Customer Experience

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Customer Experience is provided by Dr. Hauck Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
TO BE ADVISED
To request further information about Dr. Hauck through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Customer Experience
History
Service Culture Skills, Inc. DBA Communico
The word Communico, by definition (Latin), means “to communicate.” Its roots stem from the British Isles. In 1979, the American subsidiary of Management and Staff Training (MAST), British Communico Ltd., was founded in Salisbury, Connecticut. For over 30 years, Communico has helped companies transform their interpersonal communication. Communication is the foundation of organizational culture. Communico partners with organizations in embracing a service mindset that builds lasting relationships with customers and employees.
Initial focus and at the heart of our commitment is The MAGIC® Service Culture System. MAGIC, which stands for Make A Great Impression on the Customer, is an integrated system of assessment, training and consulting that ensures consistently exceptional service. Every element of this system is grounded in common-sense models and carefully tailored to meet specific client needs. The MAGIC Service Culture includes 33 Points describing specific behaviors required to optimize customer experience. The intended results of using the 33 Points are measurably improved service ratings, employee performance, and customer loyalty. Customer loyalty is the most important outcome because it is a predictor of financial success. (Disco, 2017)
Communico was owned by a British company (and was formerly known as British Communico Ltd.) until 1988. This British company had a telephone customer relations program that became the core of Communico’s first MAGIC program.
MAGIC and the acronym MAGIC evolved during an emotional meeting with Tom Larkin, Sandy Wilder, Diane Berenbaum, and Barry Arye. It was emotional because we wanted to measure an interaction. Communico had experience measuring the quality and speed of reading and comprehension. We wanted to apply a measure to the quality of communication also.
In 1981, Communico moved to Greenwich, CT and a partnership was formed in 1985 among Barry L. Ayre (founder), Thomas S. Larkin and Carl E. Rohde. Our clients included Fortune 500 companies and the private school sector, where we taught reading and study skills. We subsequently sold the schools business in 1989.
Diane T. Berenbaum joined the company in 1986 and became a partner in 1988, the same year that the company became independent of the parent organization. The company was officially renamed Communico Ltd. Mr. Rohde resigned from Communico in 1987.
Sanford C. Wilder joined the company in 1984 and also became a partner in 1988. Westport, Connecticut became the new home for Communico when Sandy became President and Chief Executive Officer in 1993. Together with Tom Larkin and Diane Berenbaum, Sandy leads the team dedicated to inspiring organizations to make a difference.
In 2009, Sandy left Communico to pursue other interests. Tom Larkin assumed the role of President and Chief Executive Officer. In 2017, Diane retired; 2020 Tom Larkin retired.
In August of 2020, Wally Hauck, a long-time Independent Contractor of Communico Ltd. and Gregg Barratt, employee and previous contractor, started a company called Service Culture dba Communico. They carry on the work and joy of MAGIC today.
Link Between Customer Satisfaction and Financial Measures
Numerous studies by other organizations have also shown that companies known for customer satisfaction outperform their industry in key financial measures such as average annual sales growth and average return on equity (Compustat Inc. Company Reports and Business Week March 12, 1990, article entitled King Customer: At Companies that Listen Hard and Respond Fast, Bottom Lines Thrive). Research thirty years later confirms this same result. (Disco, 2017)
Foundational Research in the 1980’s and early 1990’s
Communico conducted research to update the British program and adapt it to meet the needs of the U.S. market. We read a wide variety of books, watched videos and read research studies on customer service, interpersonal communication and telephone interactions.
A Sample of Research Studies that Influenced MAGIC Development
• William Wilsted, an advisor to Ernst & Young, surveyed banking, high tech and manufacturing customers. He found that these people considered “the personal touch” to be the most important element of service. He defined “personal touch” as how committed a company representative is to a client and whether s/he remembers and uses the customer’s name
• Opinion Research Corp. of Princeton, NJ surveyed 400 executives of the nation’s largest companies. They found that how much a company “cares about its customer” is as important as prompt and efficient service.
• A survey by Burger King found that customers ranked courtesy number one (over speed of service, which used to be number one).
• Fortune Magazine released The Service 500 in June 1990 (Top 500 diversified service companies). In an article entitled, “What Customers Really Want”, they highlight some of the organizations that made the list. Mike Wright, The CEO of Super Valu (number 3 on the list), notes that “customers want empathy, and not even the world’s most sophisticated computer can provide that.”
• The Service Edge by Ron Zemke and Dick Shaaf clarifies a 5-Point service recovery system.
– Apology – more powerful when it is in the first person (“We’re sorry” lacks sincerity).
– Urgent reinstatement.
– Empathy – “Expressing compassion may be the mother lode of all service gold.” The customer feels heard, affirmed, and cared about.
– Symbolic Atonement.
– Follow-up.
• Babson College study on rudeness: More than 50% of those surveyed said they get angry or upset when treated rudely. About half said that they get rude in return. Most people feel good when they meet or speak with courteous people.
• Dr. Denis Waitley, a specialist in understanding the relationship between self-development and high performance, expressed the following themes in his work: “Self-management and self-determination allows one to be successful;” “When you listen you learn more”; “no one is more important than someone else.”
Return on Investment
TARP (Technical Assistance Research Programs) has conducted research on the link between good customer service and return on investment. They found that better customer service leads to increased sales from existing customers and new customers, which in turn yields significant return on investment (e.g., automobile and consumer durable goods companies average over 100% ROI on customer service).
Impact on Market Share and Business Performance
The most well-known research about quality and market share was conducted by the Strategic Planning Institute as part of the Profit Impact of Market Strategies Program (PIMS). The conclusion reached by this study: In the long run, the most important single factor affecting a business unit’s performance is the “relative quality” of its products and services (level of perceived quality relative to competitors). Any differentiation in service will be a factor for creating loyalty.
The Representative’s Demonstration of Behaviors Impacts Customer Perception of the Company
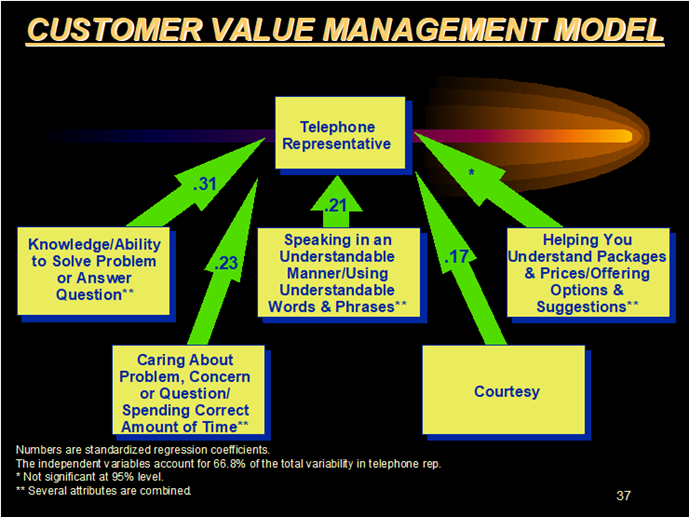
The Fraser Group further analyzed the performance of the representative and measured the relationship between the specific skills of the rep and the customer’s overall assessment of the representative. The studies showed that the top skills/behaviors are (see Chart 5):
1. Knowledge/Ability to solve problem or answer questions
2. Caring about the problem or concern
3. Speaking in an understandable manner, using understandable words
4. Courtesy
The Fraser Group also linked Communico’s 33 Points to those skills/behaviors that have the greatest impact on customer perception of the overall experience with the company.
In 2008 – 2010, Communico did additional research to ensure the standard reflected customer perceptions, and higher service expectations. We adapted the scorecard and made additions/changes to reflect exceptional respect and accountability behaviors.
Research on Empathy: Dr. Gerard Egan, Professor of Psychology and Organizational Studies at Loyola University. Author of The Skilled Helper: A Systematic Approach to Helping.
Client Input
The 33 Points were refined over the first few years, based on client input. Initially, Communico uncovered 31 elements that created an impression over the phone. We later edited points and added new ones. We introduced the official “33 Points of MAGIC” (with The Five MAGIC Steps) in 1989.
Why Five MAGIC Steps?
After finalizing the 33 Points of MAGIC, we knew that the Points needed to be broken into categories to ensure understanding and retention. Since Communico began as a communication skills training organization (Communico is Latin for “to communicate”), we were aware of research on memory and the brain.
The human brain can only retain 7 + or – 2 bits of information at a time. Therefore, people are not able to remember 33 elements. The 33 Points must be broken into categories or steps with no more than 7 + or – 2 items in each category.
Communico developed The 5 MAGIC Steps to mirror the flow of a customer contact and then incorporated the 33 points into these steps.
Validation of Quality Service Index
Customer Perception and QSI Categories
The Quality Service Index shows the impact of The 33 Points on an organization’s culture. The verbiage on the QSI shows that customer perception is affected by the demonstration of MAGIC points:
To ensure that these perceptions were accurate, Communico worked with several clients to validate them. These clients (in the health care and financial services industry) conducted customer research to see if there was alignment between actual customer perceptions and the QSI categories.
They surveyed random customers at the end of telephone contacts and asked them to describe the impression that the company representative made. They were given five response choices (the QSI categories: Discouraging, Indifferent, Routine, Very Good and Exceptional). These same telephone calls were also recorded so that the company could rate the calls using The 33 Points of MAGIC.
The clients’ perceptions matched the category on The 33 Points (i.e., calls that clients rated Routine scored 23 – 25 on The 33 Points, and so on).
This Culture Makes You Money and This Culture Costs You Money
Market Research on Customer Value Management
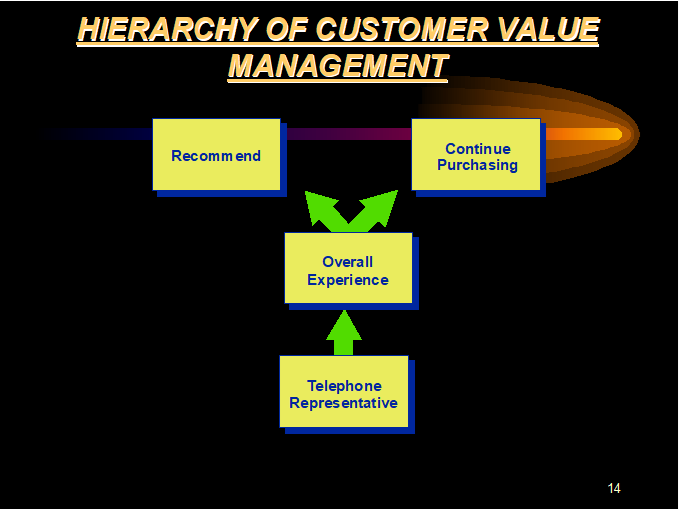
The Fraser Group, a market research organization based in Indianapolis, has conducted multiple research projects on customer value management. They found that the performance of an organization (call center or any service-focused organization) is significantly correlated with the likelihood the customer will:
• recommend the client’s product or service to others
• continue to purchase the product or service
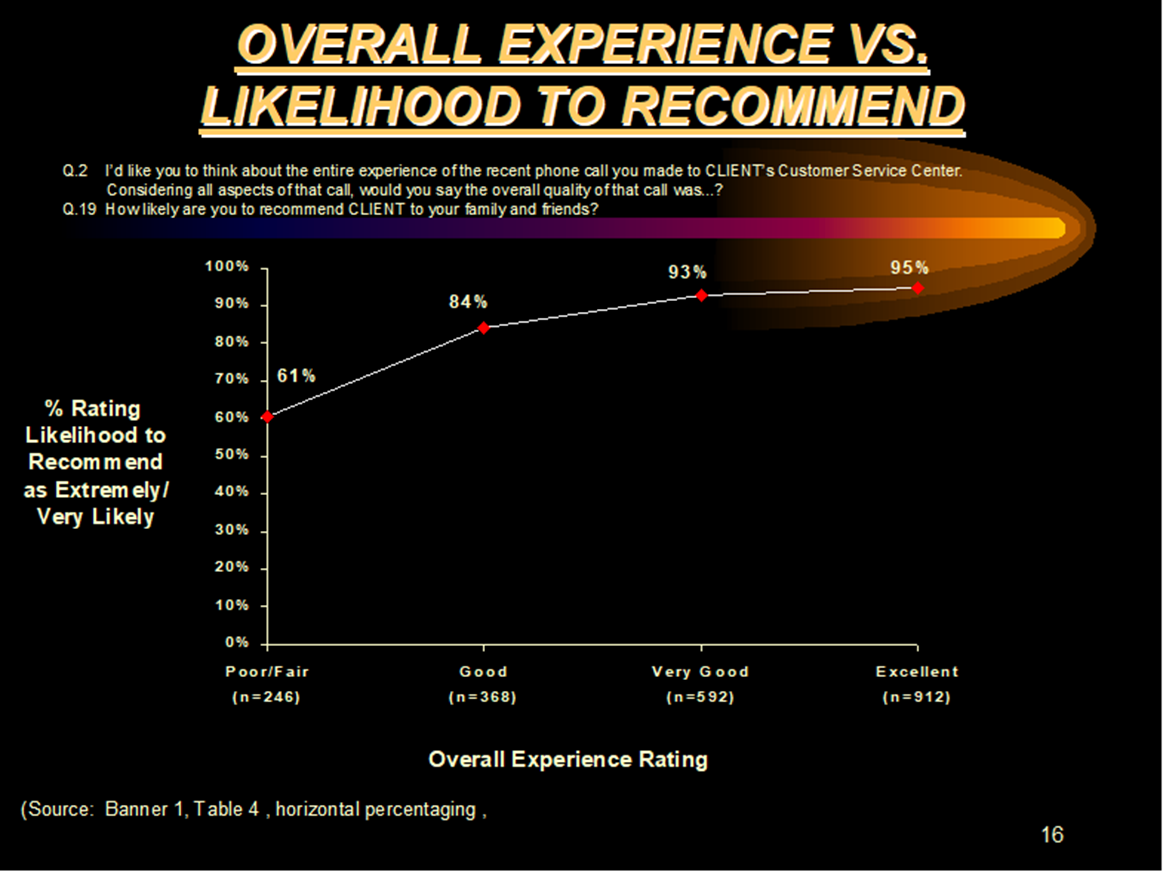
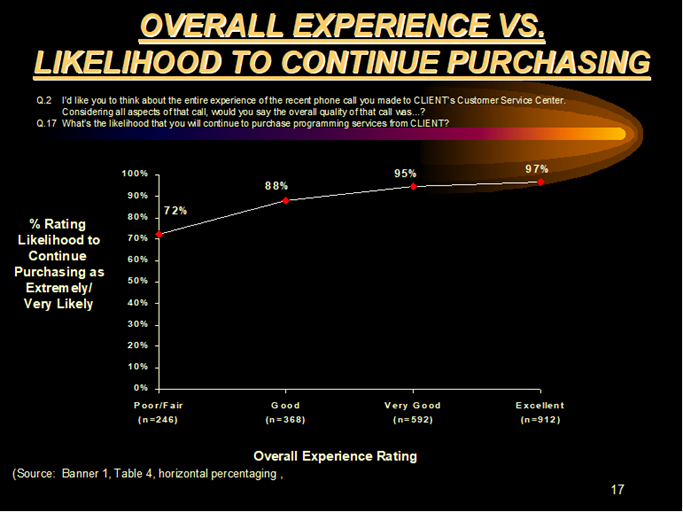
The hierarchy is as follows: The experience with the telephone representative is correlated with the customer’s overall experience with the Organization, which is then correlated with the customer’s likelihood to either 1) recommend the company to others or 2) continue purchasing from that company. (See Chart 1 for a graphic representation of this hierarchy.)
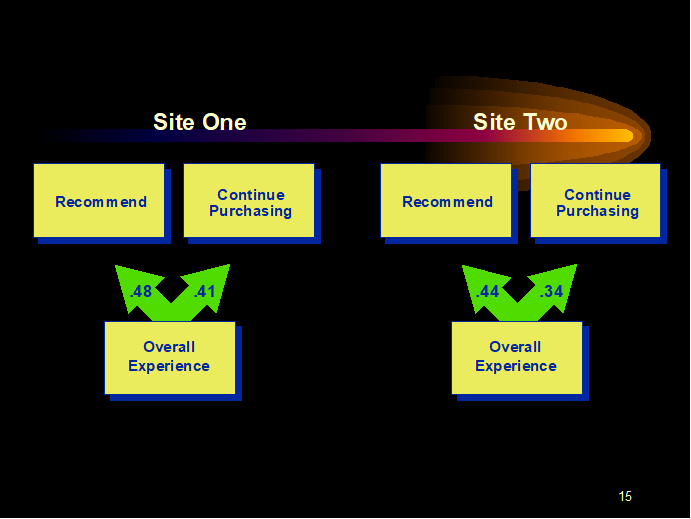
In other Fraser Group studies, the relationship between the overall experience with a company was correlated to the customer’s likelihood to recommend the company and continue purchasing. (See Charts 2, 3 and 4.)
Communico’s client list continues to grow with Fortune 500 companies in a variety of industries including health care, utilities, financial services, insurance, mortgage servicing, information technology, hospitality, consumer products and other service companies.

Current Position
MAGIC Transformational Leadership is a corporate focused training program that provides leaders with the critical success skills needed to create a service culture environment. The leadership team plays a crucial role in the development of an exceptional service culture. Leaders need to model and reinforce the principles of MAGIC to ensure culture change and long-lasting results. By inspiring associates to make every contact MAGIC, they will help create a service climate that strengthens customer relationships and loyalty. The MAGIC Service Culture System is best implemented when the MAGIC Transformational Leadership skills are employed.
Also, by treating their associates “with MAGIC” leaders instill a greater sense of trust and improved employee engagement and loyalty.
Changing times call for evolving leaders. Leaders must ask, “Why would anyone choose to follow you?” We help leaders to explore this question and learn to lead in a way that engages the high achiever within. Leaders begin with a vision for themselves of what kind of leaders they want to be and develop their purpose and direction. And, they learn to communicate in a way that inspires people to commit to the organization’s purpose.
Leadership skills are an essential factor to sustaining a customer and employee-focused service culture. Our MAGIC Transformational Leadership training, one-on-one coaching and consulting supports the development of leaders at all levels who champion service, model effective relationships, and optimally communicate.
This program helps leaders transform themselves and their teams and develop the strong foundation of trust organizations need to achieve and exceed their service culture goals.
By exploring each of these areas, participants can:
• Identify and leverage their own strengths
• Gain insight into effective interpersonal communication utilizing a communication assessment.
• Learn key strategies to direct, align and support their teams
• Understand and apply systems thinking to influence the organization’s culture and its effectiveness
Participants explore how leaders communicate to align and inspire others. The focus is on learning what they can control and what they can influence to bring about improved performance in themselves, associates and teams.
This program aligns with the vision and strategies of the organization as well as the internal systems and processes that encourage Transformational Leadership. It also aligns perfectly with the MAGIC of Customer Relations program and the 33 Points of MAGIC.
The MAGIC Transformational Leadership Model is ideal for organizations that want to create and continuously improve their customer service competencies. The MAGIC Transformational Leadership Model is five sets of skills:
1. Make a Great Environment
2. Act with Values and Trust
3. Get Goals Going
4. Improve Interactions Continuously
5. Continuous Coaching & Feedback
The roots of this leadership model are in the MAGIC of Customer Relations. First and foremost, leaders need to know how to communicate. Communication is the single most important factor to influence and inspire others and leaders must be able to influence and inspire to implement positive change.
Make a Great Environment
The purpose of this set of skills is to appreciate and adopt the most useful leadership mindsets. These include systems thinking, servant leadership, the growth mindset, and the strategic mindset.
Systems thinking is a set of principles which enable leaders to create a service culture. With systems thinking, employees can self-manage within a context. It explains how the performance of individuals is influenced more by the system (environment) within which they work than by their individual efforts or skills. Systems thinking principles explain why it’s more important to focus on the context of the work environment for continuous improvement than to attempt to change people individually.
Servant leadership combines two dimensions to achieve results, the concern for accomplishing goals and the needs of those who are working towards those goals. Both are equally important, and leadership is just another special reason and method for delivering effective service.
The growth mindset refers to Carol Dweck’s work “Mindset”. A growth mindset accepts mistakes as opportunities to learn. A static mindset tends to avoid risk and considers mistakes as a reflection on the flaws in the person.
A strategic mindset refers to how the vision, mission, values, and strategy combine to create a high-performance environment.
Act with Values and Trust
The purpose of this set of skills is to adopt observable behaviors which contribute to and reinforce the great environment.
The context of an organization can also be thought of as the culture of that organization. A culture can be defined as how things get done and how the priorities are demonstrated. The values of an organization are the priorities and behaviors are how those priorities are demonstrated and reinforced. If the priority of an organization is service, then its values will describe that, and its culture will demonstrate it.
The ability to manage trust is a critical success factor for effective leadership. This ability enables leaders to optimize their influence and therefore achieve more with less waste.
Get Goals Going
The purpose of this set of skills is to understand and appreciate how to create results with accountability and ownership while honoring the needs of those who work toward those goals.
To optimize service, engagement, and costs leaders must know how to optimize results. This means balancing the two dimensions of servant leadership. Goals aligned with vision, mission, and strategy where employees have understanding and autonomy to self-manage is a key.
Improve Interactions Continuously
The purpose of this set of skills is to make every interaction effective while balancing task achievement and relationship development. Process and interpersonal interactions both need to be optimal (both internal and external interactions).
When leaders embrace systems thinking they appreciate how improving the quality of the interactions is a high priority. High quality service to employees and customers relies on the quality of interactions.
Continuous Coaching & Feedback
The purpose of this set of skills is to understand and appreciate how to effectively coach and to give and receive feedback.
To learn, self-manage and develop our full potential we all need feedback. Feedback is the data needed to optimize learning. The skills to deliver feedback are critical success factors for optimal service. Leaders who aspire to be servant leaders must learn how to help employees receive the feedback they need to build their full potential.
Embedded within these 5 sets of skills is the learning cycle: Plan-Do-Check-Act. The Learning Cycle, Deming Cycle, Shewhart Cycle or Scientific Method can be traced back to as early as the 16th Century China. The learning cycle is a critical success factor tool that enables leaders to transform their organizations into a learning organization. Learning organizations continuously improve their capability to achieve its vision.

Future Outlook
According to research, 75% of executives agree customer experience is incredibly important for the business success. (Morgan, 2019)
There are three major trends which explain why every organization and every leader must commit to a customer experience improvement strategy if they want to optimize their results. First, the way organizations interact with their customers is growing more and more complex. There is greater competition and a growing number of communication channels. Many of the new channels are digital (Acquia, 2020) and require self-service. Consumers, and even business to business, customers are demanding faster, and more efficient ways of service and thus self-service options are increasing. The experience of the interaction (digital or not) is still more important than the channel the customer uses. The customer still wants a personal connection.
Secondly, this changing context of customer demands, and their increasing expectations are causing the quality of customer service to fall because the customer service representatives are largely unprepared for the more complex issues they must address. With consumers handling more and more issues via self-service, when customers need answers beyond their self-service capabilities, that is when the emotions can become intense. This is when those responsible for creating a positive customer experience can be unprepared.
Third, research continues to prove the quality of the interactions is an increasingly important factor affecting customer loyalty and how much (more) the customers are willing to pay for excellent service.
In summary, the skills of addressing emotionally charged customers in complex situations are more important now than ever before in large part because of these trends. The challenge for leaders and their organizations is the need to make an emotional connection with customers. The interactions need to be emotional to be memorable. Yet, when those emotions appear, those interacting with customers are less likely to be skilled enough to handle the complexity and intensity.
The latest research (Morgan, 2019) confirms consumers’ desire for exceptional service:
• 81% of companies view customer experience as a competitive differentiator.
• 85% of consumers said they would avoid doing business with an organization due to bad customer service.
• 81% would abandon a purchase if they were experiences poor service
• “86% are willing to pay more for excellent service
• 75% said they are more likely to purchase if a company provides personalized recommendation
• 77% would return for great service vs. a great marketing campaign
• 63% switched to a competitor to receive better service
• 69% expect to be a high priority if they were upset
• 76% expect organizations to proactively follow-up if there is a problem
Research confirms the benefits of improved service (Morgan, 2019):
• 96% of customers say customer service is important in their choice of loyalty to a brand.
• 83% of companies that believe it’s important to make customers happy also experience growing revenue.
• Brands with superior customer experience bring in
• 5.7 times more revenue than competitors that lag in customer experience.
• 73% of consumers say a good experience is key in influencing their brand loyalties.
• 77% of consumers say inefficient customer experiences detract from their quality of life.
• Customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than companies that don’t focus on customers.
• Customers switching companies due to poor service costs U.S. companies a total of $1.6 trillion.
• Loyal customers are five times more likely to purchase again and four times more likely to refer a friend to the company.
• American consumers will pay 17% more to purchase from a company with a reputation for great service.
Leaders who embrace these insights are experiencing exceptional service results for their organization. Employee engagement is a critical success factor in achieving optimal customer experience.
Companies that excel at customer experience have 1.5 times more engaged employees than less customer-focused companies.
Companies with initiatives to improve their customer experience see employee engagement increase by 20% on average.
Companies with engaged employees outperform the competition by 147%.
81% of companies view customer experience as a competitive differentiator.
68% of customers say the service representative is key to a positive service experience.
The financial results achieved by having clear strategic initiatives for customer experience and employee engagement are compelling.
64% of companies with a customer-focused CEO believe they are more profitable than their competitors.
63% of CEOS want to rally organizations around customers as the top investment priority.
90% of CEOs believe the customer has the greatest impact on their business.
59% of companies with a CEO who is involved in customer experience report higher revenue growth, compared to just 40% of companies without a customer-focused CEO reporting growth.
In summary, there are four compelling factors that portend a positive outlook for those who focus on improving customer focus:
1. The economic trends demand the need for a strategic focus on customer experience
2. Consumers desire a personal connection
3. Employee engagement moves with customer experience
4. Financial rewards are enormous
References
Acquia. (2020). DESIGN RESILIENT DIGITAL CUSTOMER EXPERIENCES IN DISRUPTIVE TIMES. acquia.com.
Disco, J. (2017, October 19). Why personalization is key for retail customer experiences. Retrieved from www.retailcustomerexperience.com: https://www.retailcustomerexperience.com/blogs/why-personalization-is-key-for-retail-customer-experiences/
Morgan, B. (2019, September 24). 50 Stats That Prove The Value Of Customer Experience. Retrieved from www.forbes.com: https://www.forbes.com/sites/blakemorgan/2019/09/24/50-stats-that-prove-the-value-of-customer-experience/?sh=27c7626b4ef2
Curriculum
Customer Experience – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 MAGIC of Customer Relations
- Part 1 Month 2 MAGIC of Customer Relations
- Part 1 Month 3 MAGIC Champions and Mentors Workshop
- Part 1 Month 4 MAGIC Email and Chat Writing
- Part 1 Month 5 MAGIC Presentations Skills – Tricks of the Trade
- Part 1 Month 6 MAGIC Transformational Leadership Make a Great Environment
- Part 1 Month 7 Act with Values and Trust
- Part 1 Month 8 Get Goals Going
- Part 1 Month 9 Improve Interactions Continuously
- Part 1 Month 10 Continuous Coaching & Feedback
- Part 1 Month 11 Managing Change with Trust and Team Mastery Workshop
- Part 1 Month 12 Team Problem Solving – The Six Thinking Hats and Waste-Free Meetings Workshop
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Customer Experience corporate training program.
Customer Experience- Part 1- Year 1
Month 1 and Month 2: MAGIC of Customer Relations
Four interactive modules address the skills and attitudes needed to create high-quality experiences for every customer and employee.
What Outcomes Does MAGIC Provide?
– A standard for all members of an organization or team to relate to and communicate with one another
– A common way for everyone in the organization to communicate with and serve customers (both internal and external).
– A behavioral checklist for observing, measuring, and coaching performance

Month 3: MAGIC Champions and Mentors Workshop
½ day-Creating a community of MAGIC® Champions, you can begin to anchor MAGIC attitudes and behaviors in your organization’s culture.
This dynamic workshop establishes the foundation for your service initiative. By creating a community of MAGIC Champions, you can begin to anchor MAGIC attitudes and behaviors in your organization’s culture. Participants experience a first-hand taste of MAGIC, while developing a deeper understanding of a service culture. They engage in conversations focused on vision-driven business results which build ownership and accountability.
This highly interactive workshop develops role clarity, enhancing participants’ ability to inspire and support your organization’s commitment to MAGIC service.
Participants will be able to:
• Describe MAGIC in a way that engages the hearts and minds of others
• Begin modeling MAGIC attitudes, skills and behaviors individually and as a team
• Link MAGIC to the company vision and strategy
• Identify specific drivers and barriers to service excellence within your organization
• Develop strategies to overcome barriers to creating and sustaining your MAGIC culture.

Month 4: MAGIC Email and Chat Writing
½ day-Write professional emails that Make A Great Impression on the Customer™ and employee every time.
It’s time to take control so that you can better manage your time and your
emails. You need to know the crucial elements of a professional email to ensure your emails are read and deliver results. Equally important, you need to know what NOT to do so you avoid damaging miscommunications.
Your messages may be chipping away at your credibility and, ultimately, your success. Here’s what you will gain with MAGIC Email Writing:
• Target your emails to the right audience to ensure results
• Identify commonly used phrases that undermine your message
• Get rid of the fluff so your emails are concise and to the point
• Measure the clarity of any email so you hit the target every time
• Structure your message for greatest impact
• Create subject lines that generate interest and curiosity
• Avoid the top 15 etiquette mistakes that will detract from your brand

Month 5: MAGIC Presentations Skills – Tricks of the Trade
1-day-Specific communication skills and tools needed to give powerful, persuasive presentations, so you Make A Great Impression on every Customer™ and employee.
Presentations to internal or external customers are not just an opportunity to deliver information. They’re a chance to motivate your audience, achieve desired results and build relationships. Take your public speaking to the next level to ensure success.
Participants practice and revise presentations, so they see immediate improvement.
Managing Perception:
• Connect with your audience and focus on:
• Appearance, movement and posture
• Eye contact, hands and gestures
• Voice volume, pitch and emphasis
Preparation:
• Tap into the strengths of your own communication style
• Tailor a presentation to customer needs and objectives
• Use an efficient and effective preparation process
Structure:
• Grab the audience’s attention with your introduction
• Use the right flow for results-oriented presentations
• Close with impact
Audience Interaction:
• Use visuals/handouts effectively to enhance your message
• Overcome objections and master Q&A sessions
• Persuade with benefits

Month 6: MAGIC Transformational Leadership Make a Great Environment
¼ days-Appreciate and adopt the most useful leadership mindsets: Systems Thinking, Servant Leadership, Growth Mindset, Strategic Thinking.
The purpose of this set of skills is to appreciate and adopt the most useful leadership mindsets. These include systems thinking, servant leadership, the growth mindset, and the strategic mindset. Systems thinking is a set of principles which enable leaders to create a service culture. With systems thinking, employees can self-manage within a context. It explains how the performance of individuals is influenced more by the system (environment) within which they work than by their individual efforts or skills. Systems thinking principles explain why it’s more important to focus on the context of the work environment for continuous improvement than to attempt to change people individually.
Servant leadership combines two dimensions to achieve results, the concern for accomplishing goals and the needs of those who are working towards those goals. Both are equally important, and leadership is just another special reason and method for delivering effective service.
The growth mindset refers to Carol Dweck’s work “Mindset”. A growth mindset accepts mistakes as opportunities to learn. A static mindset tends to avoid risk and considers mistakes as a reflection on the flaws in the person.
A strategic mindset refers to how the vision, mission, values, and strategy combine to create a high-performance environment.

Month 7: Act with Values and Trust
1/2 day-Adopt Observable Behaviors which reinforce the Great Environment: Connect organizational values, adopt a definition of trust, appreciate emotional intelligence.
The purpose of this set of skills is to adopt observable behaviors which contribute to and reinforce the great environment.
The context of an organization can also be thought of as the culture of that organization. A culture can be defined as how things get done and how the priorities are demonstrated. The values of an organization are the priorities and behaviors are how those priorities are demonstrated and reinforced. If the priority of an organization is service, then its values will describe that, and its culture will demonstrate it.
The ability to manage trust is a critical success factor for effective leadership. This ability enables leaders to optimize their influence and therefore achieve more with less waste.

Month 8: Get Goals Going
¼ days-Understand and appreciate how to create results with accountability and ownership: Appreciate S.M.A.R.T. Goals, build accountability with trust and not fear.
The purpose of this set of skills is to understand and appreciate how to create results with accountability and ownership while honoring the needs of those who work toward those goals.
To optimize service, engagement, and costs leaders must know how to optimize results. This means balancing the two dimensions of servant leadership. Goals aligned with vision, mission, and strategy where employees have understanding and autonomy to self-manage is a key.

Month 9: Improve Interactions Continuously
½ day-Make every interaction effective both system and interpersonal (both internal and external): Appreciate two types of interactions i.e. interpersonal and system, building the skills of influence, managing conflict with trust, creating high performance team, problem solving, decision making.
The purpose of this set of skills is to make every interaction effective while balancing task achievement and relationship development. Process and interpersonal interactions both need to be optimal (both internal and external interactions).
When leaders embrace systems thinking they appreciate how improving the quality of the interactions is a high priority. High quality service to employees and customers relies on the quality of interactions.

Month 10: Continuous Coaching & Feedback
1 day-Understand and appreciate how to effectively coach and give and receive feedback: Adopt a definition of coach, appreciate the difference between feedback and criticism, create a safe context for feedback.
• Note: The interaction with the elements in Make and Great Environment and the predictable coaching techniques enables leaders to positively influence individuals and the culture to make it safe to learn from mistakes
• The purpose of this set of skills is to understand and appreciate how to effectively coach and to give and receive feedback.
• To learn, self-manage and develop our full potential we all need feedback. Feedback is the data needed to optimize learning. The skills to deliver feedback are critical success factors for optimal service. Leaders who aspire to be servant leaders must learn how to help employees receive the feedback they need to build their full potential.
• Embedded within these 5 sets of skills is the learning cycle: Plan-Do-Check-Act. The Learning Cycle, Deming Cycle, Shewhart Cycle or Scientific Method can be traced back to as early as the 16th Century China. The learning cycle is a critical success factor tool that enables leaders to transform their organizations into a learning organization. Learning organizations continuously improve their capability to achieve its vision.

Month 11: Managing Change with Trust and Team Mastery Workshop
1 day-Developing and sustaining Team Mastery: aligning the four key areas of an optimum team.
Change can create anxiety that can lead to unintended behaviors, reduced productivity and lower performance. Leaders must be prepared. They need the proper theory and honed skills to facilitate and sustain lasting changes. Leaders must know how to inspire people to change on their own. Because high levels of trust can minimize the depth and duration of productivity and performance decline during organizational change leaders must understand how to create and sustain trust.
Participants will learn:
• The 3 key success factors that improve an organization’s adaptability.
• How trust will increase adaptability to change.
• How to minimize the depth and length of disruption to employee productivity.
• How to improve the probability of success by managing the four key elements of trust

Month 12: Team Problem Solving – The Six Thinking Hats and Waste-Free Meetings Workshop
Provide the tools and the process necessary to optimize the speed and quality of decisions in meetings while building trust, relationships, and teamwork.
The average executive attends 3-4 meetings per day and estimates tell us nearly 50% of that meeting time is wasted. This translates into 30-40 hours per month of wasted time (4 workdays). Time is one of the most important resources. Organizations that are unable to manage meeting time will remain or become uncompetitive.
Managing meetings is one of the most important competencies for making decisions, achieving goals, and motivating others. Many, if not most, professionals are unaware of the key elements that make meetings successful, nor do they possess the skills to effectively and predictably manage those elements.
Participants will understand the key elements of a Waste-Free Meeting including:
• Preparation
• Assigning clear roles and responsibilities
• Evaluating the quality of the meeting
• Meetings are more productive (less wasted time)
• The quality and speed of decisions are improved
• Team members reach aligned decisions more quickly and more frequently
• Team members will be able to explain decisions more clearly and quickly to employees and motivate them to follow through on those decisions
• Higher employee engagement
In the age of information, we can never spend enough time absorbing all the information that is thrust at us during each waking hour. The key to handling this barrage of information is the ability to think clearly.
No matter how good we think we are at thinking we can always improve, and we must. In this world of global competition, the most important strategic advantage of any company is its ability to learn. The better the employees can think, the more quickly the organization can learn.
One of the main difficulties in thinking is trying to think about too much at once. The other main difficulty is confusion that is often caused by difficulty number one.
The key to this dilemma is a predictable process for thinking clearly. This process has been developed by Edward De Bono. He calls it his Six Thinking Hats Process. The main purpose of this process is to help a group to focus attention in one direction at a time. The outcomes of this focus are:
• Agreement on action
• Acknowledgement of all opinions
• Evaluation of all points of view
• Everyone feel acknowledged and appreciated for their views
• All options are identified (that the group is capable of generating)
• Optimal creativity
• Shorter meeting times
• Better decisions
• Increased fun
To save time in meetings it is highly recommended the Six Thinking Hats method be applied to every meeting that requires decisions and problem solving.
Methodology
Customer Experience
Program Development
Accelerated Learning is a multi-dimensional methodology that enables students to be active participants in their own learning. It shortens the learning cycle while enabling students to absorb and put into practice the concepts and tools shared during the workshop much more quickly, with a greater buy-in and increase the retention in long-term memory.
Accelerated learning is required to break through old habits and encourage participants to embrace new behaviors and work enthusiastically toward making those new behaviors habits.
Experiential learning is also employed to encourage self-management of the new skills. The learning cycle of Plan-Do-Check-Act is also employed as part of the experiential learning. The learning cycle enables the participants to immediately see for themselves the efficacy of the new skills. This experience encourages long-term change.
The combination of accelerated learning, experiential learning and the learning cycle optimizes the release of untapped potential in individuals and teams which leads to substantial performance improvement.

Program Implementation
MAGIC is not just a training program. It is an initiative to create an exceptional service culture. Because your leadership wants to optimize the investment of time and treasure to improve the probability of success of a change initiative, a fertile foundation for change is created to optimize success.
MAGIC is a predictable process for service delivery. The MAGIC program takes the guesswork out of service delivery. There are four steps to prepare the “soil” for acceptance of skill development and reducing resistance to change.
Step #1: Explain why the change is needed and to do it in a way that everyone can see it. This will often include the following key elements:
• Align the change to the Vision, Mission, Values, and Strategy of the organization
• Identify and communicate (create a process) the benefits of the change to the:
– Organization
– Team
– Individuals
• Identify and communicate (create a process) the consequences if the change is NOT made:
– Organization
– Team
– Individuals
• Identify and communicate the behaviors necessary for success and align those to MAGIC
Step #2: MAGIC Prepares Leaders to Lead the Change
Most managers are not naturally change agents. Managers often hired because they are good at reinforcing (or enforcing) the current processes and policies. Clarifying their “new” roles and responsibilities for change is critical. We must also listen to their concerns and acknowledge their fears. We must treat them the way we want them to treat the employees who are also excellent at using the current processes and policies.
Key implementation steps to help you implement:
• Design and deliver a training to boost change management skills
• Identify a small group of committed change agents: Don’t try to change everyone at once. Find a small group of committed, well connected, and credible people who can help you communicate your very clear and compelling message of change. This idea was clearly articulated in the book the Tipping Point by Malcom Gladwell. (Gladwell, 2000)
Step #3: MAGIC Offers Evidence and Understanding to Those Who Doubt
I find the “four stage model” for change useful. The four stages in a change process are:
1. First, we start out in comfort with how things are. There is no need for change.
2. The second stage is denial. This is where everything that is not working is someone else’s fault. “There is no need for me to change because the conditions just don’t justify it.”
3. The third stage is anxiety. This is where we know we need to change but we are unsure if it is possible. We may feel shame or embarrassment that we messed up and we can feel depression. Sometimes we avoid feeling depressed and stay in denial. It is normal to move back and forth between denial and anxiety especially if the change we are being asked to make is a big one.
4. The final stage is insight. This is where we try something new to address the desired change and it works. This gives us hope that we CAN make the change and it is working. This is the positive feedback stage.
Providing those who are in denial and anxiety with empathy, understanding (love) and data helps them to get the insights they need to make the changes. This is part of the managers’ responsibilities.
Step #4: Create a Process to Identify and Communicate Small Successes
To help people remember the clear messages and the benefits we need a ritual. Find one, create it and stick with it. We encourage clients to use huddles to reinforce the benefits, consequences, and small successes. This frequency of reinforcement is like a ritual that reminds everyone they made a choice, it is working, and it is benefiting them personally.
Other rituals that reinforce positive change include:
• Consistently facilitating agreements with people instead of telling them what to do.
• Looking for processes that need improvement and delegate the “fix” to the staff instead of doing it yourself.
• Hold appreciation huddles. Express appreciation for all the excellent work, and tie the results to the change initiative.
MAGIC training methodology is organized into four components.
Component #1: The MAGIC mindset. How leaders and employees think about service is an essential first step for delivering exceptional service.
Component #2: Creating a MAGIC Relationship. Creating a Respectful Relationship is an essential next step to create cooperation between the service provider and service receiver (internal or external customer). Full cooperation is the foundation for optimal innovation (problem solving) and service.
Component #3: Accountability. Respect and Accountability form the solid roots of exceptional service. Making and keeping promises is the essential method for creating accountability.
Component #4: Providing skills to handle difficult situations. Skills to address emotionally charged situations and/or how to deliver bad news in a way that protects loyalty and cooperation are essential for both leaders and those employees on the frontline of customer interactions. Without these skills customers can see reasons to leave and the whole purpose of exceptional service is to always keep customers. Research shows it costs t least 5 times more to get a customer than to keep a customer.
Advanced Emotional Intelligence (EI) skills are required to lead these challenging interactions. Emotional intelligence skills provide better options on “how” to deliver messages in difficult situations. EI provides a set of skills to influence others respectfully to ask for and get what you want or need. Aristotle once said, “Anyone can become angry – that is easy. But to be angry with the right person, to the right degree, at the right time, for the right purpose, and in the right way – this is not easy.” These skills provide enormous benefits for both the individual employee and their organizations, and, thanks to Aristotle, we have been aware of them for at least 2,400 years.
For the individual, the benefits include a reduction in unhealthy stress, an improvement in personal brand image (reputation), an improvement in trust, stronger working relationships, improved teamwork, and a boost in cooperation. For the organization, the benefits include improved productivity, reduced turnover, improved flow of communication, and improved financial results (Talent Smart, 2020).
MAGIC trainings challenge participants to reach their full potential. It is possible for all participants to reach the level of skills necessary to provide exceptional service if everyone is challenged with the new high standard of behavior.
Participants are asked to demonstrate their current skills often with recorded skill practices. The new MAGIC methods are then shared so the participants can see the difference between where they started and where the y are asking to excel. The MAGIC standard of behavior is a high standard that participants come to appreciate, practice, adopt, and then commit to implement.
Participants then receive feedback. The feedback to participants is organized, specific and valuable. The feedback is positive. It “catches people doing right”. Intensive and truthful coaching is the key to the sustained culture.
It is possible to deliver the MAGIC workshops in both the virtual or face-to-face environments. Our experiences over the past 10 years, most especially 2020 – 2021 has demonstrated the efficacy of the MAGIC virtual training implementation. Fully 25 years of experience has demonstrated the efficacy of the face-to-face workshop experience.

Program Review
The Kirkpatrick Model for workshop evaluation offers numerous advantages for both participants and organizations. There are four levels of the model for evaluating training processes. The first level is evaluating the reaction of the learners. This is done with a workshop assessment instrument which collects such reactions as:
• What did you learn?
• Was the workshop engaging?
• Did you get value (was it worth your time)?
• Can you apply the learning?
• What are you going to change or improve?
• Would you recommend the workshop?
These reactions are valuable because they are available immediately and are often immediately actionable for improving the workshop. A drawback is the reactions can be biased and therefore may not be as useful.
Level two is measuring what the participants have learned. This is immediately measurable with MAGIC because the 33 Points of MAGIC offers immediate feedback. The participants see for themselves immediately that they have learned, made changes and the impact of the change.
Level three is a measure of long-term behavior change. MAGIC offers coaching to reinforce the learning, and this leads to long-term change and habit changes. Without coaching and reinforcement there is a high probability participants will return to old habits.
Level four measures results and impact. With MAGIC this can be measured with a Net Promoter Score tool or some other customer survey measurement tool. Because MAGIC is measurable, using the 33 points, management and staff can work as a team to continuously improve this measure and they can be confident it will lead to financial results improvements.
( ) https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/how-to-use-the-kirkpatrick-evaluation-model
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Financial Services
Financial services industry includes various offerings within the finance industry, including money management and digital banking technology. The financial services sector is accelerating its adoption of digital technology. Paying with cash, participating in in-personal meetings with financial consultants, and even using an ATM are all fading facets of financial services. This has occurred faster in the past two years due to the stress caused by lockdowns in the Covid-19 pandemic.
From investing in real estate to paying for college, consumer finance helps people afford products and services by paying in installments over a fixed period. The consumer financial services market is made up of key players including credit card services, mortgage lenders, and personal and student loan services.
The influence of tech-savvy consumers, looming threat of big tech companies, and shifting attitudes of regulators toward new tech, are all impacting the financial services industry. This is making the need for great customer experience even more challenging. The simple and easy interactions can be done by the consumer without help. The more complex interactions are more emotional and challenging for the consumer and therefore more challenging for the customer facing representatives. This creates a major opportunity for MAGIC to help the representatives to handle the extra challenges and the difficult emotional interactions.
The challenges of the financial services sector include increased competition, regulatory compliance and costs related to same, customer retention, security breaches, the increased complexity of the interactions which impacts customer retention.
Working with MAGIC, clients in the financial services industry have experienced the following benefits:
• Retention improved 80% (saving $9M)
• 10% improvement in talk time
• Recognition for service excellence/financial professionals & shareholders (3 consecutive yrs.)
• Won top mutual fund service award for industry
• Improved average collection amount
• Achieved top quartile service level with their mutual fund
• Went to Top Block on Gallup
• 10% improvement in call time
Mortgage Companies
Low interest rates is creating an overwhelming number of refinancing and loan origination requests. Therefore, mortgage companies are spending significant amounts of resources prioritizing their workload. During the origination process, the questions that must be answered include: Which leads are likely to close? What are the key issues affecting loan officer performance and productivity? How can we reduce cycle time?
For servicers it’s all about productivity: How can we make our team more efficient? Which workflows can be automated? Can we reduce the number of systems? Can we improve call deflection? (https://atrium.ai/resources/intelligent-call-deflection-strategies-help-you-and-your-customers/)
Mortgage lenders are now finding themselves in the enviable, yet tricky to manage situation of an exploding number of customer requests. The combination of low rates combined with economic uncertainty, and the pandemic lockdowns are all driving this. The biggest challenge is addressing how to handle this overwhelming volume while keeping the quality of customer experience high.
This turbulent business landscape, along with shelter-in-place mandates, have left customer service representatives dealing with a new challenge: working remotely in addition to heightened complexities due to changing cancellation policies. The sheer volume of calls coming in can easily overwhelm newly remote agents, increasing their stress levels and decreasing the quality of service they offer. This, as we know, leads to dissatisfied customers.
Implementing a customer experience process such as MAGIC can prevent this from happening?
Working with MAGIC, clients in the mortgage industry have experienced the following benefits:
• Increased satisfaction rating
• 10-15% increase in buyers
• Increased customer satisfaction and productivity
• 40% increase in originations
• Reduction in stress
• Improved case resolution methods and reduced average case handle time
Insurance
Customer expectations for insurance have changed dramatically and quickly in the last year in large part due to the lockdowns caused by the pandemic. Some research show that digital activity (online retail) has jumped ahead by 5-years just in the past 12 months.
Digital convenience is critical for customers of the future. Future insurance customers will be smarter about avoiding decision fatigue. They will rely on easy-to-understand solutions that are most meaningful for their home, community, and environment. Customer service representatives interacting with these customers must be knowledgeable, quick to respond, and avoid wasting the consumers’ time. Insurance companies need to radically dial up their ability to create products that are adaptable and flexible and interact in a frictionless, instant-access method(s).
Consumers of insurance will want to oversee their data, receive a customized product specifically designed for them, deal with a company with the highest ethical standards, trust the brand, and stay in touch with me to provide the highest level of support. When the future insurance consumer needs to interact with a service provider (because the frictionless self-service option did not satisfy), the skills to manage emotionally charged and highly complex interaction will require a very high level of soft skills, product knowledge, and problem-solving skills. MAGIC can help.
MAGIC provides a method for insurance companies to provide a customized, personalized, and efficient level of service.
Working with MAGIC clients in the insurance industry have experienced the following benefits:
• Highest courtesy score in company history 98%
• Decrease in employee turnover
• Improved teamwork
• Improved skill sets that match the needs of the new consumer
• Inspired associates who can solve problems, demonstrate respect an accountability to the new consumer demands
• Improved case resolution methods and reduced average case handle time.
Technology
The shift to remote work and digital everything in 2020 forced change at a pace unheard of before. Companies had to both abruptly shift their workforce and their product/service delivery models to accommodate health and safety measures imposed by the global pandemic.
We see this evident in the challenges the C-suite is focusing on, where they’re investing, and what technology teams are now responsible for. The pandemic caused a necessary shift in priorities for the C-suite. Before COVID-19 technology executives were focused on operational efficiency, customer engagement and developing new products and services. This has changed now to include a focus on workforce enablement to increase remote work.
Spending changed dramatically to adapt to new customer expectations and market conditions. Spending on digital transformation increased in 2020, with 83% of companies planning to accelerate their efforts, and 65% expecting to increase the amount they’re investing in 2021—despite the economic downturn.
According to the 2020 Harvey Nash/KPMG CIO survey, workforce enablement has jumped from the 8th priority for CIOs to a top priority. Other workforce challenges—including out/insourcing, off/onshoring, acquisitions and more—are still on the C-suite’s radar, but thriving in 2021 will require keeping teams engaged, productive and adaptable to ever-changing circumstances.
Employers would be well advised to embrace remote work for the long term and capitalize on the learnings from the sudden shift. It’s more important than ever to have data on your team’s workflow efficiency to empower them to continue to contribute remotely. Now is the time to provide tools that allow your team to collaborate effectively and offer visibility into the data behind their work.
Productivity and teamwork are essential elements for IT professionals to address the exploding growth in remote work. MAGIC can help improve productivity by improving case resolution methods and reducing average case handle time. When the priority shifts back to customer engagement, MAGIC can help there as well.
Working with MAGIC clients in the technology industry have experienced the following benefits:
• Increased customer satisfaction 10 percentage points
• Targeted response time targets were above 90%
• Improved case resolution methods and reduced average case handle time
Healthcare
Baby Boomers reaching age 65 is increasing every day. Patients are living longer. The ability to treat patients with chronic disease, such as heart disease, is clearly lengthening their lives; in the next 30 years, the number of people with heart disease in the United States is expected to double and their life expectancy will also increase because of the advances in research and techniques.
Markedly improved less invasive imaging (e.g., computer assisted diagnosis of coronary artery disease combining echo, magnetic resonance, and positron emission tomography) along with other less invasive treatment provide better functional outcomes while increasing patients’ willingness to seek these treatments portend explosive growth.
Reliance on technology will also improve efficiency of service which leads to improved consumer satisfaction.
Information deriving from patient care will also improve. With the Internet, the electronic medical record will not only be able to store patient information but also to provide information on “best practice” instantaneously. The ability to manage the data of large numbers of patients and large segments of the general population may provide overall improved definitions of “quality” from the patient perspective.
Patients will become the ultimate consumers. Measures of patient satisfaction and other patient-oriented report cards will assume increasing importance. This is especially where MAGIC can help protect and enhance satisfaction.
There will be greater self-diagnosis and self-care as patients obtain more information from the Internet. With this information, as well as direct Internet video communication with a provider, the need to visit the practitioner will decrease. The speed and effectiveness of video communication will place a high demand on improving the quality of virtual interactions. This also creates a great opportunity for growth in MAGIC. Higher quality and faster speed of care will be expected by the consumer.
Working with MAGIC clients in the healthcare industry have experienced the following benefits:
• Loyalty index rose from 55 to 71 after training
• Lower % of escalation calls and handle time in escalation group decreased by 218 seconds.
• Improved case resolution methods and reduced average case handle time.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

New York City, NY
New York City’s economy continues to show signs of positive but slower growth. Total private sector payroll employment expanded by 80,100 or 2.0% in 2019 compared to 2018. While still very healthy growth compared to historical rates, it has been decelerating from the 83,000 jobs added in 2018, and 86,500 in 2017. This two percent growth in 2019 marks the slowest pace of growth since 2010.
Last year New York City experienced its worst single-year job loss since the 1930s. In 2020, the city lost on average an estimated 750,000-plus payroll and self-employed/independent contractor jobs between the months of February and December, nearly one out of every six jobs. While the new year is brightened by the late December $900 billion federal aid package and the prospect of additional federal economic recovery aid, 2021 will bring monumental challenges in addressing the lopsided economic impact of the pandemic in the U.S. and in New York City.
New York City initial jobless claims for regular State unemployment insurance averaged 25,000 from mid-January to mid-February, more than four times the pre-pandemic level of a year ago for the same weeks. In addition, initial claims in the city for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance provided to independent contractors and others who don’t qualify for regular unemployment insurance averaged 20,000-23,000 for the four weeks through mid-February.
Industries that are highlighted in New York City include:
• Manufacturing. This sector is responsible for a wide array of exports to foreign countries and states as well as local use.
• Financial Services. New York is home to the famous Wall Street in Manhattan.
• Media And Entertainment. New York City is considered the world’s media capital for a good reason.
• Health Care. With a population of close to 20 million people and the prevailing life trends, it is crucial for each state to be equipped with top medical facilities

Chicago, IL
Chicago has one of the world’s largest and most diversified economies, with more than four million employees and generating an annual gross regional product (GRP) of over $698 billion. The city is an efficient economic powerhouse, home to more than 400 major corporate facilities, including 36 in the Fortune 500, and 31 in the S&P 500.
Chicago’s diversified economy is based on manufacturing, printing and publishing, finance and insurance, and food processing (the city is still considered the nation’s “candy capital”) as primary sectors. A substantial industrial base and a major inland port contribute to the city’s position as a national transportation and distribution center. The source of nationally distributed magazines, catalogs, educational materials, encyclopedias, and specialized publications, Chicago ranks second only to New York in the publishing industry. The city is home to the Federal Reserve Bank, the Chicago Board of Trade, and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. Common items and goods produced are: telephone equipment, musical instruments, surgical appliances, machinery, earthmoving and agricultural equipment, steel, metal products, diesel engines, printing presses, office machines, radios and television sets, auto accessories, chemicals, soap, paint, food products and confections.
Since its founding, Chicago has been an important transportation and distribution point. At one time, it was a crucial link between the Great Lakes and Mississippi River waterways, and today the city ranks among the world’s busiest shipping hubs. The city became a world port in 1959 with the opening of the St. Lawrence Seaway, which provides a direct link from the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. The Port of Chicago handles marine, rail, and overland freight. The state of Illinois maintains the third-highest combined mileage of railroads and paved highways in the country. Approximately 750 motor freight carriers serve the metropolitan area, and trucking companies ship more than 50 million tons of freight each year; railroads average more than 40 million tons. Chicago’s airports handle more than one million metric tons of cargo annually.
COVID 19 has been a significant challenge to the economy where travel and tourism has been greatly impacted.

Atlanta, GA
Atlanta’s recovery from the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic will outpace the nation’s in 2021, driven by the metro area’s educated workforce, consistent business development and innovation, above-average population growth, and strong housing market, according to the Selig Center for Economic Growth’s Georgia Economic Outlook 2021 released earlier this month.
Locally, Atlanta’s commercial real estate market continues to improve with preliminary data suggesting a nice rebound for the office sector in Q2. Still, the number of jobs added nationally last month missed estimates and remains behind the pace of the recovering economy.
Tack on the most recent inflation data showing U.S. consumer prices increasing 5% and market sentiment becomes muddled. The good news is the overall economy continues to recover with most states having lifted their pandemic restrictions.
Although April’s jobs gain for Atlanta was mediocre at 5,800; employment for the metro area continues to inch back to pre-pandemic levels with the year-over-year number being positive for the first time in 12 months.
Leisure and hospitality led the way in May with the bulk of the jobs added being in restaurants and bars. Public and private education experienced solid gains as well thanks to continued reopenings throughout the country.
The Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) reached its highest level on record back to 2000. The 9.3 million figure shows a continued struggle for employers to fill positions in Atlanta.
Factors including continued unemployment benefits, worker concerns and a fast-paced recovery of the economy have been cited by economists as contributing to the strong number of openings.
Dallas, TX
Dallas’ GDP will grow at an average rate of 2.2% between 2020-2021, down from 3.6% from 2014-2018, according to Oxford Economics. Projecting out two more years to 2023, both the Dallas and Houston economies are forecast to grow at a 2.4% rate. The Sprint Business Survey called Dallas the most productive area in the U.S., based on its vibrant economic climate and its fast-growing industries in technology, communications, professional services, banking, and financial services.
Dallas has seen the job market increase by 3.3% over the last year. Future job growth over the next ten years is predicted to be 45.1%, which is higher than the US average of 33.5%. The Sales Tax Rate for Dallas is 8.3%. The US average is 7.3%. That was an increase of 7.4% from the same month a year earlier, by their estimation. The company’s forecast for the Dallas real estate market predicts that prices will continue to climb over the coming months, perhaps through 2021 and into 2022.
Payrolls in Dallas/Fort Worth expanded an annualized 4.4 percent (40,200 jobs) in the second quarter, an acceleration from the gains seen in the first quarter. Growth was mixed across sectors. Goods-sector employment contracted, with payrolls in manufacturing (0.7%, or 500 jobs) and construction and mining (7.2%, or 4,100 jobs) shrinking. On the services side, leisure and hospitality led growth (26.1%, or 20,300 jobs) and was followed by other services (14.4%, or 3,800 jobs) and professional and business services (6.8%, or 10,700 jobs). Payrolls in education and health services contracted 3.9%, or a loss of 4,500 jobs.
While Dallas is well known for tourism, sports, the Dallas Cowboys, and famous BBQ, many do not know it is home to the largest Urban Park and the largest art district in the US.

Los Angeles, CA
Los Angeles has an estimated population of four million and is the cultural, financial, and commercial center of Southern California. Nicknamed the “City of Angels” partly because of its name’s Spanish meaning, Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, Hollywood and the entertainment industry, and sprawling metropolis.
In 2021 and 2022, the combined total payroll employment growth forecast for Los Angeles County (broken down by industry) is as follows: 76,100 jobs leisure/hospitality; 59,300 trade/transportation and utilities; 37,400 education and health services; 36,000 information technology; 22,600 professional and business services; 18,400 manufacturing; 9,300 construction and natural resources/mining; 6,500 financial activities; 6,000 local/state and federal government; and 8,300 “other” services.
Small business revenues are down 40% statewide, compared to pre-pandemic levels. Some of the largest industries — including entertainment and tourism — continue to struggle. Los Angeles Economic Development economists expect that it’ll take until 2023 or even 2024 for the county’s economy to recover. Los Angeles, CA Unemployment Rate is at 5.50%, compared to 4.80% last month and 6.20% last year.
The Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach combine to make seaports complex the largest in the Western Hemisphere, handling over 40% of all inbound containers for the entire United States. Over time, a sophisticated and mature logistics economy has developed around these ports, including high-capacity rail networks, endless warehousing and distribution options, and businesses that have located in L.A. County to leverage this infrastructure. Over 160,000 workers in L.A. County alone support the international trade sector.
In addition to being the movie capital of the world, the city also has a major international airport allowing for easy access to Los Angeles. In 2019, LAX handled 88,068,013 passengers, making it the world’s third busiest and the United States’ second busiest airport following Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. As the largest and busiest international airport on the U.S. West Coast, LAX is a major international gateway to the United States, and also serves as a connection point for passengers traveling internationally. The airport holds the record for the world’s busiest origin and destination airport, since relative to other airports, many more travelers begin or end their trips in Los Angeles than use it as a connection. It is also the only airport to rank among the top five U.S. airports for both passenger and cargo traffic.
Program Benefits
Customer Service
- Service philosophy
- Service tools
- Improve skills
- Reduced stress
- Accelerated service
- Listening skills
- Performance standard
- Higher engagement
- Higher loyalty
- Improved communication
Human Resources
- Motivating environment
- Motivating philosophy
- Reduced stress
- Improved trust
- Enhanced relationships
- Leadership skills
- Listening skills
- Improved performance
- Fewer conflicts
- Performance culture
Leadership Improvement
- Proactive decisions
- Performance measures
- Create culture
- Positive attitude
- Respectful behaviors
- Motivating environment
- Remove barriers
- Adopt vision
- Adopt strategy
- Create goals
Achievements & Testimonials

Achievements
Healthplex
Employees at Healthplex have implemented a customer service culture that buzzes with success: a culture that cross-pollinates across the organization as it focuses on delivering exceptional customer service to internal and external customers. Headquartered in Uniondale, New York, Healthplex is the largest dental insurance provider in the state of New York.
H.M. Royal
Everyone in the organization recognizes that sales and service are primary; that’s their mission. After all, H.M. Royal contracts with manufacturers of materials and signs up to be extensions of their sales force. Every associate has a role in that sale, no matter the position or department —whether it’s customer service, receiving, shipping, logistics, or quality. And, every interaction counts.
Colonial Supplemental Insurance
MAGIC is promoted throughout … It allows our representatives to practice their skills and 33 points to earn their MAGIC Bucks. It helps them discover that MAGIC can generate compliments and enhance customer service with both internal and external customers. It creates joy and makes a great impression on all involved! We are often told that MAGIC “spills over” into personal lives, with spouses and children.
Colgate Palmolive and Indianapolis Power and Light
Colgate-Palmolive and Indianapolis Light and Power are partnering to build MAGIC service cultures. … if you think of your Quality Assessment as a Motivating Form, you shift the approach from improving machines to improving human performance. Discussions based on a Motivating Form tend to be about education, development of knowledge, and improvement of customer relations skills through coaching.
Coldwell Banker
While most companies in the industry tout a focus on customer service, Joe knew that it shouldn’t stop there. His goal was to create a culture with a focus on internal service as well. Partnering with Kendall Forbes, regional director of Human Resources, Joe chose to bring MAGIC® training to their organization.
Community Health Group
Norma Diaz, Community Health Group CEO, is committed to MAGIC® of Customers Relations to deliver a consistently exceptional customer experience. As one of the oldest health plans in the country, they are dedicated to taking care of every member whenever there is a health concern, no matter how large or small.
Beltmann
From the very start, Beltmann’s vision has been to be the most customer-focused company in the moving industry. And, they have demonstrated an unwavering commitment to this vision for over 50 years.
Beltmann also realized the value of developing their people, and sought to provide their associates with the skills needed to deliver consistently exceptional service. Many organizations assume their associates know how to do to this, especially if they have experience in the business. While many associates may know the technical aspects of their roles, they may not know how to manage some of the tougher scenarios with professionalism and grace.
Beltmann’s national customer care team participated in a MAGIC training program, delivered by a certified MAGIC facilitator at Cartus Corporation.
Blue Cross and Blue Shield
“MAGIC at BCBS-Kansas City brings customer service to the attention of all employees,” explained Robin, Supervisor – HMO & PPO Claims. Stephanie McIntosh, Technical Trainer and newly certified MAGIC Trainer says, “I feel this is the right step in improving our customer service levels at Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City.”
American Modern Insurance
Each policy is a promise—and American Modern is confident that MAGIC will help them deliver on that promise every day.
American Modern’s deep commitment to providing superior services and results led to a search for a customer service training solution that would align with their commitment and values. The MAGIC of Customer Relations® , quickly became the frontrunner for many reasons.
Affinion Group
Mark Jackson, Director of Training and Quality/Contact Center Operations, and the leadership team realized they needed to create a service culture. MAGIC created an additional certification program for leaders who coach others. Affinion won top accolades from Contact Center World’s Best in World competition.
EMC Corporation
“Since your first MAGIC session, our customer satisfaction has increased ten percentage points. In addition, the number of customer e-mails praising individual engineers continues to increase and the engineers feel better prepared to handle difficult situations.”
Subaru of America
“We already had a good team, but we wanted to challenge them to rise to the next level. After previewing many offerings, I zeroed in on MAGIC! MAGIC stands out because it offers our people a no-nonsense, down to earth approach that everyone could use immediately with positive results.”
Budd Van Lines
The entire organization goes through MAGIC and senior management communicates the importance of the initiative and helped design creative ways to support it. In 2009, BVL recorded measurable improvements to Client Services’ Quality Assurance scores in a short amount of time.
• Overall moving experience with Budd Van Lines:
The number of excellent scores increased 129% since 2004 and 44% from 2006.
• Communication (helpfulness) of your move coordinator throughout the move:
The number of excellent scores increased 109% since 2004 and 42% from 2006.
• Timeliness and professionalism of Budd Van Lines’ drivers and crew:
The number of excellent scores increased 87% since 2004 and 35% from 2006
In 2008, BVL achieved unprecedented success in the industry:
• Rated the Nation’s Top Carrier in the 2008 Survey of Corporate Relocation Managers by Trippel Survey & Research
• Rated highest net satisfaction score in the 2008 Nationwide Relocating Employee Survey by Trippel Survey & Research
• Made Parsifal Corporation’s 2008 Benchmarking Report and was rated “the best of the best”
• Won six awards at the 2008 Cartus Global Network, including the most prestigious Cartus Cup award
• Achieved a higher close rate and sales increase than other carriers in this difficult economy
Morreale Real Estate Services Inc. (MRES)
In 2008, they saw increases in key measures:
• They received a an overall approval rating of 96.64% from its clients
• In phone skills, the approval rating was an outstanding 93.17%.
Additionally, one of its clients bestowed its highest honor to MRES for exemplary customer service
American Modern Insurance Group
They saw customer service scores increase as much as 20% after their MAGIC training initiative. And, they found that it even helps associates who
haven’t even taken the training yet. They hear the MAGIC around them and start to model it.
K. Hovnanian Homes
They partnered with MAGIC to implement a company-wide initiative to increase customer satisfaction. In 2008, an extremely tough economic time, they won two prestigious awards:
• Silver National Housing Quality Award for outstanding relationships with their trade partners
• Honorable Mention in the 2009 National Housing Awards for employee satisfaction
DST Systems
Since implementing MAGIC, DST Funds have consistently won key honor awards as well as the highest award granted by the industry, DALBAR’s Quality Tested Service Seal, symbolizing excellence in service to customers, distributors and employees.
Presentation Systems
They measured a 15 to 20 percent increase in the average value of their deals as the sales force became more attuned to customer needs.
Unum
They reported the highest courtesy score ever in their history – 98%.
Cendant Mortgage
They realized a 40% increase in originations after implementing MAGIC.
Vytra Health Plans
They saw a direct link between MAGIC and customer loyalty. Their loyalty index rose from 55 to 71 after MAGIC.
The Alger Fund
The Alger Fund was recognized for excellence in service to financial professionals and shareholders for three consecutive years and won the top mutual fund service award for the industry.
John Hancock Signature Services
They saw employee turnover decrease and teamwork improve.
Cartus
They realized a 12% improvement in teamwork and partnering, as well as an increased number of “Top Block” (highest service) ratings.

Testimonials
Budd Van Lines
“MAGIC was a natural fit for [Budd Van Lines]. It provides greater expressions of respect for the customers and more accountability for customers’ needs.”
“From the start, I set out to build the best moving company in America. It’s really all in the details of taking care of customer needs,” explained Budd. He always believed that consistency of quality standards and control over the move process provides a better experience for his customers. He also noticed there were varying levels of commitment amongst most household drivers. That inspired him to develop a moving company offering a consistent level of quality.
Collins Aerospace
“I really enjoyed the interaction and the hands-on materials. We were able to make the training fun and personalized.”
Sun Life
“I completed the MAGIC training. Have to say this was one of the best training sessions that I have attended in my professional career in various industries. I really loved the interactive nature of this training, the use of some real-world examples, and the powerful “tweaks” we can make during interactions with our internal and external customers.”
San Francisco Health Plan
“The class had a great flow and was easy to transition to real world situations.”
Anthem Blue Cross/Blue Shield
“I just wanted to let you know again how much I enjoyed the MAGIC® Training. It’s not only applicable at work but in personal life also. MAGIC is doing a great service by providing this training. All customer-related companies/businesses should offer this training.”
EMC
“I would like to thank you for the excellent soft skill classes you have provided to the software support team. As you know almost 30% of the team have been with the company less than two years which has presented a huge challenge for our management team and customers. Since many of the engineers are new and lacked strong customer skills and often an engineer created a customer situation unknowingly.”
What have managers said about MAGIC?
“Since we implemented MAGIC, our call center has measurably improved its customer service. Our teamwork is thriving and employee turnover has decreased.”
“After MAGIC training and practice, the customer service performance of front-line representatives improved by about 30%. Additionally, the average length of phone calls decreased by about 8%, as customer service representatives became more efficient in controlling each interaction.”
“Before the MAGIC training, managers were not able to consistently pinpoint and assess performance behaviors of front-line representatives. After the training, scoring reliability among managers increased to 90-95%.”
“The 33 Points of MAGIC gives us the strategy for showing our customers we really care about them. The impact on our staff has been amazing. Our area has become an example to the rest of the firm as to how to treat our customers right.”
“MAGIC has made a significant difference for us. Before our support team started the training, we only heard from our customers when they were angry. Now, we get letters on a daily basis thanking us for the level of service we provide.”
What have participants said about MAGIC?
“Clearly, MAGIC has great implications for our organization and we look forward to embracing the 33 Points on a daily basis. I also appreciate all the ideas that you provided to keep MAGIC alive in the months and years ahead.”
“Our group found the sessions very productive and pertinent to running a “first class” operation. The concepts we learned can be applied to all aspects of interaction with people, both professionally and personally.”
“This class showed us that there are always ways to improve our methods. This course makes you very aware of your own actions and behaviors, and that we choose our consequences by deciding how we respond. Thank you and senior management for implementing this initiative.”
“You’ll be happy to know that I have had the opportunity to utilize what I learned with an unsatisfied customer. The end result was the customer called me a second time to thank me for resolving her issue. I could not have done without the Regional Vice President’s prompt assistance and the tools I learned in my MAGIC session.”
“I have received nothing but great feedback from those who participated in the MAGIC programs. Our Associates have stated that the course was very interactive. We look forward to an increase in our customer satisfaction scores.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.

















