Business Performance Integrity
– Enabling you to deliver on your promise more often
The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Business Performance Integrity is provided by Mr. Danielsen Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.
Personal Profile
Mr. Danielsen is an accomplished professional with 30+ years of experience in various industries, including five years in civil works and 25 years in management consultancies, both external and internal.
He holds an Executive MBA from the Technical University of Copenhagen (DTU) and a B.Sc. in Civil and Structural Engineering from the Engineering College of Copenhagen.
After ending his 5-y chapter as a corporate QEHS Director in a Danish highway and railway construction company, Mr. Danielsen engaged in delivering management consultancy services within EHS and Lean Enterprise across several industrial sectors for the following nine years.
He wanted to get closer to one company. He spent the next eight years as a business transformation leader in a Danish Danaher medical device company (Radiometer Medical) before moving to Amsterdam and joining the Philips’ Group Business Transformation organization, heading and deploying the Continuous Improvement and Performance Management practices globally.
Mr. Danielsen recently concluded his career within large corporations and started his freelance consultancy, LeanDK.
Mr. Danielsen has industry experience within the following sectors: Consulting Services, Medical Devices, Pharmaceuticals, Construction, Industrial Products, and Energy.
Although his focus locations are now the Scandinavian capitals and Amsterdam, Mr. Danielsen has delivered consultancy services in the US, Latin America, Japan, China, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, Finland, Sweden, Germany, Switzerland, Poland, and Latvia since 1999. He traveled throughout India, Indonesia, Thailand, and Africa in the eighties and nineties.
His achievements include facilitating/driving the Strategy Deployment process for eight years, which resulted in a yearly 50% reduction of the external quality footprint and significantly contributed to the company’s growth of 8% YoY—double the speed of the market (Radiometer Medical, part of Danaher).
Global top-down and bottom-up capability building within continuous improvement and performance management resulted in a significant step up in the predictability of short- and long-term outcomes. The company share price grew from EUR 21 to EU 51 during his 6-year tenure (Royal Philips).
The service skills of Mr. Danielsen lie mainly within Operational Excellence and Business Transformation, comprising capability building in strategy deployment, mission control (by daily management and problem-solving), and servant leadership.
To request further information about Mr. Danielsen through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Business Performance Integrity
If you are a member of a group of managers or leaders who share an accountability structure and, therefore, own business problems arising from daily operations or the execution of strategic initiatives – and if you would like to improve your ability to solve current and future business problems, including the closing of gaps defined in corporate Strategy – in other words, if you would like to increase your ability to shape the future of your organization – then please continue reading.
Reflecting on your performance management
Do you always know whether you win or lose on any given day? Are you monitoring the appropriate metrics? Do you believe you are always prompt in addressing red metrics? Do you find yourself repeatedly confronting the same issues? What do you do when it’s difficult to escape the red? Does your current strategy execution approach consistently yield the intended results? Do you find it challenging to translate strategy into concrete actions? Can you always determine whether your strategy execution is on track?
If reflecting on the above questions makes you curious about how these challenges can be effectively addressed, you and your peers should consider enrolling in this 12-month learning journey.
The cornerstones of Business Performance Integrity
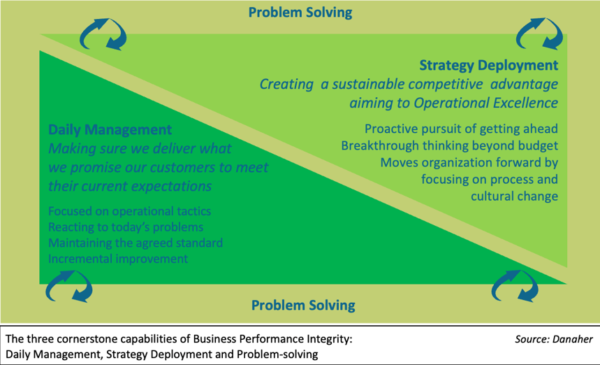
Three foundational processes are core to any organization’s Planning and Execution System: Daily Management (DM), Problem-solving (PS), and Strategy Deployment (SD). They serve as the foundation for all other development tools and apply to every aspect of your business. The three processes operate as a system capable of enhancing Business Performance Integrity.
Strategy Deployment transforms Strategy into sustainable processes that yield breakthrough results. Daily Management is a method of disciplined routine that ensures our operations consistently meet our customer (internal or external) requirements by measuring the most critical process metrics and regularly reviewing them as a team to drive timely action.
Lastly, problem-solving is our means of structured course correction. It is the thought process used to define problems, investigate and isolate the fundamental causes, verify and implement countermeasures, and ensure long-term sustainability.
Focus, speed, and agility
As we move beyond the years of pandemics and need a solid response to megatrends such as Digitalization & Automation, AI & Machine Learning, Transformation, and the multiple ESG Megatrends, the ability as an organization to chart your course and effectively shepherd your people on the journey with focus, speed, and agility becomes increasingly critical. The companies that truly master the cornerstone capabilities of Business Performance Integrity have a better chance of maneuvering through these challenges and harvesting the opportunities within. Let’s have a look at one of the most successful ones.

Case Study: The Danaher case
Danaher (NYSE: DHR) is a Washington DC-based Fortune 500 science and technology conglomerate. Danaher was established in 1984 with the ownership of a handful of manufacturing companies, and it was one of the first companies in North America to adopt Kaizen, the Japanese business philosophy of continuous improvement.
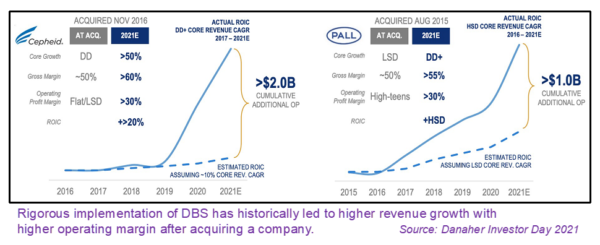
Inspired by Toyota’s success with the Toyota Production System, they developed the Danaher Business System (DBS), which was implemented in all new acquisitions, leading to massive growth, inorganic and organic. The numbers speak for themselves. They have acquired hundreds of companies over the past three decades (e.g., more than 50 between 2001 and 2006) and delivered a compound annual growth rate of 20% over almost four decades. The stock value has increased by a factor of 800 since 1987.
Starting mainly as a system to drive Lean Manufacturing, DBS quickly added capability building for all kinds of business challenges in all functions, including Growth and Leadership. A lean mindset focused on building an organization of problem-solvers at all levels of the organization has always been at the core of DBS, and it is a critical priority that all managers drive Daily Management with their team at a regular cadence.
Larry Culp was CEO of Danaher from 2001 to 2014 and is now (since 2018) the CEO of General Electric (NYSE: GE). A Wall Street analyst once asked Larry: ‘What is Danaher?’, he answered: ‘It is DBS!’. To the question: ‘If you could have only one tool from DBS, which one would you choose?´, he answered: ‘No doubt Strategy Deployment.’
Danaher has indeed relied upon implementing and evolving the Danaher Business System to stay focused, fast, and agile in a fast-changing world, and Daily Management, Strategy Deployment, and Problem-solving are vital tenants of DBS.
Link to Video below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hjVJumUWEcU

Providing transparency and driving accountability
How do you always know whether you win or lose on any given day, and how can Daily Management (DM) facilitate timelier problem-solving, thus contributing to the integrity of business performance?
DM is a team effort. The team determines the organizational boundaries and scope of processes to be managed and defines the most meaningful critical metrics, delegating individual ownership for accountability. They agree on a regular cadence to come together as a team to review the metrics and act whenever they are off track. As these metrics are chosen by their criticality to critical stakeholders, actions to close the gaps and get back on track should be taken urgently.
Problem-solving is a step-by-step process
Problem-solving is the procedure and collaborative effort by which you close the gaps and regain the lead. Problem-solving is a sequential process that begins with identifying the problem and determining its contributing root causes. It ends with selecting countermeasures to address the root causes and close the gap between where you are now and where you want to be (= winning).
Problem-solving your way to the learning organization
Transformations have become an integral part of the daily agenda for employees in most organizations. Developing problem-solving skills is necessary for creating an agile learning organization that can adapt to all the transformations, inherent processes, and organizational changes that these transformations entail.
Problem-solving is a crucial aspect of creating a learning organization. The majority of business issues stem from how we operate our business processes, and by analyzing them, we can glean numerous lessons along the way.
The leaders of your organization bear the responsibility for the health and continuous improvement of these business processes; therefore, to best support, coach, and challenge your people performing root cause analysis, it is beneficial for you to gain hands-on experience with the core methods, particularly 5xWHY analysis *.
If someone claims that 5xWHY analysis is straightforward, they have likely never performed one. Although it is simple to convey, it requires considerable effort to master.
*5xWHY is a tool to get to the root cause of a problem by asking ‘WHY’ several times in a sequence
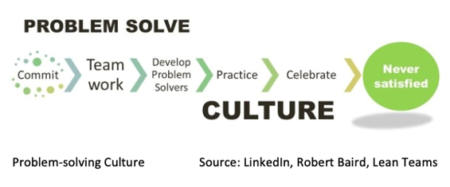
The leader’s role in driving a Problem-solving Culture
Building an organization of problem-solvers should be a top priority for upper management; therefore, understanding your position in creating a Problem-Solving Culture is a central goal of this program.
A crucial aspect is defining the problem at the appropriate organizational level and obtaining accountability through explicit problem ownership.
Growing your problem-solving culture presents a significant opportunity to accelerate your transformations, and there is much more to this than building capabilities in the above steps of your problem-solving process by appointing trainers and critical practitioners.
Unquestionably, it is also about promoting behaviors such as making problems visible, ensuring a no-blame environment and ‘can-do’ attitudes around problem-solving activities, and utilizing the Daily Management (tier) system to delegate firm problem ownership to the appropriate organizational level. Building an organization of problem-solving needs a top-down, bottom-up approach, and leaders have a crucial role.
Strategy Deployment is orchestrating the ‘do-differents’
Numerous notable individuals have remarked, “If you always do what you’ve always done, you’ll always get what you’ve always gotten.” Pursuing your strategy requires identifying the critical things you must do differently and orchestrating the transformation voyage to the new way of working that will produce the strategy’s desired outcomes. This is what Strategy Deployment (SD) refers to.
Most organizations can produce sensible strategy documents. Nonetheless, only a minority can achieve the defined outcomes through a structured, repetitive process that is efficient and effective at fulfilling the promise. One of the most significant pitfalls in strategy execution is attempting to do too many things and failing to prioritize the essential few that comprise a true breakthrough.
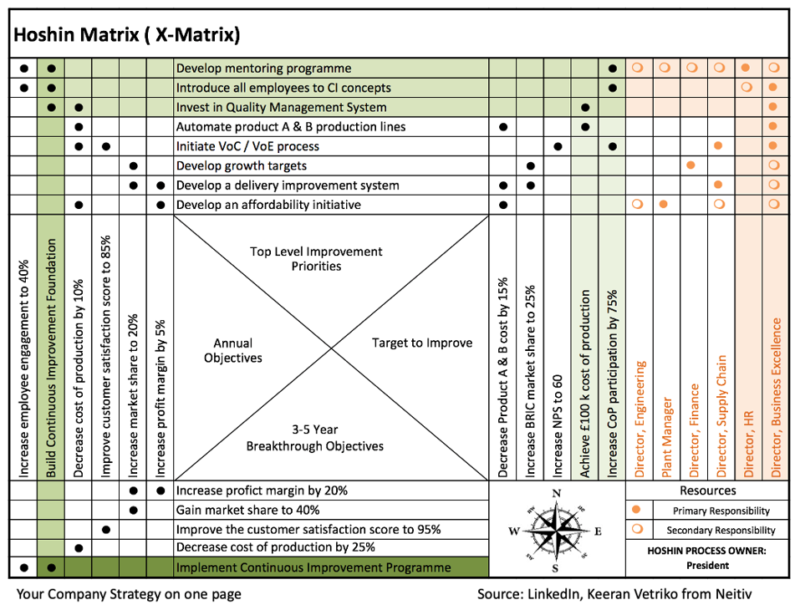
Your strategy orchestration on a one-pager
For most organizations, strategy takes the form of an extensive PowerPoint presentation or voluminous Word document. This format presents challenges in multiple contexts, such as how to communicate concisely and succinctly to an audience that has yet to participate in the creation of the deck, but most significantly, when it comes to deploying the strategy and bringing the strategic intent to life.
What if we could capture the essential breakthrough elements of the strategy on a single page that outlines the quantified long-term gaps we want to close and the first-year journey in terms of quantified objectives, prioritized processes, and capabilities we need to build or change, as well as the metrics to measure progress and the shared ownership of driving the transformation?
A common pitfall in this context is having excessive objectives and transformational change initiatives in your one-pager. Therefore, ‘less is more’ and prioritization are crucial.
The magic occurs when actions to implement the strategic initiatives are firmly anchored ‘where the rubber meets the turf’ – at the point of impact – with connected leading follow-up metrics.
Without reaching this point, the one-pager strategy is merely – a plan!
Successful companies pursuing operational excellence with a history of exceeding their strategic objectives use this approach to deploy their strategy. Danaher, mentioned above, is one of them.
Performance reviews can be Great!
Performance evaluations are excellent opportunities for leaders to coach their team members and for everyone to learn. The program will cover how effective and ineffective behaviors can impact the success of the reviews and share the characteristics of ‘Servant Leadership’ in establishing a problem-solving culture that will enable the learning organization to thrive.
When discussing performance evaluations, it is essential to distinguish between Daily Management meetings and Strategy Deployment progress reviews and hold these meetings at distinct times.
DM ensures that our day-to-day operations run as smoothly as possible by implementing timely course corrections, whereas SD safeguards traction on the strategic initiatives that will put us ahead of the competition.
Daily Management capabilities are crucial for SD review execution. In contrast to DM reviews, however, behaviors and expectations should be different due to the nature of the problems being discussed: bridging created strategic gaps and building new methods of working versus catching up or repairing foundations. Actions and agreement on needed problem-solving are outcomes of both meetings, but the dialogue at the individual forums should be distinct.
Wrapping up the program title
Finally, we should coin the program title term with a definition that can set the expectation for what capabilities this 12-month program can bring to you and your organization.
The pursuit of excellence in ‘Business Performance Integrity’ can be defined in three steps:
1) Having a plan to win (solid action plan with connected metrics and clear accountability)
2) Enabling transparency – are you winning or losing? (solid Daily Management practices)
3) Timely course correction (solid Problem-solving – fit for purpose)
Curriculum
Business Performance Integrity- Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Current State
- Part 1 Month 2 Daily Management (DM)
- Part 1 Month 3 Improving Your Daily Management
- Part 1 Month 4 The Problem-solving Process
- Part 1 Month 5 Identifying and breaking down your problems
- Part 1 Month 6 Getting to the root causes
- Part 1 Month 7 Building sustainable countermeasures
- Part 1 Month 8 Evolving Your Problem-solving Culture
- Part 1 Month 9 Strategy Deployment
- Part 1 Month 10 Getting your Strategy to One Deployable Page
- Part 1 Month 11 Deploying the Strategy into the Organization
- Part 1 Month 12 Effective Business Performance Reviews
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Business Performance Integrity corporate training program.
Business Performance Integrity – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Current State – Core to the Planning and Execution System of any organization are three fundamental processes: Daily Management, Problem Solving, and Strategy Deployment. They form the foundation for all other improvement tools and apply to every business function and facet of your organization. The three processes function together as a system that can leverage Business Performance Integrity. Strategy Deployment is transforming Strategy into sustainable processes that will deliver breakthrough results. Daily Management is applied as a disciplined routine method to ensure, at a regular cadence, that our processes are meeting our customers’ needs (internal or external customers). If we use trains as an analogy for processes, you can think of Daily Management as the way we keep the trains running on time and Strategy Deployment as the way we invent new and breakthrough means of railway transportation. Finally, problem-solving is the thought process used to define problems, investigate and drive to root cause, verify and implement countermeasures, and ensure sustainment. In part one, we will get to a common high-level understanding of the three fundamental processes, sufficient to do a self-diagnosis and understand the baseline and the opportunity it poses to strengthen these crucial elements of the Planning and Execution System, thus creating further appetite for the 12-month capability building journey and the value it will bring to you and your company. Coming out of Module 1, you will have a concrete plan to confirm the current state during Month 1 and prepare for Part 2 by further mapping elements of the Daily Management processes in your area of responsibility.
- Part 1 Month 2 Daily Management (DM) – We all want to be on the winning team more often, but how do we know whether we are winning or losing at a given time? In the second part of the program, we will dive into the elements of a DM system and, based on the confirmed diagnosis, begin to build your DM setup. We will use a step process that covers several reflection questions like: What are you currently tracking, and can you tell if you are winning or losing? Does the data you are using drive timely course correction (actions, problem-solving, etc.)? What behaviors is your daily management process currently trying to drive? What processes are you controlling with your DM? Who are the customers of your DM process, and what are their needs? What else might you need to measure? What is your process for monitoring and communicating progress? Through this process, you will familiarize yourself with the components and interdependencies of the DM System you are part of. You will map your accountability structure and the KPI hierarchy you act within. You will understand the related vital processes and the relevant stakeholders, including internal and external customers, your DM team, and the colleagues in the (vertical) reporting line. We will explore different ways of doing DM for various purposes to understand your organization’s needs. Based on these insights, you will decide on concrete actions to refine and improve your DM. At the end of Module 2, you will be ready to make the planned changes in your DM processes and organization with your team and test them using a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) approach. With your new insights, you will be on an accelerated learning curve related to DM.
- Part 1 Month 3 Improving Your Daily Management – We will start the third part of the program with a joint team reflection session related to your introduction of changes in the way you shape and execute your DM process. We will then discuss the role DM plays in your company’s Planning and Execution System. A short, high-level overview of the elements of the Problem-solving Process will then enable a team discussion on how DM can help drive more timely problem-solving and thus contribute to Business Performance Integrity. We will introduce a maturity self-assessment framework that will enable you to continue improving your own and your company’s DM System following a structured approach. The criteria will include relations to problem-solving but also address elements related to organization, terms of reference, and the evolution of valuable behaviors. While module 2 provided concrete building blocks to establish a new current state of your DM structures and processes, module 3 gives you a proven set of criteria and a reflection framework to develop a structured, agreed way of moving towards operational excellence in DM. Coming out of module 3, you will complete your initial assessment and define the first actions in your plan to improve your DM continuously. In the following modules, you will focus on building capabilities related to problem-solving (PS) and Strategy Deployment (SD) and continue to reflect on the evolvement of your DM and how it interrelates with PS and SD to form a joint Planning and Execution System in your company.
- Part 1 Month 4 The Problem-solving Process – While Daily Management is the process that, at an agreed frequency, enables you and your team to quickly see if you are winning or losing and take timely action, Problem Solving is the process and team-based effort whereby you close the gaps and get back on track to win. Problem-solving is a step process that starts with identifying the problem, finding the contributing root causes, and then selecting the countermeasures to address the root causes and closing the gap between where you are and where you would like to be (= winning). It seems like a simple process, but there are multiple common pitfalls and best practices to learn at every step. We will take them one at a time and practice in between to ensure that your process is refined and re-installed in a sustainable way that will bring value to your business. Problem-solving is a critical lever in building a learning organization. Most business problems derive from how we operate our business processes, and by analyzing them, we can harvest many learnings. Building an organization of problem-solvers should be a key priority for top management; thus, understanding your role in building a Problem-Solving Culture is a core objective of this program. Parts 4 through 8 of this program will revolve around the problem-solving process and what it takes to install a strong one in your organization. As mentioned, we will install the process step by step and start in Module 4 by understanding how we define problems, where problems come from, how we measure different problems, and what a structured Problem-Solving process looks like. We will then work through the first step of identifying and defining problems and the business rationale for solving them, covering the pitfalls and helpful practices in this phase. Based on your initial self-diagnosis and the learnings from this Module, you will plan and implement actions to refine the front end of your company’s problem-solving process. Coming out of module 4, you will have a plan to make changes in your organization in the way you identify, define, prioritize, and select the critical few problems you want to solve next. In addition, you will choose one or more real business problems to use as cases in the next period.
- Part 1 Month 5 Identifying and breaking down your problems – Einstein once said, “If I had an hour to solve a problem, I’d spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and five minutes thinking about solutions”. The ratio is exaggerated, but it is true that time spent in the upfront part of the problem-solving process is well spent and that if you install the excellent practices taught in modules 4-6, you are likely to spend 65-75% of your time on identifying the problem and finding the root causes whereafter the remaining phases of building and implementing the countermeasures should run significantly faster. The most common pitfall of the upfront stages is to skip them, assuming the first phrase suggested about the problem really IS the problem, and then jump to offering solutions that address the supposed problem. Building on the theories and practices around problem identification covered in part 4 and your experience with applying some of the methods in your organization, we will go deeper into the front end of the problem-solving process and practice on your case problems. This exercise should enable you to prioritize and select the most critical measurable problems to solve and build a solid rationale, considering the relevant stakeholders. A key point here is to define the problem at the right level of the organization and get accountability through clear problem ownership. At this point, you will be ready to discover the best practices for breaking down problems – the first step in funneling through your root cause analysis in the most efficient and effective way – data-driven and with full traceability back to the quantitively defined problem. The investigation now narrows in on a few possible areas or locations where the root causes can be found, and the next step in the process is to put together a plan to investigate the actual root causes further, following an evidence-based approach. By the end of Module 5, you will have defined the actions it will take to implement the selected new practices in the way your organization attacks chosen problems to ensure that root cause analysis starts in the most effective way (right parts of the problems) and with most efficiency (least effort). Apart from the actions to implement the above new elements of your organization’s refined problem-solving process, a key deliverable will be a plan to investigate your case problems and exercise the new concepts. This plan should evolve between modules 5 and 6 and map out where in your organization you need to go to talk to whom and directly observe what (including what data). This effort will accelerate the learning process in Part 6, where we will cover the remaining part of root cause analysis—how to get to the true root causes following an evidence-based approach.
- Part 1 Month 6 Getting to the root causes – The header purposely uses plural – root causes – as we often deal with a set or system of root causes bringing about the problem. Funneling down from several causes to a few possible causes with quantitative and logical traceability back to the problem is an essential prerequisite for initiating the effort of getting to the root causes and confirming them beyond doubt with objective evidence. It is paramount that the learning process in conference rooms is supplemented with exercising where the problems can be directly observed – where people work. Root causes of business problems derive from business processes performed in your organization. The responsibility for the health and continuous improvement of these business processes lies with the leaders of your organization, so to best support, coach, and challenge your people performing root cause analysis, it is valuable for you to learn the common pitfalls and best practices and get hands-on experience with the core methods – in particular 5xWHY analysis. If someone says that 5xWHY analysis is simple or easy, they probably never did it. It is easy to explain what it is, but it takes a lot of practice to get good at it. In this sixth Module, we will learn and practice the ins and outs of 5xWHY analysis and other methods to identify and confirm root causes while discussing the application and formalization of this part of the problem-solving process in your organization. We will do hands-on simulation case exercises and, to the extent possible, practice on your case problems. A critical common pitfall in 5xWHY analysis is to do it in a conference room, rather than where the work takes place and where you can confirm with objective evidence; it is a firm recommendation to get your learnings between the modules and reflect in class. We will also reflect on the problem cases you have worked on and discuss the next steps in a plenary session, covering the challenges you see in performing the last part of the root cause analysis. Module 6 should leave you with a plan to formalize root cause identification and confirmation as part of the problem-solving process in your organization, as well as a solid plan to take the following steps on your case problems and bring root causes to share in module 7.
- Part 1 Month 7 Building sustainable countermeasures – At this stage of the problem-solving process, we know the root causes of the problem and have confirmed them with evidence at the places where you can directly observe the causes. The hardest part is now done, and identifying solid solutions to the problem will require less time and effort. We have restrained ourselves, so far, to not jump to suggesting countermeasures – but now that we know the actual root causes, we can let go and bring out all the suppressed creativity on crafting countermeasures that collectively control these root causes and effectively close the quantified business performance gap that we defined as the problem. In this seventh Module, we will initially reflect on your efforts to implement new practices in your organization regarding root cause analysis and experiences from exercising on your case problems. Following this activity, we will take you through the final steps of the problem-solving process, from brainstorming on multiple countermeasures – the more, the merrier – to narrowing in on the selected few that can fully close the gap sustainably. As with the former phases, you will learn the pitfalls and proven best practices on this journey, from confirmed root causes to sustainable countermeasures. This session will comprise efficient ways to select the critical few countermeasures and validate that their joint impact effectively addresses the problem, as well as ways to consider the change management aspects of implementing the countermeasures and ensuring they sustain so you don’t face the same problem next time around. We will have plenary discussions on how to bring these new practices to life in your organization and how you can use your case problems as vehicles for this. Coming out of module 7, you will have defined actions to implement changes to these last parts of the problem-solving process in your organization and efforts related to taking the next steps on your case – selecting and testing countermeasures as well as getting an understanding of the possible change management challenges.
- Part 1 Month 8 Evolving Your Problem-solving Culture – Change is inevitable, and transformations have become an integral part of the everyday agenda for employees in most organizations. Building Problem-Solving capabilities is a prerequisite for evolving a learning organization that can cope with all the transformations, inherent processes, and organizational changes that these transformations entail. Growing your Problem-Solving Culture poses a huge opportunity to accelerate your transformations, and there is a lot more to this than merely building capabilities in the above steps of your Problem-Solving process by leaders becoming coaches and appointing trainers and key practitioners that can facilitate. It is undoubtedly also about promoting behaviors like making problems visible, ensuring a no-blame environment and ‘can do’ attitudes around Problem-Solving activities, and utilizing the Daily Management (tier) system to delegate solid problem ownership at the right level of the organization. We will start this Module with a plenary sharing and round-up of your latest efforts to complete the changes to your problem-solving process and the crafting of solid countermeasures for your case problem. This session then discusses the change management challenges related to your case countermeasures and defines various measures and actions to ensure sustainment. You will then learn about specific aspects that can be brought into play when actively orchestrating changes in your organization’s Problem-Solving Culture and be able to recognize symptoms of ineffective and effective behaviors related to this culture. We will introduce a problem-solving maturity model and self-assessment. Before we wrap up Module 8, you will use this tool to identify actions that will shape your plan to improve your problem-solving processes and your organization’s problem-solving culture.
- Part 1 Month 9 Strategy Deployment – Many famous people have said, ‘If you always do what you’ve always done, you’ll always get what you’ve always got.’ Pursuing your Strategy means identifying the critical things you need to do differently and orchestrating the transformation journey to the new way of working that will bring the desired outcomes defined in the Strategy. This is what is meant by Strategy Deployment (SD). Most organizations can craft a sound strategy document. Still, only some can drive to the defined outcomes using a structured, repeatable process that is efficient and effective in delivering on the promise.
We will get you started on the learning journey in the remaining modules of this program. A problem is a gap (preferably quantified) between how something is and how you want it to be. SD relates to Problem-solving in the way that the problems we solve in the pursuit of our Strategy are ‘created’ gaps that we need to bridge. If we can quantify these ‘created’ gaps, we can apply most steps in the Problem-Solving process covered in modules 4 – 8 while bridging the gaps by crafting actions that will move us towards the new ways of working. Applying a rigorous follow-up process entailing timely course corrections on the journey is an integral part of SD and has its foundation in solid Daily Management practices. In this ninth Module, you will learn the common pitfalls that lead to unsuccessful strategy execution and reflect on these, related to the organizations you have been part of during your career and your current organization, picking up on the current state analysis from module 1. We will cover how SD plays into your Planning and Execution System and how the elements of SD form a system of countermeasures that can prevent the pitfalls we present to you when used effectively, together with Daily Management and problem-solving best practices. One of the major pitfalls in strategy execution is trying to do too many things – not being able to prioritize the critical few that truly constitute a breakthrough. Using external examples and bringing into play your own strategy documents, we will learn how to distinguish breakthroughs by a set of proven criteria and take the first steps of evaluating and shortlisting input to SD in your organization and how to engage the right people in the front end of the SD cycle. You should leave Module 9 with a firm understanding of how Daily Management, Problem Solving, and Strategy Deployment interact as critical components in an effective Planning and Execution System and how to identify common SD-related weaknesses. Depending on where your organization is in the year wheel (execution cycle), you will have identified actions to confirm different hypotheses related to SD improvement opportunities and mobilize the organization for the first changes in how you deploy Strategy. You will also have defined what parts of your organization’s Strategy indeed constitute breakthrough and thus also identified some ‘created’ gaps that SD can address. The following modules will teach you the steps, tools, and behaviors that shape the structured, repeatable process we call Strategy Deployment.
- Part 1 Month 10 Getting your Strategy to One Deployable Page – For most organizations, Strategy materializes through a lengthy PowerPoint deck or a massive Word document. This format poses a challenge in many contexts, such as how to communicate shortly and sweetly to an audience who have yet to take part in crafting the deck, but even more importantly, when it comes to deploying the Strategy and making the strategic intent come to life. What if we could capture the essential breakthrough elements of the Strategy on one page that covers the quantified long-term gaps we want to bridge and charts out the first-year journey in terms of quantified objectives, prioritized processes/capabilities we need to build or change, the metrics to measure progress and the defined shared ownership of driving the transformation? During Module 10, you will learn how to build a one-pager called an X-matrix through examples and exercises. Eventually, you will start on an X-matrix for your organization. This X-matrix is the anchor reference point of all the Strategy Deployment efforts, getting you to meaningful, transformative actions and setting a solid frame for execution and follow-up. You will find that successful companies pursuing operational excellence with a track record of overachieving their strategic goals use this best practice approach to deploying their Strategy. We will discuss how to orchestrate the process of building the X-matrix, including the timeline, who to involve when – in the organization’s mobilization, and how to avoid the usual pitfalls. By the end of module 10, you will have a firm understanding of the X-matrix mechanics and hands-on experience applying the method to your corporate Strategy. You will have filled in some parts of the template and defined actions to confirm these and identify further content that will guide the program’s next steps. You may already be able to make formal changes to your Planning and Execution System regarding the front-end of deploying Strategy.
- Part 1 Month 11 Deploying the Strategy into the Organization – It is all about getting from Strategy to action, so the X-matrix provides the framework to define the change and move to action and the means to communicate the concrete breakthrough transformation each year. But it is when actions to implement new ways of working are truly anchored ‘where the rubber hits the turf’ – at the point of impact – that the magic happens. Building the X-matrix happens through iterations while mobilizing the leaders who will own the transformational change initiatives and the Point-of-Impact people who can own the actions of building the new ways of working and the new capabilities. These actions are captured in SD action plans along with metrics to track the changes compiled in dashboards to enable follow-up. The activity of building the X-matrix and the action plans plus dashboards to go with it is a multi-month iterative effort that requires deep and broad engagement of the organization. One of SD’s common pitfalls is having too many lines in your X-matrix, which means having too many objectives and transformational change initiatives. So, ‘less is more,’ and prioritization is of the essence. In module 11, you will learn the mechanics of operationalizing your X-matrix into action plans with dashboards anchored at the Point of Impact (POI) and how best-in-class companies successfully maneuver through the multi-month effort required to set the organization up for the execution of breakthrough initiatives. We will go through tips and tricks for crafting robust action plans to help you support the effort in your teams and discuss how to match actions with metrics that can enable solid tracking of the execution journey in dashboards with monthly targets as well as recommendations on setting up meeting cadence for the teams. You will get hands-on practice evaluating your case action plans and pulling samples from your organization. Depending on where your organization is in the yearly execution cycle, you will practice crafting actual action plans with metrics to confirm with your teams and further develop in the following months. Coming out of module 11, you will understand how the X-matrix, the SD action plan, and the SD metric dashboard form a system to realize the bridge from a strategy document or deck to solid action – ready for execution reviews and follow-up. You will have identified the subsequent steps to make your X-matrix come to life with action plans, metrics, and new elements to formalize your organization’s Planning and Execution System related to the middle steps of deploying Strategy.
- Part 1 Month 12 Effective Business Performance Reviews – Getting back to the title of this program: ‘Business Performance Integrity,’ what does it mean, and how do we set ourselves up for success in our strategy execution based on the steps we learned, exercised, and began implementing through the past three modules? We can define the pursuit of excellence in ‘Business Performance Integrity’ in three steps: 1) Having a plan to win (solid action plan with connected metrics and clear accountability) 2) Enabling transparency – are you winning or losing? (solid Daily Management practices) 3) Timely course correction (solid Problem Solving – fit for purpose). Through modules 9-11, we have focused on breaking down the real breakthrough elements of our Strategy into executable action bits with connected follow-up metrics in formats that make it easy to review progress and traction toward year-end targets. Along with the X-matrix, which anchors the connection to our Strategy and communicates the ‘true north’ high-level objectives and initiatives, the SD action plans and dashboards with connected monthly targets form the primary input to initiate strategic performance reviews. These elements, along with a strong organization of the teamwork between the reviews to execute the actions that will realize Strategy, are crucial prerequisites for a successful strategy review. When discussing performance reviews, it is essential to distinguish between Daily Management meetings and Strategy Deployment reviews and do these meetings in separate timeslots. DM ensures that our day-to-day business runs as smoothly as possible with timely course corrections, whereas SD safeguards traction on the strategic initiatives that will ensure we get ahead of the competition. Daily Management capabilities are critical when executing SD reviews. Still, behaviors and expectations should be different as the problems discussed are around created gaps and building new ways of working, not so much catching up and fixing foundations as in DM reviews. Both meetings have actions and agreed on problem-solving as outcomes, but the dialogue in the actual forum should be different, given the character of the problems discussed. We will start this last Module with a plenary reflection on your efforts to implement new SD practices in your organization’s Planning and Execution System and the status of practicing these on current strategic initiatives. You will learn how to benchmark organizations set up their performance reviews, separating daily operations from the strategic agenda and the pitfalls that made them choose this way. Performance reviews are great opportunities for leaders to exercise coaching their team members and great learning moments for everyone. We will discover how effective and ineffective behaviors can affect the success of the reviews and share the traits of ‘Servant Leadership’ in the context of building a problem-solving culture that will leverage the learning organization. After sharing some best practice examples of review Standard Work, we will discuss and evaluate how reviews run in your organization and what changes you would consider implementing. At the end of the program, you will capture all outstanding ideas for integrating improvements regarding DM, PS, and SD into your organization’s Planning and Execution System in a plan document. Finally, we will bring it all together in a wrap-up on Business Performance Integrity.
Methodology
Business Performance Integrity
The 12-months program increases your organization’s Business Performance Integrity level by enhancing three cornerstone capabilities: Daily Management, Problem-solving, and Strategy Deployment. Along with building these capabilities, relevant areas of your organization’s Planning and Execution System will undergo the changes needed to truly harvest the program’s potential of bringing sustained value creation.
The changes will affect how your recurrent planning and follow-up meetings (daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly) are planned and executed. Through the program, you will look at these meetings as processes that can gradually be improved in terms of better input, orchestration, teamwork, leadership support, problem-solving, and decision-making for better outcomes in the shorter and longer-term (strategy).
Creating the baseline and seeing the opportunity
In the initial stage of the program, you will establish the current state of your Planning and Execution System in terms of performance management setup for budget planning and follow-up, strategic planning, deployment, and execution. A vital aspect of this current state analysis is understanding your organization’s ability to solve problems and close performance gaps sustainably.
This current state analysis will be done in the first workshop, and the baseline in your organization will be confirmed in the weeks after that.
A key part of the first couple of workshops is inspiring change by bringing cases and examples of how best-in-class organizations establish performance integrity by building a robust problem-solving culture.
Building capabilities and strengthening the processes
Throughout the program, you will strengthen your Daily Management, Problem-solving, and Strategy Deployment capabilities via theory sessions with practical examples and exercises and bring real-life challenges to work on from your own organization. All modules will conclude with a challenge for you to enhance the processes that shape your Planning and Execution System and, thus, address gaps identified in your current state analysis, making you move from baseline toward excellence.
Growing as leaders and delivering on your promise
In addition to the learning journey of building muscles in the three cornerstone capabilities while making your processes more robust, the program equally focuses on reshaping leadership skills that will help you play your role and enable you to shepherd your teams on the journey to build a more robust problem-solving culture that will enhance business performance integrity in your organization and make you deliver on your promise more often.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Health Tech Industry
The health tech industry is revolutionizing how we approach our well-being. By harnessing the power of innovation, this sector is transforming the landscape of healthcare delivery, empowering patients, and optimizing medical practices.
At its core, health tech encompasses a diverse range of technologies aimed at improving all aspects of healthcare. From wearable devices that monitor vital data to telemedicine platforms that remotely connect patients with doctors, health tech is making healthcare more accessible, convenient, and personalized. Electronic health records streamline information sharing, while artificial intelligence (AI) makes inroads in disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans.
The impact of health tech extends beyond individual patients. Hospitals and clinics are utilizing data analytics to improve efficiency and resource allocation. Public health initiatives leverage wearable technology and AI to track disease outbreaks and promote preventive care. These advancements hold immense potential to address global health challenges, improve population health outcomes, and ultimately reduce healthcare costs.
The future of health tech is brimming with possibilities. Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) with healthcare promises further advancements in remote monitoring and personalized medicine. Technologies that leverage virtual and augmented reality will revolutionize medical training, rehabilitation, and even surgery.
However, the path forward has its challenges. Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security in the digital health landscape must be addressed. Regulatory frameworks must adapt to address the emergence of new technologies, ensuring their safe and ethical use within the healthcare system. Additionally, bridging the digital divide remains crucial to ensure access to these advancements for all communities.
In conclusion, the health tech industry is an engine of transformation in the healthcare sector. By embracing innovation and addressing the existing challenges, this dynamic field holds the potential to create a future where everybody can access healthcare in a personalized, effective way. As we move forward, it is crucial to harness the power of technology responsibly, ensuring that these advancements empower individuals and strengthen healthcare systems globally.

Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturing, the backbone of modern economies, encompasses the large-scale production of goods using various processes, from assembly lines to chemical transformations. This sector, a cornerstone of the global economy, has driven innovation, shaped societies, and continues to evolve in the face of constant change.
Industrial manufacturing is vastly diverse, encompassing everything from automobiles and aircraft (heavy manufacturing) to electronics and pharmaceuticals (light manufacturing). This industry is crucial in creating jobs, fostering technological advancements, and driving international trade. It is an intricate ecosystem where raw materials are transformed into finished products, often through complex global supply chains.
However, the industrial manufacturing landscape has challenges. Globalization and automation have intensified competition, forcing manufacturers to readjust and innovate to remain competitive constantly. Sustainability concerns also push the industry to adopt cleaner production methods and minimize environmental impact.
Additionally, automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the workforce, requiring a shift towards upskilling and reskilling employees to adapt to these changes.
The future of industrial manufacturing is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
• Embracing technology: The industry will continue integrating advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and enhance production quality.
• Focus on sustainability: Environmental considerations will play an increasingly significant role, driving manufacturers to adopt cleaner energy sources, implement resource-efficient practices, and minimize waste generation.
• Customization and personalization: Meeting the growing demand for customized and personalized products will require flexible production systems that adapt efficiently to changing consumer preferences.
• Reskilling the workforce: As automation and AI continue to reshape the industry, the demand for workers with specialized skills in data analytics, robotics, and cybersecurity will grow.
In conclusion, the industrial manufacturing industry stands at a crossroads, facing the challenges of a rapidly changing world. However, by embracing technological advancements, prioritizing sustainability, and investing in a skilled workforce, this sector can continue to drive economic growth and innovation for years. The future of industrial manufacturing is not just about producing goods; it’s about shaping a sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come.

Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is a pillar of modern medicine, fostering innovation to combat diseases and improve global health. It encompasses a complex network of companies involved in discovering, developing, manufacturing, and marketing drugs and medications.
Remarkable breakthroughs have marked the industry’s journey. From the discovery of antibiotics to the development of life-saving vaccines, its contributions have extended lifespans, alleviated suffering, and transformed the course of countless illnesses.
However, the landscape has challenges. The new drug research and development process is lengthy, expensive, and risky. Stringent regulations, while ensuring safety and efficacy, can add to the time and cost of bringing new medications to market. Additionally, the industry faces ethical considerations regarding drug pricing, access, and the potential for commercial interests to overshadow public health priorities.
The pharmaceutical industry is poised for significant change in the future. The rise of personalized medicine, which leverages an individual’s unique genetic makeup to tailor treatments, holds immense potential for more targeted and effective therapies. Gene editing and artificial intelligence advancements offer exciting possibilities for accelerating drug discovery and development.
The industry must also address ongoing concerns about affordability and access to medications. Striking a balance between commercial interests and ensuring equitable access to life-saving treatments will be crucial.
In conclusion, the pharmaceutical industry plays a vital role in safeguarding and advancing global health. While challenges remain, the future holds promise for continued innovation and breakthroughs. By embracing new technologies, addressing ethical considerations, and fostering collaboration, the industry can continue its mission of improving lives and shaping a healthier future for all.
Energy Industry
The energy industry, encompassing the extraction, production, and distribution of energy resources, forms the lifeblood of modern civilization. From the oil that fuels transportation to the electricity that powers our homes, access to reliable and affordable energy is fundamental to societal well-being and economic development.
However, the industry faces a complex and dynamic environment shaped by evolving demand patterns, technological advancements, environmental concerns, and geopolitical uncertainties.
The energy mix has historically been dominated by fossil fuels (oil, coal, natural gas). While they continue to provide significant global energy needs, their dominance is gradually decreasing. Growing concerns over climate change and the related environmental consequences have spurred a global push towards cleaner and renewable energy sources and technologies like solar, wind, and geothermal, which are witnessing rapid growth and cost reductions.
Both challenges and opportunities characterize the outlook for the energy industry. On the one hand, the transition towards a low-carbon future necessitates massive investments in renewable energy infrastructure, grid modernization, and energy storage solutions. This transition will also affect the traditional fossil fuel sector, likely facing declining demand and stricter regulations in the long run.
However, the transition also presents significant opportunities. The development and deployment of innovative technologies have the potential to unlock new avenues for energy generation and consumption. Producing energy closer to the point of use and rapid adoption of electric vehicles are just a few examples. Moreover, the growing focus on energy efficiency can reduce overall energy demand, mitigating environmental impact.
Geopolitical uncertainties also play a crucial role in shaping the energy landscape. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has highlighted the vulnerability of global energy supply chains and the importance of energy security. This has led to renewed interest in diversifying energy sources and fostering energy independence for nations.
In conclusion, the energy industry stands at a crossroads. While navigating the challenges of a changing energy landscape, it also holds the potential to unlock a more sustainable and secure future. By embracing technological advancements, fostering innovation, and prioritizing environmental responsibility, the industry can play a critical role in powering the present and shaping a brighter future for future generations.

Clean Technology Industry
Clean technology, often shortened to “cleantech,” rapidly transforms how we interact with the environment. Encompassing a diverse range of products, services, and processes, the cleantech industry focuses on minimizing environmental impact through advancements in various sectors. From renewable energy and sustainable materials to efficient waste management and green transportation, cleantech offers solutions to some of our most critical environmental challenges.
The driving force behind this industry is the increasing awareness of climate action and the urgent need for sustainable practices. Cleantech emerges as a beacon of hope as the world grapples with rising greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and pollution. By providing viable alternatives to traditional, often environmentally detrimental practices, cleantech paves the way for a more sustainable future.
One of the most prominent areas within cleantech is renewable energy, which is covered in the above paragraph. Advancements in battery storage technology further enhance the viability of renewables, enabling a more reliable and efficient energy grid.
Beyond energy, cleantech extends its reach to other crucial sectors. Sustainable materials from recycled or organic sources replace conventional ones, minimizing waste and environmental footprint. Innovative agriculture practices that utilize data analytics and precision technology are optimizing resource use and minimizing environmental impact in the food production sector. Additionally, advancements in waste management are leading to efficient recycling and resource recovery, promoting circular economies.
The outlook for the cleantech industry is undeniably positive. Due to the increasing environmental concerns, government regulations promoting sustainability, and growing investor interest, the industry is poised for significant growth in the coming years. Market reports estimate the global cleantech market to reach a staggering value of over $6 trillion by 2027, highlighting its vast potential.
However, challenges remain. Technological advancements require ongoing research and development, and widespread adoption necessitates overcoming economic and infrastructural hurdles. Additionally, ensuring social equity and inclusivity within the cleantech transition is crucial to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities.
In conclusion, the cleantech industry represents a critical step towards a sustainable future. By catalyzing innovation and collaboration across various sectors, cleantech offers a pathway to mitigate environmental damage and build a more resilient and responsible world. As the industry continues to evolve and tackle challenges, its potential to address environmental concerns and create a thriving future for coming generations is undeniable.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Copenhagen
Copenhagen, Denmark’s capital city, has become a vibrant hub for commerce and business in recent years. It fosters a fertile ground for diverse industries. The city is a magnet for knowledge-based sectors like life sciences, clean technology, and information and communication technology. This is fueled by a highly skilled workforce fostered by strong educational institutions like Copenhagen Business School and the Technical University of Denmark. Additionally, Copenhagen boasts a well-developed maritime sector and a flourishing creative and design scene.
A defining characteristic of Copenhagen’s business environment is its emphasis on innovation and sustainability. The city actively promotes green initiatives, becoming a global leader in cleantech and sustainable urban development. This focus attracts businesses and investors aligned with these values, further solidifying Copenhagen’s position as a frontrunner in responsible business practices.
The Danish business culture is known for its openness and collaborative approach. This fosters a sense of transparency and trust, which is particularly attractive to foreign investors and businesses seeking to establish themselves in the European market. Additionally, Copenhagen boasts a well-connected startup ecosystem, offering support and resources to young entrepreneurs.
Copenhagen’s commercial and business environment presents promising prospects. The city’s continued commitment to innovation, sustainability, and fostering a welcoming business environment will solidify its position as a leading commercial hub. However, challenges remain. Attracting and retaining skilled talent, particularly in the tech sector, and ensuring equitable access to opportunities within the thriving business ecosystem will be crucial for sustained growth.
In conclusion, Copenhagen’s commercial and business environment is characterized by diversity, innovation, and a strong focus on sustainability. With a commitment to addressing emerging challenges and capitalizing on its strengths, Copenhagen is poised to remain a thriving and dynamic business hub for years.
Amsterdam
Amsterdam has quietly established itself as a formidable European commercial and business hub. It boasts a strategic location at the heart of Europe with excellent connectivity through its renowned Schiphol Airport and extensive waterways. This positioning makes it a prime gateway for international companies seeking an entry point to the European market, facilitating imports, exports, and efficient distribution networks. The city fosters a vibrant ecosystem for innovation, particularly in sectors like technology, finance, and life sciences. This is evident in the presence of renowned research institutions, thriving startups, and established corporations, all collaborating and driving advancements. Additionally, Amsterdam prioritizes sustainability, attracting businesses focusing on ethical practices and eco-friendly solutions.
The city actively supports entrepreneurship through initiatives like the Amsterdam Enterprise Programme. This program aims to simplify regulations, reduce administrative burdens, and offer support services to businesses, creating a more streamlined and welcoming environment.
Despite its strengths, Amsterdam faces its share of challenges. The city’s growing popularity has led to concerns about rising housing costs and attracting skilled talent. Additionally, navigating the legal and bureaucratic landscape can be complex, particularly for international businesses.
Amsterdam’s commercial and business environment continues to evolve with a positive outlook. The city’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and fostering a supportive business ecosystem positions it for continued growth. As it navigates challenges like affordability and attracting talent, Amsterdam is well-positioned to remain a thriving hub for international commerce and business in the years to come.

Helsinki
Helsinki, the dynamic capital of Finland, boasts a thriving commercial and business environment that fosters innovation, sustainability, and global connectivity. It is a breeding ground for groundbreaking ideas. The city boasts a highly educated population, ranking consistently high in global education reports. This, coupled with a strong network of universities and research institutions, fuels a dynamic ecosystem for innovation. The city actively supports its entrepreneurial spirit through initiatives like Helsinki Business Hub, which provides resources and guidance to startups and established businesses. This focus on innovation has led to solid clusters in critical sectors like Information and Communication Technology, Healthtech, and Edtech, positioning Helsinki as a global leader in these fields.
Sustainability is deeply ingrained in Helsinki’s commercial and business DNA. The city prioritizes environmentally conscious practices, strongly focusing on the circular economy. This approach of minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization creates new business opportunities for waste management and resource recovery. Helsinki’s commitment to clean energy and green infrastructure also attracts businesses seeking to align their operations with sustainable practices.
Helsinki’s strategic location at the crossroads of the Baltic Sea region and Northern Europe provides easy access to a vast market. The city facilitates the seamless movement of goods and people by maintaining an excellent transportation infrastructure, including an international airport and a well-developed network of ports and railways. This connectivity, coupled with Finland’s membership in the European Union, opens doors for businesses to tap into the broader European market and beyond.
The future of Helsinki’s commercial and business landscape appears bright. The city’s continued commitment to innovation, sustainability, and global engagement will solidify its position as a leading business hub in the future—additionally, emerging trends like digitalization and artificial intelligence present exciting opportunities for further growth and development. With a focus on fostering a business-friendly environment and attracting skilled talent, Helsinki is well-positioned to adapt and thrive in the ever-evolving global landscape.
In conclusion, Helsinki’s commercial and business environment presents a compelling combination of innovation, sustainability, and global connectivity. The city’s commitment to these core values, strategic location, and supportive infrastructure position it for continued success. As the world embraces new technologies and prioritizes responsible business practices, Helsinki will remain a thriving hub for businesses seeking to operate in a dynamic, sustainable, and globally connected environment.

Stockholm
Stockholm boasts an active commercial environment characterized by innovation, stability, and a strong focus on sustainability. The capital of Sweden has emerged as a hub for innovation, fostering a thriving ecosystem for startups and established companies. The “triple helix” model, fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and the government, has driven this growth. This collaborative approach has nurtured the development of cutting-edge technologies in fintech, life sciences, and cleantech, making Stockholm a global player in these sectors.
Sweden’s long history of political and economic stability provides fertile ground for businesses to flourish. A transparent regulatory framework and a skilled and multilingual workforce further enhance the city’s attractiveness as a business destination. This stability fosters long-term planning and investment, which is crucial for sustainable business growth.
Stockholm is a leader in sustainability initiatives, integrating environmental consciousness into every aspect of its business landscape. From eco-friendly infrastructure and green building practices to a strong emphasis on renewable energy, the city is committed to creating a sustainable future. This focus positions Stockholm as a responsible business center and attracts companies and investors aligned with these values.
Despite its strengths, the Stockholm business environment faces some challenges. The high cost of living and doing business can be a barrier for some companies. Attracting and retaining top talent remains a competitive endeavor. However, these challenges also present opportunities. Embracing diversity and inclusion can broaden the talent pool while fostering a more competitive and innovative environment.
The future of Stockholm’s business landscape looks promising. Continued investment in research and development, coupled with a focus on attracting and retaining talent, will be crucial for maintaining the city’s competitive edge and adopting innovation while upholding its commitment to sustainability, which will solidify Stockholm’s position as a leading global business hub.
In conclusion, Stockholm’s business environment is a unique blend of innovation, stability, and sustainability. While challenges exist, the city’s commitment to progress and its thriving ecosystem position it for continued success.

Oslo
Oslo, the capital of Norway, has a productive commercial and business environment brimming with opportunity. The city is a recognized hub for innovation, fostering a robust knowledge-based economy. Maritime industries, including shipping and offshore oil & gas, remain significant contributors, while the city actively nurtures emerging sectors like cleantech, fintech, and life sciences. This focus on innovation attracts global talent and fosters a collaborative environment, propelling business growth.
Norway is renowned for its robust social safety net and transparent business practices. This fosters a stable and predictable environment, attracting foreign investment and promoting ethical business conduct. The government actively supports entrepreneurship through grants and initiatives, further bolstering the commercial landscape.
Like the other Scandinavian capitals, Oslo prioritizes sustainability, integrating it into all aspects of commerce and business. The city aims to become carbon-neutral by 2030, driving innovation in green technologies and attracting eco-conscious companies and investors. This focus on sustainability contributes to a healthier planet and positions Oslo as a leader in the global green economy.
Regardless of its strengths, the commercial landscape faces challenges. The high cost of living and operating can be a barrier for some businesses, while the relatively small domestic market necessitates a strong export focus. However, by leveraging its unique strengths in innovation and sustainability, Oslo can attract companies seeking to tap into new markets and contribute to a greener future.
Oslo’s commercial landscape outlook is bright. With its focus on innovation, transparency, and sustainability, the city is well-positioned to attract talent, investment, and businesses seeking to succeed in a dynamic and responsible environment. As the city embraces new technologies and prioritizes sustainability, it is poised to solidify its place as a thriving commercial hub.
In conclusion, Oslo’s commercial environment offers innovation, transparency, and an unwavering commitment to sustainability. While challenges exist, the city’s strengths and proactive approach position it for continued success and solidify its status as a vibrant and promising place to do business.
Program Benefits
Management
- Increased predictability
- Mission control
- Strategy execution
- Leadership effectiveness
- Performance Improvement
- Timely intervention
- Increased focus
- Effective problem-solving
- Employee empowerment
- Transparent accountability
Human Resources
- Increased productivity
- Employee satisfaction
- Higher engagement
- Reduced stress
- Team collaboration
- Success criteria
- Improved communication
- Employee development
- Leadership development
- Improved problem-solving
Operations
- Improved quality
- Process improvement
- Timely Problem-solving
- Improved resilience
- Team effectiveness
- Inclusive environment
- Better alignment
- Tiered accountability
- Skilled problem-solvers
- Problem ownership
Testimonials

Honeywell
“Mr. Danielsen and I served in the same Group Continuous Improvement team at Philips, where he proficiently anchored the global train-the-trainer cascade in Daily Management and Problem-solving, radically advancing the level of transparency and accountability throughout the company and enabling a more solid performance management with timely, structured course correction on the most critical business issues.
Together, we re-launched the week-long Executive Lean Leadership training and drove the effort to train the top 1200 executives with great success—a critical top-down initiative to orchestrate a problem-solving culture.
Mr. Danielsen is an excellent facilitator and capability builder with a solid ability to communicate with – and coach people from any culture and at all organizational levels.”

Cynosure Consult
“Working alongside Mr. Danielsen was a learning experience that I deeply value. Mr. Danielsen’s ability to drive the global training cascade of Daily Management and Problem-solving was nothing short of inspiring. He had a unique approach to making complex methodologies not only accessible but also engaging and practical.
In addition, his leadership in implementing the 5-day Executive Lean Leadership training, complete with a certification scheme, was a testament to his commitment to transformative change. Mr. Danielsen’s approach was always thoughtful and inclusive, ensuring that these methodologies were perfectly tailored to our needs, which was vital for me to gain buy-in across all 15 markets.
I highly recommend Mr. Danielsen to any company looking to enhance its performance and deliver on its promises more consistently. His blend of strategic insight, practical experience, and a genuine passion for organizational excellence makes him an ideal guide in this journey.”

Bergman Clinics
“During my tenure as Market Leader of EMEA and later as Global Business Leader for our MR Scanner business, I experienced the impact of Mr. Danielsen’s engagement in the transformation of the companies’ core performance management processes through deep integration of Daily Management and problem-solving into the preparation and execution of our monthly performance reviews.
This change drove more actions and timely course corrections, thus increasing the predictability of company performance.”

General Electric
“Mr. Danielsen is an inspirational leader who drove significant, sustained business results by creating a global Lean Management System. He was instrumental in orchestrating a Lean Management System that contained global deployment of Tiered Daily Management linked to problem-solving and coached executives and Lean Leaders. Mr. Danielsen created a comprehensive approach to driving the adoption of Lean from individual contributors to Executive Leaders.”

Versuni
“While serving as Chief of International Markets, I was excited to have Mr. Danielsen organize a 5-day executive lean leadership training for the leadership teams in my 15 markets, which gave them the tools and conviction to drive continuous improvement, and they did!
Mr. Danielsen helped and coached the teams on daily management and problem-solving in an effective and engaging way.”

Signify
“Mr. Danielsen and I worked together on the Lean / Operational Excellence journey, where we teamed up on the development and delivery of Daily Management and Problem-Solving boot camps that laid the foundation for applying lean thinking.
Mr. Danielsen brought years of experience and calm to the table, which supported boosting the approach within the Enterprise. Unfortunately, our career paths went in different directions, but continuing the journey would have been great!”

Bloomberg LP
“Mr. Danielsen is a very hands-on Lean practitioner who can coach and apply Lean principles to solve business problems in a very pragmatic way.
During my interactions with Mr. Danielsen, he was always able to start with outcomes and a clear definition of the problem before bringing about any of the tools that can be used to address the solution. He is one of a few business managers who can use lean to achieve results.
I have seen how Mr. Danielsen addressed a class full of executives, cascading the 5-day Executive Lean Leadership training. He was addressing the problems as they were brought to him by the leaders, and observing the deep problem-solving occurring on the fly gave me a lot of respect for him.
Mr. Danielsen drove this program across the global organization, which included a certification scheme to drive accountability by the executives and delivered a cultural shift towards problem-solving.”

Global Financial Planning & Analysis, Royal Philips
“I worked closely with Mr. Danielsen as we rolled out the Continuous Improvement methodology in the Philips Finance function. Mr. Danielsen acted as the internal consultant/expert as the Finance leadership took on board this vital methodology to drive enterprise performance. The Hoshin planning and Daily Management tools he rolled out remain very much in place and form part of our bi-weekly performance management cycle.
Mr. Danielsen also acted as my personal coach/mentor as I gained my Continuous Improvement, Daily Management Trainer & Hoshin Planning certifications. I am very grateful for his thoughtful and insightful advice as I learned the methodologies, particularly during the Lean Leadership class work, train-the-trainer sessions, and individual one-on-one sessions. These skills have proven particularly useful as I lead the 375 Philips FP&A professionals.
I strongly recommend Mr. Danielsen for the Lean expertise, personal insights & integrity he brings to bear in his ongoing work and interactions.”

Capabilities & Performance IT
“Mr. Danielsen has in-depth knowledge of effectively deploying strategy (from high-level words to actual measures), daily management, and problem-solving. He helped implement problem-solving techniques in all our performance reviews, ensuring leaders were driving a problem-solving culture. He led the way using the strategy deployment tools in an office environment. To date, we are still using these techniques as they help us make strategy become a reality.”

Diagnostic X-ray and Imaging Regions
“Mr. Danielsen served as a Sensei to me in implementing Strategy Deployment (Hoshin Planning) in one of the Business Units I was responsible for supporting as a business transformation leader.
He played a pivotal role in putting the proper structure and methodology in place and guiding the leadership team in maintaining the right level of business integrity by having a plan to win, closely monitoring performance, and initiating timely course correction when needed.”

Hospital Patient Monitoring
“I have had the privilege to work, collaborate with, and learn from Mr. Danielsen in various capacities during his tenure. He has been one of the transforming pillars that worked on the Perform & Transform agenda of the Continuous Improvement practice by deploying three essential tools: Daily Management, Problem Solving, and Hoshin Planning. This led to improved strategy deployment and discipline in execution across Businesses/Markets/Functions. Mr. Danielsen’s contribution to these critical tools’ overall creation, adoption, and driving impact has been invaluable.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.