Customer Success

Executive Summary Video
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Customer Success is provided by Mr. Adams Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 36 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Adams is an author, trainer, and consultant, specializing in helping technology companies deliver measurable business value through Customer Success Management best practices. Adams has over 25 years’ experience of working in the IT industry, including founding his own SaaS (software-as-a-service) business which he ran for six years before selling it in 2012.
Adams has delivered training and consultancy in over thirty countries across four continents. His courses have been attended by over 120,000 students worldwide, and his custom development work includes Cisco Systems’ Cisco Certified Customer Success Manager global certification program.
His book ‘Practical Customer Success Management: A Best Practice Framework for Rapid Generation of Customer Success’ was published in 2019 and is available from Amazon and all other book retailers.
Adams, as Founder and CEO, provides high quality training for Customer Success Management best practice. Adams has won numerous awards for his achievements in his field, and acted as a judge for the annual Customer Success Excellence Awards in EMEA in 2022 and the Americas in 2023.
To request further information about Mr. Adams through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Customer Success
History
Customer Success management is a relatively new discipline that emerged in the technology service industry and the professional services industry. It focuses on ensuring that customers achieve their desired outcomes and derive value from the products or services they have purchased. While the concept of customer success can be traced back to various business practices throughout history, its formalization as a distinct role and function is a more recent development.
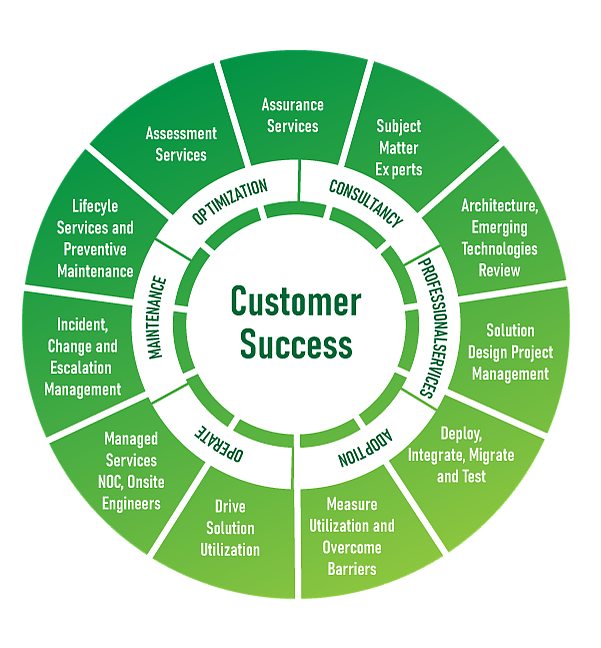
Source: www.alpha.ae
In the Technology Service Industry:
The origins of Customer Success management in the technology service industry can be traced back to the early 2000s with the rise of software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies. As these companies transitioned from traditional software sales models to subscription-based services, they realized the need to go beyond just acquiring customers and instead focus on ensuring their long-term success and satisfaction.
In 2006, the term “Customer Success” was coined by Dan Steinman, the former Vice President of Customer Success at Salesforce.com. Salesforce.com was one of the pioneering companies that embraced the customer success approach and recognized the importance of actively managing customer relationships beyond the initial sale. They established the first dedicated customer success team to proactively engage with customers, understand their needs, and help them achieve their desired outcomes.
Over time, the customer success function gained recognition and became an integral part of many technology service companies. The industry started adopting customer success practices, methodologies, and tools to drive customer retention, expansion, and advocacy. The Customer Success Managers (CSMs) became responsible for understanding customer goals, providing personalized guidance, and ensuring the successful adoption and utilization of the products or services.
In the Professional Services Industry:
In the professional services industry, customer success management has its roots in the broader field of account management and client services. Professional services companies, such as consulting firms and agencies, have long recognized the importance of building strong relationships with their clients and ensuring their satisfaction.
As the technology landscape evolved, professional services companies began offering technology-based solutions to their clients. This shift brought about the need for dedicated customer success efforts to ensure that clients were not only satisfied with the services but also achieved their desired business outcomes.
The professional services industry embraced customer success management by adapting and applying its principles to their specific context. They started focusing on understanding client objectives, defining key success metrics, and establishing ongoing relationships beyond project delivery. Customer Success Managers in professional services became responsible for managing client relationships, facilitating effective communication, addressing concerns, and identifying opportunities for additional value.
Today, both the technology service industry and the professional services industry heavily rely on customer success management as a strategic function. It plays a vital role in driving customer satisfaction, retention, and loyalty by ensuring that customers achieve their goals and realize the full value of the products or services they have invested in.

Current Position
Customer Success Management continues to be a rapidly evolving field in both the technology service industry and the professional services industry. Many companies across various sectors have recognized the importance of customer success and have established dedicated customer success teams or functions.
In recent years, customer success has expanded beyond its initial focus on software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies and has become relevant to a broader range of industries and business models. The principles and practices of customer success have been adopted by companies offering diverse products and services, including subscription-based businesses, e-commerce platforms, and more.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have also influenced the field of customer success. Companies now leverage customer success software platforms and tools to track customer health metrics, proactively identify potential issues, deliver personalized experiences, and drive customer engagement. Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are also being integrated into customer success processes to enhance data analysis, predict customer behavior, and provide more targeted recommendations.
Overall, customer success management continues to play a crucial role in organizations’ efforts to build strong customer relationships, drive customer satisfaction and retention, and maximize customer lifetime value.

Future Outlook
The future of Customer Success management holds several exciting possibilities and trends. Here are a few potential developments that may shape the field:
Expansion into new industries
While customer success has gained significant traction in the technology service and professional services industries, it is likely to expand further into other sectors. As businesses across various industries increasingly focus on customer-centricity and subscription-based models, customer success principles and practices will become more prevalent and adapted to different business models.
Data-driven customer success
With the growth of big data, analytics, and artificial intelligence, customer success management will increasingly rely on data-driven insights. Customer success teams will leverage advanced analytics tools to gather and analyze vast amounts of customer data, enabling them to identify patterns, predict customer behavior, and proactively address customer needs. This data-driven approach will help optimize customer success strategies and enable more personalized and proactive customer engagement.
Adoption of automation and AI
Automation and AI technologies will play a larger role in customer success management. Routine and repetitive tasks, such as onboarding processes, data collection, and basic customer inquiries, can be automated, freeing up customer success managers to focus on higher-value activities. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants may be used to provide immediate support, answer common customer queries, and guide customers through self-service resources.
Focus on customer health and sentiment analysis
Monitoring customer health and sentiment will become increasingly important. Companies will invest in tools and technologies that track and analyze customer sentiment through various channels, such as social media, surveys, and support interactions. This real-time feedback will allow customer success teams to proactively address concerns, identify areas for improvement, and take corrective actions to ensure customer satisfaction and success.
Integration with product development
Customer success management will become more integrated with product development processes. Customer feedback and insights collected by customer success teams will be directly incorporated into product roadmaps and feature enhancements. This collaboration will help align product development efforts with customer needs, improve product-market fit, and enhance customer success outcomes.
Expansion beyond customer acquisition and retention
Customer success management will extend its focus beyond customer acquisition and retention to encompass broader business goals. Customer success teams will increasingly collaborate with sales, marketing, and product teams to drive cross-functional alignment and achieve business outcomes, such as customer expansion, advocacy, and revenue growth.
These are just a few potential directions that customer success management may take in the future. As technology advances and businesses continue to prioritize customer-centricity, the field is expected to evolve and adapt to meet the changing needs and expectations of customers.

Customer Success – A Driver for Growth and Sustainability
Customer Success Management is the best practice process of helping customers to realize the maximum possible value from their investments in your solutions. By helping customers to become more successful, we gain greater levels of trust and loyalty from them, enabling us to sell more to them, and to keep them for longer.
It is a well-established fact that for the vast majority of businesses, gaining a new customer is an expensive process. This is why customers are considered to be precious assets, and once they have been attained, the wise company will do all it can to maximize the value they get from their relationship with it.
Source: www.nextiva.com
This is especially so in times of uncertainty, such as we face today. In uncertain times, companies are less likely to take any risks on new investments and are less likely to fund innovative initiatives, preferring instead to keep their money in the bank as a hedge against difficult times ahead. In this type of climate, it becomes even harder to attain new customers, and the need to both retain and generate maximum value from existing customers therefore becomes all the more urgent.
At the same time, there has been an increasing trend towards companies selling their solutions via renewable contracts. Customers love this trend because it provides greater flexibility for decision making, reduces onerous capital purchase requirements, and minimizes the risk of making a wrong purchasing decision.
For the supplier, the rise in X-as-a-service contracts has increased the need for Customer Success Management still further, since it is now even more essential to ensure that newly acquired customers continue to renew their contracts. The best way to maximize renewals is to ensure customers receive as much value as possible, from as early-on as possible, and for as long as possible. Doing so will increase the likelihood for customers to renew their existing contracts, to purchase additional solutions, and to continue to remain loyal for longer.
The ways in which customer success contributes to these objectives:
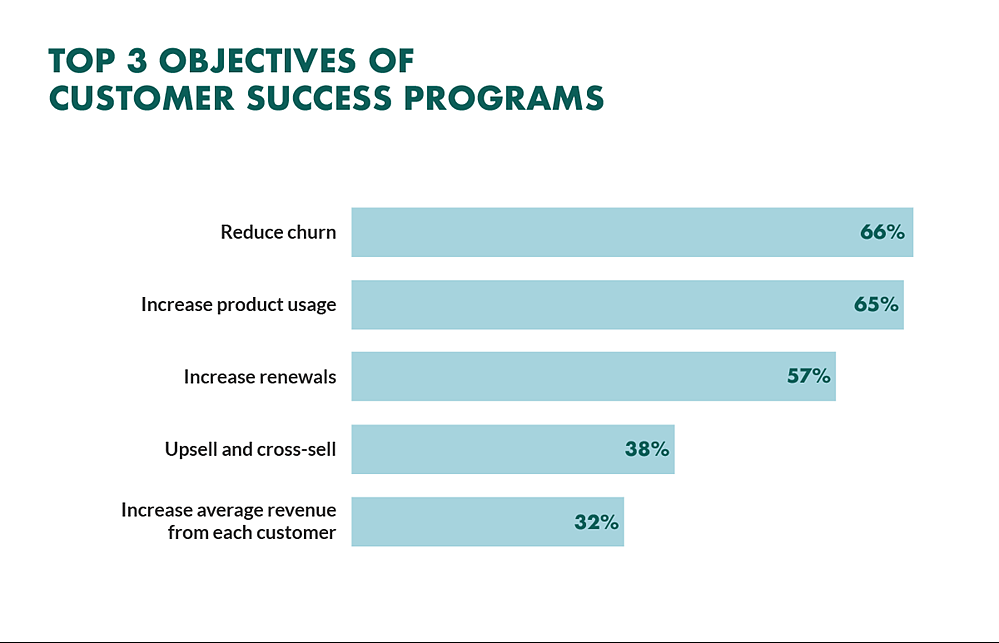
Source: www.superoffice.co.uk
Retention and Renewals
Customer success efforts aim to ensure that customers achieve their desired outcomes and derive maximum value from the products or services provided. By helping customers succeed, businesses increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and trust. Satisfied customers are more likely to renew their contracts or subscriptions, leading to higher customer retention rates. Retaining existing customers is generally more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, providing a stable revenue stream for sustainable growth.
Upselling and Cross-selling
When customers achieve success and realize the value of the products or services, they are more receptive to additional offerings. Customer success teams can identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities based on a deep understanding of the customers’ needs and goals. By expanding the breadth and depth of the relationship with existing customers, businesses can drive revenue growth and increase customer lifetime value.
Referrals and Advocacy
Satisfied customers are not only more likely to continue their own relationship but also more likely to recommend the supplier or provider to others. Word-of-mouth referrals from happy customers can be a powerful driver of new business. Customer success initiatives that foster advocacy and encourage customers to share their positive experiences can lead to new leads, conversions, and business growth.
Competitive Differentiation
In competitive markets, customer success becomes a key differentiator. When businesses consistently deliver exceptional customer experiences and help customers achieve their goals, they stand out from their competitors. Positive customer feedback and testimonials can enhance a supplier or provider’s reputation, attracting new customers and helping to establish a sustainable market position.
Customer Feedback and Product Improvement
Customer success teams act as a valuable feedback channel, collecting insights and suggestions from customers. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and drive product or service enhancements. Continuously iterating and refining offerings based on customer input leads to increased customer satisfaction, reduced churn, and long-term business sustainability.
Adaptability and Innovation
By closely engaging with customers and understanding their evolving needs, technology suppliers and professional service providers can stay ahead of market trends and proactively address emerging challenges. A customer success mindset fosters a culture of adaptability and innovation, enabling businesses to develop new solutions, expand their service offerings, and maintain relevance in a rapidly changing landscape.
Overall, customer success initiatives promote growth and sustainability by maximizing customer satisfaction, retention, and revenue generation, while also fostering a customer-centric approach that fuels innovation and differentiation in the marketplace.
Examples
These examples demonstrate how customer success practices have positively impacted various industries:
Salesforce: Salesforce, a leading CRM platform, is often cited as a prime example of leveraging customer success for business growth. Through their customer success program, known as “Trailblazer Community,” Salesforce focuses on customer enablement, adoption, and success. The company has achieved remarkable growth by prioritizing customer satisfaction, retention, and expansion, resulting in a loyal customer base and increased market share.
HubSpot: HubSpot, a provider of marketing and sales software, emphasizes customer success as a core value. Their customer success team works closely with customers, offering guidance, support, and training to help them achieve their marketing and sales goals. HubSpot’s customer-centric approach has contributed to their strong customer retention rates and steady growth.
Zendesk: Zendesk, a customer service software company, attributes a significant portion of its growth and success to its customer success strategy. They prioritize proactive engagement with customers, providing personalized assistance and resources to drive successful adoption and utilization of their products. By focusing on customer satisfaction and success, Zendesk has seen increased customer loyalty, referrals, and sustainable growth.
SaaS Industry: The software-as-a-service (SaaS) industry as a whole recognizes the importance of customer success. Many SaaS companies invest heavily in customer success programs, recognizing that customer retention and expansion are key drivers of their business growth. Several SaaS companies, such as Slack, Dropbox, and Zoom, have experienced remarkable growth by prioritizing customer success and ensuring positive user experiences.

What This Program Offers
Like any other professional service, Customer Success Management can be done well or done badly, with concomitant results for the business. This three-year program provides a tried and tested, best practice approach to planning for, adopting and measuring the ROI from the implementation of a fully functioning Customer Success Management service. By following best practice processes and by applying best practice tools and techniques, organizations who adopt the training contained within this program will be able to create a powerful Customer Success Management capability that is tailored to meet their specific needs and that will help to minimize churn, increase adoption and renewals, grow customer loyalty, and maximize the value of every customer relationship.
The Customer Success Management Training Program is designed to equip individuals in the professional service and technology services industries with the knowledge, skills, and strategies necessary to drive customer success and maximize business growth. The program focuses on understanding customer needs, fostering strong relationships, and delivering exceptional customer experiences throughout the customer lifecycle.
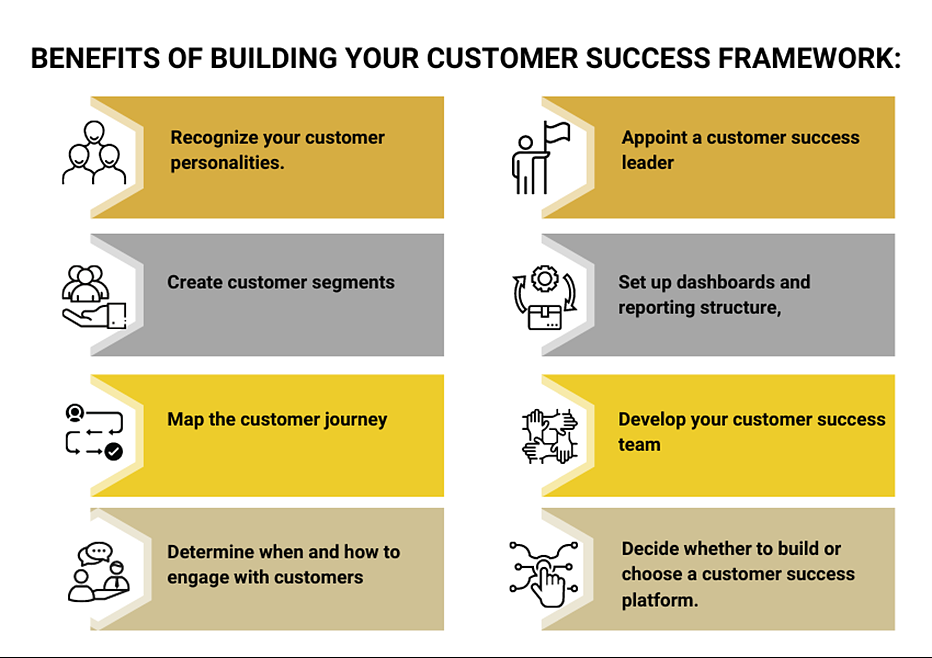
Source: www.csmpractice.com
Key Learning Objectives:
Fundamentals of Customer Success: Participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of the core principles and concepts of customer success management. They will learn how customer success contributes to business growth, retention, and long-term sustainability.
Customer Engagement and Relationship Building
Participants will learn effective strategies for engaging with customers and building strong relationships. They will explore techniques for proactive communication, understanding customer goals, and aligning service offerings to customer needs.
Customer Success Metrics and Analytics
Participants will learn how to identify, track, and measure key customer success metrics and use data-driven insights to enhance customer outcomes. They will gain proficiency in leveraging analytics tools to monitor customer health, identify risks, and prioritize proactive actions.
Customer Journey Mapping
Participants will understand the customer journey and learn how to create customer journey maps to visualize and optimize the customer experience. They will gain insights into identifying touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities for delivering exceptional customer value at each stage.
Customer Success Strategies and Best Practices
Participants will explore proven customer success strategies and best practices specific to the professional service and technology services industries. They will learn how to tailor these strategies to meet the unique needs and challenges of their organizations.
Cross-functional Collaboration
Participants will understand the importance of cross-functional collaboration in achieving customer success. They will learn how to collaborate effectively with sales, marketing, product, and support teams to ensure a seamless and cohesive customer experience.
What can happen if you do not prioritize customer success?
Not prioritizing customer success can pose several risks and negative consequences. Here are some of them:
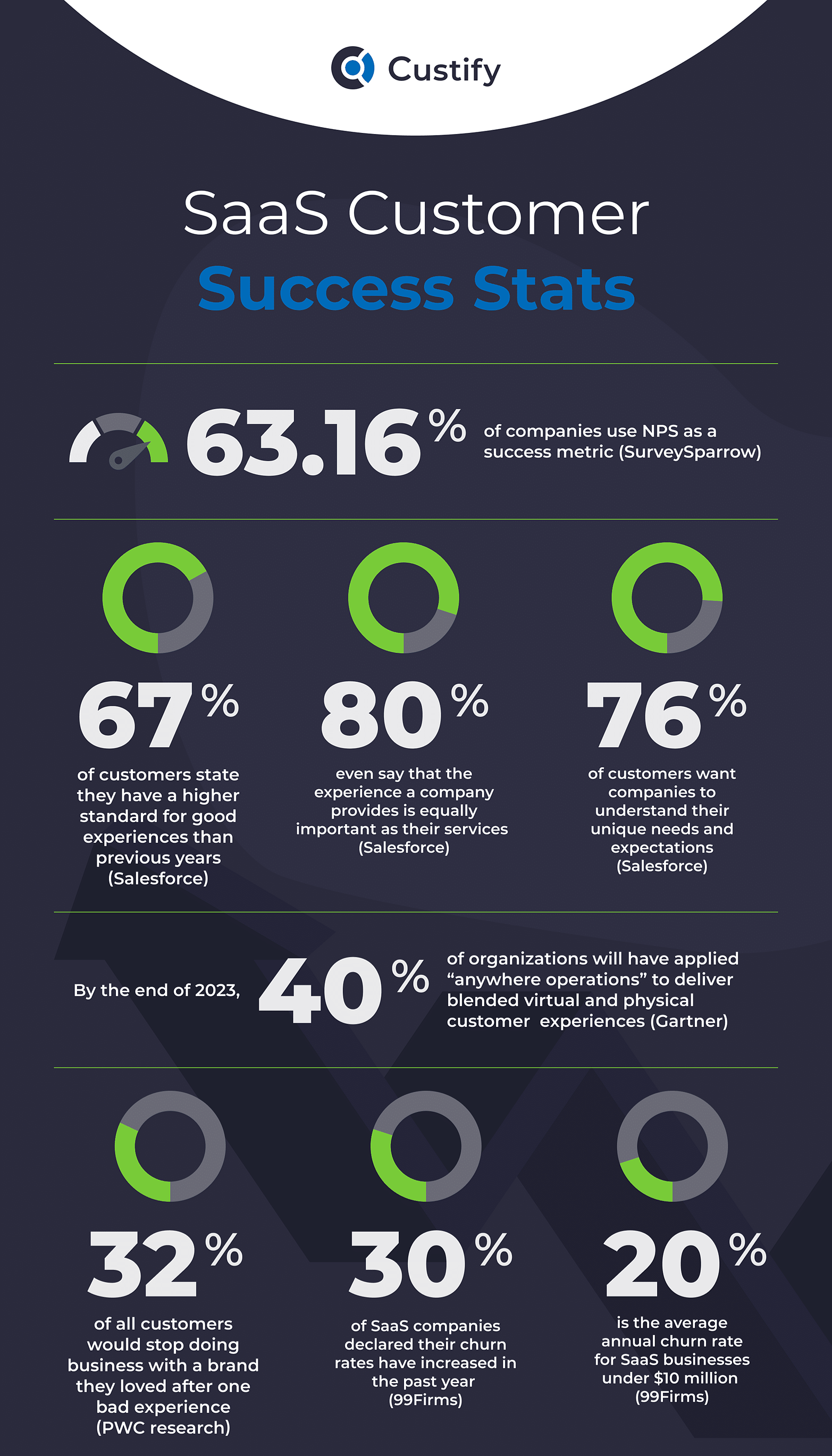
1. Customer dissatisfaction: When customer success is not prioritized, clients may not receive the necessary support and assistance to effectively use the technology or services provided. This can result in dissatisfaction, frustration, and disappointment, leading to negative feedback and potential loss of business.
2. Decreased customer retention: Neglecting customer success can lead to higher customer churn rates. Clients who do not achieve their desired outcomes or experience difficulties in utilizing the technology or services are more likely to seek alternatives or cancel their subscriptions. This can have a direct impact on revenue and profitability.
3. Damaged reputation and decreased referrals: Unsatisfied customers may share their negative experiences with others, tarnishing the reputation of the company. This can hinder new customer acquisition and reduce the number of referrals from existing customers, resulting in missed growth opportunities.
4. Reduced competitive advantage: Customer success plays a vital role in maintaining a competitive edge. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors, enhance their brand reputation, and attract new customers. Failing to prioritize customer success may result in losing this advantage and struggling to stay ahead in the market.
5. Missed cross-selling and upselling opportunities: When customers achieve success with a particular technology or service, they are more likely to explore additional offerings or upgrades. By neglecting customer success, companies may miss out on valuable cross-selling and upselling opportunities, impacting revenue growth potential.
6. Increased support costs: Inadequate customer success efforts can lead to a higher volume of customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests. This places an additional burden on customer support teams, increasing costs associated with resolving issues and providing assistance.
7. Lack of customer insights: Prioritizing customer success allows companies to gather valuable feedback, insights, and data regarding customer needs, pain points, and expectations. Without these insights, businesses may struggle to make informed decisions, improve their products or services, and effectively address customer concerns.
Overall, not prioritizing customer success can have significant detrimental effects on customer satisfaction, retention, reputation, revenue, and overall business growth. It is crucial for companies in the technology service and professional service industries to recognize the importance of customer success and invest in strategies and resources to ensure their clients achieve their desired outcomes.
Example
One notable real-life example of the risks of not prioritizing customer success is the case of BlackBerry (formerly Research In Motion), a once-prominent player in the mobile technology industry.
BlackBerry was a leading smartphone manufacturer and provider of mobile services in the early 2000s. However, as the industry evolved, BlackBerry failed to adapt quickly and neglected to prioritize customer success. Here’s how it played out:
Lack of customer-centric innovation:
BlackBerry initially gained popularity for its secure messaging and email capabilities, targeting professionals and business users. However, as smartphones became more advanced and app ecosystems flourished, BlackBerry’s devices and operating system fell behind in terms of user experience, app availability, and touchscreen technology. They failed to address the changing preferences and needs of their customers.
Customer dissatisfaction and declining market share:
As competitors such as Apple’s iPhone and Android devices gained traction, BlackBerry users began to experience frustrations with the outdated technology, limited app selection, and clunky user interface. The lack of customer success initiatives left users feeling dissatisfied, leading to a decline in customer loyalty and a loss of market share.
Missed opportunities and revenue decline:
BlackBerry’s failure to prioritize customer success resulted in missed opportunities for cross-selling and upselling. They did not invest in app development, ecosystem expansion, or significant improvements to their devices to meet evolving customer demands. As a result, BlackBerry lost potential revenue from customers seeking newer, more feature-rich smartphones.
Damaged reputation and brand perception:
BlackBerry’s inability to keep up with the competition and address customer needs negatively impacted their reputation. Dissatisfied customers shared their experiences, and the perception grew that BlackBerry was no longer a desirable choice. This tarnished their brand and made it difficult for them to attract new customers.
Market irrelevance and decline:
Ultimately, BlackBerry’s failure to prioritize customer success, adapt to changing market dynamics, and deliver a compelling user experience led to a significant decline in their market position. They went from dominating the smartphone industry to becoming a niche player with dwindling market share.
This example highlights the risks of not prioritizing customer success. BlackBerry’s failure to listen to customer needs, innovate, and deliver a satisfying user experience resulted in declining sales, loss of market share, damaged reputation, and ultimately, their diminished relevance in the industry. It serves as a reminder of the importance of putting customers’ success and satisfaction at the forefront of business strategies in the technology service industry.

How to Deliver What Your Customers Really Want
Contrary to what might seem obvious, your customers (and in particular your business customers) do not purchase your solution because they like or want it. Businesses do not tend to make decisions based upon desire, but upon need. It’s not your product or your service that they want, it’s the things your solution can do for them that they want. What they want is results.

Source: www.sixteenventures.com
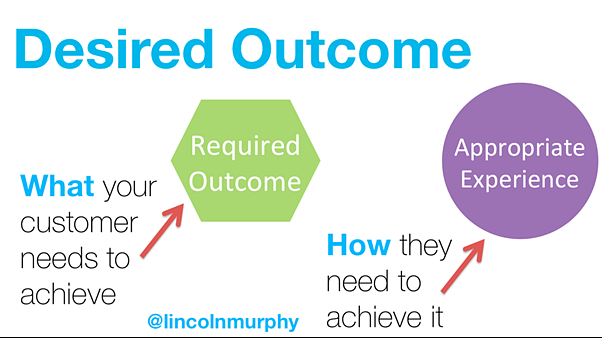
In the field of Customer Success Management these results are often referred to as customer outcomes, or simply “outcomes”, and the maximization of your customers’ outcomes is precisely what Customer Success Management is designed to provide. This is done by a series of interventions that are designed to help your customers at each stage in their “customer journey”. The “customer journey” begins when the customer recognizes a need for something you sell and identifies you as a possible supplier of that solution. Customers then go through a series of pre-sales journey stages, ending up at the contract negotiation stage.
However, for most customers the real journey is only now beginning. Now they own your solution they need to go through the stages of onboarding (understanding what they have purchased), adoption (absorbing your solution into the day-to-day operations of their business), and value realization (gaining the value required from their initiative so that they attain their outcomes).
These stages of onboarding, adoption, and value realization are essential for the Customer. Done well it will mean that they attain their goals and can report back on a successful initiative. Done poorly, targets may be missed and the customer may find themselves to be dissatisfied with their initiative and with the selection of your solution to help them with it.
Customer Success Management is all about giving customers what they really want – outcomes. By following a best practice framework, Customer Success Managers lead and guide customers through the stages of onboarding, adoption, and value realization, using tried and tested best practice processes, tools and methodologies to do so. Customers will come to rely upon their Customer Success Manager to provide this guidance and assistance to them. In doing so, loyal trust relationships are created between buyer and supplier that will help to make your customer come back to you time and again for more help with their business needs.
In short, customers do not just want a product, they want a service – a service that includes the help they need to extract the maximum value from that product as quickly as possible and for as long as possible. By providing Customer Success Management, you position your company not just as a supplier, but as a value added business partner.
How Accenture gave their customers what they really needed
An example of a company that successfully gave customers what they wanted in the professional services industry is Accenture, one of the world’s leading consulting and professional services firms.
Accenture recognized the evolving needs and demands of their clients and proactively adapted their services to meet those requirements. Here’s how they achieved it:
Embracing digital transformation:
Accenture understood the growing importance of digital technologies and their impact on businesses. They invested heavily in building expertise in areas such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, data analytics, and cybersecurity. By doing so, they positioned themselves as a trusted advisor for clients seeking to navigate the complexities of digital transformation.
Industry specialization:
Accenture identified the need to offer specialized knowledge and expertise tailored to specific industries. They established dedicated industry practices, such as financial services, healthcare, energy, and consumer goods. This industry-focused approach allowed them to understand the unique challenges and opportunities faced by their clients and deliver tailored solutions.
Client collaboration and co-creation:
Accenture adopted a collaborative approach with clients, working closely with them to understand their goals, challenges, and desired outcomes. They involved clients in the solution design process, encouraging co-creation and ensuring that the services provided truly addressed their specific needs.
Agility and flexibility:
Accenture recognized the importance of agility in a rapidly changing business environment. They developed flexible service models that could adapt to client requirements. This included offering a range of engagement options, such as strategic consulting, implementation support, managed services, and ongoing support, based on the client’s unique circumstances and objectives.
Thought leadership and knowledge sharing:
Accenture invested in thought leadership initiatives to provide valuable insights and research to their clients. They published reports, white papers, and articles on emerging trends, industry challenges, and best practices. This demonstrated their expertise and commitment to staying at the forefront of industry knowledge, while also empowering clients with valuable information.
Continuous learning and upskilling:
Accenture recognized the importance of upskilling their workforce to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving industry. They established robust training and development programs to ensure their consultants had the necessary skills and expertise to deliver high-quality services to clients. By investing in their employees, Accenture was able to provide superior service and expertise to their clients.
Through their customer-centric approach and focus on understanding client needs, Accenture has established itself as a trusted partner for businesses seeking professional services. By adapting to changing market demands, industry specialization, collaboration, and thought leadership, they have been able to deliver services that align with the evolving needs of their clients, helping them achieve their business objectives and drive growth.
This example illustrates the significance of understanding customer needs, adapting services to meet those needs, and fostering strong partnerships in the professional services industry to provide value and achieve customer success.
Curriculum
Customer Success – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Customer Needs
- Part 1 Month 2 Customer Success
- Part 1 Month 3 Business Transformation
- Part 1 Month 4 Customer Experience
- Part 1 Month 5 Determining Value
- Part 1 Month 6 Your Vision
- Part 1 Month 7 Customer Segmentation
- Part 1 Month 8 Customer Journeys
- Part 1 Month 9 Capability Refinement
- Part 1 Month 10 First Hire
- Part 1 Month 11 Developing Strategy
- Part 1 Month 12 Measuring Progress
Customer Success – Part 2 – Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Customer Success Fundamentals
- Part 2 Month 2 Phase 1: Preparation
- Part 2 Month 3 Phase 2: Onboarding
- Part 2 Month 4 Phase 3: Adoption Planning
- Part 2 Month 5 Phase 4: Adoption Implementation
- Part 2 Month 6 Phase 5: Customer Value Realization
- Part 2 Month 7 Phase 6: Supplier Value Maximization
- Part 2 Month 8 Phase 7: Engagement Evaluation
- Part 2 Month 9 CS Operations
- Part 2 Month 10 Scaling CS
- Part 2 Month 11 Automating CS
- Part 2 Month 12 Customer Communities
Customer Success – Part 3 – Year 3
- Part 3 Month 1 Business Capabilities
- Part 3 Month 2 Executive Relevance
- Part 3 Month 3 Proactive Consulting
- Part 3 Month 4 Discovery Workshops
- Part 3 Month 5 People Management
- Part 3 Month 6 Change Management
- Part 3 Month 7 Project Management
- Part 3 Month 8 Measurement and Reporting
- Part 3 Month 9 Existing Customers
- Part 3 Month 10 Creative Problem Solving
- Part 3 Month 11 Combined Revenue Operations
- Part 3 Month 12 Product Development
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Customer Success Management corporate training program.
Customer Success – Part 1 – Year 1: Business Transformation
Year One is primarily about strategy and planning. In this first year we go on a voyage of discovery, starting with the modern relationship between technology suppliers and their customers and looking at the changes, trends, and desires around this topic. Then we move to an analysis of the impact of Customer Success Management within the business and start to calculate the potential value a Customer Success Management function might be able to create. After the need for and likely value of Customer Success Management has been firmly proven, we then turn to the creation of a vision and strategy for it, via a profound understanding of the current and desired Customer Journey each customer segment undergoes. We end Year One by determining initial hire requirements, documenting the initial strategy, and reviewing potential measurement ideas.
- Part 1 Month 1 Customer Needs – Our first module introduces participants to the fundamental shifts in requirements and consumption patterns in technology acquisition and utilization by modern businesses. It explains how the need for agility to keep pace with change and the desire for reduced risk as well as improved cash flow from staged payment plans has driven the “as-a-service” consumption model. It describes the requirements of potential customers for technology suppliers to go beyond selling high quality products and services and instead to focus on selling outcomes. It provides participants with the tools to determine these impacts on their own business and invites them to consider the relevancy of these shifts to themselves and their customers and prospects.
- Part 1 Month 2 Customer Success – The second module focuses on the “customer journey” and in particular on the post-sales aspects of that journey. It builds upon the realization from Module 1 of the need for technology suppliers to provide services that deliver outcomes by examining how this can actually be achieved. This module serves as an introduction to key Customer Success concepts and philosophies and helps participants to start thinking about how Customer Success Management might fit within their own organization.
- Part 1 Month 3 Business Transformation – Module Three is more practical in nature. In this module, participants start to think about the impact to their business of moving from products and services-led customer engagements where the focus is technical and on features and capabilities, to business outcomes-led ones where the focus is on strategic and tactical business value and ROI. It enables participants both to consider the wider picture in terms of the impacts on all departments and functions within the organization, and the more specific aspects of implementing a dedicated Customer Success Management team. By the end of this module participants will be able to list and describe these impacts as they relate to their own business.
- Part 1 Month 4 Customer Experience – There is often some confusion between Customer Experience (CX) and Customer Success (CS). In truth both are important concepts for modern Technology suppliers to get right within the business strategy. This module compares and contrasts both CX and CS and enables participants to clarify the differences between them and to ascertain how they currently fit together within the context of their own specific business and how this might be amended to create the ideal overall experience for customers whilst maximizing revenue opportunities and controlling costs.
- Part 1 Month 5 Determining Value – In Module 5 we turn to the concept of value and specifically of the ROI (return on investment) that Technology suppliers might be able to attain from an investment in Customer Success Management. Use is made of case studies and simple “rule of thumb” tools to enable participants to think about and start to calculate and demonstrate to business decision makers the potential short, medium, and long-term benefits that might accrue from the implementation of a Customer Success Management initiative within their own organization.
- Part 1 Month 6 Your Vision – For Module 6 our focus moves to the development and documentation of a Customer Success Vision that complements and supports the pre-existing corporate vision and the main strategies and core initiatives within the business that support its fulfilment. This Customer Success Vision is effectively a “Statement of Intent” for the role and purpose of Customer Success Management within the company and sets out at a high level the role and the outcome expectations from Customer Success Management over the coming years. All future decision making within the Customer Success team should reference this Customer Success Vision.
- Part 1 Month 7 Customer Segmentation – For most businesses, customers (or clients) come in a variety of shapes and sizes. If you have a large portfolio of products and services then it is entirely likely that you can provide your customers with a wide range of solutions to a variety of quite different challenges or problems faced by your customers. Similarly, if you have a complex product then it might be adaptable to meet a number of quite different challenges or problems faced by your customers. Segmenting customers by their requirements helps the CS team to understand the entire range of Customer Success-related needs that your clients will have, and therefore what Customer Success capabilities you need to create.
- Part 1 Month 8 Customer Journeys – The Customer Journey is a very important concept within the context of Customer Experience (CX). It could be defined as being a representation of the entire experience that a client has of interacting with their supplier throughout their relationship with it. To do this, the Customer Journey is broken down into major phases and ultimately into individual touchpoints (activities or events where the customer comes into contact with the company in some way). These are then documented alongside a description of the actual experience customers undergo (ie how positive or negative it was) at each touchpoint. This documentation provides powerful insight into the existing relationship between the supplier and its customers, which of course becomes a stepping stone for enabling improvement.
- Part 1 Month 9 Capability Refinement – Having documented finally to analyze this research to determine both overall and specific strengths and weaknesses. The information provided by this exercise can then be used as guidance for both strategic and tactical decision making around the deployment of new services and improvement of existing services, including of course those that are or will be delivered by the Customer Success Management team.
- Part 1 Month 10 First Hire – The type and nature of a company’s first Customer Success Management hire will be determined by a number of factors relating to the company’s age, maturity, existing capabilities, and core strategic requirements. Each factor that might impact this decision will be carefully discussed and considered, and by the end of the module, students will have been provided with the tools and expertize to make a high quality “first hire” decision for their own organization.
- Part 1 Month 11 Developing Strategy – Once the “first hire” is in place, the initial focus of their role is to work closely with the senior leadership team to develop a fully-fledged Customer Success Strategy for the organization. This strategy is based upon the role and outcome expectations that have already been documented within the Customer Success Vision. The purpose of the Customer Success Strategy is to set out at a sufficiently detailed level, the core tasks and methodologies for how the Customer Success Management will go about the fulfilment of the Customer Success Vision’s outcome requirements. By the end of the module, students will know what their own organization’s Customer Success Strategy should include and be confident about how they can go about the completion of its documentation.
- Part 1 Month 12 Measuring Progress – The final module for Year One focuses on the important topic of measurement. In the words of Peter Drucker “You can’t manage what you don’t measure”. Meaningful measurement is therefore essential to any department or business function in order to be able to manage it, report on it and refine and improve its performance over time. This module will review all of the most commonly used KPIs for measuring Customer Success Management, including how to perform the measurements and calculations, the pros and cons of each KPI, and the most common pitfalls and stumbling blocks that are encountered when using them.
Customer Success – Part 2 – Year 2: Value Generation
In Year Two the focus moves away from pure strategy and planning and towards practical implementation and management. We kick off with an overview of the tasks and activities associated with Customer Success Management and then we spend the next seven modules taking a deep dive into the Practical CSM Framework, taking one module for each phase of the framework. Each of these modules prepares students for both managing and fulfilling the Customer Success Management role, and is therefore relevant both to managers and individual practitioners alike. The final four modules provide practical overviews for how to support, scale, automate, and finally measure the ROI from the Customer Success Management department that has by now been created and implemented.
- Part 2 Month 1 Customer Success Fundamentals – Before diving into the detail, it is always a good idea to get a sufficient understanding of the overall situation, and this is the purpose of Module 1. In this module we overview the entirety of the role of Customer Success Management, preparatory to undergoing the series of “deep dives” into each major phase of the CS journey in upcoming modules. This “scene setting” provides context for the learning to come and provides students with sufficient understanding of the overall role of Customer Success Management to understand how each component fits and why, when, and how it is important.
- Part 2 Month 2 Phase 1: Preparation – This module takes a deep dive into the first of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 1: Preparation, the core activities and process steps for preparing the CSM through the appropriate research, analysis and planning to meet and engage with a new customer are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 3 Phase 2: Onboarding – This module takes a deep dive into the second of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 2: Onboarding, the core activities and process steps for meeting and engaging with a new customer and gaining their trust and consent to work with them to deliver maximum value are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 4 Phase 3: Adoption Planning – This module takes a deep dive into the third of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 3: Adoption Planning, the core activities and process steps for helping the customer’s key stakeholders to determine their outcome requirements and current situation and then develop a Success Plan for attaining maximum value from their initiative are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 5 Adoption Implementation – This module takes a deep dive into the fourth of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 4: Adoption Implementation, the core activities and process steps for helping the customer’s key stakeholders to implement and project manage their Success Plan for attaining maximum value from their initiative are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 6 Customer Value Realization – This module takes a deep dive into the fifth of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 5: Customer Value Realization, the core activities and process steps for helping the customer’s key stakeholders to determine appropriate KPIs, take regular measurements, and analyze and report on progress towards outcome attainment from their initiative are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 7 Supplier Value Maximization – This module takes a deep dive into the sixth of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 6: Supplier Value Realization, the core activities and process steps for ongoing relationship enhancement and building customer closeness, for building new revenue streams within the customer organization and for maximizing existing revenue streams, for obtaining customer advocacy in various forms and styles, and for gaining greater customer assistance with product development are reviewed and explained, and students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 8 Phase 7: Engagement Evaluation – This is the final module in the series, and it takes a deep dive into the seventh of seven phases within the Practical CSM Framework. In Phase 7: Engagement Evaluation, the student is invited to take a step back from their day-to-day activity with each individual customer and instead to examine the tasks and process steps relating to measuring, analyzing, reviewing and improving their capabilities as a CSM and reviewing and improving the health of the relationships between their own company and each of the customers they are responsible for. As before, students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises. This hands-on day ensure that by the end of the training students clearly understand the expectations for CSMs during this phase and how to apply those within their own individual role requirements
- Part 2 Month 9 CS Operations – In this module the specific role of Customer Success Management Operations (CS Ops) is defined and explained. Students are shown the importance of CS Ops in supporting the quality, productivity, and scalability of the overall CS team. The common tasks for a CS Ops team are defined and described, and time within the module is spent considering the specific needs of the students’ own CS team for the support of CS Operations. As before, students are given the opportunity to try out these activities in a series of role play and scenario-based exercises.
- Part 2 Month 10 Scaling CS – In Module 10 students get to review and discuss the need for scaling Customer Success Management to deliver CS services to all customer segments, and the relative pros and cons of doing so. A pragmatic debate is held around types and levels of Customer Success Management services and in particular the dichotomy between value and cost is explained and reviewed in the context of the students’ own company and its customer segmentation strategy. By the end of this module, students are positioned to understand the options for scaling CS services and how to decide when and where it would be appropriate to do so.
- Part 2 Month 11 Automating CS – One of the key ways in which the cost of delivery of Customer Success management services can be controlled and even reduced is through digitalization and automation. As it happens, automated services can not only reduce costs, but sometimes they can also help to actually improve the quality and perceived value of the Customer Success management service as seen through the eyes of the customer. Module 11 examines how the students’ organization can plan and prepare for the automation of aspects of both existing and newly planned for Customer Success Management services, and then deliver and measure the ROI from those automated services on an ongoing basis.
- Part 2 Month 12 Customer Communities – In the final module for Year Two, the focus moves to the concepts and practical considerations relating to developing, implementing, and then managing one or more Customer Communities. This module starts by assessing the need for Customer Communities and the types of value they return for both customers and suppliers. It then provides step-by-step guidance for planning for and then launching the first Customer Community, including discussion around common pitfalls and challenges, and how to deal with them. The discussion and exercises then move to the ongoing management (including measurement) of Customer Communities, and again the tasks and steps required are listed and reviewed for students to learn and try out.
Customer Success – Part 3 – Year 3: Beyond Customer Success
In Year Three we can start to build upon the strong foundations of strategic planning in Year One and strong implementation and management in Year Two. In Year Three we review both vision and strategy in the light of new information uncovered overed the past two years and where necessary refine, amend, drop, and adopt new CS initiatives and capabilities to meet the currently understood needs of the business. We then focus on refining and improving the core skills and capabilities needed for Customer Success excellence, starting with executive relevance in Module 2 and moving through the various required capabilities to end with Customer Success-driven product development in Module 12.
- Part 3 Month 1 Business Capabilities – Time and again, Customer Success management teams fail to engage successfully (or as successfully as they could do) with senior decision makers, simply because they lack an awareness of the perspective of the world from a senior decision maker’s viewpoint. Module One focuses on helping CSMs understand the perspective of the senior leadership team through learning about their world. Module One goes right to first principles with discussions on and examples of vision, strategies, initiatives, and capabilities, and how each of these is grown or developed from the previous one. Practical concerns around time to value (TTV) and shareholder support are also discussed and examined.
- Part 3 Month 2 Executive Relevance – Module Two follows directly from Module One. Where Module One examined the world from the perspective of the senior decision maker, Module two looks at how CSMs can make themselves relevant to that perspective through their discussions, reports, and actions. The focus of Module Two is to help the CSM fit into the world of the senior executive and make themselves not just useful but indispensable through the support and guidance they provide.
- Part 3 Month 3 Proactive Consulting – The principal job of the consultant is to consult. To consult means to ask questions, to analyze the answers and then to come up with a report detailing the consultant’s recommendations regarding whatever it is they have been consulted on. This report needs to provide the consultee with the information they need to be able to reach their decision about what to do. Module Three examines this consultative relationship in the context of Customer Success management and explains how CSMs can use consultative best practices to deliver high quality best practice advice and guidance to their customers.
- Part 3 Month 4 Discovery Workshops – Meetings in general and discovery workshops in particular are fundamental tools used by consultants of all types to interact with customer stakeholders. CSMs often need to use these tools to work with a range of stakeholders on outcome requirements, current and planned capabilities, strategic and tactical priorities, and in-depth situational analysis. The outputs from meetings and workshops can include documentation of the situation, formation of consensus agreements, commitments on roles and responsibilities, and many others. This module provides the best practice processes of determining meeting outcomes and content, writing, and distributing the agenda, determining, inviting, and managing attendees, resolving disputes, encouraging creative problem solving, and meeting administration and management and record keeping.
- Part 3 Month 5 People Management – Business are legal entities, but it’s people (human beings) that actually get the work done. People are not all the same. They have emotions, desires, affiliations, beliefs, and prejudices. Different people need to be handled in different ways in order to attain the required results. This module focuses on helping CSMs to understand the different types and styles of personalities and how these can be best managed through the adoption of tried and tested, best practice management and leadership skills and techniques.
- Part 3 Month 6 Change Management – In purchasing and adopting the CSM’s company’s solution, the customer organization will undergo some level of change. Change by its nature is often uncomfortable and difficult to deal with, and often results in loss of productivity. An important aspect of the CSM’s role is to understand how individuals and teams are impacted by change, and what best practice processes in the field of change management can be applied to reduce the negative impacts from the undergoing of change in order to get to value creation as quickly and efficiently as possible. This module will provide students with a deep dive into change management best practice and how to apply it to the role of Customer Success Management.
- Part 3 Month 7 Project Management – Once the client has developed a Success Plan for their initiative they then have to move from the planning stage to the implementation stage. This is where Project and Program Management best practices come to the fore. This module gives students a deep dive into “Project Management 101”. It helps them to apply project management tools, processes, and best practices to a wide range of Customer Success Management challenges and problems to help customers overcome these issues and get to “value” as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Part 3 Month 8 Measurement and Reporting – In the words of Peter Drucker (a world-famous management consultant) “What does not get measured does not get managed”. Module 8 reviews the concepts and theories behind selecting and using Key Performance Indicators both to measure and track actual performance and (equally essentially) to provide forward-looking analyses to predict future trends and growth patterns. care is taken in this module to ensure students understand how to select the right KPIs for the given situation and how to measure and analyze these KPIs to provide sufficiently accurate and meaningful information for management decision making purposes.
- Part 3 Month 9 Existing Customers – Many people who are not sales professionals themselves can hold a quite negative opinion of and attitude towards the sales profession. Yet in reality the very noble professional of Sale sis a profession that helps people and companies to make the right purchasing decisions that enable their personal and corporate growth to occur. This module examines Sales best practice methodologies and looks at how these can be adapted to fit the CSM. Emphasis is placed on needs analysis, storytelling, presenting, negotiating, and closing deals within the context of renewals, upsells and cross-sells with existing customers, as these are commonly the responsibility of CSMs.
- Part 3 Month 10 Creative Problem Solving – Innovation and creative problem-solving fall somewhere between an art and a science. Whilst the creative impulse is by its nature unbounded by process, managers in particular can encourage innovation and creativity through the careful establishment and nurturing of a “culture of innovation” within the company or department. This module explains the different types of innovation, the concepts of Agile, the methodologies to establish an innovation culture, and the tools to manage innovation.
- Part 3 Month 11 Combined Revenue Operations – The last decade has seen the rise of the Chief Revenue Officer (CRO), who is increasingly tasked with oversight of all revenue generation activities including marketing (attracting new and existing prospects), selling to new customers (net new revenue generation) and customer success management (renewals, upsells and cross-sells). Putting all of these activities under one umbrella can make a lot of strategic sense. However, in doing so it underlines and re-emphasizes the critical need for Sales, Marketing and Customer Success Management functions to co-ordinate, to collaborate, and to share data and resources as much as possible. This module focuses on how this can be achieved.
- Part 3 Month 12 Product Development – Whilst the majority of Customer Success Management activities focus on working with individual customers to generate and realize maximum value for both the client and the supplier, it is also true to say that CSM should most definitely play an active role in helping the Product team to design new versions of existing products and even entirely new products to meet the new and ever-changing needs of the company’s customers. The final module in our series examines this role and provides best practice guidance for how CSMs can add potentially a lot of value within the product development lifecycle.
Methodology
Customer Success
Why Customer Success is Uniquely Powerful
When recommending a best practice framework for Customer Success Management, I am sometimes faced with a business leader who objects because they believe that their company is uniquely different to other businesses, and so a best practice framework will not really fit their requirements. Whilst it is true to say that in fact all businesses are unique to some extent, it is also true to say that all (or at least the vast majority of) businesses follow certain well-established similarities. For example, all businesses have employees, all businesses have owners (or investors), all businesses provide one or more products and services, all businesses have to market and sell those products and/or services, and all businesses need to support their existing customers after the purchase has been made.
In other words, whilst a business might be unique in the details (precisely what it sells, precisely who it sells to, precisely where it operates, etc) in fact the differences between itself and other well managed companies are actually probably quite minor compared to its similarities.
Source: www.custify.com
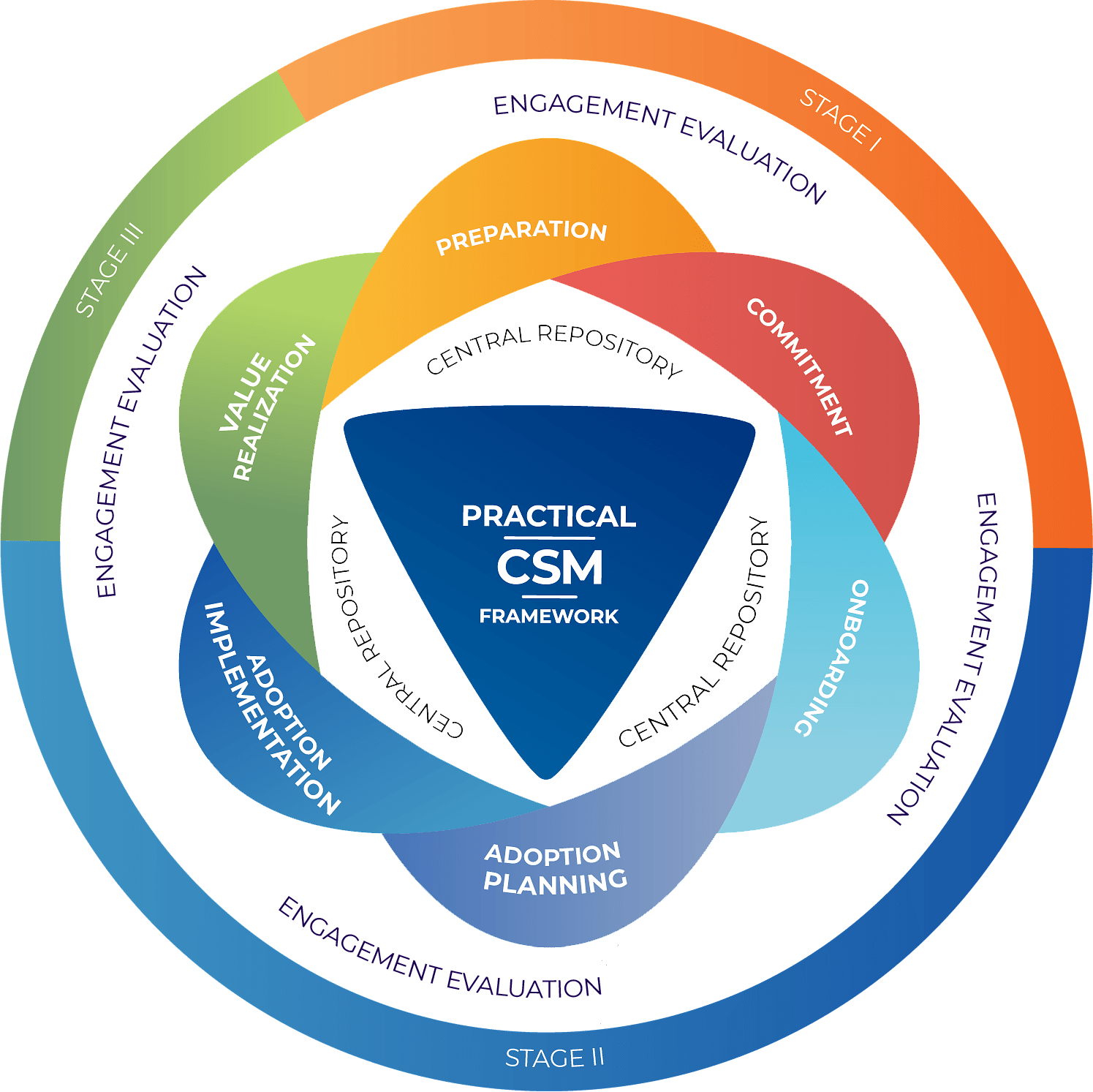
This is why this Customer Success Management training program is so uniquely powerful. Within this program lies the Practical CSM Framework. The Practical CSM Framework (now in its second iteration) is the de facto best practice methodology and toolset for modern Customer Success Management. It divides a “typical” post-sales customer engagement into seven phases, and provides training, advice, tools and process steps for each phase. There may be some minor customization to be done to make this process fit exactly within your organization, but at most this is likely to be 10% to 20%, saving you 80% to 90% of hard work to get you to the same position, whilst simultaneously ensuring that the destination you arrive at is one that utilizes high quality, tried and tested best practices that are already known to work well.
By attending this Customer Success Management program, you will position yourself not just to understand the Practical CSM Framework but also to actually implement it and where necessary customize it to meet your specific needs.
Source: www.practicalcsm.com
The seven phases of the Practical CSM Framework are as follows:
1. Assess: In this phase, CSMs assess the current state of the customer and their desired outcomes. They gather information about the customer’s business goals, pain points, and expectations to understand how the organization can best support them.
2. Define: CSMs work with the customer to define clear and measurable goals for success. This phase involves setting key performance indicators (KPIs), determining benchmarks, and establishing a shared understanding of what success looks like for the customer.
3. Plan: CSMs collaborate with the customer to create a comprehensive success plan. This plan outlines the specific actions, milestones, and strategies required to achieve the defined goals. It serves as a roadmap for both the customer and the CSM to work towards success.
4. Execute: In the execution phase, CSMs implement the success plan and support the customer throughout their journey. They provide guidance, training, and resources to help customers adopt and maximize the value of the product or service.
5. Measure: CSMs track and measure the customer’s progress towards their defined goals. They monitor relevant metrics, analyze data, and evaluate the customer’s overall health and satisfaction. This phase enables CSMs to identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions.
6. Renew: The renewal phase focuses on ensuring customer retention and renewal of contracts. CSMs engage with customers to reinforce the value delivered, address any concerns, and identify opportunities for expansion or upselling. They work towards building long-term partnerships and maximizing customer lifetime value.
7. Expand: In the final phase, CSMs proactively identify opportunities for growth and expansion within the customer account. They leverage their understanding of the customer’s needs and business objectives to introduce additional products or services that can further support their success.
These seven phases provide a structured approach for CSMs to guide their interactions with customers, from initial assessment to long-term expansion. By following this framework, organizations can enhance their customer success efforts and build strong, mutually beneficial relationships with their customers.
How the Customer Success Management Framework works
Source: www.dalet.com
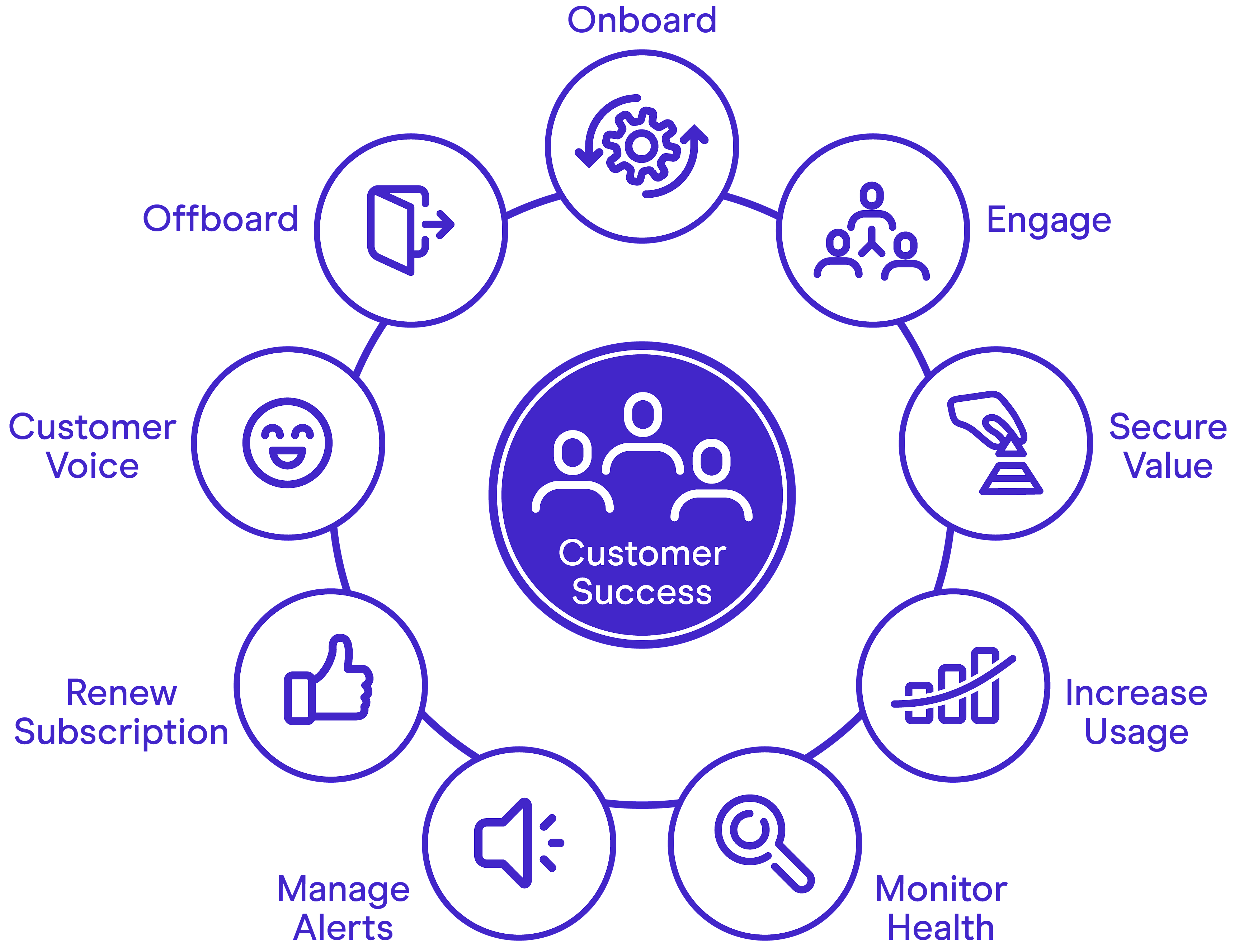
As discussed, the Practical Customer Success Management (CSM) Framework is a structured approach that guides companies in effectively managing and driving customer success. It provides a framework for understanding customer needs, aligning business goals with customer outcomes, and delivering value throughout the customer journey. While specific frameworks may vary across organizations, here is a general outline of the Practical CSM Framework:
Define success criteria: Clearly articulate the desired outcomes and success criteria for your customers. Work closely with them to understand their goals, challenges, and expectations. This step helps establish a shared understanding of what success looks like.
Onboarding and implementation: Develop a comprehensive onboarding process to ensure a smooth transition for customers. Provide the necessary resources, training, and support to help them successfully implement and adopt your product or service.
Proactive relationship management: Assign dedicated Customer Success Managers (CSMs) to build strong relationships with customers. CSMs serve as trusted advisors, regularly engaging with customers to understand their evolving needs, provide guidance, and address any concerns or issues.
Continuous value delivery: Regularly assess and track customer progress towards achieving their desired outcomes. Identify areas where you can deliver additional value and provide recommendations for improvement. This involves proactive monitoring, data analysis, and ongoing communication with customers.
Adoption and product usage: Monitor customer adoption and usage of your product or service. Identify potential roadblocks or areas where customers may be underutilizing the solution. Offer guidance, training, and resources to encourage full product utilization and drive value realization.
Customer health assessment: Develop a system for assessing customer health and identifying potential risks or opportunities for improvement. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure customer satisfaction, engagement, retention, and expansion potential.
Proactive communication and education: Establish regular touchpoints with customers to communicate product updates, best practices, and relevant industry insights. Provide educational resources, webinars, and workshops to help customers maximize their success with your offering.
Escalation and issue resolution: Establish clear channels for customers to report issues and concerns. Quickly respond to and resolve customer issues, ensuring that they feel heard and supported. Utilize cross-functional collaboration to address complex challenges effectively.
Renewal and expansion: Proactively work with customers to ensure timely contract renewals. Identify opportunities for expansion and upselling based on the customer’s evolving needs and goals. Provide tailored recommendations for additional products, services, or features that can further support their success.
Continuous feedback and improvement: Actively seek customer feedback on their experience, challenges, and suggestions for improvement. Use this feedback to refine your processes, enhance product offerings, and continuously improve the customer experience.
The Practical CSM Framework emphasizes the importance of proactively managing customer relationships, understanding their needs, delivering ongoing value, and driving mutual success. By implementing this framework, companies can foster long-term customer loyalty, increase customer retention, and drive business growth.
Companies using a Customer Success Management Framework:
Several companies across various industries implement customer success management frameworks similar to the one described. Here are a few examples:
Salesforce: Salesforce, a leading customer relationship management (CRM) platform, emphasizes customer success through their “Customer Success Cloud” framework. They provide customers with personalized onboarding, dedicated success managers, and ongoing support to ensure they achieve their desired outcomes with the platform. Salesforce focuses on continuous value delivery, adoption tracking, customer health assessment, and proactive communication to drive customer success.
HubSpot: HubSpot, an inbound marketing and sales software provider, follows a customer success framework called “Flywheel.” They prioritize customer delight by offering comprehensive onboarding, training resources, and ongoing support. HubSpot focuses on customer health monitoring, continuous value delivery through regular product updates, and proactive communication to nurture strong customer relationships and drive growth.
Gainsight: Gainsight is a customer success platform that helps companies manage and drive customer success. Their framework encompasses elements such as onboarding and implementation, proactive relationship management, customer health scoring, expansion and renewal strategies, and continuous feedback loops. Gainsight’s platform provides analytics, automation, and collaboration tools to enable companies to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Atlassian: Atlassian, a collaboration software company, is known for its customer-centric approach. They have a framework called “Playbooks” that guides their customer success efforts. The Playbooks focus on onboarding, customer engagement, value realization, feedback collection, and proactive support to ensure customers achieve their desired outcomes.
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS, a cloud computing provider, emphasizes customer success through their “AWS Customer Engagement Framework.” It includes an extensive onboarding process, continuous support and guidance, technical expertise, and proactive customer engagement to drive success and help customers maximize the value of their cloud services.
These are just a few examples of companies that prioritize customer success and adopt frameworks similar to the Practical CSM Framework. While the specific details may vary, these companies share a common commitment to understanding customer needs, driving adoption and value, and maintaining long-term customer satisfaction through proactive relationship management and ongoing support.

How our Program Works
Each month, the senior business leaders you assign to the program will meet with our highly trained, expert consultants to undergo training. The training takes the form of a highly engaging and interactive, one day (six hours of training delivery) workshop. During each workshop, key concepts are explored, before practical exercises are used to ensure essential knowledge is embedded and that delegates have both the confidence and the competence to apply what they have learned when back in their own real-world environment.
Follow The CS Learning Process
As the program is so process-oriented, and in particular because it itself is based upon a best practice framework, the overall engagement is very logical in terms of how topics are covered, and in what order the materials are undertaken.
The first year focuses mainly on the preparation stages of planning and implementation, year two moves to value realization though management and measurement, and finally year three is where you refine, scale and improve the performance of your newfound capabilities.
Year One – Planning & Implementation
The Planning & Implementation Phase is crucially important for success. This phase sets the foundation and framework for the entire program and ensures that it aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Year One is primarily about strategy and planning. In this first year we go on a voyage of discovery, starting with the modern relationship between technology suppliers and their customers and looking at the changes, trends, and desires around this topic. Then we move to an analysis of the impact of Customer Success Management within the business and start to calculate the potential value a Customer Success Management function might be able to create. After the need for and likely value of Customer Success Management has been firmly proven, we then turn to the creation of a vision and strategy for it, via a profound understanding of the current and desired Customer Journey each customer segment undergoes. We end Year One by determining initial hire requirements, documenting the initial strategy, and reviewing potential measurement ideas.
Here are some key reasons why the Planning & Implementation Phase is vital:
1. Clear Program Objectives: During this phase, you define the objectives and outcomes you want to achieve with your CSM program. This includes identifying the key metrics to measure success, such as customer retention, expansion, and satisfaction. Establishing clear objectives enables you to align the program with the organization’s strategic goals and ensure everyone understands what needs to be achieved.
2. Stakeholder Alignment: The Planning & Implementation Phase allows you to involve key stakeholders from various departments, including sales, marketing, product, and customer support. By engaging these stakeholders early on, you can gather their input, address concerns, and gain buy-in for the program. This alignment is crucial for the program’s success and ensures cross-functional collaboration and support.
3. Resource Allocation: During this phase, you determine the necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and technology, required to implement and run the CSM program. It involves identifying and allocating the right people with the necessary skills and expertise to manage customer relationships effectively. Adequate resource allocation is critical to ensure the program can be executed efficiently and deliver the desired results.
4. Customer Segmentation and Onboarding: The Planning & Implementation Phase involves segmenting your customer base and determining the appropriate onboarding processes for each segment. It helps identify which customers need more attention and tailor engagement strategies accordingly. Effective customer onboarding lays the foundation for long-term success by ensuring customers fully understand the value of your product or service and are set up for success.
5. Process and Workflow Design: This phase includes designing and documenting the processes, workflows, and best practices for managing customer relationships. It involves defining touchpoints, communication channels, escalation procedures, and other operational aspects of the CSM program. A well-defined process helps streamline customer interactions, promotes consistency, and enables scalability as the program expands.
6. Technology Evaluation and Integration: Planning & Implementation Phase allows you to evaluate and select the appropriate technology stack for your CSM program. This may include customer relationship management (CRM) systems, customer success platforms, analytics tools, and communication platforms. Integrating these technologies seamlessly is crucial to enable efficient data management, automation, and proactive customer engagement.
By investing time and effort in the Planning & Implementation Phase, you lay a solid foundation for your CSM program, increasing the chances of its success. It ensures clarity, alignment, and effective resource allocation, setting the stage for providing exceptional customer experiences and driving long-term customer satisfaction, retention, and growth.
Year Two – Value Realization
In Year Two the focus moves away from pure strategy and planning and towards practical implementation and management. We kick off with an overview of the tasks and activities associated with Customer Success Management and then we spend the next seven modules taking a deep dive into the Practical CSM Framework, taking one module for each phase of the framework. Each of these modules prepares students for both managing and fulfilling the Customer Success Management role, and is therefore relevant both to managers and individual practitioners alike. The final four modules provide practical overviews for how to support, scale, automate, and finally measure the ROI from the Customer Success Management department that has by now been created and implemented.
The Value Realization Phase is equally important in this Customer Success Management (CSM) program as it focuses on ensuring that customers are achieving the expected value from your product or service. Here’s why the Value Realization Phase is crucial:
1. Customer Satisfaction and Retention: The Value Realization Phase aims to deliver the promised value and outcomes to your customers. By focusing on helping customers realize the value they expected, you enhance their satisfaction and increase the likelihood of long-term retention. When customers perceive tangible value and positive outcomes, they are more likely to renew their contracts, expand their usage, and become loyal advocates for your brand.
2. Maximizing Customer Success: This phase emphasizes actively working with customers to identify their goals, track progress, and overcome any obstacles in achieving those goals. It involves continuous monitoring and analysis of customer data and behavior to identify areas where customers may be struggling or underutilizing your product or service. By proactively addressing these issues and providing guidance, training, or additional resources, you increase the chances of customers realizing the full potential of your offering.
3. Upsell and Cross-sell Opportunities: The Value Realization Phase presents opportunities for identifying and pursuing upsell and cross-sell opportunities. When customers achieve initial success with your product or service, they are more likely to be receptive to expanding their usage or adopting additional features. By actively engaging with customers during this phase, you can uncover their evolving needs, understand their growth potential, and present relevant upsell or cross-sell opportunities that align with their goals and drive additional revenue for your organization.
4. Customer Advocacy and Referrals: When customers realize significant value and achieve their desired outcomes, they become enthusiastic advocates for your brand. The Value Realization Phase provides an opportunity to nurture these relationships and leverage customer success stories to drive referrals and expand your customer base. Satisfied customers are more likely to provide testimonials, refer new business, and participate in case studies or success stories, which can significantly impact your organization’s reputation and attract new customers.
5. Continuous Improvement: The Value Realization Phase involves gathering feedback from customers, analyzing their experiences, and identifying areas for improvement. By actively seeking customer insights, you can gain a deeper understanding of their evolving needs, challenges, and expectations. This feedback loop enables you to refine your product or service offerings, enhance your customer engagement strategies, and continuously improve the value you deliver.
In summary, the Value Realization Phase is critical for driving customer satisfaction, retention, and growth. It ensures that customers achieve their desired outcomes, identifies upsell and cross-sell opportunities, cultivates customer advocacy, and provides valuable insights for continuous improvement. By focusing on helping customers realize value, you establish long-term partnerships and position your organization as a trusted advisor and strategic partner.
Year Three – Refining, Scaling & Improving
In Year Three we can start to build upon the strong foundations of strategic planning in Year One and strong implementation and management in Year Two. In Year Three we review both vision and strategy in the light of new information uncovered over the past two years and where necessary refine, amend, remove, and adopt new CS initiatives and capabilities to meet the currently understood needs of the business. We then focus on refining and improving the core skills and capabilities needed for Customer Success excellence, starting with executive relevance in Module 2 and moving through the various required capabilities to end with Customer Success-driven product development in Module 12.
The Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase is highly important in this program as it focuses on continuously enhancing and expanding the program’s effectiveness and impact. Here’s why this phase is crucial:
1. Program Optimization: The Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase allows you to evaluate the performance of your CSM program and identify areas that can be optimized. By analyzing key metrics, customer feedback, and internal insights, you can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas of improvement in your processes, workflows, and strategies. This optimization ensures that your CSM program remains agile, adaptable, and aligned with evolving customer needs and organizational objectives.
2. Scalability and Growth: As your customer base and organization grow, the Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase becomes vital for scaling your CSM program effectively. It involves developing strategies and implementing systems that can handle increased customer volumes without compromising the quality of customer interactions. By optimizing and streamlining your processes, utilizing automation where appropriate, and leveraging technology, you can scale your CSM program while maintaining a personalized and high-quality customer experience.
3. Proactive Customer Engagement: During this phase, you can refine and expand your proactive customer engagement strategies. By analyzing customer data, behavior patterns, and usage metrics, you can identify opportunities to engage customers at the right time with relevant and valuable information. This proactive engagement helps address potential challenges or roadblocks, ensures customers are aware of new features or updates, and fosters a sense of continuous value throughout their journey.
4. Knowledge Sharing and Training: The Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase enables you to enhance knowledge sharing and training within your CSM team. By leveraging the experiences and best practices gathered over time, you can develop training programs, playbooks, and resources to equip your CSMs with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively manage customer relationships. This promotes consistency, enables faster onboarding of new team members, and ensures a cohesive approach to customer success across the organization.
5. Data Analysis and Insights: This phase emphasizes the importance of leveraging customer data and analytics to gain valuable insights. By analyzing customer behavior, usage patterns, and feedback, you can identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement. These insights can inform product development, marketing strategies, and customer engagement initiatives, allowing you to make data-driven decisions and deliver more targeted value to your customers.
6. Collaboration and Alignment: The Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase fosters ongoing collaboration and alignment between different departments within your organization. By regularly sharing insights, success stories, and customer feedback, you can create a culture of cross-functional collaboration and customer-centricity. This collaboration helps refine processes, align strategies, and drive a unified approach to customer success, ultimately benefiting both the organization and the customers.
In summary, the Refining, Scaling & Improving Phase is critical for the long-term success and sustainability of your CSM program. It enables program optimization, scalability, and growth while promoting proactive customer engagement, knowledge sharing, and data-driven decision-making. By continuously refining and improving your CSM program, you can ensure its relevance, effectiveness, and ability to deliver exceptional customer experiences and drive mutual success.

Is This Program Right for My Company?
Solution providers of all types are increasingly aware of the critical importance of guiding customers beyond the pre-sales journey into value realization. By providing Customer Success Management services, suppliers increase the overall ROI for their clients whilst simultaneously reducing time to value (TTV). In doing so, the technology provider enhances the customer relationships, reduces churn, increases NRR (net revenue retention) and sets themselves on a path for maximum revenue growth. My program provides a clear, process-driven methodology for researching, planning, and implementing a Customer Success Management strategy, and managing that strategy through to the attainment of measurable results.
By the end of this process, businesses who have attended the three year program will have determined whether Customer Success Management is right for their business. They will have researched and understood the customer journey for each core customer segment. They will have determined their current strengths and weaknesses in terms of capability. They will have created a top down “vision and mission” for their new Customer Success Management team.
Following this, they will have determined their initial hiring strategy and made their first specialist hire who in turn will have helped the business to flesh out a complete Customer Success Management development plan. This plan will then have been implemented and project managed to ensure the right capabilities get acquired and adopted and the Customer Success Management team is adequately staffed, funded and resourced.
As the rubber hits the road, the businesses who have followed this program will be empowered to take measurements for meaningful KPIs that enable progress towards and ultimately attainment of ROI to be captured, analyzed and presented to business decision makers. Finally, these businesses will be able to culturally adopt and consume Customer Success Management not just as an additional team or capability but as a holistic philosophy and approach to all customer interactions throughout the organization.

Your Call to Action
For companies that are prepared to invest in their Customer Success Management activities and work hard to ensure its adoption within the wider organization, the results from this program will include reductions in customer churn, increases in customer retention, expansion of customer revenues, maximization of customer loyalty, and extension of customer lifetime. Combined, these benefits will return considerable and measurable value to the business in terms both of growth and profitability. Act now by joining us on this program, and letting us help you to ensure a sustainable future for your organization and to maximize your company’s growth and profitability.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Technology
The origins of the technology sector can be traced back to the mid-20th century with the advent of electronic computers. The development of mainframe computers in the 1950s and 1960s marked a significant milestone in computing technology. Over time, advancements in hardware and software led to the rise of personal computers in the 1980s, which revolutionized the way people interacted with computers.
History
The 1990s witnessed the rapid growth of the internet and the World Wide Web, which brought about a new era of connectivity and communication. This period also saw the emergence of tech giants like Microsoft, Apple, and IBM. The early 2000s saw the dot-com bubble burst but also marked the rise of e-commerce, online services, and search engines.
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, the proliferation of smartphones and the introduction of mobile apps led to a mobile revolution. Companies like Apple and Google became dominant players in the tech industry, while social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram gained immense popularity. Additionally, cloud computing gained prominence, enabling scalable and flexible storage and processing capabilities.
Current Position
The technology sector today is characterized by constant innovation and disruption. It encompasses various subsectors such as hardware manufacturing, software development, telecommunications, artificial intelligence (AI), biotechnology, fintech, and more. Tech companies play a critical role in shaping the global economy, driving productivity, and transforming industries across sectors.
Some of the prominent trends in the current technology landscape include:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies are being widely adopted across industries, powering advancements in areas such as autonomous vehicles, natural language processing, healthcare diagnostics, and personalized recommendations.
2. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. This technology is being used in various domains, including smart homes, industrial automation, and smart cities.
3. Blockchain: Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and secure way of recording and verifying transactions. It has applications in finance, supply chain management, and digital identity verification.
4. Cybersecurity: With the increasing digitization and interconnectedness of systems, cybersecurity has become a top priority. Companies are investing in robust security measures to protect their networks, data, and user privacy.
Future Outlook
The future of the technology sector appears highly promising and dynamic. Here are a few key trends and areas of interest for the future:
1. 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks is expected to revolutionize connectivity, enabling faster speeds, low latency, and supporting emerging technologies like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and immersive augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences.
2. Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces latency and enables real-time data analysis, which is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT, and robotics.
3. Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems at an unprecedented scale. While still in its early stages, this technology holds promise for breakthroughs in cryptography, optimization, drug discovery, and more.
4. Sustainable and Green Tech: As environmental concerns grow, there is an increasing focus on developing sustainable and eco-friendly technologies. This includes renewable energy solutions, energy-efficient hardware, and responsible manufacturing practices.
5. Ethical and Responsible Tech: With the increasing influence of technology on society, there is a growing emphasis on ethical considerations and responsible use of technology. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and digital divide are gaining attention, and efforts are being made to address them.
Overall, the technology sector is expected to continue its rapid evolution, driving innovation, economic growth, and societal transformation in the years to come.

SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a model in which software is delivered over the internet, allowing users to access and use applications on a subscription basis, rather than installing and maintaining software locally on their computers. Here’s an overview of the history, current position, and future outlook of the SaaS industry sector:
History
The concept of delivering software remotely can be traced back to the 1960s with the emergence of time-sharing systems, where multiple users could access a mainframe computer remotely.
The term “Software as a Service” was coined in the early 2000s when the internet became more accessible and reliable, enabling the delivery of software applications over the web.
Salesforce, founded in 1999, is often credited as one of the pioneers of the modern SaaS industry. They introduced the concept of delivering customer relationship management (CRM) software as a service.
Current Position
The SaaS industry has experienced significant growth and has become a dominant force in the software market. It has gained popularity due to its numerous advantages, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, easy accessibility, and automatic updates.
SaaS applications cover a wide range of functionalities, including CRM, enterprise resource planning (ERP), human resources management, project management, collaboration tools, and more.
Major players in the SaaS industry include Salesforce, Microsoft (with their Office 365 suite), Adobe, Oracle, and many others. These companies offer a variety of SaaS applications to businesses and consumers.
The SaaS market has seen increased adoption across industries, from small startups to large enterprises, due to its flexibility and ability to cater to diverse business needs.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of SaaS solutions, as remote work became more prevalent and organizations sought cloud-based tools for collaboration and productivity.
Future Outlook
The SaaS industry is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. According to various reports, the global SaaS market is projected to reach substantial revenues and expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
The increased focus on digital transformation, remote work, and cloud-based technologies is likely to drive further adoption of SaaS applications.
As SaaS offerings become more specialized, we may see a rise in niche SaaS providers catering to specific industries or solving specific business challenges.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in the future of SaaS. These technologies can enhance automation, data analysis, and personalized user experiences within SaaS applications.
Security and data privacy will continue to be crucial concerns for SaaS providers and users, with an increasing emphasis on robust security measures and compliance with regulations like GDPR.
Overall, the SaaS industry has transformed the software landscape, offering accessible and scalable solutions to businesses and consumers. With ongoing advancements and evolving market demands, the future of the SaaS sector appears promising.

Scientific
The scientific sector has a rich history of advancements and discoveries that have shaped our understanding of the world and revolutionized various fields. Here’s an overview of the scientific sector’s history, current position, and future outlook:
History
The scientific sector’s roots can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Greeks, Egyptians, and Chinese, who made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. However, modern science as we know it today began to emerge during the scientific revolution of the 16th and 17th centuries. Prominent figures like Galileo Galilei, Isaac Newton, and Johannes Kepler pioneered new methods of observation, experimentation, and mathematical analysis.
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed tremendous advancements in various scientific disciplines. The Industrial Revolution brought about advancements in physics, chemistry, and engineering, leading to innovations such as the steam engine and electricity. In the 20th century, groundbreaking discoveries in quantum mechanics, relativity, genetics, and other fields transformed our understanding of the fundamental laws of nature.
Current Position
In the present day, the scientific sector is a thriving and dynamic domain with numerous branches of study. Scientists and researchers around the world work in universities, research institutions, and private companies to expand the frontiers of knowledge. The scientific sector encompasses fields such as physics, chemistry, biology, astronomy, geology, medicine, environmental sciences, computer science, and many more.
Advancements in technology and the availability of vast amounts of data have accelerated the pace of scientific discovery. Collaborative efforts, interdisciplinary research, and open access to information have become increasingly important. The scientific community relies on rigorous peer review processes and publication in reputable journals to ensure the quality and validity of research findings.
Future Outlook
The future of the scientific sector holds tremendous potential and numerous challenges. Here are some key aspects of its outlook:
1. Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, gene editing, quantum computing, and nanotechnology, are expected to revolutionize scientific research and open up new avenues for exploration.
2. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaborative research across different scientific disciplines is becoming increasingly important. The complex challenges we face, such as climate change, healthcare, and sustainable development, require multidisciplinary approaches and the integration of knowledge from various fields.
3. Global Challenges: The scientific sector will play a crucial role in addressing global challenges like climate change, food security, public health, and renewable energy. Research and innovation will be essential in finding sustainable solutions to these pressing issues.
4. Ethical Considerations: As scientific advancements continue, ethical considerations become more critical. Debates surrounding topics like genetic engineering, artificial intelligence ethics, and privacy will shape the future of scientific research and its applications.
5. Open Science and Accessibility: There is a growing movement towards open science, promoting transparency, reproducibility, and accessibility of research findings. This includes open access publishing, open data sharing, and collaborative platforms for knowledge exchange.
6. Communication and Public Engagement: Bridging the gap between scientists and the general public is vital. Effective science communication and public engagement efforts will be necessary to foster scientific literacy, trust, and informed decision-making.
Overall, the scientific sector’s future outlook is promising, with the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and transformative advancements. However, it also faces challenges that require careful consideration and ethical decision-making to ensure responsible and beneficial progress.

Security
The security sector has a rich history that spans centuries, evolving alongside the changing nature of threats and the development of technology. Here’s a brief overview of its history, current position, and future outlook:
History
The origins of the security sector can be traced back to ancient times when early civilizations employed guards to protect their assets and maintain order. As societies grew more complex, security measures became more sophisticated, with the establishment of standing armies, fortifications, and surveillance systems.
In modern history, the security sector experienced significant growth during the Industrial Revolution and the rise of nation-states. The World Wars further fueled the expansion of the sector, with a focus on military defense, intelligence agencies, and the development of advanced weaponry and encryption systems.
Current Position
Today, the security sector encompasses a broad range of areas, including national defense, law enforcement, cybersecurity, intelligence agencies, private security firms, and more. Governments play a crucial role in ensuring national security through military forces, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement organizations. Meanwhile, private security companies provide services such as physical security, asset protection, and cybersecurity to individuals, businesses, and government entities.
With the increasing interconnectivity of the world and the rise of digital technologies, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical aspect of the security sector. Protecting computer networks, data, and critical infrastructure from cyber threats has become a global concern, and governments, organizations, and individuals are investing heavily in cybersecurity measures.
Future Outlook
The future of the security sector is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
1. Cybersecurity Dominance: As society becomes increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, cybersecurity will continue to be a major focus. The sector will witness advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to detect and respond to evolving cyber threats.
2. Emerging Technologies: The proliferation of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and autonomous systems will impact the security sector. These technologies have the potential to enhance surveillance, intelligence gathering, and operational capabilities.
3. Privacy and Ethics: The balance between security and privacy will continue to be a topic of debate. Striking the right balance while leveraging emerging technologies will be crucial to avoid infringing on civil liberties.
4. Global Threats: The security sector will grapple with complex global challenges, including terrorism, transnational organized crime, geopolitical tensions, and environmental risks. International cooperation and information sharing will become increasingly important to address these threats effectively.
5. Data Protection and Privacy Regulations: The growing awareness of data breaches and privacy concerns will lead to stricter regulations. Organizations will need to comply with data protection laws and implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information.
Overall, the security sector is expected to remain dynamic and adaptive, driven by technological advancements and the evolving nature of threats. Collaboration between governments, organizations, and individuals will be crucial to mitigate risks and ensure a secure future.

Telecommunications
The telecommunications sector has a rich history and has undergone significant transformations over the years. Let’s explore its history, current position, and future outlook.
History
The history of telecommunications dates back to ancient times when humans used smoke signals, drums, and carrier pigeons to communicate over long distances. However, the modern telecommunications industry began to take shape with the invention of the telegraph in the 19th century. The telegraph enabled long-distance communication through the transmission of electrical signals over wires.
The next major milestone was the invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876, which revolutionized communication by allowing voice transmission. The telegraph and telephone networks expanded rapidly, leading to the establishment of telecommunication companies around the world.
In the 20th century, the development of radio and television further expanded the reach of telecommunications. The introduction of satellites in the mid-20th century enabled global communication and paved the way for the modern era of telecommunications.
Current Position
Today, the telecommunications sector is a crucial part of the global economy, connecting people, businesses, and devices worldwide. It encompasses a wide range of services, including fixed-line and mobile telephony, broadband internet, data transmission, satellite communications, and more.
The industry is dominated by both traditional telecommunications companies and newer players in the market, such as internet service providers (ISPs), mobile network operators (MNOs), and Over-the-Top (OTT) providers. The sector has witnessed significant advancements in technology, with the proliferation of smartphones, fiber-optic networks, 4G/LTE, and the ongoing deployment of 5G networks. These developments have facilitated faster data transmission, improved connectivity, and the rise of digital services.
Future Outlook
The future of the telecommunications sector looks promising as it continues to evolve and adapt to new technological advancements. Here are some key trends and developments that shape its future outlook:
1. 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks is expected to continue, offering significantly faster speeds, low latency, and increased capacity. This technology will enable the growth of new applications like autonomous vehicles, the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR).
2. Internet of Things (IoT): The number of connected devices is projected to grow exponentially, fueling the expansion of IoT applications across various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, smart cities, and agriculture. Telecommunications networks will play a vital role in connecting and managing these devices.
3. Cloud Services: The demand for cloud-based services is increasing, as individuals and businesses rely on cloud storage, software-as-a-service (SaaS), and other cloud-based applications. Telecommunications providers are likely to play a crucial role in delivering secure and reliable connectivity to support these services.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technologies are expected to have a significant impact on the telecommunications sector. AI can enhance network optimization, automate customer service interactions, and improve overall network efficiency.
5. Network Security: With the growing reliance on digital communication and data transmission, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures will be paramount. Telecommunications companies will continue to invest in advanced security solutions to protect networks and user data.
6. Rural Connectivity: Efforts to bridge the digital divide and provide internet access to underserved rural areas will continue. Governments and telecommunications providers are investing in initiatives to expand broadband infrastructure and connectivity in remote regions.
Overall, the telecommunications sector is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by advancements in technology and evolving customer demands. The industry will play a pivotal role in shaping the digital economy and connecting the world more than ever before.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

London, UK
London has a rich and fascinating history that spans over two millennia. It was founded by the Romans in AD 43 and was originally called Londinium. Throughout its history, London has played a pivotal role in shaping the economic, cultural, and political landscape of not only the United Kingdom but also the world.
Historically, London has been a center of trade and commerce. Its strategic location on the River Thames made it a hub for maritime activities and international trade. During the Middle Ages, London became a prominent financial center, with the establishment of the Bank of England in 1694 and the London Stock Exchange in 1801.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, London witnessed significant industrialization and urbanization. It became a leading center for manufacturing, particularly in sectors such as textiles, engineering, and food processing. The city also expanded its transportation infrastructure, including the development of the London Underground, which is now one of the oldest and most extensive metro systems in the world.
Today, London remains a global economic powerhouse. It is a major financial center and is home to numerous international banks, insurance companies, and financial institutions. The City of London, often referred to as the Square Mile, is the heart of the city’s financial district. It is renowned for its stock exchanges, including the London Stock Exchange and the Lloyds of London insurance market.
London has diversified its economy beyond finance and banking. It is a center for professional services, including law, consulting, and advertising. The creative industries, such as film, television, fashion, and design, also thrive in the city. Additionally, London has a vibrant tourism sector, attracting millions of visitors each year to its iconic landmarks, museums, and cultural events.
In terms of GDP, London contributes significantly to the UK’s economy. London accounts for approximately 22% of the UK’s total GDP. It generates substantial tax revenue and employment opportunities, attracting talent from around the world.
Looking towards the future, London is expected to maintain its position as a global economic and cultural center. It continues to attract foreign investment and nurture innovation and entrepreneurship. The city is investing in infrastructure projects, such as the Crossrail (Elizabeth Line) expansion, which will improve transportation links and connectivity.
Here are some key factors that contribute to London’s positive future prospects:
1. Financial Services: London’s financial sector is expected to remain robust, despite challenges such as Brexit. The City of London has a long-standing reputation for financial expertise and innovation. The UK government has expressed its commitment to maintaining London’s competitiveness as a global financial center, and efforts are underway to attract investment and foster collaboration with international partners.
2. Tech and Innovation: London has a thriving tech and startup scene, with numerous tech companies and innovation hubs. The city benefits from a highly skilled workforce and a supportive ecosystem for entrepreneurship. Initiatives like Tech City UK (now Tech Nation) and the opening of tech-focused campuses, such as the Here East innovation hub, have further bolstered London’s tech credentials. The city’s future outlook in terms of technology and innovation is promising, with continued growth expected in sectors like fintech, artificial intelligence, and digital services.
3. Infrastructure Development: London is investing in infrastructure projects to enhance connectivity and accommodate its growing population. The completion of Crossrail (Elizabeth Line), which is set to become the largest infrastructure project in Europe, will improve transportation links and ease congestion within the city. Other infrastructure projects, such as the expansion of Heathrow Airport and the development of the East Bank cultural district, will further contribute to London’s future growth and attractiveness.
4. Cultural and Creative Industries: London’s cultural and creative industries, including film, fashion, design, and the arts, are vital components of its economy. The city’s cultural diversity and vibrant arts scene continue to attract talent and visitors from around the world. London’s future outlook in these sectors is positive, with ongoing investments in cultural infrastructure, support for creative initiatives, and the hosting of major events like the London Fashion Week and the London Design Festival.
5. Sustainability and Green Initiatives: London has set ambitious goals to address climate change and promote sustainability. The city aims to become a zero-carbon city by 2050, with plans to improve air quality, expand green spaces, and encourage renewable energy usage. These efforts align with global trends and will contribute to London’s attractiveness as a sustainable and livable city in the future.

New York, NY
New York has a rich history and occupies a prominent position in terms of industry, economy, and its contribution to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the United States.
New York’s history dates back to its founding as New Amsterdam by the Dutch in 1624. In 1664, the British captured the city and renamed it New York. Over the centuries, New York became a hub of immigration, trade, and finance, attracting people from diverse backgrounds and cultures. The construction of the Erie Canal in the early 19th century further fueled the city’s growth, making it a major center for transportation and trade.
Industry and Economy: New York City, particularly Manhattan, has long been recognized as a global financial and commercial center. Wall Street, located in Lower Manhattan, is renowned as the heart of the American financial sector. The city houses the headquarters of numerous major banks, financial institutions, and stock exchanges. The finance and insurance sectors contribute significantly to the city’s economy.
Apart from finance, New York City has a diverse and thriving economy. It is a major center for media, entertainment, advertising, fashion, and the arts. The city is home to Broadway, which hosts world-class theater productions, and it attracts tourists from around the world. Additionally, New York has a robust technology sector, with companies involved in software development, e-commerce, and digital media.
The state of New York also has a strong manufacturing industry, particularly in areas such as chemicals, machinery, electronics, and food processing. The region benefits from its access to international markets, well-developed infrastructure, and a skilled workforce.
New York’s contribution to the GDP of the United States is substantial. The state has consistently ranked among the top contributors to the national economy. As of 2021, New York had the third-largest state economy in the United States, after California and Texas. The GDP of New York State exceeded $1.7 trillion in 2019.
New York City alone accounts for a significant portion of the state’s GDP. It is estimated that the city’s economy is larger than that of many countries. The finance and professional services sectors play a crucial role in driving the city’s economy and contributing to the national GDP.
The future outlook for New York’s industry, economy, and GDP remains positive, but it is important to note that economic conditions can be subject to various factors and uncertainties. New York City will likely continue to maintain its position as a global financial and commercial hub, attracting businesses and talent from around the world.
Technological innovation, particularly in the fields of information technology and biotechnology, is expected to drive growth in the coming years. Additionally, the city is investing in infrastructure development, such as transportation and renewable energy, which will support economic expansion and create new opportunities.
However, it is worth considering that economic trends can evolve, and external factors such as global economic conditions, regulatory changes, and geopolitical events can impact New York’s future outlook. It is crucial for the state and city to adapt to these changes and foster an environment that encourages innovation, entrepreneurship, and investment to sustain and enhance their economic contributions.

San Francisco, CA
San Francisco, often referred to as the cultural, commercial, and financial hub of Northern California, has a rich history in terms of business, culture, and its contributions to the overall economy and GDP. Let’s explore its significance in these areas:
Economy and GDP Contributions:
San Francisco is a major economic powerhouse, playing a crucial role in the overall economy of the United States. It contributes approximately $501 billion to the nation’s GDP through various sectors, including technology, finance, tourism, and healthcare. Here are some key highlights:
• Technology: San Francisco is renowned as a global center for technology and innovation. The city is home to numerous tech companies, startups, and venture capital firms. Silicon Valley, located just south of San Francisco, is known for its concentration of high-tech companies and research institutions, driving innovation and economic growth.
• Finance: San Francisco has a strong presence in the financial industry. The city houses the headquarters of several major banks and financial institutions, including Wells Fargo and Charles Schwab. Additionally, it is a key center for private equity, venture capital, and investment management firms.
• Tourism: San Francisco attracts millions of visitors each year, contributing significantly to its economy. The city’s iconic landmarks, such as the Golden Gate Bridge, Alcatraz Island, and Fisherman’s Wharf, draw tourists from around the world. The hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, benefits from this influx of visitors.
• Healthcare: San Francisco has a robust healthcare sector, hosting prominent medical institutions, research centers, and biotechnology companies. It is a leader in biomedical research, pharmaceuticals, and medical technology, making substantial contributions to both local and national economies.
Business and Entrepreneurship
San Francisco has a vibrant business and entrepreneurial ecosystem. The city has been at the forefront of fostering innovation and startups. It has a history of nurturing successful companies across various industries, including technology, finance, retail, and hospitality. The entrepreneurial spirit and access to venture capital have made San Francisco a hub for aspiring entrepreneurs and business professionals.
Cultural Significance
San Francisco has long been associated with cultural movements and counterculture. In the 1960s, it was a focal point for the hippie movement and the Summer of Love. The city has a diverse and inclusive culture, embracing various ethnicities, lifestyles, and artistic expressions. It is renowned for its thriving arts scene, including theater, music, visual arts, and film festivals.
San Francisco’s cultural landscape is further enriched by its historical landmarks, such as the Victorian houses in the Haight-Ashbury neighborhood, the vibrant Chinatown district, and the LGBTQ+ community in the Castro district. The city’s cultural institutions, including museums, galleries, and performance venues, contribute to its dynamic artistic and cultural heritage.
In summary, San Francisco’s contributions to the overall economy and GDP are significant, primarily driven by the technology sector, finance industry, tourism, and healthcare. The city’s history in terms of business, culture, and countercultural movements has shaped its identity and made it a thriving metropolis known for innovation, entrepreneurship, and a diverse and vibrant cultural scene.

Dublin, IE
Dublin, the capital city of Southern Ireland, has a rich history that spans over a thousand years. Here’s an overview of Dublin’s history, current position, and future outlook in terms of industry, economy, and its contribution to GDP.
Dublin’s history dates back to its establishment as a Viking settlement in the 9th century. It grew into an important medieval city and became the center of English administration in Ireland during the 12th century. Dublin played a significant role in the struggle for Irish independence and saw major political and social changes throughout the 20th century. Today, it is a vibrant, cosmopolitan city that blends its historical heritage with modern influences.
Dublin is a major economic hub in Europe and has emerged as a leading global city. It serves as the headquarters for many multinational corporations, financial institutions, and tech companies. The city’s strategic location, skilled workforce, favorable business environment, and strong educational institutions have contributed to its current position as a center for innovation, technology, finance, and entrepreneurship.
Dublin’s economy is diverse, with various sectors playing significant roles. The city has a thriving technology and digital sector, often referred to as the “Silicon Docks,” which is home to major tech companies like Google, Facebook, Twitter, and many others. The financial services industry is also well-established in Dublin, with numerous international banks, insurance companies, and asset management firms operating there. The pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors are robust, with several leading companies having a presence in the city. Additionally, Dublin has a vibrant tourism and hospitality industry, benefiting from its cultural attractions, historical sites, and renowned Irish hospitality.
Dublin’s contribution to Ireland’s GDP is substantial. The city’s economic output accounts for a significant portion of the country’s overall GDP. In recent years, Dublin has experienced strong economic growth, driven by its thriving industries and the presence of multinational corporations. However, it’s important to note that Dublin’s economic prosperity has resulted in some regional disparities within Ireland, with other parts of the country seeking to attract more investment and development. In 2020, the Dublin NUTS2 region recorded the highest Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in the state at €157.2 billion, followed by the South-West region at €103.2 billion.
Dublin’s future outlook remains positive, with continued growth anticipated across various sectors. The city is investing in infrastructure development, including transportation, housing, and digital connectivity, to support its expanding economy. Efforts are being made to foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and research and development, which will likely strengthen Dublin’s position as a global hub for technology and innovation. Additionally, sustainability and environmental considerations are gaining importance, with Dublin aiming to become a greener and more sustainable city in the coming years.
Overall, Dublin’s history, current economic position, and future outlook showcase its significance as a vibrant city with a diverse economy, contributing significantly to Ireland’s overall GDP and serving as a hub for innovation and industry.

Raleigh, NC
Raleigh, North Carolina, has a rich history and has emerged as a vibrant city with a strong economy and diverse industries.
History: Raleigh was founded in 1792 as the capital of North Carolina and was named after Sir Walter Raleigh, an English explorer. The city was carefully planned and designed as a center for government and education. Throughout its early years, Raleigh experienced slow but steady growth, primarily driven by its role as the state capital.
Raleigh’s economy has transformed significantly over the years. Historically, it relied heavily on government-related activities due to its status as the capital. However, in recent decades, the city has diversified its economic base and emerged as a major center for technology, research, and innovation.
Today, Raleigh is part of the Research Triangle region, which also includes Durham and Chapel Hill. The Research Triangle Park (RTP), established in 1959, has been a catalyst for the city’s growth. RTP is one of the largest research parks in the world, housing numerous high-tech companies, research institutions, and startups.
The city’s economy is characterized by a strong presence in sectors such as technology, healthcare, education, finance, and professional services. Raleigh is home to numerous technology companies, including software development, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications, and information technology firms.
Raleigh has a thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem, with many startups and small businesses contributing to its economic vitality. The city also benefits from the presence of renowned universities like North Carolina State University, which fosters innovation and research.
Raleigh’s economic growth and development have led to a significant contribution to the state and national GDP. While exact figures may vary, the city’s diverse industries and robust economic activity make it a substantial contributor.
Raleigh’s future outlook remains promising. The city continues to attract talent, investment, and new businesses due to its favorable business climate, skilled workforce, quality of life, and access to research and educational institutions.
The technology sector is expected to continue playing a vital role in Raleigh’s economy, with ongoing innovation and expansion. The city’s commitment to sustainable and clean energy initiatives, coupled with its efforts to enhance transportation infrastructure, position it well for future growth.
Furthermore, Raleigh’s cultural attractions, diverse culinary scene, and outdoor recreational opportunities contribute to its appeal as a destination for tourism and a desirable place to live.
In conclusion, Raleigh, NC, has transitioned from being primarily a government-centric city to a thriving center for technology, research, and innovation. Its diversified economy, strong industry presence, and contributions to the GDP make it a dynamic and promising city with a bright future.
Program Benefits
Marketing
- Testimonials/case studies
- Referral programs
- User-generated content
- Segmentation insights
- Messaging/positioning
- Upselling/cross-selling
- Feedback for strategy
- Renewal/retention
- Content insights
- Customer acquisition
Operations
- Customer feedback
- Process optimization
- Support enhancement
- Data-driven decisions
- Product improvement
- Efficient onboarding
- Proactive resolution
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Scalability/growth
- Feedback loop
Finance
- Increased revenue
- Predictable cash flow
- Upsell opportunities
- Improved CLV
- Lower acquisition cost
- Higher margins
- Enhanced cash flow
- Pricing optimization
- Risk mitigation
- Improved metrics
Testimonials

Dov Mendelovich, VP Global Customer Services, Semperis
“As a company we had no previous background in Customer Success Management, so our first priority was to select a framework that would provide us with a shared language and set of best practices. This would enable us to recruit and train a new team efficiently and effectively. Mr. Adams’ training content provided us with a comprehensive end-to-end solution for all of our Customer Success management responsibilities, including establishing a common language within the team. Working with Mr. Adams and his team was straightforward, with quick response times and detailed assistance. The training content was not only engaging and easy to understand, but also highly practical. It helped my team and me understand what was required of us and served as an excellent ongoing resource. The training was delivered in a logical and sequential manner, allowing us to develop a complete Customer Success practice over the course of the program.”

Kristi Faltorusso, Chief Customer Officer, Intellishift
“I needed to provide my entire team with comprehensive training and certification in Customer Success Management. I was fortunate enough to be familiar with all the CS training programs currently being offered, and I chose Mr. Adams’ program because it provided the necessary breadth and depth of coverage, while being up-to-date, accurate, and of high quality. It was also relevant to our own CS requirements, ensuring that my team could quickly and easily adopt and implement what they learned. The training process was thorough, and the exercises and tools provided were powerful for us. The major takeaway from the program was Mr. Adams’ framework for Customer Success which was particularly valuable as it aligned perfectly with our customers’ post-sales journey. This provided us with a detailed process to enhance quality, increase productivity, and ensure a consistent approach with every client.”

Rebecca Nerad, VP Customer Success, E2Open
“Dealing with Mr. Adams and his training team was a great experience. I highly recommend his CS training program to others and am excited to work with him again in the future. The program’s rigorous content and structured approach was phenomenal, enabling a deep understanding of how to elevate our Customer Success strategies, not just for me, but for my entire team. We acquired extensive knowledge during the course, and the content was easy to follow, highly relevant to our daily customer engagements, and extremely valuable for us.”

Val Kearney, Customer Success Team Lead, NewsWhip
“At the time, our team members had varying levels of knowledge and experience in different aspects of customer success management and were at different stages of their careers. To achieve a consistent, high standard across all our customer success management activities, we needed an overall program. We chose Mr. Adams’ training program because it matched our requirements and needs for delivering customer success to our clients, and we had confidence in his background and experience to answer our questions and evolve our thinking. The content was fantastic, covering everything we wanted in great detail, and presented in an engaging style that allowed us to learn and apply concepts with our customers. The thorough and practical training resulted in significant learning for everyone, progressing us as a team. We were thrilled with the outcomes and hope to engage Mr. Adams’ services again in the future.”

Richard Fetter, Regional Director, Customer Success, Talkwalker
“I had been following Mr. Adams’ work for several years and was impressed with the model he had built and his framework approach to Customer Success Management best practice. Based on this, we selected his training program, and it exceeded our expectations. By leveraging Mr. Adams’ experience and expertise, we were able to overcome our challenges and equip the team with the materials they needed for their day-to-day work. The team provided excellent feedback on the program, and this feedback was even shared with the CEO in the United States. The training sessions were engaging and interactive, with Mr. Adams making it a two-way conversation. We were excited to undertake the program, and we are now focused on implementing what we learned into our daily processes and best practices to maximize the value of the training for the whole team.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.











