Commercial Excellence
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Commercial Excellence is provided by Mr. Jansen & Mr Weertman Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
Personal Profile
Mr. Jansen
Mr. Jansen is a seasoned sales trainer, known for designing tailored programs that drive measurable business results. With extensive experience in sales leadership and coaching, he specializes in areas like selling based on value, negotiation, and sales and business strategy execution.
Mr. Jansen his professional journey spans roles in sales leadership, business development, and training, giving him firsthand insights into the challenges and opportunities within modern sales environments. He works closely with organizations to align training with business goals, delivering impactful solutions that improve sales metrics and foster team excellence.
A passionate mentor, Mr. Jansen is dedicated to empowering sales professionals and leaders to unlock their full potential and achieve lasting success.
He believes that sales training should be actionable, measurable, and aligned with business outcomes. His mission is to empower sales teams not only to achieve but to exceed their goals through tailored, impactful training solutions.
With a forward-thinking mindset and a results-driven approach, Mr. Jansen continues to make a lasting impact, helping organizations unlock the full potential of their sales teams and drive long- term success.
Mr. Weertman
Mr. Weertman is a experienced trainer, specializing in innovative sales training and performance development. With extensive experience in sales strategy, leadership, and coaching, he designs tailored programs that deliver measurable results.
Mr. Weertman combines traditional sales principles with modern approaches like digital selling and data-driven decision-making.
A trusted advisor to diverse industries, Mr. Weertman has helped organizations improve key sales metrics, foster high-performing teams, and achieve transformative growth. His vision is to empower sales professionals to excel through actionable, results-driven training.
Mr. Weertman believes that effective sales training is a partnership, requiring collaboration between the trainer, the organization, and the participants. His philosophy revolves around creating practical, engaging, and results-oriented programs that empower sales professionals to excel.
To request further information about Mr. Jansen & Mr Weertman through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Commercial Excellence
The Commercial Excellence Program:
Unlock Strategic Business Growth and Build Trusted Partnerships
In today’s complex B2B environment, offering technical solutions, financial products, and consultancy services comes with its unique challenges. The buying process has become intricate, involving multiple decision-makers and longer buying cycles. Significant resources are required to respond to RFIs and RFPs. As a result, refining commercial strategies is essential for success.
Traditional sales approaches no longer suffice. The Commercial Excellence Program addresses these complexities, equipping commercial teams with the attitude, methods, skills, and tools to excel in high-stakes environments. This program helps transform challenges into opportunities and fosters long-term customer partnerships.
Key Questions for Commercial Success:
Evaluate your current practices with these questions:
1. Sales Performance:
• How do our win rates compare to our sales cost investments?
• Are we qualifying opportunities early and professional enough?
• How many of our proposals reach the negotiation stage?
2. Opportunity Strategy:
• Do we have defined strategies for each sales opportunity?
• Are we communicating strategies clearly within the team?
3. Customer Understanding:
• Do we understand the buying criteria of stakeholders?
• Are we aware of our customers’ KPIs, goals, and challenges /the customer’s value chain?
• Do we understand the different buyer roles for a Must Win Battle?
4. Stakeholder Engagement:
• Have we engaged with all relevant stakeholders?
• Are we tailoring our communication for different stakeholders?
5. Competitive Positioning:
• How do we assess our position against competitors?
• What unique value propositions do we offer?
6. Team Collaboration:
• Are our teams collaborating effectively on major opportunities?
• Are we sharing insights across the organization efficiently?
7. Value Creation:
• Are we consistently delivering measurable value beyond the product?
• How do our customers view us—as suppliers or strategic partners?
8. Long-term Relationships:
• Are we building trusted partnerships with key accounts?
• What strategies do we have for growing wallet share with customers?
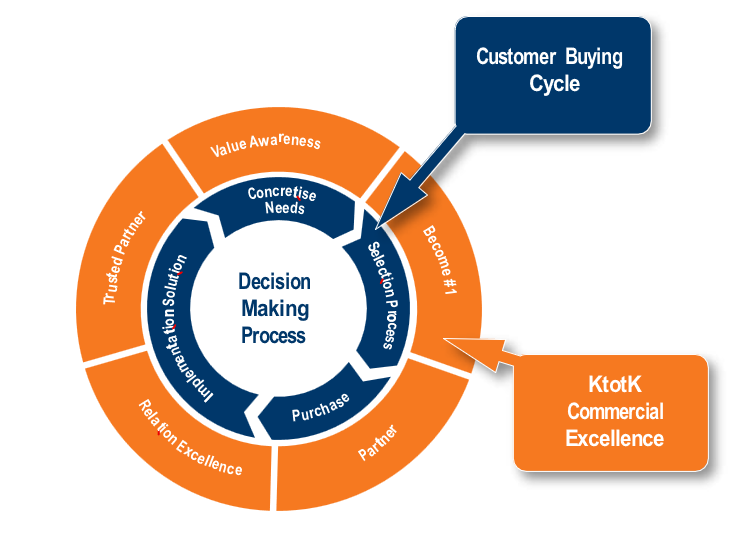
Understanding the Customer Buying Cycle (CBC)
The Customer Buying Cycle (CBC) consists of phases that customers move through, from need awareness to post-purchase evaluation. Each phase demands specific strategies for success.
• Value Awareness Phase:
At the start of the CBC, customers realize they have a need but may not be able to articulate it. Engaging with customers early allows us to support them with insights, ideas, value propositions, resulting in sweetspots. This phase is crucial for understanding the customer’s goals and building strong relationships with stakeholders. By aligning with their needs, we increase our chances of influencing the outcome positively.
• The “Become Number 1” Stage:
Developing winning strategies for complex deals is key to success. Many companies struggle with poor win rates due to misalignment between their strategy and customer buying criteria. In this phase, customers often invite multiple providers for proposals. If we weren’t involved earlier, our influence on the solution is limited. The more we were engaged in previous stages, the better we can create value and influence the buying process.
• Partnering for Success Phase:
As customers evaluate options, the challenge is to align different stakeholders’ goals and perceived risks. In industries like IT and finance, technical leads may prioritize system integration while finance teams focus on cost savings. The program helps identify buying criteria and address concerns across all stakeholders. When negotiations arise, we use the value and relationships we’ve developed to achieve a win-win outcome.
• Beyond the Sale: Building Relationship Excellence:
Closing a deal is important, but long-term relationship building is essential for sustained success. The Commercial Excellence Program emphasizes post-sale engagement, ensuring that commercial teams continue to create value through implementation and by nurturing the client relationship. This ensures we become not just suppliers but trusted partners.
For example, a financial services firm may have multiple vendors providing different solutions. By positioning ourselves as trusted partners, we can identify additional opportunities to expand our offerings, whether through cross-selling or upselling complementary services.

Case Study: Stork (a Bilfinger company) – Increasing Commercial Power through Commercial Excellence
Stork, now part of Bilfinger, initiated a project to enhance the commercial power of its organization. After a thorough assessment of the “Ist” situation, it became clear that the win-rate on RFQs was far too low. The root cause was identified as an ineffective commercial organization, where the Value Awareness phase of account management was neglected.

Solution: Commercial Excellence Approach
To address this, Stork implemented a Commercial Excellence framework that transformed the organization:
• The account team assumed responsibility for all phases of the Customer Buying Cycle (CBC).
• Each phase was assigned specific roles and responsibilities within the account team.
• The entire account team, including technical professionals responsible for project execution, received comprehensive training and coaching on Commercial Excellence principles.
• The approach focused on equipping the team with tools to influence the customer journey proactively, rather than reactively.
• Training sessions included real-life “Must Win Battles”, ensuring practical application and immediate impact.
Results: The implementation of Commercial Excellence created a significant improvement in the organization’s win-rate on RFQs: The win-rate more than doubled.
Teams gained an understanding of the customer buying cycle and recognized that each phase of the cycle can be influenced with the right actions at the right time.
Key Impact: The most significant outcome was the team’s ability to recognize and influence every stage of the customer journey. By adopting a standardized approach, they developed a consistent and effective method for managing opportunities.
Recommendation: We strongly recommend the Commercial Excellence training and approach. This is not just theoretical training; it is a hands-on, results-driven program where teams train with real challenges and achieve measurable development and success.
Tangible Benefits of the Program
By implementing the Commercial Excellence Program, organizations can expect transformative results:
1. Increased Win Rates: Focusing on the right opportunities and approaching them strategically leads to better success.
2. Improved Profit Margins: A better qualification process and value-based selling increase profitability on deals.
3. Enhanced Customer Loyalty: The program typically results in higher retention rates and expansion of key accounts.
4. Shortened Buying cycles: Improved stakeholder engagement and strategic alignment reduce buying cycle times.
5. Improved Team Performance: Collaboration and knowledge sharing within the team boost overall effectiveness.
6. Greater Predictability: A structured approach enhances the accuracy of revenue forecasting.
Conclusion:
The Commercial Excellence Program is more than just a sales methodology. It’s a transformative approach to managing customer relationships in complex environments. With a deep understanding of the Customer Buying Cycle and a strategic long-term focus, this program enables teams to manage opportunities effectively, increase win rates, and build lasting partnerships. For businesses navigating complex sales landscapes, this program provides the tools and insights needed to foster relationships that stand the test of time.
Curriculum
Commercial Excellence – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Strategic Preparation
- Part 1 Month 2 Participant Intake
- Part 1 Month 3 Buying Cycle
- Part 1 Month 4 Relation Excellence
- Part 1 Month 5 Value Strategy
- Part 1 Month 6 Sweetspots
- Part 1 Month 7 Anchoring Value
- Part 1 Month 8 Value Mapping
- Part 1 Month 9 Stakeholder Alignment
- Part 1 Month 10 Winning Strategy
- Part 1 Month 11 Risk Alleviation
- Part 1 Month 12 Value Negotiations
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Commercial Excellence corporate training program.
Commercial Excellence – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Strategic Preparation – The process of developing a Commercial Excellence program begins with setting challenging, measurable goals through a comprehensive gap analysis between the current (“Ist”) and desired (“Soll”) states. This requires a thorough evaluation of team competencies, deep understanding of the company’s developmental environment, and securing management commitment through transparent communication and formal sign- off. Critically, the program must precisely define its target group, tailoring strategies to address specific organizational challenges and opportunities. By methodically addressing these dimensions, the approach creates a dynamic framework that enables continuous improvement, fosters innovation, and drives sustainable competitive advantage.
- Part 1 Month 2 Participant Intake – Assessing individual competence involves creating detailed gap analyses between current and target performance states, enabling personalized professional development. By engaging participants through transparent communication and collaborative goal-setting, the approach transforms skill assessment into a mutually committed journey of professional growth. The process focuses on understanding individual potential, creating empowering development plans, and building a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- Part 1 Month 3 Buying Cycle – The Commercial Buying Cycle (CBC) concept is a comprehensive approach to sales that emphasizes understanding customer needs and creating value throughout the buying process. By exploring buyer roles (COI, COID, COD), utilizing relation maps, and embracing the principle that “selling is motivating other people to buy”, participants learn to view sales as a strategic, customer-centric journey. The approach focuses on creating genuine customer value, understanding stakeholder interests, and tailoring the sales approach to specific product and service contexts, ultimately transforming traditional sales methodology into a more nuanced, relationship-driven process.
- Part 1 Month 4 Relation Excellence – The session explores motivation through Fred Luthans’ organizational behavior framework, focusing on understanding five core motives: power, achievement, affinity, recognition, and safety. Participants learn how these motives significantly impact contact quality in sales interactions, examining how individual and interlocutor motivations interplay during the sales process. By introducing concepts like “Treasurechest questions” and analyzing contact quality on a 1-10 resistance scale, the training aims to transform sales professionals’ understanding from basic relationship management to achieving trusted partnership status through deep motivational insights.
- Part 1 Month 5 Value Strategy – This workshop focuses on selecting and qualifying a Must Win Battle (MWB) by developing comprehensive account strategies through detailed analysis. Participants learn to create “Share of Wallet” assessments and to develop growth, defend, or disrupt strategies, and construct value chains. The session explores stakeholder needs across financial, performance, and reputation dimensions, helping participants understand the intricate connections between organizational challenges and customer value creation, ultimately enabling more strategic and value-driven sales approaches.
- Part 1 Month 6 Sweetspots – The training session focuses on developing a comprehensive understanding of the company’s internal capabilities, including products, services, and human resources. Participants learn to strategically select and align these capabilities with customer needs, creating value by identifying “Sweetspots” where the company’s strengths directly address stakeholder requirements. The approach emphasizes creating specific, tangible value propositions that demonstrate how the company’s offerings can solve customer challenges and meet their strategic objectives.
- Part 1 Month 7 Anchoring Value – The training focuses on value anchoring for the Center of Influence with Decision power (COID), emphasizing strategic selection of “Sweetspots” tailored to specific stakeholders. Participants learn to create compelling “Pain & Gain” narratives, identify Centers of Decision (COD), and develop engagement strategies that leverage convinced COIDs to effectively present value propositions to key decision-makers, ultimately building momentum for the Must Win Battle (MWB).
- Part 1 Month 8 Value Mapping – The training introduces the “Value Map” concept, guiding participants to identify, prioritize, and apply stakeholder buying criteria for a Must Win Battle (MWB). Participants learn to categorize and position “Value Winners, Losers, and Potentials,” understanding their impact on creating measurable value. The session focuses on strategically repositioning value propositions during stakeholder meetings, enabling more effective and targeted sales approaches.
- Part 1 Month 9 Stakeholder Alignment – The training introduces the “Stakeholder Alignment” concept, focusing on identifying, mapping, and strategically positioning stakeholders for a Must Win Battle (MWB). Participants learn to create and influence a “Stakeholder Map,” understanding how to empower or depower stakeholders to optimize engagement and influence during the sales process.
- Part 1 Month 10 Winning Strategy – The training explores competitive analysis for a Must Win Battle (MWB), guiding participants to identify, weight, and score selection criteria against competitors. Participants learn to assess their company’s perception relative to competitors, developing strategic approaches to leverage strengths and address weaknesses in stakeholder decision-making processes.
- Part 1 Month 11 Risk Alleviation – Objective of this module is to understand that Risk is another factor that needs to be challenged in a Must Win Battle. Manage in this case means to prevent or cure a perceived risk. We focus on understanding risk perception in a Must Win Battle (MWB), exploring how stakeholders perceive financial, performance, and reputation risks. Participants learn to recognize that risks are often perceived rather than factual, developing strategies to prevent or alleviate these risks through targeted management approaches during the customer buying process.
- Part 1 Month 12 Value Negotiations – The workshop aims to teach participants to negotiate based on the value their solution creates, requiring a clear understanding of the value they bring to all stakeholders involved. It focuses on key elements such as non-negotiables, gives, and gets. Participants will learn and practice the concept and process of value-based negotiation, identify and manage non-negotiables, effectively utilize gives and gets for MWB, and enhance the created value using COIDs.
Methodology
Commercial Excellence
Customer Buying Process
This 12-month program is designed around the customer’s buying journey, referred to as the Customer Buying Cycle. Using the High-Performance Learning Journey Methodology, the program aligns with the natural progression of the buying process. The program focuses on developing a winning strategy and building long-term, trusted partnerships.
The buying cycle consists of four main phases, during which the commercial organization plays a crucial role in guiding and influencing the customer’s buying process. We define five corresponding phases from the perspective of the commercial team:
Customer
Concretize Needs
Selection Process
Purchase
Implementation of Solution
Commercial Team
Value Awareness
Become #1
Partner
Relation Excellence
Trusted Partner

Commercial assurance Strategy
The five phases led by the commercial team form the Commercial Assurance Approach. This 12- month program comprehensively addresses each phase, equipping participants to craft a winning commercial strategy at every phase for a Must Win Battle.
Our philosophy, when people learn and implement once what has been learned on a MWB, they will not forget this
The Commercial Assurance Approach operates on three levels:
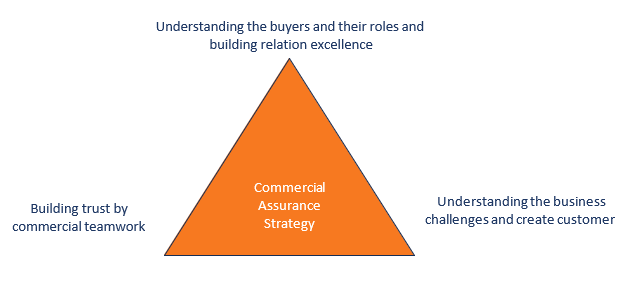
The learning methodology is blended learning, where we apply the visual, auditive, reading and kinesthetic learning style.
Account Strategy Form
Building a successful strategy relies on relationships, teamwork, and a deep understanding of the customer’s business and challenges. It all begins with gathering essential information: insights into stakeholders, buying roles, needs, challenges, and detailed business data on customers and competitors. Understanding stakeholder dynamics is also critical.
The Account Strategy Form is the tool introduced in this program to capture and share these insights within the commercial team. Over the 12 months, participants will learn to use this form step by step, supporting them in creating a robust Winning Strategy for their Must Win Battles.
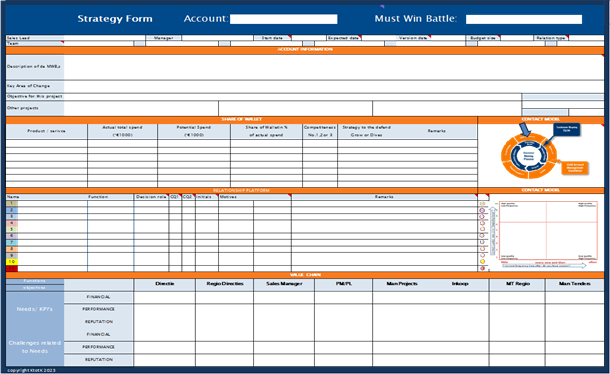
Must Win Battle, the learning case:
To practice all aspects of developing a winning strategy, a template will be provided for customers to create their own tailored business case, based on their specific business environment. Throughout the 12-month period, this case will apply as a practical tool, allowing participants to apply the theory incrementally and develop a winning strategy step by step.

Must Win Battles
To ensure the program’s practical application, each participant selects one or more critical commercial projects, known as Must-Win Battles (MWBs). Throughout the program, participants apply theory to these real-life cases. Using the Account Strategy Form for their MWBs, they develop their winning strategies progressively. Working in commercial teams, participants will support one another, applying what they learn and fostering collaborative growth.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

The Professional Services
The professional services market, encompassing industries like consulting, legal services, accounting, architecture, and marketing, plays a critical role in providing specialized, knowledge- based solutions to businesses and individuals. These services are client-centric, reliant on talent, and often operate on fee-for-service models, making them highly adaptable yet simultaneously exposed to significant commercial challenges in an evolving landscape.
One of the primary challenges in the professional services market is changing client expectations. Clients increasingly demand greater value, faster results, and highly personalized solutions tailored to their unique needs. The expectation for real-time insights and measurable outcomes places immense pressure on service providers to innovate and demonstrate tangible results. Firms must invest in tools and processes to deliver more efficiently without compromising quality, often requiring them to rethink traditional service delivery models.
Technological disruption is another transformative force reshaping the professional services industry. Advances in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics are both an opportunity and a threat. While these technologies have the potential to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making, they also pose risks to traditional service models. For instance, automated legal document review or AI-driven tax preparation can undercut demand for entry-level professional services. However, integrating technology comes at a cost, often requiring significant investment in software, infrastructure, and upskilling the workforce, which can strain resources.
Talent management remains a critical challenge in the professional services sector, as firms struggle with high turnover rates, skill gaps, and evolving workforce expectations. Younger generations, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, value work-life balance, flexible working conditions, and career development opportunities more than ever before. This shift has forced firms to rethink their recruitment and retention strategies, offering not just competitive compensation but also opportunities for professional growth, mentorship, and a positive workplace culture. Attracting and retaining top talent is critical, as the sector relies heavily on the expertise and relationships of its workforce.
Economic and geopolitical fluctuations also pose global economic uncertainty that directly impacts the professional services market. Clients facing budget constraints during economic downturns often scale back their spending on external services, putting pressure on revenue streams. Geopolitical instability adds layers of complexity, as firms must navigate regulatory changes, trade restrictions, and unpredictable market conditions.
Adding to the complexity is the rise of competitive pressures from new entrants, including freelancers, boutique agencies, and tech-driven firms offering lower-cost alternatives. These disruptors challenge traditional players to innovate and differentiate themselves. The commoditization of some professional services, particularly those easily replicated by technology, forces firms to focus on high-value, strategic offerings that emphasize expertise and industry- specific insights.
Another dimension of complexity arises in the buying process for commercial projects, which often involves multiple stakeholders. On the supplier side, teams across functions—such as sales, delivery, and support—must collaborate to craft compelling strategies and solutions. On the client side, decisions are rarely made unilaterally; instead, they require alignment among diverse stakeholders, such as executives, department heads, and procurement teams. Effective communication and cross-functional collaboration are essential to building trust, addressing pain points, and ultimately closing deals.
To address these challenges, professional services firms must focus on technological integration, talent investment, and adaptive pricing models. Value-based pricing, for example, links fees directly to outcomes, aligning with client expectations while differentiating from competitors. Diversification of services and building resilience to economic fluctuations are also crucial. By embracing innovation, fostering a culture of collaboration, and prioritizing adaptability, firms can navigate the complexities of this competitive market and position themselves for sustained growth.
In conclusion, the professional services market is evolving rapidly, with firms facing unprecedented demands from clients, technological shifts, and competitive pressures. Success in this environment requires not only operational efficiency and innovation but also a deep understanding of client needs, workforce dynamics, and market trends. Those that embrace change and remain client-focused will thrive in this challenging yet opportunity-rich landscape.
Often the commercial projects have a complex buying process which requires a team effort from the supplier. Different functions must work together to have a maximum influence. At the buyer site many stakeholders will be involved. Sharing information and working together on the strategy is a must
Technology
The technology market is a sprawling and dynamic ecosystem that extends far beyond traditional IT sectors, encompassing a diverse array of fields such as clean technology, biotechnology, advanced manufacturing, robotics, and consumer technology. These sectors are at the forefront of global innovation, leveraging cutting-edge advancements to address critical challenges, improve quality of life, and drive economic growth. However, despite their immense potential, these industries face a range of commercial challenges that can hinder their ability to scale and thrive.
One of the most impactful areas of the technology market is clean technology (cleantech), which focuses on renewable energy solutions, energy storage, and sustainable resource management. Cleantech is instrumental in addressing climate change and promoting environmental sustainability, with innovations like solar and wind power, advanced battery storage, and carbon capture technologies leading the charge. However, the sector faces significant hurdles, including regulatory uncertainty, infrastructure limitations, and the high upfront costs of adoption. For example, transitioning to renewable energy often requires overhauling outdated grids and ensuring reliable energy delivery—a process that demands extensive funding and political alignment. Furthermore, navigating global regulations, which can vary widely between regions, adds layers of complexity for companies aiming to scale their operations internationally.
Biotechnology, another transformative sector, is driving breakthroughs in healthcare, agriculture, and industrial production. Innovations like precision medicine, CRISPR-based gene editing, and lab-grown meat have the potential to revolutionize industries, improving health outcomes, food security, and sustainability. However, biotech companies face intense commercial pressures, particularly in securing funding for research and development (R&D). Clinical trials and regulatory approvals are lengthy and expensive processes, often consuming years of effort and billions of dollars with no guarantee of success. Moreover, ethical debates surrounding genetic engineering and other biotechnological advancements can spark public resistance, complicating market adoption.
Advanced manufacturing, which includes technologies like 3D printing, automation, and smart factories, is redefining production processes by enhancing efficiency, customization, and scalability. However, the sector must balance innovation with sustainability, ensuring that emerging technologies do not exacerbate environmental challenges. For instance, while 3D printing reduces material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods, questions remain about the recyclability of printed products and the energy consumption of industrial printers. Additionally, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often struggle to adopt advanced manufacturing technologies due to the high cost of integration and skill gaps in the workforce.
Robotics, once confined to industrial settings, is now expanding into areas like medical surgeries, logistics, and customer service. Robots are performing complex surgeries with precision, optimizing supply chains, and even assisting in retail. However, commercialization in this sector often clashes with public perception and trust issues, particularly in areas like AI ethics and job displacement concerns. Robotics companies must navigate these challenges while continuously innovating to meet diverse applications and maintain a competitive edge.
Finally, consumer technology, encompassing wearables, smart home devices, and augmented reality (AR), has reshaped how people interact with their environment and health. While these products have mass-market appeal, competition is fierce, with companies needing to differentiate themselves in a saturated market. Additionally, ensuring data privacy and security for connected devices is a growing concern that can impact consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
Across all these sectors, one of the most pressing challenges is talent acquisition and retention. Specialized expertise in fields like AI, biotechnology, and advanced engineering is in high demand, creating intense competition for skilled professionals. Companies must not only attract top talent but also invest in ongoing training to keep pace with rapid technological advancements.
In conclusion, the technology market beyond IT offers transformative solutions across diverse sectors, from clean energy to advanced robotics. These industries present immense opportunities to drive global progress, but they must navigate complex challenges such as regulatory hurdles, funding constraints, sustainability concerns, and talent shortages. Success in this fast-evolving landscape requires a strategic focus on innovation, collaboration, and adaptability to ensure long- term growth and impact.
Long term trusted relations are key in this market. That means that everybody at the supplier side must works together to build the relations and trust. The buyer wants to be sure that the team of the supplier understands their goals and challenges. Sharing information, creating value and working together on the strategy is a must.
Long term trusted relations are key in this market. That means that everybody at the supplier side must works together to build the relations and trust. The buyer wants to be sure that the team of the supplier understands their goals and challenges. Sharing information, creating value and working together on the strategy is a must.
The IT Market
The Information Technology (IT) market is a cornerstone of the global economy, driving innovation, improving efficiencies, and transforming industries worldwide. It spans diverse sectors such as software development, hardware manufacturing, cloud computing, cybersecurity,
and IT services, all of which are essential to modern businesses. From managing vast amounts of data to automating processes and enhancing customer experiences, the IT market underpins the functionality and growth of economies on a global scale.
Key segments of the IT market include enterprise software for business operations, cybersecurity solutions to protect sensitive data, hardware like computers and networking devices, and cloud computing services offered by industry giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. As businesses increasingly migrate operations to digital platforms, cybersecurity has become a top priority. The growing sophistication of cyber threats has led to a surge in demand for advanced security solutions, while IT services providers play a critical role in helping organizations implement and maintain robust technology infrastructures.
Despite its rapid growth and central importance, the IT market faces significant commercial challenges that test its resilience and adaptability. These challenges span cybersecurity risks, talent shortages, technological disruption, regulatory compliance, cost pressures, and the persistent digital divide.
Cybersecurity Risks: One of the most pressing challenges is the escalation of cybersecurity risks. Cyberattacks, including ransomware, phishing, and data breaches, have become increasingly frequent and complex, costing businesses billions annually. The constant need to stay ahead of cybercriminals requires continuous innovation in security technologies and strategies. However, implementing these advanced measures is resource-intensive, creating a financial strain for smaller businesses that lack the budgets of larger enterprises.
Talent Shortages: Another critical challenge is the shortage of skilled IT professionals, particularly in high-demand fields like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. This talent gap makes it difficult for companies to scale their operations and remain competitive. Organizations are forced to invest heavily in recruitment, training, and retention strategies, often competing with each other to attract top talent. The high turnover rate in the tech industry exacerbates this issue, further straining resources.
Rapid Technological Changes: The rapid pace of technological innovation is another commercial challenge, requiring businesses to constantly adapt and invest in new technologies. Companies must stay ahead of trends like edge computing, blockchain, and quantum computing while maintaining and upgrading legacy systems. Balancing innovation with operational stability is a delicate act, and failure to adapt can lead to obsolescence in a market where agility is crucial.
Regulatory Compliance and Cost Management: The rising tide of data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and the CCPA, adds layers of complexity to IT operations. Compliance requires significant investments in legal expertise, system upgrades, and operational changes. At the same time, companies face pressure to manage costs, particularly as competition intensifies and clients demand more for less. Achieving a balance between affordability and quality remains a key challenge.
The Digital Divide: Lastly, the digital divide presents a long-term challenge for the IT market. In developing regions, limited access to infrastructure and technology inhibits market growth and global economic inclusivity. Bridging this divide requires collaboration among governments, NGOs, and private companies to improve connectivity and provide affordable solutions.
Customer-Centric Approache: In this competitive and complex environment, customers increasingly seek long-term partnerships with IT providers who can align with their values, goals, and strategies. These clients expect not only technical expertise but also adaptability and a deep understanding of their business needs. For suppliers, this means fostering collaboration across sales, consultancy, project management, and service teams to create tailored, value-driven solutions.
Conclusion: The IT market remains a driver of global economic growth and innovation, but it must navigate a rapidly changing landscape filled with significant challenges. From addressing cybersecurity risks and talent shortages to adapting to technological advancements and managing regulatory pressures, IT companies must demonstrate resilience, agility, and a customer-focused
approach. By investing in innovation, fostering partnerships, and bridging divides, the IT market can continue to thrive and shape the future of global industries.
Customers look for long term partnerships with companies who understand their values, goals and strategy. Who can easily adapt to the fast technologies demand of the business of the customer. At the supplier site sales, consultancy, projects and services must work together to demonstrate their knowledge and address the values important for their customer.
The Finance Market
The finance market is a cornerstone of the global economy, orchestrating the movement of capital, enabling investment opportunities, and offering risk management solutions. Encompassing sectors like banking, investment, insurance, and financial services, it provides essential resources for individuals, businesses, and governments. As the lifeblood of the global economic system, the finance market facilitates economic growth, empowers wealth creation, and supports risk mitigation across industries. However, while its influence is vast, the finance market is not without its commercial challenges, which demand agility, innovation, and strategic foresight to navigate effectively.
Key Segments of the Finance Market: The finance market operates across several interconnected domains.
• Banking is its backbone, with commercial banks offering savings accounts, loans, and payment services, while central banks manage national monetary policies and ensure economic stability.
• Investment markets encompass stocks, bonds, private equity, and venture capital, enabling wealth creation and funding for businesses.
• Insurance provides coverage against risks such as health issues, property damage, and life events, safeguarding individuals and businesses.
• Financial services, including asset management, financial advising, and fintech innovations, streamline processes such as lending, payments, and wealth management, adding new dimensions to traditional financial activities.
Despite these services’ essential role, the finance market faces significant commercial and operational challenges, demanding continual adaptation and innovation to remain viable.
Regulatory Pressures: Since the 2008 financial crisis, regulatory pressures have intensified globally. Governments and regulatory bodies have implemented stricter laws governing banking practices, capital adequacy requirements, and risk management to prevent future crises. While these regulations aim to ensure stability, they also introduce compliance burdens that can stifle agility and innovation. Financial institutions must allocate significant resources to meet these requirements, which often increase operational costs and reduce flexibility in introducing new products or services. Striking a balance between compliance and innovation is a persistent challenge.
Market Volatility and Globalization: Market volatility poses another critical obstacle. Financial markets are inherently sensitive to economic uncertainty, geopolitical tensions, and unexpected global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic. These factors can lead to dramatic fluctuations in asset prices, impacting both institutional investors and retail clients. Furthermore, globalization, while expanding opportunities, brings its own complexities. Currency fluctuations, cross-border regulations, and interconnected economies amplify risks. For instance, a banking crisis in one region can have ripple effects across the globe, making risk management and foresight more crucial than ever.
Technological Disruption: Technological innovation is reshaping the finance market, with fintech and cryptocurrencies challenging traditional models. Fintech startups have disrupted sectors like lending, payments, and wealth management, offering faster, more user-friendly solutions. Similarly, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies promise efficiency and transparency but bring new risks, such as regulatory uncertainty and cybersecurity threats. Fraud and data breaches are rising concerns, compelling financial institutions to invest heavily in cybersecurity and digital infrastructure, further driving up costs.
The Competitive Landscape: In the business-to-business (B2B) financial market, competition is fierce. Financial service providers must differentiate themselves not only through pricing but also by demonstrating their ability to deliver tailored solutions that align with clients’ goals and challenges. Success in this domain requires a deep understanding of the customer’s industry, pain points, and decision-making processes. A consultative approach is vital, where sales, advisory, and delivery teams collaborate to present capabilities in a way that resonates with all stakeholders involved in the buying decision. Clear communication of value, expertise, and alignment with client objectives becomes the key differentiator.
Navigating Challenges: To thrive in this evolving landscape, financial institutions must focus on innovation, agility, and client-centricity. Adopting technologies like AI and big data analytics can enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Additionally, building trust through robust compliance, ethical practices, and transparent communication is critical in a market where reputation often determines success. Finally, fostering long-term client relationships by aligning services with their values, goals, and strategies ensures a competitive edge.
Conclusion: The finance market is an indispensable driver of economic activity, supporting the flow of capital, risk management, and investment opportunities. However, it faces a myriad of challenges, from regulatory complexities and market volatility to technological disruption and fierce competition. Financial institutions must innovate, differentiate, and build resilience to navigate these hurdles. By focusing on client needs, leveraging technology, and maintaining adaptability, the finance market can continue to thrive as a foundation of global economic growth.
In the business-to-business part of the financial market, the competition is strong. So how do you differentiate yourself from the competition. How can you present the value of your capabilities towards the needs of the goals and challenges of the customer and al the decision-makers
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:
Amsterdam
Amsterdam stands as a vibrant commercial powerhouse, strategically located in the heart of Europe’s economic landscape. Renowned for its exceptional infrastructure, world-class digital connectivity, and highly skilled multilingual workforce, the city offers an unparalleled business environment that attracts global corporations, startups, and professionals from across the globe. A Gateway to Europe: As part of the Amsterdam Metropolitan Area, the city enjoys the advantages of the Netherlands’ progressive business regulations and strategic geographic location. The port of Amsterdam, one of the largest in Europe, plays a pivotal role as a logistics hub, facilitating the movement of goods across the continent and beyond. Coupled with Amsterdam’s advanced transportation networks, including Schiphol Airport—one of Europe’s busiest international airports—the city provides seamless global connectivity, making it a gateway for international trade and business.
A Magnet for Global Corporations: Amsterdam hosts numerous multinational headquarters, spanning sectors such as technology, finance, creative industries, and sustainable innovation. The city’s attractive tax climate and highly educated talent pool make it an appealing destination for businesses seeking to establish a foothold in Europe. Companies like Netflix, Tesla, and Philips have chosen Amsterdam as their regional base, benefiting from its supportive economic policies and exceptional quality of life.
A Thriving Startup Ecosystem: The city’s startup ecosystem is one of the most dynamic in Europe, driven by a culture of entrepreneurial innovation, access to substantial venture capital, and collaboration with cutting-edge research institutions. Initiatives like Amsterdam Science Park and the StartupAmsterdam program foster innovation and provide resources to budding entrepreneurs. Emerging industries such as fintech, green technology, and digital media are particularly flourishing, as the city embraces its role as a hub for forward-thinking solutions.
A Sustainable and Creative Economy: Amsterdam is at the forefront of sustainability and creative industries. As one of the world’s most bicycle-friendly cities, Amsterdam sets an example in green innovation, from urban planning to renewable energy initiatives. This commitment to sustainability has attracted companies in the green tech sector, further solidifying the city’s reputation as a leader in environmental innovation. Additionally, Amsterdam’s thriving cultural scene and creative economy fuel industries such as fashion, design, and digital media, contributing to its dynamic commercial appeal.
World-Class Talent and Collaboration: The city’s multilingual and highly educated workforce is a key driver of its success. Home to world-class universities and research institutions, Amsterdam consistently produces top talent across various fields. Moreover, its open and collaborative business culture fosters partnerships between corporations, startups, and academic institutions, creating a fertile ground for innovation.
Conclusion: Amsterdam’s blend of strategic location, progressive business environment, and innovative culture positions it as a premier destination for international commerce. Its robust infrastructure, thriving startup ecosystem, and commitment to sustainability attract a diverse range of businesses and professionals. By embracing emerging industries and fostering collaboration, Amsterdam continues to solidify its status as a global leader in trade, innovation, and economic growth.
London
London stands as a preeminent global financial and commercial center, driving international business with unparalleled dynamism. The city’s financial district, centered in the historic Square Mile, is home to some of the world’s most significant financial institutions, investment banks, and global corporate headquarters. With a legacy of excellence and innovation, London continues to attract businesses, investors, and professionals seeking to capitalize on its unique advantages. Its strategic geographic positioning, robust regulatory framework, and sophisticated financial ecosystem have firmly established it as a magnet for international commerce and a cornerstone of the global economy.
The London Stock Exchange (LSE) plays a pivotal role in cementing the city’s financial prominence. As one of the oldest and most influential stock exchanges globally, the LSE attracts investors and corporations from all over the world, providing them with access to liquidity, funding, and global visibility. Beyond finance, London’s commercial strength extends across diverse industries, including technology, creative services, professional consultancy, and digital innovation. For instance, Tech City, situated in East London, has emerged as a major hub for startups and innovation, earning a reputation as Europe’s answer to Silicon Valley. The convergence of talent, funding, and technological ingenuity in this area highlights London’s capacity to lead in the tech- driven global economy.
London’s allure is further enhanced by its multilingual and highly skilled workforce, which enables businesses to thrive in a globalized market. With professionals fluent in a wide range of languages and cultural competencies, the city is uniquely positioned to facilitate international transactions and partnerships. Furthermore, London boasts world-class infrastructure, including advanced telecommunications networks and comprehensive public transportation systems, that ensure seamless business operations. Its international airports, such as Heathrow and Gatwick, offer direct connectivity to virtually every major city worldwide, making London a hub for global mobility.
Legal and professional services in London also play a critical role in sustaining its commercial appeal. Renowned for their expertise, reliability, and innovation, London-based law firms, consultancy agencies, and financial advisors consistently provide cutting-edge solutions to clients across various sectors. These services are supported by a transparent and predictable legal system, which reassures businesses and investors of a stable operating environment.
Additionally, London’s diverse economic landscape fosters resilience and adaptability in an ever- changing global market. Its robust network of venture capital firms and angel investors ensures that businesses—whether startups or established enterprises—have access to essential funding. The city’s supportive regulatory framework and pro-business environment encourage entrepreneurship, enabling ambitious companies to scale globally. Moreover, the presence of numerous trade organizations and networking platforms further enhances opportunities for collaboration and growth.
In conclusion, London continues to stand at the forefront of global commerce and innovation. Its unparalleled financial infrastructure, dynamic business ecosystem, and global connectivity make it a premier destination for corporations, entrepreneurs, and investors alike. By seamlessly blending tradition with innovation, London remains a city where commercial and professional ambitions can thrive, solidifying its status as a global powerhouse for years to come.

Frankfurt
Frankfurt stands as a pivotal commercial and financial epicenter in Europe, renowned for its central role in driving global commerce and serving as Germany’s most significant financial hub. Hosting the European Central Bank (ECB), Frankfurt is not only the heart of monetary policy in the Eurozone but also a gateway to international financial markets. Its robust banking sector, strategic geographic positioning, and advanced business infrastructure make it a magnet for corporations, investors, and professionals worldwide.
At the core of Frankfurt’s commercial influence lies the Frankfurt Stock Exchange (FSE), one of the largest and most influential trading platforms globally. Operated by Deutsche Börse, the FSE attracts significant investment flows, facilitating capital market transactions and fostering innovation in financial instruments. Frankfurt’s financial ecosystem extends beyond traditional banking, incorporating commercial banking, asset management, investment services, and a burgeoning fintech sector. The city’s forward-looking approach to digital finance has made it a hub for blockchain innovations, digital payment solutions, and financial technology startups.
The Frankfurt Financial District, affectionately referred to as “Mainhattan” due to its striking skyline along the River Main, is a testament to the city’s economic vitality. This district is home to a dense concentration of global financial institutions, insurance companies, and professional service firms. Major multinational banks, such as Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank, have headquarters or significant operations in Frankfurt, capitalizing on its stable regulatory environment and proximity to European markets. Frankfurt’s strategic location at the heart of Europe allows businesses to access major markets with ease, further enhancing its appeal to corporations seeking a centralized operational base.
Beyond its dominance in finance, Frankfurt boasts a diversified commercial landscape that includes professional services, technological innovation, and international trade. Legal, consultancy, and accounting firms in the city provide expertise to support the complex needs of multinational enterprises. Meanwhile, Frankfurt’s burgeoning tech scene has attracted startups and established technology companies, particularly in areas such as data analytics, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence. The city’s annual Frankfurt Book Fair, the largest of its kind globally, underscores its leadership in creative and cultural industries.
Frankfurt’s world-class infrastructure is a cornerstone of its commercial success. Frankfurt Airport, one of Europe’s busiest, connects the city to more than 300 destinations worldwide, enabling seamless global mobility for businesses and professionals. Complementing this is an extensive transportation network that includes high-speed rail links and an efficient public transit system, ensuring swift connectivity across Europe. This infrastructure, combined with the city’s multilingual and highly skilled workforce, positions Frankfurt as a prime location for international business operations.
The city’s commercial strength is further bolstered by its supportive business environment, characterized by pro-business policies, access to venture capital, and strong trade networks. The presence of international trade fairs, such as Frankfurt Messe, attracts global enterprises and fosters collaboration across industries, reinforcing Frankfurt’s status as a hub for innovation and growth.
In conclusion, Frankfurt represents a dynamic blend of financial expertise, technological innovation, and global connectivity. Its strategic importance, advanced infrastructure, and commitment to fostering business growth make it a linchpin of the European and global economy, offering unmatched opportunities for corporations, professionals, and investors alike.

New York
New York City represents the pinnacle of global commercial and professional excellence, functioning as one of the world’s most dynamic and influential economic metropolises. Anchored by Wall Street, the city’s financial district stands as a global symbol of economic power, hosting the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq, the two largest stock exchanges by market capitalization. These institutions not only drive global financial markets but also serve as hubs for capital formation, fostering economic growth and attracting investors from around the world.
New York’s commercial landscape transcends its financial core, encompassing a diverse array of industries such as media, technology, fashion, real estate, and professional services. The city’s vibrant corporate ecosystem is concentrated in Manhattan, where towering skyscrapers house the headquarters of multinational corporations and world-leading professional firms. This dense concentration of business activity enables unparalleled opportunities for networking, collaboration, and innovation. Companies across industries establish strategic operations in New York to leverage its unique access to talent, clients, and global markets.
The city’s professional services sector is particularly renowned for its sophistication and expertise. New York is home to some of the world’s largest and most influential law firms, management consultancies, and accounting firms, including Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom, McKinsey & Company, and PricewaterhouseCoopers. These firms provide essential support to global corporations, offering cutting-edge legal counsel, strategic advice, and financial auditing services that are indispensable in today’s competitive global economy.
New York’s media and creative industries also play a vital role in its commercial dominance. As the headquarters for major media conglomerates such as The New York Times, ViacomCBS, and Warner Bros. Discovery, the city serves as a global hub for publishing, advertising, and digital media. Its influence extends into the entertainment sector, with Broadway, film, and television production driving billions of dollars in annual revenue.
The city’s technology sector, often referred to as Silicon Alley, has emerged as a thriving startup ecosystem. Areas like the Flatiron District and Brooklyn have become hotbeds of innovation, attracting venture capital and fostering the growth of companies in fintech, artificial intelligence, e-commerce, and health tech. This entrepreneurial dynamism positions New York as a leader in shaping the industries of tomorrow, complementing its traditional strength in finance and professional services.
New York’s commercial success is underpinned by its world-class infrastructure and global connectivity. Its international airports—John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), LaGuardia Airport, and Newark Liberty International Airport—connect the city to major economic hubs worldwide, facilitating seamless business interactions. Meanwhile, its advanced public transportation and digital networks support the efficient functioning of one of the busiest and most complex urban economies.
The city’s appeal is further enhanced by its highly skilled and multilingual workforce. Professionals from every corner of the globe are drawn to New York by its unmatched
opportunities and cosmopolitan culture. This diversity fuels creativity, innovation, and resilience, reinforcing the city’s status as a commercial powerhouse.
In conclusion, New York City’s unmatched combination of financial leadership, professional services expertise, diverse industries, and global connectivity cements its position as the epicenter of global commerce. Its dynamic entrepreneurial ecosystem, supported by world-class infrastructure and a talented workforce, ensures that it will remain a beacon of commercial and professional excellence for decades to come.
Dublin
Dublin has firmly established itself as one of Europe’s most vibrant commercial hubs, renowned for its thriving technology sector, professional services, and multinational corporate presence. The city has become a magnet for global businesses, particularly in technology, financial services, and pharmaceuticals, leveraging its strategic location within the European Union and its pro-business environment.
At the heart of Dublin’s commercial appeal is its status as a hub for global technology companies. Leading tech giants such as Google, Facebook (now Meta), Apple, and Microsoft have established their European headquarters in the city, drawn by its sophisticated digital ecosystem and access to a highly skilled workforce. The presence of these companies has catalyzed the development of a robust technology cluster, fostering innovation and creating a wealth of opportunities for local startups and professional service providers alike. Dublin’s Silicon Docks, an area often compared to Silicon Valley, epitomizes this growth, housing not only tech giants but also a thriving ecosystem of smaller tech firms, entrepreneurs, and investors.
Ireland’s favorable corporate tax framework is another key factor in Dublin’s commercial success. With one of the lowest corporate tax rates in Europe, coupled with a network of international tax treaties, Dublin offers a compelling value proposition for multinational corporations seeking to optimize their global operations. This, combined with the city’s political stability and supportive regulatory environment, has attracted companies across industries, including technology, pharmaceuticals, and financial services. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has seen significant growth, with global players like Pfizer, AbbVie, and Johnson & Johnson choosing Dublin as a key base for their European operations.
Dublin’s financial services sector has experienced substantial expansion in recent years, particularly in the areas of fintech, banking, and investment services. The city is home to the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), which houses a wide range of financial institutions, including global banks, asset management firms, and insurance providers. Dublin’s access to European markets, combined with its sophisticated regulatory framework and expertise in areas such as fund management and financial technology, positions it as a leading destination for financial and professional services.
The city’s startup ecosystem is another cornerstone of its commercial dynamism. Dublin has fostered a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship, supported by substantial venture capital, government initiatives, and partnerships with world-class research institutions like Trinity College Dublin and University College Dublin. Sectors such as biotechnology, digital services, and artificial intelligence are thriving, with startups benefiting from access to mentorship, funding, and collaborative spaces. This ecosystem not only drives innovation but also creates synergies with larger corporations, further solidifying Dublin’s position as a leader in global commerce.
Dublin’s multilingual and highly skilled workforce is one of its greatest assets. With professionals from across the globe choosing to work in the city, Dublin offers a rich pool of talent fluent in multiple languages and equipped with expertise in a wide range of fields. This diversity, combined with the city’s connectivity through Dublin Airport and its advanced infrastructure, ensures that businesses can operate seamlessly on an international scale.
In conclusion, Dublin has transformed into a dynamic commercial and professional services hub, excelling in technology, finance, and innovation. Its strategic location, favorable business climate, and vibrant workforce make it a premier destination for multinational corporations, entrepreneurs, and professionals seeking success in an increasingly globalized economy.
Program Benefits
Finance
- Improved forecast
- Robust pipeline
- Improved EBITDA
- Investment focus
- Empowered employees
- Information sharing
- Process Improvement
- Shorter cycles
- Team performance
- Predictive Insights
Management
- Leadership Excellence
- Coach tools
- Increased collaboration
- Better focus
- Strengthen engagement
- Profitable deals
- Improved forecasts
- Shared objectives
- Team selling
- Coaching culture
Marketing
- Win rates
- Customer Understanding
- Buying cycles
- Value proposition
- More influence
- Effective strategies
- Improved retention
- Multi-level selling
- Better qualifications
- Stronger relationships
Testimonials
![]()
Honeywell process Solutions
“We worked together with Mr. Jansen on the commercial excellence project with the goals to improve business with identified global clients and improve awareness of importance of personal and company planning.
Most significant impact of this training on the team is increased business in $ with these clients over duration of 3 years cycle plus increased spirit and cooperation amongst the different team members, not only from Sales but also Business side and Operation side.
I can therefore strongly recommend Mr. Jansen as a strong and reliable and long-term partner for our company.”
![]()
Rondahl
“We worked together with Mr Jansen on the commercial excellence project and our goals to were to determine a business strategy, set a clear direction, and establish focus within the business.
For us the significant impact of this training on the team is that we came together as a team, collectively establishing focus, fostering a sense of unity (“we’re in this together”), and openly putting all ideas and perspectives on the table.
We would recommend Mr. Jansen because we greatly appreciated working with him to define our strategy. Mr. Jansen provided structure to our discussions, offered guidance and clarity, and introduced fresh insights that shaped our renewed strategy. Through this collaboration, we stay sharp, ensure alignment within the team, and always have a solid foundation to fall back on.”
![]()
ORTEC
“Worked together with Mr. Jansen on the commercial excellence project with the goals to make the customer/sales journey a process which can be influenced at the right time with the right actions. To accomplish this, we worked with the sales team on a standard approach and used real world opportunities during the training. The theory was used in the existing sales opportunities.
Most significant impact of this training on the team is that they learned that there is a customer buying cycle and that every phase of this cycle can be influenced by themselves and/or other people of the company. In the latter case they learned how to use this.
We recommend this training/approach because this is not a training where you train and nothing really changes. Because of the real change we changed some things in our CRM and used templates for the larger deals and strategic account management.”
![]()
Honeywell Ltd.
“I had the pleasure of working with Mr. Jansen on an extensive commercial excellence and account leadership project aimed at enhancing our team’s sales capabilities and bolstering our overall market competitiveness.
The most significant impact of this training on our team was the newfound confidence and strategic skills acquired for engaging with clients, resulting in a marked increase in our conversion rates and customer satisfaction. The practical insights and tailored strategies provided by Mr.
Jansen have genuinely revolutionized our sales approach. The effects of their program are long- lasting; it has fundamentally changed our client engagement strategy, and the methodologies we adopted continue to be relevant and effective today, every day. The value they delivered was truly exceptional.
Recommendation: I wholeheartedly recommend Mr. Jansen to any organization looking to enhance their commercial strategies. Their expertise and unwavering commitment to our success were evident throughout the project, making them an invaluable partner.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.





















