Equitable Finance

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Equitable Finance is provided by Ms. Thobias Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Ms. Thobias, an approved Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene, is a financial expert and business strategist renowned for her extensive experience in the financial, technology, and agtech sectors. Widely respected as a thought leader in financial and social impact enterprises, Ms. Thobias has been at the forefront of critical innovation in highly competitive markets.
As a sought-after consultant and strategist for numerous market-disrupting institutions that aim to democratize access to financial resources, Ms. Thobias has successfully spearheaded multiple capital raises, financial product launches, deal structurings, fintech launches, and go-to-market strategies. Her expertise extends to serving as an interim Chief Credit Officer for multinational operations. Throughout her career, she has demonstrated a remarkable ability to transform complex organizations amidst dynamic and uncertain market conditions, earning the trust and support of employees, customers, vendors, owners, corporate leadership, investors, and external partners.
At both the personal and team level, Ms. Thobias excels as an engaged leader. She fearlessly challenges the status quo, embedding inclusive practices within solution design and fostering effective senior teams and investors. Additionally, she is highly engaged within her industry, often taking on leadership roles and acting as a mentor to others.
Beyond her impressive professional achievements, Ms. Thobias contributes her expertise as an active Advisory Board member with Kiva, a micro-lending platform focused on increasing financial access to underserved communities. She also holds a position on the Advisory Board of Village Micro Fund, a financial organization dedicated to empowering entrepreneurs with access to business capital. As the founder and CEO of a research and technology company known for catalyzing entrepreneurial innovation across various sectors, Ms. Thobias has fostered strategic partnerships with esteemed organizations like Amazon, MasterCard, New Voices Fund, and Podia.
Ms. Thobias’s notable role as the Chief Credit Officer of Hello Tractor, Inc., involved engineering an innovative tractor financing solution targeting traditionally underbanked populations in Sub-Saharan Africa. Through her efforts, she secured over $10 million in commercial financing to launch smallholder farming tractor pilot programs in Kenya, Nigeria, and Uganda. Ms. Thobias managed cross-functional project management for innovation, overseeing user experience, mobile application development, and client relationship management. She also implemented credit policies, transaction scoring models, and process automation for optimal efficiency. Her leadership yielded exceptional portfolio quality, with an impressive annual repayment rate exceeding 100% and a 0% NPL. She further strengthened symbiotic relationships with key stakeholders such as USAID, World Food Program, and John Deere.
Prior to this, Ms. Thobias worked at Bank of America in Global Corporate & Investment Banking, where she managed a diverse portfolio of emerging markets middle-market and large corporate technology clients. Her responsibilities included structuring, underwriting, and documentation of credit facilities, managing a substantial $19 billion of term and intraday credit exposure across various financial instruments. She showcased her exceptional training skills as the Instructor for Bank of America’s Wholesale Credit Analyst Training Program, educating credit analysts worldwide on the fundamentals of underwriting, financial analysis, bank product offerings, and regulatory compliance.
In addition to her professional achievements, Ms. Thobias is a community leader and mentor to early-stage entrepreneurs. She has led educational trips to South Africa and Costa Rica, offering valuable insights on international expansion strategies and social good. Ms. Thobias serves as a management consultant to The Literacy Lab, where she contributes to increasing literacy rates for underresourced youth across the United States through sustainable and relevant approaches in an ever-evolving technological landscape. She is also a sought-after speaker at esteemed colleges and universities such as the University of South Carolina, Dartmouth, and Wharton Business School, inspiring young adults with her wisdom on the importance of entrepreneurship for continued innovation and inclusion.
Ms. Thobias holds a Bachelor’s degree in Corporate Finance from the University of South Carolina.
To request further information about Ms Thobias through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Equitable Finance
Financial institutions face a complex landscape defined by slow growth in saturated markets and the rising influence of socially-conscious Millennials and Gen Z consumers. These forces demand a fundamental rethinking of financial service design and delivery. The Equitable Finance corporate training program offers a transformative framework, addressing the key pain points that hinder institutions from capitalizing on underserved markets and aligning with the values of a growing, impact-driven consumer base.
A new wave of financial incumbents is rapidly disrupting the landscape. Fintech solutions are democratizing access to capital, outpacing the traditional banking model. These agile players streamline credit decisions, bypassing the cumbersome paperwork and bureaucracy that once defined the industry. Money movement solutions now operate with unprecedented speed, enabling consumers to transfer funds within seconds using just a mobile phone. This ease of use diminishes the traditional role of banks. Furthermore, tech-powered platforms have revolutionized crowdsourcing capital, making it simpler for individuals and businesses to secure funding. Financial institutions must urgently adopt similar levels of agility and user-centric design to avoid losing significant market share to these innovators. This base of consumers who demand convenience and speed will only continue to grow.
Is your institution struggling with missed growth opportunities in untapped markets? You’re not alone. But continuing down the same path will only lead to further stagnation. Disruptors in the financial sector are outpacing traditional solutions with user-friendly products an experience that resonate wit the underserved. The Equitable Finance corporate training program will help you design hyper-localized financial products that cater to the specific needs of communities and populations typically excluded from traditional banking. Imagine the possibilities when you truly understand and serve these overlooked markets. It’s not about keeping up – it’s about getting ahead.
Perhaps your organization has been attempting to serve underbanked populations, but are finding your risk management approaches to be ineffective. You’re realizing that traditional credit models simply don’t work for everyone, leaving you frustrated and missing out on potential revenue. Together, we will explore how your company can leverage alternative credit scoring models, social capital metrics, and AI-driven insights for enhanced risk assessment and portfolio health. You’ll unlock the potential of these communities while protecting your institution’s financial stability.

Speed and agility matter in the current landscape, as offering to a new market is not a complete solve. If your organization’s pipelining, screening, and underwriting processes are outdated and slow, that is a hindrance in today’s competitive landscape. Bureaucratic approval procedures and reliance on legacy systems hinder agility and innovation. It’s costing you time, money, and the chance to capture new customers. The Equitable Finance corporate training program will help your institution think creatively about optimizing operational efficiency with digitized workflows, automated decision-making, and API integrations for speed and scalability. Imagine the efficiency gains and the deals you could close with a streamlined process!
Overcoming lags in tech adoption is vital for organizational success. Many times, it seems as if harnessing the power of AI, data analytics, and seamless user experiences are out of reach given budget or expertise constraints. However, let’s be honest. Being too slow to respond in this rapidly evolving landscape will cost your organization significant market share anyway. It is important that you explore how to tap into rich data pools and predictive analytics for tailored lending solutions and improved customer experiences. With the right strategic investments, your organization will realize increased revenue at a fraction of the historical cost – giving you a competitive edge.
Doing this work around fresh innovation is vital, but the Equitable Finance corporate training program is not designed to have you work through these potential adaptions in a silo. Building meaningful relationships and brand presence within underbanked communities is complex and time-consuming. Especially if you lack the in-house experience and on-the-ground connections to make a real impact. This program will help you develop a community-centered strategy. You will receive strategies on building trust and establishing strong local partnerships for sustainable long-term growth in emerging markets. This is about more than just transactions – it’s about creating lasting relationships.
Impacting communities will require that you give attention to the brand health of your financial institution. Is there an image disconnect? Does your institution struggle to resonate with younger, impact-driven consumers who demand ethical and equitable solutions? It’s time to position your brand as a force for good. The Equitable Finance corporate training program will help you align with the values of Millennial and Gen Z investors and consumers with demonstrated impact on wealth equity and inclusive growth. This isn’t just about marketing, it’s about making real-world change that gets consumers excited to work with your institution.
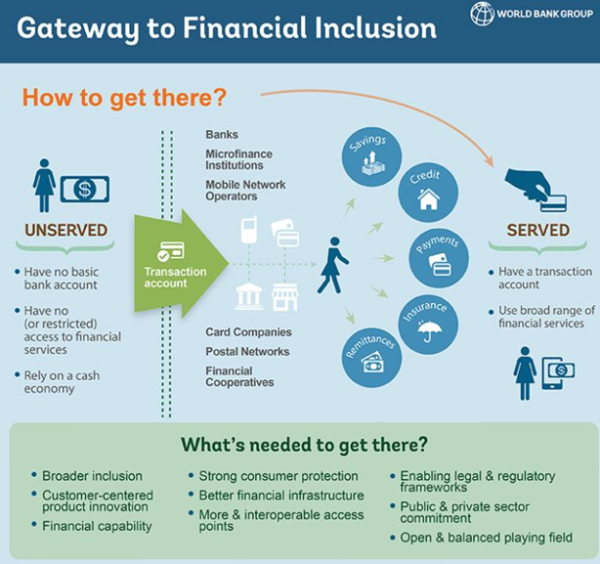
The wealth gap continues to widen under financial institutions’ watch. Traditional lending models, even if unintentionally, tend to perpetuate economic inequality, missing the mark on creating positive social change. It’s time to break the cycle. Empower underbanked individuals and communities with the tools and access to build wealth, fostering greater economic equality. Be the institution that leads the way in creating a more equitable future.
Your involvement is closing wealth gaps will help your organization combat its own limitations with narrow funding pools. Attracting socially-conscious investors remains a challenge without demonstrating your unwavering commitment to inclusive finance models. You’re missing out on a massive source of capital. Position your institution as a leader in driving social good, attracting capital from investors who seek financial returns alongside measurable social impact. This is about tapping into a whole new world of financial opportunities.
Perhaps navigating regulatory complexities in emerging markets, especially regarding data privacy and consumer protection, has been daunting. The fear of getting this wrong likely holds you back from even trying. With this corporate training program, you will develop strategies for compliance with evolving regulations in emerging markets, mitigating risk and ensuring operational security. Enter these markets with confidence and peace of mind.
Let’s be frank: Building meaningful relationships in this space, attracting the right investors, and truly bridging wealth gaps with traditional approaches feels impossible. And that’s why you’re here.
The Equitable Finance program delivers exceptional results. Your institution will experience significant growth by breaking into lucrative, previously overlooked markets. You’ll benefit from a healthier portfolio due to enhanced risk mitigation. The program empowers your institution to be a catalyst for social change through wealth creation and community empowerment, building brand loyalty within the rising, purpose-driven consumer base.
Join the Equitable Finance movement. Embrace the future of inclusive finance, capture substantial new market share, and create a more equitable future. If your institution is serious about unlocking sustainable growth while positively impacting society, you’ve come to the right place.
Curriculum
Equitable Finance – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Core Beliefs
- Part 1 Month 2 Due Diligence
- Part 1 Month 3 User-Centric Design
- Part 1 Month 4 Credit Scoring
- Part 1 Month 5 Process Digitization
- Part 1 Month 6 Autonomous Finance
- Part 1 Month 7 Program Piloting
- Part 1 Month 8 Building Partnerships
- Part 1 Month 9 Catalytic Funding
- Part 1 Month 10 Risk Management
- Part 1 Month 11 Organizational Design
- Part 1 Month 12 Future Roadmap
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Equitable Finance corporate training program.
Equitable Finance – Part 1- Year 1 
- Part 1 Month 1 Core Beliefs – In the first month of our program, participants will delve into understanding the core beliefs that underpin the company’s mission and culture. They will also engage in identifying and challenging any limiting beliefs about the organization and target audience. Moreover, this month will focus on exploring opportunities for creating greater value and enhancing opportunities for currently under-resourced regions and populations. The purpose of this module is to create a foundational understanding of the company’s mission and culture. Through this module, participants will examine the beliefs that underpin the organization’s mission and identify any limiting beliefs that may be hindering the company’s ability to serve under-resourced populations. The first step in this process is to clearly define the company’s core beliefs. This will involve engaging in a discussion about the company’s core values, principles, and mission. Through this process, participants will assess how well existing services align with what their organization stands for and how it aligns with their personal values. Once the core beliefs have been established, participants will engage in a self-reflection exercise, where they will examine their own beliefs about the target audience. This exercise will help participants to understand any implicit biases or limiting beliefs they may have about the audience they are serving. It will also help to identify any gaps in understanding that need to be addressed. The next step is to challenge these beliefs and assumptions by seeking out data from under-resourced populations. This may involve conducting surveys, focus groups, or other forms of research to gain a better understanding of the audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors. By doing so, the company can start to create solutions that are more accessible to these audiences and tailored to their unique needs. Finally, this module will focus on identifying opportunities for creating greater value and enhancing opportunities for currently under-resourced regions and populations. This may involve exploring new markets or segments, partnering with community-based organizations, or leveraging technology to improve access to financial services. By the end of this module, participants will have a deeper understanding of the company’s mission and values, as well as a heightened awareness of their own beliefs and biases. They will also have concrete strategies for challenging assumptions and seeking out data to better serve under-resourced populations. This knowledge and skills will be an essential foundation for the rest of the Equitable Finance corporate training program and the solutions that the company will manufacture in the context of its target audience.
- Part 1 Month 2 Due Diligence – During the second month, participants will learn effective strategies for conducting due diligence in new or under-penetrated regions. This will involve exploring opportunities for aligning products to increase client adoption and ensuring compliance with regulations and legal requirements. Additionally, participants will work on developing a framework for responsible and ethically sound practices that are responsive to regional idiosyncrasies. The objective of Module 2, Due Diligence, is to equip participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to conduct thorough due diligence when expanding into new or under-penetrated regions. This module will focus on strategies for aligning products to increase client adoption, ensuring compliance with regulations and legal requirements, and developing responsible and ethically sound practices that are responsive to regional idiosyncrasies. The first part of this module will cover effective strategies for market research and analysis. Participants will learn how to gather and analyze data on the target region, including information on demographics, economic conditions, cultural norms, and regulatory frameworks. They will also explore techniques for identifying and assessing market opportunities, as well as potential risks and challenges. Building on this foundation, participants will then delve into aligning products to increase client adoption. This will involve understanding the unique needs and preferences of the target audience and identifying opportunities for tailoring existing products or developing new ones that meet those needs. Participants will learn how to gather customer feedback, conduct usability tests, and iterate on product design and features to maximize adoption and customer satisfaction. Compliance with regulations and legal requirements is a crucial aspect of operating in any region. In this module, participants will explore the regulatory landscape of the target region and learn how to navigate the complexities of compliance. They will gain an understanding of the specific regulations and legal requirements that apply to financial services, as well as best practices for ensuring adherence to these regulations. Emphasis will be placed on the importance of responsible and ethical practices and participants will work on developing a framework that aligns with the company’s values and supports long-term sustainability. Regional idiosyncrasies can have a significant impact on the success of financial initiatives. Participants will learn how to identify and understand these idiosyncrasies, such as cultural norms, language barriers, and local business practices. They will explore strategies for adapting products, services, and operations to meet the unique needs and preferences of the target region, while respecting and valuing the local culture. This module will emphasize the importance of taking a nuanced and contextualized approach to the development and delivery of financial products and services. By the end of this module, participants will have the knowledge and skills necessary to conduct comprehensive due diligence when expanding into new or under-penetrated regions. They will be able to effectively align products to increase client adoption, ensure compliance with regulations and legal requirements, and develop responsible and ethically sound practices that are responsive to regional idiosyncrasies. This will enable the company to expand its reach and impact, while also fostering long-term sustainability and positive relationships with local communities and stakeholders.
- Part 1 Month 3 User-Centric Design – In the third month, the focus will be on user-centric design principles and methodologies. Participants will learn how to apply these principles in product and service development, aiming to flatten the learning curve for customers through intuitive design. Establishing feedback loops that drive actionable insights will also be a key element of this month’s activities. The objective of Module 3, User-Centric Design, is to equip participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to apply user-centric design principles and methodologies in product and service development. This module will emphasize the importance of designing intuitive experiences that flatten the learning curve for customers and establishing feedback loops to drive actionable insights. The first part of this module will focus on understanding the principles of user-centric design. Participants will learn about the importance of empathy and understanding the needs, goals, and pain points of the target audience. They will explore techniques for conducting user research, such as interviews, observations, and surveys, to gather rich insights about customer preferences and behavior. Participants will also learn how to use personas and user journey mapping to create a holistic view of the customer experience. With a solid understanding of the target audience, participants will then dive into the application of design thinking in product and service development. They will learn how to ideate and generate innovative solutions that meet the needs of the users. Participants will engage in brainstorming sessions, prototyping, and iterative testing to refine their ideas and ensure that the final product or service aligns with user expectations. Intuitive design plays a crucial role in creating a seamless user experience. Participants will learn about the principles of intuitive design, such as simplicity, clarity, consistency, and discoverability. They will explore techniques for creating user-friendly interfaces and interactions, ensuring that customers can easily navigate and understand the product or service from the outset. Emphasis will be placed on reducing the learning curve, so that customers can quickly and effortlessly engage with the company’s offerings. Another key element of this module is establishing feedback loops that drive actionable insights. Participants will learn how to gather customer feedback on an ongoing basis, through channels such as user testing, surveys, and analytics. They will explore techniques for analyzing and interpreting this feedback, identifying patterns and trends that can inform product and service improvements. Participants will also learn how to prioritize and implement changes based on these insights, fostering a continuous improvement culture within the organization. By the end of this module, participants will have the knowledge and skills necessary to apply user-centric design principles and methodologies in product and service development. They will be able to empathize with the target audience, ideate and prototype innovative solutions, design intuitive experiences, and establish feedback loops that drive actionable insights. This will enable the company to deliver products and services that align with user needs and preferences, creating a positive and satisfying customer experience.
- Part 1 Month 4 Credit Scoring – The fourth month of the program will concentrate on understanding various approaches to credit scoring methodologies. Participants will also explore innovative credit factors that could be integrated, such as relationship history, strategic partner referrals, social capital, and social and environmental impact. The pros and cons of different approaches will be evaluated to enable informed decision-making on credit assessment. In Module 4, Credit Scoring, participants will focus on understanding different approaches to credit scoring methodologies. This module will also explore innovative credit factors that can be integrated into the assessment process, such as relationship history, strategic partner referrals, social capital, and social and environmental impact. The pros and cons of various approaches will be evaluated to enable informed decision-making on credit assessment. The first part of this module will provide participants with an overview of traditional credit scoring methodologies. They will survey commonly used credit scoring models, such as the FICO score, and understand the factors that influence creditworthiness, such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, and types of credit used. Participants will also explore and assess the limitations of traditional credit scoring models and the potential for bias or exclusion. Building on this foundation, participants will then delve into innovative credit factors that can be integrated into the assessment process. They will explore the concept of relationship history, which considers the borrower’s existing relationship with the institution and their track record of timely payments and responsible financial behavior. Participants will also learn about the potential for strategic partner referrals, where the creditworthiness of a borrower is affected by their association with trusted partners or organizations. Additionally, participants will explore the integration of social capital, which considers the borrower’s network and community connections, as well as the assessment of social and environmental impact, where creditworthiness is influenced by the borrower’s commitment to sustainability and positive social contributions. The module will then evaluate the pros and cons of different approaches to credit scoring. Participants will explore the advantages and disadvantages of traditional credit scoring models, as well as the potential benefits and challenges of integrating innovative credit factors. They will consider factors such as scalability, accuracy, fairness, and ease of implementation when evaluating different approaches. Through case studies and interactive discussions, participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of the trade-offs involved in credit assessment decision-making. By the end of this module, participants will have a deep understanding of various approaches to credit scoring methodologies. They will be able to critically evaluate the pros and cons of traditional credit scoring models and make informed decisions about integrating innovative credit factors into the assessment process. This knowledge will enable them to develop more inclusive and comprehensive credit assessment strategies that consider not just financial history, but also relationship history, strategic partnerships, social capital, and social and environmental impact. Ultimately, this will support the company’s goal of fostering financial inclusion and promoting positive social and environmental outcomes through responsible lending practices.
- Part 1 Month 5 Process Digitization – During the fifth month, participants will explore the impact of digitization on the finance industry. They will learn about de-risking strategies enabled by data transparency, speed of engagement, insights-to-action, and artificial intelligence in the digital age. Balancing innovation with risk mitigation will be a key focus area in understanding digitization and risk management. Module 5, Process Digitization, in the fifth month of the program, will focus on the impact of digitization on the finance industry. Participants will explore the strategies and advancements made possible by digitization, including de-risking strategies, data transparency, speed of engagement, insights-to-action, and artificial intelligence in the digital age. Balancing innovation with risk mitigation will be a key aspect of understanding digitization and risk management. The module will begin by providing participants with an overview of the transformational impact of digitization on the finance industry. They will learn about the key drivers behind the adoption of digital technologies, such as increased efficiency, enhanced customer experience, improved risk management, and accelerated innovation. Participants will explore how digitization has disrupted traditional business models and transformed industry dynamics, leading to the emergence of new players and innovative fintech solutions. Participants will then delve into the concept of de-risking strategies enabled by digitization. They will explore how digital technologies can enable better risk assessment and mitigation through increased data transparency. Participants will learn about the use of real-time data analytics and predictive modeling in identifying and managing risks more effectively. They will also investigate the role of digitization in automating compliance processes and reducing operational risks. Another key area of focus in this module is the speed of engagement and insights-to-action enabled by digitization. Participants will learn how digital technologies have revolutionized customer engagement, enabling real-time interactions and personalized experiences. They will explore the role of customer data analytics in driving actionable insights and decision-making. Participants will also examine the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in automating decision-making processes and driving efficiency. Balancing innovation with risk mitigation is a critical consideration when it comes to digitization and risk management. Participants will explore the potential risks and challenges associated with the adoption of digital technologies, such as cybersecurity threats, data privacy concerns, and regulatory compliance. They will learn about best practices and strategies to mitigate these risks, including establishing robust cybersecurity measures, implementing data protection frameworks, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. By the end of this module, participants will have a comprehensive understanding of the impact of digitization on the finance industry. They will be able to identify and evaluate de-risking strategies enabled by digitization, such as data transparency and real-time analytics. Participants will also understand how digitization has facilitated speed of engagement and insights-to-action. They will have a clear understanding of the risks and challenges associated with digitization and be equipped with strategies to mitigate these risks effectively. This knowledge will enable participants to navigate the evolving digital landscape of the finance industry, leveraging the opportunities offered by digitization while ensuring responsible and secure operations.
- Part 1 Month 6 Autonomous Finance – The sixth month will focus on unpacking the role of AI in autonomous finance. Participants will assess opportunities and challenges in implementing AI technologies, leveraging AI for decision-making, and improving operational efficiency. The focus will be on understanding how AI can enhance financial processes and decision-making. In Module 6, Autonomous Finance, participants will explore the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in autonomous finance. The focus of the sixth month will be on unpacking the opportunities and challenges associated with implementing AI technologies, utilizing AI for decision-making, and enhancing operational efficiency. Participants will delve into how AI can improve financial processes and decision-making within the realm of autonomous finance. The module will commence with an in-depth examination of the significance of AI in autonomous finance. Participants will gain an understanding of how AI technologies are revolutionizing the financial sector by enabling automation, data-driven decision-making, and predictive analytics. They will explore the potential benefits of implementing AI in financial operations, such as enhanced accuracy, increased speed, and improved customer experiences. Participants will also examine the challenges and considerations that come with integrating AI into financial systems, including data privacy, regulatory compliance, and ethical implications. Participants will then assess the various opportunities presented by AI technologies in the context of autonomous finance. They will explore how AI can be leveraged for decision-making processes, risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service. Participants will learn about the applications of machine learning and natural language processing in improving operational efficiency and facilitating personalized financial services. They will also examine case studies and examples showcasing successful implementations of AI in the financial industry. A key focus area of this module will be understanding how AI can enhance financial processes and decision-making. Participants will delve into the specific ways in which AI technologies can streamline tasks, reduce errors, and optimize resource allocation in financial operations. They will explore the role of AI in automating repetitive tasks, enabling real-time insights, and supporting strategic decision-making. Participants will also discuss the ethical considerations surrounding AI implementation and the importance of transparency and accountability in utilizing AI for financial services. By the end of this module, participants will have a comprehensive understanding of how AI is transforming autonomous finance. They will be equipped to evaluate the opportunities and challenges associated with implementing AI technologies in financial systems. Participants will understand the potential benefits of leveraging AI for decision-making and operational efficiency in financial processes. This knowledge will empower them to navigate the evolving landscape of autonomous finance and harness the capabilities of AI to drive innovation, improve customer experiences, and optimize financial operations.
- Part 1 Month 7 Program Piloting – In month seven, participants will pilot and iterate program implementations. This involves designing effective feedback loops for program evaluation and ensuring exceptional customer support throughout the process. The month will also focus on facilitating collaboration among program cohorts and developing robust reporting systems to measure the impact of the program. Module 7, Program Piloting, in the seventh month of the program, will focus on piloting and iterating program implementations. Participants will learn how to design effective feedback loops for program evaluation and provide customers with exceptional support throughout the process. The module will also emphasize the importance of fostering collaboration among program cohorts and developing robust reporting systems to measure the impact of the program. The module will commence with an overview of the importance of piloting program implementations. Participants will explore the benefits of piloting programs, such as identifying and addressing potential challenges, testing program effectiveness, and refining program processes. They will learn about the key steps involved in program piloting, including planning the pilot program, collecting feedback, and analyzing results. Participants will also examine case studies and examples of successful program pilots in the financial industry. Participants will then delve into the process of designing effective feedback loops for program evaluation. They will learn about the importance of gathering customer feedback and analyzing it to identify areas for improvement. Participants will explore the different methods for collecting feedback, including surveys, focus groups, and interviews, and learn how to apply the results to improve program implementations. The module will also cover strategies for providing exceptional customer support throughout the process, including rapid response times, clear communication, and proactive problem-solving. Another key focus area of this module is facilitating collaboration among program cohorts. Participants will learn about the importance of building strong relationships with program participants and fostering a sense of community within the program. They will examine different approaches to group work and learn how to facilitate collaboration in a remote environment. The module will also cover best practices for developing communication and collaboration tools to support program cohorts. Finally, the module will cover the development of robust reporting systems to measure the impact of the program. Participants will learn about the importance of data-driven decision-making and explore different metrics for measuring program effectiveness. They will learn how to design and create reports that provide insights into program performance and progress, including operational and financial metrics. By the end of this module, participants will be equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to pilot and iterate program implementations successfully. They will understand how to design effective feedback loops to gather customer feedback and use it to refine program processes. Participants will know how to provide exceptional customer support and build strong relationships with program participants. They will also be well-versed in developing robust reporting systems to measure program impact. This knowledge will enable them to launch successful programs and drive innovation within their organizations.
- Part 1 Month 8 Building Partnerships – During the eighth month, participants will work on identifying and developing well-aligned partnerships that align with company values. They will learn to move away from rigid systems and foster mutually beneficial relationships through collaboration with partners. Module 8, Building Partnerships, in the eighth month of the program, will focus on the identification and development of well-aligned partnerships that align with company values. Participants will learn how to move away from rigid systems and foster mutually beneficial relationships through collaboration with partners. The module will begin by emphasizing the importance of partnerships that align with company values. Participants will explore the benefits of partnering with organizations that share similar values and goals. They will learn how such partnerships can enhance brand reputation, drive innovation, and create new business opportunities. Participants will also examine case studies of successful partnerships in the finance industry and explore the key factors that contributed to their success. Participants will then delve into the process of identifying and selecting partners that align with company values. They will learn how to conduct a thorough assessment of potential partners, considering factors such as their company culture, values, track record, and areas of expertise. Participants will also explore different approaches to partner selection, including strategic alliances, joint ventures, and ecosystem partnerships. They will learn how to evaluate the potential risks and benefits of different partnership models and select the most suitable approach for their organization. Another key focus area of this module is fostering mutually beneficial relationships through collaboration with partners. Participants will explore strategies for building trust, maintaining open communication, and resolving conflicts within partnerships. They will learn the importance of establishing clear expectations, setting mutual goals, and defining roles and responsibilities. Participants will also examine collaborative tools and techniques that can facilitate effective collaboration with partners, such as shared project management platforms and regular performance reviews. Throughout the module, participants will be encouraged to move away from rigid systems and embrace a more flexible and adaptive approach to partnerships. They will learn how to adapt to changes in the business environment and adjust partnership strategies accordingly. Participants will also explore the concept of co-creation and the potential for innovation that can arise from collaborative partnerships. By the end of this module, participants will have the skills and knowledge necessary to identify and develop well-aligned partnerships that align with company values. They will understand the benefits of partnering with organizations that share similar values and goals. Participants will be able to assess potential partners effectively and select the most suitable partnership model for their organization. They will also know how to foster mutually beneficial relationships through collaboration and navigate the challenges that may arise in partnerships. This knowledge will empower participants to build strong and successful partnerships that drive innovation and create new business opportunities.
- Part 1 Month 9 Catalytic Funding – The focus of the ninth month will be on exploring alternative sources of capital beyond traditional financiers. Participants will understand the benefits and limitations of alternative capital sources and how catalytic funding can support innovation and flexibility in financial endeavors. Module 9, Catalytic Funding, in the ninth month of the program, will focus on exploring alternative sources of capital beyond traditional financiers. Participants will gain an understanding of the benefits and limitations of alternative capital sources and how catalytic funding can support innovation and flexibility in financial endeavors. The module will begin by emphasizing the importance of exploring alternative sources of capital. Participants will learn about the limitations of traditional financiers and the potential benefits of diversifying funding options. They will explore the concept of catalytic funding, which involves leveraging funding mechanisms that go beyond purely financial returns. Participants will examine case studies and examples of organizations that have successfully utilized alternative capital sources to support their financial endeavors. Participants will then delve into the different types of alternative capital sources available. They will explore options such as impact investing, venture capital, crowdfunding, social impact bonds, grants, and loans from socially responsible institutions. Participants will learn about the benefits and considerations associated with each source, including the potential for social and environmental impact, risk levels, and the alignment of values and goals. Another key focus area of this module is understanding how catalytic funding can support innovation and flexibility in financial endeavors. Participants will explore how alternative capital sources can provide the financial resources necessary for organizations to pursue innovative projects and initiatives. They will learn about the flexibility that comes with catalytic funding, including the potential for longer-term investments, patient capital, and customized funding structures. Participants will also examine strategies for effectively accessing and utilizing catalytic funding, including developing a clear value proposition and aligning with the funding priorities of potential investors or donors. Throughout the module, participants will be encouraged to critically evaluate the benefits and limitations of alternative capital sources. They will learn how to analyze the risks and rewards associated with each type of funding and determine which sources are best suited for their organization’s needs. Participants will also explore strategies for building relationships with alternative capital providers and effectively communicating their financial goals and impact. By the end of this module, participants will have a comprehensive understanding of alternative sources of capital and the role of catalytic funding in supporting innovation and flexibility in financial endeavors. They will be equipped to identify and evaluate different types of alternative capital sources and determine which ones are suitable for their organization’s goals and values. Participants will understand how to access and utilize catalytic funding effectively to support their financial initiatives and drive positive social and environmental impact. This knowledge will enable participants to diversify their funding options and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
- Part 1 Month 10 Risk Management – Participants will concentrate on developing proactive risk management strategies in the tenth month of the program. This includes creating principles for asset and liability management, mitigating risks through scenario analysis and stress testing, and embedding risk management practices into organizational culture. Module 10, Risk Management, in the tenth month of the program, will focus on developing proactive risk management strategies. Participants will concentrate on creating principles for asset and liability management, mitigating risks through scenario analysis and stress testing, and embedding risk management practices into organizational culture. The module will commence by underlining the importance of proactive risk management. Participants will gain an appreciation for the benefits of identifying and addressing risks proactively, including protecting assets, minimizing financial losses, and maintaining long-term stability. They will explore case studies and examples of organizations that have effectively managed risks and learn from their experiences. Participants will then delve into developing principles for asset and liability management. They will learn how to assess and manage the risks associated with various types of assets and liabilities, such as loans, investments, and funding sources. Participants will explore strategies for diversifying assets and liabilities and optimizing the risk-return trade-off. They will also learn about asset and liability management frameworks and tools that can facilitate effective risk management. Another key focus area of this module is mitigating risks through scenario analysis and stress testing. Participants will learn how to identify and analyze potential risks by conducting scenario analysis, which involves simulating different scenarios and examining their impact on financial performance. They will also explore stress testing, which involves evaluating the resilience of a financial institution or system under extreme or adverse conditions. Participants will gain the skills to use scenario analysis and stress testing to inform risk mitigation strategies and enhance financial resilience. Participants will also learn about the importance of embedding risk management practices into organizational culture. They will explore strategies for creating a risk-aware culture within their organizations, including fostering accountability, promoting transparency, and providing ongoing risk management training. Participants will learn about the role of risk committees and governance structures in facilitating effective risk management. Throughout the module, participants will be encouraged to adopt a holistic and integrated approach to risk management. They will learn how to align risk management strategies with organizational objectives and develop a risk appetite statement that guides decision-making. Participants will also explore emerging trends and challenges in risk management, such as cybersecurity risks and climate-related risks, and learn how to incorporate these considerations into their risk management strategies. By the end of this module, participants will have the skills and knowledge necessary to develop proactive risk management strategies. They will understand how to create principles for asset and liability management and optimize the risk-return trade-off. Participants will know how to conduct scenario analysis and stress testing to identify and mitigate risks effectively. They will also be equipped to embed risk management practices into organizational culture, fostering a risk-aware environment. This knowledge will enable participants to proactively manage risks and enhance the stability and resilience of their financial endeavors.
- Part 1 Month 11 Organizational Design – The eleventh month will focus on effective organizational design within the finance sector. Participants will learn about hiring and training strategies, building a workforce that embraces innovation and agility, as well as fostering a culture of continuous learning and professional development. Module 11, Organizational Design, in the eleventh month of the program, will focus on effective organizational design within the finance sector. Participants will learn about hiring and training strategies for building a workforce that leverages technology and data analytics, as well as fostering a culture of innovation and agility. The module will commence by underscoring the importance of organizational design in driving success in the finance sector. Participants will explore the key components of effective organizational design, including structure, roles, and processes. They will learn how to align organizational design with strategic objectives and create a framework that supports innovation, agility, and collaboration. Participants will then delve into strategies for building a technology-focused finance team. They will learn about the growing importance of technology in the finance sector and the role of engineers and computer programmers in driving innovation and efficiency. Participants will explore best practices in hiring and training these professionals, including recruiting from diverse talent pools and offering opportunities for continuous learning and professional development. They will also gain insights into fostering a culture of innovation that encourages experimentation, risk-taking, and collaboration between finance and technology teams. Another key focus area of this module is leveraging analytics and data to drive performance within the finance organization. Participants will learn about the importance of data analytics in financial decision-making and explore strategies for integrating data analytics into various aspects of the finance organization, such as risk management and financial operations. They will also learn about the role of machine learning and artificial intelligence in finance and gain insights into best practices for leveraging these technologies in decision-making. Participants will also explore strategies for fostering an innovative and agile culture within the finance organization. They will gain insights into creating a culture that embraces experimentation, encourages collaboration and knowledge-sharing, and supports risk-taking. Participants will learn about the role of leadership in fostering an innovative and agile culture and explore strategies for overcoming resistance to change. Throughout the module, participants will be encouraged to adopt a strategic and holistic approach to organizational design. They will learn how to align organizational design with their strategic objectives and create a structure that supports innovation, agility, and collaboration. Participants will also explore strategies for building a technology-focused finance team that leverages analytics and data to drive performance. By the end of this module, participants will have the skills and knowledge necessary to design and develop effective finance organizations. They will understand how to attract and retain top technology talent through strategic hiring and training strategies. Participants will know how to foster a culture of innovation and agility within their organizations and leverage analytics and data to drive performance. They will be equipped to create a framework for organizational design that supports their strategic objectives and enhances organizational performance. This knowledge will enable participants to build high-performing finance organizations that leverage technology to drive innovation and success in the competitive finance sector.
- Part 1 Month 12 Future Roadmap – In the final month of the program, participants will recap key learnings and insights gained throughout the training. They will identify areas for further improvement and growth, culminating in the creation of a roadmap for future organizational development and success. In the final month of the program, participants will recap key learnings and insights gained throughout the training. They will reflect on their individual and organizational growth and identify areas for further improvement and development. This module will culminate in the creation of a strategic roadmap for future organizational success. The module will commence with a comprehensive review of the program’s key learnings and insights. Participants will reflect on the knowledge and skills acquired during the training and identify the most impactful takeaways for their roles and responsibilities within the finance sector. They will also assess their personal growth and development throughout the program and identify areas for further improvement. Participants will then embark on creating a customized roadmap for future organizational development and success. They will consider the strategic objectives of their organization, market dynamics, and emerging trends in the finance sector. Participants will assess their current organizational capabilities and identify areas for enhancement or transformation. They will set clear and measurable goals and develop actionable strategies to achieve them. The roadmap will encompass various aspects of organizational development, including talent management, technology adoption, process improvement, and organizational culture. Participants will explore strategies for attracting and retaining top talent, fostering a culture of innovation and agility, and leveraging technology to drive efficiency and productivity. They will also consider the importance of data analytics and continuous learning in achieving organizational success in the rapidly evolving finance landscape. Throughout the module, participants will be encouraged to think critically and creatively about the future of their organization. They will explore emerging trends and disruptions in the finance sector and consider their implications for organizational strategy. Participants will also gain insights into effective change management strategies and ways to overcome resistance to change within their organizations. By the end of this module, participants will have developed a comprehensive roadmap for future organizational development and success. They will have identified key areas for improvement and growth, aligned with their strategic objectives. Participants will have set clear goals and developed actionable strategies to achieve them, taking into account the evolving landscape of the finance sector. The roadmap will serve as a guide for participants to drive organizational transformation and ensure long-term success. It will provide a framework for enhancing organizational capabilities, fostering innovation and agility, and leveraging technology and data analytics to stay ahead in the competitive finance industry. Overall, this module will enable participants to consolidate their learning and insights from the program and channel them into a strategic roadmap for future organizational development and success. By reflecting on their journey, assessing organizational needs, and setting clear objectives, participants will be equipped to lead their organizations towards a prosperous and sustainable future in the dynamic and evolving finance landscape.
Methodology

Equitable Finance
The proven methodical approach to this program helps companies build a solid, well-structured foundation that supports an innovative financial program that scales. We will help you incorporate a comprehensive approach to achieve program objectives.
Many financial organizations struggle in expanding to underserved consumers because they attempt to “copy-paste” exusting solutions into new environments. This leads to poor product-market fit, unnecessary learning curves, and poor positioning against market competitors. The Market Insights & Immersion (MII) approach involves integrating various methods and approaches to foundational research to gain a thorough understanding of the market, consumer customs, behavior, and access to financial products.
In the MII approach, we equip organizations to deploy a blended approach to understanding potential market segments using the following techniques:
● Market research studies: Study existing case studies or conduct in-depth interviews with individuals from the target market who have knowledge and experience related to banking practices and consumer behavior. This can provide valuable insights into customer preferences, access to banking products, and any barriers or challenges present.
● Focus Groups: Organize focus group discussions with representatives from the target market. This qualitative research method allows students to engage in open-ended discussions to gain a deeper understanding of consumer customs, preferences, and attitudes towards banking products.
● Surveys: Design and administer surveys to collect data on consumer customs, preferences, and behaviors. You can use online survey tools such as Google Forms or SurveyMonkey to reach a larger audience and gather insights about customer behavior and attitudes.
● Business Ethnography: Organizations can conduct field observations in the target region to observe customer behavior, customs, and cultural nuances related to banking practices. They can also engage in ethnographic research by immersing themselves in the local community to gain first-hand insights into customer habits and preferences.
● Partnerships: Partner with local organizations, businesses, or community groups in the target region who specialize in consumer research or banking services. This collaboration can provide access to existing data, local expertise, and valuable insights.

Of these approaches, we emphasize the power of business ethnography due to its ability to contextualize data through immersion. We draw inspiration from successful implementations by companies like Xerox and Intel, who have used ethnographic research to gain invaluable insights into customer behavior, needs, and preferences for their products and services.
Xerox used ethnographic research to understand how people used their copiers in office settings. Through observation, researchers found that people commonly made copies of their own faces, leading Xerox to create a “self-portrait” feature on their machines. Additionally, researchers discovered that many office workers were hesitant to ask for help when using the copier, which inspired Xerox to simplify their user interface to make it more intuitive and user-friendly.
Intel has also utilized ethnographic research to improve their products and services. In the mid-1990s, Intel began using ethnography to gather information on how customers used their products in order to improve the design and functionality of their microprocessors. By observing how people interacted with technology in their daily lives, Intel researchers were able to design more intuitive products that met the needs and expectations of customers. More recently, Intel has used ethnography to gain insights into the digital content creation market, which has led to the development of new products and strategic business decisions.
During our Due Diligence workshop, participants will learn effective strategies for conducting due diligence in new or under-penetrated regions. This workshop sets the foundation for our User-Centric Design workshop, where we apply insights towards product and service development. Our goal is to flatten the learning curve for customers through intuitive design.
Every training session will integrate enriching learning experiences with fun engagement activities. These sessions are designed to help you understand and humanize your target audiences, enabling you to develop highly in-demand solutions that they cannot live without. Each workshop includes a comprehensive course manual that provides tools, frameworks, and recommended methodologies for research and internal KPI tracking, ensuring accountability. Additionally, the manual will contain suggested frameworks for credit scoring and tested partnership strategies.
We are excited to guide you through this comprehensive program that will transform the way you approach product and service development in the financial industry. Let’s build a strong foundation together and unlock new opportunities for growth and success.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Banking and Finance
History:
The banking and financial services industry dates back centuries. In the past 10 years, the industry has experienced significant growth and transformation. With the advent of advanced technology and changing economic systems, banking has adapted to meet the demands of a digital era. The establishment of central banks, the introduction of credit cards, and the development of electronic payment systems have revolutionized the way individuals and businesses conduct financial transactions.
The rise of globalization has also had a profound impact on the industry. It has led to the growth of international banking and the expansion of financial services across borders. As the world becomes more interconnected, the need for seamless and efficient financial services has become paramount.
Current Position:
Today, the banking and financial services industry is a crucial pillar of the global economy. It encompasses various subsectors, including commercial banking, investment banking, insurance, asset management, and fintech. Commercial banks serve as intermediaries between depositors and borrowers, providing essential financial services such as lending, payment processing, and deposit-taking. Investment banks facilitate capital raising, mergers and acquisitions, and securities trading. Insurance companies protect individuals and businesses against financial risks, while asset managers manage investments on behalf of clients. The emergence of fintech has disrupted traditional banking models by leveraging technology to offer innovative financial solutions, such as digital banking, peer-to-peer lending, and robo-advisory services.
The industry faces unique challenges and opportunities in the current business landscape. Regulatory frameworks have become more stringent in the aftermath of the global financial crisis, aiming to ensure stability and consumer protection. The rise of digital transformation has compelled traditional banks to adapt their operations and customer experiences to meet the growing expectations of tech-savvy consumers. Additionally, increasing cybersecurity threats have pushed the industry to invest heavily in advanced security measures to protect sensitive customer data.
Future Outlook:
Looking ahead, the banking and financial services industry is poised for continued evolution. Technological advancements will continue to drive innovation and reshape traditional business models. Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and open banking are expected to become more prevalent, enhancing efficiency, security, and customer experience. The industry will witness a greater integration of financial services with technology, leading to the development of personalized offerings, automated processes, and improved data analytics capabilities.
Regulatory changes will also play a significant role in shaping the industry’s future. Stricter regulations are likely to remain in place to prevent systemic risks, promote transparency, and maintain consumer trust. Companies will need to stay agile and adaptable to comply with evolving regulations while seizing opportunities for growth.
Furthermore, the rise of sustainable finance and the increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are expected to influence the industry’s direction. Financial institutions are under pressure to incorporate ESG considerations into their investment decisions and risk management practices, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the banking and financial services industry has a rich history and currently sits at the heart of the global economy. With technological advancements, regulatory changes, and ESG factors driving the industry’s future, participants in the sector must prioritize innovation, adaptability, and responsible practices to thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape.

Technology
History:
Over the past 10 years, the technology industry has experienced rapid growth and transformative changes. With advancements in digital technology and the widespread adoption of the internet, the industry has revolutionized various aspects of human life and business operations across sectors.
The emergence of smartphones and mobile devices has played a major role in shaping the industry. Companies like Apple, Samsung, and Google have introduced innovative mobile platforms and ecosystems, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services on the go. This has transformed how we communicate, work, and consume information.
The rise of social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, has revolutionized how we connect and interact with others. Social media has not only changed the way we communicate but has also become a powerful tool for marketing, advertising, and influencing consumer behavior.
Cloud computing revolutionized the technology industry in the past decade. Companies like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have provided scalable infrastructure and services, allowing businesses to store and process vast amounts of data, build innovative applications, and deploy them with ease.
Current Position:
The technology industry currently dominates the global business landscape. It encompasses a range of subsectors, including software development, hardware manufacturing, telecommunications, internet services, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. Technology companies have become household names and are known for their innovative products and services, including smartphones, social media platforms, cloud computing, and advanced data analytics.
The sector has experienced exponential growth driven by increasing digitalization and the proliferation of smart devices. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Facebook have disrupted traditional business models and become global giants, leveraging digital platforms to offer diverse services beyond their initial offerings. The industry has also witnessed the rise of startups and unicorns, fueled by venture capital funding and entrepreneurial ambition.
Future Outlook:
The technology industry’s future looks promising, with continued innovation and disruption on the horizon. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and quantum computing are set to redefine industries and create new opportunities.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will revolutionize decision-making processes, automate routine tasks, and improve customer experiences. Blockchain technology will enable secure and transparent transactions across various sectors, including finance, supply chain, and healthcare. The IoT will connect billions of devices, creating a networked ecosystem that enhances efficiency and enables real-time data analysis. Quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems and advance fields such as cryptography, drug discovery, and weather forecasting.
As technology advancements continue, challenges such as cybersecurity threats, data privacy concerns, and ethical implications must be addressed. Governments and regulatory bodies will play a crucial role in ensuring responsible and inclusive innovation, balancing innovation with consumer protection and societal well-being.
The tech industry’s future is also intertwined with global trends such as digital inclusion and sustainability. Bridging the digital divide and providing equal access to technology will be critical for fostering economic and social development worldwide. Additionally, sustainable technology solutions and greener practices will be essential in mitigating the environmental impact of the industry and meeting global sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the technology industry has deep roots in innovation and has transformed our society and economy. With emerging technologies on the horizon and the need to address ethical and sustainability considerations, the industry must continue to foster innovation while navigating evolving regulatory landscapes and societal expectations. By doing so, the technology industry is poised for ongoing growth and disruption.

Agriculture
History:
The agriculture sector has played a significant role throughout human history, providing food, raw materials, and livelihoods for communities around the world. Technological advancements, such as the introduction of mechanization, improved crop varieties, and irrigation systems, have greatly increased productivity and efficiency in modern agriculture. However, despite its importance, the sector continues to face challenges related to underdevelopment, limited access to finance, and the plight of smallholder farmers.
Current Position:
In the present day, the agriculture industry remains a vital part of global economies, contributing to food security, employment, and rural development. Smallholder farmers, who operate on small plots of land, form the backbone of agriculture in many developing countries, particularly in rural areas. These farmers face numerous obstacles in accessing capital, market opportunities, and technology. Limited access to financial services hampers their ability to invest in improved farming techniques, machinery, and inputs like seeds and fertilizers. This lack of access restricts their potential for innovation, productivity, and mechanization, especially in the last mile of the supply chain.
Future Outlook:
The future of the agriculture industry will be shaped by several key trends and challenges. Firstly, there is a growing recognition of the importance of inclusive finance in driving agricultural development. Lending to underbanked individuals, including smallholder farmers, is seen as crucial for unlocking innovation, increasing productivity, and promoting mechanization across the last mile. Financial institutions are beginning to offer tailored financial products such as microloans, agricultural insurance, and mobile banking solutions to reach these underserved populations.
Furthermore, the adoption of technology and digital solutions is expected to play a significant role in the future of agriculture. This includes the use of precision farming techniques, IoT devices, drones, and remote sensing technologies to optimize input utilization, monitor crops, and enhance decision-making. However, there is a need to ensure that these innovations are accessible and affordable to smallholder farmers, as the digital divide can exacerbate inequities in the sector.
Sustainable practices and climate resilience will also shape the future of agriculture. There is a growing focus on developing climate-smart agriculture techniques that mitigate the effects of climate change, conserve natural resources, and promote resilience. This includes promoting agroecological approaches, diversification of crops, and efficient water management practices.
In conclusion, the agriculture industry has a rich historical background and continues to be of paramount importance worldwide. To drive sustainable development and ensure the well-being of smallholder farmers, there is a need for increased access to finance, technological advancements, and sustainable practices. By prioritizing lending to underbanked individuals, supporting innovation, productivity, and mechanization across the last mile, the agriculture sector can navigate the challenges ahead and contribute to a more inclusive and sustainable future.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Washington, DC
History:
Washington DC, the capital of the United States, has a rich history dating back to its establishment in 1790. In recent years, Washington DC has been at the forefront of political and social movements. The city has witnessed significant events that have shaped the nation’s history. From the inauguration of the first African American President, Barack Obama, in 2009, to the Women’s March in 2017, where millions gathered to advocate for gender equality and women’s rights, the city has been a focal point for activism and change.
Washington DC has also experienced economic growth and development in the past decade. The city has seen a rise in technology companies, startups, and innovation hubs, attracting a dynamic workforce and contributing to its flourishing economy. The revitalization of areas such as the Wharf and the transformation of neighborhoods like H Street have brought new life and vitality to the city.
Furthermore, Washington DC has continued to serve as a cultural hub, offering a diverse range of museums, galleries, theaters, and music venues. Visitors and residents can explore the rich history and diverse cultural heritage of the city through institutions such as the Smithsonian museums, the Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, and numerous festivals and events throughout the year.
As the seat of government, Washington DC remains a symbol of democracy and political power. From historic debates and legislation to the recent presidential elections, the city continues to be a center for decision-making and policy development.
Current Position:
Today, Washington DC is not only home to the federal government but also a vibrant cultural, educational, and business center. The city houses numerous government agencies, including the White House, the Capitol, and the Supreme Court, making it a hub for political activities. It is also home to many international organizations and embassies, fostering diplomatic relations on a global scale.
Washington DC has a diverse economy that goes beyond government-related activities. The city has a thriving professional services sector, including law firms, consulting firms, and think tanks. It has a robust healthcare industry, with renowned medical and research institutions. The education sector is also prominent, with several prestigious universities and research centers.
The city’s cultural scene is dynamic, with an array of museums, galleries, theaters, and music venues. It attracts tourists from around the world who come to explore landmarks such as the National Mall, the Smithsonian museums, and historic neighborhoods like Georgetown.
Future Outlook:
Looking ahead, Washington DC’s future is promising. As the capital of the United States, it will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping national policies and promoting global relationships. Given the growing emphasis on technology and innovation, the city is likely to see increased investments in these sectors. Startups and technology companies are emerging in the area, contributing to job creation and economic growth. Moreover, the city’s commitment to sustainability and green initiatives is likely to drive progress in renewable energy, urban planning, and environmental policies.
The continued development of infrastructure, including transportation networks, will enhance connectivity and make the city more accessible. The increasing focus on education and research will foster a knowledge-based economy, attracting bright minds and nurturing innovation.
Washington DC’s robust cultural scene, with its museums, theaters, and festivals, will continue to flourish, supporting tourism and contributing to the city’s overall appeal.
In conclusion, Washington DC’s historical significance, governmental presence, diverse economy, and cultural offerings make it an influential and attractive location. With its central role in politics and policy-making, coupled with a growing focus on technology and sustainability, the city is poised for continued growth and prosperity.

Nairobi, Kenya
History:
Over the past 10 years, Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, has undergone remarkable growth and transformation, solidifying its position as one of Africa’s leading and dynamic cities.
During this period, Nairobi has experienced rapid urbanization, becoming a thriving economic and financial hub. The city’s skyline has changed with the construction of modern high-rise buildings, symbolizing its economic progress and attracting global businesses. The development of business parks, such as the sophisticated Two Rivers Mall and the bustling Westlands district, has contributed to Nairobi’s reputation as a major commercial center in East Africa.
Current Position:
Today, Nairobi is a vibrant and cosmopolitan city that serves as the economic, political, and cultural center of Kenya. It is a regional hub for finance, commerce, and innovation in East Africa. The city is home to the Nairobi Securities Exchange, the largest stock exchange in East Africa, facilitating capital raising and investment activities for businesses in the region.
Nairobi’s economy is diverse, encompassing various sectors such as finance, telecommunications, tourism, manufacturing, and agriculture. The city has a growing technology scene, earning it the nickname “Silicon Savannah.” Startups and tech companies are emerging, leveraging advancements in mobile technology to provide innovative solutions in e-commerce, fintech, and agritech.
The city is also a major transportation hub, with Jomo Kenyatta International Airport connecting Nairobi to international destinations. The construction of the Standard Gauge Railway has improved connectivity within the country and enhanced trade links to neighboring countries, boosting commerce and economic integration.
Nairobi’s cultural landscape is vibrant, with numerous art galleries, museums, theaters, and music venues. The city is known for its lively nightlife and rich music scene, contributing to its reputation as a regional cultural center.
Future Outlook:
Looking ahead, Nairobi’s future is promising. The city is positioned to continue its growth and become an even more significant regional player. Kenya’s Vision 2030, a development blueprint, aims to position Nairobi as a regional financial hub and a center for technology and innovation.
The technology sector is expected to thrive, driven by a young and tech-savvy population, increased internet penetration, and supportive government policies. Mobile banking and digital financial services have already gained widespread adoption, and Nairobi is poised to strengthen its position as a fintech hub.
Nairobi’s location in East Africa, coupled with ongoing infrastructure development, presents opportunities for increased regional trade and investment. The city’s commitment to sustainable development and green initiatives is also likely to shape its future trajectory.
However, challenges such as income inequality, inadequate infrastructure, and traffic congestion need to be addressed. The government and private sector investments in these areas will be crucial to overcome these hurdles and drive sustainable growth.
In conclusion, Nairobi’s historical significance, diverse economy, technological advancements, and cultural offerings make it an attractive and influential location in East Africa. With its growing regional importance, vibrant startup ecosystem, and favorable policies, Nairobi is poised for continued economic and technological growth.

San Francisco, California
History:
San Francisco, located in Northern California, has continued to be a dynamic and thriving city over the past 10 years, building upon its rich history and cultural heritage.
In recent years, San Francisco has become a global hub for technology and innovation. The city is home to some of the world’s most influential tech companies, such as Google, Apple, and Facebook, attracting a diverse and talented workforce from around the world. This influx of tech talent has contributed to the city’s economic growth and transformed the local startup scene.
San Francisco has also demonstrated a commitment to environmental sustainability and combating climate change. The city has implemented policies promoting renewable energy, recycling, and clean transportation, aiming to become a zero-emissions city by 2050. The San Francisco Bay Area has also seen the development of bike-sharing and car-sharing systems, providing residents with alternative modes of transportation.
In addition, San Francisco has continued to be a cultural and artistic center, hosting world-renowned events such as the San Francisco International Film Festival and the San Francisco Jazz Festival. The city’s diverse neighborhoods, such as Chinatown and the Mission District, offer residents and visitors a unique blend of history, culture, and food.
Furthermore, San Francisco has raised its voice for social justice and equality. The city has played a significant role in the Black Lives Matter movement, as well as advocating for the rights of marginalized communities, including the LGBTQ+ community and immigrants.
As San Francisco looks to the future, the city faces challenges such as affordable housing, income inequality, and congestion. Despite these obstacles, San Francisco’s continued growth, innovation, and cultural significance make it an exciting destination for those seeking to experience the cutting edge of technology, art, and culture.
Current Position:
San Francisco is currently one of the leading technology hubs in the world, often referred to as the “Tech Mecca” or the “Silicon Valley.” It is home to numerous technology companies, including industry giants like Apple, Google, and Facebook. The city’s proximity to renowned educational institutions such as Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley, has contributed to its status as a hub for innovation and talent.
San Francisco’s economy is characterized by a strong emphasis on technology, finance, and professional services. The city is known for its startup ecosystem and venture capital investments, attracting entrepreneurs from all over the world. It has a thriving arts and culture scene, with numerous museums, theaters, and festivals.
The city faces challenges related to income inequality, housing affordability, and homelessness. The high cost of living has made it difficult for many residents to find affordable housing, leading to social disparities. However, efforts are being made to address these issues through initiatives aimed at increasing affordable housing options and support for marginalized communities.
Future Outlook:
Looking ahead, San Francisco’s future as a technology hub looks promising. The city will continue to thrive as companies focus on innovation, attracting talent, and investing in research and development. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology are expected to shape the city’s future economic landscape.
San Francisco’s commitment to sustainability and environmental consciousness is likely to drive developments in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation. The city aims to be carbon neutral by 2050, aligning with global sustainability goals.
However, the city faces ongoing challenges related to affordability, income inequality, and
transportation infrastructure. Addressing these issues will be crucial to maintaining a diverse and inclusive workforce and ensuring sustainable growth.
In conclusion, San Francisco’s historical significance, status as a technology hub, and cultural offerings make it an attractive location for businesses and individuals. With its ongoing technological advancements, commitment to sustainability, and efforts to address social challenges, San Francisco is poised for continued growth as a global leader in innovation and entrepreneurship.
Program Benefits
Finance
- Financial Inclusion
- Financial Modeling
- Portfolio Health
- Increasing ROI
- Regulatory Compliance
- Financial Transparency
- Financial Planning
- Cost Efficiency
- Strategic Planning
- Increasing Revenues
Management
- Value Alignment
- Risk Mitigation
- Market Expansion
- Product Innovation
- Thought Leadership
- Operational Efficiency
- Talent Development
- Change Management
- Sustainable Practices
- Relationship Management
Marketing
- Market Research
- Brand Positioning
- Market Expansion
- Competitive Advantage
- Customer Experience
- Content Marketing
- Digitial Marketing
- Social Media Engagement
- Brand Awareness
- Marketing Analytics
Testimonials
Hello Tractor
“Mrs. Thobias is a fearless and dedicated leader who was the tip of the spear in launching Hello Tractor’s innovative tractor finance product. Her commitment to attacking bias forced me to address the bias that I brought to our work and I am a better leader for it.”
I helped Hello Tractor in the development of an innovative pay-as-you-go (PAYG) solution for aspiring agribusiness entrepreneurs, allowing tractor operators to pay down a leasing contract as they service nearby farms. These small, weekly repayments are made based on actual work completed, increasing the ease of repayment at the time at which revenue is generated. With the strategic assistance provided across program development, go-to-market strategy, and implementation, the company deployed more than $10MM within its first 12 months of running the pilot program and PAYG customers across three countries are consistently repaying more than 100% of what they owe.

Kiva US
I have helped Kiva US in the strategically revamp its partnership model and technology so that it provides deeper connectivity and usefulness at scale (as juxtaposed to continuing with traditional interactions that are merely transactional). I have supported Kiva US in working to creatively balance the tradeoffs between risk and reward in ways that mobilize a new class of borrowers who are not yet ready for the CDFI and commercial bank stages of capital.

Bank of America
“I’ve known Mrs. Thobias for a long time and have had the opportunity to work with her on several transactions and projects – many of them being franchise defining and/or business critical. And every single time, I have witnessed her deliver a fantastic, thorough and thoughtful end product. Specifically, I’d call out us being on the SME team for rolling out a new pricing platform. Ms. Thobias’s ability to grasp nuances, understand them end to end and then be able to summarize in simple language is second to none. Throughout her tenure with the firm, she delivered solid results while working relentlessly in high pressure situations – while always maintaining her positive attitude and grace. She exemplifies a quote by Robert Collier “Success is the result of small efforts, repeated day in and day out “.

The Literacy Lab
“You are incredibly flexibile. I appreciate your ability to adapt to our needs, add items, and chance course throughout the process.”
The Literacy Lab, an organization that provides research- and evidence-based early literacy intervention to students in Pre-K through grade 3, has faced recruitment challenges for tutors and fellows in the current competitive landscape. The education sector has been flooded with more competitors, and the COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated the situation. Additionally, the stagnation of talent attraction into the sector, stemming from existing stigma around education sector work conditions, has posed additional hurdles. These impacts presents challenges to their funding, continuitym and relevancy in the marketplace.
To address these challenges, I partnered with The Literacy Lab to conduct a comprehensive range of services and drive innovation that is more optimally funded while driving deeper impact to marginalized individuals. This included internal gap analysis, field interviews, market research, competitive analysis, product development, and piloting. Given the relatively fragmented nature of the sector, it was essential to streamline insights and identify opportunities for improvement. My expertise in strategic planning and financial modeling was crucial as the company grapples with high execution costs, the emergence of new edtech incumbents with limited market history, and talent pipeline leakage.
I involved the entire firm in the exploration process, prioritizing collective buy-in and fostering a positive company culture. My carefully paced and phased approach allows for concentrated focus and flexibility throughout the partnership timeline. By collaborating with The Literacy Lab, I aided the organization in selecting key initiatives to test and scale, aligning with their strategic objectives.
My assistance provides The Literacy Lab with a strategic advantage in navigating the challenging landscape of tutor and fellow recruitment. With their expertise in analyzing and understanding the sector, my insights will help alleviate the recruitment challenges that the organization faces. By identifying key initiatives to test and scale, The Literacy Lab can strategically evolve and adapt to the changing environment, ensuring the continued delivery of high-quality early literacy intervention to students in need.
In summary, my partnership with The Literacy Lab demonstrates their proven expertise in assisting clients within the education sector to overcome challenges and strategize for the future. By conducting a thorough analysis of the sector and involving the entire firm in the exploration process, I provide valuable insights and recommendations to streamline operations and improve recruitment efforts. Due to this collaborative approach, The Literacy Lab can continue to deliver effective early literacy intervention to students while evolving to meet the demands of a competitive and evolving landscape.

Village Micro Fund
My facilitation with the Micro Village Fund has been instrumental in their efforts to create an apprenticeship program between entrepreneurs in Atlanta, Georgia, and South Africa. The goal of this program is to help small businesses sustainably source supply chain inputs from the continent of Africa. Throughout this process, I have helped the company think through the nuances across the cultural and financial experiences of Black populations in the United States and South Africa.
By taking into consideration factors such as inclusion, accessibility, familiarity with global travel, and historical contexts, I have helped the Micro Village Fund design a program that is sensitive to the diverse backgrounds and experiences of participants. This collaborative approach involved working closely with all stakeholders to ensure that the program is inclusive, equitable, and reflective of the local context.
Furthermore, my facilitation has contributed to the design of a sustainable program that can evolve over time. By constantly iterating and being agile in our approach, we are able to drive insights to action in a meaningful way that has a tangible impact on the ground. This approach not only ensures the success of the program but also creates a model that can be scaled to benefit many more companies across the country and the globe.
Bringing in evidence- and experience-based thought leadership helps Micro Village Fund in the creation of an apprenticeship program that fosters sustainable supply chain sourcing from Africa. Through careful consideration of the cultural and financial experiences of Black populations in the United States and South Africa, we have designed an inclusive and accessible program. By working collaboratively with all stakeholders, we have developed a sustainable and scalable model that will drive meaningful impact for small businesses and entrepreneurs while fostering economic growth and collaboration.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.