Quality Maturity

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Quality Maturity is provided by Mr. Clark Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Clark is a distinguished quality and regulatory affairs consultant, renowned for guiding over 200 firms to FDA compliance and beyond. His unique executive, entrepreneurial, and legal background make him an exceptional figure in the field, particularly adept at addressing the complex regulatory requirements of the FDA with an innovative, strategic, and forward approach. His achievements span across all FDA-regulated industries, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements, food production, and cosmetics. Ten years of consulting have only amplified his comprehensive understanding of quality management systems and his ability to enhance operational efficiency and market readiness. Mr Clark’s hands-on approach has made him a pivotal asset for hundreds of organizations aiming for the highest standards of quality excellence.
Mr. Clark has served in various executive positions in FDA-regulated organizations and has owned several of his own companies. Through his years of development in the industry, Mr. Clark has achieved several professional certifications, including the following: Certified Pharmaceutical GMP Professional (CPGP), Certified Manager of Quality and Organizational Excellence (CMQ-OE), Project Management Professional (PMP), and Certified Quality Auditor (CQA). Mr. Clark holds two advanced degrees, a Master of Business Administration (MBA) and Juris Doctorate (JD).
To request further information about Mr. Clark through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Quality Maturity
This is a comprehensive program for assessing and advancing the quality maturity of your FDA-regulated quality management system. Quality maturity is a measure of how well your processes, practices, and systems are developed, implemented, and ingrained such that you meet and exceed quality standards, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations.
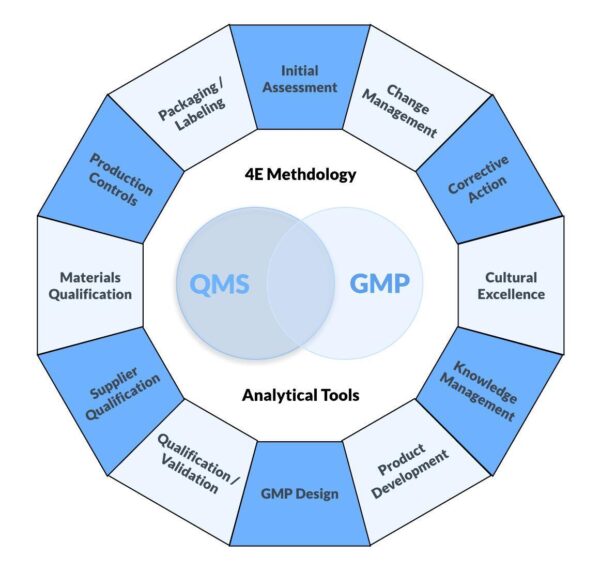
This program comprises twelve (12) carefully crafted modules designed to augment every dimension of your FDA-regulated Quality Management System (QMS) and related Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) in order to achieve a high level of quality maturity.
Through the application of the 4E improvement methodology—Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate—we will systematically enhance the efficacy of every aspect of your quality management system.
Through the application of practical and systematic quantitative and qualitative assessment tools, we will determine your system’s current state of maturity.
Finally, using established maturity benchmarks for your industry, we will set your new target maturity level and the precise improvement objectives to propel your system to new heights of performance.
The tools and benchmarks used in this program are based on documented and verified best practices for your industry, including cosmetics, food and beverage, dietary supplements, and drugs. These tools will help you exceed all FDA requirements and will allow your company to achieve new heights in quality maturity.
What is Quality Management Maturity?
Quality Maturity refers to the level of sophistication of your organization with respect to its Quality Management System. It is a measure of how well your processes, practices, and systems are developed, implemented, and ingrained such that you meet and exceed quality standards,
regulatory requirements, and customer expectations.
Why is Quality Maturity important?
Safe and Quality Product: There are many reasons to enhance your quality maturity. For FDA-regulated industries, foremost among those reason is the need to provide consumers with an exceptionally safe and satisfying product, whether it be cosmetics, dietary supplements, food or beverage, or drugs.
FDA Initiative: Recently, the FDA has announced its Quality Management Maturity (QMM) initiative. There is considerable dispute as to whether the FDA should be getting involved in rating the quality maturity of FDA-regulated organizations. Many trade organizations would prefer that this remained in the purview of voluntary programs, such as this program.
False Motivation Effect: Fundamental to understanding why you should target advanced quality maturity is the acceptance of the fact that when organizations target mere compliance, they will inevitably fall short of that goal. This is due to the false motivation effect. The false motivation effect states that actions based on rules alone (the false motivation) are inadequate for adapting to the fast-paced and ever-changing environment of today’s markets. Only a target of excellence will lead to the organizational maturity capable of maintaining and exceeding compliance.
Enhance Competitive Advantage: The advantages to elevating your quality maturity are too many to elaborate here. In short, a high level of quality maturity will lead to a better company culture, enhanced customer satisfaction, cost savings, reduced liability, and an overall competitive advantage.
Increased Profitability: The pursuit of excellence is the strongest driving force of profitability.
Curriculum
Quality Maturity – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Initial Assessment
- Part 1 Month 2 Change Management
- Part 1 Month 3 Corrective Action
- Part 1 Month 4 Cultural Excellence
- Part 1 Month 5 Knowledge Management
- Part 1 Month 6 Product Development
- Part 1 Month 7 GMP Design
- Part 1 Month 8 Qualification/Validation
- Part 1 Month 9 Supplier Qualification
- Part 1 Month 10 Materials Qualification
- Part 1 Month 11 Production Controls
- Part 1 Month 12 Packaging and Labeling
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Quality Maturity corporate training program.
Quality Maturity- Part 1- Year 1
Part 1 Month 1: Initial Assessment
In this foundational module, we focus on conducting a comprehensive initial assessment of your organization’s Quality Management System (QMS). The module is meticulously structured to provide a thorough understanding of your current QMS status, leveraging both quantitative and qualitative insights. We then use this information to focus the program on your greatest needs and priorities. The training component of this module covers various aspects of how to perform a proper assessment, including:
Introduction to Comprehensive Pre-Assessment:
• Understanding the importance and objectives of the initial QMS assessment.
• The role of the assessment in establishing a baseline for tracking progress.
Assessment Methodology:
• Introduction to the quantitative and qualitative questionnaire.
• Overview of the metrics used to evaluate each aspect of the QMS.
• Guidance on how to effectively use the pre-assessment tool.
Execution of the Pre-Assessment:
• Conducting the assessment, either by the quality maturity team or a designated cross-functional assessment team.
• Collecting objective evidence to gauge the current state of the QMS.
Analysis and Reporting:
• Analyzing the results of the pre-assessment.
• Generating a comprehensive report to highlight the company’s quality maturity and GMP performance.
• Identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for strategic improvement.
Strategic Selection of Quality Priorities:
• Utilizing the assessment results to inform the selection of quality improvement initiatives.
• Allocating resources effectively to areas that will meaningfully enhance quality maturity.
By the end of this module, your organization will have a clear and comprehensive understanding of its current quality management state. This initial assessment will serve as a critical benchmark, aiding in the strategic planning of quality improvements and setting the stage for future advancements in your QMS.
Part 1 Month 2: Change Management
In this module, utilizing the 4E Improvement Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – we take a comprehensive approach to refine and enhance your change management program, ultimately aiming to boost your organization’s quality maturity level.
Examine: We start by meticulously examining your current change management system. Using established assessment tools, we conduct a thorough evaluation to identify the key components, system variables, and controls within your change management framework. This step is crucial in pinpointing areas that are prime for improvement and understanding the current state of your change management processes.
Envision: Next, we envision the ideal state of your change management system by benchmarking against well-established maturity models. This vision-setting process involves setting ambitious yet achievable targets, tailored to your organization’s unique context. It’s about aiming for a future state where your change management process not only meets but exceeds industry standards.
Execute: Following the vision setting, we formulate and implement a detailed action plan. This plan includes specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities to ensure the successful achievement of the target objectives. This phase is critical in translating the envisioned changes into tangible actions and measurable outcomes.
Elevate: Finally, we focus on elevating your change management system to the desired maturity level. This involves verifying that the improvement goals have been successfully achieved. Upon the conclusion of the module, we conduct a comprehensive review to ensure that the changes made have had the intended impact and that your change management system is operating at the newly established higher maturity level. The training component of this module covers various aspects of Change Management, including:
• Understanding Change Dynamics: Learning about the key drivers of change and how they impact organizations.
• Communication Strategies: Developing effective communication plans for change initiatives.
• Stakeholder Engagement: Techniques for engaging and managing stakeholders throughout the change process.
• Resistance Management: Identifying and addressing resistance to change within the organization.
• Change Implementation: Best practices for implementing change effectively and sustainably.
• Monitoring and Evaluation: Methods for tracking the progress of change initiatives and evaluating their success.
• Continuous Improvement: Strategies for ensuring continuous improvement in change management practices.
• Leadership in Change: Role of leadership in driving and sustaining change.
• Cultural Considerations: Understanding and managing the cultural aspects of change in organizations.
• Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with change initiatives.
This module, with its blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application, is designed to not only enhance your change management capabilities but also to foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability within your organization.
Part 1 Month 3: Corrective Action
In this module, we strategically enhance your Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) Program by employing the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate. This approach is tailored to refine and bolster your CAPA processes, ensuring they are both effective in addressing current issues and robust in preventing future occurrences.
Examine: We initiate the process by conducting a thorough examination of your existing CAPA system. This involves a detailed analysis using advanced assessment tools, where we scrutinize your current corrective and preventive actions. This critical examination helps us identify key areas needing improvement, inefficiencies in the process, and opportunities for enhancement.
Envision: Upon a comprehensive understanding of your current CAPA processes, we then move to envision an optimized state. In this phase, we establish clear, attainable goals for your CAPA program that align with industry best practices. This includes developing a strategic action plan that is specifically tailored to address the identified gaps and enhance your CAPA measures.
Execute: With a clearly defined vision and plan, we proceed to the execution phase. This involves the practical implementation of the outlined CAPA strategies. Key activities in this phase include deploying resources, conducting staff training, and ensuring complete alignment with the new CAPA processes. Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are emphasized to facilitate a smooth transition and integration of the improvements.
Elevate: The final phase is focused on elevating your CAPA program to the newly set standards. This involves a rigorous review of the implemented actions to assess their effectiveness in achieving the set objectives. We evaluate the tangible improvements made and ensure that the changes not only resolve existing issues but also strengthen your processes against potential future risks. The training component encompasses various essential aspects of developing a mature CAPA program:
• Root Cause Analysis: Techniques for identifying underlying issues.
• Risk Management: Methods for assessing and prioritizing risks.
• Strategic Planning: Developing effective corrective and preventive actions.
• Document Control: Best practices for CAPA documentation.
• Performance Monitoring: Monitoring the effectiveness of CAPA actions.
• Regulatory Alignment: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
• Continuous Improvement: Building a culture of ongoing enhancement.
• Staff Training: Role-specific training in CAPA processes.
• Effective Communication: Strategies for CAPA-related communication.
• Feedback Integration: Establishing feedback mechanisms for CAPA improvement.
This module, through a blend of strategic planning and practical application, is designed to fortify your organization’s CAPA program, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Part 1 Month 4: Cultural Excellence
In this module, we focus on cultivating Cultural Excellence within your organization by applying the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate. This approach is designed to deepen and enrich your organization’s culture, aligning it with your core values and strategic goals.
Examine: The first step involves an in-depth examination of your current organizational culture. We employ comprehensive diagnostic tools to assess the cultural landscape, identifying existing strengths and areas for improvement. This phase is crucial in understanding the underlying beliefs, behaviors, and practices that define your organization’s culture.
Envision: Building on our findings, we then envision an enhanced cultural state. In this phase, we collaborate with your leadership to define a clear and inspiring vision of cultural excellence tailored to your organization. This vision includes setting achievable yet ambitious goals for cultural development, aligned with your organization’s mission and values.
Execute: With a clear vision in place, we move to the execution phase. This involves implementing targeted strategies and initiatives designed to foster the desired cultural change. Key activities in this phase include leadership development, employee engagement programs, and communication strategies. We focus on embedding the envisioned cultural attributes at every level of the organization, ensuring that they are reflected in day-to-day practices and interactions.
Elevate: The final phase is about elevating your organization’s culture to the newly established standards of excellence. This involves a continuous review and assessment of the cultural initiatives implemented, measuring their impact against the set goals. We ensure that the cultural changes are not only achieved but are sustainable and deeply ingrained within the organization. The training component of this module covers various key aspects of Cultural Excellence:
• Values Integration: Embedding core values into everyday practices.
• Leadership Modeling: Training leaders to exemplify desired cultural traits.
• Team Dynamics: Enhancing collaboration and team cohesion.
• Communication Skills: Effective internal and external communication.
• Diversity Embrace: Fostering inclusivity and diversity.
• Employee Empowerment: Encouraging initiative and ownership among staff.
• Feedback Culture: Creating a culture of open and constructive feedback.
• Conflict Resolution: Effective management of workplace conflicts.
• Change Management: Navigating cultural changes smoothly.
• Recognition Programs: Acknowledging and rewarding cultural contributions.
Through this module, your organization will be equipped to foster a culture of excellence, characterized by strong values, engaged employees, and effective leadership. This transformation will not only enhance the internal environment but also positively impact overall organizational performance and reputation.
Part 1 Month 5: Knowledge Management
In this module, we will focus on enhancing your organization’s Knowledge Management capabilities using the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate. This systematic approach is designed to optimize the way knowledge is captured, shared, and utilized within your organization, fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
Examine: Our first step is to conduct a thorough examination of your current knowledge management practices. We’ll use a variety of assessment tools to analyze how knowledge is currently collected, stored, and disseminated within your organization. This phase is essential in identifying any gaps or inefficiencies in your existing system and understanding the specific knowledge management needs of your organization.
Envision: Building on the insights gained from our examination, we then envision an ideal state for your knowledge management system. In this phase, we collaborate with your team to define a clear vision that aligns with your organizational goals and culture. We set specific, realistic targets for improving your knowledge management practices, including the development of a strategic plan that outlines the steps needed to achieve these goals.
Execute: With a clear vision and plan in place, we move to the execution phase. This involves implementing the strategies and initiatives outlined in the action plan. Key activities during this phase include the introduction of new knowledge management tools and technologies, training for employees on effective knowledge sharing and utilization, and the establishment of processes that encourage and facilitate knowledge exchange within the organization.
Elevate: The final phase is focused on elevating your knowledge management practices to the new standards of excellence we have set. We continuously monitor and review the progress of the implemented strategies, ensuring they are effectively contributing to the achievement of your knowledge management objectives. We assess the tangible improvements made and ensure that the changes not only enhance knowledge sharing and retention but also support the overall strategic goals of your organization. The training component of this module covers various crucial aspects of Knowledge Management:
• Information Capture: Techniques for effectively capturing critical knowledge.
• Data Analysis: Skills for analyzing and interpreting knowledge data.
• Tool Utilization: Training on knowledge management tools and platforms.
• Collaborative Sharing: Encouraging and facilitating knowledge sharing.
• Best Practices: Implementing best practices in knowledge management.
• Content Curation: Techniques for curating and managing knowledge content.
• Community Building: Developing communities of practice within the organization.
• Learning Culture: Fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
• Knowledge Retention: Strategies for retaining critical organizational knowledge.
• Innovation Encouragement: Leveraging knowledge for innovation and growth.
Through this module, your organization will be equipped to effectively manage and leverage knowledge, enhancing collaboration, innovation, and decision-making capabilities. This transformation will drive a more informed, agile, and knowledge-driven organizational culture.
Part 1 Month 6: Product Development
In this module, we employ the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to enhance your organization’s product development process. This structured approach is tailored to streamline and innovate the way new products are conceived, designed, and brought to market.
Examine: We commence with an exhaustive examination of your current product development practices. Utilizing a range of analytical tools, we assess the various stages of your product development cycle, from initial concept to market launch. This phase is essential in identifying any inefficiencies, potential areas for innovation, and alignment with market needs and organizational goals.
Envision: Based on our comprehensive analysis, we then envision a more optimized and innovative product development strategy. Collaborating closely with your team, we define a clear, forward-looking vision that encompasses cutting-edge practices and aligns with your business objectives. We set achievable, yet ambitious goals for enhancing your product development process, including a detailed strategic plan to realize these objectives.
Execute: Moving into the execution phase, we implement the strategies outlined in the action plan. This phase includes the introduction of new development methodologies, the adoption of advanced technology tools, and the facilitation of cross-functional collaboration. We focus on refining each stage of the product development cycle, ensuring efficient resource allocation, creativity in design, and rigorous testing protocols.
Elevate: The final phase involves elevating your product development process to the envisioned level of excellence. We continuously monitor and review the progress of the implemented initiatives, ensuring they effectively contribute to your product development goals. We evaluate the enhancements made, ensuring they not only streamline the development process but also foster a culture of innovation and market responsiveness. The training component of this module includes:
• Market Analysis: Techniques for identifying and understanding market needs.
• Creative Ideation: Encouraging creative thinking and idea generation.
• Design Principles: Training on modern design and prototyping techniques.
• Agile Methodologies: Implementing agile development practices.
• Cross-functional Collaboration: Facilitating teamwork across departments.
• Quality Assurance: Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing.
• Time Management: Effective management of product development timelines.
• Risk Assessment: Identifying and mitigating development risks.
• Sustainability Focus: Incorporating sustainability into product design.
• Feedback Integration: Utilizing customer feedback in the development process.
Through this module, your organization will be equipped to enhance its product development capabilities, leading to more innovative, customer-focused, and market-relevant products. This transformation is designed to not only improve your product development process but also to align it with your broader strategic objectives.
Part 1 Month 7: GMP Design
In this module, we apply the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to optimize your organization’s GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) design, particularly focusing on facility and equipment design. This approach is structured to enhance the effectiveness and compliance of your manufacturing infrastructure, ensuring it meets and exceeds industry standards.
Examine: The first step involves a comprehensive examination of your existing facility and equipment design. Utilizing advanced assessment tools, we analyze how your current setup aligns with GMP requirements. This phase is crucial for identifying areas that may need improvement, potential risks, and opportunities for enhancement in both facility layout and equipment functionality.
Envision: Building on our initial findings, we then envision an optimized state for your GMP facility and equipment design. Collaborating with your team, we establish a clear vision that incorporates the latest in manufacturing technology and compliance standards. Our goal-setting process includes developing a tailored plan with achievable and measurable objectives to enhance your manufacturing setup’s efficiency and compliance.
Execute: With a detailed plan in hand, we move into the execution phase. This involves the implementation of the proposed design improvements. Key activities include upgrading equipment, reconfiguring facility layouts, and integrating advanced technology solutions. We focus on ensuring that every change aligns with GMP standards and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Elevate: The final phase is about elevating your facility and equipment design to the new standards of GMP excellence. We conduct a thorough review of the improvements implemented, assessing their effectiveness in meeting the set objectives. This includes verifying compliance with GMP regulations and evaluating the impact on manufacturing efficiency and product quality. The training component of this module includes:
• Regulatory Compliance: Understanding GMP requirements for facility and equipment.
• Design Principles: Training in GMP-compliant design principles.
• Efficiency Optimization: Techniques for optimizing manufacturing efficiency.
• Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating design-related risks.
• Technology Integration: Leveraging advanced technologies in design.
• Process Flow: Ensuring efficient process flow in facility layout.
• Maintenance Best Practices: Effective maintenance strategies for GMP compliance.
• Cleanroom Standards: Designing and maintaining cleanroom environments.
• Safety Protocols: Integrating safety measures in design.
• Sustainability Practices: Incorporating sustainable practices in facility and equipment design.
Through this module, your organization will be well-equipped to enhance its GMP facility and equipment design, leading to improved compliance, efficiency, and product quality. This transformation aims to elevate your manufacturing capabilities, ensuring they meet the highest standards of GMP excellence.
Part 1 Month 8: Qualification/Validation
In this module, we adopt the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to enhance your organization’s approach to CQV: Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation. This structured method is designed to ensure that your CQV processes are efficient, compliant, and effective, thereby solidifying the foundation of your operational integrity.
Examine: Our first phase is an in-depth examination of your existing CQV practices. Through detailed assessments, we evaluate the current methodologies and procedures you employ during commissioning, qualification, and validation. This critical analysis identifies areas for improvement, compliance gaps, and opportunities for streamlining processes.
Envision: Following the thorough examination, we envision an optimized CQV process. In collaboration with your team, we define a strategic vision that aligns with both industry standards and your organizational goals. Setting clear, achievable objectives, we outline an actionable plan for enhancing your CQV practices, focusing on both efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Execute: With a strategic vision and plan in place, we proceed to the execution phase. This involves the implementation of the identified improvements in your CQV processes. Key steps include adopting advanced methodologies, updating protocols, and ensuring comprehensive staff training. We focus on integrating these improvements seamlessly into your operations, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum benefit.
Elevate: The final phase involves elevating your CQV processes to the newly established standards. We conduct a detailed review and assessment to ensure that the enhancements effectively meet the set objectives. This review is critical to confirm that your commissioning, qualification, and validation processes are not only compliant with regulatory standards but also optimized for operational excellence. The training component of this module covers:
• Regulatory Standards: Understanding and complying with relevant regulations.
• Best Practices: Implementing industry best practices in CQV.
• Process Efficiency: Enhancing efficiency in commissioning, qualification, and validation.
• Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks in CQV processes.
• Documentation Control: Ensuring thorough and accurate CQV documentation.
• System Integration: Integrating CQV processes with overall system operations.
• Quality Assurance: Embedding quality assurance throughout CQV.
• Team Training: Providing comprehensive training for all involved personnel.
• Continuous Monitoring: Establishing protocols for ongoing CQV process monitoring.
• Innovation Adoption: Incorporating innovative approaches and technologies in CQV.
Through this module, your organization will develop a refined, streamlined, and compliant approach to Commissioning, Qualification, and Validation, ensuring that your operations are not only efficient but also adhere to the highest standards of quality and regulatory compliance.
Part 1 Month 9: Supplier Qualification
In this module, we implement the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to refine and enhance your supplier qualification processes. This approach is specifically designed to ensure that your supplier selection, evaluation, and management practices are robust, compliant, and aligned with your organizational objectives.
Examine: We start by conducting a detailed examination of your current supplier qualification procedures. Using comprehensive assessment tools, we analyze how you currently assess, select, and manage your suppliers. This phase helps identify gaps, inefficiencies, and potential areas for improvement in your supplier qualification process, ensuring a solid foundation for reliable and effective supply chain management.
Envision: Building on the insights from the examination phase, we then envision an optimized supplier qualification system. In collaboration with your procurement and supply chain teams, we establish a clear vision that encompasses best practices in supplier management. We set realistic yet ambitious targets for enhancing your supplier qualification process, including developing a strategic plan that outlines actionable steps to achieve these objectives.
Execute: With a well-defined vision and plan, we move to the execution phase. This involves implementing the proposed strategies for improving supplier qualification. Key activities during this phase include introducing new evaluation criteria, adopting advanced supplier assessment tools, and enhancing supplier relationship management practices. We focus on ensuring that all improvements are effectively integrated into your procurement processes.
Elevate: The final phase is about elevating your supplier qualification process to the new standards of excellence. We conduct a thorough review of the improvements implemented to assess their effectiveness in meeting the set objectives. This includes verifying that the supplier qualification process not only meets compliance standards but also contributes to improved supply chain reliability and organizational efficiency. The training component of this module covers:
• Evaluation Criteria: Developing effective supplier evaluation criteria.
• Risk Assessment: Techniques for assessing and mitigating supplier risks.
• Compliance Standards: Ensuring suppliers meet regulatory and industry standards.
• Performance Monitoring: Monitoring and evaluating supplier performance.
• Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong supplier relationships.
• Continuous Improvement: Encouraging continuous improvement in supplier practices.
• Audit Techniques: Effective techniques for auditing suppliers.
• Contract Management: Managing contracts and agreements with suppliers.
• Communication Skills: Enhancing communication with suppliers.
• Global Sourcing: Strategies for global supplier sourcing and qualification.
Through this module, your organization will be equipped to strengthen its supplier qualification processes, ensuring a reliable, compliant, and high-performing supply chain that supports your overall business goals.
Part 1 Month 10: Materials Qualification
In this module, we leverage the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to optimize your organization’s raw materials qualification process. This comprehensive approach is designed to ensure the integrity, quality, and compliance of the raw materials used in your production, aligning with industry standards and best practices.
Examine: We initiate the module with a thorough examination of your current raw materials qualification process. Using advanced evaluation tools, we analyze how you assess, procure, and verify the quality of raw materials. This critical assessment helps in identifying any inefficiencies, quality gaps, and areas for improvement, laying the groundwork for a more robust raw material management system.
Envision: Upon the detailed analysis, we then envision an enhanced state for your raw materials qualification. Collaborating with your team, we develop a clear, strategic vision tailored to your organization’s needs. We establish realistic, yet ambitious goals for improving the raw materials qualification process, including a comprehensive action plan with specific steps and benchmarks.
Execute: With the vision and plan in place, we move to the execution phase. This involves implementing the strategies and initiatives outlined in the plan. Key activities include introducing new qualification criteria, adopting advanced testing methodologies, and enhancing supplier collaboration. We ensure that these improvements are seamlessly integrated into your procurement and quality assurance processes.
Elevate: The final phase focuses on elevating your raw materials qualification process to the new level of excellence. We conduct a rigorous review of the implemented improvements, evaluating their effectiveness against the set objectives. This assessment ensures that the raw materials qualification process not only meets but exceeds quality standards, contributing to the overall integrity and compliance of your production processes. The training component of this module includes:
• Quality Standards: Understanding and applying industry quality standards.
• Supplier Vetting: Effective techniques for vetting raw material suppliers.
• Testing Protocols: Implementing robust testing protocols for raw materials.
• Compliance Adherence: Ensuring adherence to regulatory compliance.
• Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks in raw material sourcing.
• Documentation Control: Managing documentation for traceability and quality assurance.
• Process Optimization: Streamlining the qualification process for efficiency.
• Sustainability Considerations: Incorporating sustainability in raw material selection.
• Continuous Monitoring: Establishing ongoing monitoring mechanisms.
• Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders in the qualification process.
Through this module, your organization will be equipped to enhance its raw materials qualification process, ensuring high-quality, compliant, and efficiently sourced materials. This transformation aims to solidify the foundation of your production quality and supply chain reliability.
Part 1 Month 11: Production Controls
In this module, we apply the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate – to refine and enhance your organization’s production controls. This approach is specifically crafted to optimize your production processes, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and quality in your manufacturing operations.
Examine: We begin by conducting an in-depth examination of your current production control systems. Through detailed assessments, we evaluate your existing controls, processes, and workflows. This phase is crucial for identifying inefficiencies, compliance gaps, and areas for process improvement, providing a comprehensive understanding of your production operations.
Envision: Based on our examination, we then envision an optimized state for your production controls. Working in collaboration with your team, we define a strategic vision that incorporates the latest advancements in production technology and methodologies. We establish achievable yet ambitious targets for enhancing your production processes, including the development of a strategic action plan with clearly defined steps.
Execute: With a clear vision and actionable plan in place, we move into the execution phase. This involves the implementation of strategies and initiatives aimed at improving production control. Key activities include the introduction of advanced process monitoring tools, the adoption of automation where beneficial, and the refinement of quality control measures. We ensure that these improvements are effectively integrated into your production operations, enhancing both efficiency and product quality.
Elevate: The final phase involves elevating your production control systems to the new standards of operational excellence. We conduct a thorough assessment of the improvements implemented to ensure they effectively meet the established objectives. This review is critical to confirm that your production controls are not only compliant with industry standards but also optimized for peak performance. The training component of this module covers:
• Process Optimization: Techniques for streamlining production processes.
• Quality Assurance: Implementing robust quality control measures.
• Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations.
• Efficiency Improvement: Strategies for improving operational efficiency.
• Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating production risks.
• Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced technology for process control.
• Performance Metrics: Establishing and monitoring key performance indicators.
• Continuous Improvement: Fostering a culture of ongoing process enhancement.
• Employee Training: Providing comprehensive training on new control systems.
• Sustainability Practices: Incorporating sustainable practices in production.
Through this module, your organization will develop an enhanced production control system, leading to more efficient, compliant, and high-quality manufacturing operations. This transformation will not only improve your current production processes but also position your organization for future growth and success in an increasingly competitive market.
Part 1 Month 12: Packaging and Labeling
– In this module, we focus on elevating your organization’s Packaging and Labeling practices using the 4E Methodology – Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate. This structured approach is specifically tailored to enhance the efficiency, compliance, and overall quality of your packaging and labeling processes.
Examine: We begin with a thorough examination of your current packaging and labeling systems. Utilizing a range of analytical tools, we conduct a detailed assessment of how packaging and labeling are managed across your operations. This phase is crucial for identifying areas for improvement, potential compliance issues, and opportunities for enhancing your practices in this domain.
Envision: Based on our in-depth analysis, we then craft an optimized framework for packaging and labeling. Working alongside your team, we establish a clear vision that incorporates industry best practices. We set specific, achievable goals for enhancing your processes, including a strategic plan with actionable steps and benchmarks for success.
Execute: With a solid vision and plan, we progress to the execution phase. This involves the implementation of the strategies and initiatives detailed in the plan. Key activities include introducing new packaging technologies, refining labeling protocols, and ensuring comprehensive staff training. Our focus is on seamlessly integrating these improvements into your daily operations, thereby boosting efficiency and packaging quality.
Elevate: The final stage is about raising your packaging and labeling processes to the newly established standards of excellence. We conduct a thorough review of the implemented improvements to evaluate their effectiveness. This ensures that your processes not only comply with industry standards but also contribute to enhanced product integrity and customer satisfaction. The training component of this module includes:
• Compliance Standards: Understanding and adhering to industry standards in packaging and labeling.
• Continuous Monitoring: Implementing ongoing monitoring mechanisms for packaging quality.
• Risk Assessment: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with packaging and labeling.
• Process Improvement: Techniques for continuous enhancement of packaging and labeling processes.
• Documentation Control: Maintaining accurate and comprehensive documentation.
• Data Analysis: Using data analysis to improve packaging and labeling quality.
• Team Collaboration: Encouraging collaborative practices across departments.
• Customer Feedback: Integrating customer feedback into packaging and labeling strategies.
• Employee Training: Offering extensive training to all relevant personnel.
• Innovation Integration: Adopting innovative technologies and methods in packaging and labeling.
Through this course, your organization will not only refine its current practices but also foster a culture of excellence in packaging and labeling, ensuring high-quality, compliant, and customer-focused products.
Methodology
Quality Maturity
4E Improvement Methodology
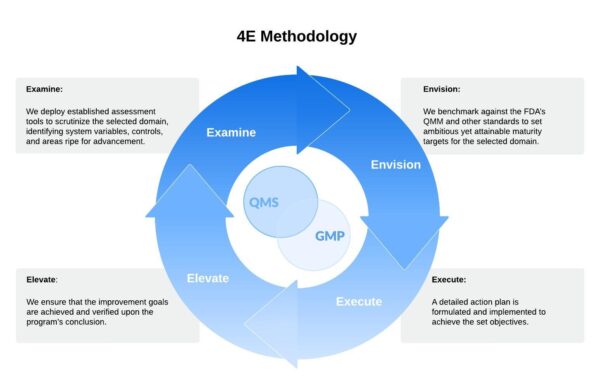
The 4E Improvement Methodology — Examine, Envision, Execute, and Elevate — is an assessment and improvement process that is applied in each subject matter to ensure enhanced quality performance and maturity.
Examine: We deploy established assessment tools to scrutinize the selected domain, identifying system variables, controls, and areas ripe for advancement.
Envision: We benchmark against the FDA’s QMM and other standards to set ambitious yet attainable maturity targets for the selected domain.
Execute: A detailed action plan is formulated and implemented to achieve the set objectives.
Elevate: We ensure that the improvement goals are achieved and verified upon the program’s conclusion.
The overarching objectives of this program and its methodology are to:
1. Promote strategic allocation of improvement resources
2. Assess and enhance quality maturity through practical and systematic tools
3. Encourage continual improvement through an ongoing quality maturity program
4. Cultivate a quality culture within your company that extends beyond mere compliance
5. Achieve high levels of quality performance and a sustainable competitive advantage
The primary tools for achieving the above objectives are:
• Program Guidebook
• Maturity Framework
• 4E Improvement Methodology
• Quality Maturity Team
• Evaluation Team
• Tools and Reports
• Trainings and Guides
• Implementation Team
• Project Plan
• Project Close-out (Verification of New Maturity Level)
Quality Maturity Team
A quality maturity team is established to lead your quality maturity program from within. The quality maturity team oversees the Evaluation Team and Implementation Teams and assists in the below activities.
Comprehensive Pre-Assessment
In order to track your progress in this program, we must establish a baseline of initial performance by performing a comprehensive pre-assessment. The results of this pre-assessment will act as an important baseline against which to compare future improvement results.
This pre-assessment tool is simple and easy to use, while delivering a solid and balanced overview of your company’s quality maturity and GMP performance. The pre-assessment tool includes metrics for every aspect of your quality management system. The pre-assessment is performed by the quality maturity team (or another cross-functional assessment team created for this purpose). The corresponding report will allow your company to understand its individual strengths and weaknesses and where to strategically focus its limited improvement resources to meaningfully enhance its quality maturity.
Maturity Assessment (per domain)
The Maturity Assessment is a deep evaluation of the selected domain for its current maturity level. An assessment team is created for this purpose. The team will use the maturity assessment tool. This tool is an in-depth analytical tool that incorporates both quantitative and qualitative measures for assessing the maturity of a specific domain. The assessment team utilizes this tool to assess the current state of the domain, to substantiate its findings with concrete evidence, and to assign an objective maturity score to the domain. This assessment process will lay the groundwork for setting objective, relevant, and measurable improvement goals, and for ultimately elevating the maturity of the domain to the highest levels.
Maturity Target Report (per domain)
After agreeing on the current state of maturity, the assessment team analyzes the results to identify the most strategic improvement opportunities based on the assessment. Also, the team determines by how much the company can capably and timely elevate its maturity within the improvement timeframe. This information will be summarized in a Maturity and Target Report and presented to relevant parties for endorsement.
Implementation of Project Plan (per domain)
After the conclusions and targets of the Maturity and Target Report have been endorsed, an implementation team is created for the purpose of managing the improvement project. The implementation team develops an action plan. Depending on the scope and complexity of the project, the project may be governed, for example, by a project management office, or by the continual improvement or change management processes with the oversight of the quality unit. While this project is being planned and executed, the quality maturity team will continue by selecting the next domain for assessment.
Verification of New Maturity Level and Report
After the project is executed, the implementation team will report its completion of the project to the assessment team. The assessment team will review and verify whether the project succeeded in elevating the domain to the targeted maturity level. The targeted maturity level must be confirmed to be fully effective and sustainable. A report of its findings is provided to relevant parties and, if targets were met, the project is closed. If targets were not met, the relevant parties are expected to continue the project and take corrective action until the targets are met. The New Maturity Level Report is kept as the new benchmark for the current state.
The Maturity Model
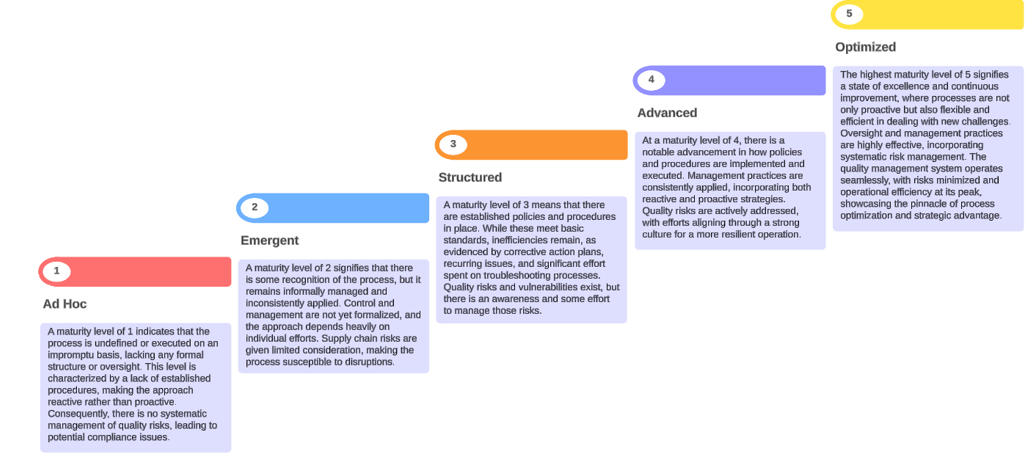
The Maturity Assessment Tool incorporates quantitative scoring against a 5-Level Maturity Model, where Level 1 represents the lowest level of maturity and Level 5 represents the highest level of maturity.
The below diagram provides descriptions for each of the five levels in the maturity model. These five levels are applicable to all domains.
The maturity assessment tool utilizes distinct qualitative criteria for each of the five levels in the maturity model to decide the appropriate maturity rating. The assessment team should compare the maturity evidence against these criteria before assigning a suitable rating for that domain.
The five maturity levels are characterized as follows:

Level 1 – Ad Hoc: A maturity level of 1 indicates that the process is undefined or executed on an impromptu basis, lacking any formal structure or oversight. This level is characterized by a lack of established procedures, making the approach reactive rather than proactive. Consequently, there is no systematic management of quality risks, leading to potential compliance issues.
Level 2 – Emergent: A maturity level of 2 signifies that there is some recognition of the process, but it remains informally managed and inconsistently applied. Control and management are not yet formalized, and the approach depends heavily on individual efforts. Supply chain risks are given limited consideration, making the process susceptible to disruptions.
Level 3 – Structured: A maturity level of 3 means that there are established policies and procedures in place. While these meet basic standards, inefficiencies remain, as evidenced by corrective action plans, recurring issues, and significant effort spent on troubleshooting processes. Quality risks and vulnerabilities exist, but there is an awareness and some effort to manage those risks.
Level 4 – Advanced: At a maturity level of 4, there is a notable advancement in how policies and procedures are implemented and executed. Management practices are consistently applied, incorporating both reactive and proactive strategies. Quality risks are actively addressed, with efforts aligning through a strong culture for a more resilient operation.
Level 5 – Optimized: The highest maturity level of 5 signifies a state of excellence and continuous improvement, where processes are not only proactive but also flexible and efficient in dealing with new challenges. Oversight and management practices are highly effective, incorporating systematic risk management. The quality management system operates seamlessly, with risks minimized and operational efficiency at its peak, showcasing the pinnacle of process optimization and strategic advantage.
Quantitative and Qualitative Aspects
Specific qualitative criteria are linked with each maturity level to aid the assessment team in accurately evaluating capabilities, competencies, and behaviors. These are then reflected in the assigned maturity ratings. A diagram illustrates the interplay between the quantitative (Maturity Rating) and qualitative (Maturity Criteria) components of the Maturity Assessment.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Pharmaceutical
History of the Pharmaceutical Industry:
The pharmaceutical industry, unlike other sectors, has been under stringent regulation almost since its inception, primarily due to the direct impact drugs have on public health. The history of drug regulation can be traced back to tragedies that underscored the need for oversight, such as the Elixir Sulfanilamide disaster of 1937, which led to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. This act significantly increased the authority of the FDA to regulate drugs. Over the decades, as medical science advanced, so did the complexity of pharmaceutical products, necessitating evolving regulatory frameworks. Another major milestone is the Kefauver Harris Amendment of 1962, which was introduced after the Thalidomide tragedy, and which heightened drug efficacy standards and required drug manufacturers to prove the effectiveness of their products before gaining FDA approval.
Current Events in the Pharmaceutical Industry:
Today, the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve rapidly, influenced by technological advancements, emerging new therapies, and changing regulatory landscapes. One of the recent significant shifts has been the growing emphasis on personalized medicine, which tailors medical treatments to individual patient characteristics.
Key developments include:
• Enhanced Focus on Biologics: The rise of biologics and biosimilars has brought new challenges and opportunities, requiring specific regulatory pathways due to their complexity and unique manufacturing processes.
• Digital Health Technologies: The FDA is adapting its regulatory approach to accommodate digital health technologies, including health apps and wearable devices, which are increasingly integrated into patient care.
• Globalization of Pharmaceutical Supply Chains: Ensuring the quality and safety of drugs has become more challenging and crucial with globalized supply chains, prompting the FDA and other regulatory bodies to strengthen international collaboration and oversight.
• Increased Focus on Quality Management Maturity: In order to succeed in today’s fast-paced and evolving environment, especially under the regulatory scrutiny of the FDA, shifting the focus from basic compliance to advanced quality maturity is becoming an imperative. Due to rapid changes, mere compliance is no longer a sufficient target; one must aim ahead of the moving target, by establishing a deep-rooted commitment to advanced quality maturity.
Future Outlook for the Pharmaceutical Industry:
Looking forward, the pharmaceutical industry is poised for further transformation, influenced by several key trends:
• Precision Medicine and Genomics: As our understanding of genomics and disease mechanisms grows, so will the development of precision medicines, requiring regulatory bodies to adapt to the nuances of these treatments.
• Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies are expected to play a significant role in drug discovery and development, potentially reshaping regulatory requirements around clinical trials and data analysis.
• Global Regulatory Harmonization: There is a trend towards greater harmonization of regulatory standards internationally, with organizations like the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) playing a pivotal role.
• Sustainable and Ethical Practices: Like other industries, pharmaceuticals are moving towards more sustainable and ethically responsible practices, influenced by both regulatory pressures and consumer expectations.
In conclusion, the pharmaceutical industry is continually adapting to the rapid pace of scientific advancements and shifting regulatory landscapes. The focus remains steadfast on ensuring drug safety, efficacy, and quality, while also embracing innovation and responding to global health challenges. As the industry evolves, so too will the regulatory frameworks that safeguard public health, with an increasing emphasis on personalized medicine, technological integration, and international collaboration.
Biotechnology
History of the Biotechnology Industry:
The biotechnology industry, a fusion of biology and technology, has been a field of innovation and controversy since its inception. Its roots can be traced back to the 1970s with the advent of recombinant DNA technology, marking the beginning of modern biotech. This period saw the emergence of pioneering companies like Genentech, which successfully expressed insulin and human growth hormone in bacteria. Early regulatory challenges were marked by debates over the ethical and safety implications of manipulating genetic material, leading to guidelines like the Asilomar Conference on Recombinant DNA in 1975, which set the tone for future regulation.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed rapid advancements in biotechnological methods, including the development of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and the sequencing of the human genome. These breakthroughs expanded the industry’s scope from pharmaceuticals to agriculture, biofuels, and environmental conservation.
Current Events in the Biotechnology Industry:
The biotech industry today is characterized by its fast-paced growth and the diversity of its applications. Key developments include:
• CRISPR and Gene Editing: The emergence of CRISPR technology has revolutionized genetic engineering, offering unprecedented precision and ease of use. However, it has also raised ethical and safety concerns, prompting regulatory bodies to evaluate and update guidelines.
• Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics have led to more personalized medical treatments, particularly in oncology, where therapies are increasingly tailored to individual genetic profiles.
• Biologics and Biosimilars: There is a significant focus on the development of biologics (complex medicines derived from living organisms) and biosimilars (similar to existing biologic medicines), which require unique regulatory pathways due to their complexity.
• Industrial and Environmental Biotechnology: Biotechnology applications have expanded to environmental management, biofuels, and sustainable industrial processes, reflecting a growing emphasis on eco-friendly solutions.
Future Outlook for the Biotechnology Industry:
The future of the biotech industry is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
• Advancements in Gene Therapy and Genomics: Continued innovation in gene therapy and genomics will likely lead to new treatments for a wide range of diseases, necessitating updated regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and efficacy.
• Integration of Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are expected to become increasingly integral in biotech for drug discovery, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine, challenging traditional regulatory and ethical frameworks.
• Global Regulatory Harmonization: As biotech companies increasingly operate on a global scale, there will be a push towards harmonizing regulatory standards internationally to facilitate research, development, and distribution of biotech products.
• Ethical and Societal Implications: The ethical implications of biotechnological advancements, particularly in gene editing and reproductive technologies, will continue to be a significant area of discussion and regulation.
• Quality Management Maturity in Biotech: Similar to the pharmaceutical industry, the biotech sector will need to emphasize Quality Management Maturity in order to stay ahead of changes and regulatory requirements. This will involve implementing robust quality systems, risk management, and continuous improvement practices to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy. Regulatory bodies may increasingly assess the maturity of biotech firms’ quality management systems, influencing both market access and public trust.
In conclusion, the biotechnology industry is poised for continued growth and transformation, driven by scientific breakthroughs, evolving regulatory landscapes, and increasing societal and environmental needs. The focus on Quality Management Maturity, ethical considerations, and integration of new technologies like AI will be pivotal in shaping the future of biotech, ensuring sustainable and responsible growth in this dynamic field.

Manufacturing
Initially, Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) products were manufactured and sold in small quantities, often locally or regionally. The industrial revolution in the 19th century brought about mass production, enabling companies to manufacture goods on a larger scale. This period marked the emergence of recognizable brands and the beginning of modern advertising strategies.
Cosmetics, dietary supplements, food and beverages, and drug products are all regulated by the FDA. The regulatory framework that applies to all of these CPG industries is called “Current Good Manufacturing Practices.”
Current Developments in Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) Manufacturing:
The landscape of Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) manufacturing today is marked by intense competition and rapid evolution, driven by several key trends:
• Eco-Conscious Manufacturing: The shift towards sustainability is prominent, with a rising consumer preference for eco-friendly products. This shift has led manufacturers to focus on sustainable practices, such as sourcing materials responsibly, minimizing packaging waste, and reducing their overall environmental impact.
• Technological Advancements in Marketing and Sales: The advent of digital technology, particularly e-commerce and digital marketing, has revolutionized the way CPG products reach consumers. Companies are increasingly utilizing data analytics to gain insights into consumer behavior, allowing for more targeted and personalized marketing strategies.
• Strengthening Supply Chain Capabilities: The recent global health crisis has highlighted the fragility of international supply chains. In response, there’s an escalating focus on fortifying supply chains to ensure they are robust and can effectively manage future disruptions.
• The Rise of Health-Conscious Consumerism: A growing segment of consumers is placing a premium on health and wellness, resulting in increased demand for products that are organic, natural, and health-promoting.
• Evolving Regulatory Landscape: The FDA is in the process of enhancing regulatory requirements for CPG products within its purview.
In terms of regulatory landscape, the manufacturing of cosmetics, dietary supplements, food, and drugs is governed by the principles of Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs). These regulations encompass aspects such as Quality Management Systems (QMS) and extend to more technical areas like facility design, product development, equipment qualification, and others.
Recently, there has been a notable regulatory shift, particularly in the cosmetics sector, with the introduction of the Modernization of Cosmetic Regulations Act (MoCRA). This act aims to enhance the existing cGMPs for cosmetics, aligning them more closely with the rigorous standards seen in other regulated sectors. Despite this, when comparing the core systems and requirements dictated by cGMPs across these industries, a high degree of similarity is observed. The primary differences lie not in the presence of unique programs but in the extent and manner of their application within each industry.
Future Outlook for Fast-Moving CPG Manufacturing Under FDA cGMPs:
Looking ahead, the manufacturing CPGs is set to evolve further, influenced by several factors:
• Advancements in Manufacturing Technologies: The use of advanced manufacturing technologies, including 3D printing and automated production lines, is expected to increase, improving efficiency and allowing for more personalized product offerings.
• Regulatory Evolution: The FDA’s cGMPs are likely to continue evolving in response to new scientific developments and public health needs. This could involve more stringent regulations for dietary supplements and a greater focus on the safety of novel ingredients in cosmetics and food products.
• Consumer-Driven Change: Consumer awareness and demand for transparency, safety, and quality will continue to shape manufacturing practices. This includes a growing interest in clean-label products and those with health and wellness benefits.
• Emphasis on Quality Management Systems (QMS): There will be an increased focus on robust QMS across all sectors, ensuring consistent compliance with cGMPs. Manufacturers will likely invest more in quality assurance and control processes.
• Globalization and Compliance: As these industries continue to operate on a global scale, compliance with international standards and regulations, alongside FDA cGMPs, will become increasingly important.
In conclusion, the future of CPG manufacturing will be characterized by a blend of technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and shifting consumer preferences. Manufacturers will need to balance innovation with strict adherence to quality and safety standards, navigating a dynamic and increasingly complex regulatory environment.

Food and Beverage
History of the Food and Beverage Industry:
Unlike the cosmetics industry, which historically enjoyed minimal regulation, the food and beverage industry has always been subject to rigorous oversight by the FDA. This heightened level of regulation stems from the direct impact that food products have on public health. The risks associated with food consumption, such as foodborne illnesses and nutritional mislabeling, have necessitated stringent regulatory measures. Over time, as food products have become more diverse and complex, the FDA has adapted its regulatory approach to ensure food safety and quality. This includes addressing new technologies in food processing, additives, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Current Events in the Food and Beverage Industry:
The food industry is continuously evolving, with recent regulatory shifts focusing on improving food safety and consumer transparency. Key developments include the implementation of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which is one of the most significant changes in food regulation in recent decades. The FSMA emphasizes prevention of food safety issues rather than responding to outbreaks post-facto. Key elements of the FSMA include:
• Preventive Controls: Manufacturers must analyze potential hazards and implement preventive controls.
• Foreign Supplier Verification Programs: Importers are responsible for verifying that their foreign suppliers meet U.S. safety standards.
• Traceability and Recordkeeping: Enhanced tracking and recordkeeping requirements enable quicker response to food safety issues.
• Increased Inspections and Compliance: The FDA now conducts more frequent facility inspections and has more authority to enforce compliance.
These changes reflect a proactive approach, aligning more closely with international food safety standards.
Future Outlook of the Food and Beverage Industry:
Looking ahead, the food industry is likely to see further integration of global food safety standards and practices. This could involve harmonizing U.S. regulations with international standards like the Codex Alimentarius, a collection of internationally recognized standards, guidelines, and codes of practice relating to foods, food production, and food safety.
Additionally, the rise of new food technologies, such as lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives, will prompt the FDA to establish new regulatory frameworks. These innovative products challenge traditional definitions and standards, necessitating a reevaluation of existing food laws.
In terms of manufacturing practices, the industry is expected to continue its shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, responding to consumer demands for “clean” and ethically sourced products. This shift may include greater transparency in labeling, more stringent controls on organic certification, and a focus on reducing the environmental impact of food production.
Overall, the future of food regulation is poised to become even more integrated with global standards, focusing on preventive measures, technological adaptation, and sustainability.
In conclusion, drug regulation is expected to evolve with advancing scientific knowledge, patient-centric approaches, and global collaboration, ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products while fostering innovation and addressing public health needs.

Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (CPG)
History of Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (CPG) regulated by the FDA
The FDA-regulated consumer goods include cosmetics, food and beverage, dietary supplements, and drugs. As food and beverages are covered as a separate industry in this program, this consumer goods section will discuss cosmetics, supplements, and drugs.
Cosmetics
Historically the cosmetics industry has been the least regulated of the FDA-regulated industries. This is probably due to the perception that cosmetics products are less risky than food, supplements, or drugs. However, the FDA has very recently stepped up its regulation of the cosmetics industry, probably due to the expansion of the industry into more advanced products and broader applications, some of which implicate drug regulations due to making certain health claims.
Dietary Supplements
The regulation of dietary supplements has always been distinct from both the food and cosmetics industries. Initially, dietary supplements were regulated more leniently compared to pharmaceuticals, under the assumption that these products were more akin to food products in their risk profile. However, the increasing complexity of supplements, the introduction of potent and novel ingredients, and a surge in their popularity necessitated more stringent oversight. The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA) marked a significant regulatory milestone, acknowledging the unique nature of dietary supplements and setting specific standards for their safety, manufacturing, and marketing.
Drugs
The regulation of drugs has always been one of the most stringent areas under the FDA’s purview, a consequence of the high potential risks associated with pharmaceutical products. Historically, drug regulation has evolved in response to public health crises and medical breakthroughs, leading to increasingly comprehensive and rigorous standards. Key legislative milestones include the Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938, and the Kefauver-Harris Amendment of 1962. These laws introduced requirements for safety testing, efficacy proof, and quality manufacturing practices, significantly shaping today’s drug regulatory landscape.
Current Events of the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (CPG) regulated by the FDA
Cosmetics
The cosmetics industry has recently undergone some major regulatory changes under the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulations Act, or MoCRA . These changes represent the intention of the FDA to regulate cosmetics in a manner much more similar to food and dietary supplements than it has in the past. Some of the new requirements include: i) registration of cosmetic manufacturing facilities and their products, ii) reporting adverse events, iii) providing access to records and product safety information, and iv) additional enforcement powers to the FDA. Such regulations will undoubtedly force some manufacturers into a greater awareness of their regulatory obligations.
Dietary Supplements
Recent years have seen a heightened focus on the regulation of dietary supplements due to their growing use and the diversification of their ingredients. The FDA has been working to strengthen the regulatory framework to ensure consumer safety without stifling innovation. Recent regulatory updates and initiatives include:
• New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) Notifications: Enhanced scrutiny of new ingredients introduced into the market to ensure safety.
• Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs): Stricter enforcement of GMPs to ensure that supplements are produced in a quality manner, are free from contaminants or impurities, and are accurately labeled.
• Labeling and Claims: Tighter regulations on labeling, including claims made about the health benefits of supplements, to ensure they are not misleading.
• Market Surveillance: Increased monitoring of the market for any potentially dangerous products or ingredients.
These changes reflect the FDA’s commitment to keeping pace with the evolving landscape of dietary supplements while protecting public health.
Drugs
The drug industry is currently experiencing significant regulatory developments driven by advances in pharmaceutical research, public health needs, and the advent of personalized medicine. Current regulatory focuses include:
• Expedited Approval Processes: Programs like Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy, Accelerated Approval, and Priority Review are designed to speed up the approval of drugs that address unmet medical needs.
• Enhanced Safety Surveillance: Post-market safety monitoring has been strengthened to promptly identify and address adverse effects that may not have been apparent in clinical trials.
• Biosimilars and Biologics: As patents for many biologics expire, the FDA is establishing pathways for the approval of biosimilars, which are similar, but not identical, to original biologic drugs.
• Opioid Crisis Response: In response to the opioid epidemic, the FDA has implemented measures to encourage the development of abuse-deterrent formulations and to tighten the regulation of opioid prescribing.
Future Outlook of the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (CPG) regulated by the FDA
Cosmetics
MoCRA promises to establish cosmetic regulations more consistent with national and international standards. These new regulations are likely to be a simple codification of cGMP requirements very similar to those already found for food and supplements in 21 CFR Part 111 and 117. More precisely, it is expected that the new cGMP requirements will closely mirror the requirements of ISO 22716, an international GMP standard for cosmetics manufacturers.
Dietary Supplements
Looking ahead, the dietary supplement industry is likely to encounter more rigorous regulatory landscapes. This could involve:
• Harmonization with Global Standards: Like the food industry, dietary supplement regulations may become more aligned with international standards, facilitating global trade while ensuring safety.
• Advanced Testing and Safety Protocols: As the complexity of supplements increases, more sophisticated testing methods may be required to assess safety and efficacy, possibly including genetic and molecular testing techniques.
• Regulation of Novel Ingredients: The introduction of new, scientifically engineered ingredients will likely require the development of new regulatory pathways to assess their safety and efficacy.
• Focus on Consumer Education: With the proliferation of misinformation, there may be greater emphasis on educating consumers about the safe use of supplements and understanding product labels.
• Increased Transparency: There could be more stringent requirements for ingredient sourcing, manufacturing processes, and supply chain transparency to build consumer trust.
The future trajectory of dietary supplement regulation points towards a more comprehensive and robust framework, focusing on safety, transparency, and informed consumer choices. This evolution will likely involve balancing the need to protect public health while encouraging innovation in the supplement industry.
Drugs
The future of drug regulation is poised to be shaped by several emerging trends and challenges:
Personalized Medicine and Genomics: As treatments become more tailored to individual genetic profiles, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to assess the efficacy and safety of these personalized therapies.
• Artificial Intelligence in Drug Development: The integration of AI and machine learning in drug discovery and development may lead to the establishment of new regulatory pathways to evaluate these innovative methodologies.
• Global Harmonization of Drug Standards: Increasing globalization of drug development and manufacturing might lead to greater harmonization of regulatory standards internationally, facilitating global access to new therapies.
• Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs): The rise of ATMPs, including gene and cell therapies, presents unique regulatory challenges due to their novel mechanisms of action and production processes.
• Focus on Patient-Centered Outcomes: There is a growing emphasis on including patient experiences and outcomes in the drug approval process, leading to a more holistic view of drug benefits and risks.
• Continued Response to Public Health Emergencies: The recent pandemic highlighted the need for agile regulatory responses to public health emergencies. Future regulations may include streamlined processes for the rapid development and approval of drugs in response to global health crises.
In conclusion, drug regulation is expected to evolve with advancing scientific knowledge, patient-centric approaches, and global collaboration, ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products while fostering innovation and addressing public health needs.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:
Dallas, TX
History of Dallas for the FDA-regulated sector:
The manufacturing landscape in Dallas, Texas, has historically been diverse, with significant contributions from electronics, aerospace, and defense sectors. However, in recent years, there’s been a noticeable shift with the growth of FDA-regulated industries, including cosmetics, food, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals. This shift aligns with the broader national trend of increasing regulation and quality standards in these industries. Dallas’s strategic location, business-friendly environment, and skilled workforce have contributed to its emergence as a hub for GMP-focused manufacturing.
Current Events in Dallas for the FDA-regulated sector:
Currently, Dallas is experiencing substantial growth in the FDa-regulated sector. Key developments include:
• Expansion of Facilities: Numerous companies in the GMP industries are expanding their operations in the Dallas area, leveraging the region’s robust infrastructure and logistics capabilities.
• Investment in Workforce Training: Local educational institutions and companies are collaborating to provide specialized training programs to meet the growing demand for skilled workers in GMP industries.
• Regulatory Compliance Focus: With increasing regulatory scrutiny, Dallas-based GMP manufacturers are investing in technology and processes to ensure compliance with FDA regulations, particularly in areas like quality control and traceability.
• Innovation and R&D: Dallas is becoming a focal point for research and development in GMP industries, attracting investments and partnerships aimed at product innovation and improved manufacturing processes.
Future Outlook in Dallas for the FDA-regulated sector:
The future of FDA-regulated industries in Dallas looks promising with several trends and opportunities on the horizon:
• Continued Sector Growth: The FDA-regulated manufacturing sector in Dallas is poised for further expansion, driven by ongoing investments and the city’s conducive business climate.
• Technological Advancements: The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as AI, IoT, and automation is expected to increase efficiency and compliance in GMP facilities.
• Sustainability Initiatives: There is a growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing practices, aligning with global trends and consumer demands.
• Collaborations and Partnerships: Strategic partnerships between local businesses, academic institutions, and government entities are likely to foster innovation and growth in the FDA-regulated sectors.
• Focus on Export Markets: Dallas’s manufacturing sector may increasingly look towards international markets, leveraging its strategic location for export opportunities.
In summary, Dallas’s manufacturing industry, particularly in the FDA-regulated sectors, is on a trajectory of growth and innovation, driven by technological advancements, a skilled workforce, and a supportive business environment. The city is well-positioned to become a leading hub for FDA-regulated manufacturing in the United States.

Los Angeles, CA
History in Los Angeles of the FDA-regulated sector:
Los Angeles has long been a major player in the manufacturing sector, traditionally dominated by aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. In the context of FDA-regulated industries, such as cosmetics, food, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals, Los Angeles has seen a significant evolution. The region’s diverse population, combined with its extensive port facilities and status as a cultural and economic hub, has laid the groundwork for the growth of GMP-focused manufacturing.
Current Events in Los Angeles for the FDA-regulated sector:
The current landscape of FDA-regulated industries in Los Angeles is marked by dynamic growth and innovation. Key developments include:
• Diverse Manufacturing Base: Los Angeles hosts a wide range of FDA-regulated manufacturing facilities, including cutting-edge pharmaceutical companies, growing dietary supplement brands, and established cosmetic and food manufacturers.
• Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards: GMP facilities in Los Angeles are increasingly focusing on compliance with stringent FDA regulations, reflecting the city’s commitment to quality and safety in manufacturing.
• Technological Integration: There’s a significant push towards adopting new technologies such as automation, AI, and blockchain for traceability and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
• Investment in Sustainable Practices: Aligned with California’s overall environmental ethos, there is a notable trend towards sustainability and eco-friendly practices in GMP facilities.
• Workforce Development: Los Angeles is leveraging its extensive educational and research institutions to develop a skilled workforce capable of meeting the demands of the evolving GMP sector.
Future Outlook in Los Angeles of the FDA-regulated sector:
The future of GMP industries in Los Angeles appears robust, with several emerging trends:
Growth in Biotech and Advanced Pharmaceuticals: The city is poised to become a key player in biotechnology and advanced pharmaceuticals, driven by research, innovation, and venture capital investments.
• Global Trade and Export: Given its port facilities and global connections, Los Angeles is expected to expand its role in the international trade of GMP products.
• Collaborative Ecosystems: The convergence of industries, academia, and government agencies in Los Angeles is likely to create collaborative ecosystems, fostering innovation in FDA-regulated manufacturing.
• Focus on Personalized Medicine and Wellness Products: Reflecting global health trends, there’s likely to be an increase in the production of personalized health products, including bespoke dietary supplements and wellness products.
• Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: With global markets in view, Los Angeles manufacturers may further enhance their compliance with international as well as federal GMP standards.
In conclusion, Los Angeles is setting itself up as a major hub for FDA-regulated manufacturing, characterized by innovation, a commitment to quality and sustainability, and a strategic focus on leveraging its diverse resources and global connections. The city’s manufacturing sector is likely to see continued growth and evolution, driven by technological advancements and a deepening commitment to meet the highest standards in product safety and quality.

Austin, TX
History of Austin in the FDA-regulated sector:
Austin, Texas, traditionally known for its technology and innovation sectors, has seen a notable expansion in its manufacturing base. This expansion includes a growing presence in FDA-regulated industries like cosmetics, food, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals. Austin’s transformation into a manufacturing hub is partly attributed to its booming tech industry, which has created a synergistic environment for high-tech manufacturing and innovation. The city’s favorable business climate and access to a skilled workforce have also been pivotal in attracting GMP-related manufacturing.
Current Events in Austin for the FDA-regulated sector:
The current state of GMP industries in Austin is characterized by rapid growth and diversification. Key aspects include:
• Increasing GMP Facilities: Austin is attracting an array of GMP-compliant facilities, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food sectors, bolstered by the city’s strong tech and research infrastructure.
• Focus on Quality and Compliance: With the stringent regulatory landscape of GMP industries, Austin-based manufacturers are heavily investing in quality control and compliance measures to meet FDA standards.
• Innovation and R&D Investments: There’s a notable emphasis on research and development, with companies leveraging Austin’s rich tech environment to drive innovation in product development and manufacturing processes.
• Workforce Development: The city’s educational institutions, renowned for their science and technology programs, are key in providing a talent pipeline for the burgeoning GMP sector.
• Sustainability Initiatives: Reflecting a city-wide emphasis on sustainability, FDA-regulated manufacturers in Austin are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices and sustainable manufacturing processes.
Future Outlook of Austin in the FDA-regulated sector:
The future trajectory for GMP industries in Austin points to continued growth and innovation, with several trends likely to shape this sector:
• Technological Advancements: Integration of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and automation in manufacturing processes is expected to enhance efficiency and compliance.
• Expansion in Biotech and Nutraceuticals: Given Austin’s strong tech background, there is potential for significant growth in biotechnology and nutraceuticals, blending health, technology, and manufacturing.
• Collaborative Ecosystems: The convergence of tech companies, startups, academic institutions, and manufacturing could lead to a collaborative ecosystem, fostering innovation and growth in GMP manufacturing.
• Increased Regulatory Focus: As global standards evolve, Austin’s GMP sector may see heightened regulatory focus to ensure product safety and quality, particularly for export markets.
• Sustainable and Ethical Manufacturing: In line with global trends, there will likely be a continued push towards more sustainable and ethically responsible manufacturing practices.
In summary, Austin’s manufacturing industry, particularly in the GMP sectors, is poised for dynamic growth, driven by technological innovation, a skilled workforce, and a strong emphasis on quality and sustainability. The city is emerging as a key player in the GMP manufacturing landscape, blending its tech prowess with a commitment to manufacturing excellence.

New York, NY
New York, NY
History of New York City in the FDA-regulated sector:
Historically, New York City has been a hub for diverse industries, ranging from fashion and publishing to finance and technology. In the context of manufacturing, particularly for FDA-regulated industries such as cosmetics, food, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals, New York has held a significant position. The city’s dense population, extensive infrastructure, and global connections have historically supported a robust manufacturing sector, though it has evolved over time from heavy industry to more specialized, high-value sectors.
Current Events of New York City in the FDA-regulated sector:
The landscape of FDA-regulated industries in New York City is currently marked by several key developments:
• Diversification into GMP Sectors: There’s a growing emphasis on GMP industries, with particular growth in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, supported by the city’s strong research base and consumer market.
• Regulatory Compliance and Innovation: Manufacturers in New York are increasingly focusing on meeting FDA regulations, especially in areas like quality control, while also investing in innovation to stay competitive.
• Strategic Collaborations: Partnerships between academic institutions, healthcare organizations, and manufacturers are fostering a collaborative environment for research and development in GMP sectors.
• Sustainability Initiatives: In line with global trends, New York’s manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
• Workforce Development and Training: The city’s diverse and skilled workforce is being further strengthened through targeted training programs in GMP-related fields.
Future Outlook of New York City in the FDA-regulated sector:
Looking ahead, the FDA-regulated industries in New York City are likely to experience several key trends:
• Continued Growth in Biotech and Advanced Pharmaceuticals: New York’s strong foundation in research and healthcare positions it well for growth in these advanced sectors.
• Technological Integration: Adoption of technologies like AI, data analytics, and automation is expected to increase, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and compliance.
• Focus on Personalized Medicine and Health Products: Reflecting global health trends, there could be an increase in the production of personalized health products, including precision medicine and specialized dietary supplements.
• Global Market Expansion: New York’s manufacturers may increasingly look towards international markets, leveraging the city’s global connections for export opportunities.
• Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: As global standards evolve, New York’s manufacturers are expected to maintain a strong focus on regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
In conclusion, New York City’s manufacturing industry, particularly in the FDA-regulated sectors, is expected to continue evolving, driven by a combination of technological innovation, strong research and development capabilities, and a focus on quality and sustainability. The city’s unique position as a global hub positions it well for continued growth and leadership in these sectors.
Program Benefits
Management
- Productivity Boost
- Quality Improvement
- Compliance Adherence
- Innovation Cultivation
- Team Cohesion
- Morale Boost
- Strategic Alignment
- Risk Mitigation
- Competitive Advantage
- Reputation Enhancement
Operations
- Process Optimization
- Efficiency Gains
- Cost Reduction
- Error Minimization
- Safety Enhancement
- Standardization Achievement
- Workflow Streamlining
- Resource Utilization
- Sustainable Practices
- Technology Integration
Human Resources
- Skill Enhancement
- Knowledge Growth
- Performance Improvement
- Career Advancement
- Job Satisfaction
- Enhanced Creativity
- Problem Solving
- Personal Development
- Leadership Skills
- Adaptability Increase
Testimonials

Cosmetic Innovations
Since mid-2020 Cosmetic Innovations had been wanting to add drug products to their product line. But after struggling for over two years to bring themselves into compliance with the requisite FDA requirements, they finally realized that they needed professional help to make this significant leap. TAKA hired Mr. Clark in early 2023 to assist them in building an FDA-compliant quality management system. Using a system very much like the Program outlined here, Mr. Clark has brought TAKA into substantial compliance and TAKA is currently awaiting FDA approval to begin drug production.

Royal Pharma
Royal Pharma was a new company that had innovative new cosmetic and drug products to bring to market. With a program very much like this one, Mr. Clark assisted the organization from A to Z, including facility and equipment design, to Process Planning, to Production Controls, to Label Development and more. Royal is now ready to begin production of their cosmetic product and is pursuing market authorization for its drug product. Royal selected Mr. Clark due to their desire to exceed mere compliance and target quality excellence. Royal is continuing to work with Mr. Clark as a valuable strategic partner.

HERA
HERA confronted a significant challenge in its endeavor to bring a new animal drug to the market. This ambitious venture required strict compliance with FDA and cGMP standards, a formidable undertaking for the new facility. In response to this challenge, HERA turned to Mr. Clark’s comprehensive program for expert guidance.
Mr. Clark’s involvement catalyzed a series of transformative changes within HERA. His systematic approach to improvement meticulously aligned the organization’s operations with the stringent requirements of drug manufacturing. Under his guidance, HERA adeptly navigated the complex regulatory landscape, successfully meeting the high standards set by the FDA and cGMP for drug production. Mr. Clark’s program played a crucial role in HERA’s transition, ensuring the company’s readiness to introduce its innovative animal drug to the market.

Nutra-Wellness
In the competitive field of dietary supplements, NutraWellness faced unique challenges in aligning with FDA standards while keeping pace with market demands. Despite having an innovative product line, the journey towards FDA compliance slow and arduous. Recognizing the need for expert guidance, NutraWellness adopted Mr. Clark’s approach, mirroring the program described here. The program guided them through every aspect of our Quality Management System, from raw material qualification to final product testing. Mr. Clark’s expertise was particularly invaluable in refining our production controls and ensuring GMP compliance.
Under Mr. Clark’s guidance, NutraWellness not only achieved FDA compliance but also enhanced its operational efficiency significantly. NutraWellness can now confidently focus on expanding market reach, thanks to Mr. Clark’s awesome quality improvement program.

FreshFare, Inc.
In the dynamic world of food production, FreshFare Inc. faced the intricate challenge of expanding their product line to include health-centric food items. The endeavor required rigorous adherence to FDA and food safety standards, a complex task for the company’s burgeoning operations. Realizing the need for specialized expertise, FreshFare Inc. enlisted Mr. Clark in mid-2023 to guide them through this critical transition.
Mr. Clark, leveraging a strategy akin to the comprehensive Program presented here, meticulously spearheaded the transformation of FreshFare Inc.’s Quality Management System. His approach was holistic, addressing every facet from facility design and process planning to production controls and packaging compliance. Under his tutelage, FreshFare Inc. not only navigated the complexities of FDA regulations but also integrated advanced food safety practices into their operations.

DermAdvance
As a startup specializing in skincare products, DermAdvance struggled to navigate the complex regulations of both cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. DermAdvance was struggling to reach its goal to not only meet, but surpass, industry standards in quality and safety. Mr. Clark’s program, , was instrumental in improving GMP processes. From the initial facility and equipment design to the intricate details of label development and production controls, Mr. Clark’s holistic approach not only prepared us for compliance but also set a foundation for quality excellence. DermAdvance has now successfully launched its cosmetic line and is on the verge of obtaining market authorization for its innovative pharmaceutical skincare products. Its ongoing partnership with Mr. Clark continues to be a pivotal asset in its pursuit of excellence and innovation in the skincare industry.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.