Culture Invigoration

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Culture Invigoration is provided by Ms. Elfouly Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 24 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
With over a quarter-century of groundbreaking work in the technology sector, Ms. ElFouly is a beacon of multifaceted excellence, blending operational management, human resources, sales, digital transformation, communications, marketing, and strategy with unparalleled expertise. Their experience stretches across various business units, both globally and at the headquarters level, embodying a leadership style that breaks through conventional barriers.
Holding the distinguished title of Certified Chair™ of Advisory Boards, she excel in driving change management, devising organizational strategies, and fostering transformative cultures aimed at growth. Their leadership approach, deeply rooted in a Multi-certified Executive & Human Potential Coaching philosophy, employs a holistic, system-eclectic methodology that promises enduring success and the unlocking of full potential within collective projects.
Fueled by a passion for building profound relationships, empowering individuals, and developing talent, their compassionate and inclusive leadership style resonates deeply. An American-Egyptian and a Citizen of the World, they are a true Multipotentialite, showcasing an exceptional ability to excel across various fields with agility and excellence.
Currently, they are channeling their focus towards nurturing ventures in health, well-being, and people-centered projects, aiming for their successful and impactful realization. As a polymath and avid learner, they are deeply involved in exploring Quantum Physics-based Alternative Medicine, working towards a Double Board Certified Doctorate and Ph.D. in Natural Medicine.
Their interests extend into the realms of the Metaverse, Web3, Cryptocurrency, NFTs, and XR, with a commitment to unlocking the transformative potential of these technologies. Advocating for mental and physical health, mindfulness, energy work, biohacking, and personal growth, they are dedicated to fostering success, productivity, self-awareness, and the establishment of healthy boundaries.
A staunch supporter of diversity, equity, and inclusion, they stand beside those brave enough to share their truths. As a speaker, they engage in select discussions on the Metaverse, mindfulness, biohacking, and well-being. As a coach, they attract ambitious, empathetic executives, solopreneurs, and entrepreneurs looking to elevate their personal and professional lives.
Ms. ElFouly sits on multiple technology industry and start-up Advisory Boards with a key focus on establishing transformative cultures and supporting culture invigoration across enterprise organizations.
To request further information about Ms. Elfouly through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Culture Invigoration
Your company’s organizational culture is a strong force. It reinforces workers’ trust in their job and keeps them inspired and motivated to perform at their highest level. A workplace’s culture is a collection of attitudes and beliefs about how things are done there. Even though it may not be acknowledged frequently, culture has an impact on all of the work that is completed — or not. It has to do with people.
People want to work for an organization whose values they share in the wake of the Great Resignation. According to a recent study, 35% of American workers wouldn’t accept a position even if it was a great fit if the company culture conflicted with their personal beliefs. Furthermore, an incredible 91% of managers believe that a candidate’s fit with the corporate culture is just as important as or even more important than their education and expertise.
According to another poll, 71% of employees would look for new possibilities elsewhere if the workplace culture declined. It makes logical that companies that concentrate on developing their culture and defining their mission would have the best success keeping their current workforce and luring top talent.
How devoted, connected, and enthusiastic are your employees about their work for your company? You may assess this by keeping a careful eye on employee engagement, or how your team forms deep ties with your company. High employee engagement has enduringly beneficial effects on the business as a whole.
Engagement is greatly increased by a strong culture that values collaboration, community, and diversity. Employee engagement is up to 72% greater in organizations with strong cultures than in those with weaker or misaligned cultures.
Let’s look at seven factors that make organizational culture crucial.

7 factors that make organizational culture crucial
1. It establishes the internal and exterior identity of your business.
Here is an exercise in thinking: Five characteristics that best reflect the culture of your firm should be listed on paper. You may use something like “good work-life balance” or “lots of meetings” or even “team-oriented.”
Now, take a moment to consider why each of those qualities is significant for your firm in particular. Why is it important for your business to have a healthy work-life balance? What makes your employees and customers value these cultural traits?
According to Peter Ashworth, your organization’s culture “defines for you and for all others, how your organization does business, how your organization interacts with one another, and how the team interacts with the outside world, specifically your customers, employees, partners, suppliers, media, and all other stakeholders.”
In other words, because it embodies your corporate culture, it will have an impact on every area of your company. It affects how your colleagues and clients view you because it serves as both your identity and your image.
2. Organizational culture involves upholding your business’s guiding principles.
Your company’s essential beliefs may be reflected in (or betrayed by) your culture. Your firm’s operations, workflow management, teamwork, and customer service practices all combine to create an experience that should reflect who you are as a company and how you see a business operating. In other words, your company’s principles in action make up your culture.
However, it is an issue if your professed ideals do not align with your culture. It can imply that your employees are aware that your “core values” are nothing more than a series of useless jargon.
Your company’s basic principles should be at the forefront of all daily activities and organizational decisions thanks to a strong corporate culture. Doing so has enormous benefit.
3. Employees can become supporters (or detractors) of your culture.
One of the biggest benefits of an effective corporate culture is its capacity to convert workers into supporters.
More than a reliable income and adequate benefits, your employees desire a sense of purpose in their work. Additionally, when employees feel valued, they are more likely to become culture ambassadors—that is, those who not only contribute to the culture of your company but also advocate for it and embody it both internally and outside.
How can you accomplish this? One strategy is to reward excellent effort. A sense of accomplishment can be found in a culture that recognizes and rewards team and individual accomplishments and that provides credit where credit is due. That is one method to encourage employees to become champions.
However, if your workplace culture doesn’t support this, you risk drawing negative attention.
4. A solid company culture aids in retaining your top talent
It shouldn’t come as a surprise that staff members who feel like they belong to a community rather than just a cog in the machine are more inclined to stick with your business. In actuality, that is what the majority of job seekers seek in an employer.
Any high performer will tell you that the people are what keep them at their organization. It’s due to the strong appeal of a people-centered business culture. It enhances engagement, offers a distinctive employee experience, and strengthens the sense of community among your workforce.
Hiring for cultural fit is one strategy for luring great performers who are innate culture champions.

5. A healthy culture facilitates onboarding
The culture of your organization may also serve as a unifying factor there. This is especially true for recent workers who, more often than not, have given the culture they are joining a lot of attention.
It’s crucial that your company’s culture begins with onboarding because it will serve as a sort of compass for them.
George Bradt, in a Forbes article, elaborates further: “People struggle in new professions because they don’t fit well, don’t perform well, or don’t adapt well to future changes. Your onboarding program should cater to their needs (so they can do real work), assimilate them into the organization (so they fit the culture), and accelerate their progress (so they can deliver and adjust), presuming you’ve successfully aligned the organization around the need for your new employees and acquired them in the right way.
6. Your organization becomes a team because of your culture.
Successful organizational cultures unite and maintain alignment across your workforce. When your culture is obvious, people from various viewpoints can unite behind it for a common goal. Your company’s culture establishes standards for how employees should act, collaborate, and perform as a team.
In this manner, culture can help to blur the lines between siloed teams, direct decision-making, and enhance overall workflow. On the other hand, a poisonous organizational culture has the power to have the exact opposite effect.
7. Culture affects productivity and employee happiness
According to reports, corporate culture directly affects performance and, more crucially, the happiness of your staff. In order to solve both of these issues, a healthy culture strikes the right balance based on shared business values.
Does your organization place such a high value on performance that you feel that your physical and emotional well-being are being neglected? There may be certain circumstances in which it won’t be an issue, but in the vast majority of situations, it will hurt your business.
“Employee wellbeing strategies have the potential to bring significant benefits to employees and employers alike, but they need to be introduced in the right way for the right reasons, and at the right time,” writes Paul Barrett, summarizing the situation nicely. They must be built holistically in accordance with a business culture that supports their success if they are to be effectively successful. That entails accommodating management practices, flexible work arrangements, and an open culture that gives workers a voice and some influence over the workplace environment.

Trends and Competition
The fact that corporate culture is becoming a more common topic of discussion and growth is one of the main motivators. More businesses are focusing on developing thorough brand cultures and maintaining them through continual development. Why? It’s caused, at least in part, by the increased conversation about culture. Studies have shown quantifiable increases in turnover for businesses with weak or nonexistent cultures, and entrepreneurs routinely bring up culture in casual conversation.
You might believe that we’re just jumping on the bandwagon here and telling you to pay more attention to culture since other businesses are. But keep in mind that these are the businesses you are up against when it comes to luring new employees and winning over clients. You will lag behind if you don’t find a means to stand out and at least keep up with a powerful culture.
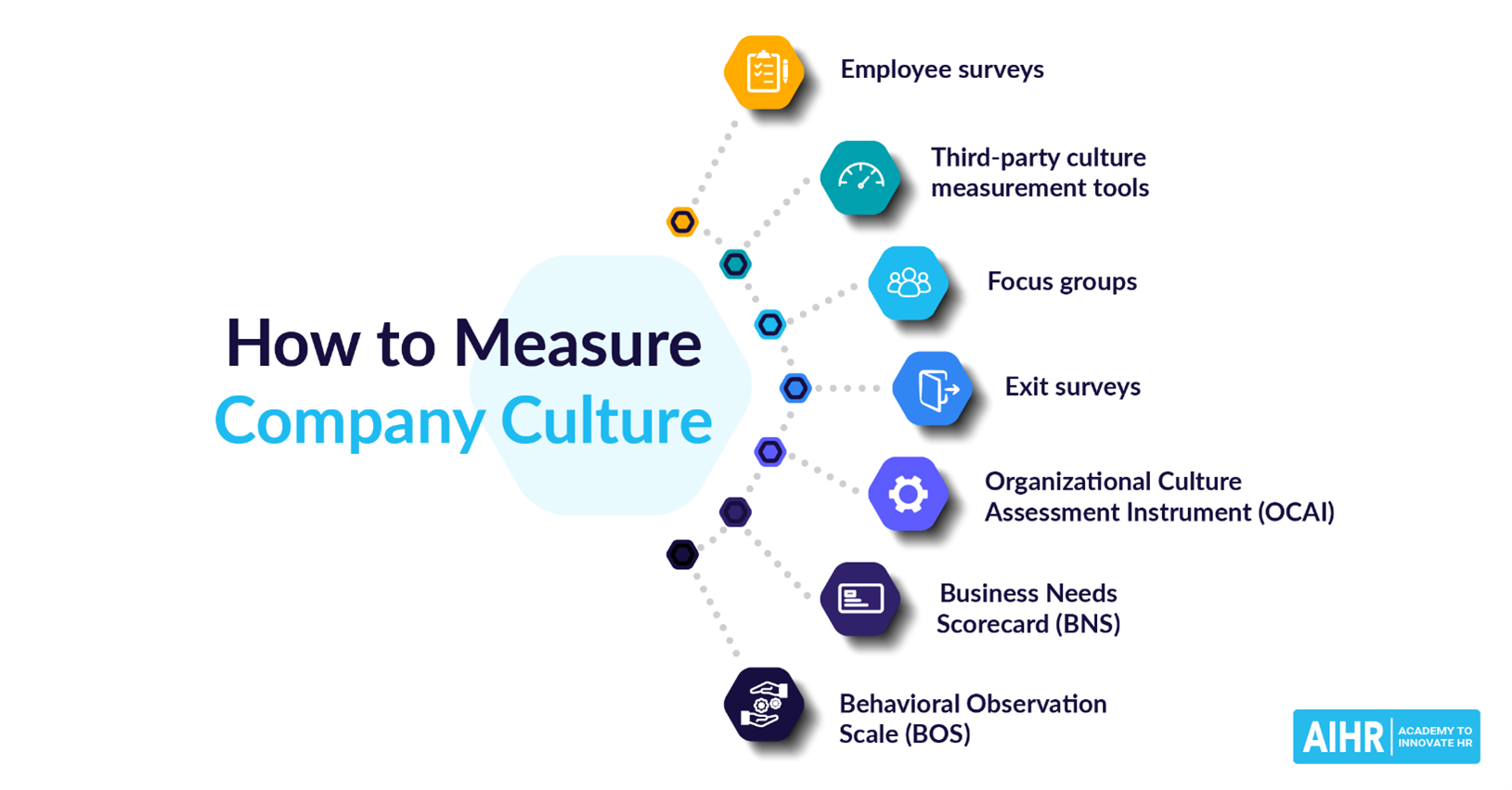
Millennial Expectations
Millennials, whether they like it or not, are the generation in charge of the upcoming changes in the workplace. Your growth can stagnate if you are unable to draw in young talent, and you might eventually run into a talent scarcity.
However, when choosing a company to work for, millennials care most about having a good company culture (in one way or another). You’ll start losing the war on hiring if your organization doesn’t have a compelling company culture.
Startup Economics
It’s also important to note that the entrepreneurial community has benefited from several intriguing new factors brought about by the modern startup economy. Today’s business owners have access to nearly limitless digital resources to create businesses, and such businesses (particularly in the IT industry) have the potential to succeed or fail rather quickly. This makes distinctiveness in the market more important, especially in competitive industries, and pushes businesspeople to identify a sticking point for employees who may otherwise quit after a brief assignment.

Is a Culture Audit Necessary?
Once you realize how crucial company culture is to the future of your firm—and how crucial it is going to become—you might want to conduct a “culture audit.” Basically, this is a means to assess where your culture is at the moment, identify any gaps, and develop a strategy to fill them.
• Theory. How well-defined is the culture at your company? What is its definition? Do your new hires have access to these plans and how precisely is it defined?
• Understanding. How would you rate the present awareness of your corporate culture among your employees? Take a survey of your employees. Do they understand your brand’s core principles?
• Consistency. Even though your employees are aware of your culture, they might not continuously “live and breathe” it or enforce it. How frequently do you notice that your team leaders don’t follow your ideal culture? What about your employees?
Every firm has a unique culture, so there is no single standard for a “correct” one. However, if you want to be competitive in the near future, you’ll need a strong set of values that are consistent and enduring. From here, it will only gain in importance.
Curriculum
Culture Invigoration – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Corporate ID
- Part 1 Month 2 Future Vision
- Part 1 Month 3 Executive Ethos
- Part 1 Month 4 Organization ID
- Part 1 Month 5 Vision Statement
- Part 1 Month 6 Coaching Culture
- Part 1 Month 7 Motivation Catalysts
- Part 1 Month 8 Investor Alignment
- Part 1 Month 9 Customer Engagement
- Part 1 Month 10 Leadership Development
- Part 1 Month 11 Leadership Cascade
- Part 1 Month 12 Organization structure
Culture Invigoration – Part 2- Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Change Management
- Part 2 Month 2 Refined KPIs
- Part 2 Month 3 Updated Image
- Part 2 Month 4 Communication Cascade
- Part 2 Month 5 Championing Change
- Part 2 Month 6 Learning & Development
- Part 2 Month 7 Resistance
- Part 2 Month 8 Recognizing Excellence
- Part 2 Month 9 Coaching Culture
- Part 2 Month 10 Our Identify
- Part 2 Month 11 Refined Organization
- Part 2 Month 12 Continuous Improvement
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Culture Invigoration corporate training program.
Culture Invigoration – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Corporate ID – Workshops to identify the organization’s core identity, Culture, and characteristics.
- Part 1 Month 2 Future Vision – An exercise in framing the vision of the future & determining the ideal Culture to create.
- Part 1 Month 3 Executive Ethos – Unveiling Executive work ethos
- Part 1 Month 4 Organization ID – Culture assessments to identify team motivations, strengths, and growth areas
- Part 1 Month 5 Vision Statement – Develop updated vision and mission organization statements.
- Part 1 Month 6 Coaching Culture – Defining the right style, scope, and frequency of coaching for the organization.
- Part 1 Month 7 Motivation Catalysts – Leveraging assessments where relevant to identify & map motivation team motivation.
- Part 1 Month 8 Investor Alignment – Putting investor expectations into perspective and alignment with corporate strategies.
- Part 1 Month 9 Customer Engagement – Capturing the current sales and marketing strategy used to maintain engagement.
- Part 1 Month 10 Leadership Development – Complementing coaching with developed internal mentorship programs.
- Part 1 Month 11 Leadership Cascade – Strategy to engage organization leaders and secure support in culture transformation.
- Part 1 Month 12 Organization structure – Assess and build strategic reorganization or recruiting requirements as needed.
Culture Invigoration – Part 2- Year 2
- Part 2 Month 1 Change Management – Develop a plan to manage cultural change.
- Part 2 Month 2 Refined KPIs – Establish metrics to monitor, capture feedback and continuously improve the plan.
- Part 2 Month 3 Updated Image – Change in customer engagement strategies captured and cascaded to relevant teams.
- Part 2 Month 4 Communication Cascade – Develop fit-for-purpose communication plans for the vision & need for cultural change.
- Part 2 Month 5 Championing Change – Identify and onboard champions passionate about cultural transformation.
- Part 2 Month 6 Learning & Development – How to create a learning and development plan that supports cultural transformation.
- Part 2 Month 7 Resistance – Addressing resistance to change and providing support to those struggling.
- Part 2 Month 8 Recognizing Excellence – Develop a corporate recognition program to recognize desired new cultural behaviors.
- Part 2 Month 9 Coaching Culture – Assess the impact of coaching on the organization and implement refinements.
- Part 2 Month 10 Our Identify – Capturing the feedback from the population and revisiting the vision of the future.
- Part 2 Month 11 Refined Organization – Modifications to the team and reporting structure based on insights captured.
- Part 2 Month 12 Continuous Improvement – An opportunity to assess the impact of cultural change and implement refinement.
Methodology
Culture Invigoration
Cultural invigoration is an exciting journey of self-discovery for an organization, a time to reflect on our core identity, Culture, and characteristics. Through engaging workshops, we will identify our organization’s unique personality, strengths, and areas for growth. As we envision the future, we will determine the ideal Culture we want to create, and our vision statement will guide us toward our goals. Unveiling our Executive Ethos is critical for leading cultural change, and we will define the right style, scope, and frequency of coaching to support our journey. We will develop a plan to manage cultural change, establish metrics to measure our progress, and provide fit-for-purpose communication plans to keep everyone informed. We will cascade our leadership’s commitment to the vision of cultural transformation and reassess our organization’s structure to align with our goals. Our culture transformation program will thrive with champions passionate about cultural change, and we will identify and onboard these champions to support our journey. We will create a learning and development plan that aligns with our goals, and our recognition program will celebrate Excellence and recognize the desired new cultural behaviors. We are excited about the journey of culture invigoration and its positive impact on our organization. While we expect resistance to change, we will support those struggling and continuously improve our plan to ensure success. Let’s work together to make this journey successful and transform our organization into a thriving culture of growth, Excellence, and collaboration.

How To Invigorate Your Culture
You can’t go wrong investing in organizational culture because it’s been discovered that companies with strong work cultures have employee satisfaction rates that are 20% higher. Increased output and higher-quality work are the results.
Management’s Function
The cultural shift starts off exciting management, just like any other organization-wide endeavor, but ultimately, it frequently fails to maintain the enthusiasm throughout the transformation. Each top executive and member of management must assume responsibility for the process and continue to be involved.
Here are some strategies for creating a solid cultural pillar in your business:
People. No matter how great your product or service is, if you don’t invest in finding and keeping the appropriate employees, you might as well give up. When staff training is insufficient, you may desire an open forum where workers feel comfortable sharing their opinions. Many workers are reluctant to approach their management. If that’s the case, a modification is definitely needed. Time to commit to the conversation.
Describe your goals and objectives. You’d be shocked at how many employees are unaware of the vision, purpose, and values of their company. It happens all too frequently, despite the fact that it is a relatively typical scenario. Please go the extra mile to clearly explain to your staff what your organization’s vision, mission, and values are. They may continue to be more alert, motivated, and active as a result. Additionally, keep in mind to carry out this action each time you get the chance to interact with a larger group of individuals. Overcommunicating is acceptable.
Collaboration. The secret to creating high-performing teams is collaboration; the devil is in the details. Most essential, the team must be alert for cues and identify the root of any potential unfavorable opinion.
A leader’s backing. The leadership of your company has a stronger impact on team empowerment. The team members should feel comfortable approaching the team leaders, which could be accomplished by maintaining an open-door policy where anyone is welcome to drop by any leader’s office and chat. Develop a “dinner seating” style of arrangement where every employee, including the leadership, sits and works in the open as you move toward eradicating the culture of offices.
Openness: Due to a lack of openness and procedure opacity, many employees frequently feel demotivated. It is crucial to inform employees of the activities in which they participate or may participate. Give them a sense of ownership and explain their significance. We are only human after all, and it feels wonderful to be respected.
Rewards. A rewards system can be challenging since it might incorporate things like experiential rewards in addition to financial benefits. A rewards system must be created with a variety of options so that practically everyone may find something they like. That’s definitely not a simple undertaking, and it can need for:
• Regular internal tests of management and workplace culture.
• Regularly reviewing the incentives program.
• Cooperating with an outside partner.
Challenges. According to a Ladders poll (via Glassdoor), not having a demanding role is depressing and causes firms to lose talent. If used properly, challenging objectives can maximize your talent’s potential and promote employee engagement and retention.
• Planning for regular staff cross-mapping for various positions is one instance. Employees might gain new insights as well as new ideas as a result of this.
• If you’re starting a new technology program, your staff members need to be aware of the “whys” behind believing in the results and prepared for the change. It could be unproductive to constantly push for change.
Flexibility. Perhaps everything about corporate practice has changed since Covid-19. Being adaptable is no longer simply an option; it is now more of a must. By balancing between creating an engaging and challenging — but flexible — work environment, employee morale and productivity can be raised.
Diversity. Diversity and inclusion are important elements that foster many opportunities, concepts, and creative ideas. It is excellent for boosting employee enthusiasm and can assist with adjusting to shifting social dynamics, which can enable a variety of viewpoints to contribute to your success story.
How to Invigorate Innovation in a Stagnant Organization
1. Establish a classroom environment. The learning environment (or lack thereof) that a company adopts has a significant impact on innovation, if there is one characteristic that matters. Without an environment that is open to idea exchange, professional growth, and dialogue that encourages idea production naturally, innovation simply cannot exist. Openness to working together goes hand in hand with this learning. Most frequently, resistance to change, compartmentalized structures, and a disregard for ongoing learning are to blame for organizations becoming stagnant. Think of unconditional learning as a crucial component of developing a learning environment, despite how challenging it is to implement. As a result, every interaction, every exchange of ideas, and every occasion may be used to learn. Even individuals who appear to be averse to a change can learn something if they approach it with an open mind.
2. Think about your outlook. Any endeavor by management to implement change must be supported by a culture that fosters an environment at work that is open, honest, collaborative, and supportive of sharing and the exploration of novel thoughts. The worst thing a company can say is, “Well, this is how we have always done it, so we are sticking to it,” and refuse to change their mentality. Cultures can be exceedingly difficult to alter, but in a setting where individuals are willing to take risks, see success, and are acutely aware that failure can be (and frequently is) a benefit, a culture can transform from sluggish to vibrant and creative. It’s also critical to remember that invention of any type actually results from a lack of fear. Organizations shouldn’t be afraid of change or unable to work across organizational and group boundaries. They must comprehend the value of a friendly, open atmosphere. An article in Psychology Today discusses some of the covert factors that contribute to organizations’ reluctance to change and how leaders can get through them while demonstrating empathy for their staff members’ emotions.
3. Establish a trusting environment. Employees must believe they are a part of a trustworthy culture where it is safe for them to share their thoughts and where they are valued for their viewpoint for any form of creativity to exist. A culture of innovation can also thrive when everyone in your firm has a keen awareness of how they interact with and respect one another. It is necessary to comprehend the various personalities present in every culture; Forbes has listed nine of them. For employees to feel like a vital part of a trusting culture, each of these personalities has specific demands that must be satisfied. The capacity to experiment, collaborate with others, cross borders, carry out fluid processes, and build dynamic organizations can happen once trust has been built.
When such a culture is established, it automatically fosters a positive environment where creativity is not only possible but also expected.
4. Celebrate small victories. Employee recognition needs to be given basic importance if any firm is to experience creativity. Employees want verbal encouragement and gratitude for their efforts more than awards, salaries, benefits, and bonuses. A win should be recognized even if it comes from learning about what doesn’t work because it results in increased knowledge and understanding. There is great strength in encouraging and sustaining minor victories and an organic sense of progress, as the Harvard Business Review notes.
5. Conduct numerous experiments. Innovation is aided by failure and experimentation. In actuality, both success and failure can teach us something new. Any firm seeking to innovate must provide staff members the flexibility to attempt new things and naturally develop through a “yes” rather than a “no” culture. This is especially true when the organization looks ahead to the upcoming year. The most prosperous individuals are those who are not frightened of failure and who are eager to grow and develop as a result of their experiences.
These are just a few of the characteristics that can promote and foster a creative culture.

How Content Can Revitalize Your Company Culture
In addition to strengthening corporate culture and creating a stream of fascinating material, sharing success stories about your business can also increase profits.
“I’ve been learning about a whole new universe within my firm thanks to the new narrative technique and thanks to you. Seriously.”
Obviously, that’s just the beginning. The benefits for the involved companies will be larger the more individuals can be engaged by the story-driven content strategy.
Sharing experiences, ambitions, and accomplishments through tales inside a company helps to foster a culture of mutual respect and understanding. That facilitates their collaboration. and improves organizations.
Upon unlocking storylines, interesting new things take place. A top business school started a 50-year retrospective and published a number of pieces detailing its accomplishments. These were disseminated externally, but they also had a domestic use. At their weekly meeting, the project manager requested that each member of her team give a brief presentation on one of the themes. This made it possible for each person to engage more deeply with the accomplishments and mission of the institution. Although it wasn’t the project’s intended goal, as the stories were written, it emerged and increased its impact.
Improved Communication
A new kind of communication is emerging that bridges the gap between internal and external messaging. As a content firm, it is our goal to produce content that is suitable for both audiences.
We want to know what someone has been doing and why, not just see a picture of them holding their Employee of the Month award. To reveal their craft and knowledge, as well as the drive that has kept them working hard at their jobs. Building bridges within businesses and attracting interest from those outside the organization are also possible benefits of sharing such knowledge.
When the London Business School’s Adjunct Professor Dominic Houlder and Executive Fellow Nandu Nandkishore urge chief executives to become “chief storytelling officers” and managers to share their failures and successes in order to strengthen a company’s sense of purpose, they are referring to this. “Recounting vulnerable times invites people – customers, employees and shareholders – into an insider’s network, it makes people trust and belong,” explain the authors. People must comprehend how the organization fits into the larger world, as well as where it has been and where it is going, in order for them to feel and, eventually, act.
Those stories can be heard with the help of a strong content strategy. Additionally, it’s critical that leadership at all levels support it.
Energizing workers
Obviously, not every article will be seen by others, but as journalists, we are accustomed to looking everywhere for a story. And the majority of businesses are hiding jewels from view. A company’s profile may be built with the help of such a strategy, which can also maintain the business at the top of Google searches and in customers’ minds.
Businesses are succeeding, and those working for them are dedicating their time and effort to them. From senior leaders who feel cut off from their marketing teams to the everyday Joanne who is willing to believe fervently in what they do, we want to unleash that potential.
According to the business academics who spoke to us, revealing these tales can support the development of corporate culture. People will work harder to achieve their goals if they feel their contributions are valued and that they are building something together as a result of being recognized for them. All of which contributes to the improvement and profitability of their businesses.
Conclusion
Culture and strategy complement one other in a variety of ways. According to Peter Drucker, “culture eats strategy for breakfast,” which means that even with the best strategy, your teams won’t be inspired to step outside of their comfort zones if your culture does not support change and embrace failure. As a result of the business reforms, a motivated and passionate staff goes above and beyond goals, bestowing firms with innumerable innovations and the ability to endure any difficulties.
Work on organizational culture must be ongoing and cannot be put off because of a hectic schedule. Being patient will assist because you are in this for the long run. It’s not too late to reconsider organizational culture or to take it seriously in order to achieve success beyond planned technology results.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Technology
The technology industry, often referred to as the tech sector or the information technology (IT) industry, is a vast and rapidly growing sector that encompasses various subsectors such as hardware, software, telecommunications, internet services, and electronic components. As of 2021, the global technology industry was valued at several trillion dollars.
To provide some context, in 2020, the global technology industry’s total revenues reached an estimated $5.2 trillion, according to research from IDC. This includes revenues from hardware sales, software licensing and services, telecommunications services, and IT consulting and support. The technology industry has consistently demonstrated robust growth over the years, driven by innovation, digital transformation, and the increasing reliance on technology in various sectors.
The worth of the technology industry is further reflected in the market capitalization of prominent technology companies. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Google (Alphabet), and Facebook have achieved enormous market valuations, often exceeding the trillion-dollar mark. These tech giants dominate various segments of the industry, such as consumer electronics, software, e-commerce, cloud computing, and digital advertising.
Additionally, the technology industry has been a major driver of economic growth and job creation. It fosters innovation, productivity, and efficiency across multiple sectors, enabling digital transformation, automation, and new business models. The sector also creates a significant number of high-skilled jobs, from software developers and engineers to data scientists and cybersecurity experts.
Moreover, the worth of the technology industry can also be seen in its contribution to the overall gross domestic product (GDP) of countries. In many advanced economies, the tech sector represents a substantial portion of the GDP. For example, in the United States, the tech industry accounted for about 10% of the GDP in 2020, according to the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The sector’s economic significance extends to tax revenues, trade balances, and overall economic competitiveness.
It’s important to note that the worth of the technology industry is constantly evolving due to technological advancements, market dynamics, and shifts in consumer behavior. New emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G connectivity are expected to drive further growth and shape the industry’s worth in the coming years.
FinTech
As of September 2021, the global fintech (financial technology) industry is valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars and continues to experience significant growth. Fintech refers to the use of technology to provide innovative financial services, including online banking, payment solutions, digital lending, investment platforms, and blockchain-based solutions.
The exact worth of the fintech industry can vary depending on the specific subsectors and geographic regions considered. According to various reports, the global fintech market was estimated to be worth around $1.3 trillion in 2020, and it is projected to reach a valuation of over $4.8 trillion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 23%.
The fintech industry has been fueled by several factors. First, advancements in technology and the widespread adoption of digital platforms have created opportunities for new financial service providers to disrupt traditional banking and financial sectors. Second, changing consumer preferences and expectations, particularly among younger demographics, have driven the demand for more accessible, convenient, and personalized financial solutions. Lastly, regulatory frameworks and government support for fintech innovation have encouraged the growth of the industry.
Fintech companies span a broad range of activities, from digital payments and remittances to online lending, wealth management, and insurance technology (insurtech). The sector includes both established financial institutions incorporating digital technologies and startups developing disruptive solutions. Major fintech hubs exist in various global financial centers, including Silicon Valley, London, Singapore, and Hong Kong.
The worth of the fintech industry is further reflected in the market capitalization and valuations of prominent fintech companies. Companies like PayPal, Square, Stripe, Ant Group, and Revolut have achieved significant market valuations, often in the tens or hundreds of billions of dollars. These companies, along with numerous emerging startups, have attracted substantial investments from venture capital firms, private equity, and traditional financial institutions.
Moreover, the fintech industry’s worth can be seen in its impact on traditional financial services. Fintech innovations have prompted established banks and financial institutions to adapt and incorporate digital technologies to remain competitive. This has led to collaborations and partnerships between fintech startups and traditional incumbents, driving further growth and expansion of the industry.
Startups
The startup industry encompasses a wide range of entrepreneurial ventures across various sectors, including technology, healthcare, fintech, e-commerce, and more. Estimating the exact worth of the startup industry is challenging due to the constant emergence and closure of startups, as well as the varying stages of development and funding they undergo.
However, the startup industry has been gaining significant traction and attracting substantial investments over the years. In 2020, despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, global venture capital funding reached approximately $300 billion, according to data from PitchBook. This indicates the substantial financial resources flowing into startups worldwide.
To provide further context, according to Statista, in 2020, the United States had the highest number of startups valued at over $1 billion, commonly referred to as “unicorns.” The cumulative value of these unicorns in the U.S. alone exceeded $1.3 trillion. The global unicorn club, consisting of startups valued at $1 billion or more, continued to grow rapidly, with thousands of companies achieving unicorn status across different regions.
Furthermore, the startup industry’s worth can be assessed through the overall economic impact it generates. Startups play a crucial role in job creation, innovation, and economic growth. They often introduce disruptive technologies, business models, and solutions that drive productivity, competitiveness, and industry transformation. Many startups go on to become successful companies that contribute significantly to the overall economy.
The startup industry’s worth is also reflected in the valuations of successful startups that have gone public or been acquired by larger companies. High-profile acquisitions and initial public offerings (IPOs) of startups, particularly in the technology sector, have commanded billions of dollars. These transactions further underscore the value and potential of startups.
However, it is important to note that the startup industry is highly dynamic, with a high failure rate and significant variation in outcomes. While some startups achieve tremendous success and generate substantial value, many others face challenges and may not reach their intended goals.
The worth of the startup industry can vary across different regions and sectors. Silicon Valley in the United States has historically been a hotspot for startups and venture capital investments, but other regions, such as London, Berlin, Tel Aviv, and Bangalore, have emerged as prominent startup ecosystems.
Given the constantly evolving nature of the startup industry, its worth is subject to change. It is advisable to refer to the latest reports and data from reputable sources, such as venture capital databases, startup accelerators, and industry research firms, to obtain the most up-to-date information on the current worth of the startup industry.
Energy
The energy industry is a crucial component of any economy, providing the necessary power and fuel to drive various sectors and activities. It encompasses a wide range of sources, including fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear power, each with its unique economic implications.
The global energy sector is a multi-trillion-dollar industry. It is challenging to provide an exact figure for the sector’s overall worth as it encompasses a wide range of subsectors, including fossil fuels (such as oil, gas, and coal), renewable energy (such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal), nuclear power, and energy services.
The value of the energy sector is influenced by various factors, including energy prices, demand-supply dynamics, investments, and government policies. The sector’s worth can be measured through indicators such as revenues, investments, and contributions to the gross domestic product (GDP) of individual countries or the global economy.
To provide some context, in 2019, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that global investments in the energy sector reached around $1.85 trillion, with the majority directed towards renewables and power grids. The fossil fuel sector, particularly oil and gas, historically held a significant share of the industry’s worth due to their high market value and global demand. However, renewable energy has been gaining momentum in recent years, with investments steadily increasing as countries aim to transition to cleaner and more sustainable sources.
Moreover, the energy sector’s worth can also be assessed by examining the revenues and market capitalization of energy companies. Large multinational corporations in the oil and gas industry, for instance, generate substantial revenues and have high market valuations. Additionally, the growth of renewable energy companies and their market capitalization has been noteworthy, reflecting the increasing importance of clean energy sources.
It’s worth noting that the worth of the energy sector is not static and can vary over time due to changes in energy prices, advancements in technology, shifts in government policies, and global economic conditions. As the world moves towards decarbonization and sustainable energy systems, the value of the energy sector is expected to evolve further, with increased investments and market opportunities in renewable energy and energy transition technologies.
The energy industry’s growth is closely tied to the overall economic development of a country. As economies expand, the demand for energy increases, leading to greater investment in energy infrastructure and production capabilities. This, in turn, creates job opportunities and stimulates economic activity across multiple sectors, from manufacturing and construction to transportation and services.
Employment within the energy industry is diverse and covers a wide range of occupations. It includes engineers, technicians, project managers, researchers, and skilled workers involved in energy extraction, production, transmission, and distribution. Additionally, the sector supports employment indirectly through related industries, such as equipment manufacturing, construction, and maintenance.
Investments in the energy industry play a significant role in economic growth and development. Energy companies invest substantial capital in exploring, developing, and extracting energy resources. These investments contribute to job creation, infrastructure development, and technological advancements. Moreover, renewable energy investments have gained momentum in recent years, fostering innovation, reducing carbon emissions, and creating new business opportunities.
One of the critical challenges facing the energy industry is the need for a transition to cleaner and more sustainable sources of energy. As concerns about climate change and environmental impact grow, there is a growing shift towards renewable energy and efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This transition presents both challenges and opportunities, as it requires significant investments in renewable energy technologies, infrastructure upgrades, and policy support.
Technological advancements also play a significant role in the energy industry’s economy. Innovation in areas such as renewable energy generation, energy storage, and smart grid systems can enhance energy efficiency, reduce costs, and create new business opportunities. Moreover, the adoption of digital technologies and data analytics improves operational efficiency and decision-making processes within the industry.
In conclusion, the energy industry is a vital driver of economic activity and development. Its size, growth, employment opportunities, investments, and challenges have significant implications for economies worldwide. The transition to cleaner energy sources, the need for energy price stability, and the utilization of technological advancements are some of the key factors that will shape the future of the energy industry’s economy, influencing both its sustainability and its contributions to economic growth.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry plays a critical role in any country’s economy, encompassing a wide range of sectors and activities. It is an essential component that affects individuals, businesses, and governments, both in terms of financial implications and public health outcomes.
The healthcare industry is one of the largest and fastest-growing sectors in many economies worldwide. In the United States, for example, it represents a significant portion of the GDP, accounting for approximately 18% of the total economy. This highlights the substantial economic impact of healthcare, as it generates a substantial amount of revenue and job opportunities.
One of the primary drivers of the healthcare industry’s growth is the increasing demand for healthcare services due to population growth, aging demographics, and the prevalence of chronic diseases. As the population ages, the need for medical care and long-term care services rises, leading to greater demand for healthcare providers, facilities, and pharmaceuticals. This translates into a higher level of economic activity within the industry.
The healthcare industry is a major employer, creating numerous job opportunities across various sectors. It encompasses not only physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals but also administrative staff, researchers, technicians, and support personnel. The sector provides stable employment and contributes to reducing overall unemployment rates. Additionally, healthcare jobs tend to offer competitive wages and benefits, making them desirable for many individuals seeking stable careers.
Expenditures on healthcare have also been rising steadily. As healthcare technology advances, new treatments and medications become available, but they often come at a high cost. Moreover, the administrative complexities and regulatory requirements within the healthcare system contribute to increased expenditures. Government spending on healthcare, through public insurance programs like Medicare and Medicaid, has also been rising due to the growing aging population and healthcare needs.
However, the healthcare industry faces several challenges that impact its economy. One of the major concerns is rising healthcare costs. As expenditures increase, individuals, businesses, and governments struggle to afford necessary care and insurance coverage. This has led to debates about healthcare reform, cost containment strategies, and the need for greater efficiency and transparency in the industry.
Another challenge is the uneven distribution of healthcare resources. In many countries, access to quality healthcare is unequal, with disparities between rural and urban areas or different socioeconomic groups. Addressing these disparities and ensuring equitable access to care pose economic and social challenges that require coordinated efforts from policymakers, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders.
Technological advancements and digital transformation also influence the healthcare economy. The integration of electronic health records, telemedicine, and artificial intelligence in healthcare delivery systems has the potential to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance patient outcomes. However, the adoption and implementation of these technologies require substantial investments and may disrupt traditional healthcare practices, leading to economic uncertainties.
In conclusion, the healthcare industry’s economy is significant and multifaceted, with implications for individuals, businesses, and governments. Its size, growth, employment opportunities, and expenditures contribute to the overall economic landscape. However, challenges such as rising costs, access disparities, and technological advancements require ongoing attention and proactive measures to ensure a sustainable and thriving healthcare industry that benefits both the economy and public health.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:
Houston, TX
Houston, Texas is the fourth-largest city in the United States and is a hub for various industries, including energy, healthcare, aerospace, and technology. The economy of Houston is diverse and has a significant impact on the overall economy of Texas and the United States.
Houston’s economy is heavily reliant on the energy sector, which has historically been a major contributor to the city’s growth and development. Houston is home to numerous energy companies, including oil and gas exploration and production companies, refineries, and pipeline operators. According to data from the Greater Houston Partnership, the energy sector employed over 300,000 people in the Houston metropolitan area in 2020.
However, the Houston economy has evolved in recent years, with diversification into other industries. The healthcare sector is another significant contributor to the Houston economy, with the Texas Medical Center, the world’s largest medical complex, located in the city. Other notable industries in Houston include aerospace and aviation, manufacturing, technology, and logistics. According to the Greater Houston Partnership, in 2020, the Houston metropolitan area had a gross domestic product (GDP) of over $530 billion, with a workforce of approximately 3.5 million people.
The Port of Houston is another critical driver of the city’s economy, serving as a major gateway for international trade. It is one of the busiest ports in the United States and plays a vital role in the transportation and distribution of goods. The port also supports various industries, including manufacturing, energy, and agriculture.
Houston’s economy has faced significant challenges in recent years, including the COVID-19 pandemic and the impact of natural disasters, such as Hurricane Harvey in 2017. However, the city has shown resilience and has continued to attract new investments and businesses across different sectors.
Furthermore, Houston’s favorable business environment, low cost of living, and high quality of life have contributed to its attractiveness as a destination for businesses and individuals. The city’s entrepreneurial ecosystem has also been growing, with numerous startup incubators, accelerators, and coworking spaces supporting innovation and economic growth.
In summary, the economy of Houston, Texas is diverse and heavily reliant on the energy sector, healthcare, aerospace, and other industries. The city’s GDP is significant, and it serves as a vital hub for international trade through the Port of Houston. While facing challenges, Houston has continued to attract new investments and businesses, with a favorable business environment and a growing entrepreneurial ecosystem.

San Francisco, CA
San Francisco, California has one of the most dynamic and diverse economies in the United States. The city’s economy is characterized by a thriving technology industry, robust tourism sector, financial services, and a vibrant arts and culture scene. Here are some key aspects of the San Francisco economy:
1. Technology: San Francisco is renowned as a global hub for technology and innovation. The city is home to numerous tech giants, startups, and venture capital firms. Silicon Valley, located just south of San Francisco, further strengthens the region’s position as a leader in technology and entrepreneurship. Companies like Apple, Google (Alphabet), Facebook, Salesforce, and Uber have a significant presence in the area, driving innovation, job creation, and economic growth.
2. Financial Services: San Francisco serves as a major financial center on the West Coast. It is home to several large financial institutions, including banks, investment firms, and insurance companies. The city’s financial district, known as the “Wall Street of the West,” houses the headquarters of many prominent financial companies and serves as a hub for banking and financial services.
3. Tourism and Hospitality: San Francisco attracts millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to its economy. The city offers iconic landmarks such as the Golden Gate Bridge, Alcatraz Island, Fisherman’s Wharf, and diverse cultural attractions. The hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, plays a crucial role in supporting the tourism sector.
4. Biotechnology and Life Sciences: San Francisco has a thriving biotechnology and life sciences industry. The region is home to prestigious research institutions, including the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and numerous biotech companies. This sector focuses on developing innovative healthcare solutions, conducting cutting-edge research, and attracting investments in biopharmaceuticals, medical devices, and genomics.
5. Creative and Cultural Industries: San Francisco boasts a vibrant arts and culture scene, contributing to its economic vitality. The city supports various creative industries, including film and television production, performing arts, design, and fashion. It hosts world-class museums, galleries, and music festivals, fostering creativity and attracting visitors.
6. Green and Sustainable Industries: San Francisco has positioned itself as a leader in sustainability and green initiatives. The city is committed to environmental preservation, renewable energy, and sustainable transportation. The clean technology sector, including renewable energy companies and sustainable startups, thrives in the region.
7. Real Estate and Construction: San Francisco’s robust economy has driven demand for real estate and construction projects. The city experiences high property values and a competitive housing market. Major commercial and residential developments contribute to the growth of the construction industry.
8. Entrepreneurship and Startups: San Francisco has a strong entrepreneurial ecosystem, attracting innovators and startups from various industries. The region provides access to capital, resources, and a supportive network for aspiring entrepreneurs. Startup incubators, accelerators, and co-working spaces fuel the growth of new businesses and contribute to job creation.
Overall, the economy of San Francisco is driven by technology, finance, tourism, creative industries, and sustainability initiatives. The city’s economic strength and innovation ecosystem have made it a global powerhouse, attracting talent, investment, and fostering a dynamic business environment.
London, UK
London, the capital city of the United Kingdom, has one of the largest and most diverse economies in the world. It serves as a global financial center, a hub for various industries, and a major tourist destination. Here are some key aspects of the London economy:
Financial Services: London is renowned as a leading global financial center. The City of London, also known as the Square Mile, houses major financial institutions, including banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, and the London Stock Exchange. The city’s financial services sector contributes significantly to the economy, attracting international businesses and talent.
Professional Services: London is a major center for professional services, including law, accounting, consulting, and advertising. The city hosts numerous professional service firms, providing expertise to clients from around the world. These industries benefit from London’s global connectivity and the presence of multinational corporations.
Technology and Innovation: London has a thriving technology and innovation sector. The city is home to numerous tech startups, digital agencies, and research institutions. Tech hubs like Tech City (also known as Silicon Roundabout) and the East London Tech Cluster have attracted entrepreneurs, investors, and tech talent. The sector spans areas such as fintech, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and e-commerce.
Creative Industries: London has a vibrant creative sector encompassing film, television, music, fashion, design, and the arts. The city is known for its theaters, museums, galleries, and cultural events. The creative industries contribute to tourism, job creation, and international recognition.
Tourism and Hospitality: London is a major tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year. Iconic landmarks like the Tower of London, Buckingham Palace, and the British Museum draw tourists from around the globe. The hospitality industry, including hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, plays a vital role in supporting tourism.
Education and Research: London is home to prestigious universities and research institutions. Institutions such as University College London (UCL), Imperial College London, and the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE) contribute to research, innovation, and the knowledge economy. The presence of international students also adds to the city’s economic vitality.
Real Estate and Construction: London’s real estate market is a significant driver of the economy. The city experiences high demand for residential and commercial properties, which fuels construction projects and property development. London’s skyline continues to evolve with new skyscrapers and infrastructure developments.
Retail and Consumer Goods: London offers a vibrant retail sector, with renowned shopping districts like Oxford Street, Bond Street, and Knightsbridge. The city attracts luxury brands, department stores, and flagship stores, contributing to the retail industry’s growth and employment.
Manufacturing and Trade: Although the manufacturing sector in London has diminished compared to its historical prominence, the city still has significant manufacturing activities in areas such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and printing. Additionally, London is a major center for international trade, facilitating the movement of goods and services between the UK and the rest of the world.
Healthcare and Life Sciences: London has a thriving healthcare and life sciences sector, with renowned medical institutions, research centers, and pharmaceutical companies. The city attracts investment in medical research, biotechnology, and healthcare services.
London’s economy is characterized by its global connectivity, diverse industries, and entrepreneurial spirit. It has a highly skilled workforce, attracts international investment, and fosters innovation. However, it is important to note that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the London economy, as it has globally. The full extent of the pandemic’s effects on the city’s economy is still evolving, and recovery efforts are ongoing.
Dubai, UAE
Dubai, located in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), has a robust and diverse economy. Over the past few decades, the city has transformed itself into a global business and tourism hub. Here are some key aspects of the Dubai economy:
Trade and Logistics: Dubai’s strategic geographic location has positioned it as a major trade and logistics hub connecting markets in the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and Europe. The city boasts state-of-the-art infrastructure, including Jebel Ali Port, one of the world’s busiest ports, and Dubai International Airport, one of the busiest airports globally. The free trade zones in Dubai, such as Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA) and Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), attract foreign investments and facilitate international trade.
Tourism and Hospitality: Dubai is renowned for its tourism industry, attracting millions of visitors each year. The city offers luxurious hotels, magnificent shopping malls, iconic landmarks like the Burj Khalifa and Palm Jumeirah, and a wide range of entertainment and leisure activities. The tourism sector contributes significantly to Dubai’s economy, driving employment, retail, hospitality, and leisure industries.
Real Estate and Construction: Dubai has experienced rapid growth in real estate and construction, with impressive skyline developments and iconic projects. The city has attracted foreign investment in residential, commercial, and mixed-use properties. The construction sector has played a vital role in shaping the city’s infrastructure, including residential buildings, hotels, and transportation networks.
Financial Services: Dubai has emerged as a leading financial center in the Middle East. The Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) serves as a financial free zone, hosting international banks, financial institutions, asset management firms, and insurance companies. The DIFC offers a regulatory framework and favorable business environment, attracting global financial players.
Business and Free Zones: Dubai has established several free zones and business parks, offering tax incentives, simplified regulations, and business-friendly environments. These zones, including JAFZA, Dubai Media City, Dubai Internet City, and Dubai Healthcare City, promote entrepreneurship, innovation, and attract companies across various sectors.
Manufacturing and Industry: Dubai has a growing manufacturing sector, focusing on industries such as food processing, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. The city’s strategic location, logistical infrastructure, and business-friendly environment have facilitated the growth of manufacturing activities, including light industries and assembly plants.
Aviation and Aerospace: Dubai is home to Emirates, one of the world’s largest and most successful airlines. The city has positioned itself as an international aviation and aerospace hub, with Dubai International Airport serving as a major connecting point for global air travel. Dubai also hosts the Dubai Airshow, a renowned aerospace exhibition.
Healthcare and Education: Dubai has invested significantly in healthcare and education, attracting medical institutions, research centers, and universities. The city offers world-class healthcare facilities, medical tourism services, and a growing number of international education institutions, making it a regional hub for healthcare and education services.
Dubai’s economy is continuously evolving, with ongoing efforts to diversify beyond its traditional sectors. The city’s government has implemented policies to encourage innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of knowledge-based industries.

Singapore, SG
Singapore, a small island nation located in Southeast Asia, has one of the most advanced and prosperous economies in the world. Despite its limited land and natural resources, Singapore has transformed into a global financial and business hub. Here are some key aspects of the Singapore economy:
Financial Services: Singapore is a leading global financial center. The city-state hosts numerous international banks, financial institutions, and asset management firms. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) regulates the financial sector and promotes Singapore as a hub for banking, insurance, wealth management, and fintech. The Singapore Stock Exchange (SGX) is one of the largest and most vibrant exchanges in Asia.
Trade and Logistics: Singapore is a major player in international trade and logistics. Its strategic location at the crossroads of major shipping routes and its world-class port, the Port of Singapore, make it a key transshipment hub and a gateway to Asia. The country has a liberal trade policy, strong connectivity, and efficient customs processes, facilitating global trade and attracting multinational corporations.
Manufacturing: Singapore has developed a strong manufacturing sector, focusing on high-value industries such as electronics, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, precision engineering, and biomedical sciences. The country has built a reputation for advanced manufacturing capabilities, research and development, and innovation. Singapore encourages companies to invest in research and development, automation, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Infocomm Technology (ICT): Singapore has made significant investments in information and communication technology. The city-state is a leader in digital innovation, smart city solutions, and technology adoption. It promotes initiatives such as Smart Nation, aiming to leverage technology to improve the quality of life, enhance connectivity, and drive economic growth.
Biomedical Sciences: Singapore has developed a thriving biomedical sciences sector, encompassing pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical technology. The country attracts multinational pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and clinical research organizations. It fosters an ecosystem that supports biomedical research, clinical trials, and the development of innovative healthcare solutions.
Tourism and Hospitality: Singapore is a popular tourist destination known for its modern infrastructure, vibrant cultural scene, and world-class attractions. The city-state offers iconic landmarks like Marina Bay Sands, Gardens by the Bay, and Universal Studios Singapore. The tourism sector contributes significantly to the economy, with hospitality services, shopping, and entertainment playing important roles.
Education and Research: Singapore has invested heavily in education and research, promoting a knowledge-based economy. The country hosts renowned universities and research institutions, attracting international students and fostering innovation. The focus on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education has helped develop a skilled workforce and support research and development activities.
Real Estate and Construction: Singapore’s real estate market has experienced significant growth, driven by residential, commercial, and infrastructure developments. The government carefully manages land supply, ensuring sustainable urban planning and maintaining a high-quality built environment. Singapore’s skyline features impressive skyscrapers, integrated resorts, and mixed-use developments.
Transportation and Connectivity: Singapore has a highly efficient and well-developed transportation system. Changi Airport, consistently ranked among the best airports globally, serves as a major air travel hub. The Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system provides reliable and convenient public transportation, connecting various parts of the city-state.
Singapore’s economic success is attributed to its strategic location, political stability, pro-business policies, skilled workforce, and commitment to innovation. The government’s long-term planning, emphasis on education and technology, and strong support for entrepreneurship have helped Singapore become a global economic powerhouse.
Program Benefits
Human Resources
- Inclusive Environment
- Diversity
- Cultural Awareness
- Sensitivity Training
- Cross-Cultural Communication
- Collaboration
- Develop Policies
- Inclusion
- Diverse Talent Pool
- Employee Engagement
Marketing
- Market Research
- Consumer Behaviors
- Relevant Campaigns
- Cultural Perspectives
- Market Reach
- Brand Perception
- Stronger Connections
- Innovation
- Improved Engagement
- Cultural Sensitivity
R&D
- Diverse Perspectives
- Broader Insights
- Cross-Cultural Collaboration
- Promotes Innovation
- Market Relevance
- Best Practices
- New Concepts
- Risk-Taking
- Push Boundaries
- Breakthrough Solutions
Achievements

Pioneering Digital Transformation Across Global Operations
Successfully led the digital transformation strategy for a multinational organization, streamlining operations across 20+ countries. This initiative resulted in a 35% increase in operational efficiency and a 25% reduction in costs, positioning the product line as a leader in digital innovation within the industry.
Architect of R&D Cultural Transformation Programs
Designed and implemented a comprehensive R&D cultural transformation program for a Fortune 500 company, which was pivotal in reshaping its R&D process and aligning it with its strategic objectives. This initiative led to a 50% increase in process efficiency and a 40% improvement in product launch times within two years.
Certified Chair™ of Advisory Boards
Earned the prestigious title of Certified Chair™ for various technology and startup advisory boards. Leveraged this role to drive transformative culture shifts and strategic growth across enterprises, resulting in a significant uptick in employee engagement and increase organizational resilience and adaptability.
Innovative Leadership in Human Potential Coaching
Developed and implemented a multi-certified modular executive coaching program adopted by diverse organizations globally. This program has empowered over 200 executives to achieve their personal, leadership, and professional potential, with measurable impacts on organizational performance and culture.

Strategic Visionary in Change Management
Successfully navigated a major organizational restructure by leading a change management strategy that minimized disruption and maximized employee buy-in. This approach preserved organizational morale and enhanced productivity by 25% during a critical transition period.

Trailblazer in AI Integration
Provided Board Advisory support in integrating artificial intelligence solutions within organizational processes. This strategic move resulted in a substantial 50% improvement in data analysis efficiency and opened up new avenues for predictive analytics and decision-making.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.






















