Clinical Process Optimization

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Clinical Process Optimization is provided by Ms. Butler Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
TBA
To request further information about Ms. Butler through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Clinical Process Optimization
Imagine a hospital hallway bustling with activity. Patients wait anxiously, some frustrated, others resigned. Doctors and nurses rush by, buried under paperwork and administrative tasks. The air crackles with tension, a stark contrast to the promise of healing and well-being that a hospital should embody. This is not just a scene from a movie; it is the harsh reality for many healthcare institutions today.
The American healthcare system, once a beacon of innovation, is facing a critical crossroads. Skyrocketing costs threaten to cripple hospitals and clinics. A labyrinth of regulations creates constant anxiety over compliance. And fragmented data systems, instead of providing clear insights, leave decision-making shrouded in uncertainty.
But amidst these challenges lies a hidden opportunity. A $10 trillion opportunity, in fact, for investors seeking solutions to a system desperately in need of transformation. This is where our Clinical Process Improvement (CPI) methodology comes in. We are not just offering a collection of tools; we are proposing a cultural transformation.
Think of CPI as a helping hand for these struggling institutions. We partner with them to identify and address ten critical pain points that are holding them back. Uncontrolled spending, for example, is draining precious resources that could be used to improve patient care. We help them identify and eliminate wasteful practices, freeing up much-needed funds.
Now, consider the following Case Study: Novant Health standardizes safety and quality control measures across its medical system
Novant Health embarked on a comprehensive clinical process improvement initiative focused on standardizing safety and quality control measures to enhance patient care and ensure consistency across its medical system. By implementing uniform protocols and best practices across all its facilities, Novant Health aimed to minimize variations in care delivery, reduce the incidence of medical errors, and improve patient outcomes. This initiative included rigorous staff training, adopting advanced real-time monitoring and reporting technology, and a commitment to continuous improvement through regular audits and feedback loops. The results of this case study demonstrate significant improvements in patient safety metrics, including reduced infection rates, fewer medication errors, and higher patient satisfaction scores. Novant Health’s success in standardizing safety and quality measures showcases the critical impact of cohesive and systematic approaches to clinical process improvement in achieving excellence in healthcare delivery.
Navigating the ever-changing regulatory landscape can feel like walking a tightrope. One wrong step can lead to hefty fines and a damaged reputation. We provide expert guidance and support, ensuring compliance while allowing healthcare professionals to focus on what they do best – caring for patients.
Fragmented data is the enemy of informed decision-making. Imagine having valuable information at your fingertips, but it’s all locked away in separate filing cabinets, inaccessible and unusable. We break down these data silos, creating a unified platform for actionable insights which empowers doctors, nurses, and administrators to make data-driven decisions that improve resource allocation and operational efficiency.
But it’s not just about numbers and paperwork. At the heart of healthcare is the patient’s experience. Long wait times, poor communication, and a lack of personalization can leave patients feeling frustrated and unheard. We help institutions redesign care pathways, prioritizing patient needs and fostering clear communication. This translates into a more satisfying experience and builds trust with patients, leading to better outcomes and improved loyalty.
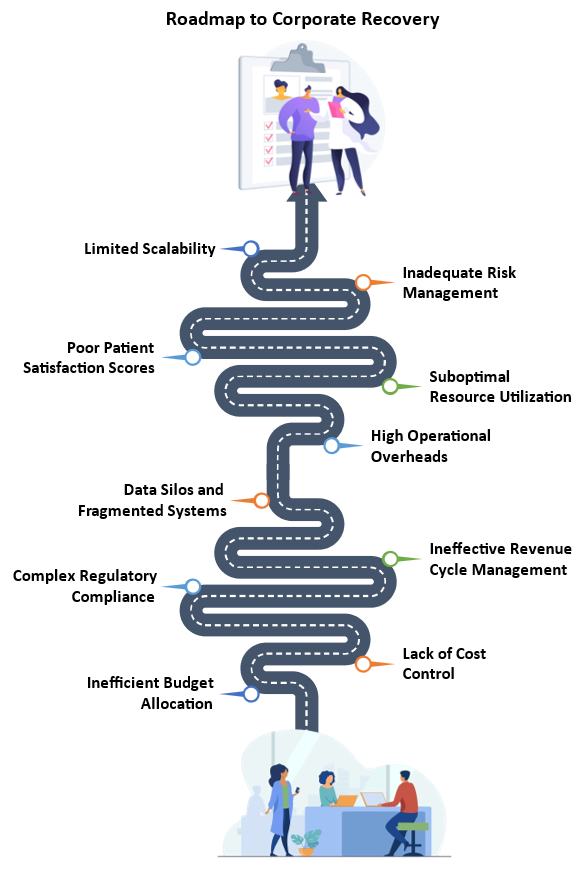
Roadmap to corporate recovery.
The healthcare system also needs to be adaptable. Inflexible financial strategies and clinical processes can’t keep pace with the rapidly changing world. We equip institutions with the tools and strategies they need to be flexible and resilient. This allows them to adapt to new market dynamics, expand services, and cater to evolving patient needs, ensuring their long-term sustainability.
Our vision is a future where healthcare institutions thrive. Doctors and nurses, relieved of administrative burdens, can devote more time to their patients, delivering exceptional care with a smile. Patients experience shorter wait times, personalized treatment plans, and a renewed sense of trust in the healthcare system. Investors benefit from a stable and adaptable healthcare landscape, reaping the rewards of their investment.
CPI presents a win-win scenario for everyone involved. It’s an opportunity to revolutionize healthcare, improve patient lives, and secure a prosperous future for all stakeholders. We can turn the tide on healthcare’s current crisis and build a brighter future, together. By joining forces, we can ensure a world where hospitals are not just places of frustration, but beacons of health and hope for all.
Curriculum
Clinical Process Optimization – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Financial Responsibility Basics
- Part 1 Month 2 HIPAA Implementation for Clinical Professionals
- Part 1 Month 3 Claims Processing Management
- Part 1 Month 4 Intellectual Developmental Disabilities Assessments
- Part 1 Month 5 Motivational Interviewing Strategies/Techniques
- Part 1 Month 6 Principles for Inter-Disciplinary Teams
- Part 1 Month 7 Mastering Regulatory Compliance in Clinical Process Improvement
- Part 1 Month 8 Continuous Improvement Integration in Healthcare
- Part 1 Month 9 Utilization Reviews – Accreditation programs
- Part 1 Month 10 Occupational Health and Wellbeing Functional Assessments
- Part 1 Month 11 Leadership Development
- Part 1 Month 12 Core Concepts for Measuring Client Satisfaction
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Clinical Process Optimization corporate training program.
Clinical Process Optimization – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Financial Responsibility Basics – The backbone of a financially sound business is having a solid payment (remittance) system in place. After completing this course, participants should be able to identify the Health Insurance responsibility of patients, identify collection methods of payments, getting appropriate authorizations etc., learn Insurance carriers and authorization code entries, identify an enhanced eligibility verification process, learn the process to collect copays and ensure payment systems are in place such as merchant services.
- Part 1 Month 2 HIPAA Implementation for Clinical Professionals – One of the responsibilities of a clinical professional is to adhere to the federal privacy laws to ensure the protection of a client’s PHI. After completing this course, participants should be able to: Identify the reasons why HIPAA was enacted, know consumers’ rights under HIPAA, Identify various examples of protected health information, know the requirements and safeguards for working with protected health information, apply HIPAA rules appropriately (in various situations) to ensure a high level of care and respect for consumers and Understand HIPAA compliance and the penalties for not complying, as mandated by law.
- Part 1 Month 3 Claims Processing Management – Appropriate claims processing is an important factor that drives third party business. There is also a need to ensure that agencies are not over billing for non-service related activities and/or noncompliance. After completing this course, participants should be able to: begin discussion on the redesign of claims processing, to include improved components for error-free on time payments, claims remittance, as well as learn ways to implement a self-service portal and identify requirements for training technical staff on how to efficiently operate the system.
- Part 1 Month 4 Intellectual Developmental Disabilities Assessments – Administering assessments are vital to determining an individual’s intellectual ability as well as the need for placement and services within facilities and/or the community. After completing this course, participants should be able to: Understand the need for assessments of persons with developmental disabilities, understand the process for administering assessments within the facility, analyze community involvement in the assessment process, critique the components and usage of the assessment and understand the interpretation of the diagnosis as it relates to access to care.
- Part 1 Month 5 Motivational Interviewing Strategies/Techniques – The most effective way of information gathering has proven to be several techniques to include motivational interviewing. At the completion of this program, participants should be able to:
Identify changes in the conception of motivation occurring in recent years, Identify the role of the clinician in working with clients using a Motivational Interviewing counseling style, Identify instances of ambivalence in the client, Identify the five principles of motivational interviewing, and Identify five motivational interviewing strategies to use in early sessions - Part 1 Month 6 Principles for Inter-Disciplinary Teams – Inter-Disciplinary teams have historically been created to address the many facets of dually-diagnosed individuals and/or individuals within the judicial system. By the end of this course, participants should be able to: Identify effective ways to formulate teams and learn from other professionals, use the information to create cohesive treatment plans, learn to formulate meeting agendas that produce results, learn how the use of these teams help improve medication choice and learn to work effectively within the judicial system.
- Part 1 Month 7 Mastering Regulatory Compliance in Clinical Process Improvement – The workshop aims to equip participants with comprehensive knowledge and practical skills to navigate and excel in regulatory compliance within clinical process improvement. It’s designed for healthcare professionals, administrators, and quality assurance personnel.
Objectives: Gain comprehensive knowledge of various regulatory bodies, laws, and standards pertinent to healthcare compliance, develop a deep understanding of key healthcare laws like HIPAA, Stark Law, and regulations governing clinical processes, Learn the nuances of compliance audits, inspection preparation, and corrective action planning. - Part 1 Month 8 Continuous Improvement Integration in Healthcare – This comprehensive course is designed to equip healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to integrate continuous improvement methodologies into their organizations, ultimately enhancing patient care, efficiency, and overall performance.
By the end of the course, participants will possess the skills and knowledge to drive and sustain continuous improvement in healthcare, contributing to enhanced patient care, operational efficiency, and organizational success. - Part 1 Month 9 Utilization Reviews – Accreditation programs – For companies to be considered a leader in the field, most companies are required to become a member of an accrediting program. By the end of this course, participants should be able to: Ensure entities will understand the correct guidelines as required by the appropriate accrediting organization, be able to train staff on how to identity the correct standards, Policies/Procedures and understand the requirements for appointing a Compliance Officer and train staff on the accreditation processes
- Part 1 Month 10 Occupational Health and Wellbeing Functional Assessments – In order for individuals who are claiming benefits get approved through the Department of Work and Pensions UK; they need to have an assessment completed. By the end of this course, participants will learn the purpose of assessments for DWP, understand the function of the Health Assessment Advisory Service, and learn how an individual’s health condition or disability affects their daily life; and finally how to properly administer these assessments for Department for Work and Pensions (United Kingdom).
- Part 1 Month 11 Leadership Development – The Leadership Development Workshop tailored for mid to senior level healthcare professional’s aims to cultivate and refine leadership competencies critical for navigating the complex healthcare landscape. This program focuses on empowering participants to lead effectively, foster innovation, and drive positive change within their healthcare organizations.
- Part 1 Month 12 Core Concepts for Measuring Client Satisfaction – Successful companies use client satisfaction surveys to improve their service delivery. In order to collect this data, there is a need to measure client satisfaction. After completing this course, participants should be able to: Identify core customer satisfaction metrics, create a customer satisfaction survey tool, meet with staff to consider ways to collect customer satisfaction data, identify a team of staff to administer the survey and create a process to review results and a scale for ways to improve service delivery.
Methodology
Clinical Process Optimization
Program Planning:
The methodology used for Program Planning will include:
Identifying key processes for improvement – Use process mapping tools to visually represent current processes and identify bottlenecks, redundancies, or areas for optimization.
Data collection and Gap analysis – Assess the current clinical processes, identify inefficiencies or areas for improvement, and define the gap between the current state and desired outcomes.
Defining the specific objectives of the improvement program – During this planning stage, we will clearly outline the workshop’s purpose, whether it’s enhancing patient care, improving operational efficiency, or addressing specific clinical challenges.
Identifying quality Improvement Tools – Implement quality improvement tools such as diagrams, charts, or 5 Whys to analyze problems and generate solutions collaboratively.
Change Management Strategies – Plan for change management by considering strategies to effectively communicate, train, and support staff through process changes.
Continuous Improvement Culture – Emphasize the importance of ongoing improvement efforts and establish a culture that encourages staff to identify and address process inefficiencies continually.
Evaluation and Metrics – Define measurable outcomes to evaluate the success of the workshop and ongoing improvements in clinical processes. Use metrics to track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
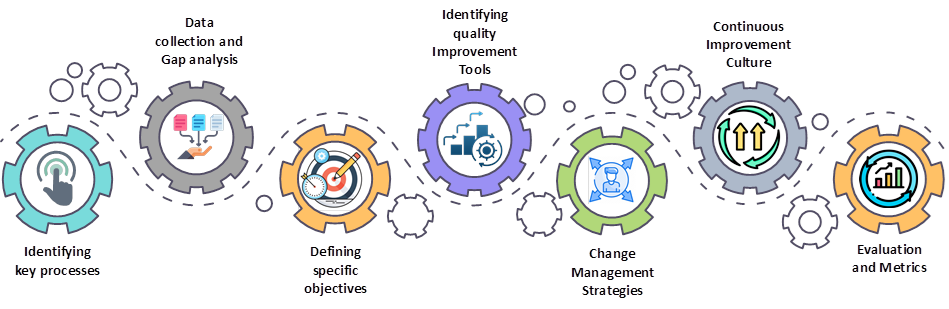
The methodology for Program Planning implementation will also involve setting goals for the program. Some of the goals may include enhancing patient safety, improving outcomes, reducing errors, or increasing efficiency.
Some other methodologies may include creating detailed action plans for each identified improvement area. The program will also consider piloting proposed changes in a limited area or department before full-scale implementation. Pilot testing allows for refinement and validation of improvement strategies.
Combining these methodologies allows for a comprehensive approach to planning a clinical process improvement workshop, ensuring a structured method to address challenges and impact positive change in healthcare delivery.
Program Development:
The methodology that will be used for Program Development is the Lean Six Sigma Methodology. This methodology emphasizes a structured approach to program development in a clinical process improvement workshop, ensuring a systematic analysis, implementation, and evaluation of initiatives aimed at enhancing healthcare delivery and outcomes.
Utilizing Six Sigma involves a data-driven approach to eliminate defects and VA Utilize Lean Methodology; Lean principles focus on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and continuously improving.
Here are some additional methodologies used for Program Development in the Clinical Process Improvement workshop:
1. Process Mapping and Flowcharts: Visualize current workflows using process mapping tools. Develop detailed flowcharts to illustrate the sequence of activities, decision points, and potential areas for improvement.
2. Quality Improvement Tools: Utilize quality improvement tools such as Fishbone diagrams, Pareto charts, and control charts to analyze data, identify root causes, prioritize issues, and track improvements.
3. Action Plan Development: Based on the identified areas for improvement, develop a comprehensive action plan. Outline specific steps, responsibilities, timelines, and measurable outcomes for each improvement initiative.
4. Change Management Strategies: Implement change management strategies to facilitate a smooth transition to new processes. Provide training, communication plans, and support to staff affected by the changes.
5. Pilot and Test Interventions: Implement proposed changes on a small scale (pilot) to assess their effectiveness before full-scale implementation. Gather feedback and make necessary adjustments.
6. Evaluation and Continuous Improvement: Measure the success of implemented changes using predefined metrics and KPIs. Continuously monitor outcomes, gather feedback, and iterate on the process to ensure sustained improvement.
7. Documentation and Knowledge Sharing: Document the entire process improvement journey, including methodologies used, challenges faced, and successful interventions. Share lessons learned and best practices across the organization.
This methodology also involves techniques like Value Stream Mapping (VSM) and involves a data-driven approach to eliminate defects and variations in processes. It emphasizes DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control) or DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) methodologies to systematically improve processes. All could prove beneficial during the program implementation phase of the workshop.
Program Implementation:
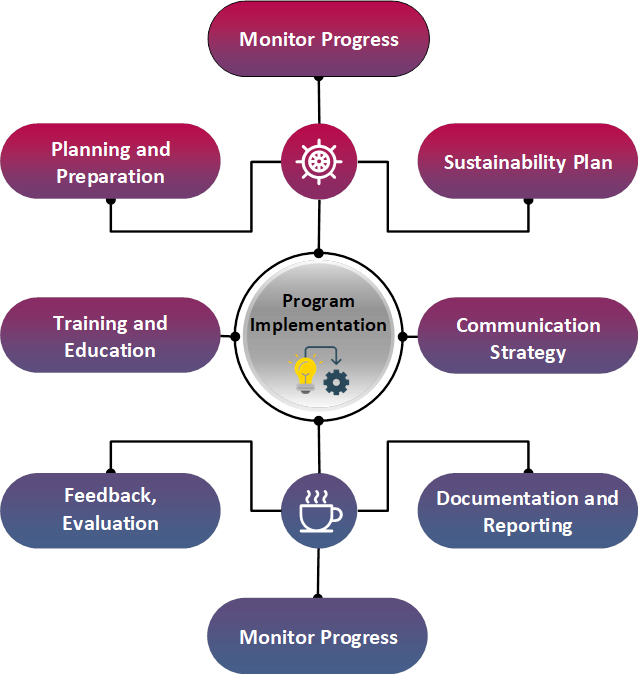
The methodology that will be used for Program Implementation will include Pilot Testing to include selecting a pilot area, collecting data and also getting feedback. As well as implement proposed changes on a smaller scale (pilot) before full-scale deployment.
Planning and Preparation will also be included in program implementation to include outlining goals, timelines, responsibilities and resources. This methodology emphasizes a structured approach to implementing clinical process improvements, ensuring thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, effective communication, and ongoing evaluation to facilitate successful changes within the healthcare setting.
Here are some other methodologies that may be used for Program Implementation in the Clinical Process Improvement workshop:
Communication Strategy – Develop a clear and consistent communication plan to inform stakeholders about the upcoming changes, the rationale behind them, and how they will be implemented.
Documentation and Reporting – Document the entire implementation process, including successes, challenges, and lessons learned, and best practices. Generate regular reports to track progress and share insights across the organization.
Training and Education – Provide training sessions and educational resources to equip staff with the necessary skills and knowledge required for the new processes or technologies being implemented.
Monitor Progress – Regularly monitor the implementation progress against predefined metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). Evaluate the effectiveness of the changes and make necessary adjustments.
Sustainability Plan – Develop a sustainability plan to ensure that the improvements made during the workshop are sustained over time. This may include ongoing training, regular reviews, and continuous improvement efforts.
Feedback, Evaluation – Establish a feedback mechanism to gather input from staff and stakeholders involved in the implementation. Use this feedback to refine processes and address any challenges or issues that arise.
Lastly, during the phase of program implementation, it is important to celebrate wins and successes.
Program Review:
Program Review will include evaluating Key Performance Indicators, establish objectives necessary for the review process and gather and analyze data. This methodology emphasizes a systematic approach to reviewing clinical process improvements, focusing on data-driven analysis, stakeholder feedback, and the generation of actionable insights to drive ongoing improvement efforts in healthcare delivery.
Other methodologies used during program review will include
Establish Review Criteria – Define specific criteria and metrics aligned with the workshop’s objectives to assess the success and effectiveness of the implemented changes. This might include metrics related to patient outcomes, process efficiency, staff satisfaction, etc.
Data Collection – Gather relevant data and information using predefined metrics and KPIs. Collect quantitative data (such as patient wait times, error rates, etc.) and qualitative feedback from stakeholders involved in or affected by the changes.
Analysis and Evaluation – Analyze the collected data to evaluate the performance of the implemented improvements. Compare current data to baseline measures to determine the impact of the changes on clinical processes and outcomes.
Stakeholder Feedback – Gather feedback from clinicians, staff, patients, and other stakeholders involved in or impacted by the changes. Use surveys, interviews, or focus groups to collect qualitative input on their experiences and perceptions.
Assessing outcomes as well as collecting feedback from staff, clinicians and patients has proven to be one of the most important methodologies to use during the review phase of the clinical process improvement workshop.
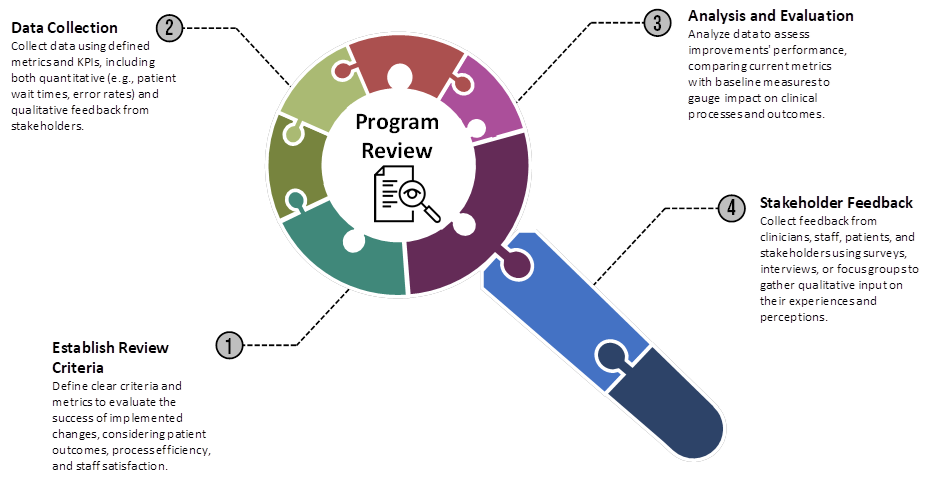
The list of methodologies continues with the following:
Review Meeting or Workshop – Convene a review meeting or workshop involving key stakeholders to discuss the findings from the evaluation. Present the data analysis, feedback, and outcomes achieved from the implemented improvements.
Identify Successes and Challenges: Identify and highlight successful outcomes and achievements resulting from the implemented changes. Also, identify any challenges, barriers, or areas where the desired improvements were not fully realized.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices: Discuss lessons learned from the implementation process. Identify best practices that contributed to successful outcomes and areas for improvement in future initiatives.
Lastly, Benchmarking, identifying areas for improvement and creating actionable recommendations will refine the Clinical Process Improvement program.
Benchmarking is a strategic management approach that organizations use to gain a competitive edge by comparing their practices, processes, and performance metrics with those of their industry counterparts or top performers. It’s a powerful tool that allows companies to identify areas for improvement, set performance targets, and implement effective strategies to enhance overall organizational performance. By analyzing data and information obtained from benchmarking partners, businesses can pinpoint performance gaps and discover best practices that can be adopted.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Healthcare
The Healthcare industry has evolved and been modernized over the years which has caused some significant changes in service delivery.
The commercial history of healthcare is extensive and has undergone significant transformations over time. In the earlier times, the introduction insurance and payment modules changed the way we as consumers have access to care. During the commercialization transition, the pharmaceutical industry grew along with various vaccines and newly introduced medications. Technology commercialization led to modernization of new tools, medical devices and equipment. Working with hospitals, clinics, and healthcare providers became commercial entities, operating on business models to provide medical care in exchange for payment.
Then, there was the rise of modern medicine. The history of modern medicine has been characterized by rapid advancements in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and healthcare technology. Breakthroughs in immunotherapy, gene editing, and precision medicine have revolutionized treatment options, leading to more targeted and effective therapies. The pharmaceutical industry has seen the development and commercialization of a multitude of new drugs, particularly in areas such as oncology, rare diseases, and chronic conditions. Additionally, the proliferation of digital health solutions, telemedicine, and wearable health technology has transformed patient care, making it more accessible and efficient. However, rising drug costs, healthcare disparities, and data security concerns have posed challenges. Despite these challenges, the past decade has seen the commercialization of modern medicine significantly improve patient outcomes and reshape the healthcare experience.
Public Health Initiatives and Hospital development are both a part of the Industrialization and Healthcare Infrastructure. The Industrial Revolution spurred the growth of hospitals, healthcare facilities, and the professionalization of medical services. In addition, improved sanitation, public health reforms, and vaccination campaigns led to significant reductions in infectious diseases.
Advancements in medical technology, pharmaceuticals, and surgical techniques revolutionized healthcare, enhancing diagnostic and treatment capabilities. Then, we seen the introduction of health insurance and government-funded healthcare systems in various countries expanded access to medical services.
The commercial history of the healthcare industry reflects a journey from early medical practices to modern, technology-driven healthcare systems.
The perception of the commercial current position of the Healthcare industry include both positive and negative perceptions: One of the positives are Medical Advancements which have been in the forefront of lifesaving efforts and technological advancements. This means those individuals who may have life threatening illness and/or conditions have a chance to obtain advance medical care which can prolong their lives. Another positive is Access to Care where the commercial healthcare industry provides access to a wide range of services, cutting edge treatment and clinical trials. The last positive perception includes the career and job opportunities with the many facets in the current commercial healthcare position.
A few of the less desirable perceptions or negative would include the high cost of health care, the complexity of healthcare plans to include deductibles, copayments and limits. There is also the stigma of the high cost and criticism of prescription drugs. In some cases physicians/practitioners may be on the receiving end of some of these drug companies who push over prescribing of drugs, performing unnecessary procedures and prioritizing profits over patient care.
The healthcare industry’s current landscape reflects a dynamic mix of rapid technological advancements, evolving patient expectations, regulatory changes, and ongoing adaptations spurred by the pandemic. The sector continues to navigate challenges while embracing innovations that are reshaping the delivery and accessibility of healthcare services.
Let’s break down a few of these concepts:
EHR Advancements and Digital Health Innovation are both part of the technological advancements. There is accelerated integration of digital technologies like AI, IoT, wearables, and health apps for remote patient monitoring and personalized care and continued adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and interoperability improvements for seamless data sharing among healthcare providers.
Shifts in Patient Behavior include patient empowerment and focus on wellness initiatives. Professionals see increasingly informed and proactive patients demanding more personalized care, digital tools, and transparency in healthcare services. Wellness programs, and holistic approaches to well-being will continue in the forefront of healthcare initiatives.
The healthcare industry continues experiencing several key trends and transformations, shaping its current commercial position.
The commercial future outlook for Healthcare appears dynamic and promising, however I foresee challenges and transformations. Telehealth and remote monitoring have increased in recent years especially in the remote and underserved areas. We have also seen many technology changes when it comes to digital health solutions such as wearable devices (Fitbits, Smart watches), health apps and the ability to login to our own EHR. Machine Learning are anticipated to revolutionize diagnostics and healthcare management. There’s a movement towards empowering patients with greater control over their health data, treatment decisions, and care plans. Patients can have options in choosing a healthcare plan that meets their personal needs. We as a whole can access our records through secure online portals.
During the Pandemic, we experienced an array of changes to your healthcare system. This included the wearing of PPE, remote learning and digital training options.
The commercial future of healthcare is poised for advancements driven by technology, patient-centric care models, and collaborations across various sectors. However, challenges such as cost effectiveness, access, regulatory complexities, and adapting to evolving health crises will demand concerted efforts and innovative solutions to ensure sustainable and inclusive healthcare systems globally.
The commercial future outlook for healthcare appears dynamic and promising, however one can foresee challenges and transformations. Telehealth and remote monitoring have increased in recent years especially in the remote and underserved areas. We have also seen many technology changes when it comes to digital health solutions such as wearable devices (Fitbits, Smart watches), health apps and the ability to login to our own EHR. Machine Learning are anticipated to revolutionize diagnostics and healthcare management. There’s a movement towards empowering patients with greater control over their health data, treatment decisions, and care plans. Patients can have options in choosing a healthcare plan that meets their personal needs. We as a whole can access our records through secure online portals.
During the Pandemic, we experienced an array of changes to your healthcare system. This included the wearing of PPE, remote learning and digital training options. This will also cause some Workforce Adaptations such as training and upskilling healthcare professionals for telemedicine, digital health, and remote care delivery as well as strategies to address healthcare worker burnout, mental health support, and workforce well-being initiatives.
Integration of Mental Health Services and Digital Mental Health Solutions are part of the focus on Mental Health and Well-being. Some of the implications include heightened focus on mental health awareness, integrating mental health services into primary care, and destigmatizing mental illness. There will also be the expansion of digital mental health platforms, apps, and tele psychiatry for increased access to mental health support.
The commercial future of healthcare is poised for advancements driven by technology, patient-centric care models, and collaborations across various sectors. However, challenges such as cost effectiveness, access, regulatory complexities, and adapting to evolving health crises will demand concerted efforts and innovative solutions to ensure sustainable and inclusive healthcare systems globally.

Government
The commercial history of Government involvement in industries is a complex narrative influenced by economic, social, and political factors. Striking a balance between regulatory oversights, fostering innovation, and meeting societal needs will continue to shape the relationship between governments and industries in the future.
The history of the government industry sector is multifaceted and has evolved significantly over time, shaped by various factors and historical developments. Expansion of Government Services includes the industrial era that saw the expansion of government services, including education, healthcare, and social welfare programs, aimed at addressing societal needs. Governments began regulating industries to ensure fair competition, consumer protection and public safety. This has led to the establishment of regulatory agencies. The function of these regulatory bodies include Oversight and Regulation, Protection of public interest, Industry compliance and standards, Public Health and Safety, Economic and Financial stability, Law Enforcement and Penalties, Research reporting and Policy Development and Information and Communication. Overall, these bodies play a pivotal role in maintaining order, protecting public interest, ensuring industry compliance, and promoting ethical and safe practices across various sectors of the economy.
• Then there is the Global impact of the government. This has led to the cooperation between governments and industries, thus encouraging trade policies international regulations, and economic cooperation.
• The commercial history of government involvement in industries is an influenced by economic, social, and political factors. Professionals however consider balance between regulatory oversight, fostering innovation, and meeting societal needs which will continue to shape the relationship between governments and industries in the future.
• These different sectors of government will continue to drive how business is conducted both locally and internationally. Organizations must keep an eye on the pulse of the governmental changes and narratives as this will continue to impact the way business is conducted in our country.
Expansion of Government Services: The industrial era saw the expansion of government services, including education, healthcare, and social welfare programs, aimed at addressing societal needs.
Regulation and Oversight: Governments began regulating industries to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and public safety, leading to the establishment of regulatory bodies.
Globalization’s Impact: Globalization led to increased interdependence between governments and industries, influencing trade policies, international regulations, and economic cooperation.
The current commercial positon of Government industry sector
The commercial current position of governments varies based on the following factors, including economic policies, governance structures, and the role they play in their respective economies. Here’s a noteworthy perspective:
Governments generate revenue mostly through taxes, tariffs, and fees. Then these funds are allocated to various sectors such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, defense, and other social welfare programs.
Most governments struggle with large amounts of debt and deficits and have the need to generate more and more revenue to cover these expenses to maintain fiscal stability.
They often provide support, incentives, and subsidies to specific industries to stimulate economic growth, innovation, and job creation. Regulatory policies impact businesses, shaping competition and trade relations both domestically and internationally.
When it comes to Healthcare and education; governments provide these services along with social welfare programs to ensure the wellbeing of their citizens, this mostly from the tax dollars of the public.
Additionally, through various policies, governments aim to reduce income disparities and address poverty by redistributing wealth and providing social safety nets. In some cases, these types of programs may have the opposite effect on society overall.
Governments develop and enforce environmental regulations, promoting sustainability and addressing climate change concerns. They also incentivize green technologies, renewable energy, and sustainable practices to combat environmental challenges.
Fast growing technologies, demographic shifts, global crises, and the evolving nature of economies have all proven to bring their challenges to government as well. The commercial position of governments involves navigating the complexity of economic, social, and global factors, with their roles spanning generating revenue, investment, regulation, and social welfare. The need to adapt to changing circumstances and balance diverse interest will remain at the center of their current commercial position.
Adapting to changing circumstances, fostering innovation, and balancing diverse interests remain central to their commercial positioning within economies.
• Environmental Policies: Governments develop and enforce environmental regulations, promoting sustainability and addressing climate change concerns.
• Green Initiatives: Many governments incentivize green technologies, renewable energy, and sustainable practices to combat environmental challenges.
Adapting to Change: Governments face challenges in adapting to rapid technological advancements, demographic shifts, global crises, and the evolving nature of economies.
Reform and Governance: Reforming governance structures, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and ensuring transparency remain ongoing challenges for many governments.
The future outlook for the Government industry sector will be impacted by various trends and transformative forces, influencing how governments operate, interact, and serve their constituents. Let’s look at an overview of what the future outlook of this sector entails:
Digital Transformation will be at the forefront of this industry. Governments are likely to expand digital services, enhancing accessibility and efficiency in service delivery through online platforms and streamlined processes. Leveraging data and analytics will enable governments to make data-driven decisions, enhance policymaking, and improve citizen services.
They will likely adapt regulations to keep up with technological advancements, ensuring responsible innovation and consumer protection. More emphasis will be on transparency, open data initiatives, and mechanisms to enhance accountability in government operations. We will see collaborations with private entities for infrastructure development, service delivery, and innovation and Cross-Sectoral Collaboration including collaboration with non-profits and educational institutions.
Governments will continue to focus on Sustainability and Resilience preparedness; meaning preparedness for global crises, pandemics, and cybersecurity threats will become focal points, requiring investments in resilience measures.
Efforts will continue to provide inclusive and citizen-centric services, focusing on equity, accessibility, and responsiveness to diverse societal needs. There might be increased emphasis on participatory governance models, involving citizens in decision-making processes and forming policies.
International cooperation will become increasingly important as they will intensify efforts to collaborate globally, addressing transnational issues, trade relationships, and global health challenges through alliances and agreements. Diplomatic efforts will expand into cybersecurity and digital diplomacy realms to address threats and promote secure global communication.
The future outlook for the government sector involves leveraging technology, collaboration, promoting sustainability, and adapting governance structures to meet evolving societal needs and global challenges. Creating a balance between innovation, inclusivity, and ethical governance; all of these things will likely shape the commercial future of the government industry sector.

Real Estate
The commercial history of the Real Estate industry is rich and diverse, shaped by economic trends, societal needs, and technological advancements. Let’s look at the overview:
Real estate transactions have ancient roots, dating back to property ownership and land tenure systems in civilizations like ancient Egypt, and Rome.
Feudal societies established landownership structures that laid the groundwork for property ownership and real estate transactions. As defined by scholars in the 17th century, the medieval “feudal system” was characterized by the absence of public authority and the exercise by local lords of administrative and judicial functions formerly (and later) performed by centralized governments; general disorder and endemic conflict; bonds between lords and free dependents (vassals), which were forged by the lords’ bestowal of property called “fiefs” and by their reception of homage from the vassals. (Google definition)
Due to growth and urbanization; the rise of industrialization led to urbanization, creating a demand for housing and commercial spaces, fueling the development of cities and infrastructure.
Governments introduced regulations to standardize real estate transactions, protect property rights, and ensure fair practices, leading to the formalization of the industry. The introduction of MLS systems streamlined property listings, enhancing market transparency and accessibility.
The rise of the Investment and Modernization: Real estate became an increasingly popular investment vehicle, leading to the development of investment trusts, REITs, and other financial instruments. The modernization of real estate includes technology, including GIS, online listings, and digital platforms, transformed how properties are marketed, bought, sold, and managed.
The real estate markets experienced cycles of booms and recessions due to factors like economic downturns, bubbles, and the 2007-2008 mortgage crises. This crisis attributes to the issue of affordable housing. Although data suggest that challenges in housing affordability arose in various regions due to rising prices, supply shortages, and income disparities.
Real estate markets became more interconnected globally, attracting international investors and fostering cross-border transactions. The commercialization of residential properties for rental income and short-term rental models (e.g., Airbnb, VRBO etc.) became prominent.
The commercial history of the real estate industry illustrates its evolution from ancient land ownership systems to a modern, tech-driven sector. Challenges like market fluctuations, affordability issues, and the need for sustainability are expected to shape its future trajectory.
The current commercial position of the Real Estate industry is impacted by various factors and trends, showcasing an array of opportunities, challenges, and ever-changing transformation. Let’s take a look at some of these ideas and phenomenon:
The current market presents high demand and supply constraints. Many regions experience robust demand for both residential and commercial properties, driven by factors like population growth, urbanization, low mortgage rates, and a desire for homeownership. Many regions experience high demand for both residential and commercial properties, driven by factors like population growth, urbanization, low mortgage rates, and a desire for homeownership.
Real estate shows increasing amounts of advanced technology. The industry increasingly integrates technology such as AI, data analytics, virtual tours, and digital platforms to streamline processes, enhance marketing, and facilitate transactions. There are other property technology advancements. This allows for a more streamline process for the property management field.
This industry sector continues to attract investors seeking diversification, stable returns, and alternative assets, including institutional investors and individuals. Additionally, there’s a shift in investment preferences towards sustainable and environmentally conscious properties, driven by ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) considerations.
There is also a change in consumer preferences. The rise of remote work has influenced homebuyers’ preferences, leading to increased interest in suburban and rural areas, larger living spaces, and properties with home office setups. The public shows a growing inclination towards eco-friendly, energy-efficient homes and properties that promote wellness and quality of life.
Of course the current real estate trends has its challenges including Affordability Concerns and the supply chain disruptions. Rising prices, particularly in housing markets, pose challenges to affordability, impacting first-time buyers and lower-income households. Supply chain disruptions and construction material shortages have affected new construction projects, delaying completions and adding to costs.
The industry is adapting to the normalcy of the post pandemic, including hybrid work arrangements, flexible living spaces, and increased emphasis on health and safety measures.
The real estate industry’s current position reflects a blend of market resilience, technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and ongoing challenges related to affordability, supply constraints, and regulatory changes. Strategies that embrace innovation, sustainability, and adaptation to evolving consumer needs are likely to shape its trajectory.
The future outlook for the Real Estate industry appears to be evolving, driven by various trends and shifts in consumer behavior, technology, sustainability, and economic factors. Here are potential trajectories:
Further integration of technology in real estate processes, including AI-driven analytics, virtual reality property tours, block chain-based transactions, and IoT-enabled smart buildings. Greater reliance on data analytics for market insights, property valuation, and predictive modeling to make informed investment and development decisions.
There will be a change in the market dynamics: There is continued interest in suburban and rural areas due to remote work flexibility, while urban markets might adapt with mixed-use developments catering to live-work-play needs. There is also a transformation to unused commercial spaces into mixed-use developments, residential units, or flexible office spaces to meet changing demands.
There is a growing demand for sustainable buildings and eco-friendly developments, with a focus on energy efficiency, renewable resources, and green certifications like LEED or BREEAM. These sustainability and Green initiatives will continue to be on the rise. Customers continue to change in their demands and perspectives; there is more demand for properties designed to promote wellness, featuring amenities focused on health, fitness, and mental well-being.
Professionals continue to see emphasis on health-conscious design elements and safety measures within buildings and communal spaces.
The commercial future outlook for the real estate industry reflects a landscape shaped by technological innovations, sustainability imperatives, changing consumer behaviors, and economic shifts. Embracing innovation, sustainability, and flexibility in design and investment strategies may be crucial for navigating the evolving real estate landscape.

Education
The commercial history of the Education industry has undergone significant transformations over time, influenced by the needs of society, technological advancements, and changing approaches to learning. Let’s explore some key points:
Let’s start with the Early Education Systems
Early civilizations had systems for transmitting knowledge, often through oral traditions, apprenticeships, and religious institutions. Then there is the rise of formal education. Education was primarily accessible to the elite and focused on religious teachings in monasteries and cathedral schools. Universities evolved in Europe during the middle Ages, becoming centers for higher learning, fostering academic disciplines, and professional education.
Public Education Systems: The Industrial Revolution of Public Education Systems led to the development of compulsory education systems, aiming to provide basic education to a broader population. Standardized Curriculum is also apparent where education became more standardized with set curricula, grade levels, and teacher training programs.
Later in the 20th century, we see some modernization with the introduction of technology, like audio-visual aids and later computers, began to influence classroom teaching methods. There was also a significant increase in access to higher education, with the establishment of universities and colleges. There is the integration of digital technology into education, leading to e-learning, online courses, and virtual classrooms. The emergence of private schools, charter schools, and for-profit educational institutions introduced different models and options for education was part of was part of modernization and commercialization.
There was then the evolution to Skill-based Education and Innovation. There’s a shift towards skills-based education, emphasizing practical skills, vocational training, and preparing students for the workforce. Innovations such as adaptive learning, personalized education, and gamification aim to improve engagement and learning outcomes became part of innovation teaching.
The commercial history of the education industry reflects an evolution from traditional, localized systems to modern, technology-integrated, and diverse educational approaches. The industry has experienced a shift towards innovation, globalization, and a focus on skills, but challenges remain in achieving equitable and affordable education for all.
Currently, professionals see the position of the Education industry undergoing significant shifts and adaptations driven by technological advancements, learning preferences, and the ever changing market demands.
There is an increase in the use of the following technological platforms such as of e-learning, online courses, and digital sources for remote and flexible learning experiences. In addition, integration of educational technology (EducationTech) tools such as AI, virtual reality, and interactive learning platforms to enhance engagement and personalized learning.
As mentioned in the history of education, from my personal educational experience I participated in distance learning. This model entailed the combination of traditional classroom teaching with online components, offering a more flexible and dynamic educational experience. This is especially beneficial for “adult and/or non-traditional learners.”
Some market and industry changes include the expansion of private schools, online academies, and alternative education models offering specialized curricula or niche programs. Corporate and Workforce Training include programs, certifications, and skill development courses to meet evolving job market requirements which had increasingly gained more popularity and acceptance in the education sector. Apparent focus on Practical Skills and Continuing Education is common. There is a growing demand for lifelong learning and continuous professional development to adapt to evolving industries and job roles.
Next, let’s discuss the global implications in the education sector. There is a rise in international student mobility, with more students seeking educational opportunities abroad, contributing to the global education market. During my college years, I was astonished by the number of international students I encountered on the campus here in the United States. Remote Learning has also picked up momentum and improved access to education for remote or underserved populations through online courses and distance learning programs.
The current commercial education industry sector will continue addressing challenges related to accessibility, affordability, and adapting to evolving learning paradigms will likely remain key focal points in the industry’s evolution .
The future outlook for the Education industry presents concepts shaped by technological advancements, evolving learning paradigms, and a focus on innovation.
The following are the potential Segway’s
Here is a look at the Technological implications. There will be continued integration of AI, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and adaptive learning technologies for personalized and immersive learning experiences. Also, more Investment in robust digital infrastructure to support remote and hybrid learning models, ensuring accessibility and connectivity.
Hybrid learning models will become the norm. Hybrid learning approaches becoming more prevalent, blending online and in-person instruction for flexibility and varied learning experiences. There will be a rise of on-demand and micro learning platforms offering bite-sized, easily accessible courses catering to specific skills or immediate learning needs.
Skills-based and lifelong learning will also increase in visibility. Education is pivoting towards developing future-proof skills like critical thinking, creativity, adaptability, and digital literacy and there is growing emphasis on continuous education and upskilling throughout one’s career to meet the demands of evolving industries.
There will also be movement towards Personalized Education with adaptive learning systems tailoring educational content and pacing to individual student needs and learning styles. In addition, an increased use of data analytics to inform teaching strategies, student progress tracking, and personalized interventions.
With these futuristic models, comes a potential increase in the financial burden. This will lead one to collectively look towards new alternative financing models including the exploration of new financing models, scholarships, and income-sharing agreements to address affordability concerns and mitigate student debt burdens. Historically, government initiatives and policies will aimed at making education more affordable and accessible to all. Some initiatives with our current administration the push to eliminate student loan debt.
The future outlook for the education industry sector embraces innovation, global collaborations, promotes lifelong learning, and addresses accessibility and affordability challenges which are all crucial for shaping a progressive and inclusive educational landscape.

Logistics
The commercial history of the Logistics industry is driven by technological advancements, globalization, and changing trade dynamics and has evolved significantly over time.
The commercial history of the logistics industry has been characterized by remarkable technological advancements, globalization, and a growing demand for efficient supply chain solutions. The rise of e-commerce has been a significant driver, prompting the industry to adapt and innovate. Automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence have played crucial roles in optimizing logistics processes, leading to improved efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and route optimization have become standard practices, enabling companies to meet the increasing demands of consumers. The industry has also had to address challenges such as geopolitical tensions, environmental sustainability, and cybersecurity threats. Increasing globalization led to expanded trade volumes, requiring efficient logistics networks to support global supply chains and the adoption of standardized containers revolutionized shipping, reducing costs and streamlining international trade. Both of these concepts were part of Globalization and Trade Expansion.
Moving into the 20th century, there are technological advancements such as the integration of IT, leading to automation, GPS tracking, and real-time logistics management and the rise of e-commerce transformed logistics, demanding faster delivery, last-mile innovations, and sophisticated order fulfillment systems.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) became part of Specialization and Service Expansion. These providers offered comprehensive logistics services, including warehousing, transportation, and supply chain management. Of course with these rapid changes come its own set of challenges and adaptations; the major one being supply chain disruptions. Instances of supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, and global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
The commercial history of the logistics industry illustrates a progression from ancient trade routes to modern, technologically-driven supply chains. Adaptation to technological innovations, globalization, sustainability, and evolving market demands remains central to the industry’s continued evolution.
The current commercial position of the Logistics industry reflects a landscape shaped by several key trends and transformations, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and changing consumer expectations.
As with all industry sectors; there are technological integrations. Increased adoption of digital platforms, automation, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics for streamlined operations and data-driven decision-making. Supply Chain Visibility drives enhanced visibility across supply chains, leveraging real-time tracking, block chain for transparency, and predictive analytics for demand forecasting.
There is a surge in online shopping leading to increased demand for efficient last-mile delivery, warehouse optimization, and agile logistics networks. Omni channel Logistics is also significant with the integration of online and offline retail channels, necessitating flexible logistics to meet varying customer preferences.
As a result of the various global tragedies, there is a need for Supply Chain Resilience including a heightened focus on building resilient supply chains capable of adapting to disruptions, including diversifying suppliers, nearshoring, and contingency planning.
Professionals experienced reshaping logistics operations to accommodate changes in consumer behavior, supply chain disruptions, and remote working conditions post-pandemic. In my personal experience, Health and Safety Protocols have become a major adjustment with the implementation of stringent health and safety protocols within logistics facilities and during transportation to ensure worker well-being.
The current commercial position of the logistics industry showcases a landscape characterized by technological innovation, sustainability imperatives, supply chain resilience, and adaptation to evolving market dynamics. Strategies focusing on digital transformation, sustainability, resilience, and collaboration are key to navigating the industry’s current challenges and opportunities.
Here’s a glimpse of potential trajectories. The future outlook for the Logistics industry presents a landscape poised for continuous transformation and adaptation driven by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and evolving market demands.
Starting with the technology integration, there will be further automation; including an increased adoption of AI, machine learning, and robotics for warehouse automation, predictive analytics, and process optimization across logistics operations. In addition, interconnected logistics networks, expanded use of IoT devices for real-time tracking and supply chain visibility.
There will be a greater reliance on big data analytics for demand forecasting, route optimization, inventory management, and predictive maintenance and leveraging predictive modeling and AI algorithms for proactive decision-making and risk mitigation within supply chains.
Sustainable practices will include Green Initiatives and Circular Supply Chains. There will be an accelerated focus on sustainability, integrating renewable energy sources, eco-friendly packaging, and carbon-neutral transportation solutions.
Last-Mile Innovations will drive business to the smaller companies and allow for growth. This includes Continuous innovation in last-mile delivery solutions, including drone delivery, autonomous vehicles, and micro-fulfillment centers to optimize urban logistics.
The other focus is Customer-Centric Solutions; which is customized delivery options and enhanced customer experiences through personalized last-mile logistics.
Further adaptations and refinements in logistics operations to accommodate post-pandemic market changes, health protocols, and remote working norms. We will also see continued focus on health and safety measures for workers, customers, and supply chain participants.
The future outlook for the logistics industry embraces innovation, sustainability, collaboration, and talent development will be pivotal for navigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities in the evolving logistics sector.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Columbus, OH United States
History
Over the past decade, Columbus, Ohio, has experienced significant growth and development from a commercial perspective. Focusing on 8 key aspects of its commercial landscape including: Tech, Retail and Hospitality, Financial Services, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Logistics, Real Estate Development and Education and Research.
Columbus has emerged as a thriving tech hub, with a burgeoning startup scene and the presence of major tech companies like CoverMyMeds, Root Insurance, and Beam Dental. The city’s supportive ecosystem for entrepreneurs and tech talent has contributed to its reputation as a hub for innovation.
The city’s retail and hospitality sectors have seen steady growth, fueled by a strong local economy and a growing population. The Short North Arts District and Easton Town Center are popular destinations for shopping and dining, attracting both locals and visitors.
Columbus is home to several major financial services companies, including Huntington Bancshares and Nationwide Insurance. The city’s status as a regional financial center has contributed to its economic stability and growth.
With renowned institutions like The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus has a thriving healthcare sector. The city is also home to numerous healthcare startups and research organizations, driving innovation in the field.
Overall, Columbus, Ohio, has a dynamic commercial history marked by transitions from agriculture and manufacturing to a more diversified economy encompassing technology, education, healthcare, and finance. Its evolution reflects a resilient and adaptable economic landscape that continues to embrace innovation and growth.
While manufacturing has declined in some parts of the Midwest, Columbus has maintained a strong manufacturing base. The city’s central location and access to transportation networks make it an attractive location for manufacturers.
Columbus is known as a major logistics and distribution hub, thanks in part to its central location within the United States and the presence of companies like FedEx, UPS, and DHL. The city’s logistics infrastructure, including the Rickenbacker International Airport and the Norfolk Southern Railway, supports the movement of goods and materials.
Commercial real estate development has been robust in Columbus, with new office buildings, mixed-use developments, and residential projects transforming the city’s skyline. The Arena District and Downtown Columbus have seen particularly significant development activity.
Columbus is home to The Ohio State University, one of the largest universities in the United States. The university’s research initiatives and partnerships with industry have contributed to innovation and economic growth in the region.
Current Position
The city continues to hold a strong commercial position, marked by its diversified economy and sustained growth across various sectors. The city has maintained its status as a vibrant economic center with a thriving business landscape.
Over the years, major developers have come and gone leaving their mark in the city’s suburbs and most recently in the downtown corridors. Columbus has gained recognition for its emphasis on sustainability and smart city initiatives, including efforts to improve transportation, infrastructure, and access to technology, contributing to its appeal for businesses and residents alike.
The city also serves as a hub for several Fortune 500 companies and houses numerous headquarters and regional offices, contributing to its economic stability and job market.
It seems to be one of the fastest growing areas for the emerging professional as we see the modernization of commercial real estate developments around the city. These concepts have taken on a persona of their own and have gained popularity over the years. However, the landscape is subject to change, influenced by various economic factors and global events. The ongoing adaptation to emerging technologies, economic policies, and market trends will continue to shape Columbus’s commercial position.
Future Outlook
The commercial future outlook for Columbus, Ohio, appears promising and positioned for continued growth and innovation across various sectors.
The city’s emphasis on innovation, especially in technology, healthcare, finance, and logistics, positions it as a hub for startups, entrepreneurs, and established companies seeking an environment conducive to innovation and growth. This diversification is expected to continue, attracting talent and investment across multiple industries.
There has been an influx of major companies relocating to the area such as Amazon, Google, Intel, Wells Fargo and Honda.
There are 4 major influences that will drive the city’s commercial success in the future:
Technology and Innovation, Healthcare and Research, Logistics and Transportation and Business Adaptability
In essence, Columbus commercial landscape appears bright, driven by its diverse economy, emphasis on innovation and technology, strong healthcare and logistics sectors, and a business-friendly environment. The city’s commitment to fostering innovation and addressing challenges will likely contribute to its continued economic expansion and status as a dynamic and competitive business hub in the Midwest.

Chicago, IL United States
History
Chicago’s commercial has a history that has shaped its identity as a dynamic economic powerhouse in the United States. The city’s commercial evolution is marked by several key milestones and industries that have contributed significantly to its growth and prominence.
When one think of Chicago, you may immediately think of Sears Tower and the Magnificent Mile. These are the most historical places in the city that draw a crowd. Chicago has also been a center for innovation and architectural prowess. The city’s skyline stands as a testament to architectural innovation, with the development of skyscrapers and the birth of modern architecture. Innovators like Frank Lloyd Wright and the Chicago School of Architecture left an indelible mark, shaping the city’s urban landscape and setting new standards in architectural design.
There is an array of transportation options getting in and around in the Midwest region of the United States. Chicago’s commercial roots trace back to its strategic location along Lake Michigan and at the nexus of major transportation routes, including railways and waterways. Chicago was a dynamic commercial center with diverse industries driving its economy. The city’s commercial perspective was characterized Financial Hubs and corporate headquarters, Transportation, Tech and Innovation and Tourism.
Current Position
Chicago continues to be a major economic hub in the United States. The city’s ability to diversify its economic base has contributed to its resilience and adaptability in the face of changing market dynamics including finance, technology, healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, professional services, and education.
However, as with most large metropolitan areas, they face their own set of challenges. Mostly including infrastructure maintenance, fiscal concerns, and addressing socioeconomic disparities. The city’s ability to address these challenges while leveraging opportunities in emerging industries, nurturing innovation, and attracting investment will shape its future commercial position. You see these issues being portrayed on the local news stations almost daily and has been ongoing.
Overall, Chicago maintains a strong commercial footing, characterized by a diverse economy, thriving industries, technological innovation, and cultural vibrancy. Its strategic strengths across various sectors position the city as a dynamic and competitive global player in the commercial landscape.
Future Outlook
Chicago will continue to face challenges related to urban development, affordability, socioeconomic disparities, and addressing infrastructure needs. Due to the growth of the city, all of these issues won’t be addressed at once. Efforts to develop smart city initiatives, upgrade transportation infrastructure, and invest in technology and education will strengthen the city’s competitiveness on a global scale.
The local government has initiatives in place and there will be continuous efforts, however, these challenges present opportunities for investment, public-private partnerships, and sustainable growth strategies to create a more inclusive and resilient economic landscape.
Strength will continue to lie with the city’s financial and professional services hub. The city’s expertise in finance, accounting, legal services, and consulting is likely to expand, driven by its diverse talent pool and established industry presence.

Washington, DC United States
History
Washington, D.C.’s commercial history is mostly known for its role as the political and administrative capital of the United States. Although when you think of DC, you think the “white house”, the city has also seen significant commercial development and transformation over the years.
Washington DC is the capital of the United States; its initial economy revolved around government institutions, including Congress, the presidency, and the judiciary. The city’s strategic location along the Potomac River and its proximity to major ports facilitated trade and commerce in its early years.
The city saw growth over the years in education, healthcare, hospitality and technology. The expansion of universities, research institutions, and healthcare facilities contributed to this diversification. Known for the infamous Georgetown University, historical schools such as Howard University. Those along drew an influx of students from all over the world for their studies.
In short, D.C.’s commercial history is characterized by its evolution from a government-centric economy to a more diversified and dynamic economic landscape. Its role as a political center, combined with growth in industries beyond government, tourism, real estate, and social institutions, has shaped the city’s commercial identity and continues to influence economically.
Current Position
D.C. maintains a diverse and resilient commercial position, influenced by its status as the political epicenter of the United States and its evolving economy beyond government-related activities.
Currently known for its tourism displaying all of the monuments in one central location, one can spend a vast majority of time in the city exploring museums, cultural institutions, and events attract millions of visitors annually, supporting the tourism and hospitality sectors, including hotels, restaurants, entertainment venues, and tour operators.
Washington, D.C. remains heavily tied to the federal government, hosting numerous government agencies, offices, contractors, and lobbying firms. The presence of these entities contributes significantly to the city’s economy, providing employment and driving demand for professional services, legal expertise, and consulting.
The city has experienced urban renewal and revitalization in various neighborhoods, attracting commercial and residential investments, new office spaces, retail developments, and mixed-use properties. Overall, Washington, D.C.’s commercial position is characterized by its resilience, diversification efforts, and economic opportunities beyond its governmental functions. The city continues to leverage its strengths while addressing challenges to maintain its status as a dynamic economic center in the United States.
Future Outlook
The future of DC is driven by diverse sectors and ongoing efforts to bolster economic growth and innovation.
The city’s future commercial landscape is expected to continue diversifying beyond its historical reliance on government-related activities. Industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, education, hospitality, and real estate are likely to see further expansion. Efforts to foster innovation and entrepreneurship, particularly in the technology sector, are anticipated to drive job creation and economic growth.
There are initiatives to support entrepreneurship and small businesses which we can suspect will continue, with initiatives aimed at fostering a conducive environment for startups. Incubators, accelerators, and funding opportunities are likely to contribute to a vibrant ecosystem for innovative ventures.
Washington, D.C. faces challenges related to affordable housing, socioeconomic disparities, and infrastructure needs. The city’s future appears to be promising even with the challenges they face, in fact most major metropolitan cities also face similar issues yet it does not affect their success and growth.
Overall, D.C.’s commitment to embracing change, fostering innovation, and addressing challenges positions it for continued economic growth and a dynamic commercial landscape.
London, United Kingdom
History
London, United Kingdom, was a global commercial powerhouse with a diverse and dynamic economy. The city maintained its status as a leading financial center, home to major banks, investment firms, and the London Stock Exchange. The Canary Wharf and the City of London were key financial districts driving the city’s economic activity. London’s commercial landscape also encompassed a thriving technology sector, with startups and established tech companies flourishing in areas like Shoreditch and Silicon Roundabout. Additionally, the city boasted a vibrant retail sector, with renowned shopping destinations such as Oxford Street and Covent Garden attracting millions of visitors annually. London’s position as a cultural and tourism hub further bolstered its commercial perspective, with iconic landmarks like the Tower of London and Buckingham Palace contributing to the city’s allure. Overall, London’s commercial perspective ten years ago depicted a cosmopolitan metropolis with a robust economy, diverse industries, and a global reputation for innovation and commerce.
Research has shown the following.
Throughout its history, London’s commercial landscape has evolved, adapting to changes in global economics, technology, and societal shifts. Its resilience and ability to reinvent itself have played a significant role in maintaining its position as a leading global economic hub.
The following is the perception of this location and its rich history:
London is mostly shaped by their various economic factors. London has long been a global financial center. The City of London, with its historic financial district, is home to the London Stock Exchange, banks, insurance companies, and investment firms. The city’s financial prowess dates back centuries, establishing itself as a key player in international finance. Historically, London’s strategic location on the Thames River made it a significant trading port. Its role in global trade expanded during the British Empire, facilitating the exchange of goods and capital across the world.
Over time, London’s economy shifted from manufacturing to a service-based economy. It became a hub for professional services such as law, accounting, consulting, and creative industries including advertising, media, and fashion. In recent decades, London has emerged as a major technology and innovation hub in Europe. The city attracts startups, tech companies, and entrepreneurs, contributing to its reputation as a leading global tech ecosystem. London’s cultural heritage, landmarks (such as the Tower of London, Buckingham Palace, and the British Museum), theaters, and events have made it a prime tourist destination, fostering a thriving hospitality industry.
Current Position
London’s commercial position remains dynamic, leveraging its strengths in finance, technology, services, and culture. Despite challenges, the city’s ability to innovate, attract global talent, and adapt to changing economic landscapes positions it as a resilient and competitive global city. London faces challenges such as housing affordability, Brexit-related uncertainties, and occasional economic volatility, which have impacted certain sectors and business confidence.
Per popular opinion, London, United Kingdom, holds a strong and multifaceted commercial position despite challenges and fluctuations. The city has been rapidly expanding its technology sector, becoming a prominent hub for startups, tech companies, and innovation. Tech clusters, such as Tech City in East London, have attracted talent and investment, positioning London as a European tech leader.
London’s status as a hub for professional services including legal, accounting, consulting, and creative industries continues to thrive, serving as a home to a vast range of businesses in these sectors. London is a global financial center. The City of London continues to host the London Stock Exchange, numerous banking institutions, insurance companies, and financial services firms, contributing significantly to the UK’s economy. Though it faced fluctuations, the real estate market has been resilient.
It is a top tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors annually to its historic landmarks, museums, theaters, and events. The tourism and hospitality sectors have historically played a vital role in the city’s economy. As with most major metropolitan areas, The COVID-19 pandemic significantly affected various industries, including tourism, hospitality, and retail, leading to disruptions and adaptations in business operations.
Future Outlook
London’s future commercial outlook will likely be shaped by its ability to navigate uncertainties, adapt to changing global landscapes, and leverage its strengths in finance, technology, innovation, and culture. Adaptable policies, investment in emerging sectors, and fostering a conducive business environment will be crucial for sustaining its position as a global economic powerhouse.
The city’s established professional services sector is likely to adapt to changing market dynamics, leveraging London’s position as a global hub for legal, consulting, and creative industries. London’s supportive environment for startups and entrepreneurial ventures is expected to flourish. Incubators, accelerators, and investment opportunities will continue fostering innovation. This is the major draw for me and why this location is of interest to me.
London is expected to maintain its status as a global financial hub, although there might be shifts due to Brexit-related changes. Fintech innovation is likely to continue, contributing to the city’s financial services sector. The city’s tech ecosystem is poised for growth, attracting investment and talent. London’s focus on emerging technologies like AI, biotech, and cybersecurity positions it as a key player in the global tech landscape.
There’s a growing focus on sustainability and green initiatives, with London aiming to become a more environmentally conscious city, potentially driving investments and innovation in sustainable industries. The real estate market may face adjustments due to economic fluctuations and changing demand, but London’s ongoing infrastructure developments are anticipated to support commercial growth.
London’s future commercial outlook remains promising despite ongoing uncertainties. London’s rich cultural heritage will remain a driving force behind its creative industries. Fashion, design, media, and entertainment sectors are expected to continue thriving.
Houston, TX United States
History
Houston’s commercial history reflects resilience and adaptability, navigating through fluctuations in the energy sector, embracing diversification, and leveraging its strengths in multiple industries to maintain economic growth and prosperity.
Personal knowledge about the city’s commercial history is limited, however research has unveiled an abundance of vital information. Their industry centers on gas/oil and medicine but their strengths have evolved over time.
Historically, the city maintained its position as a global energy capital, home to numerous oil and gas companies, including industry giants like ExxonMobil and Chevron. Houston’s port, one of the largest in the United States, facilitated international trade and supported a bustling logistics and distribution sector. Additionally, the city’s renowned Texas Medical Center, the largest medical complex in the world, underscored its significance in healthcare and biomedical research. Houston’s diverse economy also encompassed aerospace, manufacturing, and technology sectors, with companies like NASA’s Johnson Space Center and Hewlett Packard Enterprise contributing to innovation and job growth. The city’s strategic location, business-friendly environment, and strong infrastructure further solidified its commercial perspective, making it a magnet for businesses and investors alike. Overall, Houston’s commercial landscape a decade ago portrayed a dynamic and prosperous city with a diverse array of industries driving its economic vitality.
The city has a significant healthcare industry, hosting the Texas Medical Center, the largest medical complex globally. Renowned hospitals, research institutions, and biotechnology firms contribute to Houston’s status as a healthcare hub.
Over time, Houston has diversified its economy beyond energy and aerospace. It boasts a thriving manufacturing sector, technology startups, engineering firms, and a growing presence in renewable energy. Houston houses several prestigious universities and educational institutions, contributing to research, innovation, and talent development in various fields.
The cultural diversity and vibrant arts scene contribute to its commercial appeal. The city hosts various cultural events, museums, theaters, and festivals, attracting tourism and bolstering the entertainment industry. Houston, Texas, has a diverse and robust commercial history shaped by various industries and factors.
Current Position
Houston’s current commercial position showcases a diversified economy with strengths in energy, healthcare, trade, and emerging sectors. However, challenges such as energy market volatility and the need for continued economic diversification remain focal points for the city’s growth and resilience.
The city remains a global leader in the energy industry, particularly in oil, natural gas, and petrochemicals. Their economy is deeply connected to energy markets, but it faces fluctuations due to oil price volatility and global energy transitions towards renewable sources.
Houston has actively diversified its economy beyond energy. The city has seen growth in sectors like aerospace, technology, manufacturing, and renewable energy, aiming to reduce reliance on oil-related industries.
The healthcare sector, anchored by the Texas Medical Center, continues to thrive. Houston’s concentration of medical facilities, research institutions, and biotech companies contributes significantly to the city’s economy. Houston faces challenges related to energy market fluctuations, occasional impacts from natural disasters like hurricanes, and broader economic uncertainties. These factors can influence the city’s economic stability and growth. However, the entrepreneurial ecosystem and innovation initiatives have shown promise, fostering startups, tech companies, and research collaborations.
The city’s diverse culture, culinary scene, arts, and entertainment continue to attract tourists, contributing to the hospitality and leisure industries and the real estate market has seen fluctuations in recent years due to factors like oil price fluctuations, economic cycles, and weather-related events such as hurricanes.
However, the city’s ongoing development projects and commercial construction contribute to its economic vitality. Houston is upcoming and coming and has gained popularity among the urban professional. There is a lot of movement into the city and it seems to offer opportunities in spite of ongoing challenges.
Future Outlook
Houston has historically been a major hub for the energy industry, particularly oil and gas. The future outlook for the city’s commercial sector may be influenced by global energy trends, oil prices, and the ongoing transition to renewable energy sources. Diversification efforts within the energy sector and investment in clean energy technologies could shape Houston’s commercial landscape.
Efforts to diversify the Houston economy beyond energy are ongoing. The technology sector is growing in Houston, with a focus on innovation and entrepreneurship. Factors such as international trade, geopolitical events, and the overall health of the global economy can influence the city’s commercial future. Adaptable businesses that consider global market dynamics may be better positioned for success.
The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic will likely influence the commercial future of Houston. Businesses that adapt to new ways of working, prioritize employee well-being, and embrace digital transformation may be better positioned for resilience and growth.
Collaborations between the business community and educational institutions to nurture talent and promote relevant skills development will contribute to a vibrant commercial future for Houston.
Program Benefits
Human Resources
- Employee Performance
- Enhanced Collaboration
- Reduced Costs
- Staff Engagement
- Improved Compliance
- Streamlined Communication
- Increased Retention
- Enhanced Care
- Continuous Improvement
- Better Recruitment
Marketing
- Patient Education
- Data Collection
- Attracting Talent
- Change Management
- Internal Support
- Patient Awareness
- Improved Reputation
- Increased Satisfaction
- Client Feedback
- Increased Awareness
Customer Service
- Patient Retention
- Improved Morale
- Enhanced Experience
- Patient Empowerment
- Better Communication
- Positive Reputation
- Reduced Complaints
- Operation Improvement
- Higher Efficiency
- Crisis Management
Testimonials

For the Love of You Counseling Agency, Chicago IL
“Working with Ms. Butler has been an absolute game-changer for our counseling agency. Their expertise in regulatory compliance and credentialing processes was instrumental in guiding us through a complex landscape with clarity and precision.
Ms. Butler approached our agency’s needs with a deep understanding of the industry’s intricate regulatory frameworks. Their meticulous attention to detail and comprehensive knowledge empowered us to establish robust compliance measures and attain the necessary credentials seamlessly.
Their guidance not only ensured that we met all regulatory requirements but also elevated our standards, positioning our agency for success in a highly regulated field. Their dedication, expertise, and unwavering support were integral to our agency’s growth and credibility.”

Change Reaction LLC, Hyattsville MD
“Working with Ms. Butler and her team has been an invaluable experience for our mental health agency startup. Their expertise and guidance in establishing our agency policies were instrumental in laying the foundation for our operations. Their dedication to understanding our unique needs and translating them into comprehensive policies showcased their professionalism and commitment to excellence. Thanks to their meticulous approach and insightful recommendations, we now have a robust framework that aligns seamlessly with industry standards while catering to our specific objectives. Ms. Butler and her team not only provided us with expert guidance but also became a trusted partner in our journey towards building a responsible and impactful mental health agency.”

S.A.W Transportation, Columbus OH
“Working alongside Ms. Butler was a game-changer for our transportation company. Their expertise in navigating and recovering funds from old, unpaid claims was exceptional. Their meticulous approach and tenacity in reviewing our past records and identifying overlooked claims were instrumental in recuperating substantial funds that had previously slipped through the cracks. Ms. Butler not only demonstrated a deep understanding of the complexities within the transportation industry but also exhibited a level of dedication that went above and beyond our expectations. Thanks to their expertise and relentless efforts, we were able to recover significant resources that greatly impacted our company’s financial health. We highly recommend Monica and her team for their outstanding ability to uncover untapped revenue streams and their commitment to delivering exceptional results.”

Columbus City Schools, Valleyview Elementary School Columbus, OH
“Under the guidance and leadership of Ms. Butler and her team, our school community achieved an extraordinary milestone in our fundraising efforts. Their commitment and strategic planning spearheaded a highly successful fundraiser that surpassed all expectations. Through their tireless dedication and innovative approach, we not only raised a significant amount of funds for our building but also had the privilege of assisting numerous families within our school community.
Ms. Butler and her team brought unparalleled expertise and a genuine passion for our cause, inspiring and mobilizing our community to contribute generously. Their unwavering support and hands-on involvement ensured that every aspect of the fundraiser was meticulously executed, resulting in an impactful and transformative outcome.
Thanks to Ms. Butler’s leadership and guidance, our school stands stronger today, equipped with the resources needed to enhance our facilities and, more importantly, extend support to families in need. We are immensely grateful for their invaluable contribution, dedication, and unwavering commitment to our school’s success.”

Ascend, Franklin TN
“Partnering with Ms. Butler for our two-year mental health assessment contract has been nothing short of exceptional. Their dedication, expertise, and unwavering commitment to excellence have been instrumental in achieving unparalleled success.
Throughout our collaboration, Ms. Butler and her team demonstrated an unmatched level of professionalism and proficiency in recruiting top-tier professionals. Their meticulous selection process ensured we had a team of highly skilled and compassionate individuals dedicated to our mental health assessment objectives.
The results speak for themselves—thanks to Ms. Butler’s efforts, we’ve achieved a remarkable level of success in our assessments, surpassing our initial expectations. Their ability to understand our needs, navigate challenges seamlessly, and deliver beyond our aspirations has been truly commendable.
We wholeheartedly recommend MRB Institute for their unwavering dedication, expertise, and instrumental role in our journey toward mental health assessment excellence. They have not just met but exceeded our highest standards.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.













