Mind Leadership

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Mind Leadership is provided by Ms. Wilson Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Ms Wilson is an approved Certified Learning Professional (CLP) at Appleton Greene and has experience in leadership, management, and marketing. She has achieved a Bachelor of Science in Psychology. She has industry experience within the following sectors: Health Care and Social Assistance; Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services; Retail Trade; Services. Additionally, she has had commercial experience within the following countries: the United States of America, or more specifically, within the following cities: Dallas, TX; Baltimore, MD; Harrisburg, PA. Her personal achievements include: leadership development for disruptive environment; complex issues resolved; facilitated project management improvement process; established performance improvement processes; launching new products and services in emerging markets. Her service skills incorporate: leadership development; team management; executive coaching; business development; business strategy; project management; marketing.
To request further information about Ms. Wilson through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Mind Leadership
Over the last fifty years, a slow-paced world has changed into a fast-paced world. As a result, leadership has changed from autocratic, dictating orders and making all the decisions, to a more collaborative, people-oriented, and integrative based on relationships. In addition, the world has evolved with technological and commercial innovations and disruptions to be more flexible, creative, and adaptable. As a result, organizations are adjusting strategies to connect with others to compete in the global market and focusing on producing efficient products and services that contribute to meaningful interactions with others—influencing the achievement of organizational goals and shaping individual and group behavior and decisions.
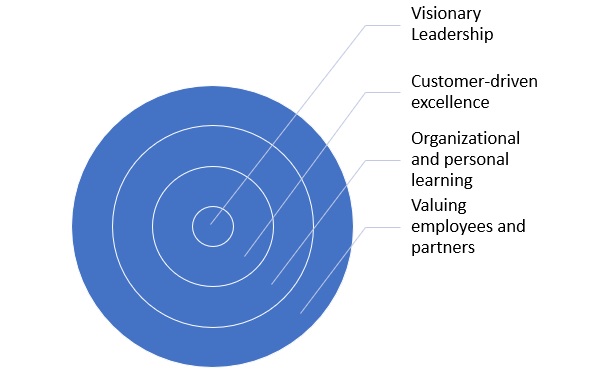
Leadership is, in essence, a “people” activity, cultivating good relationships and making people feel a part of something. At the core of a strategic network and high-performing organization is the value of visionary leadership. Keep pace and achieve organization quality standards of innovative leadership to reduce production costs, increase global impact, enhance customer satisfaction, and increase profitability and market share. Empower your organization with effective leadership processes, developing a shared vision that incorporates the organization’s values and is easy to communicate.
Leadership Development and Program
Enrolling prospective, new, and practicing leaders is a time-honored strategy for developing prospective leaders in a leadership development program. Organizational development is in the professional development of leaders. Have a competitive edge in developing effective current and future leaders. Increase the leadership spirit that encourages innovative ideas from within the organization. Focus on the context in which leadership develops through personal growth, leadership style, strategy formulation, influence, motivation, and persuasive communication. Develop leaders that can fix problems that occur or prevent them from happening. Finally, determine which leadership development program is right for your organization. Training and developing leaders provide a competitive advantage to improve recruitment, retention, productivity, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
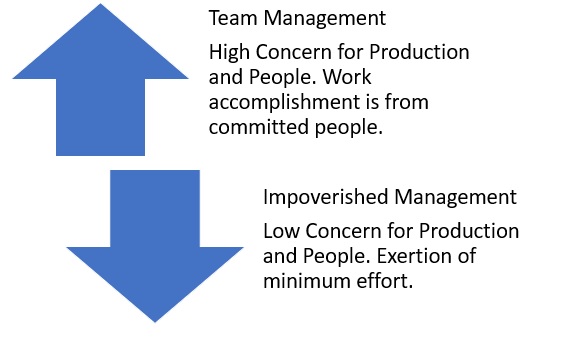
Leadership Grid
Learn to use the Leadership Grid to understand the extent of a leader’s concern for production and people. Achieve team management, resulting in a high concern for production and people. Work accomplished from committed people, improved performance, low absenteeism, low turnover, and high morale. Conversely, avoid impoverished management with a low concern for production and people and exert minimum effort.
Leadership Styles
Leadership styles influence organizational behavior, including employees’ acceptance of and adherence to organizational norms and values. Learn to select the most effective leadership style for a situation to plan, organize, and lead the company mission, goals, and environment. Leaders who obtain the best results do not rely on one style. Instead, they use several different techniques based on the situation. Adjust their approach to bring out the best in the people they lead. “The most effective leaders appear to exhibit a degree of versatility and flexibility that enables them to adapt their behavior to the changing and contradictory demands,” -Ralph Stogdill.
The Role and Habits of Ethical Leaders
Leaders are vital to influencing an organization’s culture and ethical posture. They assess risks and desire to achieve a favorable climate for organizational performance. Learn to positively impact ethical decision-making and the dimensions of organizational behavior and motivate acceptance and adherence to the organization’s norms, values, rules, and policies. View ethics holistically as a strategic component of the company’s ethical culture. Implement strategies to address and avoid misconduct, encourage professionalism, embrace and model positive workplace conduct, avoid brand damage, and drive proactive and reactive measures. Build trust of clients and partners to increase efficiency and productivity.
Traits Motives, Characteristics, and Behavior that Impact Leadership Effectiveness
Identify motives and general, relationship-related, and task-related personality traits of influential leaders related to success, task accomplishment, and satisfaction in work and personal life. Knowledge of the characteristics associated with leadership effectiveness helps select future leaders and helps identify meaningful development experiences to improve specific traits. The situation often influences which attribute will be the most important. For example, some believe leadership is about the person, and the quality of the individual, while others believe that leadership emerges from a specific situation.
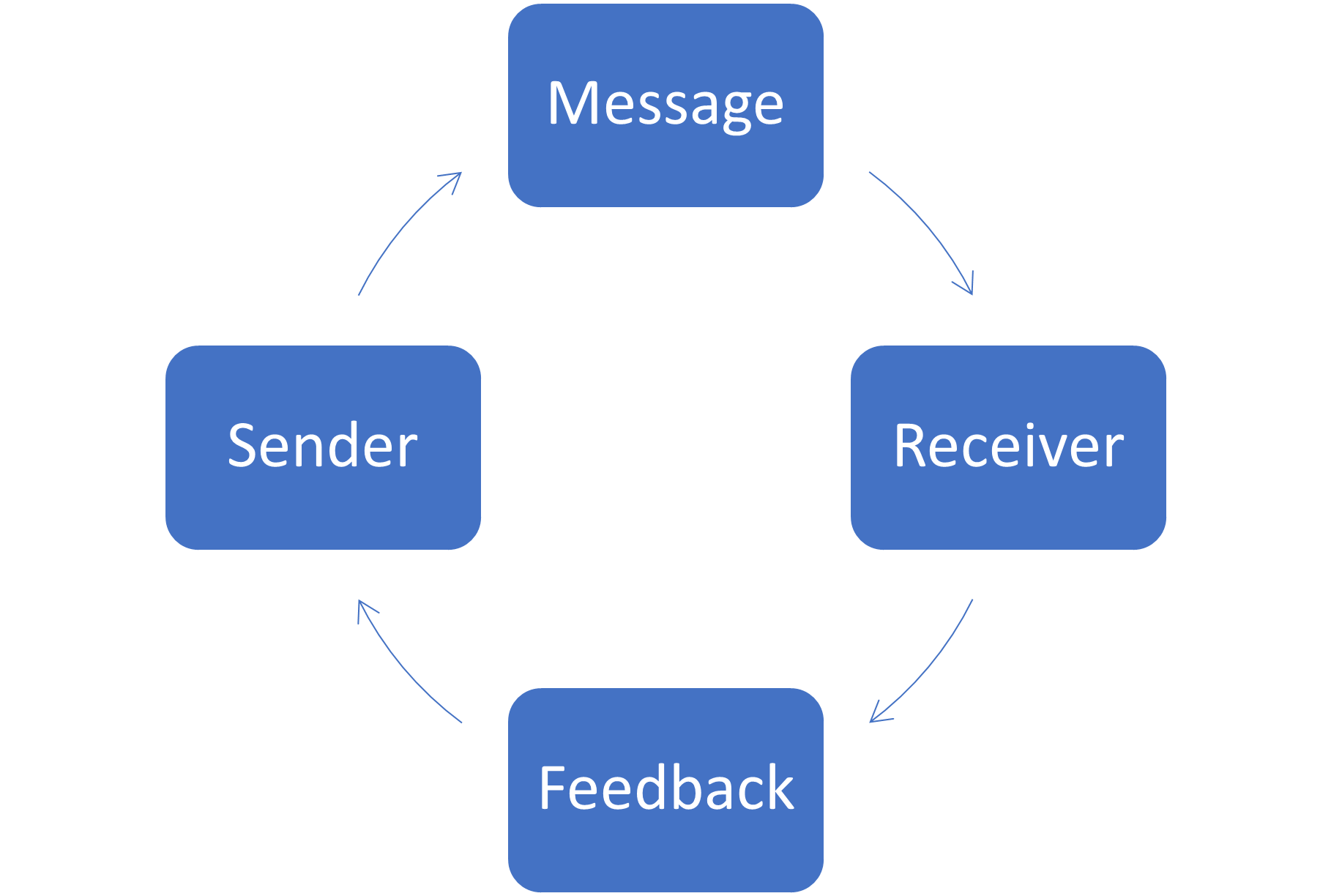
Communication and Leadership
Communication is critical for organizational success and leadership effectiveness. Whether an organization is global or in a single country, improving communication begins with the leader’s willingness to articulate the organization’s vision and operation. Explore the significant communication elements and the types of organizational communication, measure leadership effectiveness to inform, inspire, anticipate and implement change, and motivate or influence behavior with internal and external stakeholders. Develop good communication skills and overcome barriers through constant practice and active feedback. Finally, develop a classic or contemporary approach to leadership.
Investing in visionary leadership is an integral part of organizational success. Great leaders develop other great leaders. Leadership in a fast-changing modern world is on the future- an aspiration to be something at a certain point- and the tools required to achieve it through collaboration, innovation, creativity, adaptation, agility, and change. Leaders need to look at the future with teamwork, purpose, commitment, hope, and optimism and inspire others to do the same in every aspect of the organization.
Curriculum
Mind Leadership – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Leadership Development
- Part 1 Month 2 The Leadership Grid
- Part 1 Month 3 Leadership Development Programs
- Part 1 Month 4 The Role of Leadership in Developing an Ethics Program
- Part 1 Month 5 Habits of Strong Ethical Leaders
- Part 1 Month 6 Leadership Styles
- Part 1 Month 7 Traits Motives and Characteristics that Impact Leadership Effectiveness
- Part 1 Month 8 Communication and Leadership
- Part 1 Month 9 Motives of Effective Leaders
- Part 1 Month 10 Two Dimensions of Leadership Behavior
- Part 1 Month 11 Measure Leader Effectiveness
- Part 1 Month 12 Personality Traits of Effective Leaders and Task Accomplishment
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Mind Leadership corporate training program.
Mind Leadership – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Leadership Development – Leadership development is a high priority for businesses and government organizations—development through self-awareness, self-discipline, education, experience, and monitoring. Self-awareness helps avoid operating at the extremes of the dimensions of Strategic Operational and Forceful Enabling behavior. Understanding the differences between the two levels of self-awareness can help the leader better understand responses to feedback. Self-discipline is essential in continuously monitoring one’s behavior to ensure self-development occurs. Understanding how education contributes to leadership effectiveness. Experience that is challenging, sourced, and broad. Mentoring may be informal or formal through shadowing or direct work activities.
- Part 1 Month 2 The Leadership Grid – The leadership grid measures and rates a leader’s concern for production (results, bottom line, performance, profits, and mission) and concern for people. It encompasses a rating of a leader’s concern for production along a horizontal axis with scores from 1 (low) to 9 (high). Along the vertical axis is the rating of a leader’s concern for people (group members and coworkers), with scores from 1 (low) to 9 (high). A classic method of classifying the extent of a leader’s concern for production and people is to assess the management of work tasks and relationship orientations. A leader’s attitude and thinking determine their concern for production (tasks) and people (relationships).
- Part 1 Month 3 Leadership Development Programs – Enrolling prospective, new, and practicing leaders is a time-honored strategy for developing them in leadership development programs. Have a competitive edge in developing effective current and future leaders with the seven types of leadership development programs. Focus on personal growth, leadership concepts, strategy formulation, influence, motivation, persuasive communication, and behavior patterns. The leadership development program will assess, challenge, and support a developmental leadership experience. Select one leadership development program at a time or overlap programs.
- Part 1 Month 4 The Role of Leadership in Developing an Ethics Program – Conduct a thorough self-assessment of the firm’s values and its existing morals and compliance program. Maintain commitment from top managers. Publish, post, and make codes of ethics available and understandable. Communicate ethical standards through multiple channels. Provide timely training to reinforce knowledge. Provide confidential resources to whom employees can go for advice or report their concerns. Ensure consistent implementation. Respond and enforce consistently, promptly, and fairly. Monitor and assess using appropriate methods. Revise and reform to ensure continuous improvement.
- Part 1 Month 5 Habits of Strong Ethical Leaders – Habits of strong ethical leaders is a quality developed over time or early in life. Proactive in the moral interest and implications of the company. Role models upholding the company’s core values. Transparent and involved in the company decision-making. View ethics holistically as a strategic component of the company’s ethical culture.
- Part 1 Month 6 Leadership Styles – A leader’s attitudes and behaviors lead to regularity and predictability in dealing with group members. Leadership style is a relatively consistent pattern of behavior that characterizes leaders. Leadership-style research broadens our understanding of leadership behavior and attitudes. Most classifications of leadership styles are on the dimensions of deliberative and starting structures. Many ways of characterizing styles have been developed and will focus on some of the most popular approaches.
- Part 1 Month 7 Traits Motives and Characteristics that Impact Leadership Effectiveness – Leaders are influenced by many variables, from cognitive abilities, talents, and experience, to their interactions with others within their organization and the business environment in which they operate. In this section, the following aspects of leadership will explore general personality traits, task-related personality traits, motives, and cognitive factors. General personality traits are related to success and satisfaction in work and personal life. Some personality traits of effective leaders are closely associated with task accomplishment. Influential leaders possess certain traits, motives, and characteristics in certain leadership situations.
- Part 1 Month 8 Communication and Leadership – The communication process model is how we exchange information with others. Objectives may be to inform, inspire, motivate or influence behavior through effective communication. Organizational communication between national and global internal and external stakeholders is critical for organizational success and managerial effectiveness. In addition, leadership’s ability to anticipate and implement change within the organization and respond to changes in the environment is essential to achieving organizational goals.
- Part 1 Month 9 Motives of Effective Leaders – Effective leader motives are power, drive, achievement, tenacity, and resilience. Power motive is motivation to control, influence, and status. Drive and achievement motive invest in achieving work goals. Finally, perseverance and resilience are overcoming obstacles and the ability to bounce back from setbacks.
- Part 1 Month 10 Two Dimensions of Leadership Behavior – The study of leadership from various perspectives better understand the behaviors that mark effective leadership. Leadership behavior fits within two dimensions: consideration and initiating structure. Using consideration and initiating structure to know-how leadership behaviors impact organizational outcomes. Leaders categorize for how they exhibit behaviors consistent with each dimension.
- Part 1 Month 11 Measure Leader Effectiveness – Measure leadership effectiveness using a systematic method of obtaining input from a representative sample of people who work for and with a given leader. The method is sometimes also used to obtain data for performance appraisal. The feedback is communicated to the leader and interpreted with the assistance of a human resources professional. Those providing input may include customers, business partners, and suppliers.
- Part 1 Month 12 Personality Traits of Effective Leaders and Task Accomplishment – Some personality traits of influential leaders are closely associated with task accomplishment. These traits include passion, flexibility and adaptability, emotional intelligence, internal locus of control, and courage. Passion for work and people. Ability to cope with change. They are managing emotions and responses to others. Assume responsibility for actions and events. Leaders need the boldness to take risks and take action.
Methodology
Mind Leadership
The methodology for the leadership mind is the state of the leader’s mind. A leader’s cognitive and mental process to attention, memory, thinking, planning, and decisions, things we do every day, are internal information that regulates behavior, learning, and problem-solving. Internal thoughts prepare us for tasks and help us learn more. Internal information is the process of inner thoughts controlling behavior and problem-solving. The internal process of taking information, processing thoughts, and responding helps us learn more. For example, you’ve decided to meet with your team. You start planning the meeting with your team and remember the last meeting with your team. It was longer than expected, and you visualize an extended team meeting. You problem-solve by deciding to keep each topic to five minutes. The processing of internal thoughts and information can become distorted and lead to maladaptive emotions and behavior due to differences in knowledge, information processing, and distortions in attention, memory, and comprehension based on their temperament, abilities, and experiences.
Individuals learn more through internal than external support. They can visualize their activities’ results instead of relying only on external support. For example, you purchase extra inventory in the fall because you can ‘see’ the demand going up in the winter. Our cognitive capacities permit us to illuminate numerous issues internally.
Self-schemas incorporate our views on who we are, what we might end up with, what is critical to us, and different parts we possess or might involve in our social environment and impact our choice of objectives and certainty in achieving them. Patterns worldwide and self-schemas are imperative to our capacity to engage in successful and organized behavior since they empower us to center on the best essential bits of data among the astounding complex array of information accessible to our senses. Schemas are also sources of mental vulnerabilities because some of our schemas or specific aspects of our self-schemas may be distorted and inaccurate. We often hold some schemas- even distorted schemas- with conviction, making them resistant to change. We are usually not entirely conscious of our schemas, unaware of the assumptions of our daily decisions and behavior. We think we see things the way they are and often do not consider that other views might be possible or suitable might exist. Maladaptive schemas develop as a function of adverse early learning experiences leading to distortions in thinking.
A leadership mindset is not to cling to existing assumptions and not to reject or distort new information that contradicts them. Instead, work new experiences into your current cognitive framework. Take new information and reinterpret it to make it fit. We are changing the existing framework to make it possible to incorporate new information. Altering our behavior through changing the way we think about ourselves and others, interpreting events and experiences, and our emotional reaction to them.
Self-development is essential for developing leadership capabilities. Important mechanisms underlying self-development are self-awareness and self-discipline. The belief is that we can achieve goals, our talents are innate, and we can achieve personal growth and develop our abilities through our personal and work lives. Self-discipline is essential in continuously monitoring one’s behavior to ensure self-development. One’s effort and energy to stay focused on attaining an important goal. After identifying a developmental need, it is necessary to review whether one is making necessary improvements periodically.
Leadership starts with yourself. More particularly, it begins together with your mind. By understanding how your intellect works, you’ll lead yourself successfully. By understanding and driving yourself successfully, you’ll be able to understand others and lead them more successfully. And by understanding and driving others more viably, you’ll be able to understand and lead your company more successful. Mindfulness enables leaders to focus on intrinsic motivations and a sense of purpose, enabling high productivity and a more engaging workforce, creating stronger connections and company culture within and beyond your company, and improving company performance and trust.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Banking and Finance
The financial services sector is building on the banking industry. While the financial services sector includes investments, insurance, risk redistribution, and other economic activities, it primarily focuses on direct saving and lending. Financial services have many participants and moving pieces, from credit card issuers and processors to established banks and up-and-coming rivals. Additionally, financial institutions and startups are improving their technology and extending remote services as economic activity becomes increasingly computerized, particularly as consumers decide to manage their finances from home in the wake of the coronavirus outbreak. The use of digital technologies is accelerating within the financial service sector. Cash transactions, in-person consultations with financial advisors, and even utilizing an ATM are all dwindling components of financial services.
Personal, consumer and corporate financial services are the three main categories. These categories include important participants and influencers for businesses and organizations attempting to move up the industry ladder. Consumers generally search for companies that offer personal financial services, such as financial advisors. In addition, customers are searching for banks that allow them to remotely monitor individual accounts and maintain their financial condition via online platforms and mobile apps as money management activities continuously move online. Additionally, younger, tech-savvy customers choose financial institutions that provide personal finance management (PFM) tools. Finally, consumer finance enables customers to buy goods and services by making payments in installments over a predetermined period, from real estate investing to paying for education.
Credit card companies, mortgage lenders, and providers of personal and student loans are some of the major players in the consumer financial services market. Corporate financing refers to all aspects of a company’s financial operations, including funding sources, capital structure, steps taken to boost the organization’s value, and methods used to allocate resources. Accountants, analysts, treasurers, and investor relations professionals are just a few positions in the corporate finance industry that aim to increase a company’s worth.
The financial services sector impacts the influence of digital-savvy consumers, the threat posed by large tech corporations, and the changing views of regulators toward new technology. And the cutting-edge technology will lead you to success in the finance industry, whether you’re an individual looking at wealth management solutions or a CEO wanting to boost your company’s value to shareholders.
No matter how the world markets change, the financial industry will survive. Banking and financial literacy are vital to keeping the business going. Additionally, the financial sector offers many exciting development and growth potentials with the issuance of digital banking licenses and a solid real estate market.
Software and Technology
Software and IT are vital areas driving labor demand in all other industries. This sector includes companies manufacturing electronic devices, software, and computers or creating products and services related to information technology. Software and IT provide a wide range of technology products and services to customers and other companies. Economy, work, and personal life is becoming more digital, networked, and automated. This trend is constantly accelerating. There’s no question that innovation and the businesses that offer it are becoming increasingly crucial in existence. The direct growth of technology and its indirect impact on every company and every aspect of life reveal a robust and growing sector impacting the global economy.
A way to categorize the tech industry is to consider the product’s or service’s intended use. Is it the consumer or a business? Consumer goods could include mobile devices, wearable technology, household appliances, and electronics. On the other hand, companies rely heavily on technology to create enterprise software, streamline their systems, host their databases and store their information – affecting how businesses operate with their staff internally and their customers externally. The advertisement categorizes into five top-level buckets utilizing the traditional approach. The conventional technology categories are software, devices and infrastructure, IT and business services, emerging technologies, and telecom services.
Concurring to later information, the requirements for program designers have expanded. That’s since, as innovation develops and changes, so will the requirements for cybersecurity and innovative program. So, much like IT professionals, companies in the technology business (aka the channel) are starting to think more prominent again, rekindling some of the strategic initiatives and aspirations.
One of the significant noteworthy improvements influencing the industry nowadays is the rise of online marketplaces, which upends the buying preparation and impacts the taking after activities. First, companies and businesses have an online presence that needs to be protected and secured. As a result, they’re proactively safeguarding their business from external and internal threats. Second, cybersecurity is growing as cloud computing marketing rise—digitization for many sectors pushing them to cashless payments and other digital solutions. Third, the technology industry is expanding with innovation, emerging and developing markets.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is progressing to meet new needs and deliver care. The healthcare industry is fundamental to each person’s physical and financial wellbeing. Healthcare experts are crucial to sanctioning and implementing approaches and maintaining the framework proficiently. The HIPPA Act of 1996 is a government law that requires the creation of national benchmarks to ensure touchy persistent wellbeing data from being unveiled without the patient’s consent or information.
Healthcare involves many parties working together. The market supports various workers and technologies from healthcare staffing and administration to providers and patient care. Sectors include health insurance, pharmaceuticals, health administration, and healthcare tech. Services include mental health care, dental care, substance abuse treatment, laboratory and diagnostic care, and physical and occupational therapy. Healthcare levels include primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary care. The five health care facilities include hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, doctor’s offices, urgent care clinics, and nursing homes—two broad categories of health care facilities: public health services and private health facilities. The three types of healthcare providers are primary care, specialty care, and nursing care.
How clinicians deliver patient care and technology in every aspect of medicine has transformed the industry. In addition, integrating medical technologies are changing how hospitals, healthcare centers, and care providers communicate with each other and their patients. For example, electronic health records (EHR) allow patients’ health information in digital format. As a result, their data can be shared with other providers across multiple organizations—improving physician productivity and patient satisfaction.
Healthcare suppliers are leveraging the increment in buyers who need to play a more active part in observing their wellbeing by empowering tech that advances crucial following, early discovery, and illness avoidance. Further persistent checking apparatuses empower a nonstop stream of real-time wellbeing information between patients and their specialists and will account for much of this investment funds. In expansion, be that as it may, healthcare suppliers can use innovation to maintain a strategic distance from pointless specialist visits and expenses.
Telehealth portable innovation and video specialist visits empower a consistent relationship between patients and caregivers. These administrations eradicate the requirement for meaningless specialist visits and make it simpler for patients in rural areas or without straightforward transportation to see a specialist or other healthcare.
As with all computer software, and sensitive data, the main challenge is information security. All health information technology (HIT) applications must have protected databases, patient confidentiality, and privacy. Electronic records can contain sensitive information about patients. Medical devices are becoming increasingly interconnected and integrated with the enterprise network and electronic health records (EHR) and have security vulnerabilities with the potential to be targeted by cyber attackers to gain access to corporate networks.
The focus on gerontology and eldercare is a fast-growing industry in healthcare. It will require stellar nursing and healthcare management systems and staff. Moreover, with the new community hospitals and polyclinics, the public health sectors and the overall industry is bound to expand.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Dallas, TX
In 1841 John Neely Bryan, an attorney, and dealer from Tennessee, established and built the primary cabin (presently reestablished) within the region on the riverbank of the Trinity Stream. Other pilgrims moved into the locale and a town location in 1844. Most likely, the title Dallas is from early pioneer Joseph Dallas or George Mifflin Dallas.
Commercial development began from the railroads in the 1870s. A considerable value was created, with numerous of the city’s retail stores serving the American Southwest. The adjoining communities of East Dallas and Oak Cliff were attached in 1889 and 1903, individually, incredibly growing the city.
Locally produced grain, leather, cotton (grown in the black-clay fields around Dallas), insurance, and oil fed the city’s early growth. The Dallas Cotton Trade in 1907 and, within the early decades of the 20th century, was one of the world’s biggest cotton markets. In expansion, the city was the best producer of cotton-ginning apparatus. So, too, amid the early 20th century, Dallas was a center of nourishment handling and making materials and calfskin items. In addition, an automobile plant and a Federal Reserve System branch bank. Mexican workers contributed to the populace’s development. In 1930 C.M. (“Dad”), Joiner found the extraordinary East Texas oil field, which pulled in speculation and made the city a major center of the petroleum industry. Dallas’ Central Centennial Article (1936), officially recognizing the 100th anniversary of the State of Texas, was one of the nations that benefited the economy during the Great Depression and launched the Great Suburban Shopping Center in 1931.
The city entered a period of remarkable growth during and after World War II when several large aircraft factories were in the area. Electronics and automotive assembly plants followed this. In addition, DFW International Airport, which opened in 1974, attracted businesses to the site and made it an attractive location for corporate headquarters.
Dallas is the fourth biggest catholic city in the U.S., known for its tall eateries and shopping center concentration. High rises like Bank of America Square and Gathering Tower make a vital night horizon. The populace thickness is from a central metropolitan region, reflecting the prevalence of single-family homes (approximately two-thirds of all staying units). In addition, the city is ethnically different.
Dallas’s advanced economy is broad. A worldwide value of the city is the domestic of the Dallas Market Center, one of the world’s biggest discount stock complexes. In expansion, it is the world’s central station of the U.S. Armed force and Discusses Constrain Trade Benefits, giving merchandise and administration to military faculty. Discount and retail exchange combine with administrations (especially commerce, monetary, and wellbeing) to create the spine of the economy. Dallas is the driving managing an account, financial, and exchange center for the Southwest, and a few 6,000 companies have their corporate base center there. The city is also a busy convention center hub of airline services. It is a well-known medical center; the office of the American Heart Association is there, as are the Texas A&M College of Dentistry and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas.
Dallas has one of the country’s most significant concentrations of broadcast communications and high-technology manufacturing and administration companies. The beat innovation areas incorporate computer program generation, computer administrations, equipment, semiconductors, and remote communication gear manufacturing. Nourishment handling, distributing, printing, and publicizing are moreover basic.
The growth rate is consistent with longer-term trends. Dallas Fort-Worth growth has been consistent over the decades. Demographers project that DFW surpasses Chicago to become America’s third-largest metro area. They include a pro-business environment, comparatively low cost of doing business and cost of living, high quality of life, a diverse and well-educated labor pool, and our can-do attitude. DFW’s location and cost advantages have become powerful magnets for global businesses and financial institutions. With a favorable economic climate, Dallas has proven that it is a city where businesses thrive. Globally connected and centrally located, Dallas is the ideal location for business.
The impact this growth will bring will require development to manage current and future resources. Adding thousands of new jobs to the region, developers have millions of square feet under construction to house the growth. More housing and more industrial, office, and retail space to serve the needs of expanding population. Investments in technology and infrastructure upgrades. Economic Development will continue to support existing and prospective businesses and development opportunities that sustain and grow Dallas.
The transformational growth Dallas is heading for will take place gradually. Opportunities abound from great catalyst projects changing the city’s landscape to small-scale neighborhood revitalization. Little by little, the region will stretch its boundaries to remain competitive, innovative, and forward-thinking for future prosperity.

New York, NY
The pilot Giovanni da Verrazzano was the primary pioneer to reach Modern York Narrows in 1524 with the benefit of the French crown. The Algonquins and Iroquois Local Americans possessed the area he named Modern Angoulême. The advantage of the Dutch was Henry Hudson 1609 gave his title to the Hudson Waterway.
The Dutch were the primary Europeans settling within the region, building Fort Nassau in 1614, the immediate European settlement within the range known as New York.
In 1626, Peter Minuit, governor of the Dutch West India Company, bought the island of Manhattan from Native Americans for 24 dollars and founded a New Amsterdam colony. The colony developed a profitable fur trade with the Native American tribes in the region.
In 1674, the Treaty of Westminster, the island of Manhattan, was passed to the English, who renamed it, New York in honor of the Duke of York. A few years later, King James II established the Dominion of New England, comprising all neighboring colonies.
With the British presence, New York became a critical and prosperous commercial port, and in 1754 Colombia University was founded, which is today one of the most prestigious in the world.
Amid the Fight of Brooklyn at the beginning of the American Progressive War, New York was possessed by the British until November 25, 1783. On this date, marked as “Departure Day,” George Washington returned to the city, and the final British strengths cleared out the Joined together States. The Mainland Congress met in New York City beneath the Articles of Union.
On September 13, 1788, the Joined together States set New York City as the primary capital of the U.S. On April 30, 1789, the President of the Joined together States, George Washington, was presented.
Amid the nineteenth century, an innovative improvement proposition called the Commissioners’ Arrange of 1811 extended the city road to Manhattan, and the opening of the Erie Canal, which associated the Atlantic harbor with the endless agricultural markets of the Midwestern, Joined together States and Canada in 1819.
Up until 1898, New York was only Manhattan. Later, the Brooklyn, Queens, The Bronx, and Staten Island districts became part of the city. The five boroughs sit where the Hudson River meets the Atlantic Ocean. The construction of many famous bridges and a Subway in 1904 made the five boroughs.
Despite the effects of the Great Depression, the 1930s saw the building of some of the world’s tallest skyscrapers, including numerous Art Deco masterpieces that are still part of the city’s skyline today. Before and after World War II, vast city areas gave rise to bridges, parks, and parkways. In addition, a post-World War II economic and residential boom with returning veterans and immigration from Europe and vast tracts of new housing in eastern Queens.
With a globally recognizable skyline and 8.4 million people who call it home, New York City is bursting with diversity and excitement. New York is a destination for travelers worldwide, thanks to its appearance in hundreds of books, films, and series. The state is home to museums and art galleries, theatres, and dozens of performing arts centers. The style and tone of the country sit in New York City, which remains the artistic and cultural capital of the country. The home to the fashion industry, theatres on and off Broadway, television programs, broadcast and cable networks, and motion picture films.
The thickly populated Manhattan includes a commercial, money-related and social center. Iconic sites include the Empire State Building, The Statue of Liberty, Radio City Music Hall, United Nations Headquarters, Wall Street, and sprawling Central Park, to name a few. Broadway theater is in neon-lit Times Square. New York remains one of the only populous states and the central universal city within the nation, and its net financial item surpasses that of a modest bunch of countries around the world. Domestic to more Fortune 500 companies than any other state. Since the early 21st century, New York City’s economic policy has improved its business climate by encouraging the building new and expanded corporate facilities and increasing the number of new jobs. The One World Trade Center opened in 2014, and World Trade Center Transportation Center opened in 2016. New York is still a busy port. It is a major automated and money-related center and an imperative visitor goal.
New York City remains for its residents a conglomeration of local neighborhoods that provide them with familiar cuisines, languages, and experiences. The foremost ethnically assorted, religiously changed, commercially driven, famously congested, and, within the eyes of numerous, the main appealing urban center within the nation.
At a record high, New York City will surpass 9 million by 2050, with the fastest growth rate in the Bronx and Brooklyn, as New York continues to be a magnet for people searching for opportunity. As New York City develops, the differences that make it unique. The five boroughs are adding residents, with new population and centers emerging alongside a new economy in formerly commercial and industrial communities. As the population continues to reach all-time highs, new housing construction has reached its highest levels since the 1960s. Adding more than 350,000 residential units since 2000, most of which are along subway lines, reversing historical patterns of sprawl. New York City is adding more units to apartment buildings than ever. This high-density growth is in specific neighborhoods, such as Long Island City, Hudson Yards, and Flushing. In addition, the city has invested billions of dollars in affordable housing, schools, parks, and infrastructure to serve new and existing residents. New York’s growing population and the strong economy are foundational to meeting aspirations for the future. They will provide opportunities to improve the well-being of all New Yorkers in the decades to come.
New York is ranked 50th in the United States for its economic outlook. The state placed last on the American Legislative Exchange Council’s annual ranking for the seventh straight year, largely thanks to its high corporate and personal income taxes and hefty debts. In addition, public safety and policy challenges continue to affect central business districts and boroughs.
Economic growth in the city is supported by a dynamic region, with jobs, commerce, and residential neighborhoods supporting the nation’s largest metropolitan economy, with a $1.9 trillion gross domestic product. The city’s significant role in supporting regional growth demonstrates the need for continued regional partnerships. As regional collaboration and partnership surrounding New York City continue, it will add workers and residents, leading to broad implications for the transit system, housing strategies, and overall economic strength as New York City evolves.

Los Angeles, CA
Los Angeles, CA, was originally settled by indigenous tribes, including the Chumash and Tongva hunter-gatherers.
Portuguese mariner Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo was the primary European investigating the locale in 1542. Still, it wasn’t until 1769 that Gaspar de Portolá established a Spanish outpost in the Los Angeles area.
The outpost grew more significant in 1781 when a group of 44 European, African, and Native American settlers traveled from northern Mexico to establish a farming village on the banks of the Rio Porciúncula. The Spanish governor named the settlement “The Town of Our Lady the Queen of the Angels of Porciúncula.”
Spanish missions in the area, including Mission San Fernando, named for Ferdinand III of Spain, and Mission San Gabriel Arcángel, were founded by Junipero Serra. In 1821, Mexico declared independence from Spain, and all of California fell under Mexican control.
In 1846, the Mexican American War annexed California two years later. Gold was found within the Sacramento Valley in 1848, lighting the Gold Surge. The crowds of ‘49ers running to California depended on meat and other nourishments from ranches and ranches within the Los Angeles range.
In 1881, after a long time of America’s “manifest destiny” development, Southern Pacific Railroad completed a track into Los Angeles, connecting the city with the rest of the Joined together States, sparking a flurry of land speculation with promises of lush orange groves and sun.
L.A. looked to the Owens Valley for water. So after a long time of backroom bargains, bribery, and other shenanigans, director William Mulholland opened the Los Angeles Water passage in 1913 with the words, “There it is. Take it.”
D.W. Griffith was among the primary directors to film within the Los Angeles zone, pulled in by the mellow climate and low-wage, non-union laborers. By 1913, Cecil B. de Mille was filming motion pictures within the area. Before long, the little town known as Hollywood was added by Los Angeles, making the city the center of the excitement.
The city is additionally a center of the oil industry: Edward Doheny—notorious for his association with the Tea kettle Arch Scandal-hit a gusher near downtown Los Angeles in 1892, and inside many a long time, more than 500 oil wells were pumping over the L.A. bowl.
The Port of Los Angeles employed shipbuilding and warplane manufacturing workers during World War II.
Los Angeles is a city located in a county named Los Angeles County, southern California, which encompasses the city. It contains some 90 other incorporated cities, including Beverly Hills, Pasadena, and Long Beach. The most crowded city and metropolitan region within the nation. The city sprawls across a broad coastal plain between mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Nearly half of the county is mountain chains—most of them running east-west—with a dynamic history of earthquakes, firestorms, and mudslides. The massive and sprawling San Gabriel and San Bernardino mountains are to the north and northeast. Stretching in front of them—and more or less in parallel lines from west to east—are the Santa Monica Mountains, Puente Hills, Repetto Hills, and San Jose Hills. A magnificent natural feature of Los Angeles County is the coastline’s distinctive beaches, which attract millions annually.
Los Angeles is developing yearly, and its population has expanded by 0.54%, with a population of 3.9 million in 2010. The average household income is $96,416, with a poverty rate of 16.89%. The median rental cost in recent years is $1,523 per month, and the median house value is $670,700. The median age in Los Angeles is 35 years. Los Angeles is an ethnically diverse county in the United States. In addition, Los Angeles is an incredibly diverse city, home to people from over 140 countries who speak 224 languages.
Los Angeles is a dynamic economy in the world, with a fast-growing and immense high-tech industry, world-leading creative economy, tremendous strength in aerospace and advanced transportation, the nation’s most extensive manufacturing, international trade industry, and venture capital investment in startups.
With over a dozen major industries, the LA region is also known for innovation as creative collisions occur where industries overlap, driving new business concepts and entirely new sectors, making LA the creative capital of the nation. All this success is due to a highly diverse, skilled workforce and visionaries reinventing everything from transit to translational medicine.
Los Angeles is constantly evolving to offer the most cutting-edge experiences. The transformation is in full swing as the city prepares to host some of the most high-profile events in the world. LA is seeing average annual job growth of 0.5% over the five years to 2027, in line with the US average. Industries expected to contribute to development include social services with 34% of the total jobs, restaurants and drinking places, and arts and entertainment. In addition, small businesses may find creating or expanding an online presence necessary in the new e-commerce age. LA government should ensure the advancement of economic growth, sustainability, resiliency, and equity in local communities.
LA is moving toward a greener future and friendlier to pedestrians, metro users, and bicyclists. As a result, various development projects, particularly downtown and Hollywood, are becoming denser and vertically built. These projects preserve historic architecture while adding apartments, parks, retail, and entertainment. In addition, expanding rail and rapid bus routes across the county and constructing dense, multiuse development alongside those corridors.
The Los Angeles housing market continues as the most desirable market for investors across the globe. As a result, global attention is increasing activity across LA, which bodes incredibly well for everyone looking to participate in the marketplace Investors have noticed the city’s past performance and appear confident trends will continue for the foreseeable future.

Tokyo, Japan
The history of Tokyo started 400 years ago. Tokyo was initially named Edo, and Tokugawa Ieyasu established Tokugawa Shogunate. It grew into a massive city by the nineteenth century. During this time, the Emperor resided in Kyoto, the nation’s formal capital. The Edo Period lasted for 260 years until the Meiji Restoration in 1868 when the Tokugawa Shogunate ended. Then, the Emperor moved to Edo and renamed it Tokyo, becoming Japan’s capital.
From 1868 to 1912 the Meiji era, Japan began its avid assimilation of Western civilization. From 1912-1926 during the Taisho era, urban work increased, and educational standards improved. Performing expressions such as theater and musical drama flourished.
The Showa era started in a gloomy mood (1926-1989). Nevertheless, Japan opened it, to begin with, a tram line between Asakusa and Ueno in 1927, and in 1928 the 16th standard races for the House of Agents of the Slim down were held for the primary time taking after the sanctioning of all-inclusive male suffrage. In 1931 Tokyo Air terminal was completed at Haneda, and in 1941 the Harbour of Tokyo opened. By 1935 the inhabitant populace of Tokyo had developed to 6.36 million.
The 1941 Pacific War significantly impacted Tokyo. Tokyo-fu (prefecture) and Tokyo-shi (city) ended for war-time efficiency. The area and city merged to form the Metropolis of Tokyo in 1943. Tokyo metropolitan administrative system and a governor were appointed. In May 1947, Seilchiro Yasui became Governor, and the new Constitution of Japan and the Local Autonomy Law took effect. In August 1947, the present 23 special-ward system began in Tokyo.
The 1950s were a time of continuous recovery for the country. In 1953 Tv broadcasting started, and Japan joined the United Nations. Economic recovery with the procurement boom arose from the Korean War outbreak in 1950. The war led Japan to enter a period of rapid economic growth in the 1960s.
Tokyo is the focus of the vast metropolitan area called Greater Tokyo, Japan’s most significant urban and industrial agglomeration. Tokyo is the top transportation hub for Japan, as well as an essential international traffic center. In addition, Tokyo is Japan’s prominent cultural center. The Tokyo National Museum in Ueno Park displays the art and history of Japan and Asia.
The metropolitan area is Japan’s largest industrial, commercial, and financial center. Many domestic and international financial institutions and businesses are in central Tokyo. In addition, the city is an important wholesale center, where goods from all parts of the country and the world distribute. The country’s leading manufacturing region is in the Keihin Industrial Zone. They dominate light and labor-intensive industries, printing, publishing, and electronics.
The Imperial Palace, the emperor of Japan’s home, lies at the city’s heart. Art and science museums are close by, and museums are throughout the city: theatrical works, symphony, operas, dance, and music. The University of Tokyo heads a long list of major universities and colleges in the metropolitan area.
The colorful Marunouchi locale, the financial center, and a major center of Japanese commerce action are east of and adjoining the Majestic Royal residence. The Kasumigaseki area is south of the royal residence, containing numerous national government workplaces. West of that’s Nagatacho, where the National Count calories Building (parliament). Tokyo has no single central trade area but the city’s urban centers, as a rule around railroad stations, where office stores, shops, inns, office buildings, and eateries.
The brightly lit Ginza shopping district is world-renowned in the eastern part of the central city. Northeast of the Imperial Palace, the Kanda district is noted for its many universities, bookstores, and publishers. In addition, Tokyo contains exquisite Japanese gardens.
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government is working to develop specific activities, counting framework updates, measures for the environment, and the advancement of culture. Becoming the world’s best city where there is a balance between economic affluence and quality of life, and anyone can fully enjoy life.
The Metropolitan Government defined a collection of plans for 2030: Tokyo’s Long-Term Procedure. The center of this procedure is the concept of “maintainable recuperation.” Not just return to the status quo. They are instead creating a sustainable recovery and achieving a better future. The symbolic project will lead the “Future Tokyo” strategy, the “Tokyo Bay eSG Project.” In Japanese, “onkochishin” means “revisiting the old to learn a new.” In history, there are hints dealing with Tokyo’s new challenges.
They were looking back on the history of Tokyo, two famous people, Shibusawa Eiichi and Goto Shinpei. These two individuals share that their actions have left a “sustainable” Tokyo. Carrying on the spirit of their predecessors, they have added new meaning to the original concept of “eSG.” The lower-case “e” is for words like “environment,” “economizing,” and “era.” The upper-case “S” is Shibusawa’s last name, while the “G” represents Mayor Goto. Put together. They make “eSG.” The “Tokyo Bay eSG Project” will focus on the Tokyo Bay Area. This location has two areas with great potential; is Tokyo Waterfront City and a vast parcel of newly reclaimed land. The project aims to utilize this potential to create a sustainable city that combines nature and comfort.
Three core philosophies make up the image of this sustainable future city:
1. Create a human-centered space. One surrounds abundant greenery, where you can feel the water close by, and is rich in biodiversity.
2. A city continuously generates new value by gathering the world’s best human resources and knowledge.
3. It is a vital city that overcomes the threat of infectious disease and is resilient to natural disasters.
The four strategies to realize this plan are discovering net zero emissions and creating a city full of water and greenery, introducing cutting-edge digital technology, and implementing projects utilizing green finance. The fourth strategy is enhancing transportation networks for a sustainable city.
Delhi, India
Delhi, the capital of India, has a solid historical background. It ruled the most powerful rulers in the Indian record.
The chronology of the metropolis is as old as the epic Mahabharata. Then, the village was known as Indraprastha. Later, eight more cities came alive adjacent to Indraprastha: Lal Kot, Siri, Dinpanah, Quila Rai Pithora, Ferozabad, Jahanpanah, Tughlakabad, and Shahjahanabad.
Delhi’s political turmoil for over five centuries is because the Mughals ruled it.
In 1192 the legions of the Afghan warrior Muhammad of Ghori captured the Rajput town, and the Delhi Sultanate was established (1206). However, the invasion of Delhi by Timur in 1398 ended the sultanate; the Lodis, the last of the Delhi sultans, gave way to Babur, who, after the battle of Panipat in 1526, founded the Mughal Empire. The early Mughal emperors favored Agra as their capital, and Delhi became their permanent seat only after Shah Jahan built (1638) the walls of Old Delhi.
From Hindu Kings to Muslim Sultans, the reins of the city kept shifting from one ruler to another. The city’s soils smell blood, sacrifices, and love for the nation. The old ‘Havelis’ and towers from the past stand silent, but their silence also speaks volumes for their owners and people who lived here centuries back.
In the year 1803 AD, the city came under British rule. In 1911, the British shifted their capital from Calcutta to Delhi. It again became the center of all the governing activities. But, the city has a reputation for overthrowing the occupants of its throne. It included the British and the current political parties that have had the honor of leading free India.
After independence in 1947, New Delhi has officially declared the Capital of India.
Modern Delhi, popularly known as Lutyens’ Delhi, is a striking contrast to Old Delhi concerning architecture, building materials, and layout. However, Modern Delhi dates back over a century. New Delhi, designed by Lutyens, has wide-open lanes, avenues, and buildings worth traveling across the globe.
Tourist attractions of Modern Delhi are India Gate, Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament House, Birla Temple, and North and South Block. In addition, museums, temples, and memorials provide an understanding of Delhi. At the National Museum in Delhi, you can view the rich historical past of India. National Rail Museum documents the history of Indian railways, including the first steam engine from Thane, Mumbai, in 1853, marking the beginning of Indian Railways. Modern Delhi has some famous temples of Modern India that are known for their religious significance and experimental designs that challenge conventional architectural standards.
Iskon Temple boasts a vegetarian restaurant, library, animatronics center, and an upcoming museum, besides the prayers and meditation facilities. In addition, the newly built Akshardham temple is a popular destination for tourists and Delhites. The temple is on the Yamuna River banks.
Home to memorials of famous freedom fighters and national leaders. Raj Ghat, Shanti Van, and Shakti Sthal. The resting place of Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Indira Gandhi.
The capital has a charming mix of the old and new world. On one side, you can see Old architectural sites, buzzing streets, and exotic markets. On the other side, Delhi has magnificent Malls, swan-by bridges, modern, opulent high-rise buildings, and lots of greenery.
Within eight years, Delhi will surpass Tokyo to become the largest megalopolis in the world, making it the epicenter of a global phenomenon. Two-thirds of people will live in metropolitan areas of Dehli by 2050.
Every two decades or so, the official planning organization of Delhi has developed a master plan to guide the city’s future development. However, architects Delhi’s strategy has remained mostly on paper. Understanding Delhi’s present and future require looking at the ecosystem nearby.
Delhi, known as the National Capital Region (N.C.R.), the population has ballooned, growing from 15 million to 19 million. Yet, even as the megacity grows, connections to rural areas remain vital.
Delhi’s new Master Plan for 2041 envisions a megacity with tall buildings, affordable housing units, an economical start-up hub, and ample green space to replace slums.
Delhi’s expansion is driving an informally employed workforce, an estimated 70 percent. When most jobs are informal, the area has to accommodate the daily flux of people moving between job positions, shelters, offices, and shops.
Program Benefits
Human Resources
- Cohesive workforce
- Leadership development
- Improved moral
- Team effectiveness
- Reduced turnover
- Performance improvement
- Employee loyalty
- Problem solving
- Improved safety
- Employee development
Management
- Ownership thinking
- Reduced uncertainty
- Process improvement
- Consistent leadership
- Shared vision
- Strategic direction
- Client satisfaction
- Revenue growth
- Team synergy
- Performance improvement
Marketing
- Brand Loyalty
- Customer Retention
- Market Leader
- Leadership effectiveness
- Brand Sustainability
- Messaging clarity
- Team collaboration
- Client engagement
- Improve communication
- Problem-solving culture
Testimonials

Testimonial 1
Content here…

Testimonial 2
Content here…

Testimonial 3
Content here…

Testimonial 4
Content here…

Testimonial 5
Content here…
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.















