytics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of product marketing efforts in driving revenue growth. Track metrics such as customer acquisition, conversion rates, revenue generated per customer, and customer retention to assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize strategies accordingly. Overall, the objectives of product marketing to support revenue growth revolve around effectively positioning the product, generating demand, converting leads, retaining, and expanding customer relationships, analyzing the competitive landscape, gathering market insights, and collaborating across teams. By focusing on these objectives, product marketing can contribute significantly to driving revenue growth and achieving business success.
- Part 1 Month 4 Marketing Communications – The objective of this class is to learn what tasks are needed when promoting the business to grow revenues. This class will cover these objective: 1. Increase Brand Awareness: Build and increase awareness about the company’s brand, products, or services among the target market. The objective is to ensure that potential customers are aware of the company and what it offers. 2. Demand Generation: Attract and gather potential customer information by generating leads through various marketing channels, such as digital advertising, content marketing, events, or social media. The objective is to build a database of interested prospects that can be nurtured and converted into customers. 3. Drive Customer Acquisition: Acquire new customers by converting leads into paying customers. The objective is to convert the interested prospects into actual buyers, driving revenue growth through increased sales. 4. Enhance Conversion Rates: Optimize marketing efforts to improve conversion rates at each stage of the sales funnel. This may involve improving website conversion rates, email open and click-through rates, or other performance metrics. The objective is to increase the percentage of leads that convert into customers, maximizing revenue potential. 5. Increase Customer Retention: Implement strategies to ensure customer loyalty and repeat business. This can involve providing exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, loyalty programs, or ongoing communication and engagement. The objective is to retain existing customers to drive repeat sales and increase customer lifetime value. 6. Expand Market Reach: Identify and target new markets or customer segments that align with the company’s products or services. This can involve entering new geographic regions, targeting niche markets, or diversifying customer segments. The objective is to expand the company’s customer base and reach untapped revenue potential. 7. Improve Customer Engagement: Engage with customers through effective communication and marketing efforts. This can include engaging content, social media interactions, personalized messaging, or customer feedback loops. The objective is to foster a strong connection with customers, driving loyalty, word-of-mouth referrals, and repeat business. 8. Measure and Optimize ROI: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and track the return on investment (ROI) for promotional activities. Continuously analyze data and metrics to identify successful strategies and areas of improvement. The objective is to optimize marketing efforts and allocate resources to the most effective channels and tactics that generate the highest revenue growth. These objectives should align with the company’s overall revenue growth goals and be supported by a well-defined marketing strategy and clear action plans. Regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustment based on performance will help drive revenue growth effectively.
- Part 1 Month 5 Content Strategy – The objective of a content strategy is to determine how to stimulate a buyer to act. In this class we will cover these critical components of content creation: 1. Enhancing Brand Visibility: Increase brand awareness and visibility by producing high-quality content that aligns with your brand identity and resonates with your target audience. The objective is to position your brand as a thought leader and create a strong brand presence in the market. 2. Generating Qualified Leads: Develop content that attracts and engages your target audience, driving them to act and provide their contact information. The objective is to generate a steady flow of qualified leads that can be nurtured and eventually converted into customers. 3. Nurturing Leads and Conversions: Create content that caters to different stages of the buyer’s journey, from awareness to consideration to decision-making. The objective is to educate and nurture leads, building trust and guiding them towards making a purchase or taking the desired action, ultimately driving revenue growth. 4. Showcasing Product/Service Value: Demonstrate the unique value and benefits of your products or services through compelling content. This can include product demonstrations, case studies, customer testimonials, and comparisons with competitors. The objective is to showcase the value of your offerings and convince potential customers of the benefits they will gain by purchasing from your company. 5. Driving Repeat Sales and Customer Loyalty: Create content that keeps existing customers engaged and encourages repeat purchases. This can include personalized offers, loyalty programs, how-to guides, and newsletters. The objective is to foster loyalty, maintain customer satisfaction, and encourage recurring revenue from existing customers. 6. Supporting Sales Enablement: Develop content that equips sales teams with the necessary resources to effectively communicate value propositions and address customer concerns. This can include sales presentations, battle cards, product guides, and FAQs. The objective is to empower the sales team to drive revenue growth through effective communication and closing deals. 7. SEO and Organic Traffic: Create content that is optimized for search engines to improve organic website traffic. The objective is to increase visibility in search engine results and attract potential customers who are actively searching for solutions or information related to your products or services. 8. Measuring and Analyzing Content Performance: Set performance metrics and track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your content marketing efforts. Continuously analyze data and insights to identify content that is driving revenue growth and optimize your strategy accordingly. It’s important to note that these content strategy objectives should align with your overall business goals and be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Regularly assess your content strategy’s performance and adjust maximize revenue growth.
- Part 1 Month 6 Lead Generation – The objectives of Lead Generation are obvious, attract more buyers to your solution. This class will help you understand the current lead generation process and the components of establishing a highly productive demand generation system. The class will provide insights on the following: 1. Increasing the Quantity of Leads: Generate a higher volume of leads to increase the pool of potential customers for your business. The objective is to attract a larger number of interested individuals or companies who may eventually convert into paying customers. 2. Improving Lead Quality: Focus on attracting more qualified leads who are more likely to convert into customers. The objective is to target individuals or organizations that align with your ideal customer profile and have a higher propensity to purchase your products or services. 3. Enhancing Conversion Rates: Optimize lead nurturing strategies to improve conversion rates at each stage of the sales funnel. The objective is to increase the percentage of leads that progress through the sales pipeline and ultimately convert into paying customers. 4. Reducing Sales Cycle Length: Implement lead generation strategies that help accelerate the sales cycle. By attracting highly interested and well-qualified leads, the objective is to reduce the time it takes for leads to become customers, thereby increasing revenue more quickly. 5. Increasing Customer Lifetime Value: Attract leads who have the potential for long-term engagement and repeat business. The objective is to focus on lead generation efforts that result in customers with a higher lifetime value, leading to increased revenue over the long term. 6. Maximizing Marketing ROI: Optimize lead generation activities to generate the greatest return on investment (ROI). The objective is to allocate marketing resources efficiently and effectively to generate revenue growth while minimizing costs. 7. Aligning Marketing and Sales: Foster collaboration and alignment between marketing and sales teams to ensure leads are effectively handed off and managed through the sales process. The objective is to streamline the lead handoff, improve lead conversion rates, and ultimately drive revenue growth. 8. Iterating and Experimenting: Continuously test and iterate lead generation strategies to identify the most effective approaches for your target audience. The objective is to refine and optimize lead generation efforts over time, leveraging data and insights to drive revenue growth. 9. Tracking and Measuring Performance: Implement tracking and measurement mechanisms to monitor the performance of lead generation initiatives. The objective is to analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead quantity, lead quality, conversion rates, and revenue generated to assess the effectiveness of lead generation efforts and make data-driven decisions. By focusing on these Lead Generation objectives, businesses can drive revenue growth by increasing the quantity and quality of leads, improving conversion rates, reducing sales cycle length, increasing customer lifetime value, maximizing marketing ROI, aligning marketing and sales efforts, iterating, and experimenting, and tracking performance effectively.
- Part 1 Month 7 Value Selling – The objective of this class is to transform your sales group into Value Selling advocates. Value selling is an approach to sales that focuses on demonstrating and communicating the unique value and benefits of a product or service to the customer. It involves identifying and understanding the customer’s needs, challenges, and goals, and then positioning the product or service as a solution that delivers tangible value and helps address those needs: 1. Communicating Unique Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the unique value and benefits your products or services offer compared to competitors. The objective is to effectively communicate why customers should choose your offerings over alternatives in the market, ultimately driving revenue growth. 2. Differentiating from Competitors: Highlight the distinct advantages and points of differentiation that set your solution apart from competitors. The objective is to position your products or services as the preferred choice for customers, enabling you to capture a larger market share and increase revenue. 3. Aligning with Customer Needs: Understand the specific pain points and goals of your target customers and position your offerings as solutions to their challenges. The objective is to demonstrate how your products or services directly address customer needs, resulting in increased willingness to pay and higher revenues. 4. Demonstrating Business Value: Showcase the quantifiable and measurable business value that your products or services deliver to customers. This can include cost savings, revenue growth, increased efficiency, or competitive advantage. The objective is to illustrate the return on investment (ROI) and bottom-line impact of choosing your solution, thereby increasing customer willingness to pay. 5. Building Trust and Credibility: Establish trust and credibility with customers by providing reliable information, data, case studies, and testimonials that validate the value and benefits of your offerings. The objective is to reduce perceived risk and increase customer confidence in choosing your solution, leading to revenue growth. 6. Positioning as a Strategic Partner: Position your company as a strategic partner that offers ongoing support, expertise, and long-term value to customers. The objective is to build strong customer relationships, promote repeat business, and increase customer lifetime value. 7. Empowering Sales Teams: Provide sales teams with the necessary tools, training, and resources to effectively communicate value propositions and address customer needs and objections. The objective is to empower sales representatives to effectively sell the value of your offerings, resulting in increased conversion rates and revenue growth. 8. Measuring and Optimizing ROI: Implement performance metrics to track the effectiveness of value selling efforts in driving revenue growth. Develop Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure metrics such as average deal size, win rates, customer acquisition costs, and customer lifetime value. The objective is to monitor and optimize value selling strategies to maximize revenue generation. By focusing on these Value Selling objectives, businesses can support revenue growth by effectively communicating value propositions, differentiating from competitors, aligning with customer needs, demonstrating business value, building trust, positioning as a strategic partner, empowering sales teams, and measuring and optimizing ROI.
- Part 1 Month 8 Account Management – The objectives of account management in support of revenue growth is to provide strategic and ongoing process of building and nurturing relationships with key customers or accounts to foster customer satisfaction, loyalty, and growth. It involves understanding the needs and goals of the customer, providing personalized support and guidance, and serving as the main point of contact for all account-related activities. This class will examine the critical components of a world-class account management role. 1. Increase Customer Retention: Ensure high levels of customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty to retain existing customers. The objective is to minimize customer churn and maximize revenue from ongoing business with existing accounts. 2. Up-selling and Cross-selling: Identify opportunities to expand the product/service offerings within existing accounts. The objective is to increase revenue by promoting additional products or services that align with the customer’s needs and provide upselling and cross-selling opportunities. 3. Identify Growth Opportunities: Continuously analyze and understand customer needs and business challenges to identify opportunities for growth and value creation. The objective is to proactively suggest new solutions, upgrades, or customized offerings that drive increased revenue and customer satisfaction. 4. Renewal Management: Proactively manage contract renewals and negotiations to ensure customer retention and continued revenue generation. The objective is to secure prompt and favorable contract renewals with existing accounts. 5. Relationship Building: Cultivate strong and trusted relationships with key stakeholders within customer organizations. The objective is to become a trusted advisor and collaborator, enabling deeper engagement, improved customer satisfaction, and increased revenue opportunities. 6. Maximize Customer Lifetime Value: Adopt a long-term perspective and focus on maximizing the lifetime value of customer relationships. The objective is to not only generate immediate revenue but also foster repeat business, upselling, cross-selling, and referrals that contribute to sustainable revenue growth over the long term. 7. Strategic Account Planning: Develop comprehensive account plans that include growth strategies, revenue targets, and action plans tailored to each customer’s unique requirements. The objective is to align account management activities with revenue growth objectives and ensure a proactive and strategic approach to managing key accounts. 8. Collaboration with Sales and Marketing: Collaborate closely with the sales and marketing teams to align strategies and jointly pursue revenue growth opportunities. The objective is to leverage combined efforts to acquire new business, expand existing accounts, and enhance overall revenue generation. 9. Data Analysis and Reporting: Track and analyze account performance, revenue trends, customer satisfaction levels, and engagement metrics. The objective is to gain insights and make data-driven decisions to optimize account management activities, identify areas for improvement, and capitalize on revenue growth opportunities. By focusing on these account management objectives, businesses can support revenue growth by maximizing customer retention, driving upselling and cross-selling, identifying growth opportunities, effectively managing renewals, building strong relationships, maximizing customer lifetime value, implementing strategic account plans, collaborating with sales, and marketing, and utilizing data for analysis and decision-making.
- Part 1 Month 9 Channel Strategy – The objectives of this class will be to learn about the value of using partners through a channel strategy to help drive revenue growth. This class will examine the use and application of channel partners to drive revenue growth. We will review the following elements of a channel strategy: 1. Expand Market Reach: Utilize channel partners to extend the company’s market reach and access new customer segments. The objective is to tap into new markets, geographies, and customer demographics to increase the potential customer base and drive revenue growth. 2. Increase Sales Volume: Drive higher sales volumes by leveraging the sales network and capabilities of channel partners. The objective is to empower channel partners to effectively sell the company’s products or services, resulting in increased sales and revenue generation. 3. Enhance Customer Satisfaction: Provide exceptional customer experiences through well-trained and knowledgeable channel partners. The objective is to ensure that customers receive the same level of service, support, and satisfaction when purchasing through channel partners as they would when buying directly from the company. 4. Optimize Channel Performance: Set performance targets and optimize the performance of channel partners by providing training, incentives, resources, and support. The objective is to maximize the productivity and effectiveness of channel partners in driving revenue growth. 5. Facilitate Product Education and Promotion: Educate channel partners about the company’s products or services and provide marketing collateral and resources to enable effective promotion. The objective is to equip channel partners with the necessary knowledge and materials to effectively market and promote the offerings, leading to increased awareness and sales. 6. Manage Channel Relationships: Establish strong relationships with channel partners based on trust, collaboration, and mutual growth. The objective is to foster a positive and productive partnership that aligns interests, drives mutual success, and ultimately contributes to revenue growth. 7. Monitor and Evaluate Channel Performance: Measure and evaluate the performance of channel partners based on predefined key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales revenue, customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability. The objective is to identify areas of improvement, reward high-performing partners, and take corrective actions to address underperforming partners. 8. Continuously Improve Channel Strategy: Regularly review and refine the channel strategy based on market dynamics, customer trends, and partner feedback. The objective is to adapt the channel strategy to changing business conditions, optimize partner selection criteria, and improve the overall effectiveness of the channel program in driving revenue growth. 9. Collaborate with Channel Partners: Foster collaboration and communication with channel partners, encouraging feedback and ideas for driving revenue growth. The objective is to leverage the expertise and market insights of channel partners to identify new revenue opportunities and mutually beneficial strategies. These channel strategy objectives should align with the company’s overall revenue growth goals and be supported by robust channel management processes, effective partner enablement, and continuous monitoring and optimization. Regularly evaluate the performance of the channel strategy and adjust maximize revenue potential.
- Part 1 Month 10 Revenue Enablement – The objective for this class is to review the power of facilitating revenue enablement to drive revenue growth. We will review the critical components of successful revenue enablement programs which will include: 1. Sales Training and Development: Ensure the sales team is equipped with the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools to effectively sell the company’s products or services. The objective is to provide comprehensive training programs, continuous coaching, and resources that enhance the sales team’s capabilities, resulting in increased sales and revenue. 2. Content and Collateral Creation: Create compelling and relevant content and sales collateral that address customer needs and showcase the value of the company’s offerings. The objective is to provide sales representatives with the resources they need to effectively communicate value propositions and close deals, ultimately driving revenue growth. 3. Sales Process Optimization: Streamline and optimize the sales process, ensuring it aligns with customer buying journeys and provides a seamless customer experience. The objective is to remove any bottlenecks, reduce friction in the sales process, and improve sales efficiency and effectiveness, leading to increased revenue. 4. Sales Enablement Technology: Implement and leverage sales enablement tools and technologies that enhance the sales team’s productivity and effectiveness. The objective is to provide the sales team with easy access to relevant collateral, customer data, and sales analytics, enabling them to work more efficiently and make data-driven decisions to drive revenue growth. 5. Enablement for New Product or Market Launches: Support successful product or market launches by providing the sales team with the necessary training, resources, and guidance. The objective is to ensure a smooth transition and enable the sales team to effectively position and sell new products or capture new market opportunities, resulting in revenue growth. 6. Sales and Marketing Alignment: Foster collaboration and alignment between the sales and marketing teams, ensuring consistent messaging, shared goals, and effective lead handoff processes. The objective is to optimize lead generation, nurture leads effectively, and drive revenue growth through a unified and coordinated approach. 7. Sales Performance Measurement and Analysis: Implement metrics and analytics to track and measure sales performance, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. The objective is to identify and leverage successful sales strategies, optimize performance, and continuously improve revenue generation. 8. Customer Feedback and Insights: Gather customer feedback and insights to understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points. The objective is to provide valuable insights to the sales team and the organization as a whole, enabling them to tailor their sales approaches, products, and services to better meet customer demands and drive revenue growth. 9. Continuous Enablement Improvement: Regularly evaluate and improve the effectiveness of revenue enablement initiatives by gathering feedback, conducting assessments, and employing best practices. The objective is to continuously optimize the enablement process to support revenue growth and adapt to changing market dynamics. By focusing on these revenue enablement objectives, businesses can empower their sales teams, optimize sales processes, leverage technology and data, align sales and marketing efforts, and continuously improve enablement initiatives, ultimately driving revenue growth and achieving organizational goals.
- Part 1 Month 11 Customer Success – The objectives for the customer success function supporting revenue growth. Customer success refers to the proactive and strategic approach of ensuring that customers achieve their desired outcomes and derive value from the products or services they have purchased. It involves understanding the customer’s goals and needs, providing support, and guiding them throughout their entire journey with the company. The primary focus of customer success is to drive customer satisfaction, retention, and expansion by actively engaging with customers and helping them realize the full value of their investment. Customer success professionals work closely with customers to understand their desired outcomes, develop success plans, and provide ongoing support and guidance to help them achieve those outcomes. 1. Ensure Customer Retention: Focus on maintaining high customer retention rates by actively engaging with customers, understanding their needs, and promptly addressing any concerns or issues. The objective is to establish strong relationships and ensure customer satisfaction, which leads to long-term customer loyalty and revenue growth. 2. Upsell and Cross-sell Opportunities: Identify and capitalize on upselling and cross-selling opportunities within the existing customer base. The objective is to understand customers’ evolving needs and proactively offer additional products or services that provide value and contribute to incremental revenue growth. 3. Drive Product Adoption and Utilization: Aid customers in effectively adopting and utilizing the company’s products or services. The objective is to help customers derive maximum value from their investments, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and the potential for upselling and cross-selling. 4. Advocate for Customer Needs: Act as the customer’s internal advocate within the company, ensuring their voice is heard and their requirements are met. The objective is to align the company’s offerings with customer needs, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and retention. 5. Gather Customer Feedback and Insights: Continuously gather customer feedback and insights to understand their experiences, challenges, and opportunities. The objective is to use customer insights to drive product improvements, identify new revenue streams, and align customer success strategies with revenue growth objectives. 6. Identify Opportunities for Expansion: Proactively identify growth opportunities within existing accounts, such as expansion into new business units or geographies. The objective is to uncover potential areas for revenue growth and work with sales and account management teams to capitalize on these opportunities. 7. Collaborate with Sales and Marketing: Collaborate closely with sales and marketing teams to align strategies and jointly pursue revenue growth opportunities. The objective is to leverage combined efforts to drive new business, expand existing accounts, and enhance overall revenue generation. 8. Establish Renewal and Expansion Processes: Develop and implement processes for managing contract renewals and expansions. The objective is to ensure timely and seamless renewal of contracts and to identify opportunities to expand revenue within existing accounts. 9. Measure and Track Success Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the impact of customer success efforts on revenue growth. The objective is to measure and analyze metrics such as customer lifetime value, renewal rates, expansion rates, and overall revenue per customer to evaluate the effectiveness of customer success initiatives in driving revenue growth. By aligning their objectives with revenue growth, the customer success team can focus on ensuring customer satisfaction, identifying upsell and cross-sell opportunities, driving product adoption, acting as customer advocates, gathering customer insights, identifying expansion opportunities, collaborating with other departments, establishing renewal and expansion processes, and measuring success metrics. These objectives will help drive customer success and, in turn, contribute to revenue growth for the organization.
- Part 1 Month 12 Rev Ops – Revenue operations (RevOps) refers to a strategic and collaborative approach that aligns and optimizes the functions of sales, marketing, and customer success within an organization. It focuses on driving revenue growth by breaking down silos, improving efficiency, and maximizing cross-functional collaboration. The primary objective of revenue operations is to streamline and improve the end-to-end revenue-generation process, from marketing to sales to customer retention. It involves integrating people, processes, and technology to create a cohesive revenue engine that effectively engages customers, drives sales, and fosters customer success .1. Optimize Sales Processes: Streamline and optimize sales processes to improve efficiency, effectiveness, and alignment with revenue growth objectives. The objective is to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, automate manual tasks, and enhance overall sales performance. 2. Implement Sales Technology Stack: Research, select, and implement sales technologies, tools, and systems that improve sales productivity, data management, and analytics. The objective is to enable seamless sales operations, accurate forecasting, and data-driven decision-making to drive revenue growth. 3. Data Management and Analytics: Establish processes and systems for collecting, cleansing, and managing sales data. The objective is to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility, enabling reliable reporting and analytics to drive revenue growth initiatives. 4. Sales Performance Tracking and Reporting: Develop reporting frameworks and dashboards to track key sales performance metrics and revenue targets. The objective is to provide management with clear insights into sales performance, pipeline metrics, and revenue growth progress. 5. Sales Forecasting and Demand Planning: Drive accurate sales forecasting and demand planning processes. The objective is to provide visibility into future revenue and sales projections, align sales efforts with resource allocation, and optimize inventory management to support revenue growth objectives. 6. Collaboration and Alignment: Foster collaboration and alignment between sales, marketing, and finance teams. The objective is to ensure smooth coordination among departments, alignment of strategies, and effective communication to support revenue growth initiatives. 7. Training and Enablement: Develop training programs and resources to enhance the skills and knowledge of the sales team. The objective is to provide ongoing training and enablement that aligns with revenue growth strategies and equips the sales team to effectively sell products or services. 8. Process Optimization and Continuous Improvement: Continuously review and optimize revenue-related processes and workflows. The objective is to identify areas for improvement, implement best practices, and drive continuous improvement to maximize revenue growth opportunities. 9. Scalability and Efficiency: Design scalable processes and systems that support the company’s growth objectives. The objective is to enable the organization to handle increasing sales volumes effectively, efficiently, and without compromising quality or customer satisfaction. 10. Revenue Growth Strategy Support: Collaborate with cross-functional teams to develop and execute revenue growth strategies. The objective is to provide insights, analysis, and operational support to drive revenue growth initiatives and achieve organizational goals. By focusing on these objectives, the revenue operations group can optimize sales processes, implement the right technology stack, manage, and analyze data effectively, track performance and forecasting, foster collaboration, provide training and enablement, continuously improve processes, ensure scalability and efficiency, and support revenue growth strategies. This helps to drive revenue growth and enable the organization to achieve its revenue-related objectives.
Methodology
Revenue Growth
Program Planning
Utilizing a SWOT analysis methodology, we can assess an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats in the market to develop strategies for business growth. Businesses can use this methodology to create a comprehensive revenue growth plan that aligns with their strengths, addresses weaknesses, capitalizes on opportunities, mitigates potential threats, and gives them a competitive advantage. It also helps to identify areas that need improvement, potential opportunities in the market to capitalize on, and possible threats that may hinder revenue growth. This approach allows for a strategic and focused approach to revenue growth planning.
A SWOT analysis provides the client with a comprehensive understanding of their business or project’s internal and external factors, enabling them to make well-informed decisions and enhance their overall performance. The results of using the SWOT process will be a blueprint for strategic and operational actions needed to achieve its business objectives. The SWOT process will follow these steps:
1. Identification of strengths: A SWOT analysis helps identify and understand the internal strengths of the business or project. These could include unique capabilities, valuable resources, a strong brand, or a talented team. Recognizing these strengths enables the company to leverage them for a competitive advantage.
2. Awareness of weaknesses: The analysis also sheds light on the internal defects or areas that require improvement. This could involve inadequate resources, lack of specific skills, or vulnerable aspects of the business. The company can develop strategies to address weaknesses and minimize potential risks by acknowledging them.
3. Exploration of opportunities: A SWOT analysis highlights external opportunities that benefit the company. These could be emerging markets, untapped customer segments, technological advancements, or favorable industry trends. Identifying these opportunities allows companies to capitalize on them and grow their business.
4. Assessment of threats: The analysis also uncovers external dangers that may threaten the client’s business. These could include competition, changing regulations, economic factors, or emerging trends that could negatively impact their operations. Recognizing threats enables the client to develop contingency plans and mitigate potential risks.
5. Strategic decision-making: The company can make informed strategic decisions using the SWOT analysis’s insights. They can prioritize their strengths, address weaknesses, pursue opportunities, and develop strategies to mitigate threats. This helps set clear objectives, define action plans, allocate resources effectively, and position their business for success.

Program Development
When developing a revenue growth program, the best approach depends on various factors such as the industry, company size, target market, and available resources. Here is the overview of the methodology:
The methodology starts by understanding customer needs, preferences, and pain points to develop products or services that meet those needs. It involves conducting market research, customer surveys, and analyzing customer data to identify growth opportunities. By aligning the business strategy with customer demands, companies can drive revenue growth through increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
I will also utilize data analytics (such as sales data, customer behavior data, and market trends) to identify revenue growth opportunities. By leveraging this data, we will optimize pricing strategies, identify cross-selling or upselling opportunities, and personalize marketing campaigns to drive revenue growth.
Developing a revenue growth strategy involves an iterative and flexible approach. Using the data analysis generated and mapping the customer requirements, we can focus on setting short-term goals, experimenting with different strategies, measuring results, and adjusting tactics accordingly. We will emphasize continuous improvement and adaptation, allowing us to respond quickly to market changes and optimize revenue growth strategies.

Program Implementation
When implementing a revenue growth program, the approach will depend on the company’s specific goals, resources, and circumstances.
The best approach to implementing a revenue growth model emphasizes setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Timed goals. It also involves developing key performance indicators (KPIs) for each perspective functional team and aligning them with revenue growth goals. This allows for an effective system to track progress and ensure alignment across groups by clearly defining the revenue growth targets and breaking them down into actionable and measurable objectives.
This methodology encourages a structured and organized approach to implementing revenue growth strategies.

Program Review
When reviewing a revenue growth program, I would use multiple methods to ensure the assessment returns the best perspective and options for management decisions. Here is the methodology I would use for reviewing a revenue growth program:
The methodology I use contains elements from three methods.
• Data-driven analysis
• Customer feedback and satisfaction analysis
• Benchmarking and industry analysis
This review process involves data-driven analysis by analyzing and interpreting quantitative (financials, forecast, lead gen channels, etc.) and qualitative (customer feedback, market trends, etc.) data to evaluate the effectiveness of the revenue growth program. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue growth rate, customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, and conversion rates would be used to assess the program’s impact. By thoroughly analyzing the data, companies can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in their revenue growth strategies.
The next part of the methodology focuses on gathering and analyzing customer feedback to understand their satisfaction levels and identify potential areas for revenue growth. Surveys, interviews, and customer reviews can provide valuable insights into customer preferences, pain points, and opportunities for upselling or cross-selling. By incorporating the voice of the customer into the review process, companies can gain a deeper understanding of how their revenue growth program is perceived and make necessary adjustments.
The last part of the review process compares the company’s revenue growth program with industry benchmarks and best practices. By evaluating how the company’s revenue growth strategies, techniques, and performance metrics compare to competitors or industry leaders, companies can identify potential gaps and areas for improvement. This part of the review methodology helps the company stay competitive and adopt effective revenue growth strategies.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Manufacturing
History
Over the past 50 years, some of the most significant advancements in technology manufacturing occurred.
• Miniaturization and Integrated Circuits
– Developing smaller and more complex integrated circuits has enabled the miniaturization of electronic devices, leading to the emergence of smaller and more powerful technology products.
• Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM)
– The introduction of CAD/CAM systems has revolutionized the design and manufacturing process by allowing engineers to create and test prototypes digitally before physical production, improving accuracy and efficiency.
• Robotics and Automation
– Using robots and automation in manufacturing has dramatically increased productivity and efficiency. Once done manually, tasks can be automated, reducing human error and increasing production speed.
• 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing
– 3D printing allows the manufacturing of objects by adding layers of material instead of subtracting or molding. This technology has transformed prototyping and small-scale production by reducing lead time, customization costs, and waste.
• Internet of Things (IoT)
– IoT has facilitated connectivity between devices and systems, enabling them to collect, analyze, and share data. This connectivity has improved supply chain management, quality control, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
• Sustainable Manufacturing
– There has been a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly manufacturing processes and materials. Efforts to reduce waste, energy consumption, and emissions have led to the development of more sustainable manufacturing practices.
• Advanced Materials
– The development of advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites and nanomaterials, has improved products’ performance, strength, and durability across various industries.
• Smart Factories
– The integration of sensors, data analytics, and cloud computing has enabled the smart factory concept, where real-time data is used to optimize production processes, monitor equipment, and improve overall efficiency.
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
– These technologies have found applications in manufacturing for training, maintenance, and design visualization. AR and VR can enhance worker skills, facilitate remote collaboration, and improve productivity.
• Artificial Intelligence (AI)
– AI technologies, such as machine learning and computer vision, have been increasingly adopted in manufacturing for quality control, predictive maintenance, and production optimization. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data and make intelligent real-time decisions.
Current Position
Significant advancements and ongoing innovation characterize the current state of technology manufacturing. Here are some key aspects highlighting the current state of technology manufacturing:
• Automation and Robotics.
• Internet of Things (IoT) Integration.
• Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0.
• Supply Chain Digitization.
• Sustainability and Green Manufacturing.
• Customization and Personalization.
• Collaboration and Partnerships.
• Global Competitiveness.
• Agile Manufacturing and Just-in-Time Operations.
• Focus on Quality and Reliability.
These characteristics provide a snapshot of the current state of technology manufacturing, emphasizing technological advancements, digitization, sustainability, and competitiveness in an ever-evolving industry.
Future Outlook
While there have been changes in the manufacturing industry, it continues to play a crucial role in economies worldwide. Here are some reasons why manufacturing is still relevant and has a future:
• Innovation and Technological Advancements
– Manufacturing is being transformed by technological advancements such as automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics. These technologies improve manufacturing productivity, efficiency, and quality, making it more competitive and sustainable.
• Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
– Recent disruptions in global supply chains due to events like the COVID-19 pandemic have highlighted the importance of resilience and localization. There is a growing trend toward bringing manufacturing closer to the markets, increasing demand for local manufacturing capabilities.
• Customization and Personalization
– Consumer preferences are shifting towards personalized and customized products. Manufacturing can cater to these demands by leveraging technology like additive manufacturing (3D printing), which allows for flexible and tailored production at a smaller scale.
• Sustainability and Circular Economy
– Manufacturing is adapting to the growing emphasis on sustainability and the circular economy. Manufacturers are adopting sustainable practices, reducing waste, minimizing environmental impact, and exploring alternative energy sources to create a more sustainable future.
• Job Creation and Economic Growth
– Manufacturing provides employment opportunities and contributes to economic growth. While some traditional manufacturing jobs have been automated, the shift towards advanced technologies necessitates a skilled workforce to operate and maintain complex machinery and develop new manufacturing processes.
• Industry 4.0 and Digital Transformation
– The concept of Industry 4.0 emphasizes the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. This includes leveraging big data, cloud computing, IoT, and AI to create smart factories, optimize production, improve decision-making, and enhance efficiency.
• Collaboration and Advanced Manufacturing Ecosystems
– Collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, research institutions, and governments has become crucial for innovation and driving the future of manufacturing. Advanced manufacturing ecosystems are emerging, fostering partnerships and knowledge exchange to accelerate technological advancements.
With ongoing advancements in technology, sustainability initiatives, and the emergence of new business models, manufacturing continues to have a promising future.
Software Development
History
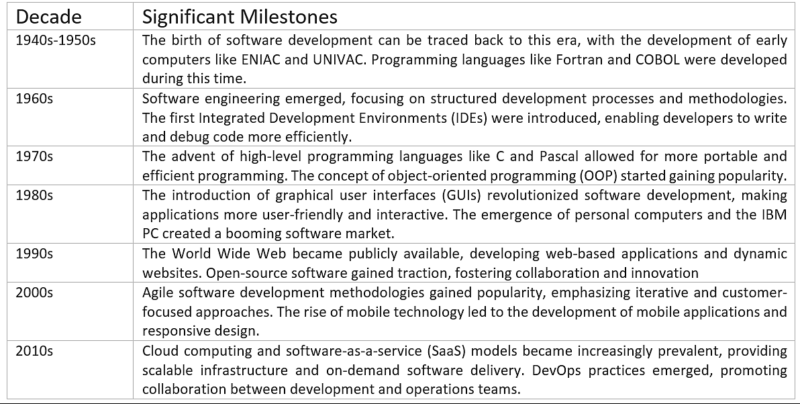
The history of software development is vast and evolving, and here is a high-level overview of significant milestones and key developments in software development:
Current Position
Software development continues to evolve rapidly with technological advancements like artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Development practices such as continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) are widely adopted.
A focus on customer-centricity, agility, and continuous innovation characterizes the current state of software development. Cross-platform and mobile development, cloud-native architecture, and secure coding practices are prominent. Additionally, ethical considerations, data privacy, and cybersecurity increasingly influence software development.
Future Outlook
Software development undoubtedly has a future and will continue to be a critical industry. Here are some key factors that contribute to the ongoing and promising future of software development:
The demand for software continues to grow across industries and sectors. Businesses rely on software to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. Additionally, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and virtual reality create new opportunities for software development.
The technology landscape constantly evolves, presenting software developers with new challenges and opportunities. Software developers must adapt and stay current as new programming languages, frameworks, tools, and libraries emerge. This constant evolution ensures that software development remains relevant and future-proof.
Organizations worldwide are undergoing digital transformation to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations. This transformation often involves the development of new software solutions or the modernization of existing systems. As a result, software developers play a crucial role in powering the digital transformation journey for businesses.
AI and machine learning are experiencing rapid advancement, opening up exciting possibilities for software development. From developing intelligent automation systems to creating predictive analytics and recommendation engines, integrating AI and machine learning into software solutions disrupts various industries and creates new opportunities for developers.
The proliferation of IoT devices presents vast potential for software development. As more interconnected devices come online, developers must build and manage the software that enables data collection, integration, and control. From smart homes to industrial IoT applications, software development will continue to play a critical role in shaping the IoT landscape.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual collaboration. Software developers have adapted to work remotely and utilize tools that enable seamless collaboration across distributed teams. This trend has opened up opportunities for developers to work for geographically diverse organizations and collaborate with talents worldwide.
Software development is inherently driven by innovation. The competitive nature of the industry necessitates continuous improvement, iterative development processes, and a focus on creating cutting-edge solutions. This innovation-centric approach ensures that software development thrives and evolves.
While it’s important to acknowledge that the software development landscape will continually change, the need for skilled software developers will persist. Adaptable professionals who continuously learn and enhance their skills and embrace emerging technologies will always find opportunities in this evolving field.
Technology Services
History
Current Position
Technology services have expanded to include a wide range of offerings. These include cybersecurity services, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) solutions, Internet of Things (IoT) integration services, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) development, blockchain solutions, and more.
As technology evolves, so do technology services. Companies continue to innovate and adapt to provide solutions that meet the ever-changing needs of businesses and individuals in an increasingly digital world.
Future Outlook
The future outlook of technology services is auspicious as technology continues to play a crucial role in shaping various aspects of our lives and industries. Here are some key trends and areas of focus that are likely to shape the future of technology services:
AI technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing, are expected to advance, enabling automation and intelligent decision-making across different industries. This includes areas such as autonomous vehicles, chatbots, and predictive analytics.
The IoT is poised to expand, connecting many devices and enabling a new data collection and analysis level. This will improve efficiency, real-time monitoring, and integration of various systems, such as smart homes, smart cities, and industrial IoT.
Cloud computing is anticipated to continue its growth trajectory, offering scalable and flexible storage, processing, and software delivery solutions. Additionally, edge computing, which allows processing closer to the data source, is expected to gain prominence for applications requiring low latency and real-time processing.
As technology becomes more integrated into our lives, robust cybersecurity measures are becoming increasingly critical. Technology service providers will be vital in developing and implementing cybersecurity solutions to protect against evolving threats.
The ongoing digital transformation across industries will require technology service providers to assist organizations in leveraging digital technologies to optimize processes, improve customer experiences, and remain competitive in the digital age.
AR and VR technologies are advancing rapidly, providing immersive and interactive experiences in various sectors such as gaming, education, healthcare, and training. Technology service providers will continue to play a role in developing and implementing AR/VR solutions.
Although still in its early stages, quantum computing can revolutionize computational power and solve complex problems currently unattainable with traditional computing. Technology service providers will contribute to developing and commercializing quantum computing technologies.
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, technology service providers will have opportunities to develop and implement eco-friendly and energy-efficient solutions in areas such as renewable energy, smart grids, and green data centers.
Overall, the future of technology services is characterized by rapid innovation and evolving needs. Service providers must stay agile, adapt to emerging technologies, and provide tailored solutions to meet the changing demands of industries and society.

Professional Services
History
The history of professional or consulting services dates back several centuries, originating from seeking advice and expertise from knowledgeable individuals. Here is a broad overview of the history of consulting services:
1. Early Beginnings: Consulting, in its basic form, can be traced back to ancient times when rulers and leaders sought advice from trusted advisors and experts in various domains such as law, finance, and strategy.
2. 19th Century: The modern consulting industry began to take shape during the 19th century, with the rise of industrialization and increasing complexity in business operations. Management consulting emerged as a profession primarily focused on providing advice on business strategy, organizational structure, and operations.
3. Early 20th Century: Consulting services expanded further in the early 20th century, with consultancies like McKinsey & Company and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) being established. These firms played a crucial role in shaping the consulting industry by introducing structured methodologies and frameworks.
4. Post-World War II: The consulting industry experienced significant growth and transformation after World War II. With the need for economic reconstruction and the rise of multinational corporations, consulting firms played a vital role in advising on business expansion, efficiency, and operational improvement.
5. 1960s-1980s: The consulting industry expanded further during these decades with the introduction of specialized consulting services in areas like technology, finance, marketing, and human resources. The Big Four accounting firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG) also expanded their consulting practices.
6. 1990s-Present: The consulting industry continued to evolve, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and increased competition. Management consulting firms diversified their services, incorporating IT, change management, digital transformation, and sustainability consulting.
Current Position
Today, consulting services cover various domains, including management, strategy, technology, finance, marketing, HR, and more. Consultants work with organizations of all sizes, from startups to multinational corporations, providing expertise, guidance, and tailored solutions to address their unique challenges and achieve their goals.
In recent years, there has been a rise in niche consulting firms focusing on specific industries, such as healthcare, energy, and technology. These specialized consultancies provide industry-specific expertise and tailored solutions. The consulting industry has been significantly impacted by technology, both as a tool for consultants and an area of consulting. Technology advancements have enabled remote consulting, enhanced data analytics, and the development of innovative digital consulting services.
With the growing importance of digital transformation and sustainability, consulting services now encompass advising on digital strategy, cybersecurity, data analytics, and environmental/social governance (ESG) practices.
Future Outlook
The consulting services field is a dynamic and evolving industry that continues to offer promising opportunities. The future of consulting services is growing and expanding as expertise is essential to being competitive. Here are a few of the reasons why Consulting Services will continue to grow and be relevant in the years ahead:
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

San Francisco, CA
History
California has a rich history of technology companies. Here is a brief overview of some prominent technology firms and milestones in California’s tech history:
1. Hewlett-Packard (HP): Founded in 1939 in Palo Alto, HP is one of California’s earliest and most influential technology companies. It started as a test and measurement equipment producer and eventually expanded into personal computers, printers, and enterprise solutions.
2. Fairchild Semiconductor: Founded in 1957 in Mountain View, Fairchild Semiconductor played a critical role in the early development of Silicon Valley. It was one of the first companies to manufacture silicon transistors, which paved the way for the modern semiconductor industry.
3. Intel: Founded in 1968 in Santa Clara, Intel is one of the world’s largest semiconductor chip manufacturers. The company is known for its microprocessors and has been instrumental in advancing computing technology.
4. Apple: Established in 1976 in Cupertino, Apple is one of the most iconic technology companies globally. It revolutionized personal computing with the Macintosh, transformed the music industry with the iPod and iTunes, and introduced game-changing products like the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch.
5. Oracle: Founded in 1977 in Santa Clara, Oracle is a leading provider of database software and enterprise solutions. It has played a significant role in shaping database management systems and cloud computing technology.
6. Google: Founded in 1998 in Menlo Park, Google (now Alphabet Inc.) has become one of the largest technology companies in the world. It is known for its internet search engine and services like Gmail, Google Maps, Google Drive, and the Android operating system.
7. eBay: Founded in 1995 in San Jose, eBay is a well-known e-commerce company that created an online marketplace for buyers and sellers. It played a significant role in the early days of online retailing.
8. Salesforce: Founded in 1999 in San Francisco, Salesforce is a cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform. It revolutionized the software industry by delivering enterprise applications through the internet, pioneering the concept of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
9. Tesla: Founded in 2003 in Palo Alto, Tesla is a leading electric vehicle and clean energy company. It has been at the forefront of electric vehicle innovation and has expanded into sustainable energy solutions, including solar panels and energy storage systems.
California’s role as a global tech hub continues to grow, with countless startups and established firms driving innovation across various sectors.
Current Position
California continues to maintain a significant advantage in technology leadership. Here are some reasons why California retains its position as a global tech leader:
1. Concentration of Tech Companies
2. Silicon Valley
3. Access to Capital
4. Top Universities and Research Centers
5. Diversity and Talent Pool
6. Entrepreneurial Culture
7. Regulatory Environment
8. Focus on Sustainability and Clean Tech
Future Outlook
While the technology landscape is dynamic and subject to global competition, California’s combination of talent, capital, culture, and innovation ecosystem provides a significant advantage in technology leadership. However, the state must continue fostering an environment that nurtures innovation, attracts talent, and embraces emerging technologies to maintain its position as a global tech leader.

New York, NY
History
New York has played a significant role in technology history, particularly in developing and growing industries such as telecommunications, finance, media, and e-commerce. Here are some key ways New York fits into technology history:
1. Telecommunications: New York has a long history in the telecommunications industry. The city has been a central telegraph and telephone communications hub since the 19th century. It was home to companies like Western Union and AT&T, which played critical roles in shaping global telecommunications networks.
2. Finance and Wall Street: New York City is renowned as a global financial center. The city’s financial district, Wall Street, has been at the forefront of technological advancements in the finance industry. Over the years, technology has transformed how financial transactions are conducted, leading to the development of electronic trading platforms, algorithmic trading systems, and fintech companies.
3. Media and Entertainment: New York is a central hub for media and entertainment industries. It has been a center for publishing, film and television production, advertising, and music. The rise of digital media and streaming platforms has further contributed to New York’s influence in technology-driven media and entertainment sectors.
4. Silicon Alley: New York’s tech ecosystem, known as Silicon Alley, has been proliferating. It is a cluster of technology companies, startups, and entrepreneurial ventures centered around Manhattan and Brooklyn. The area has attracted startups, investors, and talent in e-commerce, fintech, digital media, and fashion tech industries.
5. Internet and E-Commerce: New York has been home to several influential e-commerce and internet companies. Companies like Amazon, Etsy, and Jet.com have a significant presence in the city. Additionally, early internet service providers and Internet-focused companies emerged in New York during the dot-com boom, contributing to the growth of the internet economy.
6. Research and Innovation: New York is home to renowned research institutions, such as Columbia University and New York University. These institutions have been at the forefront of scientific research and technological innovation in computer science, engineering, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence.
7. Startup Ecosystem: New York has a vibrant startup ecosystem with numerous incubators, accelerators, and venture capital firms. The city has fostered an environment for technology entrepreneurs to launch and scale their startups, supporting innovation and attracting investment.
While California’s Silicon Valley is often associated with technology, New York’s significant contributions to the evolution of telecommunications, finance, media, and e-commerce and its emerging tech ecosystem make it an essential player in technology history. The city’s diverse industries and vital innovation-driven sectors continue to shape the technology landscape globally.
Current Position
The technology landscape in New York is dynamic, with a wide range of industries utilizing technology to drive innovation, economic growth, and societal impact. The city’s diversity, access to capital, talent pool, and entrepreneurial spirit contribute to its standing as a global technology hub.
Some critical aspects of the current technology landscape in New York:
• Startup Ecosystem
• Financial Technology
• Media and Entertainment
• Healthcare and Life Sciences
• Cybersecurity
• Tech Talent and Education
• Smart City Initiatives
Future Outlook
While challenges and uncertainties always exist, the combination of a robust tech ecosystem, access to talent and markets, industry diversity, government support, and innovative city initiatives make the future bright for New York and its technology industry. Continued investment, innovation, and collaboration are expected to drive further growth and establish the city as a global technology innovation and entrepreneurship leader.
Seattle, WA
History
The state of Washington has a significant history in technology and manufacturing. Here are some notable milestones and companies in Washington State that have helped lead the technology industry:
Boeing: Founded in Seattle in 1916, The Boeing Company has been a significant player in the aerospace industry and has significantly impacted technology manufacturing in the state. Boeing manufactures aircraft, satellites, and other aerospace-related technologies.
Microsoft: Founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975, Microsoft Corporation is one of the most renowned technology companies worldwide. While primarily focused on software development, Microsoft has also been involved in hardware manufacturing, including devices like the Xbox gaming console and Surface tablets.
Amazon: As an online book marketplace in 1994, Amazon has grown into a global e-commerce and technology giant. While primarily known for its online retail presence and cloud computing services (Amazon Web Services), Amazon has also ventured into hardware manufacturing, including devices like the Kindle e-reader, Echo smart speakers, and Fire tablets.
Nintendo of America: Nintendo has been in Washington State since the 1980s. Its American subsidiary, Nintendo of America, based in Redmond, is responsible for product localization, marketing, and distribution of Nintendo gaming systems and software.
Washington State is also home to various technology manufacturing companies involved in telecommunications, clean energy, biotechnology, software development, and more. Companies like Microsoft, Amazon, T-Mobile, Expedia, and Immunex (now part of Amgen) have made significant contributions to the technology and manufacturing landscape in the state.
Additionally, Washington State’s proximity to renowned research institutions like the University of Washington and a skilled workforce has attracted technology companies and fostered innovation in the field. The state continues to be a hub for technology, with ongoing advancements in the aerospace, software, e-commerce, and other tech manufacturing sectors.
Current Position
The state has a thriving technology sector, with prominent companies like Microsoft, Amazon, and Boeing, and a robust startup ecosystem. There is a high demand across various fields, including software development, data analysis, cybersecurity, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
The state boasts robust supporting infrastructure, including research institutions, incubators, accelerators, and venture capital firms, which contribute to the growth and success of the tech industry. This ecosystem fosters collaboration, knowledge exchange, and entrepreneurial spirit.
Future Outlook
The future looks bright for technology in Washington State. The state has a robust and diverse tech industry driven by major companies and a supportive ecosystem, which is why the future of technology in Washington State is promising. Here are some of the characteristics of Washingtons’ strengths in technology:
It established Tech Hub. Washington State, particularly the Seattle metropolitan area, has become a leading tech hub. It is home to major tech giants like Microsoft and Amazon and a robust ecosystem of startups, venture capital firms, and research institutions. This concentration of tech talent and resources fuels innovation and attracts further investment.
Emerging Technologies. Washington State is at the forefront of emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), and clean tech. These technologies hold immense growth potential, creating new job opportunities and driving economic development.
Supportive Ecosystem. Washington State has a supporting technology innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem. The presence of accelerators, incubators, venture capital firms, collaborative communities, and industry events fosters a culture of collaboration and knowledge exchange.
Government Support. The state government recognizes the importance of nurturing the technology sector and actively supports initiatives to promote its growth. This includes funding for research and development, infrastructure investment, and policies encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship.
Sustainability and Clean Tech. Washington State also focuses on sustainability and clean tech initiatives. As the demand for sustainable solutions increases, the state’s commitment to clean energy, environmental stewardship, and green technologies positions it well for future growth.
While there may be challenges and uncertainties, Washington State’s strong tech foundation, commitment to innovation, and supportive environment set the stage for a bright future in technology. The continued advancements in emerging technologies, robust talent pool, and collaborative ecosystem contribute to its growth and success in the years to come.

Denver, CO
History
Colorado has a rich history with technology companies, particularly in recent decades. Here is a brief overview of Colorado’s history with technology companies:
• Telecommunications: Colorado has a long-standing relationship with the telecommunications industry.
• Aerospace and Defense: Colorado has a strong aerospace and defense industry, which includes the presence of technology companies focused on satellite communications, navigation systems, and military applications.
• Software Development: Colorado has emerged as a hub for software development, attracting innovative tech firms.
• Renewable Energy and Cleantech: Colorado has made significant strides in renewable energy and cleantech industries in recent years.
• Bioscience and Health Tech: Colorado is recognized for its bioscience and health tech sector.
• Startup Ecosystem: Colorado has a thriving startup ecosystem that ranks among the top states for startup activity.
Overall, Colorado has seen extensive growth in technology companies across various sectors. The state’s commitment to innovation, presence of leading research institutions, favorable business environment, and quality of life have contributed to its status as a growing hub for technology innovation and entrepreneurship.
Current Position
The current business and economic landscape for technology companies in Colorado is generally bright. Here are some key factors contributing to this positive outlook:
1. Growing Tech Industry: Colorado has seen significant growth in its technology industry, with a diverse range of companies and startups. The state attracts established and emerging tech firms, drives innovation, and creates job opportunities.
2. Entrepreneurial Culture: Colorado fosters an entrepreneurial culture with a supportive ecosystem for startups and small businesses. The state offers resources, events, and mentorship programs that encourage innovation and the launch of new technology ventures.
3. Skilled Workforce: Colorado boasts a well-educated and highly skilled workforce, with renowned universities and research institutions producing a talent pool for the tech industry. The state actively supports STEM education initiatives to ensure a robust pipeline of skilled workers.
4. Collaborative Community: Colorado’s tech community promotes collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and networking. The state has numerous tech-focused meetups, coworking spaces, and industry events connecting professionals and fostering innovation.
5. Regulatory Environment: Colorado has worked to create a favorable regulatory environment for technology businesses. The state government has implemented initiatives to attract investment, spur innovation, and streamline processes for companies in the tech sector.
6. Government Support: Colorado State and local authorities actively support the technology sector’s growth through various programs and incentives. These efforts include grants, tax credits, and partnerships with industry organizations to foster innovation and economic development in the tech industry.
7. Quality of Life: Colorado offers a high quality of life with a balance of urban amenities and outdoor recreational opportunities. This attracts talent to the state, making it an appealing place to live and work for tech professionals.
While there are challenges and uncertainties in any business landscape, the overall outlook for technology businesses in Colorado remains positive. The state’s commitment to innovation, supportive ecosystem, skilled workforce, and government support create a promising environment for technology companies.
Future Outlook
The future in technology looks bright for Colorado regarding technology business opportunities for the same reasons the current environment is producing highly successful results.
While there may be challenges and uncertainties, combining a supportive ecosystem, skilled workforce, investment, and industry diversification positions Colorado for a bright future in technology. Continued advancements and innovations in various sectors are expected, contributing to the state’s overall technological growth and development.

Raleigh, NC
History
North Carolina has played a notable role in technology history, particularly in research, innovation, and industry development. Here are several ways North Carolina fits into technology history:
1. Research and Innovation: North Carolina has several prestigious research universities and institutions, including Duke University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and North Carolina State University.
2. Research Triangle Park (RTP): Research Triangle Park, located between Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill, has been a vital hub of technology and innovation since its establishment in the 1950s.
3. High-Tech Industries: North Carolina has developed a strong presence in high-tech industries such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, information technology, aerospace, and defense.
4. Telecommunications: North Carolina played a role in developing the telecommunications industry. RTP was home to Bell Labs, a division of AT&T, which played a crucial role in advancing communication technologies.
5. Textile and Manufacturing Technologies: Historically, North Carolina was known for its textile and manufacturing industries. The state adopted advanced technology in these sectors, including automation, robotics, and advanced materials.
6. Renewable Energy and Clean Technologies: North Carolina has embraced renewable and clean technologies, developing a strong presence in areas like solar power, wind energy, and energy storage.
7. Entrepreneurship and Startups: North Carolina has a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem, with organizations like the North Carolina Biotechnology Center and the Council for Entrepreneurial Development (CED) supporting startups and fostering innovation.
The state has left a lasting impact on technology advancements through research institutions, industry development, innovation hubs, and a supportive ecosystem and continues to shape the tech landscape today.
Current Position
North Carolina has a thriving technology landscape that continues to grow and attract companies in various sectors. Here are some critical aspects of the current technology landscape in North Carolina:
• Research Triangle Park (RTP): RTP is a renowned technology and innovation hub between Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill. It is home to numerous technology companies, research institutions, and startups across various fields, such as biotechnology, healthcare IT, information technology, and engineering.
• Healthcare and Life Sciences: North Carolina has a strong presence in the healthcare and life sciences sectors. The Research Triangle region is a biotech, pharmaceutical, and medical research hub.
• Information Technology: North Carolina has a robust information technology sector, encompassing areas like software development, cybersecurity, data analytics, and cloud computing.
• Charlotte has emerged as a central banking and financial technology hub.
• Education and Research Institutions: North Carolina boasts prestigious universities such as Duke University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and North Carolina State University. These institutions foster innovation and technological advancements through computer science, engineering, and biotechnology research. They also provide a talent pipeline for the technology industry.
• Digital Transformation and Innovation: Businesses across various sectors in North Carolina are embracing digital transformation and leveraging innovative technologies.
• Entrepreneurship and Startups: North Carolina provides a supportive environment for startups and entrepreneurship.
• Government Support and Collaboration: The state government offers various tax incentives, grants, and programs to support technology innovation and economic growth.
While there may be challenges and competition, the technology landscape in North Carolina continues to evolve and present opportunities across multiple sectors. The convergence of academia, industry, and government support, a strong talent pool, and a culture of innovation contribute to the state’s technology growth and development.
Future Outlook
The future is promising for North Carolina and its technology industry. Here are a few reasons why:
1. Growing Technology Ecosystem: North Carolina has a thriving technology ecosystem, with a strong presence of tech companies, research institutions, and startups. The state’s Research Triangle Park (RTP) continues to be a hub of innovation and collaboration, attracting talent and fostering technological advancements.
2. Collaboration and Talent Pool: North Carolina benefits from the collaboration between universities, research institutions, and industry stakeholders, leading to the development of a skilled talent pool. Institutions like Duke University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and North Carolina State University contribute to a strong pipeline of talent in areas like computer science, engineering, biotechnology, and more.
3. Industry Diversification: The technology industry in North Carolina spans across various sectors, including biotechnology, healthcare IT, information technology, aerospace, defense, and renewable energy. This diversification helps build resilience and opens up opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and interdisciplinary advancements.
4. Entrepreneurial Spirit: North Carolina has a supportive environment for entrepreneurs and startups. Organizations like the North Carolina Biotechnology Center and the Council for Entrepreneurial Development (CED) provide resources, funding, and mentorship programs to promote the growth of technology startups. This entrepreneurial ecosystem encourages innovation and new business ventures.
5. Government Support and Policies: The state government has shown support for the technology sector through various initiatives, tax incentives, and policies that attract and retain tech companies. These initiatives aim to foster growth, create jobs, and elevate North Carolina’s position in the rapidly evolving technology landscape.
6. Emerging Technologies and Industries: North Carolina is at the forefront of emerging technologies such as biotechnology, artificial intelligence, automation, and clean energy. The state’s focus on these areas positions it well for future growth and leadership in these industries, creating opportunities for technological advancements and economic development.
7. Quality of Life and Affordability: North Carolina offers an excellent quality of life with a combination of affordable living costs and desirable amenities. This attracts talent and businesses to the state, contributing to a vibrant technology ecosystem.
While challenges may exist, the combination of a strong technology ecosystem, collaboration, government support, and industry diversification bodes well for the future of North Carolina and its technology industry. Continued investments in research, education, and fostering innovation will likely propel the state’s technology sector forward, driving economic growth, job creation, and technological advancements.
Program Benefits
Management
- Predictable Growth
- Competitive Differentiation
- Consistent Leads
- Transaction Value
- More Transactions
- Performance Metrics
- Sales Strategy
- Organizational Requirements
- Key Partnerships
- Renewal Rate
Marketing
- Solve Problems
- Differentiation
- Value Propositions
- Market Awareness
- Understanding buyers
- Interest Development
- Demand Generation
- Content Ideas
- Competition Comparison
- Prospecting Methods
Operations
- Sales Process
- Sales Training
- Business Analytics
- Compensation Plans
- Territory Analysis
- Lead Management
- Technology Requirements
- Communications Management
- Pipeline Management
- Sales Support
Testimonials

Testimonial 1
Content here…

Testimonial 2
Content here…

Testimonial 3
Content here…

Testimonial 4
Content here…

Testimonial 5
Content here…
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.