Effective Management

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Effective Management is provided by Mr. Eysink Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr Eysink has two BSc (USA) in International Economics and Corporate Finance. He has applied his abilities to southern and central Africa, Qatar, UAE and the UK clients. His clients have come from the manufacturing, engineering and construction, mining, financial services of banking and insurance, and public sectors. He also volunteered his time to support eight struggling businesses to transform and grow during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In his career, he has filled the roles of Lead Consultant and Project Manager to determine strategy or unlock strategic value for his clients. His primary contributions include designing and implementing Management Operating Systems to focus and empower management teams to realise and sustain operational improvements. His approaches place emphasis on Lean Six Sigma, the Theory of Constraints and financial analysis in Waterfall and Agile project methodologies.
He has an excellent track record of successfully installing simple solutions to complex problems and constructively engaging with management in cross-functional teams across the breadth and depth of their organisation. His work spans business analysis, solutions design and implementation, linking performance improvements to financial KPIs to quantify and track the impact on overall company value and achieve planned ROI.
To request further information about Mr. Eysink through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Effective Management
“A bad system will beat a good person every time.”—W. Edwards Deming
Aligning everyday actions with company objectives is a common business challenge that can have significant consequences if not addressed appropriately. Many corporations tend to use generic measures across different levels of the organization rather than tailoring specific and appropriate metrics for each level. This approach often leads to a focus on lagging indicators, which do not effectively protect or unlock value. Additionally, organizations may overlook organizational gaps that can be easily resolved through the implementation of an effective system instead of attributing poor performance to equipment or skill deficiencies. This breakdown in confidence between management levels and operations can result in micromanagement and hinder overall performance.
Another prevalent issue is the neglect of planning and reviewing processes, with a disproportionate emphasis on execution. This approach often leads to reactive firefighting tactics, inconsistent information across organizational layers, and wasted time in ad hoc meetings rather than structured discussions that drive action and results. Despite the abundance of data and reporting tools, organizations fail to establish a systematic method for managing and aligning their business with strategic objectives. This can result in a range of everyday challenges and consequences, even after short-term benefits are achieved following senior management interventions.

McKinsey Case Study
“A consumer goods company previously identified several organisational inefficiencies, but because they lacked a mechanism to resolve them, they usually remained recognised but unaddressed. Then the company created an OEO (a Management Effectiveness system) to work across the business to constantly identify, prioritise, and resolve inefficiencies. As a result, the company significantly simplified its assortment process; clarified and streamlined handovers among global, regional, and local; and streamlined its overall organisation.”

Management consultants frequently encounter these challenges when assisting clients in bridging the gap between frontline operations and broader business objectives. The absence of appropriate structure and technologies to support performance management and decision-making within management teams often hampers improvement initiatives, preventing them from having a lasting impact and causing a return to subpar performance.
Identifying opportunities for value release through a top-down diagnostic is typically straightforward. However, achieving and sustaining the desired value release requires a commitment to execution from the entire organization at all levels. It is crucial to ensure the business operates as an integrated system by:
• Organisation alignment,
• clarifying roles and responsibilities,
• building management capabilities,
• developing soft skills,
• establishing effective meeting structures with information flows and feedback loops,
• implementing necessary leadership work activities, and
• enhancing problem-solving and continuous improvement processes.
These elements should be integrated into the organization’s operating strategy, cascading strategic objectives across all levels, and culminating in measurable objectives at the level of execution. A reliable Effective Management system effectively addresses these challenges.
Management consultants achieve their results by encapsulating their solutions within an Effective Management system, which enables clients to achieve stable and predictable operational performance, sustain improvement initiatives, and establish a benchmark for operations in the relevant area. These systems also provide a platform for attaining future targets and mitigating recurring failures through rapid resolutions, enhanced leading KPIs, and risk reduction.
So, what exactly is an Effective Management system? It is a comprehensive collection of tools, processes, and disciplines designed to achieve strategic business goals in a system that is both logical and intuitive.
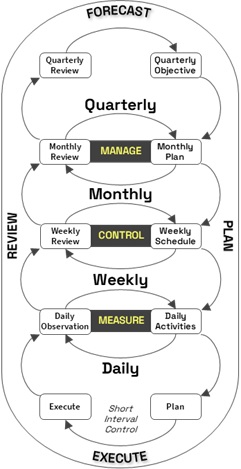
At its core, this system systematically applies these techniques through a 4-stage, closed-loop cycle: Forecast, Plan, Execute, and Review. This closed-loop approach ensures continual improvement and is highly effective in enhancing the utilization of available capacity, performance within that capacity, and product or service quality:
• Cascading metrics from strategic objectives to OKRs and KPIs, ensuring clear accountability from management to the level of execution,
• Implementing support mechanisms across the value chain to make informed decisions that drive performance,
• Facilitating and sustain a change from a reactive to a proactive mindset and behaviours across all disciplines,
• Embedding leadership practices into the system,
• Installing short-interval control at the execution level,
• Improving overall meeting and review effectiveness.
As in many situations, the logical approach provides a solid foundation and structure for decision-making, while intuition helps fill in gaps, speed things up, make connections, and provide insights that may not be immediately apparent. Managers can make well-informed and effective decisions by establishing this logical framework within which to hone their intuition.

Boeing Closed-loop Management Effectiveness System
Closed loop Management Effectiveness Systems are a key enabler of smart factories and adaptive flight control technology in Boeing. They allow for real-time data collection, analysis and feedback, resulting in improved quality, safety, efficiency and performance. By specifying the desired outcomes and adjusting the control inputs accordingly, Boeing can achieve optimal results in complex and uncertain environments.
Boeing’s strategic initiatives to ensure alignment of their business objectives with desired results will establish a foundation for sustained performance improvement while reducing operational risk and maintaining necessary changes.
The consistent application of Effective Management across all levels of the organization is crucial for sustainability and accelerating improvement. Therefore, this system is designed to be:
• easily accessible,
• transparent,
• intuitive, and
• user-friendly.
It establishes clear objectives and connects all relevant information to the company’s vision and objectives. By eliminating bureaucratic red tape and wasted effort, a well-defined system enables long-term value generation by integrating the organization and its information flow to become data driven.
With a robust Effective Management system in place, organizations can establish a stable foundation in an ever-changing world. This foundation is essential for tracking growth and performance, enabling the rapid identification of market and operational gaps, and implementing data-driven strategies for improvement. By evaluating existing meeting structures and management reviews from the perspective of Effective Management, organizations can ensure that meetings and conversations are action-oriented and results-driven. Evaluating the success of these reviews provides valuable insights and a roadmap for closing performance-related gaps. The performance of these meetings is continuously measured to further enhance the Effective Management system.

Motorola Closed-loop Management Effectiveness System
Motorola has implemented closed-loop Management Effectiveness Systems in various aspects of its business, such as product development, quality assurance, customer service, and supply chain management. These systems have enabled Motorola to achieve several benefits, such as:
• Improved efficiency and productivity by reducing errors, waste, and rework,
• Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty by delivering high-quality products and services that meet or exceed expectations,
• Increased innovation and competitiveness by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning,
• Reduced costs and risks by ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Closed-loop Management Effectiveness Systems are a key component of Motorola’s strategy to achieve operational excellence and sustainable growth. By using feedback data to measure performance and implement corrective and preventive actions, Motorola can adapt to changing customer needs and market conditions while maintaining its reputation as a leader in technology and innovation.
Excellence in Management ensures the alignment of necessary risk reduction and business performance priorities and objectives throughout the organization, with involvement from top to bottom. Transparent communication of company objectives and results allows the organization to optimize its focus and efforts proactively. Effective cascade and alignment ensure that operational objectives are directly linked to strategic objectives and the company’s vision, resulting in accelerated response times during execution. Challenges are quickly identified and guided towards timely resolutions or escalated to the appropriate authority level based on their nature and risk.
Integration is achieved through the establishment of a standardized structure that connects different departments, eliminating isolated entities and unlocking innovative potential. Predictability of performance is achieved through short-interval control applied to specific KPIs, which stabilizes processes and enables performance predictability. An Effective Management system serves as a stable foundation and management process for implementing current and future projects consistently, allowing executive Management to navigate uncharted waters with confidence.

CBi-electric: african cables Closed-loop Management Effectiveness System
A South African industrial electric cable manufacturer faced challenges in maintaining its performance improvements. A breakdown in understanding the root causes of issues ultimately led to a decrease in OEE. The decision-making process had reached a deadlock, resulting in strained relationships among the management team. The Management System was fundamental to the success of the solution. It decompressed management by refreshing the management structure and tasked managers to align with the level of their responsibilities. The system also integrated the management teams of the business Value Chain: Sales and Marketing, Planning, Procurement, Production and Fulfilment. The new Management System clarified and simplified the task of decision-making and re-established Management Control to regain lost value.
Ultimately, Effective Management should result in the consistent execution of core behaviours that promote operational excellence. This program recognizes the interconnectedness of complex organizations and emphasizes the need for an effective Effective Management system to produce sustainable results. By adopting an integrated and holistic approach to problem-solving, organizations can address management challenges, such as the need for more architecture and systems to support performance management and decision-making. This approach involves linking strategic objectives to performance, ensuring accountability at the execution level, implementing support mechanisms for consistency and sustainability, fostering a proactive mentality and behaviour, incorporating rituals and leader-standard labour tasks, and continuously improving short-interval control, problem resolution, and meeting efficacy.

By implementing an Effective Management system, organizations can achieve their best results within a rolling 12-month period, assessed quarterly. This approach allows for the realization of new performance benchmarks and sets the foundation for future goals. Highly efficient and well-structured meetings, accompanied by effective visualization and information flow, strengthen operations. Management at all levels is empowered to take full responsibility for applicable objectives, KPIs, and OKRs within their sphere of influence, ensuring swift resolution of recurring failures.

Apple Closed-loop Management Effectiveness System
Apple has been adopting closed-loop systems in its supply chain, product design and service model to achieve its sustainability goals and enhance its customer experience. Some of the benefits of closed-loop systems for Apple are:
• Reduced environmental impact by minimizing waste, energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
• Increased product quality and durability by using recycled or renewable materials and improving repairability.
• Enhanced customer loyalty and satisfaction by offering products-as-a-service, which include service packages, software updates and trade-in options.
To wrap up, an Effective Management system provides the necessary framework and tools to align everyday actions with company objectives. By implementing this system, organizations can achieve stable and predictable operational performance, sustain improvement initiatives, and establish a benchmark for operations. This approach enables organizations to proactively optimize their focus and efforts, align operational objectives with strategic objectives, quickly identify and resolve challenges, integrate different departments, stabilize performance and lay the groundwork for future improvement initiatives. Through the consistent execution of core behaviours, organizations can promote operational excellence and achieve sustainable results:
• Outcome focused,
• Transparency of business activities,
• Transparency of performance against objectives,
• Stable and predictable performance,
• Effective Organisation alignment,
• Integration across the Value Stream,
• A foundation for continual improvement and transformation initiatives.
Curriculum
Effective Management – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 True North
- Part 1 Month 2 Business Model
- Part 1 Month 3 Align Management
- Part 1 Month 4 Align Operations
- Part 1 Month 5 Management System
- Part 1 Month 6 Management Integration
- Part 1 Month 7 Meeting Effectiveness
- Part 1 Month 8 Constructive Feedback
- Part 1 Month 9 Time Management
- Part 1 Month 10 Handling Exceptions
- Part 1 Month 11 Sustained Productivity
- Part 1 Month 12 Individual Mastery
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Effective Management corporate training program.
Effective Management – Part 1 – Year 1 – Process Planning
Part 01: Establishing Strategic Objectives and cascading these through the business model.
These workshops cover topics such as understanding the role of the organization’s mission, vision, and policy framework, aligning individual roles with organizational goals, promoting strategic thinking and decision-making, understanding and utilizing the business model.
Month 01: True North
Calibrate the business compass.
An organisation’s mission, vision, and policies serve as its guiding principles. These factors influence strategic planning, decision-making, and growth. This workshop on these topics can improve the efficacy and efficiency of an organisation. This first module will establish a baseline for how the organisation’s mission, vision, and policy framework all work together to produce success through interactive exercises, group discussions, and case studies. The program will emphasise the importance of these elements in developing organisational goals and strategies and making important decisions:
• Validate the mission, vision, and policy framework of the organization by participating in interactive exercises, engaging in group discussions, and analyzing case studies.
• Emphasise the significance of these guiding principles when establishing goals, strategic objectives, and the strategies required to attain them.
• Ensure that individual roles and responsibilities align with organizational goals and empower individuals to make autonomous decisions.
• Aid participants in comprehending the impact of the mission, vision, and policies on their respective positions and how they can contribute to overall success.
• Foster strategic thinking, problem-solving, decision-making, and communication skills through role-playing, brainstorming, dialogues, and presentations.
This workshop focusing on an organisation’s mission, vision and policy framework unites participants by aligning goals and strategies to the business’ mission and vision, empowering strategic thinking, and fostering collaboration. With a shared understanding of guiding principles, participants can make informed decisions and work as a cohesive team to advance the organisation’s success.
Month 02: Business Model
Develop the business management model.
Understanding the connection between a company’s vision, mission and business model is critical to successfully implementing an Effective Management system. This program directs strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and overall business performance at a strategic level, allowing the Effective Management system to complement and enhance the relevance, knowledge, and use of a pre-existing business model.
The primary goal of this module is to give participants a solid understanding of the purpose and application of an organisation’s business model in an Effective Management system. It seeks to clarify how various business components interact and contribute to the production of value. Through this understanding, participants can make better-informed decisions, connect their work with the organisation’s strategic objectives, and contribute more effectively to the business’s success.
• Gain a solid understanding of the company’s business model, clarifying how business components interact to create value.
• Provide a new perspective on how management decisions impact the business model, identifying areas for review and optimising the business model.
• Connect work to strategic objectives through the business model to contribute to business success. Demonstrate how to drive alignment across levels and functions with a shared business model understanding to increase operational efficiency, decision-making, and corporate performance.
This module provides participants valuable insights into the company’s business strategy and model. Through interactive sessions and collaborative work, participants will strengthen their understanding of how their roles contribute to organisational success. They will also develop essential skills like strategic decision-making, communication, cooperation and problem-solving – helping to drive better business performance and achieve strategic objectives. The module establishes a strong foundation for an effective management system aligned with the company’s goals.

Part 02: Translate Strategic Objectives into measurable, actionable activities, and cascade through integrated closed-loop management systems.
These workshops provide a comprehensive understanding of strategic planning, performance measurement, and effective management practices. Participants will gain practical skills and tools to align teams with organizational goals, drive performance, and achieve measurable results.
Month 03: Align Management
Cascade policies into measurable outcomes.
With the pace of change in the corporate world, having a clear vision and objective is critical to maintaining focus. The true challenge is converting these into tangible, attainable goals. This module will demonstrate how the Key Results (OKRs) framework bridges this gap.
The main objective of this workshop is to equip the attendees with the necessary knowledge and abilities to proficiently integrate OKRs into their organisations in preparation for their use in the Effective Management system. We aim to enhance the understanding and implementation of OKRs as an essential management tool:
• The workshops provide an understanding of strategic planning, performance measurement, and management practices to align teams with business goals and achieve measurable results.
• Participants will learn the Outcome Key Results (OKR) framework to translate vision and objectives into tangible, attainable goals and bridge the gap between strategy and execution.
• OKRs will be examined as a means to quantify the company’s vision and mission into measurable goals to align teams around shared objectives and improve performance.
• Leaders will gain skills to define, track and achieve OKRs, align their teams with the company vision/mission, and increase project ROI through a foundation of transparency, accountability, and continual learning.
This workshop equips participants with strategic thinking and leadership skills to successfully cascade policies into measurable outcomes through the OKR framework. By aligning teams towards a shared vision, participants can drive operational efficiency and business growth through increased performance and results. Overall, the value lies in providing practical tools and approaches to execute strategy effectively at all levels of the organisation.
Month 04: Align Operations
Cascade OKRs into individual and activity-specific outcomes.
Setting, tracking, and achieving goals is critical for any successful organisation. This module will inform and support the transformation of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) into Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). This session highlights the importance of OKRs and KPIs in an Effective Management system and their role in encouraging autonomy within the management team. This session will promote using key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure efficiency and comprehension of strategic objectives.
This module provides a sound grasp of how to turn OKRs into KPIs to clarify and focus management for efficiency and effectiveness:
• The module will explain how to transform OKRs into KPIs to support management efficiency and effectiveness. Participants will learn how to align team objectives with organisational goals.
• Tools and techniques for performance monitoring, identifying improvement areas, and informed decision-making will be presented. This will help the organisation meet strategic goals and realise value.
• Setting, measuring, and accomplishing OKRs and KPIs is critical for professional development and will be covered. These skills can then be applied to the job.
The module is intended for managers, team leaders, and supervisors to help set and achieve goals through analysis, strategic thinking, and leadership. Case studies, discussions and workshop exercises will be used.
This workshop will provide insights and practical skills for professionals to focus their efforts. Participants will learn to align OKRs with KPIs to drive organisational success. They will increase their knowledge and skills in strategic planning and performance management, which are invaluable for navigating complex business challenges.
Participants will leave the course with a thorough understanding of how to match their team’s objectives with the organisation’s goals, providing a streamlined approach to goal achievement.
Month 05: Management System
Establish a closed-loop Effective Management system.
In today’s business, change is constant, and the pace is quickening, making effective and efficient management essential for keeping up with and staying ahead of the competition. Management teams constantly seek new and innovative ways to boost efficiency, implement programs, keep up with changing customer demands, and expand market share.
This is where a closed-loop system with a process-driven management strategy becomes essential. This closed-loop, process-driven management system improves managers’ capabilities through a revised PDCA cycle comprised of four basic steps: forecasting, planning, execution, and review. These phases are critical for effective and consistent management:
• The article discusses establishing a closed-loop management system with a process-driven approach to management. This approach includes forecasting, planning, execution, and review phases.
• It explains how the closed-loop, process-driven system accelerates decision-making, promotes accountability, and fosters proactive management. It encourages managers to take ownership of tasks and duties, improving effectiveness and sustaining optimum productivity.
• The module will demonstrate how the Effective Management system provides a basis for effective leadership and show participants how to apply their analytical, strategic and problem-solving skills.
• Through theoretical and practical exercises, participants will learn to use the closed-loop, process-driven system in their roles. It presents a roadmap for an Effective Management system to enable a process-driven approach to management.
This Effective Management workshop provides participants with multiple benefits. Individuals will be able to lead teams, drive productivity and contribute to corporate success with in-depth knowledge of the system and its importance. It offers a unique opportunity to learn and apply a process-driven approach to systematically improve effectiveness and achieve organizational goals.
Month 06: Management Integration
Cascade the Effective Management system to integrate the Business Model.
This module provides a transformative workshop designed to equip management teams with the skills to integrate and cascade closed-loop management systems across the value chain to enhance productivity and decision-making processes and sustain productivity improvements.
With a focus on improving operational efficiency and ensuring management activities align with the organisation’s purpose, the module takes a process-driven approach, focusing on implementing an Effective Management system and ensuring goals are correctly implemented across all levels. This system fosters an environment where information flows seamlessly, ensuring the correct data is available at the right time for decision-making, making this workshop perfect for bringing together strategists, managers, decision-makers, and supervisors from lower to senior levels:
• The workshop teaches how to translate strategic objectives into measurable activities and cascade them through an integrated Effective Management system.
• It provides tools and skills to align teams with organisational goals, drive performance through metrics, and achieve measurable results through effective management practices.
• Participants learn how to implement an Effective Management system that fosters seamless information flow and informed decision-making. This empowers management teams and enhances their autonomy and effectiveness.
• Interactive exercises demonstrate how to identify and resolve bottlenecks in decision-making. An integrated system speeds up outcomes by synchronising activities across the value chain and management hierarchy.
The workshop equips participants with the ability to establish an integrated Effective Management system within their organisations. By enhancing management efficiency and aligning activities, businesses can achieve operational excellence and fulfil their strategic objectives. Participants gain valuable insights and practical skills for driving engagement, improving productivity, and transforming management performance.
Month 07: Meeting Effectiveness
Improve meeting effectiveness.
Meetings are a key management activity in the Effective Management system. This module will focus on the structure, planning and execution of meetings to give the management team the tools and tactics necessary to turn meetings from time-consuming requirements into effective productivity and creativity generators.
The module offers a thoughtfully created workshop to elevate the relevance of meetings to effective management, instil autonomy within your management team, improve effectiveness, assess efficiency, and encourage better knowledge and use of meetings:
• Understand strategic planning, performance measurement, and effective management practices. Participants will gain practical skills and tools to lead meetings and align their meeting participation to drive business performance.
• Develop an autonomous culture where members feel empowered to contribute and participate effectively. This will improve team cohesion, morale, and informed decision-making.
• Improve meeting effectiveness with tools and tactics to make meetings more productive, creative, and effective for management. Assess efficiency and encourage better knowledge and use of meetings.
• Provide practical ideas to streamline meetings and ensure they are focused, engaging, and result-oriented. Learn to assess effectiveness using KPIs like time, participation, and goal achievement.
The Meeting Effectiveness module provides management teams with strategies and techniques to optimize their meetings and boost their capacity by reducing a common source of frustration and wasted time. Participants can expect increased productivity, innovation, and collaboration for bottom-line results from more strategic and effective meetings. They will leave with tactics to plan, execute and follow up on meetings and better understand their capabilities for enhancing engagement up and downstream in the business.
Month 08: Constructive Feedback
Implement constructive feedback and strategic conversations.
Following on from Effective Meetings, effective communication is the key to success. It’s not just about conveying information; it’s about engaging in meaningful, strategic conversations that drive change and foster a performance culture. Communicating with respect is a key leadership activity. This is where the art of constructive feedback comes into play. The workshop for this module, “Implementing Constructive Feedback and Strategic Conversations,” is designed to equip management teams with the skills and strategies to enhance their communication and feedback capabilities:
• The workshop teaches skills for effective communication, including active listening, empathy, clear and concise communication, and giving and receiving feedback constructively. Interactive activities and role-plays will be used to practice these skills.
• It highlights how strategic conversations can promote autonomy, ownership, accountability, and recognition within teams to maintain motivation and accountability.
• Effective communication helps assess performance, validate efforts, and foster a more open, collaborative, and feedback-rich organizational culture.
• Leaders learn to navigate difficult conversations, manage conflicts, and drive team performance to increase employee engagement, productivity, and decision-making capabilities, contributing to business growth and success.
In conclusion, participants gain practical tools and techniques to enhance their communication skills, foster better relationships with their team, and drive performance. Mastering these skills in constructive feedback and strategic conversations develops leadership competencies and the ability to become a more effective, influential leader.

Part 03: Personal alignment and mastery in Effective Management
These workshops provide participants with a comprehensive set of skills and knowledge to excel in their management roles. Participants will gain practical strategies and tools to enhance their effectiveness as managers to drive business success, foster a culture of performance, and contribute to the overall growth of their organizations.
Month 09: Time Management
Effective time management.
When managers claw back time wasted in ineffective meetings and rework, it’s not uncommon for them to feel anxious about keeping busy. This module presents an opportunity for all levels of management to learn how to elevate their productivity, improve efficiency, and optimise their priorities to get things done within the Effective Management system. This applies to managers, team leaders, and decision-makers who frequently manage various tasks, face difficulties meeting deadlines, or strive to utilise their time more efficiently to develop their management skills to the next level.
Time is the most valuable resource in any organisation. Yet, it’s often the most poorly utilised. This workshop will highlight the critical role of time management in Effective Management. It will demonstrate how efficient time management can foster autonomy within the management team, enhance effectiveness, and improve overall productivity:
• The workshop aims to improve participants’ time management skills by exploring prioritisation, delegation, goal-setting, and decision-making behaviours. Interactive sessions and exercises will help to strengthen these skills.
• Tools and strategies taught will help participants manage their time more effectively and increase their capacity. This will create a culture of efficiency where time is respected and used wisely.
• Better time management can foster autonomy, enhance effectiveness, and improve productivity within the management team. This drives business success.
• The workshop offers immediate benefits to individual participants and their management teams/organisations. Improved time management allows for more efficient operations, better decisions, and goals achieved more quickly, leading to increased profitability and competitiveness.
This workshop integrates participants deeper into an Effective Management system to boost productivity. Participants will leave with an understanding of time management’s importance, practical tools to apply daily, and confidence in their ability to manage time well and accomplish their work. The workshop provides valuable skills and insights that can significantly enhance participants’ management roles and contributions to organisational growth.
Month 10: Handling Exceptions
Manage exceptions and complexity.
Managing exceptions and complexity is a critical skill every manager should possess in the fast-paced, ever-evolving business landscape if they are to avoid getting stuck and distracted from their priorities. This module equips managers with the necessary tools to navigate towards their objectives through the intricate corridors of management with greater effectiveness and efficiency.
• The workshop aims to teach participants the skills and behaviours to handle exceptions and complex situations efficiently. It will delve into real-world scenarios and case studies, engaging in interactive discussions and group activities to foster a deeper understanding.
• Managing exceptions and complexity is critical for managers in today’s fast-paced business landscape. The workshop will equip managers with the necessary tools to navigate intricate management situations more effectively and efficiently to achieve their objectives.
• The ability to manage exceptions and complexity can significantly contribute to business success. Managers who excel in this area can confidently lead teams, drive productivity, and make informed decisions aligned with objectives.
• By mastering these skills, managers can avoid compromising productivity and becoming overwhelmed so that they can lead teams more effectively. The workshop will underline the importance of managing exceptions and complexity in enhancing management efficiency and through effective delegation.
This workshop provides a valuable platform for managers to enhance their skills in handling exceptions and complexities in their roles to stay on track. Participants can expect to leave with clear strategies that can be implemented immediately. They will gain insights into leveraging these skills to improve performance, productivity, and their overall contribution to business growth.
Month 11: Sustained Productivity
Maintain optimal productivity.
Productivity is the lifeblood that fuels success. However, maintaining productivity is more complex than it may seem. It requires a delicate balance of effective management, autonomy, efficiency, and constructive engagement. This is where our module on maintaining productivity comes into play. It is ideal for those seeking to enhance their productivity skills, learn new strategies, and gain insights into productivity management.
During the workshop, participants are given the opportunity bring into play key elements from earlier modules in this program and apply them to an Effective Management system for their organisation in a safe and supportive environment:
• Effective Communication: Clear communication helps set expectations, provide feedback, and address any issues or concerns that may arise.
• Leadership: Managers must lead by example, set a positive tone, and foster a supportive and collaborative work environment.
• Goal Setting and Planning: Managers must develop strategic plans and break down goals into actionable tasks, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
• Time Management: Effective managers prioritise tasks, delegate responsibilities, and help their team members identify and eliminate time-wasting activities to meet deadlines.
• Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: Managers need to be skilled in analysing problems and identifying root causes to make informed decisions based on available data and input from team members.
• Emotional Intelligence: Managers manage their own emotions and those of their team members to build strong relationships, resolve conflicts, and provide support when needed.
• Adaptability and Flexibility: Managers need to be adaptable and open to new ideas and approaches, encouraging innovation and being willing to adjust strategies to maintain productivity.
• Empowerment and Delegation: Effective managers empower their team members by delegating tasks and responsibilities, encouraging autonomy and growth.
• Recognition and Appreciation: Managers who recognise and appreciate their team members’ efforts and achievements create a positive work environment to boost morale, motivation, and productivity.
Managers can create a productive, engaged team that consistently delivers exceptional results by applying and improving these skills and behaviours in an Effective Management system.
This module is a valuable opportunity for management teams and leaders to enhance their understanding of applying productivity skills to learn new strategies and gain practical insights. It is a step towards creating a more productive, efficient, and successful organisation. The workshop will enhance the management team’s ability to lead effectively, manage resources efficiently, and deliver results consistently. It will also show them how to foster a culture of autonomy, where each team member is empowered to take ownership of their work and contribute to the organisation’s overall productivity.
Month 12: Individual Mastery
Achieve personal mastery within the Effective Management system.
The ability to adapt, innovate, and excel is not just a luxury but a necessity. In this context, we present our final module aimed at enhancing individual mastery within the Effective Management system. Empowering Individual Mastery is the key to an Effective Management system. This workshop is designed to equip professionals with the skills and knowledge to navigate the complexities of this management approach and harness its full potential:
• The workshop focuses on achieving personal mastery within an Effective Management system through developing critical skills like critical thinking, strategic decision-making, effective communication, and data analysis and interpretation.
• Participants will learn how to identify opportunities for improvement and implement changes that drive efficiency and effectiveness through interactive methods like group discussions, role plays and simulations.
• A key theme emphasises the importance of individual mastery for effective management and team autonomy. The workshop demonstrates how mastering core skills can improve personal and organisational performance. Confidence is critical to success.
• It promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement, empowering managers to take ownership of their roles and fostering autonomy and accountability. This leads to more effective decision-making, better team performance, and improved business outcomes.
This workshop provides an invaluable opportunity for professionals to enhance their management skills and drive business performance. Participants can expect to gain a clear understanding of closed-loop management systems and practical skills and strategies that can be immediately applied in their roles. The unique blend of theory and hands-on experience ensures they maximise their learning and impact on their organisation.
Methodology
Effective Management
The program aims to provide managers with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement a system of Effective Management within their organizations. The rationale behind this program is to address common challenges faced by managers, such as poor execution, time management, elimination of persistent problems, maintaining optimal productivity, and achieving personal mastery within an Effective Management system. By addressing these key areas, the program aims to enhance the overall effectiveness and efficiency of managers, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes.
The planning for this program is structured in a way that allows managers to progress through different modules over the course of a year. Each module focuses on a specific aspect of management and provides participants with practical tools and strategies to establish a supporting structure for themselves and implement in their daily work. The modules are designed to build upon each other, creating a comprehensive and integrated approach to Effective Management.
To prepare for these workshops, the designated participants are encouraged to collectively represent a broad cross-section of management from the business. Each participant should prepare themselves as best as possible for each part of the program as follows:
Part 1: Reviewing their organisation’s vision and mission statements and any existing strategic plans or goals would be beneficial.
Part 2: Be familiar with their organisation’s metrics, strategic planning, OKRs, KPIs and systems.
Part 3: Reflect on their own management practices and challenges. It would be beneficial for participants to identify specific areas they would like to improve upon.
Additionally, participants should come with an open mind, ready to actively engage in discussions, share experiences, and collaborate with fellow participants. The workshops aim to foster engagement, promote open communication, and provide a platform for learning and uncovering insights.
The workshops will be conducted in an interactive and participatory manner, utilising whiteboards and a variety of methods, including:
• Case studies,
• videos
• group discussions,
• brainstorming,
• hands-on exercises, and
• role-plays.
Participants will have the opportunity to apply their analytical skills, strategic thinking, and problem-solving abilities in relevant scenarios. The facilitators will guide the sessions, providing valuable insights, practical tools, and techniques to enhance management practices in a collaborative learning environment where participants can also learn from each other’s experiences and viewpoints. Overall, this program is designed to provide managers with a comprehensive set of skills and strategies to implement and maintain a Effective Management system. By addressing common challenges to management, managers can enhance their effectiveness and drive improved business outcomes.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Insurance
History
Insurance has been a vital component in the process of protecting individuals and organisations from unplanned losses since the beginning of time. Initially, merchants and traders used insurance to combine their resources in order to protect themselves from unanticipated events such as accidents, theft, and natural disasters. During the Middle Ages, guilds and cooperative organisations developed formal insurance contracts to meet the changing demands of its members. These contracts guaranteed financial protection to members. During the 17th and 18th centuries, the development of fire, marine, and life insurance led to the foundation of the modern insurance business. Over time, the industry has expanded and diversified to include products such as annuities, health insurance, property insurance, and liability insurance. Despite this, the insurance industry has faced a number of important challenges, including wars, pandemics, financial crises, and regulatory changes. Despite these difficulties, insurance is an essential component of modern living. It provides both individuals and organisations with the necessary peace of mind and financial safety.
The insurance industry arose from the premise of pooling risks and providing financial protection against unanticipated catastrophes. Management’s fundamental challenge in this era was establishing trust and credibility with consumers and other stakeholders. This was in addition to guaranteeing the company’s financial stability and profitability. The only technological advances accessible at the time were paper records, calculators, and typewriters. From intuition, experience, and long-held traditions. The business idea was to distribute standardised insurance policies to customers via independent agents or brokers who acted as go-betweens for the customer and the insurance provider. A rigid hierarchy was in place, with little room for innovation or flexibility in working practises. Customers’ interactions were largely transactional and reactive, with few opportunities for conversation and feedback.
Current Position
The insurance market is always developing and competitive because there are so many different companies and products. Artificial intelligence (AI), big data, blockchain, and cloud computing are just a few of the cutting-edge technologies the sector has used to remain ahead of the competition and significantly increase efficiencies, accuracy, customer experiences, and risk management. Despite this, the sector faces various challenges, including cyber hazards, climate change, demographic transitions, and changes in social dynamics. The industry must adapt swiftly to meet customers’ demands for personalised service, comprehensive transparency, and maximum ease. Furthermore, the sector must prepare for the introduction of new financial technologies, insurance technologies, and digital platforms, all of which are expected to create a difficult degree of competition.
The insurance industry has evolved into a highly competitive and complex sector, driven by its customers’ ever-changing needs, preferences, and expectations. The most significant challenge management has in this era is reacting to the industry’s digital revolution and disruption and keeping up with ever-increasing levels of regulation and competition. Technological breakthroughs such as internet platforms, mobile applications, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and blockchain have enabled new capabilities. Risk management tools, strategy planning tools, and performance monitoring tools have all contributed to management practices becoming more sophisticated and evidence-based in recent years. The old business model has given way to the supply of personalised and tailored policies through direct or digital distribution channels and diversification into new categories of goods and services such as telematics, micro insurance, and peer-to-peer insurance. Traditional work techniques have developed to be more collaborative and adaptable, emphasising creativity, learning, and empowerment. Customers’ involvement has recently grown more proactive and involved, with increased opportunities for contact, feedback, and loyalty.
Future Outlook
The insurance industry is going through a major change due to technological advances and shifts in how people behave. As a result, the industry must embrace digitalisation and leverage data and analytics to their fullest potential. By doing so, insurers can create value for customers and stakeholders by providing tailor-made and adaptable solutions catering to various market segments. Collaboration with other sectors and ecosystems is essential to provide comprehensive solutions for complex risks and opportunities.
To keep up with the ever-changing trends and disruptions in the insurance industry, insurers must cultivate a culture of innovation and agility. Keeping up with the most recent technologies, participating in ongoing education, and encouraging experimentation can help. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, insurers must remain flexible and open-minded, continuously seeking new opportunities to provide top-notch service to their clients. Ultimately, only those willing to embrace change and prioritise innovation will thrive in an ever-changing industry.
The insurance industry will face new challenges and opportunities, influenced by emerging trends such as climate change, social responsibility, cyber security and biotechnology. The main challenge for management in this era will be anticipating and responding to these trends and creating value and differentiation in a dynamic and uncertain environment. Technology will enable new possibilities such as smart contracts, the Internet of Things, quantum computing and augmented reality. Management methods that are more agile and innovative, such as design thinking, lean startup, and agile scrum, will be required. The business model must be more adaptable and flexible, offering solutions tailored to each customer’s specific needs and contexts while collaborating with other ecosystem actors such as regulators, partners, and competitors. Labour practises must become more diverse and inclusive, emphasising the workforce’s skills, values, and well-being. Customer engagement will need to be more engaging and meaningful, focusing on the emotional and social aspects of the relationship.
Healthcare
History
The healthcare sector has a long and illustrious history dating back to ancient times. Natural remedies, religious rituals, and traditional medicine were the principal techniques of treating ailments at first. However, as time went on, more systematic and scientific procedures emerged. Hospitals were formed by religious orders and humanitarian groups, whereas universities or guilds founded medical schools. Despite these attempts, the sector remained fragmented and unregulated, resulting in varied quality and ethical standards.
Throughout history, healthcare has faced several problems, such as contagious diseases, wars, famines, poor sanitation and cleanliness, limited accessibility and affordability, low education and awareness, and ethical quandaries and malpractices. Technological innovations have played a critical part in reshaping the healthcare industry over time. The discovery of microorganisms, vaccines, and antibiotics, the invention of anaesthesia, x-rays, and surgical instruments, the development of blood transfusion, organ transplantation, and artificial limbs, and the emergence of public health systems, epidemiology, and biostatistics have all contributed to the current state of the healthcare industry.
Previously, the healthcare industry was primarily concerned with providing acute care to people suffering from contagious diseases or accidents. The primary managerial issues were assuring the quality and safety of care, dealing with high demand and limited resources, and cooperating with other health providers and public health agencies. The discovery of antibiotics, vaccinations, anaesthetics, and diagnostic instruments were some of the significant technological achievements that assisted management in overcoming these obstacles. Standardisation of healthcare protocols, quality improvement programmes, and performance assessment systems improved management and process techniques. Fee-for-service payment mechanisms, hierarchical organisational structures, and professional autonomy for physicians were all part of the business models and labour practises. Patient satisfaction surveys and word-of-mouth referrals were the most common forms of customer involvement.
Current Position
The healthcare industry is a large and diverse worldwide sector that includes but is not limited to, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, medical equipment, diagnostics, health services, health insurance, health informatics, and telemedicine. The business is driven by a variety of reasons, including changing demographics, rising incomes, chronic diseases, environmental concerns, and regulatory frameworks and policies. However, it faces obstacles such as rising prices, inefficiencies, quality and safety concerns, access and equity disparities, worker shortages, and fatigue. The healthcare business has seen some notable technical developments in recent years, including genomics and personalised medicine, artificial intelligence and machine learning, robots and nanotechnology, digital health platforms, wearable devices, and blockchain and cybersecurity. These developments can potentially transform the field, paving the way for more efficient, effective, and personalised healthcare solutions.
As the burden of non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease rises, the healthcare business is changing from acute to chronic care. The primary difficulties for management are providing patient-centred and integrated care, implementing evidence-based and cost-effective methods, and innovating and adapting to changing requirements and expectations. Electronic health records, telemedicine, artificial intelligence, and personalised medicine are significant technical innovations allowing management to handle these difficulties. Management and process methodology advancements include lean management, clinical pathways, shared decision-making, and value-based care. Capitation or bundled payment schemes, networked or matrix organisational structures, and interprofessional collaboration and teamwork are all part of business models and labour practises. Customer engagement is improved by patient portals, online reviews, social media, and patient advocacy groups.
Future Outlook
Several significant changes will shape the healthcare industry in the coming years. One of the most significant of these is our population’s ageing, which is contributing to increasing longevity and a greater demand for healthcare services. In addition, there is a growing emphasis on preventative and holistic care, which attempts to address health concerns before they become serious and to treat patients as a whole person rather than just a collection of symptoms.
Another significant development is the rise of precision and regenerative medicine, which employs cutting-edge technologies to tailor therapies to individual patients and repair damaged tissues and organs. This is linked to the trend toward integrated and value-based care, which aims to enhance patient outcomes while lowering costs and increasing efficiency.
At the same time, there are several obstacles that the healthcare industry must overcome in order to prosper. These include new technology’s ethical and social consequences, data privacy and security threats, regulatory ambiguity and complexity, innovation dissemination and adoption impediments, and stakeholder engagement and alignment. Despite these obstacles, there are reasons to be optimistic about the future of healthcare, as new technologies such as synthetic biology and bioengineering, quantum computing and simulation, brain-computer interfaces and neurotechnology, virtual reality and augmented reality, and 3D printing and bioprinting will transform the industry. We can develop a healthcare system that is more patient-centred, effective, and sustainable than ever before if we work together to tackle these difficulties and embrace these new technologies.
The healthcare business will confront new difficulties and opportunities in the future as a result of increasing trends such as the ageing population, globalisation, climate change, and biotechnology. The major tasks for management will be to provide fair and sustainable access to care, to use data and technology for innovation and improvement, and to develop a learning and resilience culture. Agile management, circular economy, systems thinking, and learning organisations will be among the management and process methodology advances. Value-based contracting or outcome-based payment models, flat or self-managing organisational structures, and lifelong learning and well-being for health workers will all be part of business models and labour practises. Customer involvement will be transformed via digital platforms, gamification, co-creation, and patient empowerment.

Manufacturing
History
From the late 18th century until the mid-19th century, the world witnessed a major upheaval in how industries functioned. This revolution was appropriately dubbed the Industrial Revolution. It was a period of tremendous development and progress, brought about by the creation of revolutionary technology such as steam engines, railways, textile machines, and iron production. These astonishing technologies enabled mass manufacturing, increased productivity, lower prices, and enhanced quality, revolutionising how industries worked.
Furthermore, the Industrial Revolution ushered in new business models and labour standards, with factories being the major mode of production and employing a large number of workers in difficult and frequently dangerous conditions. Despite these hurdles, the revolution gave rise to key manufacturing sectors such as textiles, iron and steel, chemicals, and machinery, which forever reshaped the global economic landscape.
Manufacturing executives faced a formidable issue amid the Industrial Revolution in the late nineteenth century. As mechanised power and specialised labour became accessible, it became their obligation to organise and supervise large-scale manufacturing. The development of new technology, such as steam engines, railways, and factories, enabled mass manufacturing of commodities. However, this came with its own set of issues, such as quality control, standardisation, labour division, and cost-cutting. To solve these difficulties, management approaches such as scientific management, assembly line production, and Taylorism were developed and implemented as breakthroughs. These new ideas were critical in streamlining production processes and increasing efficiency, ultimately defining the direction of industrialisation as we know it today.
Current Position
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0, has begun a new era of production. AI, robotics, IoT, cloud computing, big data, and additive manufacturing are all employed in smart manufacturing. This technology enables real-time production system monitoring, control, optimisation, and automation.
Manufacturing has seen an increase in productivity and innovation due to Industry 4.0. Digital technologies will continue to revolutionise manufacturing. This inspires us to do better. The Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0, has altered manufacturing. Since the late twentieth century, this revolution has brought artificial intelligence, robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, big data, and additive manufacturing into production. These technologies enable smart manufacturing by providing real-time production system monitoring, control, optimisation, and automation.
Industry 4.0 has altered industrial business structures and labour practices. The Fourth Industrial Revolution necessitated more qualified people to run and maintain complex machinery and systems and more flexible, collaborative, and imaginative organisational forms. As a result, automotive, aircraft, electronics, biotechnology, and nanotechnology manufacturers confront new opportunities and challenges.
The manufacturing industry has battled to stay up with changing technologies, market advancements, and customer expectations. The late-twentieth-century Digital Revolution introduced computing, internet connectivity, robots, and artificial intelligence to the sector. Customisation, automation, and process integration improved firms’ market competitiveness.
Manufacturing leaders require flexibility, agility, innovation, and sustainability to be competitive. Lean manufacturing, agile manufacturing, and Industry 4.0 process strategies evolved as manufacturers optimised their operations and processes to stay competitive. These strategies have assisted manufacturers in reducing waste, improving product quality, and lowering their environmental and social impacts.
Future Outlook
The Fifth Industrial Revolution, which builds on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a widely anticipated period in manufacturing. It promotes sustainability, social responsibility, human-machine collaboration, and creativity. The Fifth Industrial Revolution will enable more efficient, resilient, customisable, and ethical forms of production using cutting-edge technologies such as quantum computing, bioprinting, nanomaterials, and blockchain. A new company model and labour practises will be required to reconcile economic growth with environmental protection and social fairness. This revolution will greatly impact renewable energy, healthcare, smart materials, and digital art. The Fifth Industrial Revolution has the potential to completely transform the manufacturing industry if it prioritises sustainable and ethical practises.
Transitioning to a more sustainable and socially responsible manufacturing mode can be intimidating for manufacturing executives. To achieve circular economies, bio-based materials, and smart goods, the Green Revolution necessitates the integration of modern technologies such as renewable energy, biotechnology, nanotechnology, and additive manufacturing. On the other hand, significant advances in management and process practises are projected as management teams focus on resource efficiency, waste reduction, carbon neutrality, and social impact. The emphasis on green manufacturing, circular economies, and Industry 5.0 is positive. Transitioning to a more environmentally friendly and socially responsible production style can be daunting for industrial executives. To achieve circular economies, bio-based materials, and smart goods, the Green Revolution necessitates the integration of novel technologies such as renewable energy, biotechnology, nanotechnology, and additive manufacturing. Significant improvement in management and process methodologies is projected to enhance management teams’ efforts as they prioritise resource efficiency, waste reduction, carbon neutrality, and social impact.

Construction
History
Historically, the construction industry relied significantly on human labour, using antiquated materials and processes, resulting in reduced productivity and poor quality. Safety, cost, time, and environmental effect were major problems that necessitated regular attention and posed substantial hurdles to the sector. However, the field’s ongoing technological improvements have played a key part in overcoming these difficulties and enhancing overall efficiency. Specifically, the development of new materials such as concrete and steel and the use of electricity and mechanisation have all contributed to the industry’s continuous success in overcoming these problems and enhancing the quality of construction projects.
One of the major issues encountered in the past with construction projects was a lack of uniformity and coordination among the numerous parties involved, such as architects, engineers, contractors, suppliers, and clients. This lack of consistency frequently led to project delays, expense increases, poor quality, and conflicts.
Management has utilised modern technology such as computer-aided design (CAD), building information modelling (BIM), project management software, and communication tools to offset these unfavourable results. Stakeholders can now interact more efficiently, plan more strategically, and carry out projects with better design and execution by employing these innovative technologies.
Indeed, the integration of these technologies has transformed the construction business, allowing it to operate more efficiently and effectively. This significantly improved construction project quality, shorter completion dates, and lower prices. Finally, the use of sophisticated technologies has resulted in a more efficient and prosperous construction industry that is better positioned to meet the needs of its stakeholders.
Current Position
As a result of the introduction of modern materials, digital technology, and improved management methods, the construction industry has changed dramatically over the years. This has resulted in significant efficiency gains while also promoting innovation. Sustainability, competitiveness, complexity, and customer satisfaction must all be considered. Artificial intelligence, robotics, 3D printing, and modular construction are also causing a paradigm shift in the business. These technologies have revolutionised the construction industry, making it more efficient, faster, and cost-effective. By incorporating this technology, companies have built more sustainably, reducing environmental impact and waste. Understanding the impact of these changes on the industry, its stakeholders, and the economy as a whole will become increasingly important as the sector continues to adapt and embrace new advancements.
When it comes to pursuing innovation and sustainability, businesses in today’s globalised world face a plethora of obstacles to overcome. The construction industry has high-quality standards because of the complex nature of the projects it undertakes and the discerning customers it serves. As a result, the industry requires advanced management techniques to improve its efficiency, flexibility, and overall performance. Lean construction, agile project management, integrated project delivery, and value engineering are just some of the cutting-edge approaches that businesses can utilise to overcome these challenges and achieve success. Businesses have the opportunity to boost project outcomes, reduce costs, and build a solid reputation in their respective industries if they adopt innovative methodologies such as these.
Future Outlook
The construction industry is on the verge of a major transformation. The industry is set to undergo significant changes in the coming years as a result of new technologies, innovative business models, and modern labour practices. The industry must become more adaptable, customer-focused, and resilient to adapt to this changing landscape. This transformation, however, will not be without difficulties. It will necessitate the collaboration of all stakeholders, the integration of new tools and technologies, and the creation of value for all parties involved. Biotechnology, nanotechnology, blockchain, and smart cities are the most promising technological advancements shaping the industry’s future. These technologies have the potential to transform construction practices, making them more efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective. Biotechnology, for example, has the potential to create stronger and more durable materials. Simultaneously, nanotechnology can aid in the development of self-healing materials that can repair themselves when damaged. Blockchain technology can be used to create more transparent and secure supply chains, while smart cities can aid in resource optimisation and waste reduction. As the industry evolves and adapts, it will be critical for all stakeholders to collaborate to ensure the transformation is a success.
Leaders must use cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, blockchain, smart materials, and digital twins to achieve optimal results, ensure safety, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction. This necessitates the adoption of novel business models and hiring practices such as platform-based ecosystems, crowdsourcing, co-creation, and continuous learning. By implementing these models and practices, the industry can encourage innovation, cooperation, and flexibility, paving the way for a brighter future.

Mining
History
The mining industry went through a period of tremendous growth and expansion during the course of the Industrial Revolution. As a result, it eventually became one of the most important players in the production of valuable resources such as coal, iron, and copper. Motivated by the opportunity to profit and gain influence, mining corporations frequently expanded their operations across global regions, exploiting colonial territories and indigenous communities in the process. Mining corporations frequently expanded their operations across global regions. However, with such expansion came a plethora of significant challenges and problems, ranging from environmental degradation and labour disputes to safety risks and geopolitical tensions, all of which threatened the industry’s ability to maintain its stability and sustainability.
The development of the mining industry can be traced back to the discovery and subsequent exploitation of previously untapped resources such as coal, iron, gold, and diamonds. The management team faced their greatest difficulties when attempting to gain access to these resources, maintain worker safety and productivity standards, and address the negative effects that mining has on the environment and society. The management team prevailed over these challenges with the assistance of several significant technological breakthroughs, including steam engines, dynamite, railways, and telegraphs. The development of scientific management, the division of labour, the establishment of standardisation, and the implementation of quality control were among the advancements made in process and management methodologies. Business models and labour practises have evolved over time, moving from feudalism to capitalism, paternalism to unionism, and slavery to wage labour, respectively. Customer engagement was largely driven by supply and demand, with little room for differentiation or branding.
Current Position
The mining industry faces a significant challenge in terms of reducing its negative impact on the environment and society while also meeting rising demand for minerals and metals. Mining firms are turning to more cutting-edge technology such as automation, digitalisation, and renewable energy to improve their efficacy, production, and safety. Furthermore, in order to adapt to the new environment, the sector is changing its operating methods and labour practices. Outsourcing, diversification, and involvement with many stakeholders are among the changes made to promote sustainable and profitable growth. As a result, the mining industry is undergoing a substantial transformation that will ultimately lead to a more ecologically friendly and responsible future.
Depletion of resources such as oil, gas, uranium, and rare earth metals, as well as diversification of mining activities, characterise the mining business. The management team faces several problems, the most important of which are optimising resource extraction and processing, developing and implementing new technologies, and striking a balance between the mining industry’s economic, environmental, and social implications. Automation, digitisation, biotechnology, and alternative energy sources are just a few of the important technological innovations that are supporting management in addressing these difficulties. Recent management and process improvements include lean, agile, project, and risk management.
Future Outlook
The mining industry needs to adjust in order to remain competitive in the face of shifting societal needs and expectations. As a direct consequence of this, mining companies will inevitably be confronted with a number of difficulties, the most significant of which are resource depletion, climate change, and social responsibility. In spite of these obstacles, mining companies have a wealth of opportunities to innovate and create value through a variety of channels, such as deep-sea mining, space mining, and the implementation of a circular economy. These are just a few examples. By seizing these opportunities, mining companies can ensure their continued success in the future while also making a contribution to a global economy that is more sustainable and responsible.
It is anticipated that the mining industry’s future will be influenced in significant ways by the exploration and development of new frontiers, such as the deep sea, space, and asteroids. The most significant difficulties that management will face include overcoming obstacles of a technical and financial nature, cooperating and competing with other actors, and attempting to anticipate and adapt to the shifting needs and expectations of stakeholders. The management team is now able to address these challenges thanks to a number of significant technological breakthroughs. Some of these breakthroughs include nanotechnology, artificial intelligence, robotics, and quantum computing. The future of management and process methodology will include advancements in areas such as scenario planning, foresight, design thinking, and thinking about systems. There will be a shift from product-centric business models to service-centric business models, ownership will be replaced by access, and human-centricity will be replaced by human-machine hybridity.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

London, UK
History
London has always been a global centre of trade, finance and culture, but in the 21st century it has also become a leader in innovation, technology and creativity. According to the Office for National Statistics, London’s gross value added (GVA) – a measure of its economic output – was £487 billion in 2019, accounting for 23.6% of the UK’s total GVA. London is the most significant contributor to the UK’s economy compared to other regions.
One of the key drivers of London’s economic growth has been its ability to attract and retain talent from around the world. London is home to more than 9 million people speaking over 300 languages and has a highly skilled and diverse workforce. London also hosts some of the world’s top universities, research institutions and cultural organisations, creating a vibrant environment for learning, collaboration and innovation.
Another factor that has shaped London’s commercial development is its openness to new ideas and opportunities. London has embraced digital transformation, becoming a hub for tech start-ups, fintech firms and creative industries. Tech Nation said London had 2,164 tech start-ups in 2020, more than any other European city. London also has a strong presence in professional services, media, education, health and tourism sectors, offering a wide range of products and services to domestic and international markets.
Current Position
London has also diversified its economy, becoming a global leader in fintech, creative industries, education and research, tourism and culture. London has attracted more foreign direct investment than any other European city and has been ranked the most innovative city globally by several indicators. London has also improved its infrastructure, with major projects such as Crossrail, the Olympic Park and Battersea Power Station.
London also faces some significant challenges in the 21st century, such as rising costs of living, congestion, pollution and inequality. The Covid-19 pandemic has also had a major impact on London’s economy, affecting the hospitality, retail and entertainment sectors. The UK’s departure from the European Union has also created some uncertainty for London’s businesses and workers, especially regarding trade and migration.
Despite these challenges, London remains a resilient and adaptable city with a vision for the future. The Mayor of London’s Economic Development Strategy sets out some key priorities for London’s recovery and growth, such as supporting green and inclusive growth, investing in infrastructure and skills, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, and strengthening London’s global competitiveness and collaboration.
Future Outlook
London’s economy is anticipated to expand higher than the UK’s average. However, this growth is predicted to be slower than before the COVID crisis. According to Oxford Economics, London’s GDP will grow by an average of 2% per year between 2020 and 2030, compared to 1.6% for the UK.
London will also face new opportunities and challenges in the next decade, such as:
• Digital transformation: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in various sectors of London’s economy, such as e-commerce, remote working, online education and telemedicine. New technologies can bring growth and innovation but also create skill gaps and digital disparities.
• Green transition: London has committed to becoming a net zero carbon city by 2050, which will require a radical transformation of its energy system, transport network, buildings and industries. The growth of green industries like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and circular economy could create new job opportunities and markets.
• Social cohesion: London must address its social and spatial disparities and foster a sense of belonging among its diverse population. To achieve this, London may need to increase investments in affordable housing, social infrastructure, community engagement, and inclusive growth.
Global competitiveness: London must maintain its position as a global city in a changing world order. The city can boost its position by enhancing its influence through investments in culture and diplomacy. Additionally, joining forces with other cities can help tackle global challenges like climate change and security.
Johannesburg, SA
History
The economy of Johannesburg is primarily driven by four sectors, with three of them being service sectors. The four key sectors are financial and business services; retail and wholesale trade; community and social services; and manufacturing. These sectors account for more than 80% of the city’s gross value added (GVA), which measures the contribution of each sector to the economy.
The financial and business services sector is Johannesburg’s largest and fastest-growing sector, contributing 34% of the city’s GVA in 2017, up from 28% in 2000. This sector includes banking, insurance, real estate, legal, accounting, consulting and other professional services. The retail and wholesale trade sector is the second largest sector in Johannesburg, contributing 19% of the city’s GVA in 2017, down from 21% in 2000. This sector includes wholesale and retail trade, motor trade, accommodation, food and beverage services, and personal services. The community and social services sector is the third largest sector in Johannesburg, contributing 18% of the city’s GVA in 2017, up from 17% in 2000. This sector includes public administration, education, health, social work, arts, entertainment, recreation and other services. The manufacturing sector is the fourth largest sector in Johannesburg, contributing 12% of the city’s GVA in 2017, down from 16% in 2000. This sector includes food, beverages, textiles, clothing, leather, wood, paper, printing, chemicals, plastics, rubber, metal products, machinery, electrical equipment, transport equipment and other manufacturing.
Current Position
Johannesburg’s economic structure reflects its history as a mining town that diversified into manufacturing and services. However, it also shows its ongoing transformation into a more knowledge-based and innovation-driven economy that can compete globally. Some emerging sectors with the potential for growth and job creation in Johannesburg are information and communication technology (ICT); tourism; creative industries; green economy; and biotechnology.
Johannesburg is the largest single metropolitan contributor to the national economic product, generating 15% of South Africa’s wealth and around 44% of Gauteng province’s economic output. The city’s economy is at least one and a half times bigger than that of the second biggest metro, Cape Town. Over the past 20 years (1996-2017), Johannesburg’s average growth rate was 3.6%, marginally higher than both the provincial economy (3.0%) and national (2.7%) economies. The city’s per capita gross geographic product (GGP) in 2019 was R31 000, close to the average GGP per capita of World Bank-designated middle-income countries. The average annual income per household in Johannesburg is R31 048, which is, on average, 57% higher than that for South Africa and 9% higher than the GGP per capita for Gauteng.
Future Outlook
Johannesburg faces several economic challenges that affect its growth potential and social development. These challenges include high unemployment; poverty; inequality; crime; infrastructure gaps; environmental degradation; skills shortages; regulatory barriers; and global competition. To address these challenges, the City of Johannesburg has developed various strategies and initiatives that aim to foster inclusive growth, create jobs, improve service delivery, enhance competitiveness, attract investment, support small businesses, promote innovation, and build resilience.
Some of the opportunities that Johannesburg can leverage to overcome its challenges are its large and diverse population; its strategic location as a gateway to Africa; its strong financial sector; its rich cultural heritage; its entrepreneurial spirit; its research and academic institutions; its international connectivity; its natural resources; and its potential for renewable energy.
Johannesburg’s economic structure reflects its history as a mining town that diversified into manufacturing and services. However, it also shows its ongoing transformation into a more knowledge-based and innovation-driven economy that can compete globally.

Houston, TX
History
Houston, Texas, is one of the largest and most dynamic cities in the United States, with a diverse and resilient economy that has undergone significant changes since 2000.
Houston’s economy has faced challenges and opportunities in the past 20 years. One of the most significant events was the Enron scandal in 2001, which resulted in the collapse of one of Houston’s largest and most influential companies and shook the confidence of investors and consumers. Another major challenge was the impact of Hurricane Harvey in 2017, which caused widespread flooding and damage to homes, businesses and infrastructure. The storm disrupted economic activity and cost billions of dollars in recovery efforts. More recently, Houston has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has reduced demand for oil and gas and caused unemployment and income losses for many workers.
Despite these difficulties, Houston has also demonstrated its resilience and adaptability. The city has diversified its economy by attracting new businesses and industries, such as technology, renewable energy, biotechnology and entertainment. Houston has also invested in its human capital by improving its education system, expanding its cultural offerings and enhancing its quality of life. Houston has also benefited from its favourable business climate, low cost of living, diverse population and entrepreneurial spirit.
Overall, Houston has been a remarkable success story for commercial development in the past two decades. The city has contributed significantly to the national economy by creating jobs, generating income and producing goods and services. Houston has also shown its ability to overcome adversity and embrace change by diversifying its economy and enhancing its livability.
Current Position
Houston’s economy is based primarily on the energy industry, particularly oil and gas. The city boasts more than 3,000 energy-related businesses, which include some of the leading companies in oil and gas exploration, production, and petroleum pipeline operations. Houston also hosts the world’s largest concentration of petrochemical manufacturing, producing synthetic rubber, insecticides, fertilizers and other products. The energy sector accounts for about 40 per cent of Houston’s gross domestic product (GDP), which was 537 billion U.S. dollars in 2021, making it the fourth-largest metro area in the country.
Houston’s economy is not only dependent on oil and gas. The city has also developed a strong presence in other sectors, such as health care, biomedical research, aerospace, manufacturing, trade and finance. The Texas Medical Center, located in Houston, is the largest medical complex in the world. It has more than 100,000 employees and receives over 10 million patient visits annually. Houston also boasts a vibrant aerospace industry, with the Johnson Space Center as the headquarters of NASA’s human spaceflight program. Houston’s manufacturing sector is diverse and innovative, producing everything from chemicals and plastics to machinery and electronics. Houston is also a major trade hub, with its port being one of the busiest in the nation and a gateway to international markets.
Future Outlook
As Houston looks towards its economic future, several challenges and opportunities lie ahead. One of the foremost challenges will be ensuring the city can maintain its competitiveness in an increasingly globalized market. Achieving success in business growth and investment will necessitate a continuous endeavour to draw in and retain skilled personnel, promote creativity, and establish a favourable business environment.
Another major challenge that Houston must address is environmental sustainability. The city has long struggled with air pollution and climate change, and it will be critical to take proactive steps to reduce emissions and protect the health of its citizens. Houston must focus on investing in renewable energy, green infrastructure, and sustainable transportation options to create a sustainable future.
In addition to these challenges, Houston also faces significant income inequality. While the city has a thriving economy, many residents struggle to make ends meet. Addressing this issue will require a multi-faceted approach that includes efforts to increase access to education and job training, provide affordable housing, and improve access to healthcare.
Despite these challenges, Houston also has many opportunities for growth and innovation. The city is already a leader in energy innovation, healthcare research, and aerospace exploration, and these industries are poised for continued growth in the coming years. In addition, Houston has the potential to tap into new markets, such as electric vehicles, artificial intelligence, and space tourism, which could provide new sources of economic growth and job creation. By embracing these opportunities and addressing its challenges head-on, Houston can continue to thrive and prosper in the years ahead.

Amsterdam, NL
History
Amsterdam, the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, has a rich and diverse commercial history dating back to the 12th century. Founded as a fishing village at the mouth of the River Amstel, Amsterdam became a major world port and a center of finance and trade during the Dutch Golden Age of the 17th century. However, it experienced decline in the 18th and 19th centuries due to wars, economic crises, and competition from other cities. In the 20th century, Amsterdam underwent several phases of urban expansion, social change, and cultural development.
The 1980s were a turbulent decade for the city, marked by political unrest, social movements, economic challenges, and environmental issues. Key events and dates that shaped the commercial history of Amsterdam during this period include Queen Beatrix’s coronation, the merger of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange and the European Options Exchange (EOE), the population’s decline in the 1980s, and the opening of the Amsterdam Airport Schiphol in 1987. The city council adopted the “Structure Plan Amsterdam” in 1989, aiming to balance economic growth, social cohesion, and environmental quality. The city’s economy shifted from manufacturing and trade to services and knowledge-based sectors, and its population became more diverse and multicultural. By the end of the decade, Amsterdam had emerged as a dynamic and resilient city that faced challenges and opportunities with creativity and innovation. The city has also developed a strong awareness of its environmental impact and responsibility to future generations.
Amsterdam experienced a revival in the 1990s due to economic growth, cultural diversity, and international recognition. The city hosted major events, such as the European Capital of Culture in 1987, Eurovision Song Contest in 1992, World AIDS Conference in 1998, and the European Union summit in 1997. Amsterdam also developed new economic sectors, including ICT, biotechnology, and creative industries. The city became more diverse, cosmopolitan, and progressive on social issues like gay rights, drug policy, and euthanasia. However, it faced challenges like integration difficulties, discrimination, and radicalization. Between 1998 and 2000, annual GDP in the Netherlands averaged nearly 4%, well above the European average. The global financial crisis of 2008-09 hit the Dutch economy hard, causing a recession and a rise in unemployment. Amsterdam weathered the crisis better than most other Dutch cities, thanks to its diversified and resilient economy.
Current Position
Amsterdam is currently dealing with various opportunities and challenges to consider while planning for its economic growth. One of the primary challenges is the issue of housing affordability, which has become a major concern for many residents in recent years. To tackle this problem successfully, the city must prioritize the development of affordable housing options that meet the needs of its residents.
The digital economy in Amsterdam is thriving. Tech start-ups, accelerators, and incubators foster creativity and open new city doors. Amsterdam has the best digital talent, connection, and investment in Europe. Fintech, e-commerce, cybersecurity, gaming, and artificial intelligence are the leading sectors of the digital economy.
Another emerging theme is the circular economy. The city encourages the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials. In Amsterdam, Fairphone creates ethical smartphones, The Renewal Workshop repairs and resells clothing, and Instock repurposes supermarket leftovers.
Amsterdam requires commercial aid as well. Housing affordability and scarcity are important concerns. Housing in the city is scarce, particularly for young professionals and low-income groups. Short-term rentals and visitors reduce long-term housing possibilities for locals, hurting the housing market. The city is building more social housing, regulating short-term rentals, and instituting a tourism fee.
Despite obstacles, Amsterdam has achieved commercial success. Foreign direct investment and international talent are accomplishments. Amsterdam is one of Europe’s top FDI destinations, attracting multinational corporations and start-ups. Globally skilled and diversified talent fosters innovation and competitiveness in the city. In 2020, Amsterdam ranked fourth in Europe for quality of life, scoring high on factors such as safety, health care, education, culture, and environment.
Another accomplishment is Amsterdam’s environmental and social responsibility leadership. The city has received numerous awards and rankings for its environmental, inclusive, and resilient activities. The European Commission named Amsterdam the European Capital of Innovation in 2016, Arcadis called it the most sustainable city in Europe in 2018, and Thomson Reuters Foundation named it the best city for social entrepreneurs in 2019.
Amsterdam helps the Dutch economy as a whole. The city accounts for 25% of GDP and 16% of employment. The city generates 40% of the nation’s innovation and 70% of its patent applications. Amsterdam benefits both the Dutch and global economies.
Future Outlook
Amsterdam’s economy showed signs of resilience and optimism in 2021, ranking first in Europe for foreign direct investment projects and second in Europe for startup funding.
A key challenge Amsterdam must face is congestion, which has become a significant problem due to its high population density. To alleviate this problem, the city needs to invest in more efficient public transportation systems and encourage alternative modes of transportation, such as bicycles and electric vehicles.
Inequality is also a major concern in Amsterdam, as its residents have significant disparities in income and social status. The city will need policies promoting greater equity and inclusivity to address this issue, such as affordable education and training programs for low-income individuals.
Climate change is another major challenge that Amsterdam must confront, as rising sea levels and other environmental threats threaten the city’s long-term sustainability. By 2050, Amsterdam hopes to be waste-free. Amsterdam must consider investing in green infrastructure and renewable energy sources while promoting sustainable lifestyles and consumption patterns among its residents.
To achieve its economic objectives, Amsterdam must continue investing in its human capital, infrastructure, innovation, and sustainability. By doing so, the city can create a more prosperous and equitable future for all of its residents while also contributing to the overall growth and success of the European Union.

Stockholm, SE
History
During the first ten years of the 21st century, Stockholm experienced remarkable growth, primarily attributed to the emergence of information and communication technology (ICT) and creative industries. These sectors thrived due to the city’s abundant human capital, research and development (R&D) capabilities, entrepreneurial spirit, and openness to global markets.
Ericsson, Spotify, Skype, Klarna, and King are notable ICT companies that contributed to Stockholm becoming a global hub. Additionally, creative industries such as media, advertising, design, fashion, and gaming played a significant role in the city’s growth. These sectors accounted for over 40% of the city’s GDP growth and over 30% of its employment growth between 2000 and 2010.
Despite facing challenges such as the dot-com bust of 2001-2002, which had an impact on many ICT start-ups, and the global financial crisis of 2008-2009, which led to a decrease in consumer demand and investment, Stockholm remained resilient and adaptable thanks to its diversified economic structure, sound fiscal policy, and social safety net. With an unwavering determination to succeed, the city rose above the adversities and continued to prosper.
Current Position
Stockholm’s service industry expanded significantly in the second decade of the twenty-first century, particularly in finance, business services, education, health care, and tourism. These industries benefited from the city’s high-quality infrastructure, efficient government, qualified labour, and appealing lifestyle.
Stockholm has also emerged as a green economy pioneer with a strong commitment to environmental sustainability and social equality. Between 1990 and 2019, the city lowered greenhouse gas emissions by 58 per cent per capita while growing its renewable energy contribution to 80 per cent. In addition, the city invested in public transportation, waste management, urban planning, and social housing, making it one of the world’s most livable cities.
During this time, the city also encountered certain obstacles, such as the inflow of refugees and migrants in 2015-2016, which put a strain on its social services and integration programmes, and the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020-2021, which interrupted its economic activity and public health. On the other hand, Stockholm has shown resilience and solidarity due to its high social cohesiveness, innovation potential, and international cooperation.
Overall, Stockholm has been a commercial success story in the past two decades and has the potential to remain so. The city has demonstrated its ability to adapt to changing circumstances and seize new opportunities while maintaining its core values and identity. Stockholm is a city that combines economic growth with social justice, innovation with sustainability, and tradition with modernity.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead ten years, Stockholm’s economy is expected to continue its competitiveness, innovation, and sustainability while maintaining a varied and dynamic economic structure. The city’s economy will continue to experience digital transformation, with prospects in ICT, creative industries, and artificial intelligence, big data, cloud computing, and e-commerce. Furthermore, the economy’s green transformation is projected to continue, with a focus on decreasing environmental effect and implementing circular economy concepts, as well as new opportunities in clean energy, green mobility, and the economy. The economy’s social transformation is also likely to proceed, with an emphasis on improving human capital and social inclusion policies, as well as new opportunities in lifelong learning, health care, and social innovation.
Nonetheless, despite the optimistic outlook, Stockholm may confront a number of obstacles in the future. One of the most significant concerns is worldwide competition from other cities and regions that may provide comparable or greater economic growth opportunities. Demographic changes may also have an impact on the city’s labour supply and demand, as well as its public budget and social welfare. Finally, geopolitical unpredictability may have an impact on its commercial relations and security situation.
Nonetheless, due to its innovative and sustainable approach to economic development, Stockholm’s economy is predicted to remain resilient and active. What will the economy of Stockholm look like in the coming decade? Stockholm will remain a competitive, inventive, and sustainable metropolis with a diverse and dynamic economic structure, based on current trends and projections.
Program Benefits
Management
- Enhanced agility
- Continuous improvement
- Employee satisfaction
- Empowered management
- Increased capacity
- Strategic alignment
- Risk management
- Enhanced decision-making
- Enhanced collaboration
- Resource utilisation
Marketing
- Enhanced reputation
- Competitive advantage
- Enhanced innovation
- Customer satisfaction
- Risk management
- Regulatory compliance
- Consistent standards
- Cost savings
- Customer focus
- Desirable employer
Operations
- Streamlined processes
- Improved communication
- Cost control
- Customer satisfaction
- Increased productivity
- Decision making
- Risk management
- Regulatory compliance
- Employee engagement
- Resource utilisation
Testimonials

CBi-electric: african cables
“As the Continuous Process Improvement Manager at CBi-electric: african cables, I’ve had the privilege to have worked alongside Mr Eysink on a Performance Improvement Program focused on meeting the Business plans and objectives, improving performance and controlling and improving costs.
Mr Eysink was the lead in designing the Management Operating System to provide information exposing operational problems, as well as their cause and the cost of the problems to the company. The Management operating system consisted of the following elements: Forecast; Plan; Monitor and Control; Report, review and react.
Mr Eysink facilitated working groups to define the required processes within all these elements. He also documented, trained, and implemented these processes with the working groups, and initiated an audit system to monitor compliance with these processes.
Mr Eysink is a process and data-driven individual that has excellent data analysis and critical thinking skills. He has a combination of business Acumen and People management skills that makes him an outstanding Business Consultant and Leader.”

OnOffline Data (Pty) Ltd
“Since 2015, I have had the pleasure of working with Mr Eysink on two bases: first as a client when he conducted a significant exercise on growth and reimagining the future of the organisation for the board where I served as an executive and, second as a partner when we paired up on client interventions.
I found his technical skill to be top drawer. He is at ease with large pieces of data and can leverage his diverse background across industry sectors to handle complexity of systems and interconnectedness as well. This is a relatively unique skill set in our market.
His interpersonal style is direct without being discourteous. He is adept at having tough but necessary discussions without negative emotions. He always drives toward action and measurement, backed by a foundation of fact. He manages up and sideways with ease.
I have found Mr Eysink to be scrupulously honest in all my dealings and have no hesitation with working with now or in the future. I recommend him highly to anyone looking for an impact.”

Ilanga Retail Consultants
“I met Mr Eysink in 2008, when we worked together on an analysis for an international media firm. My first impression of Mr Eysink is that he is the ideal person to work with in a high-pressure environment. His level head and unflappability have a positive influence on those around him: his contribution to the team being more than just his professional approach to work.
Over subsequent years and working with Mr Eysink on a number of consulting projects in the Southern African region, my respect for him continued to grow. Due to his understated personality, I was singularly privileged to be exposed to the depth of his intellect and ability to master every challenge that he is presented with. In my opinion, with his rare balance of both creativity and analytical ability, there is no task or responsibility that an employer cannot trust in his hands. He has over-delivered in every project that I have had the privilege to witness.”

Mr Vangelatos
“This is to place on record that I have known Mr Eysink professionally for the past 10 years, both as a colleague in Management Consulting assignments as well as from personal and professional interactions.
From my personal experience, I can recommend him as a most trustworthy individual with impeccable interactive skills, specialist technical knowledge and superb computer skills.
Mr Eysink has a very likeable personality, excellent manners, and is always there to assist his team and colleagues when called upon, well into the late hours of the night.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.














