Financial Management

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Financial Management is provided by Dr. Norman Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Dr. Norman is a 21-year United States Army veteran and Bronze Star recipient with over 10 years of financial experience. He possesses a comprehensive background in financial management, cost reduction strategies, and organizational leadership, and has managed assets of $400M. In addition to creating and executing strategies to achieve the financial objectives of various organizations, he has also administered budgets of $500M and ensured costs stayed 15% under-budgeted expectations.
Dr. Norman identifies issues and develops financial strategies to deliver more effective stewardship of assets. In one case, he identified opportunities to minimize operational expenses, resulting in a 27% decrease in overhead.
Dr. Norman is skilled in motivating and empowering others to surpass performance requirements and develop professionally. His advanced degree in Financial Management and certifications further demonstrate his vast knowledge and dedication to continuing to learn. Dr. Norman’s leadership experience enables him to seamlessly fit into a wide variety of organizations and help them grow.
To request further information about Dr. Norman through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Financial Management
Financial management is a critical aspect of any organization’s operations, regardless of its size, industry, or nature. It encompasses the planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of an organization’s financial resources to achieve its objectives effectively and efficiently. Financial management involves making strategic decisions and implementing policies and procedures to manage funds, assets, liabilities, and investments in a way that maximizes value and ensures financial stability.
One of the primary goals of financial management is to ensure the availability and optimal utilization of funds. This involves budgeting and forecasting to estimate financial needs, allocating resources appropriately, and monitoring cash flows to maintain liquidity. By effectively managing funds, organizations can meet their financial obligations, invest in growth opportunities, and navigate economic uncertainties.
Financial management involves the management of assets and liabilities. It includes determining the optimal mix of short-term and long-term funding sources to finance the organization’s operations and investments. It also involves managing inventory levels, accounts receivable, and accounts payable to optimize working capital and maintain a healthy cash conversion cycle. By efficiently managing assets and liabilities, organizations can improve profitability, reduce financing costs, and enhance their overall financial health.
Another key aspect of financial management is capital budgeting and investment decision-making. Organizations must evaluate investment opportunities, such as capital projects, acquisitions, or new product development, to allocate resources effectively and generate long-term value. Financial managers employ techniques such as discounted cash flow analysis, return on investment (ROI), and net present value (NPV) to assess the feasibility and profitability of investment projects. By making informed investment decisions, organizations can allocate resources to projects that offer the highest returns and align with their strategic objectives.
Risk management is an integral part of financial management. Financial managers analyze and assess various types of risks, such as credit risk, market risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk, and develop strategies to mitigate them. This involves implementing internal controls, insurance coverage, and hedging techniques to protect the organization’s financial interests. By effectively managing risks, organizations can minimize potential losses, protect their reputation, and maintain financial stability.
Financial management also encompasses financial reporting and analysis. It involves the preparation and analysis of financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, to provide accurate and timely financial information to stakeholders. Financial managers interpret financial data, assess performance, and communicate financial results to management, investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities. Sound financial reporting and analysis enable stakeholders to make informed decisions, evaluate the organization’s financial position, and assess its future prospects.
In addition to financial reporting, financial management involves compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Financial managers ensure that the organization adheres to accounting standards, tax regulations, and other relevant laws. They also facilitate audits and coordinate with external auditors to ensure the accuracy and transparency of financial records. Compliance with regulations and standards promotes transparency, accountability, and trust in the organization’s financial practices.
Financial management is closely linked to strategic planning and decision-making. Financial managers work alongside top management to develop financial strategies that align with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. They provide financial analysis, scenario planning, and forecasts to support strategic decision-making. By integrating financial considerations into strategic planning, organizations can allocate resources effectively, capitalize on growth opportunities, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
Technology has significantly transformed financial management practices. Financial managers leverage advanced financial software, data analytics tools, and automation to streamline financial processes, enhance accuracy, and improve decision-making. Technology enables real-time access to financial information, facilitates financial modeling, and supports efficient financial reporting and analysis.
Ethics and integrity are paramount in financial management. Financial managers are responsible for upholding ethical standards, ensuring transparency, and avoiding conflicts of interest. They must act in the best interest of stakeholders and make decisions that are consistent with the organization’s values and ethical guidelines.

Early Emphasis on Financial Management
Emphasizing good financial management practices from the early stages of a company’s operations is crucial for several reasons:
Financial Stability: Good financial management helps establish a solid foundation for financial stability. By implementing effective financial management practices early on, companies can establish healthy cash flow patterns, manage expenses, and allocate resources efficiently. This sets the stage for long-term financial stability, enabling the company to weather economic uncertainties and sustain operations.
Strategic Decision-Making: Sound financial management provides the necessary data and analysis to support strategic decision-making. From the outset, companies need to make critical choices regarding investments, growth opportunities, and resource allocation. Good financial management practices ensure that decision-makers have accurate and timely financial information, enabling them to make informed choices that align with the company’s goals and maximize shareholder value.

Case Study: Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble is a multinational consumer goods company that exemplifies sound financial management practices. The company has a disciplined approach to managing its financial resources, emphasizing cost control, efficient supply chain management, and strategic product portfolio management. Procter & Gamble’s rigorous financial discipline allows it to invest in innovation, research, and marketing initiatives while consistently delivering solid financial performance and shareholder value.
Capital Acquisition and Investment: Companies often require external capital to support growth and expansion. Good financial management enhances a company’s ability to attract investors, secure loans, or raise funds through equity financing. Well-documented financial statements, transparent financial reporting, and strong financial performance are vital in gaining the trust and confidence of potential investors and lenders. Early emphasis on financial management prepares companies for future capital acquisition and investment opportunities.
Risk Mitigation: Effective financial management allows companies to identify and mitigate risks early on. By implementing internal controls, conducting regular financial analyses, and monitoring key financial indicators, companies can identify potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them. Early identification and management of risks can help prevent financial crises, reduce potential losses, and protect the company’s reputation.
Compliance and Governance: Companies must comply with legal and regulatory requirements from the outset. Putting emphasis on good financial management practices early helps establish a culture of compliance and strong governance. This includes adhering to accounting standards, tax regulations, and reporting obligations. By establishing robust financial controls and reporting mechanisms, companies can build a reputation for transparency, ethics, and integrity.
Scalability and Growth: As companies grow, the need for effective financial management becomes even more critical. Implementing good financial management practices early ensures that the company has a strong financial infrastructure in place to support scalability and growth. This includes establishing financial systems and processes, developing financial policies and procedures, and building a skilled finance team. By proactively managing finances, companies can adapt to growth, seize opportunities, and avoid financial bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Investor and Stakeholder Confidence: Sound financial management practices early on help instill confidence in investors and stakeholders. Demonstrating financial discipline, transparency, and accuracy in financial reporting fosters trust and builds credibility. This can attract investors, partners, customers, and employees who are more likely to engage with a company that exhibits strong financial management capabilities.

The Benefits of Robust Financial Management
Financial management is an essential function for companies of all sizes and across industries. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the financial health, stability, and growth of an organization. Here are several key reasons why companies need to have robust financial management practices in place.
Financial Planning and Budgeting: Financial management allows companies to develop comprehensive financial plans and budgets. It involves forecasting revenues, estimating costs, and setting financial targets and milestones. By creating a financial roadmap, companies can align their resources, set priorities, and allocate funds efficiently. Financial planning enables companies to make informed decisions, track progress, and take corrective actions if needed.
Resource Allocation: Financial management helps companies allocate their resources effectively. It involves evaluating investment opportunities, assessing risks, and making informed decisions about capital allocation. By optimizing resource allocation, companies can fund projects that generate the highest returns and align with their strategic goals. Effective resource allocation enhances operational efficiency, promotes growth, and maximizes shareholder value.

Case Study: Amazon
Amazon is known for its meticulous financial management practices, contributing to its remarkable growth and dominance in the e-commerce industry. The company has demonstrated a keen focus on managing cash flow and working capital efficiently. Amazon’s sophisticated inventory management system enables it to optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and deliver products quickly to customers. Additionally, the company’s investments in cutting-edge logistics infrastructure, such as fulfillment centers and delivery networks, have been critical to its success in meeting customer expectations and driving revenue growth.
Cash Flow Management: Cash flow management is a critical aspect of financial management. Companies must monitor their cash inflows and outflows to ensure sufficient liquidity. Effective cash flow management enables companies to meet their financial obligations, pay vendors and employees, and invest in growth opportunities. It also helps companies anticipate and mitigate cash flow challenges, such as seasonal fluctuations or unexpected expenses.

Risk Management: Financial management involves identifying, assessing, and managing financial risks. Companies face various risks, such as market volatility, credit risks, interest rate fluctuations, and operational risks. Effective risk management practices, including diversification, hedging strategies, and insurance coverage, help companies mitigate potential losses and protect their financial well-being. Financial management enables companies to make informed risk-reward decisions and safeguard their assets and investments.
Capital Structure and Financing: Financial management involves determining the optimal capital structure for a company. It entails deciding the right mix of debt and equity financing to fund operations and investments. Financial managers evaluate various financing options, such as bank loans, bond issuances, or equity offerings, considering factors like cost, risk, and the company’s capital needs. By optimizing the capital structure, companies can manage their financing costs, balance risk and return, and support long-term growth.
Financial Reporting and Compliance: Financial management ensures accurate and transparent financial reporting. Companies must adhere to accounting standards, regulatory requirements, and industry-specific guidelines when preparing financial statements. Effective financial management practices facilitate the timely and accurate preparation of financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Compliance with financial reporting standards and regulations enhances transparency, builds trust with stakeholders, and facilitates access to capital markets.
Decision-Making Support: Financial management provides crucial information and analysis to support decision-making at all levels of an organization. Financial managers generate financial reports, conduct financial analysis, and provide insights into the company’s financial performance and trends. These insights help management make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment opportunities, pricing strategies, and cost management. Financial management ensures that decisions are grounded in financial realities and align with the company’s financial objectives.
Investor and Stakeholder Relations: Financial management plays a vital role in maintaining positive relations with investors and stakeholders. Investors, lenders, and shareholders rely on accurate and transparent financial information to evaluate the company’s performance and prospects. Effective financial management practices ensure clear communication of financial results, provide insights into the company’s financial position, and build trust and confidence with stakeholders. Strong investor and stakeholder relations support access to capital, strategic partnerships, and the overall reputation of the company.
Performance Monitoring and Evaluation: Financial management allows companies to monitor and evaluate their financial performance. It involves comparing actual financial results against budgeted targets, analyzing variances, and identifying areas for improvement. Financial performance indicators, such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and return on investment, help companies assess their financial health, efficiency, and competitiveness. Regular performance monitoring enables companies to take corrective actions, adapt strategies, and drive continuous improvement.
Long-Term Financial Sustainability: Financial management promotes long-term financial sustainability for companies. By effectively managing resources, controlling costs, and optimizing financial decisions, companies can enhance their resilience and adaptability to market changes. Financial management practices support the company’s ability to weather economic downturns, invest in innovation, and seize growth opportunities. It fosters a sustainable business model that generates long-term value for shareholders, employees, and other stakeholders.

Case Study: Apple
Apple is widely regarded as a company with exceptional financial management. The company’s success can be attributed to its ability to generate and effectively utilize substantial cash reserves. Apple has strategically managed its cash flow, allowing it to invest heavily in research and development, acquire innovative companies, and introduce groundbreaking products to the market. By carefully managing its financial resources, Apple has been able to navigate industry challenges, maintain profitability, and create significant value for its shareholders.

The Risks of Poor Financial Management
When companies don’t have effective financial management practices in place, they expose themselves to various risks that can negatively impact their financial health, stability, and growth. Here are some key risks that companies may face without proper financial management:
Cash Flow Problems: Inadequate financial management can lead to cash flow problems, such as insufficient funds to cover expenses or meet financial obligations. Companies may struggle to pay suppliers, meet payroll, or invest in growth opportunities. Cash flow problems can hinder operations, damage relationships with stakeholders, and even lead to insolvency.
Financial Fraud and Mismanagement: Without robust financial management controls and oversight, companies are at risk of financial fraud and mismanagement. Internal control weaknesses, lack of segregation of duties, or inadequate monitoring can create opportunities for fraud and embezzlement. Mismanagement of financial resources can result in misallocation of funds, ineffective cost control, and poor decision-making.
Poor Financial Planning: Inadequate financial planning can lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and financial instability. Without proper forecasting, budgeting, and resource allocation, companies may struggle to prioritize investments, optimize their capital structure, or respond to changing market conditions. Poor financial planning can also hinder the company’s ability to access financing or attract investors.
Excessive Debt and Financial Leverage: Ineffective financial management can result in excessive debt and over-reliance on debt financing. Companies that do not carefully manage their debt levels may face challenges in servicing their debt obligations, especially during economic downturns or periods of high interest rates. Excessive debt can also limit the company’s flexibility and increase its vulnerability to financial shocks.
Inefficient Working Capital Management: Poor management of working capital, including inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, can impact a company’s liquidity and profitability. Companies may face issues such as excessive inventory levels, extended payment terms, or delayed customer payments. Inefficient working capital management can tie up valuable resources, increase financing costs, and hinder cash flow.
Lack of Risk Management: Inadequate risk management practices can leave companies exposed to various financial risks, such as market volatility, credit risks, operational risks, and legal and regulatory risks. Failure to identify, assess, and mitigate risks can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and non-compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Companies need effective risk management strategies and controls to navigate uncertainties and protect their financial interests.
Inaccurate Financial Reporting: Without proper financial management practices, companies may face challenges in preparing accurate and transparent financial reports. Inaccurate financial reporting can erode stakeholders’ trust, hinder access to capital markets, and potentially lead to legal and regulatory consequences. It can also prevent management from making informed decisions and impede the company’s ability to attract investors or secure financing.
Lack of Strategic Financial Decision-Making: Effective financial management is essential for making informed strategic decisions. Without proper financial analysis, budgeting, and forecasting, companies may make poor investment choices, pursue unviable projects, or miss out on growth opportunities. Inadequate financial decision-making can result in underutilized resources, wasted investments, and loss of competitive advantage.
Lack of Compliance and Legal Consequences: Inadequate financial management practices can expose companies to legal and regulatory non-compliance. Failure to adhere to accounting standards, tax regulations, or reporting requirements can lead to penalties, fines, legal disputes, or reputational damage. Companies must ensure proper financial governance, internal controls, and compliance monitoring to mitigate these risks.
Loss of Stakeholder Confidence: Poor financial management practices can undermine stakeholders’ confidence in the company’s financial stability, transparency, and long-term prospects. Shareholders, investors, lenders, and customers may lose trust in the company, leading to a decline in share value, difficulty in attracting capital, or loss of business relationships.
In conclusion, companies that neglect effective financial management practices expose themselves to various risks that can impact their financial stability, growth, and reputation. Cash flow problems, financial fraud, poor financial planning, excessive debt, inefficient working capital management, lack of risk management, inaccurate financial reporting, strategic decision-making challenges, non-compliance, and loss of stakeholder confidence are among the key risks companies face without proper financial management. Implementing robust financial management practices is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure a company’s long-term financial health and success.
Curriculum
Financial Management – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Estimating Capital Requirements
- Part 1 Month 2 Determining Capital Structure
- Part 1 Month 3 Estimating Cash Flows
- Part 1 Month 4 Carrying out Investment Decisions
- Part 1 Month 5 Allocating Surplus
- Part 1 Month 6 Deciding on Additional Finance li>
- Part 1 Month 7 Negotiating for Additional Finance
- Part 1 Month 8 Checking for Company’s Financial Performance
- Part 1 Month 9 Maximize Company’s Profits
- Part 1 Month 10 Ensuring Compliance
- Part 1 Month 11 Framing Financial Policies
- Part 1 Month 12 Risk Management Strategies
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Financial Management corporate training program.
Financial Management – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Estimating Capital Requirements – estimating capital needs such as fixed capital requirements and working capital needs to avoid over-capitalization or under-capitalization.
- Part 1 Month 2 Determining Capital Structure – Ensure a balance between borrowed capital and owned capital. Too much owned capital results in fewer dividends and too much borrowed capital results in too much interest being paid.
- Part 1 Month 3 Estimating Cash Flows – Estimating the future sales of the business through sales forecasting as well as future business expenses
- Part 1 Month 4 Carrying out Investment Decisions – Ensures that cash is invested properly such as investing short-term cash in working capital and long-term cash on purchasing fixed assets.
- Part 1 Month 5 Allocating Surplus – Deciding on the division of the profits earned by the company among the shareholders, savings or retained earnings, and giving a bonus to the employees.
- Part 1 Month 6 Deciding on Additional Finance – Decides on whether additional finance needed for modernization, diversification or expansion would be raised from selling shares, debentures, loans from financial institutions, or from fixed deposits from the public.
- Part 1 Month 7 Negotiating for Additional Finance – Negotiating with bank managers to give loans to the company either short-term loans or long-term loans.
- Part 1 Month 8 Checking for Company’s Financial Performance – Compares the company’s financial performance with the established standards and finds ways of improving them.
- Part 1 Month 9 Maximize Company’s Profits – Work to decrease the cost of goods sold by analyzing the cost of materials used in production.
- Part 1 Month 10 Ensuring Compliance – Ensures that the state, federal, and regulations guiding the industry are met.
- Part 1 Month 11 Framing Financial Policies – Frames financial policies for cash control, borrowing, and lending: i. Financial Statement Analysis, ii. Mergers and Acquisitions
- Part 1 Month 12 Risk Management Strategies – Discuss the importance of risk management in finance and its impact on a company’s stability and success. Introduce various risk management techniques, such as diversification, hedging, insurance, and financial derivatives. Teach participants how to identify and analyze financial risks and implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
Methodology
Financial Management
When a company decides to invest in financial management, it typically follows a structured approach to ensure effective implementation and integration of financial management practices. Here are the key steps involved in approaching an investment in financial management:
Assess Current Financial Management Practices: The company assesses its existing financial management practices, systems, and capabilities. This includes evaluating financial reporting processes, budgeting and forecasting methods, risk management frameworks, and internal control systems. By understanding the current state of financial management, the company can identify gaps, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
Define Financial Management Objectives: The company establishes clear objectives for its financial management efforts. These objectives may include improving cash flow management, enhancing financial reporting accuracy and transparency, optimizing resource allocation, implementing robust risk management practices, or achieving regulatory compliance. Defining objectives helps guide the investment in financial management and provides a framework for measuring success.
Identify Key Areas for Improvement: Based on the assessment of current practices and the defined objectives, the company identifies specific areas for improvement within its financial management processes. This could involve enhancing financial reporting capabilities, implementing budgeting and forecasting tools, strengthening internal controls, investing in technology infrastructure, or developing risk management frameworks. The focus is on addressing the gaps identified and aligning improvements with the company’s objectives.
Develop an Implementation Plan: The company creates a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps, timelines, resources, and responsibilities for investing in financial management. The plan includes specific actions to be taken, such as software or system upgrades, process redesign, staff training, or hiring additional financial expertise. It ensures a structured approach to the investment and allows for effective project management and monitoring.
Allocate Resources: The company allocates the necessary resources to support the investment in financial management. This includes budgeting for any upfront costs, such as software licenses or consultant fees, as well as ongoing investments in staff training, technology infrastructure, or external expertise. Adequate resource allocation ensures that the company can implement the necessary changes and sustain the improvements in financial management practices over the long term.
Implement Changes and Enhancements: The company executes the implementation plan, making the necessary changes and enhancements to its financial management processes, systems, and controls. This may involve implementing new financial software or upgrading existing systems, redesigning reporting templates, establishing new risk management frameworks, or improving budgeting and forecasting capabilities. Effective change management practices, such as clear communication, stakeholder engagement, and training, are crucial during this phase.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance: After implementing the changes, the company closely monitors and evaluates the performance of the enhanced financial management practices. Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics are established to measure the effectiveness of the improvements. Regular monitoring allows the company to identify any issues, address emerging challenges, and make adjustments if necessary. It also provides insights into the impact of the investment on financial outcomes, risk mitigation, and overall organizational performance.
Continuous Improvement: Financial management is an ongoing process, and companies should continuously seek opportunities for improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating financial management practices, staying updated on regulatory changes, incorporating feedback from stakeholders, and adapting to evolving business needs. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, the company can ensure that its financial management practices remain effective and aligned with its objectives.
In summary, a company approaches investing in financial management by assessing current practices, defining objectives, identifying areas for improvement, developing an implementation plan, allocating resources, implementing changes, monitoring performance, and embracing continuous improvement. This structured approach helps ensure a successful investment in financial management, enhancing the company’s financial health, stability, and growth.

The Initial Approach
Leaders play a crucial role in making a plan for achieving financial management in their company. Here are the key steps leaders can take to develop a plan for financial management:
Define Financial Management Goals: Leaders need to establish clear and measurable financial management goals for the company. These goals should align with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. Examples of financial management goals may include improving cash flow, increasing profitability, reducing debt levels, optimizing working capital, or enhancing financial reporting accuracy. Clear goals provide a framework for planning and guide decision-making throughout the financial management process.

Assess Current Financial Management Practices: Leaders should assess the current state of financial management practices within the company. This includes evaluating existing financial systems, processes, controls, and reporting capabilities. The assessment helps identify strengths and weaknesses in the company’s financial management approach and serves as a foundation for determining areas that require improvement.
Identify Key Areas for Improvement: Based on the assessment, leaders identify specific areas within the financial management function that need improvement. This could involve streamlining financial processes, implementing new financial software, enhancing reporting and analysis capabilities, strengthening internal controls, or developing risk management frameworks. The focus should be on addressing the gaps between current practices and the desired state of financial management.
Set Actionable Objectives: Leaders set actionable objectives that outline the steps required to achieve the identified areas of improvement. Objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, an objective could be to implement a new financial management software within six months or to establish a quarterly financial reporting process by the end of the fiscal year. Setting clear objectives helps guide the planning and execution of financial management initiatives.
Allocate Resources: Leaders need to allocate the necessary resources to support the financial management plan. This includes budgeting for investments in technology, staff training, external expertise, or process improvements. Adequate resource allocation ensures that the plan can be effectively executed and sustained over time. Leaders should also consider the availability of skilled finance professionals or the need to hire additional talent to support the financial management initiatives.
Develop Implementation Strategies: Leaders work with their teams to develop implementation strategies for achieving the financial management goals and objectives. This involves breaking down the objectives into actionable tasks, assigning responsibilities, setting timelines, and establishing milestones. The strategies should outline the specific actions, deliverables, and timelines required to achieve the desired improvements in financial management.
Communication and Engagement: Effective communication and engagement are crucial for the success of the financial management plan. Leaders need to clearly communicate the goals, objectives, and strategies to the relevant stakeholders, including finance teams, executives, and other employees. They should provide regular updates on the progress of financial management initiatives and foster an environment of open communication to address any concerns or obstacles that may arise.
Monitor Progress and Evaluate Results: Leaders should establish mechanisms to monitor the progress of financial management initiatives and evaluate their effectiveness. This may involve setting key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure financial performance, conducting regular reviews of financial reports and analysis, and seeking feedback from stakeholders. Monitoring and evaluation provide insights into the effectiveness of the plan and help leaders make informed decisions to adjust strategies or address any challenges.
Continuous Improvement: Financial management is an ongoing process, and leaders should promote a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. They should encourage innovation, stay updated on industry best practices, and seek opportunities to enhance financial management practices. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the financial management plan ensures that it remains aligned with changing business needs and supports the company’s long-term financial goals.
Leaders make a plan for achieving financial management in their company by defining goals, assessing current practices, identifying areas for improvement, setting objectives, allocating resources, developing implementation strategies, communicating and engaging stakeholders, monitoring progress, evaluating results, and fostering continuous improvement. By taking a proactive approach to financial management planning, leaders can enhance the company’s financial performance, stability, and long-term success.

Employee Engagement
Getting employees on board with a financial management plan is essential for its successful implementation. Here are some strategies to engage and align employees with the financial management plan:
Communicate the Rationale: Clearly communicate the reasons behind the financial management plan and its importance for the company’s success. Explain how effective financial management contributes to the company’s stability, growth, and ability to achieve its goals. Help employees understand the direct impact that their actions and contributions have on the company’s financial health.
Provide Context and Education: Offer educational sessions or workshops to help employees understand financial management concepts, terminology, and how their roles connect to the company’s financial goals. Provide examples and case studies that demonstrate the significance of financial management in different functional areas of the organization. This helps employees see the relevance of financial management in their day-to-day work.
Show the Benefits: Highlight the benefits that employees and the company can gain from effective financial management. This could include improved job security, increased opportunities for growth and development, better resource allocation, or enhanced financial stability. When employees understand the positive impact that good financial management can have on their own careers and the organization as a whole, they are more likely to support and embrace the plan.
Foster Ownership and Accountability: Empower employees by involving them in the financial management process. Encourage them to contribute ideas and suggestions for improving financial practices within their respective roles. Assign clear responsibilities and hold individuals accountable for their financial management-related tasks. When employees feel ownership and responsibility for financial outcomes, they are more motivated to actively participate in the plan.

Provide Training and Support: Offer training programs or resources to enhance employees’ financial management skills and knowledge. This could include providing courses on budgeting, financial analysis, or software training for financial tools. By equipping employees with the necessary skills, they feel more confident and capable of contributing to the financial management plan.
Set Clear Expectations and Goals: Define clear expectations and goals related to financial management for each employee or team. Establish performance indicators that align with the financial management plan and incorporate them into performance evaluations. When employees have specific targets to work towards and understand how their performance contributes to the overall financial success of the company, they are more likely to engage with the plan.
Recognize and Reward Success: Acknowledge and reward employees who actively contribute to the financial management plan and demonstrate good financial practices. This can be through formal recognition programs, performance incentives, or public acknowledgment of achievements. Celebrating successes creates a positive culture around financial management and motivates employees to continue their engagement.
Encourage Collaboration and Cross-Functional Cooperation: Foster a culture of collaboration and teamwork across departments and functions. Emphasize the importance of cross-functional cooperation in achieving financial management goals. Encourage open communication and information sharing, enabling employees to see the broader financial impact of their actions and decisions.
Regularly Communicate Progress: Provide regular updates on the progress of the financial management plan and share the positive outcomes achieved. Keep employees informed about the impact of their collective efforts on the company’s financial performance. Transparent and regular communication helps maintain engagement, demonstrates the plan’s effectiveness, and encourages continuous commitment.
Lead by Example: Leaders play a critical role in setting the tone and leading by example. Demonstrate a commitment to financial management practices and behaviors. Align your own actions with the financial management plan, and visibly prioritize financial discipline and transparency. When employees see their leaders practicing what they preach, they are more likely to embrace and support the financial management plan.
Engaging employees with a financial management plan requires effective communication, education, showing the benefits, fostering ownership and accountability, providing training and support, setting clear expectations and goals, recognizing success, encouraging collaboration, regularly communicating progress, and leading by example. By involving employees and creating a sense of shared responsibility, organizations can build a culture of financial awareness and engagement.

Stakeholder Engagement
Getting stakeholders on board with financial management requires effective communication, engagement, and demonstrating the value of sound financial management practices. Here are some strategies to engage stakeholders:
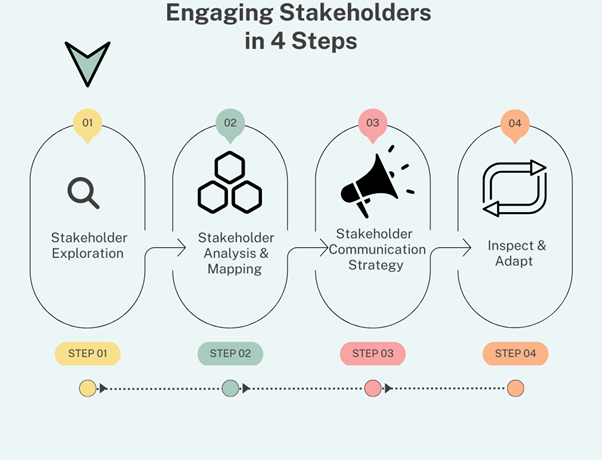
Communicate the Importance: Clearly articulate the significance of financial management to stakeholders, explaining how it contributes to the organization’s success and their interests. Highlight the benefits of effective financial management, such as financial stability, growth opportunities, risk mitigation, and stakeholder value creation. Use simple, non-technical language to ensure clear understanding across diverse stakeholder groups.
Transparency in Reporting: Provide transparent and accurate financial reporting. Timely and reliable financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, demonstrate the company’s commitment to transparency and accountability. Clearly explain financial performance and progress towards financial goals. Regular communication of financial results helps stakeholders understand the company’s financial position.
Stakeholder Engagement: Actively engage stakeholders in discussions about financial management. Seek their input, opinions, and concerns. Encourage dialogue and create opportunities for stakeholders to ask questions and provide feedback. This involvement fosters a sense of ownership and shared responsibility for financial management practices.
Education and Training: Offer educational resources and training sessions to stakeholders who may benefit from a deeper understanding of financial management. This could include workshops on financial literacy, investment strategies, or financial risk management. Empowering stakeholders with knowledge enables them to make informed decisions and appreciate the importance of sound financial management.
Tailored Communications: Customize communications to suit the specific needs and interests of different stakeholder groups. Investors may require detailed financial analyses, while employees may benefit from simplified explanations of financial goals and results. Tailoring communications ensures that stakeholders receive information in a format that is relevant and meaningful to them.
Showcase Success Stories: Share success stories and case studies that demonstrate how effective financial management has positively impacted the organization and its stakeholders. Highlight specific examples where sound financial management practices led to improved financial performance, risk mitigation, or value creation. Concrete evidence of the benefits helps stakeholders understand the tangible results of good financial management.
Lead by Example: Leaders play a crucial role in setting the tone and demonstrating their commitment to financial management. Lead by example, adhering to financial management practices, making financially sound decisions, and demonstrating ethical behavior. When stakeholders see leaders prioritizing financial management, it sends a powerful message about its importance.
Address Stakeholder Concerns: Actively address any concerns or misconceptions stakeholders may have about financial management. Be open to addressing questions, providing clarifications, and addressing any potential misunderstandings. Addressing concerns promptly and transparently helps build trust and confidence in the financial management practices.
Collaboration and Feedback: Foster collaboration with stakeholders to improve financial management practices. Seek input on potential improvements, solicit ideas, and encourage stakeholders to share their experiences and expertise. By involving stakeholders in the decision-making process, companies can enhance financial management practices and ensure they align with stakeholders’ needs and expectations.
Continuous Improvement: Demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement in financial management. Communicate the company’s ongoing efforts to enhance financial practices, systems, and controls. Highlight investments in technology, talent development, and process enhancements that support better financial management. Showcasing a culture of continuous improvement reinforces stakeholders’ confidence in the organization’s commitment to sound financial management.
Engaging stakeholders with financial management requires effective communication, transparency, education, tailored communications, showcasing success stories, leading by example, addressing concerns, collaboration, and continuous improvement. By involving stakeholders, providing information, addressing their needs, and demonstrating the value of financial management, companies can build trust, gain support, and foster a shared commitment to sound financial management practices.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Construction
The construction industry plays a vital role in the global economy, contributing to infrastructure development, job creation, and overall economic growth. It encompasses a wide range of activities involved in building, renovating, and maintaining structures such as residential homes, commercial buildings, bridges, roads, and more. This industry involves a diverse set of professionals, including architects, engineers, contractors, suppliers, and skilled laborers, who collaborate to bring construction projects to life.
One of the key drivers of the construction industry is the demand for new infrastructure and the need for existing structures to be repaired, upgraded, or expanded. Governments, businesses, and individuals invest in construction projects to meet the growing population’s needs, enhance transportation networks, create sustainable buildings, and support economic development. The construction sector is typically influenced by factors such as population growth, urbanization, technological advancements, and government policies.
Construction projects are complex endeavors that require careful planning, design, and execution. Architects and engineers are responsible for conceptualizing and designing structures that meet functional, aesthetic, and safety requirements. Once the design phase is complete, the construction process begins, involving procurement of materials, hiring subcontractors, and managing the workforce.
Financial management is crucial in the construction industry due to the high costs associated with materials, labor, equipment, and project execution. Construction companies must carefully manage their finances to ensure profitability, maintain cash flow, and meet project deadlines. Effective financial management involves accurate cost estimation, budgeting, and monitoring of expenses throughout the project lifecycle.
In addition to financial considerations, risk management is another critical aspect of the construction industry. Construction projects are subject to various risks, including delays, cost overruns, safety hazards, and regulatory compliance issues. Proper risk assessment and mitigation strategies are essential to minimize potential disruptions and ensure project success.
The construction industry is also influenced by technological advancements that improve efficiency, productivity, and safety. Construction companies are adopting advanced tools and technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), drones for surveying and inspection, prefabrication methods, and automation to streamline processes, reduce errors, and enhance collaboration among stakeholders.
Sustainable construction practices have gained significant attention in recent years. With a growing focus on environmental conservation and energy efficiency, the construction industry is increasingly adopting green building standards and sustainable materials. Energy-efficient designs, renewable energy integration, and waste management strategies are becoming integral parts of construction projects, promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly built environment.
The construction industry is a major source of employment, providing opportunities for skilled and unskilled workers alike. From carpenters and electricians to project managers and civil engineers, the sector offers diverse career paths. Training and professional development programs are crucial in ensuring a skilled workforce that can meet the industry’s evolving demands.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry plays a crucial role in society by providing medical care, promoting public health, and improving overall well-being. It encompasses a broad range of services, including hospitals, clinics, pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, insurance providers, and research institutions. The healthcare industry is characterized by its complexity, continuous advancements in medical technology, and the constant pursuit of better patient outcomes.
One of the primary objectives of the healthcare industry is to ensure access to quality healthcare services for individuals and communities. Healthcare providers, such as hospitals and clinics, offer a wide array of medical services, including preventive care, diagnostics, treatment, and rehabilitation. These services are provided by a diverse group of professionals, including doctors, nurses, technicians, and allied health workers, who collaborate to deliver patient-centered care.
In addition to providing medical services, the healthcare industry also focuses on public health initiatives. Public health efforts aim to prevent diseases, promote healthy lifestyles, and educate communities on health-related issues. This includes initiatives such as vaccination campaigns, disease surveillance, health education programs, and community outreach activities. Public health interventions contribute to the overall well-being of populations and help manage the burden of disease.
The healthcare industry is heavily influenced by advancements in medical technology and research. Breakthroughs in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and treatment protocols continually shape the way healthcare is delivered. Medical research institutions, both in the private and public sectors, work towards discovering new treatments, developing innovative therapies, and advancing medical knowledge. These advancements contribute to improved patient outcomes, increased life expectancy, and the management of previously incurable diseases.
Financial management is a critical aspect of the healthcare industry due to its high costs and complexities. Healthcare providers must carefully manage their finances to ensure the sustainability of operations, invest in medical technology, and maintain adequate staffing levels. Effective financial management involves budgeting, reimbursement strategies, revenue cycle management, and cost control measures. Insurance providers also play a significant role in the healthcare industry, managing risks and providing financial coverage for medical expenses.
Regulatory and legal frameworks heavily influence the healthcare industry to ensure patient safety, ethical practices, and quality standards. Healthcare organizations must comply with various regulations, such as patient privacy laws (e.g., HIPAA in the United States), medical licensing requirements, and clinical practice guidelines. Compliance with these regulations is essential to maintain patient trust, protect confidential health information, and uphold professional standards.
Banking & Financial Services
The banking and financial services industry is a crucial sector that facilitates economic transactions, manages financial resources, and supports individuals, businesses, and governments in achieving their financial goals. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including commercial banking, investment banking, asset management, insurance, and various other financial services. The industry serves as a backbone of the global economy, promoting economic growth, facilitating capital flows, and mitigating financial risks.
Commercial banking is one of the core components of the banking and financial services industry. Commercial banks provide a range of financial products and services to individuals and businesses, including savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, mortgages, and credit cards. They serve as financial intermediaries, collecting deposits from savers and channeling those funds towards lending activities, thus enabling businesses and individuals to access capital for investments, purchases, and other financial needs.
Investment banking plays a critical role in facilitating capital markets and corporate finance activities. Investment banks assist companies in raising capital through initial public offerings (IPOs) and secondary offerings, provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and engage in securities trading and underwriting. They act as intermediaries between companies and investors, helping them optimize their capital structure, manage risks, and execute strategic financial transactions.
Asset management is another key sector within the industry that focuses on managing investment portfolios on behalf of individuals, institutional investors, and corporations. Asset management companies offer a variety of investment options, including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and pension funds. Their role is to analyze market trends, make informed investment decisions, and maximize returns while managing risks in line with clients’ investment objectives.
Insurance is an integral part of the financial services industry, providing risk mitigation and financial protection against unforeseen events. Insurance companies offer a wide range of products, including life insurance, property insurance, health insurance, and liability insurance. They assess risks, collect premiums, and provide compensation to policyholders in the event of covered losses or damages. Insurance plays a crucial role in safeguarding individuals, businesses, and governments against financial uncertainty and helping them recover from adverse events.
Financial technology, often referred to as fintech, has rapidly emerged as a disruptive force within the banking and financial services industry. Fintech companies leverage technology and innovation to offer financial services more efficiently, enhance customer experience, and expand financial inclusion. Fintech solutions include mobile banking apps, digital payment systems, robo-advisors, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and blockchain-based solutions. These technologies have revolutionized the industry by increasing accessibility, reducing costs, and transforming the way financial services are delivered.
Technology
The technology industry, also known as the tech sector, is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector that drives innovation, transforms industries, and shapes the modern world. It encompasses a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the development, manufacturing, and distribution of technology products and services. The technology industry plays a pivotal role in the global economy, fueling economic growth, job creation, and societal advancement.
One of the defining characteristics of the technology industry is its constant pursuit of innovation. Technology companies are at the forefront of creating groundbreaking solutions that address a diverse range of needs, from communication and entertainment to healthcare, transportation, and beyond. Through research and development efforts, these companies introduce new technologies, refine existing ones, and push the boundaries of what is possible.
The technology industry is highly diverse, encompassing various sectors such as hardware, software, telecommunications, internet services, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, e-commerce, and more. Hardware companies design and manufacture electronic devices and components, while software companies develop applications, operating systems, and platforms. Telecommunications companies provide infrastructure and services for communication, while internet services companies offer online platforms and services. This diverse ecosystem collaborates and interconnects to deliver innovative products and services to consumers and businesses.
The impact of the technology industry extends across sectors and industries, driving digital transformation and reshaping traditional business models. It has revolutionized communication, making it easier and faster to connect with people globally. Information is readily accessible through the internet, allowing for instant access to knowledge, entertainment, and services. The technology industry has also transformed industries such as finance, healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and entertainment, bringing efficiency, automation, and new business opportunities.
One of the significant contributions of the technology industry is the advancement of artificial intelligence (AI). AI technologies enable machines to simulate human intelligence, perform complex tasks, and make decisions. AI applications range from voice assistants and chatbots to autonomous vehicles, medical diagnosis systems, and predictive analytics. These advancements have the potential to enhance productivity, improve healthcare outcomes, optimize resource allocation, and revolutionize various aspects of society.
The technology industry thrives on collaboration and a vibrant startup culture. Startups often disrupt established markets and challenge traditional industry players with innovative ideas and agile business models. Many successful tech giants today, such as Apple, Google, and Amazon, started as small startups. Venture capital firms and angel investors play a crucial role in fueling innovation by providing funding and mentorship to early-stage technology companies.
The global reach of the technology industry is remarkable, with companies operating on a multinational scale. Technology products and services transcend borders, connecting people and businesses across continents. International cooperation and collaboration are common, with companies leveraging talent and resources from various parts of the world to drive innovation and expansion. This global interconnectedness brings opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and knowledge sharing.
Education
The education industry plays a fundamental role in shaping individuals, societies, and the overall progress of humanity. It encompasses a wide range of institutions, organizations, and professionals dedicated to providing knowledge, skills, and opportunities for learning. The education industry includes early childhood education, primary and secondary schools, higher education institutions, vocational training centers, online learning platforms, and various educational support services.
Education is essential for personal development, empowerment, and social mobility. It equips individuals with knowledge, critical thinking abilities, and practical skills necessary for their personal and professional lives. The education industry fosters intellectual growth, nurtures creativity, and promotes lifelong learning, enabling individuals to adapt to changing environments and contribute to society.
Early childhood education is a crucial foundation in the education industry, as it lays the groundwork for children’s cognitive, social, and emotional development. Preschools and early learning centers provide a nurturing and stimulating environment for young learners, fostering their curiosity, social skills, and early literacy and numeracy abilities.
Primary and secondary schools play a central role in the education industry, providing formal education to children and teenagers. These institutions follow prescribed curricula designed to develop students’ knowledge across a wide range of subjects. They promote academic achievement, critical thinking, and personal growth, preparing students for higher education or entering the workforce.
Higher education institutions, such as universities, colleges, and vocational schools, offer specialized academic and professional programs. They provide opportunities for in-depth study, research, and skill development across various disciplines. Higher education equips students with specialized knowledge, prepares them for specific careers, and fosters research and innovation that drives societal progress.
The education industry has been significantly influenced by technology, with online learning platforms and digital tools revolutionizing the delivery of education. E-learning platforms offer flexible and accessible learning opportunities, enabling students to pursue education at their own pace and location. These platforms provide a wide range of courses, including academic subjects, professional development, and skills training, catering to diverse learner needs.
Educational support services, such as tutoring, test preparation, counseling, and educational consulting, are essential components of the education industry. These services provide personalized guidance, assistance, and resources to enhance learning outcomes, address individual needs, and support students in achieving their academic goals.
Education is not limited to formal institutions; it extends to informal and lifelong learning opportunities. Continuing education programs, professional development courses, and community-based learning initiatives cater to individuals seeking to enhance their skills, acquire new knowledge, or pursue personal interests. Lifelong learning promotes personal growth, career advancement, and civic engagement.
The education industry is influenced by various stakeholders, including educators, administrators, policymakers, parents, and students themselves. Educators, such as teachers and professors, are at the forefront of the industry, imparting knowledge, facilitating learning experiences, and inspiring students. Administrators oversee educational institutions, manage resources, and create conducive learning environments. Policymakers develop education policies, regulations, and frameworks to ensure quality, equity, and accountability in the education system.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Kansas City, MO
Kansas City’s economy is a vibrant and diverse economic hub in the Midwestern region of the United States. As the largest city in both Kansas and Missouri, Kansas City serves as a center for commerce, transportation, finance, and culture. The city’s economy is characterized by a mix of industries, including healthcare, technology, manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, and professional services.
The healthcare sector plays a significant role in Kansas City’s economy, employing a large number of healthcare professionals and contributing to the city’s economic growth. Renowned medical centers, such as the University of Kansas Health System and Saint Luke’s Health System, provide advanced medical services, research, and education. The presence of these healthcare institutions not only contributes to the well-being of residents but also attracts medical tourists, bolstering the local economy.
Kansas City has also emerged as a growing technology hub, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship. The city is home to numerous tech startups and established tech companies, particularly in the areas of software development, data analytics, and financial technology. The presence of leading tech organizations, such as Cerner Corporation, a major healthcare IT company, and Garmin, a global leader in navigation and GPS technology, contributes to the city’s reputation as a technology-driven economy.
Manufacturing is another key sector in Kansas City’s economy, with diverse manufacturing industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to food processing and machinery. The region benefits from its central location and robust transportation infrastructure, making it an attractive location for manufacturers. Major manufacturing companies, including Ford, General Motors, and Harley-Davidson, have operations in the Kansas City area, supporting employment and driving economic growth.
The logistics and transportation industry plays a crucial role in Kansas City’s economy due to its strategic location at the crossroads of major highways, railways, and waterways. The city’s central location makes it a key distribution and logistics hub for the Midwest, facilitating the movement of goods and services throughout the region. The presence of major logistics companies, such as Kansas City Southern Railway and YRC Worldwide, further strengthens the city’s position as a transportation and logistics center.
Agriculture is deeply rooted in Kansas City’s economy, given the city’s proximity to fertile farmland in the surrounding regions. The agriculture industry encompasses crop production, livestock farming, food processing, and agricultural equipment manufacturing. Kansas City is known as a major center for grain trading, with the Kansas City Board of Trade being a prominent commodity exchange for wheat futures contracts.
The professional services sector, including finance, insurance, and legal services, also contributes significantly to Kansas City’s economy. The city is home to several regional and national banks, insurance companies, and law firms. These professional services support businesses and individuals in various financial and legal matters, contributing to the overall economic growth of the region.
Kansas City has a rich cultural scene, with a thriving arts and entertainment industry. The city is renowned for its jazz heritage and hosts numerous cultural events, music festivals, and art exhibitions. The arts and entertainment sector, including museums, theaters, and galleries, not only enriches the city’s cultural fabric but also contributes to tourism and economic activity.
While Kansas City’s economy is diverse and robust, it faces challenges common to many urban areas, including income inequality, workforce development, and attracting and retaining talent. However, the city continues to invest in infrastructure, education, and economic development initiatives to foster growth and create opportunities for businesses and residents.
In conclusion, Kansas City’s economy is characterized by a diverse mix of industries, including healthcare, technology, manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, and professional services. The city’s strategic location, robust transportation infrastructure, and vibrant cultural scene contribute to its economic vitality. With its thriving sectors and ongoing investments in education and infrastructure, Kansas City is well-positioned for continued economic growth and prosperity.

St Louis, MO
St. Louis, Missouri, is a dynamic city with a diverse economy that spans multiple industries. Known for its rich history, cultural heritage, and central location, St. Louis has been a center of commerce and innovation for decades. The city’s economy is supported by sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, transportation, and technology.
The healthcare industry is a major contributor to St. Louis’ economy. The city is home to numerous renowned healthcare institutions, including BJC HealthCare, Washington University School of Medicine, and Mercy Health System. These institutions provide world-class medical services, conduct groundbreaking research, and serve as major employers in the region. The healthcare sector supports a wide range of jobs, from healthcare professionals to administrative staff, driving economic growth and providing essential services to residents.
The finance and banking sector also plays a significant role in St. Louis’ economy. The city hosts regional offices of major national banks and financial institutions, such as Wells Fargo, U.S. Bank, and Scottrade. St. Louis is home to the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, which serves as a key regional banking center. The finance industry in St. Louis provides a range of services, including commercial banking, investment banking, asset management, and insurance, supporting local businesses and individuals in their financial needs.
Manufacturing has a long history in St. Louis and remains an important sector in the city’s economy. St. Louis has a diverse manufacturing base that includes industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemicals, and consumer goods. Major manufacturing companies like Boeing, General Motors, and Anheuser-Busch have a presence in the region, providing employment opportunities and contributing to the local economy. The city’s central location and robust transportation infrastructure make it an attractive location for manufacturing and distribution activities.
Transportation and logistics are significant contributors to St. Louis’ economy due to its strategic position along the Mississippi River and its extensive rail and highway networks. The city’s location as a transportation hub facilitates the movement of goods and services throughout the region, supporting trade and commerce. St. Louis is home to major logistics companies, including Union Pacific Railroad and Schnucks, a regional supermarket chain. The transportation and logistics sector creates jobs and supports other industries by ensuring efficient supply chain management.
St. Louis has seen growth in its technology sector in recent years. The city has attracted tech startups, entrepreneurs, and venture capital investment. The Cortex Innovation Community, a technology district, has emerged as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship in St. Louis. The city’s universities and research institutions, including Washington University and Saint Louis University, contribute to the growth of the technology industry by fostering collaboration, research, and talent development.
The tourism and hospitality industry in St. Louis is another significant contributor to the local economy. The city offers a variety of attractions, including the Gateway Arch, Forest Park, and the St. Louis Zoo. These attractions, along with sports venues, museums, and cultural events, draw visitors from around the country and support hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, creating jobs and generating revenue for local businesses.
Despite its strengths, St. Louis faces economic challenges, including income inequality and urban blight in certain neighborhoods. The city continues to invest in revitalization efforts and community development programs to address these challenges and promote inclusive economic growth.
In conclusion, the economy of St. Louis is diverse and robust, supported by sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, transportation, and technology. The city’s strategic location, rich history, and cultural offerings contribute to its economic vitality. St. Louis continues to foster innovation, attract investment, and invest in community development to drive economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance the quality of life for its residents.

Dallas, TX
Dallas, Texas, is a major economic powerhouse in the United States, known for its diverse industries, robust job market, and entrepreneurial spirit. As one of the largest metropolitan areas in the country, Dallas boasts a thriving economy that encompasses sectors such as finance, technology, healthcare, manufacturing, and energy.
The finance and banking sector plays a crucial role in Dallas’ economy, with the city being home to several major banks, including Comerica, Texas Capital Bank, and the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas. The presence of these financial institutions contributes to the availability of capital, facilitates business growth, and supports the city’s overall economic stability.
The technology industry has experienced significant growth in Dallas, with the city emerging as a hub for technology companies and startups. The region is known for its concentration of telecommunications companies, software development firms, and data centers. Technology giants such as Texas Instruments and AT&T have a strong presence in the area, fostering innovation and attracting top talent.
Dallas also benefits from a robust healthcare industry, which serves both the local population and draws patients from across the region. The city is home to renowned healthcare systems, including UT Southwestern Medical Center and Baylor Scott & White Health. These institutions not only provide high-quality medical care but also contribute to research and medical education, further boosting the city’s economy.
The manufacturing sector in Dallas is diverse, encompassing industries such as aerospace, defense, automotive, and consumer goods. The city’s central location and well-developed transportation infrastructure make it an ideal distribution and logistics center. Major manufacturing companies, including Lockheed Martin and Texas Instruments, have manufacturing facilities and operations in the Dallas area, providing employment opportunities and contributing to economic growth.
Dallas has a strong presence in the energy industry, particularly in oil and gas. The city serves as a regional headquarters for several major energy companies, including ExxonMobil and HollyFrontier. Additionally, Dallas is home to a significant number of energy-related service providers and consulting firms that support the industry. The city’s proximity to major oil and gas reserves in Texas further enhances its position in the energy sector.
The entrepreneurial spirit in Dallas is vibrant, with a supportive business ecosystem and a culture that encourages innovation and new ventures. The city provides resources and initiatives for startups and small businesses, including co-working spaces, incubators, and access to capital. The thriving entrepreneurial scene in Dallas fosters job creation, attracts talent, and contributes to economic dynamism.
Tourism also plays a vital role in Dallas’ economy, with the city attracting millions of visitors each year. The city offers a wide range of attractions, including world-class museums, professional sports teams, shopping districts, and cultural events. The tourism industry creates employment opportunities and generates revenue for local businesses, hotels, and restaurants.
Dallas faces economic challenges, including income inequality and disparities in access to education and healthcare. However, the city continues to invest in education and workforce development initiatives to address these challenges and promote inclusive economic growth. Additionally, the city is actively involved in attracting and retaining businesses through economic development programs and incentives.
In conclusion, the economy of Dallas, Texas, is characterized by its diverse industries, including finance, technology, healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and tourism. The city’s strong business environment, robust infrastructure, and entrepreneurial ecosystem contribute to its economic vitality. With a favorable business climate, strategic location, and a culture of innovation, Dallas continues to be a prominent economic center in the United States, attracting businesses, talent, and investment.

Austin, TX
Austin, Texas, is a vibrant city known for its thriving economy, entrepreneurial spirit, and dynamic cultural scene. The city’s economy is diverse and driven by sectors such as technology, education, healthcare, creative industries, and tourism. Austin’s unique combination of factors, including a highly skilled workforce, supportive business environment, and quality of life, has contributed to its emergence as a major economic hub.
The technology sector is a primary driver of Austin’s economy. The city has earned the nickname “Silicon Hills” due to its concentration of technology companies and startups. Austin is home to major technology players like Dell Technologies and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It also hosts a growing number of innovative startups and incubators that fuel entrepreneurship and attract venture capital. The technology industry in Austin encompasses software development, semiconductors, information technology services, and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. The presence of these tech companies creates high-paying jobs, fosters innovation, and drives economic growth.
Austin’s education sector is another key contributor to its economy. The city is home to prominent educational institutions, including the University of Texas at Austin, which serves as a major research university. These institutions contribute to Austin’s knowledge economy, provide a skilled workforce, and support research and development activities. Additionally, the presence of universities attracts students from around the world, contributing to the local economy through their spending and potential retention of talent after graduation.
The healthcare industry is a significant component of Austin’s economy. The city has several leading healthcare providers and research institutions, including St. David’s HealthCare and Seton Healthcare Family. Austin’s healthcare sector offers a wide range of medical services, including specialized care, research, and clinical trials. The industry not only provides essential healthcare services to the community but also generates employment opportunities and contributes to the city’s economic growth.
Austin’s creative industries, including film, music, and gaming, contribute to its vibrant economy. The city hosts the annual South by Southwest (SXSW) festival, which showcases film, music, and interactive media and attracts participants from around the world. Austin’s thriving music scene has earned it the title of the “Live Music Capital of the World,” creating jobs and generating revenue from concerts, festivals, and music-related events. The gaming industry has also grown significantly in Austin, with studios producing popular video games and employing a skilled workforce.
Tourism plays a significant role in Austin’s economy, drawing visitors with its cultural attractions, outdoor activities, and events. The city offers a wide range of experiences, including exploring the state capitol, enjoying outdoor recreational areas like Lady Bird Lake and Zilker Park, and attending festivals such as Austin City Limits Music Festival. Tourism supports the hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, creating jobs and contributing to local businesses.
Austin’s economy faces challenges related to affordability, infrastructure development, and managing growth sustainably. The city continues to address these challenges through urban planning, investments in infrastructure, and initiatives to promote affordability and inclusivity. Additionally, the city fosters collaboration between public and private sectors to support innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic diversification.

Chicago, IL
Chicago, Illinois, is a bustling metropolis with a diverse and robust economy that spans various sectors. As the third-largest city in the United States, Chicago is a major financial center, a hub for commerce and industry, and a cultural powerhouse. The city’s economy is characterized by its strong sectors in finance, manufacturing, technology, transportation, healthcare, and tourism.
The finance sector plays a significant role in Chicago’s economy, with the city hosting the headquarters of major financial institutions. The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME Group) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) are prominent financial exchanges in the city. These institutions facilitate trading in derivatives and options, attracting traders and investors from around the world. Chicago’s finance industry also includes banking, insurance, asset management, and other financial services, contributing to the city’s economic stability and job creation.
Manufacturing has been a historical pillar of Chicago’s economy, although it has evolved over the years. While the city’s manufacturing base has diversified, it remains a vital sector. Chicago’s manufacturing industry includes sectors such as food processing, automotive, steel, machinery, and chemicals. The city’s central location and well-developed transportation infrastructure, including its extensive rail and highway networks, make it an attractive hub for manufacturers. Manufacturing companies provide employment opportunities and contribute to the local economy by producing goods that are used locally and exported worldwide.
Chicago has emerged as a thriving technology hub, with a rapidly growing tech sector. The city’s tech scene encompasses various industries, including software development, information technology services, e-commerce, and digital media. Companies such as Groupon, Grubhub, and Motorola Solutions have a significant presence in Chicago. The city’s vibrant startup ecosystem, coupled with the availability of venture capital, accelerators, and incubators, fosters innovation and entrepreneurship in the technology sector.
Transportation and logistics are vital components of Chicago’s economy due to its strategic location at the heart of the country. The city serves as a major transportation and distribution center, with a central hub for rail, air, and maritime networks. O’Hare International Airport and the Port of Chicago contribute to the city’s status as a crucial transportation hub. The transportation and logistics sector supports trade, commerce, and supply chain operations, generating employment opportunities and contributing to the local economy.
Chicago’s healthcare industry is robust, with numerous world-class hospitals and research institutions. The city is home to prestigious healthcare systems, including Northwestern Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, and the University of Chicago Medical Center. These institutions provide advanced medical care, conduct cutting-edge research, and attract patients from around the world. The healthcare sector generates employment opportunities, supports medical innovation, and contributes to the city’s economy.
Tourism plays a vital role in Chicago’s economy, with the city attracting millions of visitors annually. Iconic attractions like Millennium Park, Navy Pier, and the Art Institute of Chicago draw tourists from around the globe. The city also hosts various cultural events, including music festivals, art exhibitions, and theater performances. The tourism industry supports hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, and retail establishments, contributing to job creation and revenue generation.
Program Benefits
Operations
- Cost Control
- Budgeting
- Efficiency Improvement
- Inventory Optimization
- Cash Flow Management
- Performance Analysis
- Process Streamlining
- Resource Allocation
- Risk Mitigation
- Decision Support
Marketing
- Budget Allocation
- ROI Analysis
- Pricing Optimization
- Sales Forecasting
- Expense Management
- Marketing Budgeting
- Profitability Assessment
- Financial Reporting
- Campaign Analysis
- Cost-effectiveness
Research
- Cost Control
- ROI Assessment
- Project Prioritization
- Budget Planning
- Financial Analysis
- Resource Optimization
- Risk Management
- Performance Evaluation
- Investment Tracking
- Funding Allocation
Achievements

US Army
Collaborated with Senior Executive Leaders to reduce expenses.

Sam’s Club/Walmart
Reduced expenses by 11% and provided a financial strategy that increased revenue by 13%.

Webster University
Increased revenue by 26% by increasing student enrollment.

CFO Systems
Worked as a Fractional CFO for several clients; ensured all clients understood the operational impact on the financial statements.

Dominion Consulting Group
Consulted clients in several different industries. One client grew from $25M to $100M in revenue in 5 years.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.












