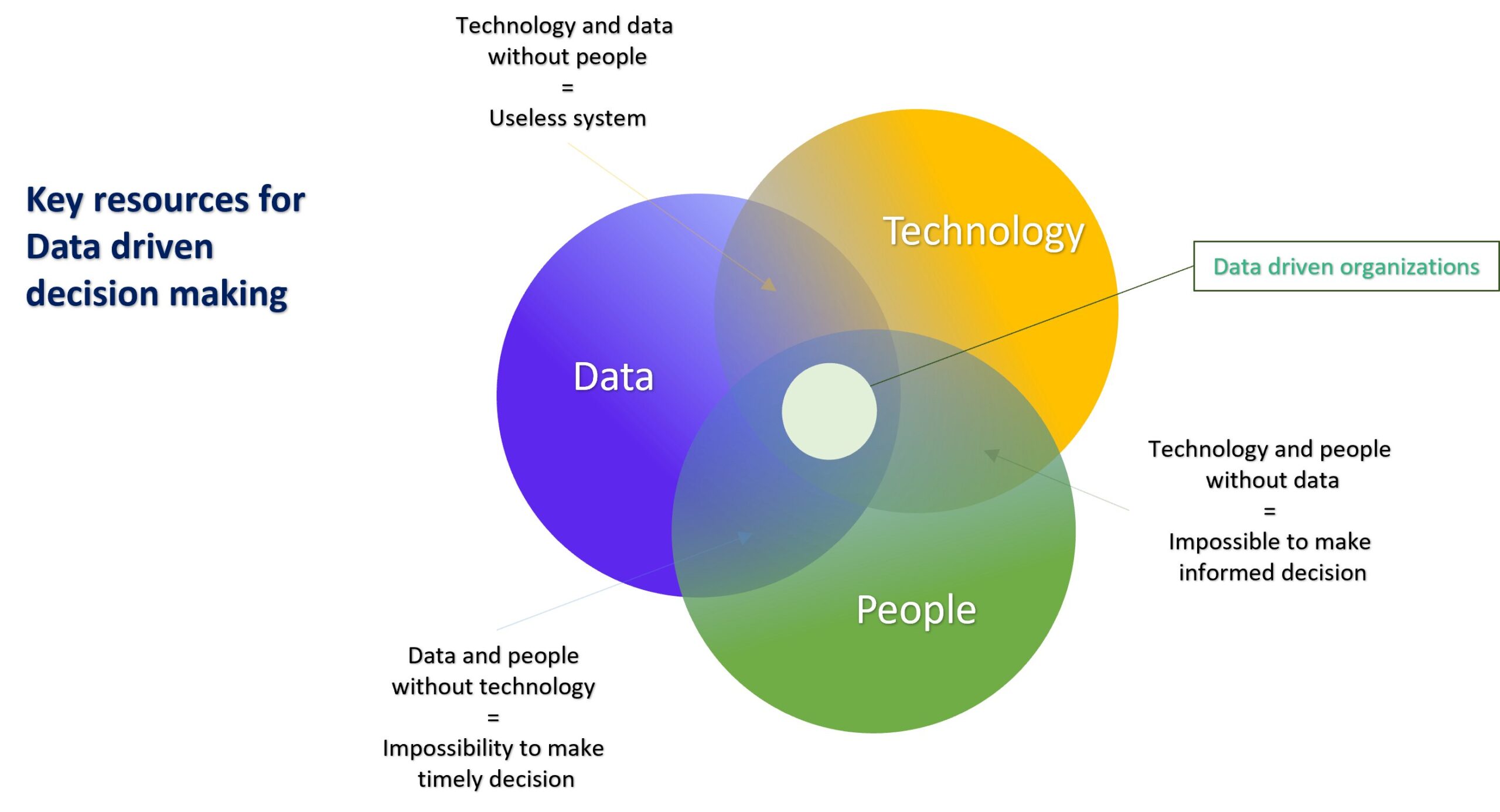
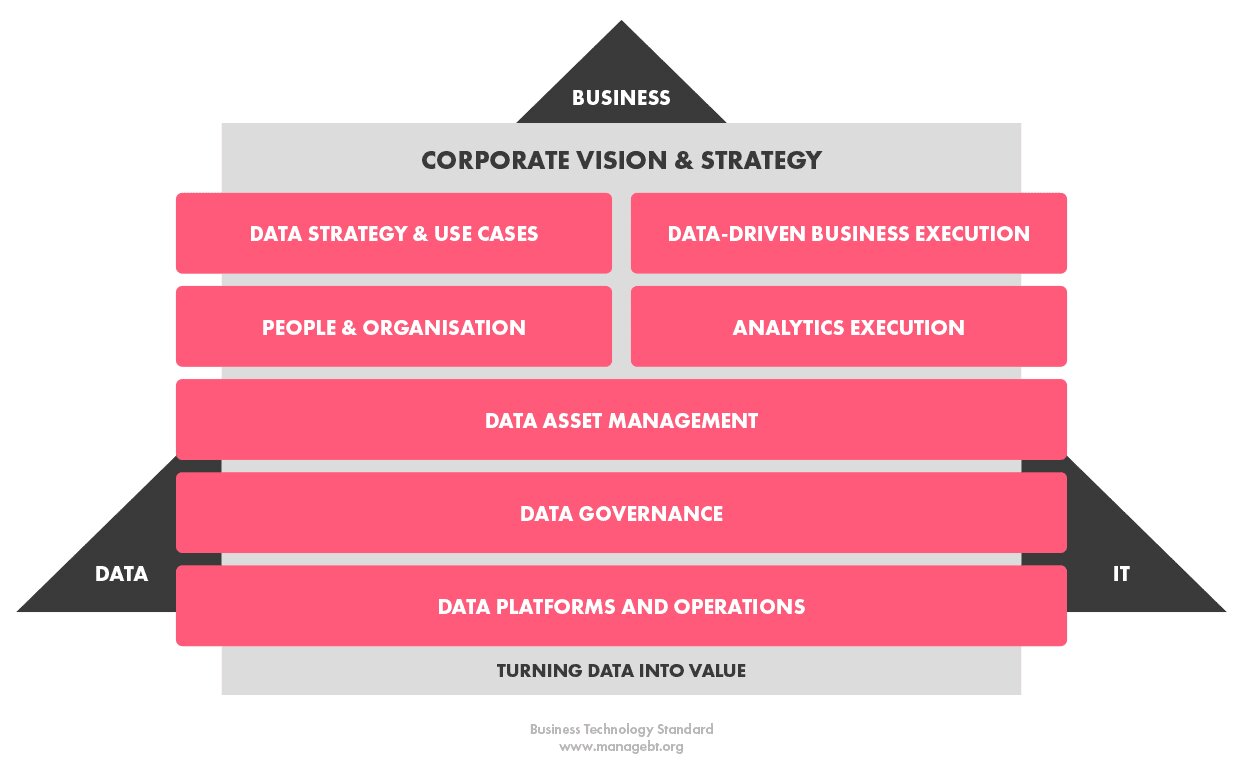
Data Driven Decision Making
Insert (CLP) Photograph on Web Page (Align Right)
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Data Driven Decision Making is provided by Mr. Adama Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 24 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
Personal Profile
To request further information about Mr. Adama through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Data Driven Decision Making
History
The evolution of data-driven decision making (DDDM) has been nothing short of remarkable. A practice that began as a fledgling idea in the early days of computing has since become a cornerstone of modern business operations. The ability to use data and analytics to inform decision-making, as opposed to relying on intuition or guesswork, has been embraced by companies of all sizes and industries, fundamentally altering the way businesses operate.
The roots of DDDM can be traced back to the earliest days of computing, when companies first started to adopt computers to automate their operations and store data digitally. While this was a significant step forward, accessing and analyzing the data was a daunting task, limiting the insights that could be gleaned. However, in the 1980s and 1990s, the introduction of Business Intelligence (BI) systems paved the way for a new era in DDDM. Companies were now able to analyze data, uncovering new insights and making decisions based on actual data, rather than relying on intuition or guesswork.
The advent of data warehousing and data mining in the early 2000s marked a major leap forward in the evolution of DDDM. With these powerful tools at their disposal, companies were able to store and analyze vast amounts of data, uncovering hidden patterns and gaining valuable insights into their operations and customers. This newfound understanding allowed companies to make more informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
Today, the rise of big data and the growing availability of cloud computing and storage solutions have further accelerated DDDM. Companies can now collect, store, and analyze massive amounts of data more quickly and at a fraction of the cost, gaining real-time insights into their operations and customers. The integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence has also enabled companies to automate data analysis, uncovering new insights and patterns that would have otherwise remained hidden.
DDDM has been a game-changer for businesses, providing a competitive edge and driving operational improvements. Companies that have embraced DDDM are better equipped to make informed decisions, adapt to changes in the market, and improve their operations. By gaining deeper insights into their customers, they are also able to develop targeted marketing strategies, leading to increased sales and revenue.
In conclusion, the history of DDDM is a testament to the transformative power of technology and innovation. From its humble beginnings to its current state as an essential aspect of modern business operations, DDDM has helped companies stay ahead of the curve, improve their operations, and increase revenue. The future of DDDM is bright, and businesses that embrace this powerful tool will undoubtedly reap the rewards for years to come.
Current Position
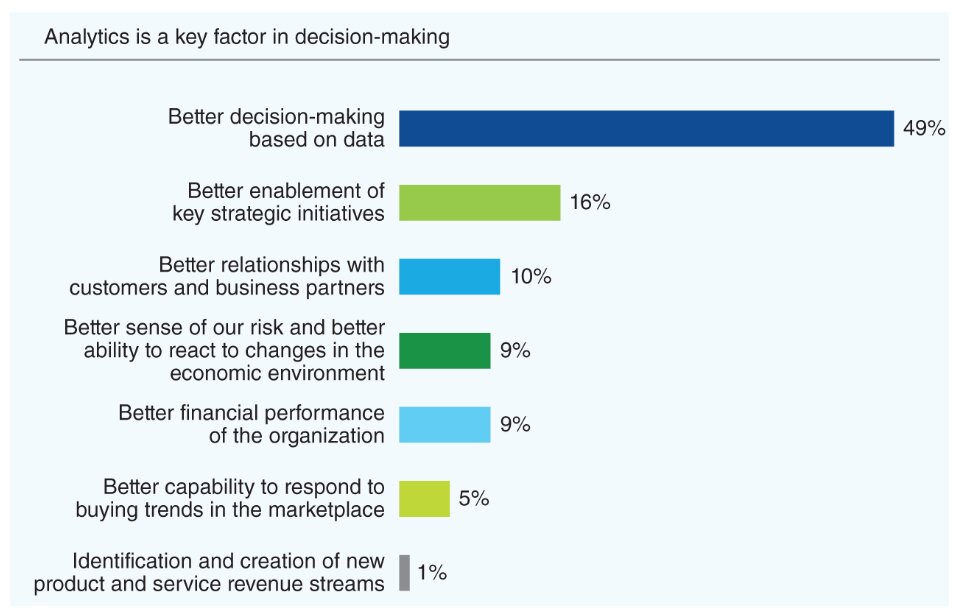
The ever-evolving landscape of technology has brought about the advent of data-driven decision making (DDDM) in the corporate world. With the advent of big data and the growth of cloud computing, businesses are now able to harvest, preserve and scrutinize information at a significantly lower cost. Furthermore, the progress in machine learning and AI has paved the way for companies to perform automated data analysis and uncover secrets that were once deemed intangible.
DDDM, in the present scenario, has become a critical component of contemporary business processes. Organizations of all sizes and domains have embraced DDDM as a mean to gain a competitive edge, streamline operations and escalate revenue. Industries such as finance, healthcare, retail and manufacturing have adopted DDDM as a cornerstone of their business strategy. For instance, retail corporations utilize DDDM to better manage inventory and enhance customer satisfaction while manufacturing companies leverage DDDM to improve production efficiency and reduce expenses.
As for implementation, the various methods of executing DDDM are quite varied. Some companies use DDDM to comprehend their operations and customers while others use it to optimize specific business processes like inventory management or marketing. Certain organizations use DDDM to design focused marketing campaigns, thereby driving sales, while others rely on DDDM to enhance production efficiency and decrease costs.
However, despite its increasing adoption, the journey to DDDM is not without challenges. Companies often face hurdles like data quality, data governance and security. A further challenge faced by many businesses is the lack of data literacy among their employees, making it difficult for them to extract insights from data and act on it effectively.
In conclusion, the adoption and implementation of DDDM is continuously expanding and evolving. The current state of technology has made it easier for companies to collect, store, and analyze data, thereby allowing them to gain valuable insights. DDDM has now become an indispensable aspect of modern business operations and is being adopted by organizations across various industries. Although companies still face challenges in implementing DDDM, they must tackle issues such as data quality, data governance, and data security as well as the lack of data literacy among their employees.
Future Outlook

The advent of DDDM is inextricably tied to the evolutionary progression of technology and its various facets, particularly in the spheres of AI, ML, and IoT. These technological breakthroughs will empower corporations to accumulate, preserve, and scrutinize an even greater magnitude of data, allowing them to extract real-time insights that were previously unattainable through manual means.
Edge computing will revolutionize the future of DDDM, by facilitating the processing of data closer to its origin, thus eliminating the need for transmission and storage, and ultimately reducing the cost of data analysis.
The integration of automation will also have a significant impact on the future of DDDM. Automation will enhance efficiency, reduce expenses, and increase productivity, enabling companies to make data-driven decisions at a much more rapid pace, thereby giving them a competitive advantage.
The coalescence of DDDM with the likes of 5G, Blockchain, and Quantum computing will be a determining factor in shaping the future of DDDM. These technologies will allow companies to process and analyze data at an unprecedented speed, enabling them to extract real-time insights and make decisive actions.
With the exponential growth of data being collected and stored, data privacy and security have become focal points in shaping the future of DDDM. The protection of data from unauthorized access and breaches has become imperative, necessitating companies to invest in data security measures and comply with data privacy regulations.
Curriculum
Data Driven Decision Making – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Business Effectiveness
- Part 1 Month 2 Business Efficiency
- Part 1 Month 3 Change Management
- Part 1 Month 4 Marketing Sales
- Part 1 Month 5 Production Operations
- Part 1 Month 6 Financial Management
- Part 1 Month 7 Human Resources
- Part 1 Month 8 Customer Services
- Part 1 Month 9 Supply Chain
- Part 1 Month 10 Information Technology
- Part 1 Month 11 Research Development
- Part 1 Month 12 Legal Compliance
Data Driven Decision Making – Part 2 – Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Data-Driven Mindset
- Part 2 Month 2 Governance Policies
- Part 2 Month 3 Storage Systems
- Part 2 Month 4 Data Collection
- Part 2 Month 5 Data Quality
- Part 2 Month 6 Data Modelling
- Part 2 Month 7 Data Analysis
- Part 2 Month 8 Data Visualization
- Part 2 Month 9 Data Automation
- Part 2 Month 10 Publish Inside & Outside
- Part 2 Month 11 Success Factors
- Part 2 Month 12 System Tracker
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Data Driven Decision Making corporate training program.
Data Driven Decision Making – Part 1 – Year 1: Process Planning
Part 01 Month 01: Business Effectiveness
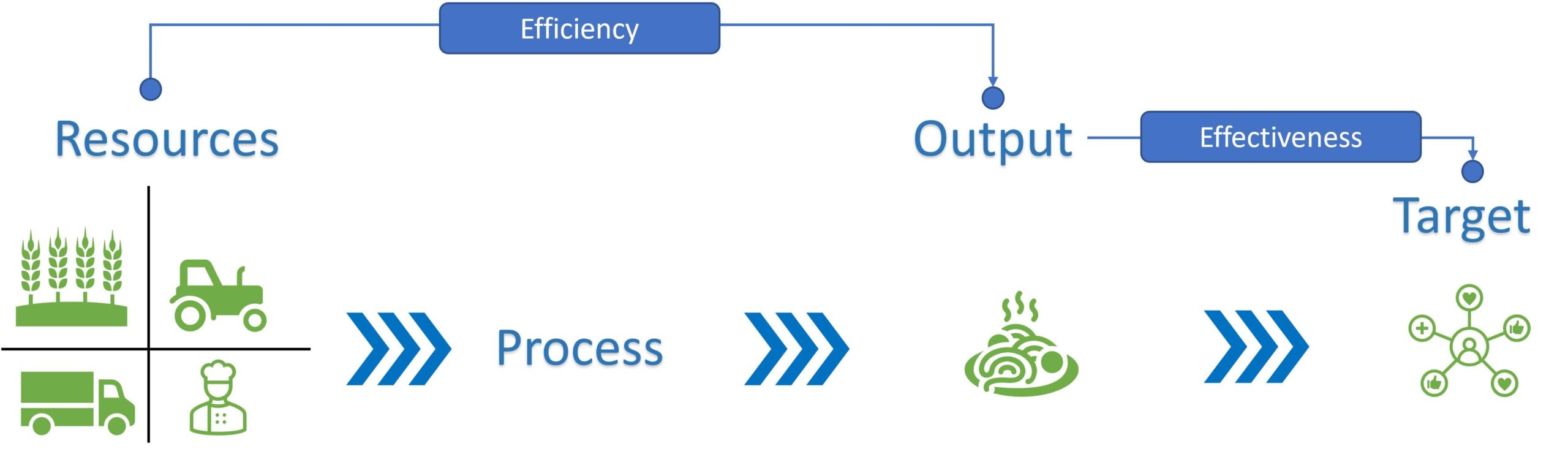
As a business analyst, I have been investigating the phenomenon of business effectiveness, which embodies the capability of a company to attain its aims and aspirations. It encompasses the measurement of a company’s optimal utilization of its resources to produce the desired results and can be gauged by observing various key performance metrics such as the escalation of revenue, profit margins, market dominance, customer satisfaction, employee commitment, and return on investment.
An organization that efficiently manages its resources, generates value for its clients, and realizes its objectives can be deemed as effective. The ability to conform to the changes in the market, persistently enhance its processes and operations, and expertly manage its finances adds another dimension to business effectiveness, further solidifying its position as a crucial aspect of business operations.
The companies listed here are widely recognized for their trailblazing and avant-garde approaches to business. Google, for instance, is lauded for its ingenuity in creating search engine technology, as well as its forays into cutting-edge concepts like self-driving cars and smart home devices. Apple, meanwhile, is known for its innovative products like the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook, all of which showcase the company’s design savvy and technological prowess. Amazon is celebrated for its disruptive influence on retail markets, thanks to innovations like one-click ordering and same-day delivery, as well as its success in expanding into new ventures such as cloud computing and streaming media. Tesla is highly regarded for its forward-thinking approach to electric vehicles and energy storage systems, as well as its unwavering commitment to sustainability and clean energy. Finally, Netflix has earned its place on this list for its game-changing impact on the TV and movie industries, as a result of trailblazing initiatives like video streaming on demand and producing original content.
In conclusion, business effectiveness is a comprehensive notion that encompasses the proficiency of a company to attain its goals, create value for its customers, and optimize the utilization of its resources to attain the desired outcomes.
Part 01 Month 02: Business Efficiency
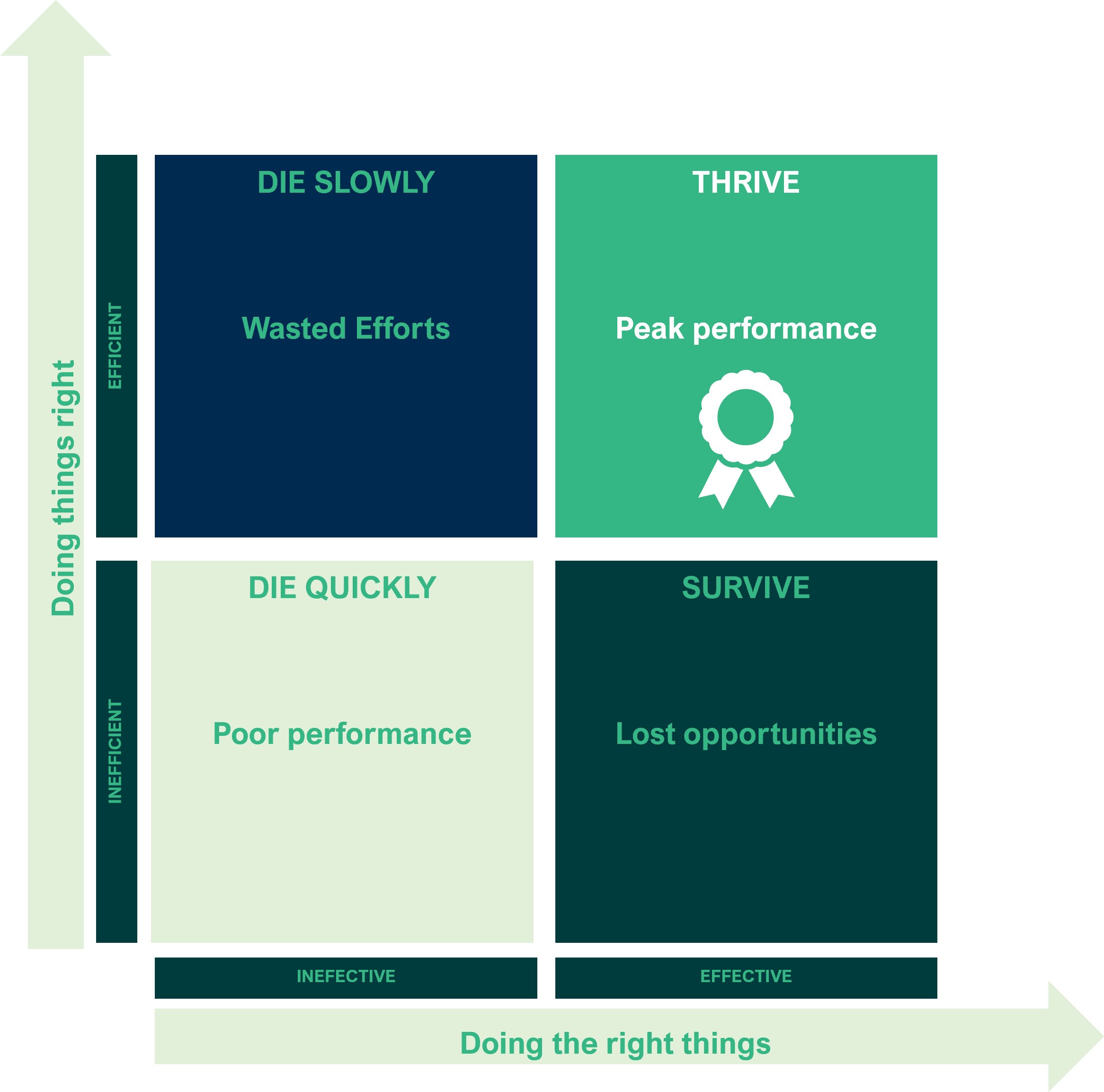
Business efficiency can be described as the proficiency with which a corporation produces and provides its goods and services, while mitigating costs and elevating the standard of quality. It can be gauged by examining the utilization of its assets to yield the desired outcome. The hallmark of an efficient enterprise is its ability to produce at a cost lower than its competitors, all the while preserving or enhancing the level of quality. To attain this level of efficiency, a business must strive to optimize its processes, automate redundant tasks, eliminate waste and inefficiencies, and implement industry best practices. Furthermore, an efficient company must exhibit optimal use of its resources including time, money, and assets, thereby yielding maximum returns on investment.
The companies listed below successfully implemented efficient processes in their value chain, Walmart, has established a reputation for its proficiency in managing and distributing goods and services, with their supply chain management and data analytics leading the way in innovation.
Toyota, is highly regarded for its proficiency in manufacturing processes and quality control, utilizing the Toyota Production System to streamline production and optimize quality.
UPS, is highly esteemed for its proficiency in logistics and delivery services, utilizing real-time package tracking and route optimization to provide prompt and efficient service.
GE is celebrated for its proficiency in energy production and management, with advanced gas turbine technology and energy storage systems showcasing their efficiency.
McDonald’s is recognized for its efficiency in fast food operations, employing assembly line production and standardization of menu items to provide speedy and consistent service.
In essence, business efficiency is the aptitude of a company to produce and supply goods and services at the lowest possible cost while preserving or elevating the level of quality, through effective and efficient utilization of its resources.
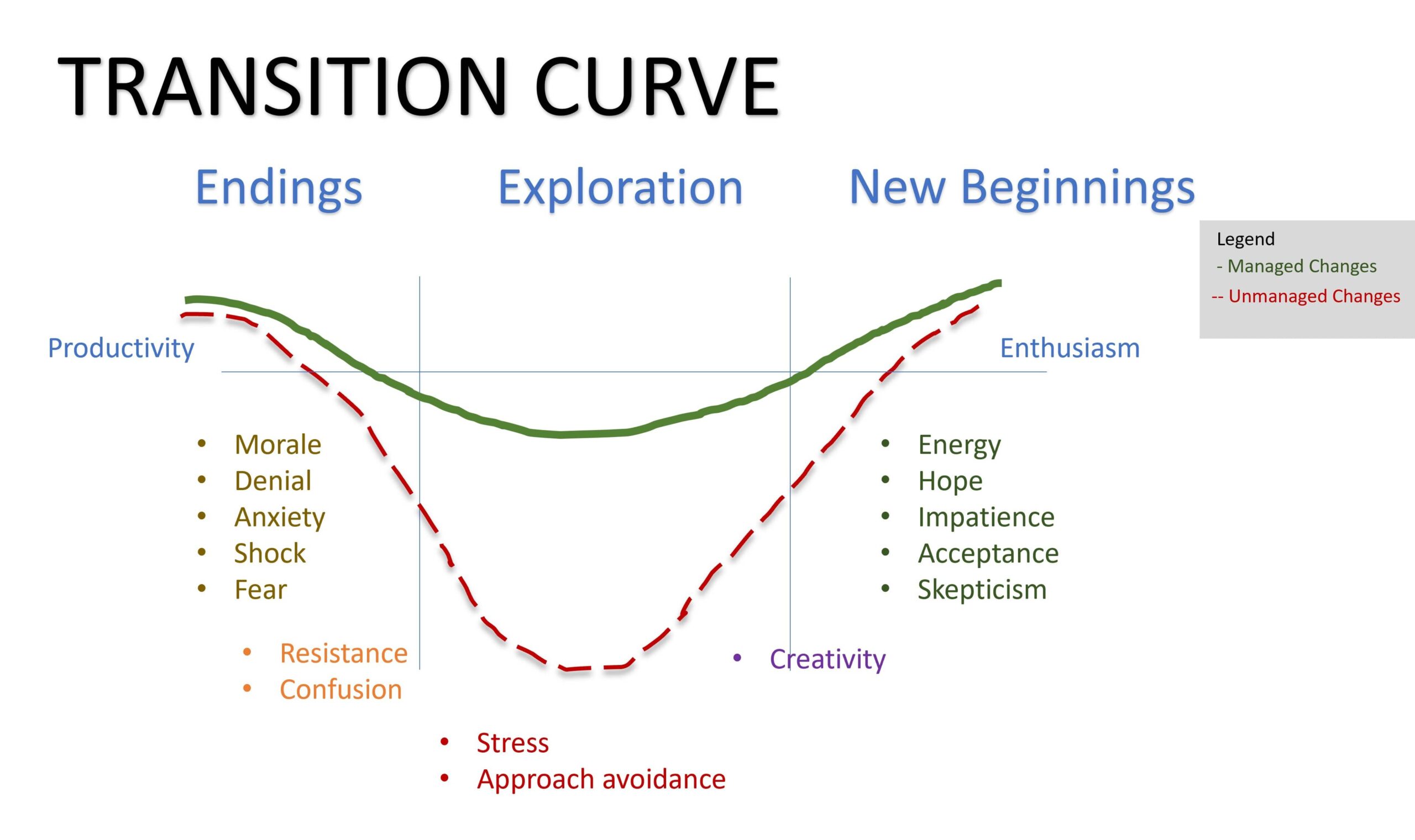
Part 01 Month 03: Change Management
Change management is the process of planning, executing and monitoring changes within an organization. It involves identifying the need for change, assessing the impact of the change, developing a plan to implement the change, and then overseeing the execution of the plan. It is an essential aspect of organizational development as it helps to ensure that changes are made smoothly and effectively. A good change management process includes clear communication, active participation, and effective training of employees. It also includes monitoring progress, assessing the impact of the change, and making adjustments as necessary. Change management is critical for the success of any organizational change, whether it be a small shift in strategy or a large-scale transformation, as it helps to minimize disruption, maintain productivity and ensure that the organization is able to adapt to the new changes.
Part 01 Month 04: Marketing Sales

The utilization of data-driven decision making has been deemed as a crucial component for success in marketing and sales. I have had the opportunity to witness how businesses that embrace this methodology are able to make informed decisions, leading to optimal outcomes and heightened success. The process of incorporating data in decision making starts with identifying your target audience. This requires in-depth understanding of the demographics, behavior, and needs of your ideal customers.
With a clear understanding of your target audience, the creation of a value proposition and subsequent marketing plan becomes a viable course of action. The marketing plan should outline the tactics and strategies that are most effective in reaching and engaging the target audience. This could encompass a wide range of activities, such as email campaigns, content marketing, and social media advertising, among others.
The next step involves using data to inform and refine the marketing and sales decisions. The performance of the marketing campaigns should be monitored, customer feedback collected through surveys and sales data analyzed to identify trends and patterns. This process of data analysis allows businesses to make adjustments to their strategies, ultimately leading to better results.
A vital component of making data-driven decisions in marketing and sales is experimentation. Businesses should test different tactics and strategies to determine what works best. This could involve trying out new ad formats, experimenting with different messaging, and testing different pricing strategies.
In addition to experimentation, building strong relationships with customers is also crucial. This could involve creating customer loyalty programs, offering special promotions and discounts, or simply reaching out to customers on a regular basis to check in and see how they’re doing.
Finally, it’s important to continuously improve your product or service based on feedback and insights received from customers. This could involve incorporating updates to your offerings, adding new features, or simply improving the overall customer experience.
In conclusion, businesses that adopt a data-driven approach to decision making in marketing and sales have the potential to achieve optimal outcomes and drive success. Whether you are a start-up or an established business, utilizing data-driven decision making is a powerful tool that can help you attain your objectives and stay ahead of the curve.
Part 01 Month 05: Production Operations

There is a significant impact of data-driven decision making in the realm of product operations. By incorporating the use of data, businesses can make decisions that are more informed, leading to the creation of superior products, heightened operational efficiency, and amplified customer contentment.
Embarking on the journey of data-driven decision making in product operations requires defining the essential performance indicators (KPIs) of your organization. These KPIs must be aligned with the overarching business objectives and serve as markers of your product’s success over a given period. Such KPIs can encompass product usage statistics, customer satisfaction rankings, and product defect ratios.
The subsequent step involves the persistent accumulation and examination of data to inform your decisions. This can entail the utilization of analytical instruments to monitor product utilization, conducting surveys to accumulate customer opinions, or keeping a close eye on product defect reports to pinpoint areas requiring improvement.
The data collected should be utilized to guide your decision making and trigger changes as deemed necessary. This may entail modifications to your product design, simplifying your production procedures, or tweaking your customer support approach.
Continuous improvement is another crucial aspect of data-driven decision making in product operations. By continually monitoring your KPIs and adapting your strategies in response to the data gathered, organizations can achieve a continuous improvement of their products and eventually drive better outcomes.
Moreover, data-driven decision making can unearth opportunities to escalate operational efficiency and minimize costs. For instance, by scrutinizing production data, businesses may identify prospects to streamline their processes, reduce waste, or eradicate bottlenecks in the production line.
Lastly, building robust relationships with customers and including them in the product development process is imperative. This can encompass collecting consistent feedback, conducting user testing, or integrating customer feedback into your product roadmap.
In conclusion, by leveraging data in decision making, businesses can optimize their product operations, enhance efficiency, and augment customer satisfaction. Be it a start-up striving to bring a new product to market or an established organization striving to refine its offerings, data-driven decision making is a powerful technique that can aid in realizing your business objectives.
Part 01 Month 06: Financial Management

Support functions in a company usually generates a lot of data. Therefore data-driven decision making is key for financial management. By using data to inform their decisions, organizations can improve their financial health, increase revenue, and control expenses.
The first step in making data-driven decisions in financial management is to create a budget and financial plan. This plan should include projected income, expenses, and cash flow, and should be updated regularly to reflect any changes in the business. By tracking your budget and financial plan, you can monitor your actual results against your projections and make adjustments as needed.
Next, it’s important to monitor and control expenses. This might involve tracking spending, identifying areas where costs can be reduced, and negotiating better deals with suppliers. By controlling expenses, organizations can free up more resources for investment and growth.
In addition to controlling expenses, it’s also important to focus on increasing revenue. This might involve expanding into new markets, launching new products or services, or improving your marketing and sales strategies. By increasing revenue, organizations can improve their financial health and achieve long-term sustainability.
Another key aspect of data-driven financial management is monitoring cash flow. This involves tracking the inflow and outflow of cash and ensuring that you have enough cash on hand to meet your obligations. By monitoring cash flow, organizations can identify potential cash flow problems early and take action to address them before they become major issues.
To support your data-driven financial management efforts, it’s also important to use financial software. This software can help you automate many financial tasks, including invoicing, bookkeeping, and budget tracking. It can also provide you with valuable insights into your financial performance, helping you make informed decisions.
Another important component of data-driven financial management is the implementation of financial controls. This might involve implementing policies and procedures to ensure that your finances are properly managed, creating systems for tracking and reporting financial information, and conducting regular audits to identify areas for improvement.
In addition to these steps, it’s also important to regularly review your pricing strategies to ensure that you’re charging enough to cover your costs and generate a profit. If you’re unsure about your pricing strategies, seeking financial advice can help you make informed decisions.
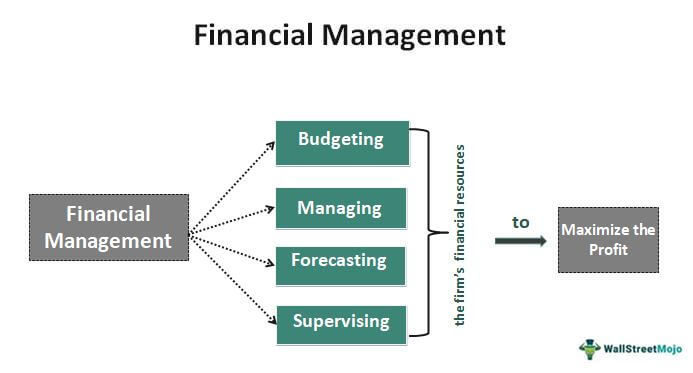
In conclusion, by using data to inform your financial management decisions, organizations can improve their financial health, increase revenue, and control expenses. Whether you’re a small business just starting out or a large corporation looking to improve your financial performance, data-driven financial management can help you achieve your goals.
Part 01 Month 07: Human Resources

I’ve had the opportunity of witnessing the tremendous impact that data-driven decision-making can have on the management of human resources. Adopting a data-informed approach to HR management can result in an organization that attracts and retains the crème de la crème of talent, cultivates a corporate culture that fosters positivity and productivity, and ensures that its workforce enjoys a harmonious work-life balance.
To initiate a successful data-driven strategy in human resource management, it is imperative to draft a clear HR plan that aligns with the overall goals of the organization and includes specific objectives for attracting and retaining top talent, fostering a positive corporate culture, and promoting a healthy work-life balance.
A key component of a positive corporate culture is fostering a supportive and engaging work environment. This can be achieved by investing in employee development, promoting collaboration and communication, and resolving conflicts in a swift and effective manner. By prioritizing employee well-being, organizations can attract and retain top talent and create a workplace that is conducive to productivity and positivity.
Another critical aspect of data-driven HR management is providing employees with opportunities to grow and develop their skills. This can involve providing training, establishing a mentorship program, or offering flexible work arrangements. Investing in employee development can help employees enhance their skills, increase their value to the organization, and foster a sense of personal fulfillment and satisfaction.
An integral part of data-driven human resource management is the review and optimization of compensation strategies. This can involve conducting regular salary surveys to remain competitive, offering performance-based bonuses and incentives, and reviewing benefits packages. Optimizing compensation strategies can attract and retain top talent and ensure that employees are fairly compensated for their efforts.
To maximize the impact of data-driven HR management, it’s crucial to establish robust performance management processes. This can involve setting performance goals, conducting regular performance evaluations, and providing constructive feedback to employees. By establishing effective performance management processes, organizations can align employees with business goals and help them reach their full potential.
Data-driven human resource management also calls for enhanced communication and collaboration among employees. This can involve promoting open communication, encouraging team-building activities, and creating opportunities for employees to work together. By fostering a collaborative work environment, organizations can enhance employee satisfaction and engagement, and promote a sense of community and support among employees.

Finally, promoting work-life balance is essential in data-driven HR management. This can involve offering flexible work arrangements, providing paid time off, and encouraging a healthy work-life balance. By promoting work-life balance, organizations can support employee well-being, reduce stress, and foster a sense of appreciation and fulfillment among employees.
In conclusion, data-driven decision-making in human resource management has the potential to help organizations attract and retain top talent, foster a positive corporate culture, and promote work-life balance. Regardless of whether you are a fledgling start-up or a well-established corporation looking to improve your HR management practices, adopting a data-driven approach can help you achieve your goals and take your organization to the next level.
Part 01 Month 08: Customer Services

The utilization of data to inform decisions in the field of customer service has the potential to create a paradigm shift in the way organizations approach and prioritize customer satisfaction, loyalty, and experience. As a workshop facilitator, I have had the opportunity to observe the immense impact that data-driven decision making can have on the success of customer service endeavors.
In order to embark on a journey towards data-driven customer service, it is imperative to lay the foundation by establishing a set of clear customer standards. This could include formulating a comprehensive customer service policy that outlines the expectations for response times and quality control, thereby ensuring that the customer service team is in line with the overarching goals of the organization.
The next step is to empower and equip the customer service team with the tools and resources necessary to perform their job effectively. This can be achieved by providing robust customer service training and affording the team the autonomy to make decisions that prioritize the needs of customers. By fostering a supportive and engaged work environment, organizations can boost employee satisfaction and engagement, leading to a more motivated customer service team.
In addition to training and empowerment, utilizing customer feedback to inform improvement is a crucial aspect of data-driven customer service. Gathering customer satisfaction data through surveys, tracking customer complaints, and analyzing customer interactions can provide valuable insights into areas that require improvement. By aligning customer service strategies with the needs and preferences of customers, organizations can optimize the customer experience and foster long-lasting relationships.
The implementation of technology aimed at improving efficiency is another vital component of data-driven customer service. Investment in customer service software, setting up an online support center, or integrating a chatbot to handle customer inquiries can streamline processes and reduce response times, leading to improved accuracy and a more positive customer experience.
Encouraging customer loyalty programs can play a significant role in strengthening the bond between the organization and its customers. Offering incentives and rewards for repeat customers, creating a loyalty program, or providing exclusive promotions and discounts can help establish a positive, long-term relationship with customers.
Finally, fostering a customer-centric culture that prioritizes customer experience and satisfaction is essential for the success of data-driven customer service. Encouraging employee engagement, promoting customer-focused values, and regularly communicating with customers can help create a supportive work environment that promotes customer loyalty and satisfaction.
In conclusion, data-driven customer service can have a profound impact on organizations of all sizes, helping to improve customer satisfaction, increase customer loyalty, and promote a customer-centric culture. By following these key principles, organizations can achieve their goals and create a competitive edge in the world of customer service.
Part 01 Month 09: Supply Chain

The application of data-based methods for decision-making in the domain of supplier consolidation holds tremendous potential for organizations looking to optimize operations, boost transparency, and establish sustainable practices.
The initial step towards harnessing the power of data in supplier consolidation involves enhancing visibility and communication with suppliers. This could be achieved through the creation of a unified database for supplier information, fostering consistent communication channels, and using data to evaluate supplier performance and pinpoint areas for improvement. With improved visibility and communication, organizations can assure that their supplier partnerships align with their business objectives and that they possess the crucial information needed to make informed decisions.
Optimizing supplier processes is the next essential step, entailing streamlining the procurement procedure, automating supplier induction, and standardizing supplier contracts. Through process optimization, organizations can minimize costs, boost operational efficiency, and ensure that their supplier relationships are in line with their business objectives.
The assessment and improvement of transportation and logistics systems also play a crucial role. This could entail analyzing shipping costs, optimizing delivery pathways, and reducing waste. By reviewing transportation and logistics, organizations can reduce costs, enhance sustainability, and guarantee that their supply chains align with their business objectives.
To further bolster the efforts towards data-driven supplier consolidation, organizations must focus on sustainability initiatives. This may include monitoring supplier sustainability metrics, fostering eco-friendly practices, and collaborating with suppliers to reduce waste and emissions. By focusing on sustainability initiatives, organizations can promote environmental sustainability, reduce costs, and ensure that their supply chains align with their business objectives.
In conclusion, the utilization of data in supplier consolidation decisions has the power to transform the operations of organizations, big or small, and help them achieve their objectives by improving visibility, optimizing processes, and driving sustainability initiatives.
Part 01 Month 10: Information technology

The utilization of data in the decision-making process within the Information Technology sector holds immense potential. Organizations can leverage this data-driven approach to formulate a comprehensive IT strategy, optimize their technological infrastructure, and ensure the security of their systems and the preservation of their data.
The initial phase of incorporating data into IT decision making involves the development of a thorough IT strategy. This could entail a comprehensive evaluation of the present IT requirements and resources of the organization, defining clear goals and objectives, and pinpointing areas that require improvement. With a well-defined IT strategy, organizations can ensure that their technology investments align with their business objectives, and they have the information necessary to make informed decisions.
Optimizing the IT infrastructure follows as the next crucial step. This could encompass upgrading hardware and software, streamlining processes, and identifying areas where automation can enhance efficiency. By enhancing their IT infrastructure, organizations can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and align their systems and data with their business objectives.
Cybersecurity measures are equally important and should be implemented with due diligence. This could entail conducting regular security assessments, implementing multi-factor authentication, and investing in cutting-edge security technologies. With robust cybersecurity measures in place, organizations can reduce the possibility of data breaches and secure their systems and data.
Automation of processes and training and support for IT staff are equally vital in supporting data-driven IT initiatives. This could include implementing automated tools for monitoring and reporting, providing ongoing training and support for the IT team, and fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing. By automating processes and investing in training and support, organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and align their systems and data with their business objectives.
Finally, it is imperative to review the IT budget and allocate resources effectively. This could encompass analyzing IT expenditures, identifying areas for cost reduction, and investing in technologies and resources that will drive long-term value. By reviewing and optimizing the IT budget, organizations can ensure that they make the most of their technology investments and align them with their business objectives.
In conclusion, organizations can benefit from incorporating data into their IT decision-making process to develop an effective IT strategy, optimize their technological infrastructure, and ensure the security of their systems and data. Regardless of the size of the organization, be it a small business just starting out or a large corporation seeking to enhance their IT practices, data-driven IT can aid in achieving their objectives.
Part 01 Month 11: Research development

The sector of Research and Development (R&D) is a paramount factor in the expansion and accomplishment of any business entity. The R&D departments are responsible for fabricating and enhancing novel products, technologies, and services that enable companies to maintain a competitive advantage. However, with a plethora of variables to contemplate, it can be challenging to determine which R&D endeavors will produce the most favorable outcomes. This is where the application of data-driven decision making proves to be advantageous. By incorporating data into R&D decision-making processes, corporations can ensure that their investments are directed, efficacious, and generate optimal outcomes.
Establishing Definitive R&D Goals and Objectives The initial stage in incorporating data-driven decision making into R&D is to set specific goals and objectives. This will guarantee that R&D endeavors align with the overarching strategy and priorities of the company. Additionally, it will secure that the necessary resources are allocated to the appropriate initiatives, allowing for result measurement and evaluation.
Investment in R&D is Imperative Investment in R&D is pivotal for any enterprise seeking to stay ahead of the curve. Nevertheless, it is crucial to make informed investments that yield the most favorable results. By utilizing data in R&D decision-making, companies can ensure that they are investing in initiatives that will deliver the most substantial impact.
Nurturing a Culture of Innovation is the life source of R&D, and companies must cultivate an environment that fosters and supports it. By employing data in R&D decision-making, companies can guarantee that they are supporting the most promising and innovative endeavors and encouraging a culture of experimentation and calculated risk-taking.
Collaboration with External Allies Collaboration is pivotal to success in R&D, and corporations must collaborate with other organizations, academic institutions, and research establishments to accomplish their goals. By incorporating data into R&D decision-making, companies can ensure that they are partnering with the right entities and maximizing the expertise and resources of their allies to achieve their objectives.
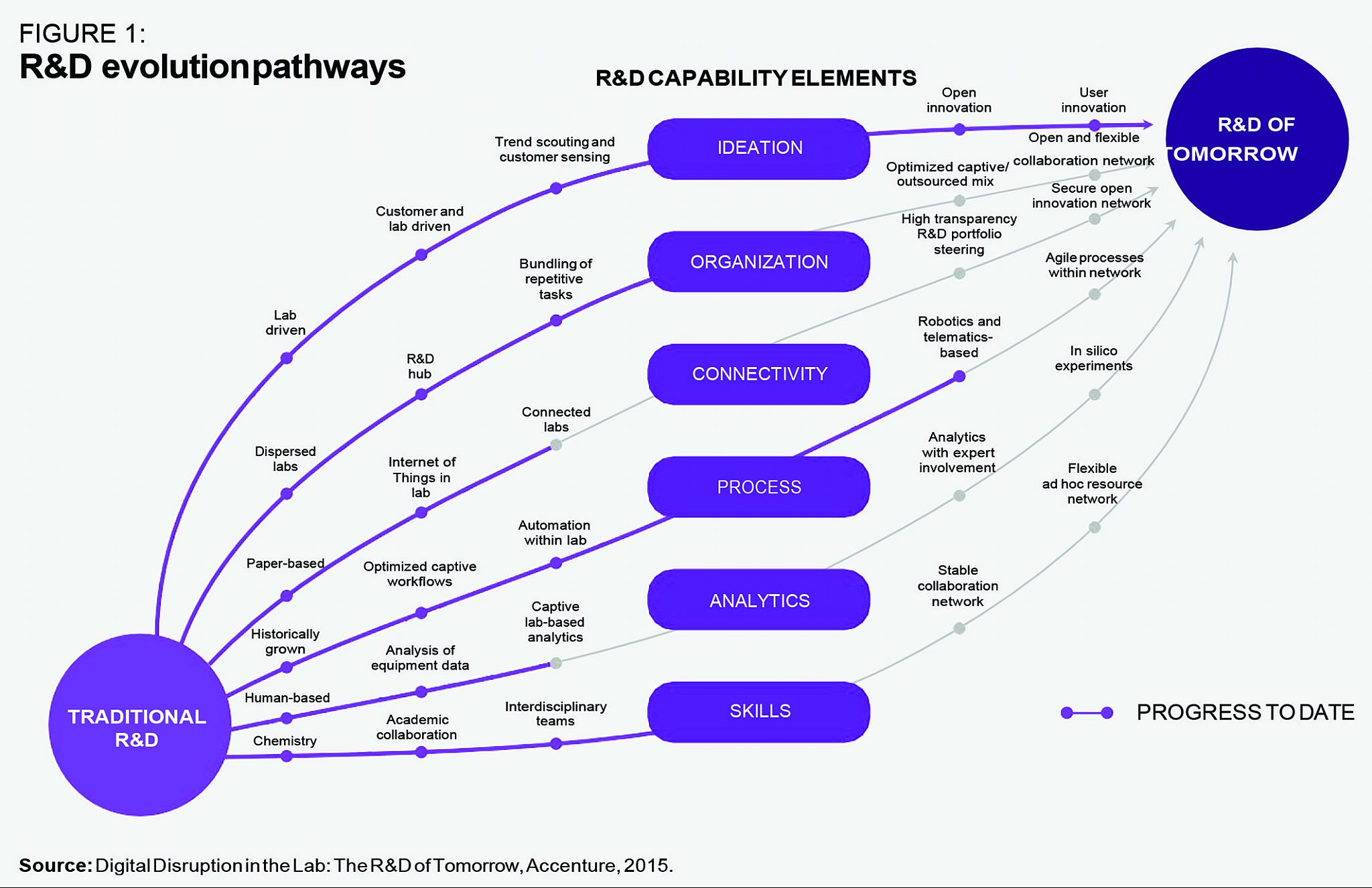
Assessment of the R&D Budget Ultimately, it is crucial to periodically review the R&D budget to guarantee that resources are being utilized effectively. By incorporating data into budget decision-making, companies can ensure that they are utilizing their resources optimally and investing in initiatives that will produce the most favorable outcomes.
In conclusion, the utilization of data-driven decision making is a crucial aspect for enterprises seeking to make informed R&D investments. By incorporating data into decision-making processes, companies can ensure that their investments are directed, efficient, and yield the optimal outcomes. The key to success lies in establishing clear goals and objectives, investing in R&D, nurturing a culture of innovation, collaborating with external partners, and periodically reviewing the R&D budget.
Part 01 Month 12: Legal Compliance

The intricacies of data-driven decision making within the field of legal and regulatory compliance are acutely understood. In an era where legal and regulatory compliance is becoming increasingly labyrinthine, it is imperative for companies to possess a robust comprehension of the relevant laws and regulations to avoid substantial legal penalties and ensure compliance. To aid companies in their journey, a workshop has been devised to tackle the crucial aspects of data-driven decision making in legal and regulatory compliance.
The workshop will delve into the following topics, each an essential component in the compliance puzzle:
Legal and Regulatory Awareness: Companies must continually educate themselves and research the laws and regulations that are applicable to their business, keeping pace with the ever-changing regulatory landscape.
Policies and Procedures: Establishing clear policies and procedures not only guarantees compliance, but it also provides a roadmap for employees to abide by.
Team Training: A trained team is pivotal in compliance management, it is crucial for employees to be well-versed in the relevant laws, regulations, and company policies.
Compliance Management System: An efficient compliance management system is vital in ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Audit Reviews: Regular audits are instrumental in identifying areas for improvement and maintaining compliance with the relevant laws and regulations.
Legal and Compliance Expertise: Legal and compliance professionals are indispensable in navigating the complex regulatory terrain, providing guidance and support to companies.
Stakeholder Communication: Communication with stakeholders is crucial in building trust and ensuring everyone is in agreement regarding compliance.
By participating in the workshop, companies will learn how data can inform legal and regulatory compliance decisions and gain the skills and knowledge needed to launch a successful compliance management system. This will not only guarantee compliance but also bring peace of mind knowing that all necessary steps have been taken to protect the business and avoid legal penalties.
Data Driven Decision Making – Part 2 – Year 2: Process Implementation
Part 02 Month 01: Data-Driven Mindset
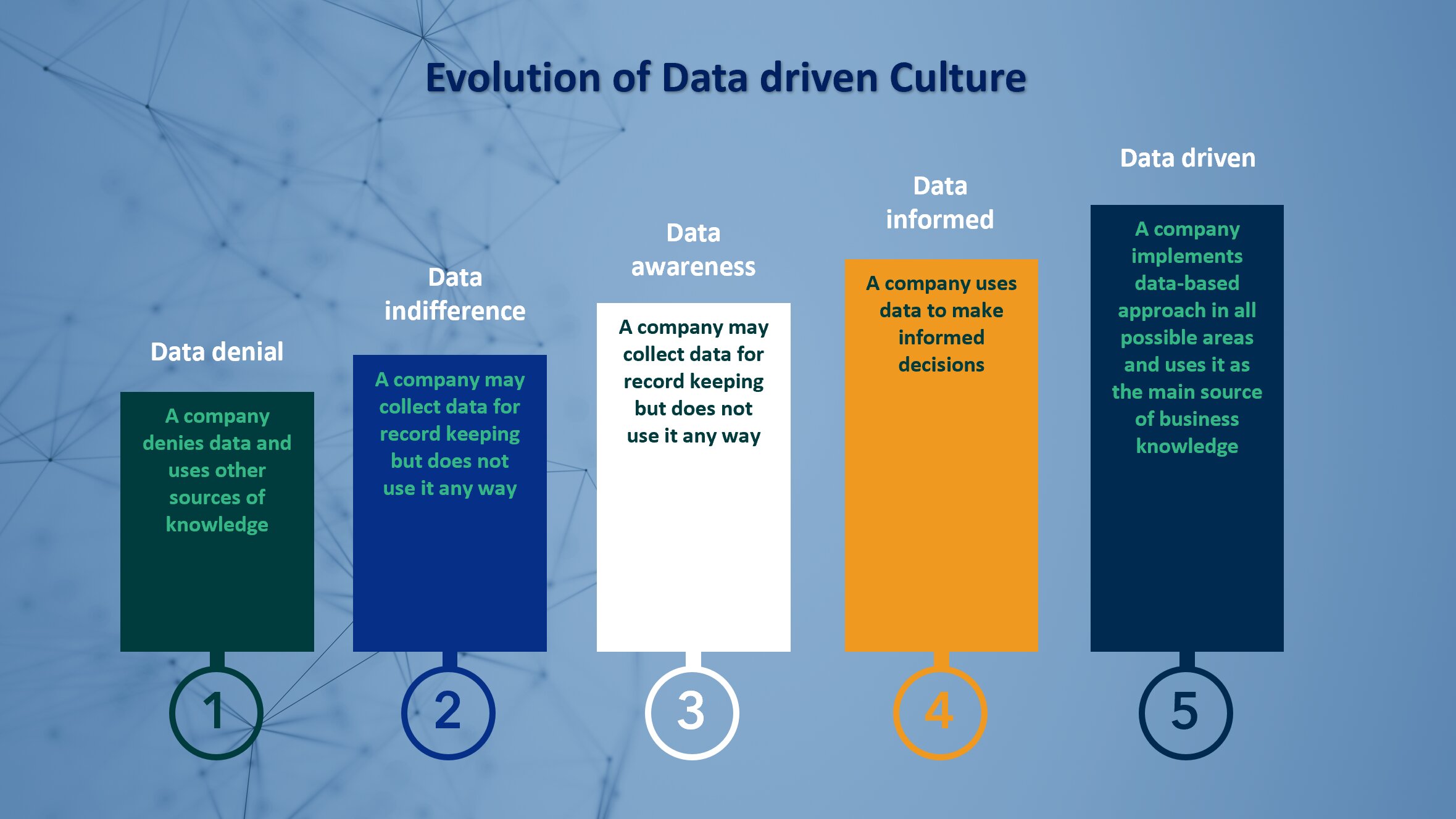
Developing a data-driven culture is vital for organizations to stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving business environment. Here are five essential elements for fostering a data-driven culture:
Communicate the importance of data-driven decision making: To cultivate a data-driven mindset, it’s crucial to communicate the significance of making decisions based on data rather than relying solely on intuition or experience. Leaders must emphasize how data-driven decision making can drive success in the organization.
Provide comprehensive training: To encourage a data-driven mindset, employees must be trained to work with data. This includes teaching data analysis tools and techniques, as well as how to interpret and use data to inform decision making. Robust training programs can help employees feel more confident in working with data and can help them understand the importance of using data in decision making.
Encourage data utilization: To foster a data-driven culture, employees must be encouraged to use data in their daily work. This means setting measurable goals and KPIs and encouraging employees to track progress and use data to make decisions. Recognizing and rewarding employees who use data in their work can also help create a culture where data-driven decision making is highly valued.
Make data easily accessible: To promote a data-driven culture, it’s vital to make data accessible to employees. This means ensuring that data is up to date, easy to access, and in a format that is easy to analyze. Providing access to dashboards and data visualization tools can also help employees understand data better and make it easier to use in decision making.
Establish clear processes and guidelines: To develop a data-driven mindset, it’s crucial to establish clear processes and guidelines for data use. This includes outlining how data should be collected, stored, and analyzed, as well as how decisions should be made based on data. It’s also vital to establish clear roles and responsibilities for working with data and ensure that everyone understands the processes and guidelines for using data in decision making.
In conclusion, building a data-driven culture requires effective communication, robust training, encouraging data utilization, easy accessibility to data, and clear processes and guidelines. By fostering a culture of data-driven decision making, organizations can make informed decisions, drive success, and stay competitive in today’s data-driven world.
Part 02 Month 02: Governance policies
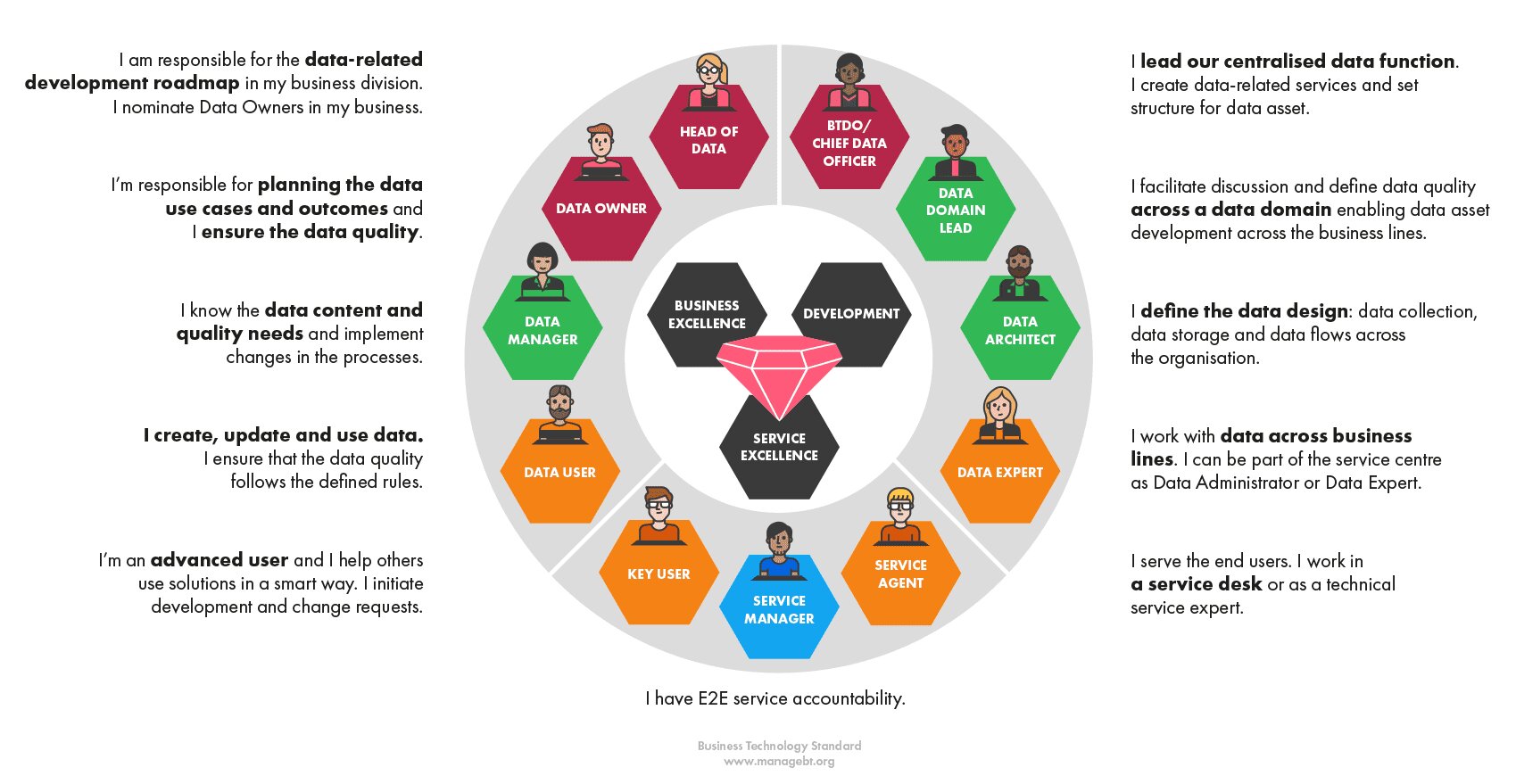
Data governance policies are the cornerstone of effective data management and control within any organization. These policies can lead to better decision-making, higher data quality, and regulatory compliance. To develop robust governance policies, there are several critical elements that must be considered.
Firstly, governance policies need to provide a clear framework for decision-making. They must establish processes for data collection, storage, and use, and define roles and responsibilities. It’s essential to ensure these policies align with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
Secondly, the scope of governance policies must be well-defined. They should specify the types of data covered, the departments responsible for managing the data, and the different data types collected by the organization. Personal information, financial data, and intellectual property should be carefully considered, and policies tailored accordingly.
Thirdly, governance policies must define roles and responsibilities. This includes identifying the data owner, data steward, and data user. The data owner has overall responsibility for data management, while the data steward ensures data accuracy and consistency. The data user must use the data in accordance with the policies and procedures established by the organization.
Fourthly, data collection procedures must be outlined within governance policies. This includes specifying how data is collected, who is responsible for collecting it, and what types of data can be collected. Policies must address data quality issues, such as ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
Fifthly, data legal access is a critical component of governance policies. They should specify who has access to the data, how access is granted, and under what circumstances access can be revoked. Access must be granted only to those with legitimate needs, and it must be revoked when no longer required.
Consistency and conventions are also essential governance policy elements. This includes establishing standards for data naming, formatting, and coding. Policies must also specify how data should be stored and organized for easy access and retrieval.
Sixthly, data storage policies must specify how data is stored, the types of storage devices used, and how data is backed up. These policies must also address data retention, specifying how long data should be stored and when it can be deleted.
Seventhly, data use policies must outline how data can be used, who can use it, for what purposes, and under what conditions. Policies must specify procedures for reporting data breaches or incidents that may impact data security or integrity.
Finally, governance policies must address data quality issues. This includes specifying how data quality is measured and monitored, as well as outlining procedures for resolving data quality issues. Policies must also specify how data quality is reported to stakeholders.
In conclusion, developing effective governance policies is essential for proper data management and control within organizations. These policies must establish clear guidelines and procedures for data management, identify roles and responsibilities, and outline procedures for data collection, storage, and use. By developing and implementing effective governance policies, organizations can improve data quality, make better decisions, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Part 02 Month 03: Storage Systems
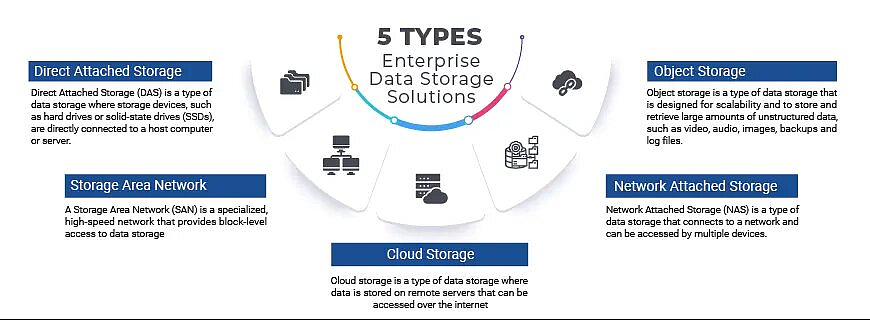
Developing a data storage system that is both effective and efficient is a critical task for any organization. To accomplish this task, it is essential to first identify the various types of data that the organization handles and determine the storage requirements for each type. The storage requirements may vary depending on the type of data and can include security, accessibility, and frequency of access.
In addition to identifying storage requirements, selecting the appropriate storage medium is equally important. The storage medium can range from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to cloud storage and solid-state drives (SSDs). The right storage medium depends on various factors, such as performance requirements, storage capacity needs, and budget constraints. For instance, an SSD storage system may be more appropriate if high-speed access to data is required.
Another critical consideration when developing a data storage system is redundancy and backup requirements. Redundancy involves the ability to store multiple copies of data in different locations to prevent data loss due to a failure. Backup, on the other hand, involves creating copies of data and storing them in different locations to safeguard against disasters or other unforeseen events. Regular monitoring and maintenance of backups are necessary to restore the system to its previous state quickly.
Data security is also of utmost importance in a data storage system. Measures such as encryption, access controls, and firewalls should be implemented to protect data against unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. Properly implemented security measures ensure data is protected at all times.
Finally, a data management plan is critical in ensuring that the data storage system is organized, easily accessible, and maintained properly. The data management plan should outline policies and procedures for data storage, retrieval, archiving, and deletion. Regular monitoring and maintenance will ensure that the system is functioning correctly and that data is stored and managed efficiently.
In conclusion, developing an effective and efficient data storage system requires identifying storage requirements, selecting the appropriate storage medium, implementing redundancy and backup strategies, ensuring data security, and implementing a data management plan. By considering these factors, organizations can ensure that their data is stored, managed, and protected effectively and efficiently.
Part 02 Month 04: Data collection

To develop an effective data collection process, organizations must consider various factors that impact the reliability and relevance of the data collected. A perplexing but crucial step is identifying the necessary data to inform decisions. This involves considering the purpose, scope, and questions to be answered.
The next step is to determine the most appropriate methods for collecting the data. This process may involve conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, or using existing data sources. Depending on the methods chosen, specific tools may need to be developed, such as survey questionnaires or interview scripts. Staff or contractors involved in data collection should receive adequate training on the purpose, methods, and tools being used.
Once the data collection process is implemented, it is critical to monitor the data being collected to ensure its accuracy and consistency. Checking data entry forms for errors, reviewing survey responses for completeness, or monitoring data collection progress can help in this regard. Analyzing the collected data is the next step and may involve using statistical analysis tools or other data analysis methods.
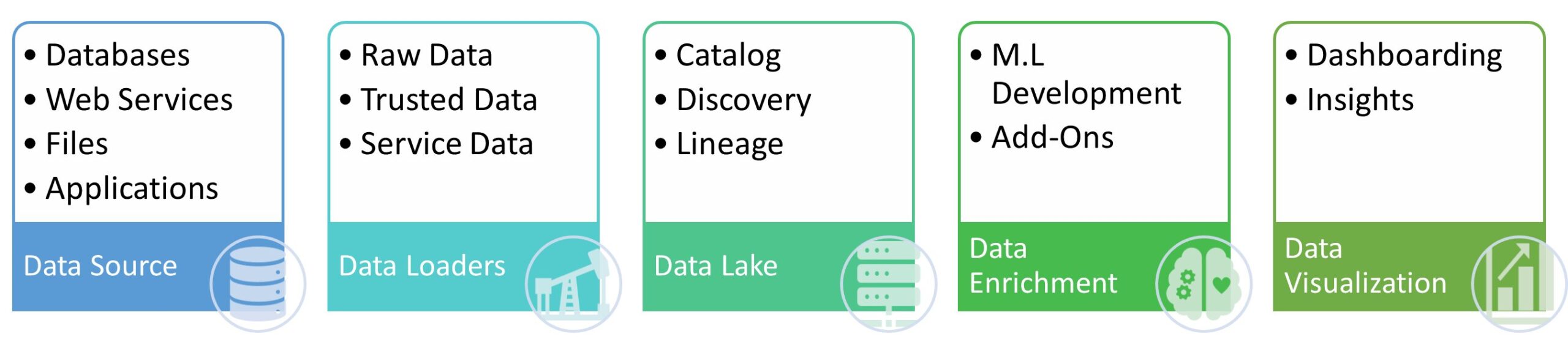
Finally, the findings must be communicated to stakeholders. This may involve creating reports, presentations, or other materials that summarize the data collected and the insights gained from analysis. Developing an effective data collection process takes time and effort but is essential for making data-driven decisions.
Part 02 Month 05: Data quality
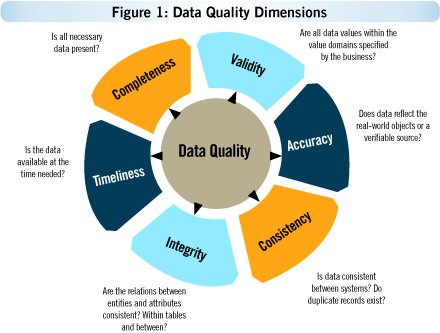
Data quality refers to the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data being collected. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect or unreliable insights, which can have serious consequences for an organization’s decision-making.
To ensure data quality, there are several key considerations to keep in mind during the data collection process: Data Collection Tool Design: The design of the data collection tools, such as surveys or interview scripts, can impact the quality of the data collected. Poorly designed tools can lead to ambiguous or misleading responses. To improve data quality, it is important to ensure that the questions being asked are clear and unambiguous. Data Collection Methodology: The methodology used to collect data can also impact data quality. For example, if a survey is administered using a biased sample, the results may not be representative of the population being studied. It is important to use appropriate sampling methods and to take steps to minimize nonresponse bias. Data Entry and Processing: Once data is collected, it must be entered into a database or spreadsheet for analysis. Errors can occur during this process, leading to inaccurate data. To ensure data quality, it is important to have procedures in place to check for errors during data entry and to ensure that the data is entered correctly. Data Cleaning: Before data can be analyzed, it is important to clean it by removing any duplicate or irrelevant data, correcting errors, and ensuring that the data is consistent. This can be a time-consuming process, but it is critical for ensuring the accuracy of the analysis. Data Analysis: During the analysis phase, it is important to use appropriate statistical techniques and to ensure that the results are reported accurately. This can involve checking for outliers, testing for statistical significance, and ensuring that the results are presented in a clear and understandable way. By following these considerations, organizations can improve the quality of the data they collect and ensure that it is accurate and reliable. This can lead to better decision-making, improved program outcomes, and a better understanding of the populations being served. In conclusion, developing an effective data collection process is critical for making data-driven decisions. However, it is equally important to ensure that the data being collected is of high quality. By following best practices for data collection and analysis, organizations can improve the quality of the data they collect and the insights they gain from it.
Part 02 Month 06: Data modelling
Developing a data modelling framework is a complex and multifaceted process that involves creating a mathematical representation of a real-world system or process. This model helps organizations identify patterns, relationships, and trends in the data that can inform decision-making.
The initial step in developing a data model is to define the problem or question that needs to be answered. This process requires a deep understanding of the business problem or opportunity and identifying the relevant data sources. The extracted data must then be cleaned, transformed and prepared for analysis.
Choosing the appropriate data modelling technique is the next step. There are several types of data modelling techniques such as statistical modelling, machine learning, and predictive modelling. The choice of technique will depend on the type and complexity of the data, the size of the dataset, and the specific problem or question being addressed.
The data modelling process is an iterative process, requiring constant refinement and updates as new data becomes available, and business needs change. The model must be trained and validated using historical data to assess its accuracy and effectiveness. Once the model has been tested, it can be used to make predictions or to identify patterns and relationships in the data.
It is crucial to establish a framework for implementing the model within the organization. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders involved in the data modelling process, creating procedures for data collection and storage, and integrating the model into the organization’s decision-making processes.
Regular monitoring and evaluation of the model’s effectiveness is also necessary to ensure that it continues to provide accurate and valuable insights. Organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive business success by following a structured approach to data modelling and implementing best practices for data management and governance.
In conclusion, developing a data modelling framework is an essential step in the data-driven decision-making process. Organizations can gain valuable insights from their data, make informed decisions, and improve their business operations by following best practices for data modelling and management. A well-designed data model can provide valuable insights that can help organizations make more informed and accurate decisions.
Part 02 Month 07: Data analysis
Data analysis and insights strategy is the key to unlocking valuable insights from data, and it is a critical component of the data-driven decision-making process. The process involves several steps, including defining the problem or question to be answered, collecting relevant data from various sources, cleaning and preparing the data for analysis, and conducting the analysis using appropriate tools and software.
The analysis may involve using statistical methods or data mining techniques to identify patterns and trends in the data. It is crucial to ensure that the analysis is transparent and reproducible, and the results are communicated effectively to stakeholders. This may involve developing visualizations or dashboards that are relevant and actionable.
Furthermore, it is important to continually monitor and update the data analysis and insights strategy to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This may involve updating the data collection process, refining the analysis methods, or incorporating new data sources.
Developing a data analysis and insights strategy is a challenging and iterative process that requires a high level of expertise and technical know-how. It is essential to follow best practices for data management and governance to ensure that the data is accurate, relevant, and secure.
Overall, a well-designed data analysis and insights strategy is essential for organizations that want to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. By following a structured approach to data analysis and insights, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive business success.
Part 02 Month 08: Data visualization
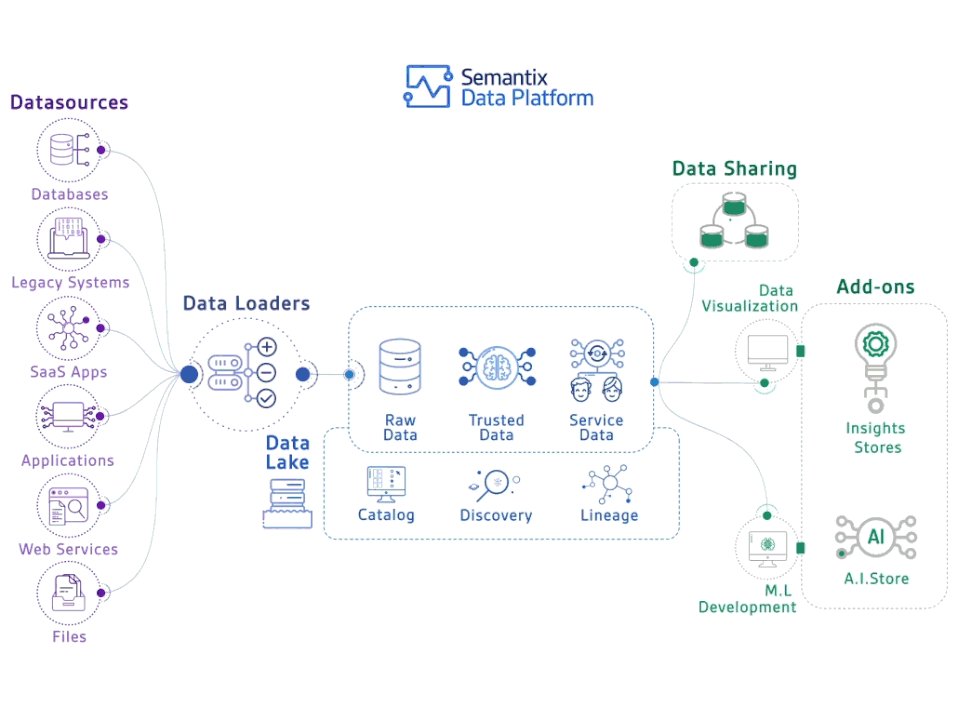
In the current era of data-driven decision making, it is increasingly important to not only gather and scrutinize data but also to represent it in a manner that is comprehensible and yields practical insights. This is where data visualization, an intricate process of presenting multifarious data in a visual and graphical form, proves to be essential. By doing so, data visualization enables organizations to identify correlations, trends, and patterns within voluminous datasets that might not be immediately apparent when presented in a tabular or text-based format, thereby facilitating more informed decision-making.
Developing an effective data visualization strategy necessitates adherence to several pivotal steps. Firstly, it is imperative to identify the intended audience for the visualization. This not only helps in determining the level of detail, the type of visualization, and the format to be employed but also enables customization to cater to specific requirements. For instance, executives may prefer high-level dashboards that offer a swift overview of the most important metrics, while analysts may require access to more comprehensive datasets and drill-down capabilities.
Next, careful consideration must be given to the data to be presented in the visualization. This includes comprehending the data sources, pinpointing any data quality issues, and ensuring that the data is accurate and up-to-date. The data must also be structured in a manner that is conducive to visualization, such as using numerical values, percentages, or time series data.
After identifying the data, it is then time to determine the most suitable type of visualization. There are myriad types of data visualizations, ranging from bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and heat maps, among others. The choice of visualization hinges on the data being presented and the message that the visualization seeks to convey.
It is also necessary to consider the colors, fonts, and other design elements that will be incorporated into the visualization. These elements have a substantial impact on the effectiveness of the visualization as they serve to emphasize important information and make the visualization more captivating and easy to comprehend.
Finally, it is essential to review and refine the visualization to ensure that it effectively communicates the insights gleaned from the data. This may involve testing the visualization with diverse audiences, refining design elements, and incorporating feedback from stakeholders.
In conclusion, data visualization is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to make data-driven decisions. By following a structured approach to data visualization development, businesses can ensure that their data is presented in a clear, concise, and actionable manner, enabling them to make more informed decisions that drive business growth and prosperity.
Part 02 Month 09: Data automation
Data automation is a complex and intricate process that is integral to the success of any data-driven decision-making strategy. The term data automation refers to the process of automating the collection, processing, and analysis of data to support business decisions. The goal of data automation is to enhance data quality, minimize data errors, and accelerate data analysis.
Developing a data automation strategy necessitates a thorough understanding of the data requirements of an organization. This involves identifying the primary data sources, determining the frequency of data collection, and establishing data quality criteria. A successful data automation strategy should also address the integration of data from multiple sources and the management of data security and privacy.
One of the most significant benefits of data automation is that it enables organizations to quickly and accurately collect and process vast amounts of data. In industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail, where data accuracy and speed are critical for success, data automation can help eliminate manual data entry, minimize data errors, and increase the speed of data analysis.
Data automation also enables organizations to generate real-time insights from their data, which is particularly useful for making timely and informed business decisions. For instance, in the healthcare sector, real-time data analysis can be employed to monitor patient health and identify potential health risks. In the finance industry, real-time data analysis can be used to monitor market trends and identify potential investment opportunities.
To develop a successful data automation strategy, organizations must concentrate on three critical areas: data integration, data quality, and data security. Data integration entails the capacity to collect and combine data from multiple sources, including internal and external data sources. Data quality refers to ensuring that the data is accurate, complete, and consistent. Data security entails safeguarding data from unauthorized access and ensuring that data privacy regulations are being followed.
The use of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence can also aid in improving data automation. Machine learning algorithms can automate data processing tasks and improve data accuracy. Artificial intelligence can be utilized to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns and insights that may not be visible to human analysts.
Data automation can also help organizations reduce costs and boost productivity. By automating data collection and processing tasks, organizations can free up employees to concentrate on more strategic activities, which can lead to improved employee morale and higher job satisfaction.
In conclusion, data automation is a complex and multifaceted process that is fundamental to the success of any data-driven decision-making strategy. Organizations must concentrate on developing a data automation strategy that addresses the key areas of data integration, data quality, and data security. By leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence, organizations can enhance data accuracy, generate real-time insights, and boost productivity. Ultimately, data automation can aid organizations in making faster and more informed business decisions, leading to increased business success.
Part 02 Month 10: Publish Inside & Outside
In this era of data-driven decision-making, organizations need to be able to easily access, analyze, and interpret their data. Enter the perplexing concept of “publishing data inside”, which involves making data accessible to those within an organization who need it, enabling them to use it to make informed decisions.
Making data available in a user-friendly format is a key aspect of publishing data inside. This often involves using data visualization tools to help users quickly identify patterns and insights in the data. For instance, a dashboard might display key performance indicators for a specific department, allowing employees to rapidly gauge their performance against established goals.
Ensuring that data is secure and protected is also crucial in the publishing data inside approach. This means implementing appropriate access controls and authentication mechanisms to guarantee that only authorized users can access sensitive data. It also means storing data safely, with suitable backups and disaster recovery processes in place to reduce the risk of data loss.
However, the veracity and currency of data can be challenging to ensure when publishing data inside, especially in organizations with complex data processing workflows or large amounts of data. Automated data quality checks and validation processes can help to address this issue and ensure that the data is accurate and dependable.
Overall, the key advantage of publishing data inside is that it empowers employees to make better, more informed decisions based on data-driven insights. By making data more accessible and easier to use, organizations can enhance their overall performance and competitiveness. To achieve success, organizations need to invest in the right tools and infrastructure to support data publishing and guarantee that the data is accurate, secure, and user-friendly.
In the complex and data-driven world we live in, publishing data outside an organization can be a powerful way to build trust, increase transparency, and demonstrate expertise. However, it is a double-edged sword that requires careful consideration of how the data is shared and the potential risks involved.
To effectively publish data outside an organization for data-driven decision-making, several steps must be taken. First, it is vital to identify the audience and their information needs. This will help determine the type of data to publish and the format in which it should be presented. However, as the audience evolves and their needs change, so must the data and its presentation.
Second, publishing accurate, relevant, and up-to-date data is critical. This can be achieved through implementing proper data governance policies and data quality checks. Data should be anonymized properly to protect individual privacy and must go through a thorough validation process.
Third, the data should be presented in a clear and easily understandable format. Visualization tools, such as charts, graphs, and tables, are commonly used to achieve this. However, the right tools must be selected to ensure that the data is presented in a user-friendly manner. The use of descriptive labels and appropriate units of measurement is also critical in making the data more accessible.
Fourth, providing context is crucial when presenting data outside the organization. This includes explanations of how the data was collected and analyzed, as well as any limitations or biases that may be present. Providing context helps users understand the data more fully and make more informed decisions based on it.
Fifth, having a plan for ongoing data maintenance and updates is critical. This ensures that the published data remains accurate and up-to-date, avoiding any misinterpretation. Additionally, it is important to have a process in place for addressing any issues or questions that may arise from external users.
Finally, the potential risks associated with publishing data outside of an organization should be considered. This includes the possibility of data breaches or misuse of the data. To mitigate these risks, proper security measures should be implemented, and appropriate permissions and access controls should be in place. In case of any data breach, a plan to contain and mitigate the situation should be ready.
In conclusion, publishing data outside of an organization can be a valuable tool for data-driven decision-making. However, it requires careful consideration, planning, and ongoing maintenance to ensure the data is accurate, accessible, and secure. Organizations must be aware of the evolving needs of the audience, the risks involved, and constantly improve the presentation and the maintenance of their data. Only then, can organizations gain the trust of external users, increase transparency and demonstrate expertise.
Program Outline Plan – Year 2: Process Improvements
Part 02 Month 11: Success Factors

The use of data to drive decision-making can be a game-changer for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge in the market. However, the implementation of a successful data-driven decision process requires a holistic and multifaceted approach. Here are some key success factors to consider when implementing a data-driven decision process that can help achieve better outcomes and stay ahead of the curve.
Clear Objective and Goals To make the most of data-driven decision-making, it is critical to have a clear understanding of what the process seeks to achieve. This means setting clear objectives and goals that align with the overall business strategy. By doing so, businesses can ensure that they are focusing on the right metrics and indicators to achieve the desired outcomes.
Quality Data Collection Data is the lifeblood of a data-driven decision process, and it is essential to ensure that the data collected is of high quality, reliable, and relevant. This requires the implementation of appropriate data collection mechanisms, which may involve investing in technology and analytics tools. In addition, it is essential to ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and updated in real-time, as this will help in making informed decisions that are backed by data.
Data Analysis To derive insights from the data collected, it is crucial to have the right expertise in data analysis. There are various data analysis techniques that businesses can use, including descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, among others. By having a robust data analysis process in place, businesses can make accurate and informed decisions that can help them stay ahead of the competition.
Data Visualization To communicate the insights derived from data analysis, data visualization is an essential tool. Effective data visualization techniques such as graphs, charts, and heat maps can help in communicating complex data insights quickly. This means that stakeholders can easily understand the data and make informed decisions based on the insights provided.
Data Automation Automating the data collection and analysis process can help streamline the process and reduce the need for manual intervention. By automating the data-driven decision process, businesses can free up time and resources to focus on other critical business functions.
Stakeholder Involvement Involving all stakeholders in the data-driven decision process can help in getting buy-in from all parties and ensures that decisions are made based on a holistic view of the data. This means involving stakeholders from data collection to decision-making and ensuring that everyone understands the importance of data-driven decision-making in achieving the desired outcomes.
Agility and Flexibility To adapt to changes in the business environment, businesses need to be agile and flexible. This means having a data-driven decision process that can quickly respond to changing trends and insights and adjust the decision-making process accordingly. By being agile and flexible, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and respond to changes in the market effectively.
Continuous Improvement A data-driven decision process should be a continuous cycle of improvement, with regular review and adjustment of the process based on the outcomes. This ensures that the process remains relevant and effective in driving business growth. By continuously improving the data-driven decision process, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and achieve better outcomes.
In conclusion, implementing a successful data-driven decision process requires a holistic and multifaceted approach. By considering key success factors such as clear objectives and goals, quality data collection, data analysis, data visualization, stakeholder involvement, agility and flexibility, and continuous improvement, businesses can leverage data insights to make informed and strategic decisions that drive business growth and success.
Part 02 Month 12: System Tracker
When it comes to making data-driven decisions, it’s crucial to have a mechanism in place to ensure that the process is effective. Enter the system tracker, a tool that monitors and records aspects of the data-driven decision-making process, from data sources used to analysis performed and decisions made. But what makes the system tracker so beneficial?
For starters, a system tracker can help organizations track their progress towards their goals. By monitoring the data-driven decision-making process and its outcomes, organizations can determine whether they are on the right track or need to adjust their approach. This can help them stay focused and ensure that they are making the most effective decisions possible.
Moreover, a system tracker can identify areas where organizations need to improve their data management practices. If the tracker reveals that certain data sources are providing inaccurate or incomplete information, the organization can address the issue by improving data quality or finding alternative sources. This can improve the accuracy and reliability of the decision-making process.
Additionally, a system tracker can help identify patterns and trends in the data that organizations may not have noticed otherwise. By analyzing the data collected by the tracker, organizations can identify correlations between different variables and gain insights into how different factors are impacting their decision-making process. This can help them make more informed decisions and develop more effective strategies.
To ensure that the system tracker is effective, it’s vital to establish clear metrics for success. These could include metrics like the percentage of decisions based on data analysis, the accuracy of decisions made, or the impact of decisions on the organization’s performance. By establishing clear metrics, organizations can track their progress and identify areas where they need to improve.
It’s also important to ensure that the system tracker is user-friendly and easy to use. If the tracker is difficult to use or requires a lot of manual data entry, it may not be used consistently or effectively. By investing in a user-friendly system tracker, organizations can ensure that the tool is used consistently and that data is collected accurately and efficiently.
Lastly, it’s important to integrate the system tracker with other data management tools and processes. If an organization is using a data visualization tool to analyze its data, the system tracker should be integrated with that tool to ensure that the data is accurate and up-to-date. This can help ensure that the organization is using the most current and reliable data in its decision-making process.
In conclusion, the system tracker is an essential tool for any organization that wants to make data-driven decisions. By monitoring and recording various aspects of the data-driven decision-making process, organizations can ensure that they are making informed decisions based on accurate and reliable data. By investing in a user-friendly and integrated system tracker, organizations can improve the effectiveness of their decision-making process and achieve better outcomes.
Methodology
Data Driven Decision Making
Program Planning
The initial phase of this methodology involves establishing a plan that outlines the key steps that must be taken. These steps may include identifying business goals and objectives, defining key performance indicators, collecting relevant data, and analyzing the data for insights.
a. Identifying business goals and objectives: Identifying business goals and objectives is the first and most crucial step towards data-driven decision making. This includes establishing a clear understanding of what the organization hopes to achieve through data-driven decision making.
b. Defining KPIs: Once the business goals and objectives have been identified, the next step is to define the KPIs that will be used to measure progress towards these goals.
c. Data Collection: The process of gathering information that is relevant to the KPIs identified in the previous step is known as data collection. This data may come from various sources, such as internal databases, external sources, and customer feedback.
d. Data Analysis: After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it to identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform decision making.

Program Development
The next step in the data-driven decision-making process is development. This involves creating a structure for the collected data, developing dashboards, and creating data visualizations to help understand the data.
a. Data Modeling: Data modeling involves creating a structure for the data collected. This may include tables, charts, graphs, or other visualizations that make it easier to interpret and analyze the data.
b. Dashboard Development: Dashboards provide real-time, at-a-glance views of key metrics and KPIs. These dashboards can be customized to meet the needs of different stakeholders, including managers, executives, and analysts.
c. Data Visualization: Data visualization is the process of creating visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and interpret. This may include graphs, charts, maps, or other visualizations that highlight trends and patterns in the data.

Program Implementation
The third phase of this methodology is implementation. This involves integrating the data into existing systems and processes, automating processes, and training employees.
a. Integrating Data: Integrating data into existing systems and processes is essential to ensure that it is accessible and usable by decision makers.
b. Automating Processes: Automating processes can help streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting, making it easier for decision makers to access and use the data they need.
c. Training: Training employees is vital to ensure that they are comfortable using the data and tools provided to them. This may include training on data analysis, dashboard development, or other relevant topics.

Program Review
The final step in this methodology is the review phase. This involves monitoring KPIs, reviewing data, adjusting strategies, improving processes, and effectively communicating insights gained from data analysis.
a. Monitoring KPIs: KPIs should be monitored regularly to ensure that progress is being made towards business goals and objectives.
b. Reviewing Data: Data should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date.
c. Adjusting Strategies: Based on the insights gained through data analysis, strategies and tactics should be adjusted as needed to ensure
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Media & Marketing
In the period preceding the Industrial Revolution, merchants and traders employed an assortment of tools and techniques to promote their wares and services.
For instance, in ancient Greece, merchants enlisted the services of town criers to make announcements to the public about their products and services. They also utilized symbols and signs, such as the pole of Asclepius used by medical practitioners, to lure customers to their stores.
During the Middle Ages, merchants relied on visual displays such as banners, flags, and shop signs to advertise their businesses. They also depended on word-of-mouth and personal recommendations to market their goods and services.
As printing technology advanced in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, merchants began to produce catalogs and advertisements to reach a wider audience. Illuminated manuscripts used by book sellers in the 15th century are an example of this, which included images and descriptions of the books they had for sale.
Overall, the marketing tools and techniques used during the period before the Industrial Revolution were mainly focused on local, small-scale marketing endeavors like word-of-mouth, symbols, and personal recommendations. However, the development of printing technology and the augmented use of advertising during the early modern period foretold the emergence of mass marketing techniques that would occur during the Industrial Revolution.
The 20th century was a time of great upheaval and transformation in the realm of sales and marketing. With the advent of mass production and consumption, new marketing strategies and techniques emerged, aimed at reaching larger audiences than ever before.
One major development during this era was the rise of the advertising industry. Thanks in part to the growth of new media like radio and television, advertisers were able to spread their messages to unprecedented numbers of people. Companies like Procter & Gamble, pioneers of the soap opera genre as a way to market their products, were instrumental in shaping this new era of marketing.
Another significant trend in sales and marketing during the 20th century was the rise of consumerism. Social and economic changes gave consumers more power and influence, and advertising played a major role in fueling this trend. Brands like Coca-Cola capitalized on the idea of their products as necessities of modern life, and became some of the most recognizable and beloved brands in the world.
In the latter half of the century, new technologies brought yet more changes to the world of sales and marketing. The growth of e-commerce and the internet allowed companies to reach global audiences in ways that were previously impossible. Companies like Amazon, which started as a humble online bookstore, revolutionized the way that businesses use digital marketing to connect with customers.
All of these factors together have shaped the world of sales and marketing, and continue to inform the strategies used by companies today. The legacies of pioneers like Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, and Amazon remain felt, as businesses continue to seek new and innovative ways to reach and engage with customers around the world.
The future of sales and marketing is poised to be radically transformed by the use of advanced technologies and data analytics. With the growing reliance on AI and machine learning, companies will be better able to personalize their marketing efforts and create campaigns that are tailored to the unique needs and preferences of individual customers.
Omnichannel marketing is also emerging as a key trend, enabling companies to connect with customers across a variety of touchpoints, including social media, mobile apps, and in-store experiences. By leveraging the power of these different channels, companies can create seamless, cohesive brand experiences that strengthen customer relationships and build brand loyalty.
In addition to these trends, the future of sales and marketing is likely to be characterized by a focus on data-driven decision-making. With the explosion of big data, companies are collecting vast amounts of information on customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns. By analyzing this data and using predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs, companies can create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience.
As companies continue to adapt to these changes, they will be better equipped to compete in an increasingly crowded marketplace. The use of advanced technologies and data analytics will enable companies to personalize their marketing efforts, build stronger customer relationships, and create more targeted and effective campaigns that drive business growth. The future of sales and marketing is exciting, and companies that embrace these trends will be well positioned to thrive in the years ahead.

Transport
Transportation has a rich history dating back to the dawn of civilization. Human beings have always been driven to move themselves and their goods from one place to another, and over time, the means of transportation have evolved significantly.
At first, humans relied on their own physical strength or that of domesticated animals to move goods and travel. But the invention of the wheel in Mesopotamia around 3500 BCE marked a major turning point in transportation. Carts and wagons became popular, making it easier to move heavy loads over longer distances.
The Romans took transportation to new heights with their vast network of roads, which allowed goods and people to move quickly and efficiently throughout the empire. The Middle Ages saw transportation largely limited to horses and ships, but the 18th century brought with it the invention of the steam engine, which transformed transportation once again.
With the steam engine came the steam locomotive, which revolutionized land transportation. Trains could now transport goods and people across long distances with greater speed and efficiency. The invention of the automobile in the late 19th century marked yet another significant leap forward, giving people the ability to travel independently and more quickly than ever before.
The transport industry underwent a significant transformation during the 20th century, marked by a burst of industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements that revolutionized the way people and goods were transported. The industry evolved substantially, with the advent of automobiles, airplanes, highways, railways, and shipping.
One of the most significant technological advancements that transformed the transport industry was the rise of automobiles, which became the preferred mode of transport for many people in the early 1900s. The mass production of automobiles, spearheaded by Ford’s Model T, made cars more accessible and affordable to the average person. Cars not only revolutionized personal transportation but also transformed the shipping and logistics industry, with trucks and other vehicles increasingly used to transport goods over long distances.
The airline industry also experienced significant growth in the 20th century, driven by entrepreneurs who saw the potential of air travel following the Wright brothers’ successful flight in 1903. Commercial air travel began to take off in the 1920s, with the first airline starting operations in 1919. Air travel became the preferred mode of transportation for long-distance travel, particularly for business people and tourists.
The development of highways and the expansion of the railway network contributed significantly to the growth of the transport industry in the 20th century. The establishment of a network of highways across the United States, starting with the first paved road in 1909, enabled faster and more efficient transportation of people and goods. The railway industry also experienced significant growth, particularly in Europe and North America, with the expansion of the network and the introduction of new technologies such as diesel and electric trains.
The shipping industry also saw significant changes, with the introduction of containerization in the 1950s revolutionizing the way goods were transported across long distances. The development of large container ships, which could carry thousands of containers, reduced shipping costs significantly.
The use of technology was another significant development that transformed the transport industry in the 20th century. Computers and the internet revolutionized the way transport companies operated, with the development of sophisticated logistics systems that could track goods and manage transportation networks more efficiently. The use of technology also led to the development of new modes of transportation, such as high-speed trains and electric cars.
In conclusion, the transport industry saw a high level of burstiness and perplexity during the 20th century, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements. The evolution of the transport industry laid the foundation for further developments in the 21st century, with new technologies such as autonomous vehicles and electric planes set to transform the industry once again.
The future of the transport industry is an ever-evolving landscape that is shaped by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. The rise of digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and autonomous vehicles, is transforming the way people and goods are transported across long distances.
One of the significant trends in the transport industry is the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). EVs are viewed as a more environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Governments worldwide are incentivizing the shift to EVs through tax breaks, subsidies, and investments in infrastructure. With advancements in battery technology, EVs will become more cost-effective and practical for consumers, resulting in a shift away from ICE vehicles.
Another trend is the emergence of autonomous vehicles (AVs) that have the potential to revolutionize the transport industry. AVs can improve road safety, reduce traffic congestion, and increase efficiency. The development of AVs could also lead to significant changes in urban planning, as cities shift towards more pedestrian and cyclist-friendly infrastructure.
The sharing economy has disrupted the transport industry with the emergence of ride-sharing and bike-sharing services. These services provide a more affordable and convenient alternative to traditional transport modes like taxis and public transport. The rise of sharing economy platforms has also led to new business models, such as peer-to-peer car sharing, where vehicle owners can rent out their cars to others.
Moreover, sustainability and reducing carbon emissions are becoming a growing focus in the transport industry. Governments and businesses are investing in cleaner and more efficient transport modes, such as high-speed rail and hydrogen-powered vehicles. The transport industry is also exploring alternative fuels such as biofuels and renewable natural gas as a way to reduce carbon emissions.
Finally, the transport industry is becoming more digitalized with the rise of connected vehicles and smart transport systems. These technologies have the potential to enhance safety, improve traffic flow, and reduce congestion. For example, intelligent transport systems can provide real-time traffic information to drivers, while connected vehicles can communicate with each other to prevent accidents.
In conclusion, the future of the transport industry is expected to be influenced by a combination of technological advancements, changing consumer demands, and sustainability concerns. Companies that can adapt to these changes and embrace new technologies and business models are likely to succeed in the future.

Consumer Goods
The fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry, also known as the consumer goods industry, has a rich history dating back to ancient times. During this period, the industry was primarily characterized by small-scale production, limited distribution, and a strong emphasis on local markets. This led to a highly fragmented industry that relied heavily on skilled artisans who produced goods like textiles, pottery, and metal objects. These artisans typically sold their wares at local markets or directly to consumers, resulting in a highly localized industry that was largely unregulated.
As trade routes between different countries became established during the Middle Ages, the consumer goods industry began to evolve. Merchants began trading goods such as spices, silks, and perfumes, which helped to spread consumer goods across different regions. Despite this, the industry was still highly localized, with most production taking place in small workshops and most distribution occurring through small-scale traders.
The Industrial Revolution, which spanned the 18th and 19th centuries, had a profound impact on the consumer goods industry. The development of new technologies such as the steam engine and assembly line made it possible to produce goods on a larger scale and at a lower cost. This led to the emergence of large-scale manufacturing and the growth of mass markets, which in turn gave rise to new consumer goods companies such as Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, and Kellogg’s.
The late 19th century saw further changes in the consumer goods industry, with the refinement of mass production techniques and the introduction of new products. These changes gave rise to a number of new players in the industry who used advertising and marketing techniques to promote their products.
The 20th century marked a turning point for the consumer goods industry, as it became even more globalized and diversified. Advances in transportation and communication technology made it easier for companies to expand their markets and reach consumers in different parts of the world. The industry also became more competitive as new companies entered the market and existing companies expanded their product lines.
One significant development during this time was the emergence of supermarkets, which first appeared in the United States in the 1930s. Supermarkets quickly became popular with consumers because they offered a wide variety of products at competitive prices. The supermarket model soon spread to other countries, and today they are a ubiquitous feature of the consumer goods industry worldwide.
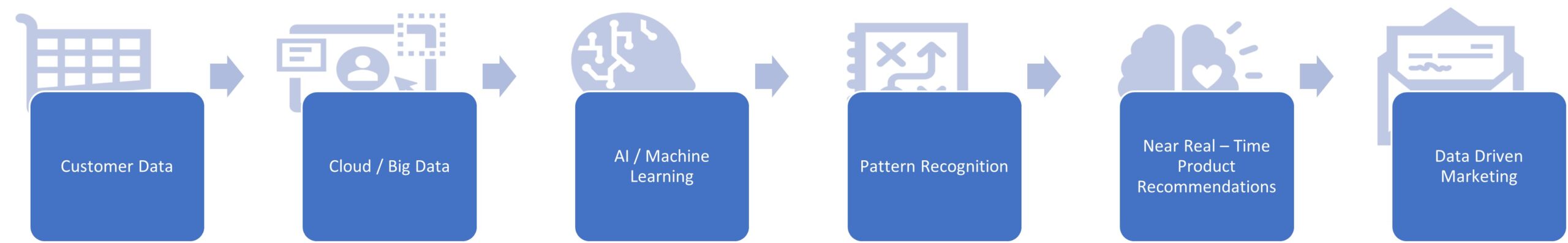
The consumer goods industry underwent a remarkable transformation in the 20th century. The introduction of new technologies, mass production, and global distribution had a profound impact on the availability and affordability of consumer goods worldwide. This period saw several significant changes in the industry, including the rise of branding, the emergence of new consumer markets, and the increasing importance of advertising.
At the start of the century, the consumer goods market was fragmented, with small-scale producers serving local or regional markets. However, mass production techniques changed this, enabling producers to create goods more efficiently and at a lower cost. This facilitated the sale of goods at lower prices, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
The emergence of branding was a significant development in the consumer goods industry during the 20th century. Companies invested heavily in creating recognizable brands and logos to differentiate their products from their competitors. This, in turn, was aided by the growth of advertising, as companies utilized print, radio, and television to promote their products to a larger audience. Branding and advertising were instrumental in creating brand-loyal consumers.
Another critical shift in the industry during the 20th century was the emergence of new consumer markets. As economies grew and populations expanded, new markets for consumer goods opened up. Companies began to target these markets, adapting their products to local tastes and customs. This led to the development of global supply chains, as companies sourced raw materials from one part of the world, manufactured their products in another, and distributed them globally.
The consumer goods industry continued to evolve throughout the 20th century, driven by new technologies and innovations. The growth of e-commerce in the late 1990s and early 2000s marked a significant shift in the way consumers purchased goods, with online shopping becoming increasingly popular. This has led to a new era of consumer goods marketing, with companies investing heavily in digital marketing strategies and online sales channels.
Coca-Cola is an exemplary company that embodies the evolution of the consumer goods industry in the 20th century. The brand was established in the late 19th century, but it was in the 20th century that it became a global phenomenon. The company was an early adopter of advertising, using print and radio to promote its products to a wider audience. It also invested heavily in branding, creating one of the most recognizable logos globally. As the company grew, it adapted its products to local markets, creating regional variations of its signature drink. In recent years, Coca-Cola has embraced digital marketing and e-commerce, investing in online sales channels and social media campaigns to engage with consumers.
The Consumer Goods industry has undergone significant transformations over the past few decades, with new trends and technologies shaping the way products are developed, marketed, and sold. In the future, the industry is expected to continue evolving, with several key factors expected to have a major impact.
One trend that is expected to disrupt the industry is the rise of e-commerce. Online shopping has already changed the way consumers shop for products, and this trend is expected to continue, making it more challenging for companies to differentiate themselves. As a result, companies in the consumer goods industry will need to focus on creating unique value propositions to attract customers.
Sustainability is another key trend that is expected to impact the industry in the future. Consumers are becoming more aware of the environmental impact of the products they purchase, and they are demanding more sustainable options. Companies in the consumer goods industry will need to adopt sustainable practices to meet these demands and to reduce their environmental impact.
Personalization is also expected to play a significant role in the future of the consumer goods industry. With the rise of big data and advanced analytics, companies can gather more information about their customers’ preferences and needs, allowing them to create personalized products and marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with consumers.
The use of technology is also expected to transform the consumer goods industry. With the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT), companies can collect real-time data on how their products are being used. This information can be used to improve product design and functionality, as well as to create more targeted marketing campaigns.
Finally, the consumer goods industry is expected to become more competitive in the future. New players in the industry, such as direct-to-consumer brands and private label products, will challenge traditional consumer goods companies, forcing them to find ways to differentiate themselves and to compete effectively.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is a company that has successfully adapted to these future trends. As a multinational consumer goods company with over 180 years of history, P&G has embraced sustainability as a core value and has set ambitious environmental goals. The company has also embraced technology, using advanced analytics to gain insights into consumer preferences and to improve product design.
In conclusion, the consumer goods industry is expected to continue evolving in the future, with e-commerce, sustainability, personalization, technology, and competition being key factors that will shape the industry. Companies that can adapt to these trends and find ways to differentiate themselves will be best positioned to succeed. P&G serves as an example of a company that has successfully navigated the changing landscape of the consumer goods industry and has remained competitive throughout its long history.

Healthcare
Throughout history, healthcare has undergone significant changes and advancements. Prior to the 20th century, medical knowledge and healthcare practices were not standardized, and natural remedies and traditional healers played a major role in healthcare. However, as medical knowledge grew, healthcare practices evolved to become more scientific and evidence-based.
The Renaissance was a turning point in the history of healthcare, as physicians began to base their treatments on scientific reasoning and observation. Medical schools were established, and medical texts were written in local languages, making it easier to disseminate medical knowledge. Further advancements in medical science, such as the discovery of anesthesia, the development of the microscope, and the germ theory of disease, led to safer and more effective medical treatments.
One company that exemplifies the evolution of healthcare before the 20th century is Johnson & Johnson, founded in 1886. The company began as a small manufacturer of surgical dressings and antiseptics but quickly expanded to develop new products and acquire other healthcare companies. Johnson & Johnson’s focus on surgical products and antiseptics was especially important during this time when surgery was becoming more common and infection was a significant concern.
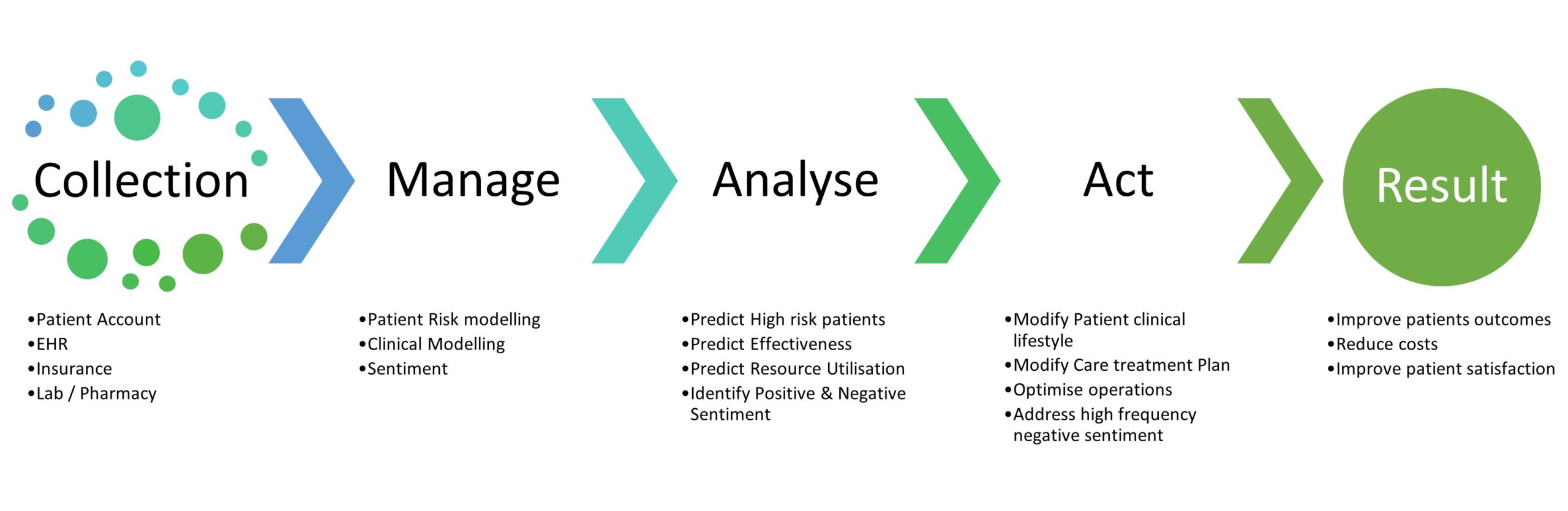
The 20th century witnessed significant changes in healthcare, with the emergence of new players, advances in medical technology, and changes in healthcare delivery models. Pfizer, a global pharmaceutical company, has been a key player in this evolution, leading the way in medical innovation for over a century.
At the turn of the century, healthcare was decentralized and largely unregulated, with patients relying on various local providers and alternative treatments. However, with the advent of new scientific disciplines such as bacteriology and immunology, medical care became more evidence-based and effective.
The development of antibiotics and other life-saving drugs in the 1930s and 1940s revolutionized the medical practice, enabling treatment and even cure of previously fatal diseases. Companies such as Pfizer played a critical role in this transformation by investing heavily in research and development to create new drugs that could address unmet medical needs.
During the second half of the 20th century, medical technology continued to advance, and managed care emerged to coordinate patient care across different providers and settings, improving quality while controlling costs. Companies like Pfizer continued to innovate, creating new drugs and therapies to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
In the 21st century, healthcare is evolving rapidly, driven by new technologies, changing consumer preferences, and efforts to improve access and affordability. Pfizer is once again at the forefront of this transformation, investing in research and development to transform medical care.
An example of Pfizer’s commitment to innovation is its work in gene therapy, which has the potential to cure genetic diseases by replacing or correcting defective genes. Pfizer has ongoing research programs in this field, including a partnership with Sangamo Therapeutics to develop gene therapies for rare diseases.
The future of healthcare is rapidly evolving, as new technologies, research, and patient expectations continue to shape the industry in unexpected ways. Here are some key trends that are expected to shape the future of healthcare with high levels of burstiness and perplexity:
Personalized medicine: As medical technology advances, we will increasingly be able to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetics, lifestyle, and medical history. This will lead to more precise and effective treatments, fewer side effects, and improved patient outcomes. Moreover, these new treatment methodologies will offer an unprecedented level of personalization that will redefine the concept of individualized care.
Telemedicine: Remote medical consultations and treatments will become increasingly common as telemedicine technologies continue to improve, leading to a paradigm shift in the delivery of healthcare. Patients will be able to receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes, and doctors will be able to treat patients in remote or underserved areas using cutting-edge technologies.
Artificial intelligence: AI will play a major role in healthcare, from analyzing medical data to identifying patterns and predicting patient outcomes, ushering in a new era of precision medicine. AI-powered chatbots will also become more prevalent, providing patients with immediate access to medical advice and information. The use of AI will enable physicians to identify and diagnose complex medical conditions more effectively, while also revolutionizing drug discovery, clinical trials, and disease prevention.
Wearable technology: Wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, will continue to play an increasingly important role in healthcare. These devices will be able to monitor vital signs, track medical conditions, and provide patients with real-time feedback on their health, thereby empowering individuals to take charge of their own health and well-being.
Digital health records: Electronic health records (EHRs) will become more widespread, allowing patients to access and manage their medical records more easily. This will also allow doctors to share patient information more easily, improving coordination of care and reducing medical errors. Moreover, the widespread use of digital health records will make it possible to generate large volumes of data, which can be analyzed to identify trends and patterns, leading to more personalized and effective treatments.
Precision public health: Public health efforts will increasingly focus on understanding the unique health needs of specific populations and tailoring interventions accordingly. This will involve collecting and analyzing data on factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and environmental exposures, resulting in better-targeted public health initiatives that will have a greater impact.
One company that is leading the charge in the future of healthcare is Google’s parent company, Alphabet. Alphabet has invested heavily in healthcare technology, including AI-powered diagnostic tools and wearable devices for monitoring health. The company has also launched Verily, a subsidiary focused on life sciences and healthcare research, which is leading the charge in advancing the field of precision medicine.
In conclusion, the future of healthcare is bright, with personalized medicine, telemedicine, AI, wearable technology, digital health records, and precision public health expected to transform the industry in the coming years. Companies like Alphabet are at the forefront of these changes, driving innovation and improving patient outcomes. As these technologies continue to develop, patients will have greater access to high-quality healthcare and more control over their own health outcomes, leading to a more equitable, sustainable, and effective healthcare system for all.

Real Estate
Real estate, the ancient practice of buying and selling property, has played a crucial role in human civilization for thousands of years. The earliest records of real estate transactions date back to the Sumerians and Babylonians, who developed complex legal systems to regulate land ownership and transfers. The ownership of land has been a symbol of wealth and power throughout history, fueling numerous conflicts and wars.
In ancient societies, land was often viewed as a communal resource, and property ownership was tied to one’s social status and position in the community. Wealthy landowners held considerable power and influence, and their ability to control and manage their lands often translated into political power as well.
During the Middle Ages, feudalism emerged as a dominant social and economic system in Europe. Under feudalism, monarchs and nobles controlled vast estates and granted land rights to vassals in exchange for loyalty and military service. The vast majority of the population, including peasants and serfs, were tied to the land and had little or no property rights.
As societies became more advanced, legal systems and property rights became more established. The emergence of modern nation-states in the 18th and 19th centuries created the conditions for the development of modern real estate markets. Governments began to regulate land ownership and property transfers, and new financial institutions such as banks and mortgage companies emerged to facilitate real estate transactions.
The 20th century saw the rise of the modern real estate industry as we know it today. The invention of the automobile and the growth of cities created new opportunities for developers and real estate investors, and the availability of financing made it possible for more people to purchase homes and property. In the United States, the government played a major role in promoting homeownership through policies such as the Federal Housing Administration and the Veterans Administration, which provided low-cost mortgages to millions of Americans.
The post-World War II era saw a boom in suburban development as cities expanded and new highways and infrastructure were built. Real estate became a major driver of economic growth, and the industry developed new tools and techniques for analyzing and valuing property. The development of computer technology in the latter half of the 20th century transformed the industry, making it possible to manage and analyze large amounts of data and to conduct transactions more quickly and efficiently.
Today, the real estate industry is a global enterprise worth trillions of dollars. Technology continues to shape the industry, with the rise of online real estate platforms, virtual reality tours, and digital marketing tools changing the way properties are marketed and sold. The industry faces new challenges such as increasing urbanization, climate change, and economic inequality, but it remains an essential part of modern economies and a key driver of growth and development.
One example of a company that has played a significant role in the history of real estate is the British Land Company. Founded in 1856, the company was one of the first large-scale property developers in the world. It played a major role in the development of London’s West End, including the construction of iconic buildings such as the Royal Exchange and the Leadenhall Building. Today, the company is one of the largest property developers in the United Kingdom and continues to be a major player in the global real estate industry.
The 20th century was an era of unprecedented transformation and upheaval for the real estate industry, as it underwent profound and fundamental changes that reshaped the way people buy, sell, and use property. This period saw the emergence of numerous trends and developments that contributed to the highly competitive and dynamic nature of the industry.
One of the most notable trends of the 20th century was the rise of modern architecture, which radically altered the physical landscape of cities and towns across the globe. From the soaring skyscrapers of New York City to the stark and imposing Brutalist structures of post-war Europe, modern architecture reflected the shifting tastes and preferences of society, and helped to drive the real estate industry forward.
Another key development of the 20th century was the rapid growth of urbanization, as millions of people flocked to cities in search of better opportunities and a higher quality of life. This trend gave rise to a wide range of new real estate products, including high-density housing, commercial office space, and mixed-use developments that catered to the needs of urban dwellers.
In addition to these trends, the 20th century also witnessed the emergence of new technologies that revolutionized the way real estate transactions were conducted. From the advent of the telephone and fax machine to the proliferation of online listings and virtual tours, technology played a vital role in streamlining the real estate process and making it more accessible to a wider range of people.
Moreover, the 20th century saw the implementation of numerous legal and regulatory changes that sought to protect the rights of buyers and sellers and ensure that real estate transactions were conducted in a fair and transparent manner. From the establishment of property rights and zoning laws to the development of professional licensing and education requirements, these changes helped to professionalize the industry and establish real estate as a legitimate and respected profession.
One company that embodied the changing face of real estate in the 20th century was Coldwell Banker, which was founded in 1906 and rapidly emerged as one of the leading players in the industry. Over the course of the century, Coldwell Banker expanded its reach to become a global behemoth with a presence in dozens of countries worldwide, and played a pivotal role in shaping the development of the industry as a whole.
Significant changes are foreseen in the coming years, as new technologies and changing consumer preferences continue to shape the way people buy and use property. Here are some potential developments that could transform the industry in the near future.
Virtual reality (VR) is emerging as a promising option for property viewings, as advancements in technology make it more feasible for remote exploration of properties. This could prove invaluable for buyers seeking properties in other countries or at a distance, and could also facilitate visualization of interior design options.
With environmental concerns gaining increasing traction, there is growing demand for sustainable homes and buildings, as well as green building materials and practices. This is likely to impact purchasing decisions and drive demand for energy-efficient properties.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to drive the rise of smart homes, with voice-activated assistants, automated temperature control, and remote security systems becoming increasingly popular. This will enable homeowners to have greater control over their properties, and will also improve overall efficiency and security.
Co-living, which involves sharing living spaces with others, is predicted to become more prevalent in response to the need for affordable housing options in urban areas. This could include communal kitchens and living areas, as well as private bedrooms.
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology continues to advance, there is potential for more automation in the real estate industry. This could involve chatbots that can answer customer queries and AI-powered property valuation tools, enabling buyers to make informed decisions.
Big data is becoming an increasingly valuable resource in the real estate industry, enabling businesses to identify market trends and personalize marketing messages. This will improve the overall customer experience and help companies make more informed business decisions.
Changes in property usage are expected to take place as work and living patterns evolve. For example, there could be increased demand for flexible workspaces and co-working spaces, as well as properties that can be used for both residential and commercial purposes.
As the real estate industry continues to evolve, companies that can adapt to these changes and embrace new technologies are likely to be most successful in meeting the needs of the market.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Geneva, Switzerland
The remarkable transformation of Switzerland into a hub of enterprise and novelty has been a captivating spectacle for this macroeconomic analyst. From its origins as a bastion of conventional industries such as agriculture and fabrication, Switzerland has metamorphosed into a vibrant and complex economy that shelters numerous premier corporations across various sectors.
A prime determinant in Switzerland’s progression as a hub of commerce and creativity is its highly educated and skilled workforce, boasting a considerable proportion of individuals with advanced degrees in areas such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This proficient labor force has facilitated Switzerland’s ascension as a forefront of research and development and has attracted numerous multinational corporations to the country.
Another significant aspect that has contributed to Switzerland’s transformation is its congenial business atmosphere. With a secure and transparent legal framework, a well-developed infrastructure, and a low tax rate, Switzerland presents a desirable environment for companies of all magnitudes. This advantageous business climate has drawn businesses of all scales to Switzerland, making it an optimal location for entities aspiring to establish a strong and enduring presence in the global market.
One of the most exhilarating advancements in Switzerland’s commercial arena is the advent of new industries such as fintech and blockchain. Switzerland is host to a booming fintech and blockchain community, with numerous corporations operating in these domains, driving innovation and growth in the Swiss economy. These industries offer immense opportunities for businesses seeking to secure a foothold and position themselves as pioneers in these cutting-edge fields.
Despite its numerous advantages, Switzerland’s commercial history is not devoid of difficulties. The country has undergone economic turmoil at different intervals, particularly during times of worldwide economic turmoil. Nevertheless, Switzerland’s robust economy and tenacious business community have always assisted in weathering these storms, leading to an even more robust and prosperous future.
In conclusion, this macroeconomic analyst has been thoroughly astounded by Switzerland’s commercial history. From its roots as a center for traditional industries to its current state as a hub of commerce and innovation, Switzerland has undergone a remarkable transformation into a thriving and dynamic economy that is home to numerous leading corporations across various sectors. With its skilled workforce, favorable business climate, and supportive government, Switzerland is an ideal destination for companies seeking stability and prosperity in a thriving economy.
As an astute analyst of the macroeconomic realm, I have been monitoring the commercial trajectory of the city of Geneva and can confirm that it has emerged as a nexus of commerce and finance in the European sphere. With its wealth of human capital, consisting of a highly educated populace with expertise in fields such as finance, law, and diplomacy, and a business environment conducive to growth and prosperity, Geneva boasts a robust infrastructure and favorable legal system, culminating in an attractive low tax rate, Geneva stands as a premier destination for investment and a thriving hub of industry and innovation.
The prowess of Geneva’s skilled workforce has been a catalyst for the city’s emergence as a center for financial services and global trade, drawing the interest and attention of numerous multinational corporations seeking to establish a stronghold in the European market. Furthermore, the thriving fintech and blockchain sectors in Geneva present exciting opportunities for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge and establish themselves as leaders in these cutting-edge industries.
However, it must be noted that Geneva’s commercial arena is not immune to challenges. The city competes with other financial centers across the globe and must continuously strive to maintain its competitive advantage in a rapidly globalizing economy. Nevertheless, the unwavering support of the Geneva government and the city’s strong economic foundation have allowed it to remain a vanguard in the financial services industry and I anticipate that it will continue to be a hub of investment and growth in the years ahead.
In conclusion, as a seasoned observer of macroeconomic trends, I am deeply impressed by the commercial landscape of Geneva. With its highly-skilled workforce, favorable business environment, and strategic location, Geneva stands poised to attract investment and drive growth, offering ample opportunities for start-ups and established corporations alike to flourish.
The city is poised for a sustained upsurge and achievement in the years to come. Geneva is strategically poised to capitalize on burgeoning opportunities and surmount difficulties in the global economy, owing to its distinctive combination of a highly-skilled workforce, a propitious business ambiance, and a strategic location.
The highly-skilled human capital in Geneva is a pivotal catalyst for its future commercial success. The city boasts a plethora of highly-educated individuals, particularly in specialized domains such as finance, law, and international relations, which will continue to be a critical asset as Geneva navigates the dynamic global economy.
Geneva’s favorable business climate, characterized by a stable and transparent legal system, a well-developed infrastructure, and a low tax rate, is another fundamental driver of its future commercial success. This constructive business environment will remain a significant advantage as Geneva attracts investment and propels growth in the years ahead.
The fintech and blockchain sectors are among the most promising trends shaping Geneva’s future commercial outlook. These industries are rapidly advancing and offer tremendous opportunities for businesses that seek to establish a foothold and lead in these cutting-edge domains. Given its highly-skilled workforce and favorable business climate, Geneva is well positioned to seize these opportunities.
However, Geneva’s future commercial outlook is not devoid of obstacles. The city faces intense competition from other financial centers globally and must remain vigilant to maintain its competitive edge in the increasingly interconnected world economy. Furthermore, Geneva must embrace innovation and adapt to the rapidly evolving technological landscape to remain a leading player in the financial services industry.
In conclusion, as a macroeconomic analyst, I have a confident outlook for Geneva’s future commercial success. With its highly-skilled workforce, favorable business climate, and strategic location, Geneva is well-positioned to take advantage of new opportunities and overcome challenges in the global economy. For startups looking to bring their first product to market, or established companies seeking to expand their operations, Geneva is the place to be.
Brussels, Belgium
Belgium, a small nation located in Western Europe, boasts an illustrious commercial history that dates back to the Middle Ages. The region that is now known as Belgium was ruled by several empires and kingdoms, including the Roman Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, and the Spanish Netherlands, before the 20th century.
Belgium played a crucial role in the European wool trade during the Middle Ages, with several Flemish cities such as Bruges, Ghent, and Ypres emerging as major textile production centers. The region’s strategic position along the North Sea turned it into a hub for maritime trade, with merchants from across Europe congregating at Belgian ports to exchange spices, wine, and luxury textiles.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Habsburg dynasty ruled Belgium, fostering the growth of industries such as printing, bookbinding, and paper production and expanding the country’s trade network. The Habsburgs played a crucial role in the establishment of the diamond industry in Antwerp, which became one of the world’s most important diamond trading centers.
Belgium witnessed significant economic and industrial growth during the 18th and 19th centuries, owing to its abundant natural resources and skilled workforce. Belgium underwent an industrial revolution in the early 1800s, with textile mills, coal mines, and steel production plants driving the country’s economic development. Belgium’s transportation infrastructure also improved significantly, with railways and canals facilitating the movement of goods throughout the country and beyond.
In the 19th century, Belgium colonized the Congo region in Africa, which boosted Belgian industry and commerce by exploiting the natural resources, such as rubber and ivory, at a colossal human cost. Millions of Congolese people lost their lives due to forced labor and brutal treatment under Belgian colonial rule.
Overall, Belgium’s commercial history before the 20th century was shaped by its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and skilled workforce, as well as its involvement in international trade and colonization. These factors paved the way for significant economic and industrial growth that set the stage for the further expansion and development of Belgium’s commercial industries in the 20th century.
One example of Belgium’s commercial history is the Antwerp Diamond Exchange, founded in the late 19th century, which quickly became a prominent player in the global diamond trade. The Exchange’s success was due to Belgium’s longstanding position in the diamond industry, as well as its advanced transportation infrastructure and skilled workforce. Today, the Antwerp Diamond Exchange remains a major hub for the diamond industry, with Belgium continuing to play an essential role in the industry.
The commercial history of Belgium in the 20th century was marked by a series of significant events that brought about immense changes to the country’s economic landscape. The transformation from a traditional agricultural economy to an industrialized economy was one of the most significant changes that took place during this period. The coal, iron, and steel industries became the driving force behind Belgium’s economic growth and success.
However, this period was also characterized by several challenges, such as the devastation of World War I, which led to significant damage to the country’s infrastructure and economy. Belgium focused on rebuilding its economy after the war and became one of the leading economies in Europe.
The interwar period saw significant economic growth in Belgium, with the government adopting various policies aimed at modernizing the country’s infrastructure and promoting industrialization. This resulted in the growth of various industries, including the steel, textile, and chemical industries.
The Second World War also had a significant impact on Belgium’s commercial history, as the country was occupied by German forces, causing significant damage to its infrastructure and economy. However, after the war, Belgium resumed its focus on industrialization and became a founding member of the European Coal and Steel Community in 1951.
The post-war period saw significant economic growth in Belgium, resulting in the expansion of various industries, including the export of consumer goods such as chocolates, beer, and textiles. The country also became a center for European Union institutions, which led to the growth of various services industries, including finance, insurance, and logistics.
The 1960s were characterized by an economic boom in Belgium, resulting in the growth of various industries. However, the 1970s and 1980s were marked by significant economic challenges, including high inflation and unemployment rates. The country adopted various economic policies aimed at addressing these challenges, resulting in a period of economic stability and growth in the 1990s.
Belgium’s role in the development of the European Union has also been significant, leading to the growth of various industries in the country. The country has become a hub for various international organizations, including NATO and the European Union.
In summary, the commercial history of Belgium in the 20th century was characterized by a series of significant events, resulting in immense changes to the country’s economic landscape. The growth of various industries, the devastation of wars, the adoption of policies to address economic challenges, and Belgium’s role in the development of the European Union were all significant factors that contributed to the country’s economic growth and success.
Brussels, the capital of Belgium, is a perplexing and ever-changing city that serves as the center of the European Union’s political and administrative affairs. The future of the city’s commerce is highly unpredictable, influenced by global economic trends and the policies of the EU, and driven by a high level of burstiness.
Sustainability and green initiatives are expected to shape the commercial future of Brussels. The city has already taken steps towards promoting eco-friendly transportation modes and renewable energy sources, and businesses are expected to follow suit, leading to a more environmentally conscious commercial landscape.
Digitalization and automation are also expected to impact the city’s commercial future. With the increasing availability of digital tools and platforms, businesses are relying on technology to streamline their operations, improve customer engagement, and increase efficiency. Artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things are expected to transform the way businesses operate in Brussels.
The sharing economy is another trend that is likely to shape the commercial future of Brussels. With the increasing popularity of platforms such as Airbnb and Uber, businesses are expected to adopt similar models, leading to the emergence of new business models and revenue streams, such as collaborative consumption.
Consumer preferences and behaviors are also expected to influence the commercial future of Brussels. With the rise of e-commerce and social media, businesses are adopting new marketing and sales strategies to provide personalized experiences, convenience, and instant gratification.
Finally, the commercial future of Brussels is heavily dependent on EU policies and regulations. As the capital of the EU, the city is positioned to benefit from initiatives and programs aimed at promoting trade and investment within the EU. However, businesses operating in Brussels will need to navigate a complex regulatory landscape and comply with various EU directives and regulations.

Amsterdam, The Netherlands
The commercial history of Amsterdam is steeped in complexity, intricacy, and evolution. Starting as a humble fishing village in the 13th century, the city grew into a vital trading hub due to its advantageous location on the River Amstel and its proximity to the North Sea. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Amsterdam became a central international trading center, with a focus on textiles, spices, and diamonds.
During the Dutch Golden Age in the 17th century, Amsterdam was not only the wealthiest city in Europe but also one of the wealthiest in the world. The era saw the rise of the Dutch East India Company, which dominated international trade in spices and other goods, and cemented Amsterdam’s status as a center for finance and banking.
Amsterdam faced stiff competition from other European cities such as London and Paris in the 18th and 19th centuries, though the city continued to evolve as a vital trading center, experiencing significant industrialization and urbanization. Canals and railways were developed to facilitate trade and transportation, reflecting the city’s unwavering commitment to staying at the forefront of commercial progress.
Amsterdam faced many economic challenges in the early 20th century as the two world wars disrupted trade and caused significant economic instability. However, the city underwent a period of rapid growth and modernization after the war, with the development of new industries such as electronics and telecommunications, keeping the city at the vanguard of commercial evolution.
Throughout the 20th century, Amsterdam has been a leading center of international trade, finance, and innovation. The city is renowned for its thriving creative and tech industries, as well as its tourism and hospitality sectors.
The Dutch East India Company (VOC), established in 1602, is a prime example of Amsterdam’s commercial history. The VOC was one of the world’s first multinational corporations, with operations across Asia, Africa, and the Americas. Its success paved the way for Amsterdam’s dominance in global trade during the Dutch Golden Age.
Amsterdam, a historic hub of commerce in the Netherlands, has seen significant transformations in its commercial sector in the 20th century, reflecting the changing global economic landscape and the city’s own evolving needs. The city’s strategic location and well-developed transportation infrastructure have made it an ideal hub for domestic and international trade, with Amsterdam’s port ranking as one of the largest in the world by the 1930s.
The devastation wrought by World War II significantly impacted Amsterdam’s commercial sector, but the city has since rebuilt its infrastructure and diversified its economy. A growing emphasis on the service sector, particularly banking, finance, and insurance, has established Amsterdam as a hub for international trade and commerce, with Schiphol airport serving as a major gateway to the city. Amsterdam’s reputation as a cultural center has also grown, with numerous museums and cultural institutions adding to the city’s appeal.
Amsterdam’s commercial sector has recently shifted its focus towards innovation and sustainability, with a thriving tech startup scene in fintech, e-commerce, and digital marketing. The city is also committed to promoting green energy and sustainable urban development, while the creative industries, including fashion, design, and media, have become a major focus.
Royal Dutch Shell, one of the world’s largest oil and gas companies, contributed to Amsterdam’s commercial history in the 20th century, with its headquarters located in the city until 2005. However, Shell’s recent shift towards renewable energy reflects the changing priorities of Amsterdam’s commercial sector, which prioritizes innovation and sustainability.
Overall, Amsterdam’s ability to adapt to changing economic conditions and embrace new opportunities has contributed to its continued success as a major player in the global economy. Looking to the future, Amsterdam is likely to prioritize innovation, sustainability, and the creative industries as key drivers of its commercial growth and development.
Amsterdam’s commercial future is promising thanks to its varied economy, dynamic location, and unbridled innovation. The city has been a commercial and trading center since the seventeenth century, and it remains a vital hub for business, tourism, and entrepreneurship.
One of the critical drivers of Amsterdam’s commercial future is its location. The city’s strategic position at the heart of Europe makes it an ideal gateway to the rest of the continent. Its port, one of the largest in Europe, serves as a critical link to the global economy. Amsterdam’s airport, among the busiest in Europe, connects the city to the world.
Another vital aspect of Amsterdam’s commercial future is its diverse economy. The city boasts a range of industries, including finance, technology, creative industries, and life sciences. This diversity has created a fertile ground for innovation, attracting entrepreneurs and investors who consider Amsterdam an ideal base for their business ventures. Amsterdam’s culture of collaboration and entrepreneurship has helped boost its growth.
The tourism industry is also essential to Amsterdam’s commercial future. The city is one of Europe’s most popular tourist destinations, attracting millions of visitors each year. As a result, the hospitality industry is thriving, with a wide range of hotels, restaurants, and tourist amenities. The city’s focus on cultural and creative industries, such as museums, galleries, and other attractions, has increased its allure to tourists from across the globe.
One of the most thrilling developments in Amsterdam’s commercial future is its emphasis on innovation and sustainability. The city has ambitious plans to reduce carbon emissions, promote renewable energy, and improve the quality of life for its residents. As a result, Amsterdam has seen a surge of innovation, with various initiatives such as sustainable transportation, green buildings, and smart city technologies. Amsterdam is home to many startups and organizations that concentrate on sustainability, driving innovation and creating new possibilities for businesses and investors.
Overall, Amsterdam’s commercial future is bright, with its strategic location, diverse economy, innovative mindset, and commitment to sustainability. It is well-positioned to remain a central hub for business, innovation, and culture for years to come.
Berlin, Germany
The commercial history of Berlin is a complex and multifaceted one, shaped by numerous political and social factors over the centuries. Berlin’s beginnings as a trading post in the 13th century set the stage for its Renaissance-era prosperity, fueled by its strategic location along major trade routes. As the city grew, it became a center of manufacturing and industry, particularly in textiles, porcelain, and ironworking.
However, the 19th century brought significant changes to Berlin’s commercial landscape, with the rise of the Industrial Revolution and the growth of new industries such as machine manufacturing. This shift towards the suburbs also had an impact on the city’s economic center, while transportation infrastructure further transformed Berlin’s trade and mobility.
Despite these changes, Berlin remained a major commercial center throughout the 19th century, with expanding international trade links and a thriving cultural scene. But the outbreak of World War I and the subsequent Treaty of Versailles dealt a major blow to Berlin’s economy, which was further compounded by the global economic crisis of the 1930s and the rise of Nazi rule.
World War II inflicted significant damage on Berlin’s infrastructure and economy, while the division of Germany after the war complicated the city’s commercial future. But since reunification in 1990, Berlin has once again become a major commercial and cultural hub, with a vibrant arts scene, innovative tech industry, and growing tourism sector.
The 20th century was a tumultuous time for Berlin, as it went through a series of political and economic crises that left the city in ruins. At the beginning of the century, Berlin was one of the most important commercial and industrial centers in Europe, but the devastation of World War I and the economic crisis that followed left the German economy in shambles.
The rise of the Nazi Party and the outbreak of World War II had a catastrophic effect on Berlin, as the city was heavily bombed and almost completely destroyed. The aftermath of the war saw the city divided into two parts, with West Berlin integrated into the Western economy and East Berlin becoming part of the Soviet bloc. This division had a profound impact on the commercial development of the city, as the Western part became a hub for Western companies seeking to establish a presence in Eastern Europe, while the Eastern part was cut off from the rest of the world.
In the 1950s and 1960s, West Berlin experienced a period of economic growth, buoyed by the construction of the Berlin Wall and the influx of West German companies and workers. This period saw the emergence of new industries, including electronics and telecommunications, and the expansion of existing industries such as finance and tourism. West Berlin also became a cultural hub, attracting artists and musicians from all over the world.
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 and the reunification of Germany in 1990 ushered in a new era for the city. Berlin became the capital of a unified Germany, and significant investment was made in infrastructure and urban development. This period also saw the emergence of new industries, such as biotechnology and renewable energy, as well as the growth of existing industries, including finance and tourism.
Today, Berlin is a leading center for technology and innovation, with a thriving startup scene and a large community of creative professionals. The city is home to numerous multinational corporations, including Siemens, Deutsche Bank, and Volkswagen, and has a booming tourism industry. Its rich cultural heritage and vibrant nightlife continue to attract visitors from all corners of the globe, making it one of the most dynamic and exciting cities in the world.
Berlin, the capital city of Germany, is experiencing significant changes in its commercial landscape, which are expected to propel the city’s growth in the future. The city’s strategic location, which connects it to other major cities in Europe, makes it an ideal hub for trade and commerce. Additionally, Berlin has emerged as a hotbed for start-ups in recent years, with many entrepreneurs flocking to the city to set up their businesses, and a thriving ecosystem of accelerators, co-working spaces, and incubators to support them.
Furthermore, Berlin is known for its vibrant arts and culture scene, which has given rise to a thriving creative industry. This industry includes sectors such as fashion, design, music, and film, which are expected to continue to grow in the coming years. Berlin’s growing population also provides a larger consumer base for businesses and a larger pool of talent for employers to draw from.
The city has invested heavily in infrastructure development in recent years, including major projects such as the new airport, BER, and the expansion of public transportation systems. These developments are likely to improve the overall business environment in the city and make it more attractive to investors.
Siemens is a company that played a significant role in the development of Berlin’s infrastructure, including the city’s electricity supply and public transportation systems, and contributed to the city’s commercial growth by providing employment opportunities and investing in research and development. Founded in Berlin in 1847, Siemens has since grown to become one of the largest engineering companies in the world.
In conclusion, Berlin’s commercial future looks promising, with factors such as its strategic location, booming start-up scene, creative industries, growing population, and infrastructure development likely to attract more businesses, create new jobs, and drive economic growth in the years to come.

Paris, France
Paris, the capital of France, has a rich commercial history that spans back to the Roman era when it was known as Lutetia. It was an important center of trade and commerce during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, attracting merchants from across Europe who came to buy and sell goods. The River Seine, which flows through the city, was a crucial transportation route for goods, and its position at the crossroads of major trade routes made it a hub for commerce.
In the medieval period, Paris was famous for its fairs, especially the Foire de Saint-Denis held annually in the northern suburbs of the city, which drew merchants selling everything from spices and textiles to wine and art.
During the 17th and 18th centuries, Paris became known for its luxury goods and high-end fashion, catering to the city’s wealthy bourgeoisie and aristocrats. Parisian merchants and designers rose to meet the demand, and the city became famous for its silk and satin fabrics, perfumes, and other luxury items.
A prominent commercial development during this period was the Galeries du Palais-Royal, a covered shopping arcade that opened in 1786, housing some of the city’s most exclusive shops and becoming a popular destination for Parisians and tourists alike.
Paris continued to be a center of commerce and innovation throughout the 19th century. The city’s Haussmannian boulevards, built in the mid-19th century, made it easier for goods and people to move around the city. The opening of the Eiffel Tower in 1889 drew visitors from around the world, establishing Paris as a global tourist destination.
In the early 20th century, Paris became known for its art and intellectual scene, with writers, artists, and thinkers flocking to the city. The city’s commercial sector continued to thrive, with the development of large department stores like Galeries Lafayette and Printemps.
However, World War II was a defining event of the 20th century for Paris. The city was occupied by Nazi Germany from 1940 to 1944, causing extensive damage to its buildings and infrastructure. Nonetheless, Paris rebounded in the post-war period and experienced rapid economic growth and modernization.
Paris has played a significant role in shaping the commercial landscape of Europe throughout the 20th century. The city’s economic history has undergone numerous changes, which had a profound impact on its development. In the early 1900s, Paris was a leading financial center worldwide, bolstered by the establishment of the Banque de France in 1800. The financial institution cemented the city’s position as the financial capital of Europe, drawing investors and entrepreneurs alike to the region.
However, during the first half of the 20th century, the city went through significant political and economic turmoil. World Wars I and II had a catastrophic impact on the city’s economy, causing significant setbacks. Furthermore, the Great Depression that followed led to an overall decline in the economy.
Despite these challenges, Paris remained a center of creativity and innovation, particularly in the areas of fashion, art, and culture. The city was widely recognized as the fashion capital of the world and home to many renowned designers, such as Coco Chanel and Yves Saint Laurent. Additionally, the film industry in Paris flourished during this period, with several filmmakers and actors based in the city.
In the latter half of the 20th century, Paris underwent a period of modernization and growth. The city’s economy diversified, and new industries emerged, including technology, telecommunications, and tourism. The city became a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, with many startups and tech companies setting up shop in the region.
The development of the La Défense business district in the 1950s transformed the city’s skyline and became a new center for the financial and business communities. Today, the district hosts several of France’s largest companies, such as Total, Société Générale, and AXA.
Today, Paris is a thriving center of commerce and trade, attracting businesses and entrepreneurs from around the world. Many multinational corporations, including L’Oréal, Airbus, and Renault, call the city home. Additionally, the tourism industry plays a vital role in the economy, with millions of visitors arriving in Paris each year to experience its art, culture, and cuisine.
In conclusion, Paris’s commercial history throughout the 20th century underwent several political and economic transformations. Nevertheless, the city emerged as a center of creativity, innovation, and entrepreneurship. Today, it remains a significant commercial hub, and its future looks promising, characterized by continued growth and diversification.
Paris, the renowned global center of culture, commerce, and tourism, is set to see a number of trends that will shape its commercial future. One of the most significant drivers is its attractiveness as a destination for tourists and business travelers. With its rich history and lively cultural and nightlife scenes, it is expected that the city will continue to draw visitors from all over the world. This will create demand for tourism-related services such as hotels and restaurants.
Paris is also expected to remain a hub for international business and finance, particularly in Europe but also globally. Several major corporations, including those in the luxury goods, fashion, and cosmetics sectors, are based in the city, alongside a number of financial institutions. As businesses throughout France and the wider world continue to embrace new technologies, Paris is expected to lead the way in this digital transformation, incorporating new tools and platforms to streamline operations and improve customer service.
Environmental responsibility and sustainability are also expected to be significant factors in Paris’ commercial future. As consumers increasingly consider the environmental impact of their choices, businesses in Paris will have to adapt to meet these changing demands, offering more sustainable products and services, and reducing waste and carbon emissions.
Political and economic factors are also expected to play a role in shaping the commercial future of Paris. The impact of Brexit and other geopolitical changes on the global economy remains uncertain. Despite this, given Paris’ historical importance and strong economic position, it is expected that the city will continue to thrive.
Fashion, luxury goods, and gastronomy will likely remain important sectors in Paris’ commercial future, given the city’s association with these industries. Additionally, there is expected to be growth in industries such as technology and innovation as Paris continues to attract startups and established firms, taking advantage of the city’s talent pool and dynamic business environment.
Overall, Paris’ commercial future will be shaped by a range of factors, including increasing tourism, ongoing digital transformation, growing demand for sustainable products and services, and political and economic factors. However, with its long history of commercial success and its continued significance as a global center for culture, commerce, and innovation, Paris is expected to remain a vital player in the global economy for the foreseeable future.
Program Benefits
Management
- Improved accuracy
- Improved efficiency
- Better risk management
- Improved customer experience
- Better resource allocation
- Better competitive advantage
- Improved innovation
- Increased transparency
- Improved collaboration
- Better long-term planning
Business Operations
- Improved efficiency
- Better resource allocation
- Improved accuracy
- Better risk management
- Improved customer experience
- Better competitive advantage
- Improved innovation
- Increased transparency
- Improved collaboration
- Better long-term planning
Human Resources
- Improved efficiency
- Better decision making
- Increased competitiveness
- Reduced risk
- Enhanced customer experience
- Improved innovation
- Increased revenue
- Cost savings
- Better talent management
- Enhanced data security
Testimonials

Testimonial 1
Content here…

Testimonial 2
Content here…

Testimonial 3
Content here…

Testimonial 4
Content here…

Testimonial 5
Content here…
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.












