Business Operational Excellence

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Business Operational Excellence is provided by Mr. Cody Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 18 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Cody is a Certified Learning Provider (CLP) at Appleton Greene. He is a highly professional and accomplished individual with diverse skills and expertise. This enabled him to start a reputable consultancy business offering a comprehensive suite of business growth-enabling services across a range of diverse industries. These services encompass Engineering, Lean & Operational Excellence, Leadership Development, and Training Programs.
With a proven track record of success, Mr. Cody has demonstrated his exceptional leadership abilities and strategic acumen while fostering strategic partnerships to execute departmental and organizational initiatives and drive change. His coaching, mentoring, and training capabilities have empowered talent to develop their technical and professional capabilities, resulting in improved performance.
Mr. Cody’s proficiency in financial forecasting and budgetary strategy has played a crucial role in creating and managing business strategies, including goal-setting at individual and departmental levels. He has overseen and led numerous high-value projects, encompassing technical, operational (lean), quality, validation, logistical, and behavioral aspects.
With a strong focus on Operational Excellence, Mr. Cody has spearheaded cultural engagement initiatives, driving Lean, Six Sigma, SPC, 5S, standard work, and visual management practices. He excels in resolving complex engineering problems, implementing technical process improvements, and reducing waste through data-driven improvement methodologies.
Throughout his career, Mr. Cody has been instrumental in developing and executing operational policies and procedures, particularly in the areas of quality and regulatory compliance. He has taken ownership of multiple CAPA events, quality risk management, GMP, and quality documentation, ensuring adherence to the highest standards.
Mr. Cody’s extensive professional experience extends beyond his consultancy business. His previous roles include leadership at Abbott Laboratories, an American multinational medical devices and health care company, where he demonstrated his project management skills and successfully executed multifaceted projects. He had similar success in the automotive industry.
Education-wise, Mr. Cody holds a Bachelor of Science Honors Degree in Computer-Aided Manufacturing, together with educational awards in Leadership, Digitization of Manufacturing, Manufacturing Technology, Mechanical Engineering, and Agriculture. These qualifications and his continuous pursuit of knowledge have equipped him with a well-rounded skill set.
Furthermore, Mr. Cody has authored several white papers on topics related to the manufacturing industry, covering subjects such as Operational Excellence, Product and Process Lifecycle, Cost Reduction Opportunities, Effective Design Solutions, Leadership Effectiveness, and more. He is also Six-Sigma Greenbelt certified and has actively mentored other employees on their journey to certification.
Mr. Cody has participated in various professional programs and courses, including the Mindful Leader, Six-Sigma, Financial and Supervisory Excellence Programs in addition to Abbott-specific courses such as the “Fast Track 50 Program” for high-potential future leaders and the Abbott Leadership Excellence Program (LEP). He possesses extensive experience in utilizing Microsoft applications and has a passion for travel, having visited over 50 countries.
With a solid foundation of experience, knowledge, and a results-driven approach, Mr. Cody is well-equipped to contribute to the success of any business.
To request further information about Mr. Cody through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Business Operational Excellence
In today’s fiercely competitive marketplace, every decision you make must be driven by one ultimate goal: growing your bottom line. The Business Operational Excellence course is your direct pathway to maximizing profitability and skyrocketing your financial success. Allow us to outline exactly why this investment will be the most transformative decision you’ll make:
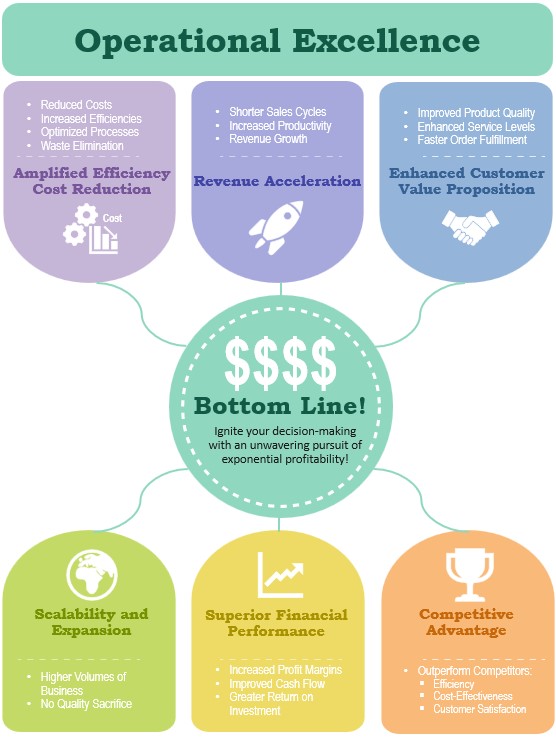
• Amplified Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Operational excellence is the catalyst for unearthing operational inefficiencies and reducing unnecessary costs. Our workshops empower you to streamline processes, eliminate wasteful practices, and optimize workflows, leading to exponential increases in efficiency. Witness as your overhead shrinks, your resources are allocated more effectively, and your profitability soars.
• Revenue Acceleration: Operational excellence doesn’t stop at cost reduction but drives revenue growth. By optimizing critical processes, you’ll experience faster turnaround times, shorter sales cycles, and increased productivity. The result? A surge in revenue that catapults your business to new heights. Prepare to outperform your competitors and seize a larger slice of the market.
• Enhanced Customer Value Proposition: At the heart of operational excellence lies a relentless commitment to delivering exceptional value to your customers. Our program empowers you to fine-tune your operations, resulting in improved product quality, enhanced service levels, and faster order fulfillment. Witness as customer satisfaction reaches unprecedented levels, leading to increased repeat business, referrals, and brand loyalty.
• Scalability and Expansion: Your ambitions know no bounds and operational excellence will be your vehicle to unparalleled growth. Optimizing processes will unlock scalability, enabling you to efficiently handle higher volumes of business without sacrificing quality. With our expertise as your guide, you’ll be primed for seamless expansion into new markets, product lines, or customer segments.
• Superior Financial Performance: Operational excellence is the backbone of sustained financial success. By adopting best-in-class methodologies, you’ll consistently generate superior financial results. Expect increased profit margins, improved cash flow, and greater returns on investment. Our course ensures you’ll wield the financial acumen necessary to secure a prosperous future for your business.
• Competitive Advantage: In the race for business supremacy, operational excellence propels you to the front of the pack. You’ll secure a dominant market position by outperforming your competitors in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. Stay ahead of the curve, leaving your rivals in the dust while becoming the go-to choice for customers seeking unparalleled value.
But how do we do it? While financial success is undoubtedly the crucial goal, the true power of operational excellence lies in its ability to revolutionize your organization in ways that extend well beyond the bottom line. Think of it as structurally improving the Key Process Indicators (KPIs) and strategic imperatives that your business currently has (or perhaps doesn’t have!) such that the bar is raised across the board. Allow us to illustrate some examples of the benefits that await you:
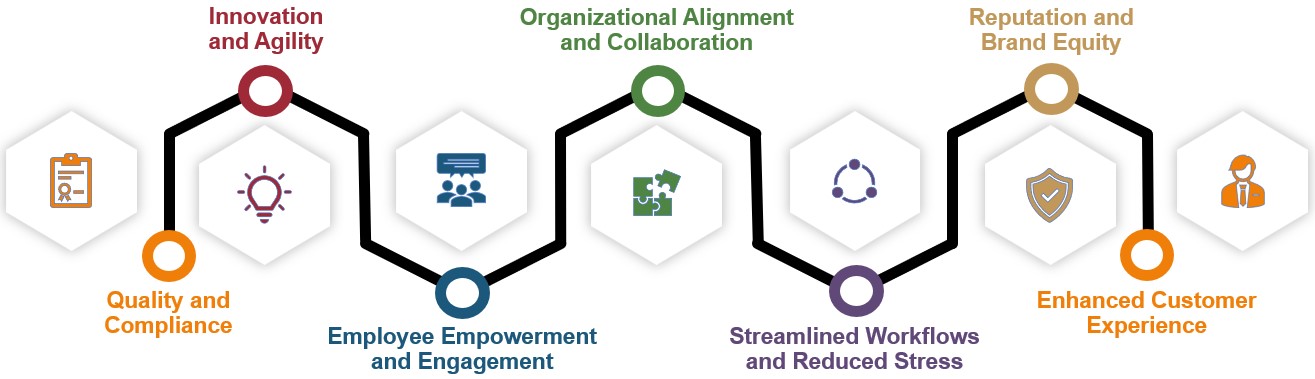
• Quality and Compliance: Operational excellence places a strong emphasis on quality control and regulatory compliance. By implementing rigorous standards, you’ll ensure that your products or services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations while adhering to industry regulations. Gain peace of mind knowing that your organization operates at the highest level of quality and integrity.
• Innovation and Agility: In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, adaptability is paramount. Operational excellence fosters a culture of innovation, encouraging your teams to seek creative solutions and embrace change. With newfound agility, your organization will be ready to seize opportunities, navigate challenges, and stay ahead of industry disruptions.
• Employee Empowerment and Engagement: Your employees are the lifeblood of your organization, and operational excellence empowers them to thrive. By equipping your teams with the tools and methodologies of excellence, you’ll foster a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and accountability. Experience increased employee engagement, higher job satisfaction, and reduced turnover, creating a work environment where everyone can unleash their full potential.
• Organizational Alignment and Collaboration: Operational excellence breaks down silos and promotes cross-functional collaboration. By aligning teams and departments around common goals, you’ll advance a sense of unity, cooperation, and shared purpose. Experience improved communication, streamlined decision-making, and a unified workforce working together toward a shared vision.
• Streamlined Workflows and Reduced Stress: Operational excellence eliminates bottlenecks, redundancies, and unnecessary complexities that burden your teams. Through process optimization and workflow standardization, you’ll streamline operations, reduce stress, and create a harmonious work environment. Expect improved collaboration, increased productivity, and a sense of clarity that allows your teams to focus on what truly matters.
• Reputation and Brand Equity: Exceptional operational performance leads to an outstanding reputation and a fortified brand. As your organization consistently delivers on its promises, customers recognize and appreciate your commitment to excellence. Your brand becomes synonymous with reliability, trust, and superior value, cementing your position as an industry leader.
• Enhanced Customer Experience: Operational excellence is the secret ingredient to crafting exceptional customer experiences. Optimizing your processes will streamline interactions, reduce errors, and deliver products and services with unparalleled quality and consistency. Witness as your customers become brand advocates, spreading the word about their outstanding experiences and propelling your business to new heights.
Now is the time to embrace a transformation that extends to and beyond financial gains. Investing in our Operational Excellence series of workshops will unlock the full potential of your organization. Witness the remarkable advantages that will revolutionize your customer experiences, empower your employees, and elevate your brand to new heights. Our Operational Excellence program is the transformative solution you’ve been yearning for, offering a multitude of advantages that will propel your business to unprecedented heights and revolutionize your bottom line.
By enrolling in our course, you will join the ranks of the most successful and financially astute business leaders. The knowledge and tools gained from our course will equip you with the strategic mindset and tactical acumen needed to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape. We provide you with the expertise and insights necessary to drive sustainable growth, achieve operational excellence, and secure your position as an industry leader.
Your journey to extraordinary success starts now! Enroll in our Operational Excellence program and embark on a transformative experience that will shape the future of your organization. Gain a competitive edge, unlock hidden opportunities, and exceed your expectations. Let us guide you toward operational excellence, where limitless possibilities await. Invest in your organization’s future today!
What is Operational Excellence?
Operational Excellence is more than just a buzzword—it’s a transformative approach to business that can revolutionize your organization’s performance. In practical terms, Operational Excellence means executing your business strategy with unparalleled effectiveness and consistency, surpassing your competition in key areas such as operational risk, operating costs, and customer satisfaction. It goes beyond being a one-time initiative or event and becomes an ingrained culture that permeates every aspect of your company. When Operational Excellence is achieved, every employee understands the core goals of the organization and how their work directly contributes to those goals.
From a philosophical standpoint, Operational Excellence represents a management ideology that places a strong emphasis on continuously improving an organization’s processes and systems to achieve better results. It involves identifying and eliminating waste, reducing variation, and enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of operations. At its core, Operational Excellence is about fostering a culture of continuous improvement that extends throughout the entire organization. It requires a relentless focus on meeting the needs and expectations of customers, along with a commitment to data-driven decision-making and problem-solving.
Operational Excellence is a versatile concept that can be applied to all facets of your organization’s operations, whether it’s manufacturing, supply chain management, customer service, or administrative functions. It takes a holistic approach, aiming to optimize the entire value stream rather than individual processes or functions in isolation.
There are several essential tools and techniques used in Operational Excellence, such as Lean, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management, and Value Stream Mapping. These methodologies provide structured approaches to identify and eliminate waste, reduce variability, and improve overall process performance.
Ultimately, the goal of Operational Excellence is to create an organization that is agile, efficient, and responsive to the ever-changing needs of customers and the market. By continuously enhancing processes and systems, your organization can achieve higher levels of performance, reduce costs, and gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
Why Operational Excellence?
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the importance of business agility and flexibility cannot be overstated. Operational Excellence empowers your organization to achieve more with the same staff through enhanced employee engagement and streamlined processes. It applies to any type of organization and industry, whether you’re producing tangible products or delivering intangible services. Operational Excellence is all about creating greater value for your external customers, regardless of who they are. Leading companies like Google, LinkedIn, Pandora, ENGIE, and Volvo continuously develop and evolve their Operational Excellence strategies to maintain their competitive edge.

By adopting a problem-solving mindset, fostering teamwork, and driving top-line growth, companies pursuing Operational Excellence create a culture of continuous improvement that generates additional value for customers. The drive to continuously improve creates the capacity for innovation and growth. It requires the management of operations in a systematic sense and a commitment to a culture of positivity that prioritizes customers’ needs and empowers staff. Empowered employees have a clear understanding of goals and plans, feel confident in taking initiative, and actively contribute to problem-solving efforts.
But why is all of this important? Let’s put it into perspective. Suppose your company operates in a market with a 30% profit margin. For every $1 worth of product you sell, $0.30 contributes to the bottom line. However, for every $1 you save through Operational Excellence efficiencies, the entire dollar goes directly to the bottom line. Consider this scenario: if your organization saves $1,500,000 through Operational Excellence, it’s equivalent to generating an additional $5 million in revenue. Think about the tremendous effort required to bring in $5 million in revenue through traditional means like sales and production. And that’s assuming everything was produced flawlessly the first time!
Operational Excellence provides you with a unique opportunity to maximize your bottom line by unlocking hidden potential within your organization. By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and enhancing efficiency, you can achieve significant cost savings
Impact of Operational Excellence
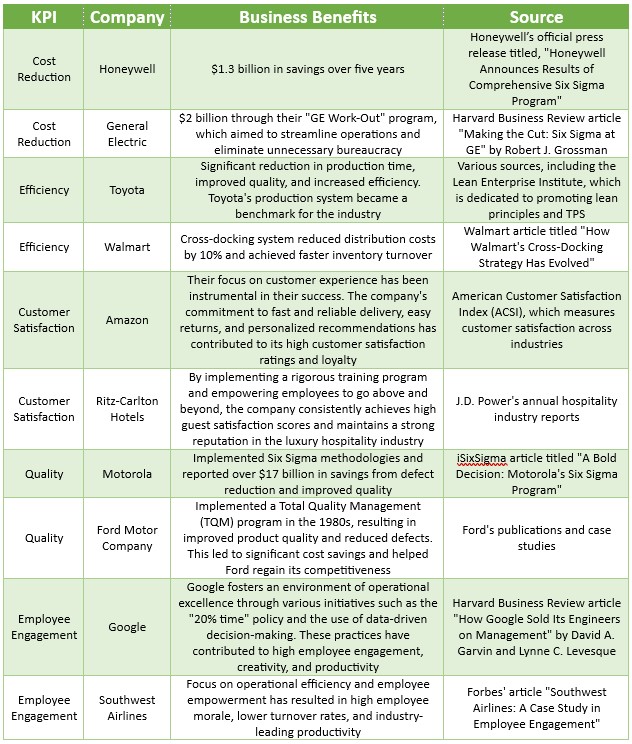
The case studies below highlight the real-world impact of Operational Excellence on various industries. By adopting and implementing the principles and methodologies associated with Operational Excellence, these companies have achieved significant improvements in efficiency, quality, customer satisfaction, and financial performance. Their success serves as evidence of the tangible benefits that Operational Excellence can bring to organizations across different sectors. The sources referenced will provide you with detailed information and case studies on how these companies implemented Operational Excellence principles and achieved positive impact.

Case Study 1: Toyota
Toyota is renowned for its implementation of Lean principles, which are central to Operational Excellence. By focusing on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and employee empowerment, Toyota has achieved remarkable results. For example, their production system, known as the Toyota Production System (TPS), has enabled them to minimize inventory, reduce defects, and improve overall efficiency. This has contributed to their reputation for high-quality vehicles, efficient operations, and sustained profitability.
Source: “The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World’s Greatest Manufacturer” by Jeffrey K. Liker. This book delves into the principles and practices of Toyota’s operational excellence and provides in-depth insights into its success.

Case Study 2: Amazon
Amazon has built its success on Operational Excellence principles, particularly in its fulfillment operations. Through meticulous process optimization, advanced automation, and data-driven decision-making, Amazon has transformed order fulfillment into a highly efficient and customer-centric operation. This has resulted in rapid delivery times, exceptional customer service, and a dominant position in the e-commerce industry.
Source: “The Everything Store: Jeff Bezos and the Age of Amazon” by Brad Stone provides an inside look at Amazon’s operations and their focus on customer-centricity and operational efficiency.

Case Study 3: General Electric (GE)
GE is a prime example of a company that has embraced Operational Excellence to drive performance improvements across its diverse portfolio of businesses. They have implemented Six Sigma methodologies to reduce defects and variations in their processes, resulting in significant cost savings, improved quality, and enhanced customer satisfaction. GE’s commitment to Operational Excellence has enabled them to stay competitive and maintain their position as a global leader in multiple industries.
Source: “Lean Six Sigma for Service: How to Use Lean Speed and Six Sigma Quality to Improve Services and Transactions” by Michael L. George discusses how GE implemented Lean Six Sigma methodologies and achieved significant improvements in their operational performance.

Case Study 4: Southwest Airlines
Southwest Airlines has consistently achieved operational excellence in the highly competitive airline industry. By focusing on efficiency, cost control, and customer satisfaction, Southwest has been able to maintain a low-cost business model while delivering exceptional service. Their commitment to operational efficiency, including quick aircraft turnarounds and optimized flight scheduling, has allowed them to achieve higher profitability compared to many of their competitors.
Source: “Nuts!: Southwest Airlines’ Crazy Recipe for Business and Personal Success” by Kevin Freiberg and Jackie Freiberg highlights Southwest Airlines’ unique culture and operational strategies that have made them successful.

Case Study 5: Procter & Gamble (P&G)
P&G is a multinational consumer goods company that has embraced Operational Excellence to improve its manufacturing and supply chain operations. By implementing Lean principles and optimizing their production processes, P&G has been able to reduce waste, increase productivity, and enhance product quality. These improvements have not only resulted in cost savings but also in shorter lead times and improved customer satisfaction.
Source: “The Lean Six Sigma Pocket Toolbook: A Quick Reference Guide to 100 Tools for Improving Quality and Speed” by Michael L. George, John Maxey, David Rowlands, and Mark Price provides insights into how P&G utilized Lean Six Sigma tools to improve their manufacturing and supply chain operations.
The table below summarises just some of the business benefits that a sample of well-known companies have achieved via the Operational Excellence journey:
History of Operational Excellence
Operational Excellence has a rich history that spans over a century, with roots in the early 20th century’s mass production techniques and the introduction of quality programs like Total Quality Management (TQM). Let’s delve into the fascinating journey of Operational Excellence and its evolution into a powerful approach that drives success in organizations worldwide.
The seeds of Operational Excellence were sown by automotive visionary Henry Ford in 1913 when he pioneered the first successful mass production techniques. Ford’s innovative assembly line revolutionized manufacturing, allowing for increased productivity, reduced costs, and greater efficiency. This marked a pivotal moment in the history of Operational Excellence, as it introduced the concept of streamlining processes and standardizing workflows for improved performance.
Building upon Ford’s breakthrough, Toyota took the reins in the 1930s and began developing the Toyota Production System (TPS). TPS, often hailed as the foundation for modern Operational Excellence practices, focused on two core principles: continuous improvement and waste elimination. By empowering employees to identify and address inefficiencies, Toyota achieved remarkable success in optimizing its operations and delivering superior value to customers.
During this time, W. Edwards Deming emerged as a prominent figure in the field of quality management. Deming expanded upon the principles of TPS and introduced the concept of Total Quality Management (TQM). TQM emphasized the importance of improving product quality and customer satisfaction through statistical methods and data-driven decision-making. Deming’s philosophy, encapsulated in his famous 14 Points for Management, highlighted the need for continuous improvement, employee involvement, and a focus on quality as a top organizational priority.
Deming’s work in Japan left an indelible mark on the development of TPS, which went on to shape modern Operational Excellence practices. The principles of TQM, with their emphasis on continuous improvement and statistical analysis, also influenced the evolution of other quality management systems, including the renowned Six Sigma methodology.
In the 1980s, Lean principles gained significant traction, thanks in part to the influential book “The Machine That Changed the World” by James P. Womack, Daniel T. Jones, and Daniel Roos. The book examined the practices of Japanese car manufacturers and introduced the term “Lean production” to describe their approach. Five core principles emerged from their observations: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection. These principles underscored the importance of creating value for customers, eliminating waste, and continually improving processes. While initially associated with manufacturing, Lean principles have since transcended industry boundaries and are now applied in diverse sectors worldwide.
In the 1990s, Motorola introduced Six Sigma as a powerful methodology for improving product quality by reducing defects. Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that focuses on identifying and eliminating the root causes of problems. By employing statistical tools and techniques, organizations can measure, analyze, and reduce process variability, ultimately achieving consistent and high-quality outcomes.
The combination of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies has become increasingly prevalent, with organizations leveraging their synergies to achieve Operational Excellence. This integrated approach allows for the elimination of waste, reduction of defects, and continuous improvement across all aspects of operations.
As you embark on your journey toward Operational Excellence, you are building upon a rich history of transformative practices that have shaped the success of renowned companies and revolutionized industries. By adopting the principles, methodologies, and mindsets that have stood the test of time, you are poised to unlock your organization’s full potential.

Operational Excellence Today
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, Operational Excellence has emerged as a key driver of success for organizations across industries. It is widely recognized as a transformative approach that enables companies to improve quality, increase efficiency, and reduce costs, ultimately paving the way for achieving sustainable competitive advantage.
Normally driven by the guiding principles of the Shingo model, Operational Excellence principles and practices have found their application in a diverse range of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and technology. While the specific methodologies and tools employed may vary, the fundamental principles of continuous improvement, waste reduction, and customer focus remain the bedrock of Operational Excellence. By fostering a culture of relentless improvement and embracing customer-centricity, organizations can enhance their operational performance and deliver exceptional value to their customers.
The digital revolution has ushered in a new era of Operational Excellence, offering unprecedented opportunities for organizations to leverage technology and automation. Cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, are revolutionizing the way businesses operate. Organizations are harnessing the power of automation to streamline processes, gather and analyze vast amounts of data, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging these technological advancements, organizations can gain valuable insights, optimize operations, and drive innovation, all while enhancing customer experiences.
Implementing Operational Excellence, however, comes with its share of challenges. It requires a dedicated investment of time, resources, and effort. Organizations must be prepared to initiate changes in their culture and leadership to align with the principles of Operational Excellence. This may involve fostering a mindset of continuous improvement, encouraging employee empowerment, and embracing a data-driven decision-making process. Sustaining Operational Excellence demands an unwavering commitment to continuous improvement, as well as the flexibility to adapt to evolving market dynamics and customer preferences.
Despite the challenges, Operational Excellence remains a compelling and transformative approach for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and generate value for their customers. By embarking on the journey of Operational Excellence, companies can foster a culture of innovation, agility, and excellence that transcends organizational boundaries. They can streamline processes, eliminate waste, and enhance operational efficiency, resulting in improved product quality, reduced costs, and heightened customer satisfaction.
As the business landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, Operational Excellence will continue to be a driving force for organizations. It will enable them to stay competitive in the face of disruptive forces, seize emerging opportunities, and adapt to changing customer needs and preferences. Embracing Operational Excellence as a strategic imperative empowers organizations to unlock their full potential, cultivate a culture of continuous improvement, and build a foundation for sustainable success in today’s dynamic and ever-evolving marketplace.
By partnering with our program on Operational Excellence, you can embark on a transformative journey that will empower your organization to embrace excellence, drive innovation, and achieve operational mastery. Our comprehensive approach, backed by proven methodologies and best practices, will equip your team with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the challenges, seize opportunities, and embark on a path of sustained growth and success. Together, we can shape the future of your organization and position it as a leader in Operational Excellence, driving unparalleled value and success in your industry.

Operational Excellence – Future Outlook
Operational Excellence is poised to play a pivotal role in the success of businesses well into the future as organizations strive to enhance the efficiency, effectiveness, and sustainability of their operations. As the business landscape continues to evolve rapidly, several key trends are expected to shape the future of Operational Excellence, revolutionizing the way it is practiced and unlocking new possibilities for organizations to excel.
One of the primary trends that will redefine Operational Excellence is the utilization of data and analytics to drive continuous improvement. The proliferation of digital technologies has led to an abundance of data, and organizations are increasingly leveraging advanced analytics tools to extract meaningful insights. By harnessing the power of data, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, uncover hidden opportunities for improvement, and make data-driven decisions that enhance performance and productivity.
Furthermore, sustainability is emerging as a crucial aspect of Operational Excellence. Organizations are recognizing that sustainable practices not only contribute to environmental stewardship but also drive long-term business success. By integrating sustainability considerations into their Operational Excellence strategies, companies can reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize their environmental footprint. This holistic approach not only aligns with the expectations of socially conscious consumers but also cultivates a positive brand image and enhances stakeholder value.
The increasing prevalence of automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) is set to revolutionize the landscape of Operational Excellence. Automation offers tremendous potential for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes. AI and ML technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, making accurate predictions and optimizing operations in real time. This intelligent decision-making capability empowers organizations to respond swiftly to changing market dynamics, identify patterns, and proactively address emerging challenges, thereby enhancing overall performance and delivering superior outcomes.
However, realizing the full potential of Operational Excellence in the future necessitates addressing several key challenges. Building a culture of continuous improvement is paramount. Organizations must foster an environment that encourages innovation, empowers employees to contribute ideas, and promotes a growth mindset. By nurturing a culture of learning and embracing change, organizations can continually adapt and evolve, remaining at the forefront of Operational Excellence.
Moreover, aligning Operational Excellence initiatives with broader business goals is crucial. Organizations must ensure that Operational Excellence strategies are tightly integrated into their overall business strategy, emphasizing the value it brings to customers, shareholders, and employees. By aligning goals and objectives, organizations can forge a cohesive and synergistic approach that propels them toward success.
Equipping employees with the necessary skills and tools is another critical consideration for the future of Operational Excellence. Organizations need to invest in developing the capabilities of their workforce, providing them with training and resources to thrive in an evolving landscape. By fostering a culture of learning and empowering employees with the right tools, organizations can cultivate a highly skilled and adaptable workforce that drives Operational Excellence and propels the organization toward its goals.
In summary, the outlook for Operational Excellence is highly promising, as organizations continue to seek innovative ways to optimize their operations and deliver exceptional value to customers. The increasing adoption of digital technologies, coupled with a growing emphasis on sustainability, will reshape the practice of Operational Excellence, propelling organizations to new heights of performance and success. By embracing these trends, addressing key challenges, and partnering with our program on Operational Excellence, organizations can position themselves as pioneers in their industries, ready to navigate the future with confidence and unlock their full potential. Together, we can embark on a transformative journey that drives sustainable growth, operational excellence, and unrivaled success.
Curriculum
Business Operational Excellence – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Building a Solid Foundation for Operational Excellence
- Part 1 Month 2 Strategic Alignment
- Part 1 Month 3 Leadership Behaviors
- Part 1 Month 4 Igniting Cultural Innovation
- Part 1 Month 5 Exceeding Customer Expectations
- Part 1 Month 6 Stimulating Employee Engagement
- Part 1 Month 7 Building High Reliability
- Part 1 Month 8 Achieving Continuous Improvement
- Part 1 Month 9 Value-Stream Mapping
- Part 1 Month 10 Workplace Organization
- Part 1 Month 11 Standard Work
- Part 1 Month 12 Measuring Operational Efficiency
- Part 1 Month 13 Define Phase
- Part 1 Month 14 Measure Phase
- Part 1 Month 15 Six Sigma Root Cause Analysis Tools
- Part 1 Month 16 Analyze Phase
- Part 1 Month 17 Improve Phase
- Part 1 Month 18 Control Phase
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Business Operational Excellence corporate training program.
Business Operational Excellence – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Building a Solid Foundation for Operational Excellence – In the first month, embark on a transformative journey as we lay the groundwork for your organization’s operational excellence. Discover a world of possibilities and gain an all-encompassing understanding of the fundamental principles that drive success.
- Part 1 Month 2 Strategic Alignment – In the second month, unlock the transformative potential of strategic alignment. We delve into the essential elements that bridge the gap between your organization’s strategy and its vision, mission, and values. Prepare to witness the harmonious symphony of your organization as all parts work synergistically toward a common goal.
- Part 1 Month 3 Leadership Behaviors – Welcome to the realm of extraordinary leadership. In the third month, embark on a transformational expedition to develop the knowledge, skills, and mindset required for effective leadership behaviors. Unleash the potential within yourself to inspire greatness and drive operational excellence.
- Part 1 Month 4 Igniting Cultural Innovation – Welcome to a world where innovation becomes ingrained in your organization’s DNA. In the fourth month, we embark on a cultural transformation journey to create an environment that fosters creativity, experimentation, and structured risk-taking. Unleash the power of innovation to drive your organization’s success.
- Part 1 Month 5 Exceeding Customer Expectations – In the fifth month, embark on a transformative exploration of customer-centricity. Discover how to exceed customer expectations, creating exceptional experiences that drive customer loyalty and satisfaction. Unlock the secrets of building lasting relationships with your customers.
- Part 1 Month 6 Stimulating Employee Engagement – In the sixth month, unlock the potential of employee engagement as a driving force for organizational success. Discover the power of an engaged workforce in fostering collaboration, motivation, and job satisfaction.
- Part 1 Month 7 Building High Reliability – In the seventh month, we shift our focus to building high reliability within your organization. This workshop empowers you with practical tools and techniques to identify and manage risks effectively, foster a culture of safety and reliability, and implement processes and systems that enhance organizational resilience.
- Part 1 Month 8 Achieving Continuous Improvement – The eighth month of our program is dedicated to achieving continuous improvement, which is the cornerstone of operational excellence. Equip yourself with the knowledge, skills, and mindset to identify improvement opportunities, develop and implement effective improvement plans, and sustain the gains achieved through continuous improvement efforts.
- Part 1 Month 9 Value-Stream Mapping – Welcome to the ninth month of our exciting Operational Excellence program, where we delve deep into the realm of Value Stream Mapping (VSM). This workshop aims to provide you with invaluable insights into your organization’s current value/revenue streams while identifying areas primed for improvement. Get ready to unlock a world of potential within your processes as we embark on this transformative journey together.
- Part 1 Month 10 Workplace Organization – As we step into the tenth month of our program, we venture into the realm of workplace organization, unlocking the secrets to creating a safe, organized, and highly efficient work environment. By embracing the renowned 5S methodology, we aim to revolutionize your workplace, fostering productivity, and elevating the quality of your operations to new heights. Brace yourself for a transformative journey that will leave a lasting impact on your organization.
- Part 1 Month 11 Standard Work – Welcome to the eleventh month of our dynamic Operational Excellence program, where we dive deep into the realm of standard work. By establishing and implementing standardized processes, we aim to unlock a world of cost reduction, enhanced safety, superior quality, and unparalleled customer service. Get ready to elevate your organization’s performance to new heights as we embark on this journey of standardization together.
- Part 1 Month 12 Measuring Operational Efficiency – In this 12th workshop, we equip you with the skills and knowledge to supercharge the efficiency of your equipment and processes. By honing your ability to calculate and optimize the Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE), you will unleash a new era of productivity, reduced downtime, and heightened customer satisfaction
- Part 1 Month 13 Define Phase – Embark on a transformative journey in our riveting 13th workshop as we unlock the secrets of problem-solving and root-cause analysis during the Define phase. Prepare to be captivated by a wealth of knowledge and skills that will empower you to tackle challenges head-on. Get ready to redefine your problem-solving capabilities, armed with practical tools and techniques that will revolutionize the way you approach problem definition and frame your path toward lasting solutions.
- Part 1 Month 14 Measure Phase – Welcome to an exhilarating exploration of the Measure phase in our captivating 14th workshop. Brace yourself as we unlock the secrets of data collection and measurement, unveiling their pivotal role in driving successful problem-solving initiatives. Equipped with practical tools and techniques, you’ll master the art of gathering relevant data, establishing baseline measurements, defining process metrics, and cultivating a structured approach that harmonizes seamlessly with the Measure phase of the esteemed DMAIC methodology.
- Part 1 Month 15 Six Sigma Root Cause Analysis Tools – Get ready to delve into the captivating world of Six Sigma root cause analysis tools in our awe-inspiring 15th workshop. Unlock the potential of these remarkable tools as we explore their practical applications in problem-solving. Prepare to be captivated by real-life examples and case studies that highlight their effectiveness in identifying and addressing root causes, empowering you to achieve remarkable results.
- Part 1 Month 16 Analyze Phase – Welcome to the transformative 16th workshop, where we delve into the Analyze phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis. Prepare to be captivated as we equip you with the knowledge and skills to analyze data effectively and identify root causes with precision. By mastering various root-cause analysis tools and techniques, you’ll develop a structured approach that will revolutionize your problem-solving capabilities.
- Part 1 Month 17 Improve Phase – Prepare to embark on an exhilarating journey through the Improve phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis in our captivating 17th workshop. This transformative session will equip you with the knowledge and skills to generate and evaluate potential solutions for the identified root causes. Discover practical tools and techniques that will empower you to develop and implement improvement actions effectively, as you pave the way for lasting organizational success.
- Part 1 Month 18 Control Phase – In our awe-inspiring 18th workshop, we cast the spotlight on the Control phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis. Prepare to be captivated as we unveil the secrets to sustaining improvements and maintaining control over your processes after implementing solutions. This session will equip you with practical tools and techniques to establish control measures, monitor ongoing performance, and cultivate a structured approach that ensures long-term success.
Methodology
Business Operational Excellence
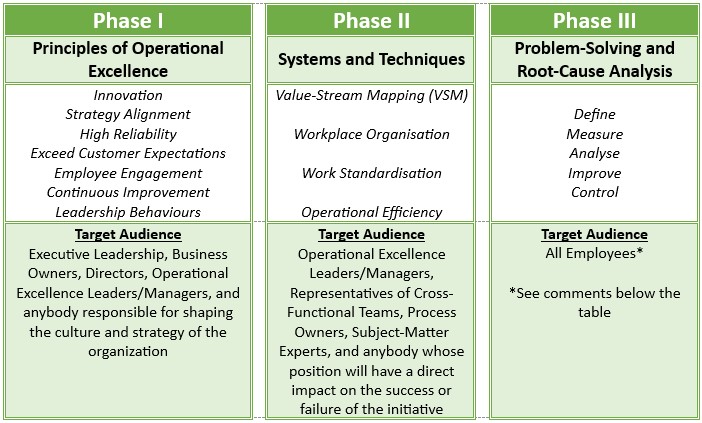
*While the ideal scenario is to have all employees developing competence in problem-solving and opportunity generation and development, the realities are:
(1) For most companies, taking all Employees offline for a day’s training is not a viable option.
(2) Not all front-line staff will engage in this initiative in the early stages.
Therefore, we propose that the workshops are used to train the Folks that will lead improvements on the ground (e.g. CI Teams, Engineers, Line Supervisors, Key Opinion Leaders, etc). These Folks should have the influence and drive to impart the learned tools and techniques to others over a period of time, eventually developing the entire organization.
Achieving Operational Excellence is a transformative journey that requires the active participation and engagement of every individual within an organization. At its core, Operational Excellence empowers employees at all levels, from the top executives to the dedicated plant floor workers, to visualize the seamless flow of value to customers and proactively address any disruptions before they occur. By embracing this holistic approach, organizations can promote a culture of accountability, problem-solving, and continuous improvement, ultimately propelling themselves toward unrivaled success.
At our program on Operational Excellence, we believe in empowering employees to take ownership of their areas of responsibility. This begins with ensuring that product and information flow within their domain is visible and transparent. By providing employees with the necessary tools and systems, we enable them to gain a comprehensive understanding of how value is created, delivered, and received by the customer. Through this enhanced visibility, employees can quickly identify any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or deviations from the desired flow, enabling them to take immediate action to rectify the situation.
Crucially, Operational Excellence also emphasizes the importance of empowering employees to solve problems and capitalize on opportunities independently. Rather than relying on a hierarchical system that necessitates escalating every issue to management, our approach encourages individuals to exercise their critical thinking skills, tap into their expertise, and collaborate with colleagues to drive meaningful change. This empowerment not only accelerates problem-solving but also fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, as employees become agents of positive change within their respective roles.
By redistributing the responsibility for performance across the organization, Operational Excellence liberates senior management from the burdensome task of individually solving every problem. This allows leaders to focus on their ultimate accountabilities, such as shaping the organizational culture, developing strategic initiatives, and driving innovation. By leveraging their expertise and vision, senior management can create an environment that nurtures continuous improvement, promotes collaboration, and aligns the entire organization toward a common purpose.
To achieve Operational Excellence, organizations must embrace a comprehensive approach that encompasses various dimensions. This includes establishing robust performance measurement systems, setting clear goals and objectives, supporting open and transparent communication channels, and investing in the development of employees’ skills and capabilities. Our program on Operational Excellence dives deep into these critical aspects, providing participants with practical tools, strategies, and frameworks to achieve transformative results.
Through our program, participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of the principles and methodologies that underpin Operational Excellence. They will learn how to create a culture of continuous improvement, where innovation and problem-solving thrive. We will explore proven techniques for identifying waste, reducing variation, and optimizing processes to enhance efficiency and productivity. Participants will also delve into the importance of data-driven decision-making, leveraging advanced analytics to gain insights and drive performance improvements.
Moreover, our program will guide participants in developing leadership skills that are essential for driving Operational Excellence. We will explore the role of leaders in creating a supportive and empowering environment, where employees are motivated to contribute their best efforts and ideas. Participants will learn how to effectively communicate the vision and goals of Operational Excellence, inspire teams, and build strong cross-functional collaborations that drive sustainable change.
At the conclusion of our program, participants will be equipped with the knowledge, skills, and strategies to embark on their Operational Excellence journey. They will be empowered to champion a culture of continuous improvement, where everyone is engaged, accountable, and motivated to deliver exceptional value to customers. By embracing Operational Excellence, organizations can optimize their operations, exceed customer expectations, outperform competitors, and achieve sustainable growth.
Join us on this transformative path toward Operational Excellence, where your organization can unlock its full potential, foster a culture of innovation, and achieve unparalleled success. Together, we will navigate the intricacies of Operational Excellence, harness the power of collaboration, and propel your organization toward a future of operational brilliance.

Operational Excellence Training Program – Macroscopic View
Embarking on the journey toward Operational Excellence can indeed feel daunting, especially for organizations taking their first steps. The complexities and challenges involved may leave you wondering where to begin. That’s why our comprehensive training program is designed to provide you with a clear roadmap, empowering individuals, teams, and organizations to identify, analyze, and improve their operational processes. Whether you’re a business owner, manager, or aspiring professional, our course will unlock the secrets to achieving operational excellence across various industries.
What sets our training apart is the calibre of expertise you’ll gain access to. Our course is crafted by industry experts who possess extensive hands-on experience in operational excellence. They have successfully transformed organizations, and now they’re ready to share their knowledge and strategies with you. By learning from the best, you’ll gain valuable insights and proven methodologies directly from professionals who have navigated the operational excellence journey themselves.
We firmly believe in a practical approach to learning. Our training goes beyond theory and provides you with hands-on experiences that allow you to apply the concepts you learn. Through practical exercises, real-life case studies, and interactive simulations, you’ll develop a deep understanding of operational excellence principles and acquire the skills to implement them in your organization. You’ll leave the course equipped with actionable solutions that are tailored to your specific business needs, ready to drive meaningful change.
Our comprehensive curriculum covers a wide range of topics essential to operational excellence. From process mapping and optimization to Lean Six Sigma methodologies and change management, our course leaves no stone unturned. We guide you through the entire journey, ensuring you gain a holistic understanding of the key components and strategies necessary for achieving sustainable improvements. You’ll emerge from the program equipped with a robust toolkit to address challenges, optimize processes, and drive operational excellence within your organization.
Flexibility and convenience are key considerations in our program design. We understand the demands of your busy schedule, which is why our course is delivered online, allowing you to access the content anytime, anywhere. Progress at your own pace, engaging with the materials, participating in discussion forums, and interacting with fellow participants whenever it suits you best. This flexibility ensures that your learning experience is tailored to your individual needs, empowering you to make the most of your educational journey.
Learning doesn’t stop with the completion of the course. When you enroll in this program, you gain access to a vibrant community of like-minded professionals who are passionate about operational excellence. This network provides ongoing support and a platform for knowledge exchange and collaboration. Additionally, we offer valuable post-course resources to further enhance your learning and support your long-term success in driving operational excellence within your organization.
Operational excellence is not a luxury; it is a necessity for any organization aiming to thrive in today’s dynamic business environment. Don’t miss this opportunity to unlock your organization’s full potential and become a catalyst for growth and innovation. Enroll in the Business Operational Excellence course today and embark on a transformative journey toward operational excellence. Together, let’s build a future of efficiency, profitability, and sustained success. Your organization deserves nothing less.

Phase I
Month 1 (1st Workshop): Building a Solid Foundation for Operational Excellence
In the first month, embark on a transformative journey as we lay the groundwork for your organization’s operational excellence. Discover a world of possibilities and gain an all-encompassing understanding of the fundamental principles that drive success. Topics explored include:
• Unleashing the Power of Operational Excellence:
– Uncover the secrets behind operational excellence and witness its profound impact on organizations. Delve into the seven guiding principles that form the bedrock of this approach. Learn how continuous improvement, waste elimination, and customer focus pave the way to unprecedented achievements.
• Cultivating a Culture of Excellence:
– Leadership plays a pivotal role in fostering operational excellence. Explore the art of effective leadership and its potential to shape organizational culture. Discover the transformative influence of employee engagement and aligning values and goals. Unleash the power of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies to optimize processes and pave the path to operational excellence.
• Measuring Success:
– In the pursuit of excellence, measurement is key. Understand the significance of performance metrics in identifying improvement areas and gauging progress. Unveil the secrets of developing robust measurement frameworks that drive accountability and continuous improvement. Prepare to embark on a voyage where data becomes your guiding star.
• Forging the Path to Excellence:
– A roadmap to success awaits. Learn how to develop a strategic implementation plan that breathes life into your aspirations. Gain insights into overcoming obstacles and leveraging opportunities. Harness the power of visionary thinking and effective planning to propel your organization toward operational excellence.

Month 2 (2nd Workshop): Strategic Alignment: Uniting Vision and Action
In the second month, unlock the transformative potential of strategic alignment. We delve into the essential elements that bridge the gap between your organization’s strategy and its vision, mission, and values. Prepare to witness the harmonious symphony of your organization as all parts work synergistically toward a common goal. Topics covered include:
• Unveiling the Power of Strategy Alignment:
– Strategy alignment is the secret sauce that propels organizations toward greatness. Discover the art of aligning strategy with vision, mission, and values. Witness the profound impact of congruence on organizational success. Immerse yourself in the world of strategy alignment, where a unified direction becomes the cornerstone of achievement.
• Elements of an Effective Strategy:
– Explore the key components of a robust strategy. Understand the significance of vision, mission, and values as the building blocks of your organization’s success. Master the art of developing a strategy alignment plan that creates coherence and unity throughout the organization. Witness how strategic clarity sparks unparalleled momentum.
• Aligning Individual Goals:
– A symphony of unified goals creates a resounding impact. Learn how to align individual aspirations with the overarching strategy. Discover the magic of synchronizing performance metrics and objectives across all levels of your organization. Witness the power of individual contributions harmonizing to create an unstoppable force.
• Communication Channels that Ignite Understanding:
– The clarity of your strategy hinges on effective communication. Explore strategies that ignite understanding and enable seamless dissemination of your organization’s direction. Learn to craft compelling messages that resonate with your teams. Discover the transformative power of transparent and engaging communication channels.

Month 3 (3rd Workshop): Leadership Behaviors: Guiding the Journey to Excellence
Welcome to the realm of extraordinary leadership. In the third month, embark on a transformational expedition to develop the knowledge, skills, and mindset required for effective leadership behaviors. Unleash the potential within yourself to inspire greatness and drive operational excellence. Topics covered include:
• The Art of Inspiring Excellence:
– Leadership is the catalyst that propels organizations to extraordinary heights. Unveil the pivotal role of effective leadership behaviors in driving operational excellence. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and learning. Harness the power of transformative leadership to create an environment where excellence flourishes.
• Mastering the Leadership Craft:
– Unleash your leadership potential as you delve into the intricacies of effective leadership behaviors. Discover the art of building high-performing teams that align with your organization’s values and goals. Acquire the skills to drive operational excellence through impactful communication, problem-solving, and decision-making. Embrace the power of accountability, ownership, and empowerment to inspire individual and team performance.
• Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
– Witness the transformational power of a culture that embraces continuous improvement. Learn how to foster innovation, creativity, and a thirst for learning within your organization. Discover strategies to encourage and nurture a mindset of problem-solving and critical thinking. Empower your teams to embrace change and drive operational excellence through adaptive leadership.
• Effective Communication for Impactful Leadership:
– Communication lies at the heart of effective leadership. Unlock the secrets of influential communication that inspires and engages your teams. Learn to craft compelling messages that motivate and align individuals with the organization’s vision. Embrace active listening and feedback techniques that promote collaboration and understanding. Witness the profound impact of clear and concise communication on driving operational excellence.
• Driving Excellence Through Problem-Solving:
– Problems are the stepping stones to excellence. Embrace the art of problem-solving and root-cause analysis as essential tools in your journey to operational excellence. Discover methodologies such as Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) and their application in identifying and addressing operational challenges. Empower your teams to become problem-solving champions and unleash their potential to drive continuous improvement.
• Empowering Through Decision-Making:
– Leadership is defined by the decisions we make. Learn the art of effective decision-making that balances analysis, intuition, and risk management. Explore decision-making frameworks that stimulate strategic thinking and agility. Develop the confidence to make tough decisions that drive organizational excellence. Witness the transformative impact of empowered decision-makers on your organization’s success.

Month 4 (4th Workshop): Igniting Cultural Innovation
Welcome to a world where innovation becomes ingrained in your organization’s DNA. In the fourth month, we embark on a cultural transformation journey to create an environment that fosters creativity, experimentation, and structured risk-taking. Unleash the power of innovation to drive your organization’s success. Topics covered include:
• Unleashing the Innovative Spirit:
– Embrace the importance of cultural innovation in driving organizational success. Discover how to create a culture that celebrates and rewards innovation. Unlock the power of leadership, employee engagement, and alignment with organizational values and goals to unleash the full potential of your teams. Witness how an innovative culture becomes the catalyst for unprecedented achievements.
• Creating an Environment of Creativity:
– Nurture the seeds of creativity within your organization. Learn how to create an environment that encourages free thinking, out-of-the-box ideas, and unconventional approaches. Embrace the power of diversity, inclusivity, and collaboration to ignite the creative spark. Foster a culture where every individual feels empowered to contribute their unique perspectives.
• Embracing Experimentation and Risk-Taking:
– Innovation thrives on experimentation and calculated risk-taking. Explore strategies to create a safe space for experimentation within your organization. Learn how to manage and mitigate risks while fostering a culture that encourages learning from failures. Discover the transformative power of embracing calculated risks as a catalyst for innovation and growth.
• Cultivating Collaboration and Inclusivity:
– Collaboration fuels innovation. Learn how to nurture a culture of collaboration and inclusivity, where ideas are freely shared, and teams work together toward common goals. Embrace the power of diverse perspectives and multidisciplinary teams. Witness the remarkable results that emerge when individuals collaborate, leverage their strengths, and collectively drive innovation.
• Aligning Innovation with Strategy:
– Innovation without direction is aimless. Explore the art of aligning innovation initiatives with strategic goals. Learn how to develop an innovation roadmap that aligns with your organization’s vision and mission. Uncover strategies to identify innovation opportunities that drive competitive advantage and sustainable growth. Witness the transformative impact of aligning innovation with your strategic aspirations.
• Harnessing Technology for Innovation:
– Technology has become an indispensable catalyst for innovation. Discover how to leverage emerging technologies to fuel your organization’s innovative endeavors. Explore the potential of automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics in driving breakthrough innovations. Embrace the power of digital transformation as a gateway to unlocking new possibilities.
• Nurturing a Culture of Rapid Prototyping:
– Prototyping is the language of innovation. Gain insights into rapid prototyping methodologies and techniques that accelerate the innovation cycle. Learn how to create an environment that encourages experimentation, rapid iteration, and learning from failures. Witness the power of prototyping as a means to validate ideas, gather feedback, and drive continuous improvement.
• Embracing Design Thinking:
– Design thinking is a powerful tool for innovation. Explore the principles of human-centered design and empathy-driven problem-solving. Learn how to apply design thinking methodologies to uncover deep customer insights, identify unmet needs, and create remarkable experiences. Witness the transformative impact of design thinking in driving customer satisfaction and organizational success.
• Sustaining an Innovation Ecosystem:
– Innovation is not a one-time event; it is an ongoing journey. Discover strategies to sustain an innovation ecosystem within your organization. Learn how to create structures, processes, and incentives that facilitate a continuous flow of innovative ideas. Explore the role of innovation champions and cross-functional collaboration in nurturing an environment where innovation thrives.

Month 5 (5th Workshop): Exceeding Customer Expectations
In the fifth month, embark on a transformative exploration of customer-centricity. Discover how to exceed customer expectations, creating exceptional experiences that drive customer loyalty and satisfaction. Unlock the secrets of building lasting relationships with your customers. Topics covered include:
• The Power of Customer-Centricity:
– Customers are at the heart of operational excellence. Embrace the significance of exceeding customer expectations in driving loyalty and satisfaction. Understand the profound impact of customer-centricity on your organization’s success. Explore the art of creating customer experiences that resonate and sustain long-term relationships.
• Unveiling Customer Needs:
– Gain deep insights into your customers’ needs and desires. Learn how to conduct effective research and surveys, and gather feedback to understand their expectations. Discover the power of empathy in uncovering hidden customer pain points and aspirations. Unleash the potential of customer insights as a catalyst for innovation and continuous improvement.
• Crafting Exceptional Communication Strategies:
– Communication is the cornerstone of exceptional customer experiences. Explore strategies to create effective communication channels that make customers feel valued and heard. Learn the art of crafting compelling messages that resonate with your customers. Discover the power of active listening and responsive communication in building trust and fostering loyalty.
• Delivering Unparalleled Quality:
– Quality is the foundation of exceptional customer experiences. Learn how to deliver products and services that consistently meet and exceed customer expectations. Uncover the secrets of quality management systems, process optimization, and error-proofing techniques. Witness the transformative impact of a culture that prioritizes quality and continuous improvement.
• Nurturing Customer-Centric Culture:
– Customer-centricity begins within. Explore strategies to create a culture that prioritizes customer satisfaction and loyalty. Learn how to align your organization’s values and behaviors with a customer-centric mindset. Discover the power of empowered employees who embrace customer focus as a core principle. Witness the profound impact of a customer-centric culture on driving operational excellence.

Month 6 (6th Workshop): Stimulating Employee Engagement
In the sixth month, unlock the potential of employee engagement as a driving force for organizational success. Discover the power of an engaged workforce in fostering collaboration, motivation, and job satisfaction. Topics covered include:
• Recognizing the Significance of Employee Engagement:
– Employee engagement is the cornerstone of operational excellence. Understand the profound impact of engaged employees on productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Explore the link between employee engagement and organizational success. Discover the key drivers of employee engagement and the role of leadership in creating an engaging work environment.
• Creating a Culture of Open Communication:
– Effective communication is the lifeblood of employee engagement. Learn how to develop communication strategies that promote transparency, collaboration, and trust. Discover the power of active listening and feedback in creating an inclusive and supportive work culture. Explore techniques for fostering open dialogue and breaking down communication barriers across all levels of the organization.
• Building a Recognition and Feedback Culture:
– Recognition and feedback are powerful tools for engaging employees. Discover the art of providing meaningful recognition that celebrates achievements and reinforces desired behaviors. Learn how to provide constructive feedback that inspires growth and development. Uncover strategies for creating a culture where recognition and feedback are embedded in daily interactions, enhancing motivation and job satisfaction.
• Empowering Employees through Autonomy:
– Autonomy is a catalyst for employee engagement. Explore strategies for empowering employees and fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. Learn how to delegate authority and decision-making, allowing individuals to take ownership of their work. Discover the transformative impact of giving employees the freedom to innovate, make decisions, and contribute their unique talents.
• Developing Career Development Frameworks:
– Career development is a powerful driver of employee engagement. Learn how to create a framework that supports employee growth, learning, and advancement. Explore strategies for providing opportunities for skill development, job enrichment, and career progression. Discover the impact of aligning individual aspirations with organizational goals, creating a win-win environment.

Month 7 (7th Workshop): Building High Reliability
In the seventh month, we shift our focus to building high reliability within your organization. This workshop empowers you with practical tools and techniques to identify and manage risks effectively, foster a culture of safety and reliability, and implement processes and systems that enhance organizational resilience. Explore the following key topics:
• Recognizing the Imperative of High Reliability:
– Understand why high reliability is vital for ensuring the long-term resilience and sustainability of your organization. Discover how organizations that prioritize reliability outperform their competitors, gain a reputation for excellence, and build trust among stakeholders. Explore real-life examples and case studies that highlight the benefits of investing in high reliability.
• Effective Risk Assessment and Management:
– Learn how to identify and manage risks proactively to safeguard your organization’s operations and reputation. Gain insights into robust risk assessment methodologies that help you anticipate potential pitfalls and develop effective mitigation strategies. Explore techniques for evaluating risks, prioritizing actions, and monitoring their effectiveness. Discover how risk management contributes to overall organizational resilience.
• Cultivating a Culture of Safety and Continuous Improvement:
– Building a culture that prioritizes safety, learning, and continuous improvement is paramount for achieving high reliability. Explore strategies for creating an environment where everyone is committed to safety and continuously seeks opportunities for improvement. Learn how to engage employees at all levels, promote a mindset of accountability, and encourage open communication for reporting near misses and potential hazards.
• Implementing Processes and Systems for Organizational Resilience:
– Discover the power of standardization and automation in enhancing organizational resilience. Explore methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, and ISO standards that drive efficiency, reduce variability, and ensure consistency across operations. Learn how to design and implement robust processes and systems that support reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction. Gain insights into best practices and success stories from organizations that have achieved remarkable results through these approaches.
• Building Leadership and Team Capabilities for High Reliability:
– Leadership and teamwork are crucial elements in fostering high reliability. Explore strategies for developing leaders who champion safety, facilitate effective communication, and inspire a culture of continuous improvement. Learn how to enhance decision-making skills, promote problem-solving capabilities, and cultivate a resilient and cohesive team environment. Discover the importance of ongoing training and coaching to nurture the skills necessary for high reliability.

Month 8 (8th Workshop): Achieving Continuous Improvement
The eighth month of our program is dedicated to achieving continuous improvement, which is the cornerstone of operational excellence. Equip yourself with the knowledge, skills, and mindset to identify improvement opportunities, develop and implement effective improvement plans, and sustain the gains achieved through continuous improvement efforts. Explore the following key topics:
• Understanding the Critical Role of Continuous Improvement:
– Uncover the pivotal role that continuous improvement plays in achieving operational excellence. Discover how it drives organizational success, enhances customer satisfaction, and positions your business as a leader in the industry. We’ll delve into inspiring case studies and success stories of companies that have embraced continuous improvement as a core strategy, showcasing the remarkable transformations they achieved.
• Identifying Improvement Opportunities through Comprehensive Analysis:
– Equip yourself with powerful tools and techniques to identify improvement opportunities within your organization. We’ll dive deep into process analysis, data analysis, and stakeholder feedback to uncover areas with the greatest potential for enhancement. By analyzing the end-to-end value stream, we’ll discover bottlenecks, waste, and inefficiencies that hinder performance. You’ll learn how to harness the power of data and feedback to make informed decisions and drive meaningful change.
• Developing Effective Improvement Plans:
– Crafting improvement plans that deliver tangible results is crucial for operational excellence. We’ll guide you through the process of developing improvement plans that are data-driven, structured, and aligned with your organization’s goals and values. Learn how to set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) improvement goals, establish key performance indicators, and develop a roadmap for implementation. By incorporating methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, and the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle, you’ll design improvement initiatives that address root causes and ensure sustainable change.
• Implementing Improvement Plans for Lasting Impact:
– Successful implementation is the key to turning improvement plans into reality. In this module, we’ll explore effective project management, change management, and stakeholder engagement techniques to facilitate smooth implementation. Discover how to navigate potential challenges, overcome resistance to change, and gain buy-in from all levels of the organization. We’ll empower you with the tools and strategies needed to execute improvement initiatives with precision and agility.
• Sustaining the Gains through Robust Monitoring and Feedback Mechanisms:
– To achieve long-term success, sustaining the gains achieved through continuous improvement efforts is vital. We’ll equip you with robust monitoring, measurement, and feedback mechanisms to ensure that progress is tracked, performance is optimized, and improvements endure. Learn how to establish a culture of accountability, create effective dashboards and scorecards, and leverage feedback loops to drive continuous learning and refinement.

Phase II
Month 9 (9th Workshop): Value-Stream Mapping
Welcome to the ninth month of our exciting Operational Excellence program, where we delve deep into the realm of Value Stream Mapping (VSM). This workshop aims to provide you with invaluable insights into your organization’s current value/revenue streams while identifying areas primed for improvement. Get ready to unlock a world of potential within your processes as we embark on this transformative journey together. Objectives:
• Empower participants to analyze and optimize their processes by distinguishing value-added and non-value-added activities.
• Enable participants to identify areas for improvement, implement streamlined processes, enhance efficiencies, and drive down costs.
Topics covered include:
• Unveiling the Principles of Value Stream Mapping (VSM):
– Discover the core principles and concepts that underpin the power of VSM, laying the foundation for effective value-driven change.
• Identifying and Defining the Value Stream:
– Gain a comprehensive understanding of your value stream and its impact on your processes, facilitating targeted improvements.
• Mapping the Current State of the Value Stream:
– Uncover the intricate flow of materials, information, and work activity within your value stream, illuminating potential areas for optimization.
• Distinguishing Value-Added and Non-Value-Added Activities:
– Sharpen your ability to discern the activities that add true value and those that are mere wastes of resources, time, and effort.
• Analyzing the Current State Map:
– Learn to extract invaluable insights from the current state map, identifying untapped opportunities for advancement.
• Crafting the Future/Ideal State Map:
– Develop a visionary map that integrates the improvements identified during the analysis, outlining the path to your ideal state.
• Creating an Action Plan for Implementation:
– Transcend theory and translate your aspirations into action as you build a robust plan for executing the future state map.
• Monitoring and Measuring Effectiveness:
– Harness the power of measurement and tracking to ensure the efficacy of your implemented improvements, maintaining a cycle of continuous enhancement.

Month 10 (10th Workshop): Workplace Organization
As we step into the tenth month of our program, we venture into the realm of workplace organization, unlocking the secrets to creating a safe, organized, and highly efficient work environment. By embracing the renowned 5S methodology, we aim to revolutionize your workplace, fostering productivity, and elevating the quality of your operations to new heights. Brace yourself for a transformative journey that will leave a lasting impact on your organization. Objectives:
• Empower participants to enhance their processes by optimizing workplace organization, minimizing waste, and maximizing efficiency.
• Equip participants with the skills and knowledge necessary to implement the 5S methodology seamlessly in their workplace.
Topics covered include:
• Unveiling the Principles of Workplace Organization:
– Discover the fundamental principles underlying an impeccably organized workspace, replete with benefits such as enhanced safety, superior quality, and reduced costs.
• Embracing the Power of a Well-Organized Workplace:
– Unearth the myriad advantages that await those who embrace workplace organization, paving the way for excellence and success.
• Mastering the Five Steps of the 5S Methodology:
– Dive into the transformative steps of Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain, witnessing the metamorphosis of your workplace.
• Crafting a Tailored 5S Implementation Plan:
– Tailor the 5S methodology to suit your unique organizational needs, fostering a sustainable and efficient environment.
• Harnessing the Power of Visual Controls:
– Harness the visual cues and indicators that promote a harmonious and streamlined workplace, elevating your operations to new levels of effectiveness.
• Establishing Sustainable Methods and Procedures:
– Cement your commitment to continuous improvement by establishing robust procedures and practices that ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your newly organized workplace.
• Measuring and Monitoring for Continuous Improvement:
– Embrace the power of measurement and monitoring to gauge the effectiveness of your 5S program, allowing for ongoing refinement and sustainable progress.

Month 11 (11th Workshop): Standard Work
Welcome to the eleventh month of our dynamic Operational Excellence program, where we dive deep into the realm of standard work. By establishing and implementing standardized processes, we aim to unlock a world of cost reduction, enhanced safety, superior quality, and unparalleled customer service. Get ready to elevate your organization’s performance to new heights as we embark on this journey of standardization together. Objectives:
• Assist participants in establishing a baseline for work processes, ensuring consistency and reliability in their execution.
• Empower participants to cultivate a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating their standard work processes.
Topics covered include:
• Unveiling the Principles of Standard Work:
– Discover the guiding principles that underpin the transformative potential of standard work, setting the stage for operational excellence.
• Unleashing the Benefits of Standard Work:
– Explore the multifaceted advantages that standard work offers, ranging from improved safety and quality to substantial cost reductions.
• Understanding the Components of Standard Work:
– Delve into the crucial components that define standard work, including clear work instructions, designated tools, and established work sequences.
• Developing Standard Work Processes:
– Acquire the skills to develop meticulous and efficient standard work processes for specific tasks or workflows, fostering consistency and reliability.
• Establishing Procedures for Maintenance and Improvement:
– Cement the foundation for continuous enhancement by establishing robust procedures to maintain and refine standard work processes.
• Nurturing a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
– Foster a mindset of continuous improvement within your organization by actively reviewing, updating, and refining standard work processes.
• Measuring and Monitoring for Sustainable Progress:
– Embrace the power of measurement and monitoring to assess the effectiveness of your standard work processes, driving sustained growth and evolution.

Month 12 (12th Workshop): Measuring Operational Efficiency
In this 12th workshop, we equip you with the skills and knowledge to supercharge the efficiency of your equipment and processes. By honing your ability to calculate and optimize the Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE), you will unleash a new era of productivity, reduced downtime, and heightened customer satisfaction. Objectives:
• Help participants grasp the calculation of Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) for their equipment and processes.
• Demonstrate how monitoring OEE serves as a catalyst for identifying improvement opportunities and nurturing a culture of continuous improvement.
Topics covered include:
• Unveiling the Principles of Overall Equipment Efficiency:
– Gain a comprehensive understanding of the core principles underlying the calculation and enhancement of OEE, unlocking the keys to operational excellence.
• Embracing the Components of OEE:
– Explore the crucial components of OEE: availability, performance, and quality, understanding how each contributes to operational efficiency.
• Calculating OEE and Identifying Improvement Areas:
– Master the art of calculating OEE for your equipment and processes, unveiling valuable insights and pinpointing areas primed for improvement.
• Crafting an OEE Improvement Plan:
– Develop a strategic plan to improve OEE, including identifying and eliminating the root causes of downtime and reducing setup.
• Nurturing a Culture of OEE Excellence:
– Cultivate a culture that prioritizes and celebrates OEE excellence, fostering a collaborative environment focused on sustained efficiency gains.
• Measuring and Monitoring for Continuous Improvement:
– Harness the power of measurement and monitoring to track the effectiveness of your OEE improvements, ensuring a trajectory of ongoing enhancement and customer satisfaction.

Phase III
Month 13 (13th Workshop): Problem-Solving and Root-Cause Analysis – Define Phase
Embark on a transformative journey in our riveting 13th workshop as we unlock the secrets of problem-solving and root-cause analysis during the Define phase. Prepare to be captivated by a wealth of knowledge and skills that will empower you to tackle challenges head-on. Get ready to redefine your problem-solving capabilities, armed with practical tools and techniques that will revolutionize the way you approach problem definition and frame your path toward lasting solutions.
Topics Covered:
• The significance of the Define phase in problem-solving and root-cause analysis
• Crafting precise problem statements that bridge the gap between the current and desired state
• Establishing crystal-clear objectives and measurement criteria to drive effective problem-solving
• Harnessing the power of tools such as problem statements, project charters, and stakeholder analysis to define problem boundaries and project scope
• Developing a comprehensive project plan that identifies team members, defines roles and responsibilities, and sets the stage for success

Month 14 (14th Workshop): Problem-Solving and Root-Cause Analysis – Measure Phase
Welcome to an exhilarating exploration of the Measure phase in our captivating 14th workshop. Brace yourself as we unlock the secrets of data collection and measurement, unveiling their pivotal role in driving successful problem-solving initiatives. Equipped with practical tools and techniques, you’ll master the art of gathering relevant data, establishing baseline measurements, defining process metrics, and cultivating a structured approach that harmonizes seamlessly with the Measure phase of the esteemed DMAIC methodology.
Topics Covered:
• Illuminating the transformative power of data collection and measurement in effective problem-solving
• Identifying and collecting diverse sources of data, encompassing both quantitative and qualitative aspects
• Establishing baseline measurements and process metrics to gain valuable insights into the magnitude and impact of the problem
• Embracing indispensable tools such as data collection plans, check sheets, and data validation techniques for systematic analysis
• Unveiling patterns, trends, and potential root causes hidden beneath the surface of data analysis

Month 15 (15th Workshop): Six Sigma Root Cause Analysis Tools
Get ready to delve into the captivating world of Six Sigma root cause analysis tools in our awe-inspiring 15th workshop. Unlock the potential of these remarkable tools as we explore their practical applications in problem-solving. Prepare to be captivated by real-life examples and case studies that highlight their effectiveness in identifying and addressing root causes, empowering you to achieve remarkable results.
Topics Covered:
• Introduction to common Six Sigma root cause analysis tools that drive breakthrough problem-solving
• Embracing the 6M (Man, Machine, Material, Method, Measurement, Mother Nature) framework for comprehensive root cause analysis
• Uncovering deeper causes of problems through the application of the 5-Why analysis technique
• Visualizing potential root causes using dynamic fishbone diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams)
• Prioritizing potential root causes based on their frequency or impact using Pareto analysis

Month 16 (16th Workshop): Problem-Solving and Root-Cause Analysis – Analyze Phase
Welcome to the transformative 16th workshop, where we delve into the Analyze phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis. Prepare to be captivated as we equip you with the knowledge and skills to analyze data effectively and identify root causes with precision. By mastering various root-cause analysis tools and techniques, you’ll develop a structured approach that will revolutionize your problem-solving capabilities.
Topics Covered:
• Unveiling the significance of the Analyze phase in problem-solving and root-cause analysis
• Applying statistical analysis techniques to identify potential root causes with confidence
• Systematically analyzing and categorizing potential root causes using the 6M framework
• Delving deeper into the underlying causes of problems through the insightful application of the 5-Why analysis
• Prioritizing potential root causes based on their impact and likelihood of occurrence, enabling you to focus your efforts on the most critical areas for improvement

Month 17 (17th Workshop): Problem-Solving and Root-Cause Analysis – Improve Phase
Prepare to embark on an exhilarating journey through the Improve phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis in our captivating 17th workshop. This transformative session will equip you with the knowledge and skills to generate and evaluate potential solutions for the identified root causes. Discover practical tools and techniques that will empower you to develop and implement improvement actions effectively, as you pave the way for lasting organizational success.
Topics Covered:
• Unveiling the pivotal role of the Improve phase in problem-solving and root-cause analysis
• Unlocking your creative potential to generate a myriad of potential solutions using brainstorming and other innovative problem-solving techniques
• Evaluating and selecting the most appropriate solutions based on predetermined criteria, ensuring maximum impact and effectiveness
• Developing comprehensive action plans that outline the steps required to implement the selected solutions, fostering a structured approach to improvement
• Applying indispensable tools such as action plans, Gantt charts, and pilot testing to ensure the successful implementation of your improvement initiatives

Month 18 (18th Workshop): Problem-Solving and Root-Cause Analysis – Control Phase
In our awe-inspiring 18th workshop, we cast the spotlight on the Control phase of problem-solving and root-cause analysis. Prepare to be captivated as we unveil the secrets to sustaining improvements and maintaining control over your processes after implementing solutions. This session will equip you with practical tools and techniques to establish control measures, monitor ongoing performance, and cultivate a structured approach that ensures long-term success.
Topics Covered:
• Unveiling the significance of the Control phase in problem-solving and root-cause analysis
• Establishing robust control measures to ensure the sustained success of your improvements
• Developing comprehensive standard operating procedures (SOPs) and work instructions that provide clarity and consistency
• Implementing mistake-proofing techniques to prevent the recurrence of problems and enhance the overall reliability
• Monitoring and evaluating process performance using dynamic control charts, statistical process control (SPC), and other cutting-edge tools, enabling you to make data-driven decisions and maintain a high level of control
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Manufacturing
History
The term “Manufacturing” derives from the Latin phrase “manu factus,” meaning “made by hand.” Since ancient times, manufacturing has played an integral role in human civilization, with early civilizations developing techniques to produce essential goods and materials. From the industrial revolution to modern automation, manufacturing has undergone significant transformations, impacting global economies and shaping nations and societies.
Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans, achieved mastery of various production techniques, laying the groundwork for future advancements in manufacturing. They pioneered innovative methods for crafting tools, pottery, textiles, and metalwork, establishing manufacturing as a formidable economic force.
The 18th and 19th centuries marked a pivotal juncture in manufacturing history with the advent of the industrial revolution. Originating in Britain and rapidly disseminating worldwide, this revolution harnessed the power of machinery, steam, and novel manufacturing processes, revolutionizing production methods and driving unparalleled economic growth.
During this period, factories emerged as epicenters of production, supplanting traditional cottage industries. Mass production techniques, championed by textile mills and ironworks, facilitated the creation of goods on an expansive scale while concurrently reducing costs. The industrial revolution catalyzed societal transformation as people flocked from rural areas to urban centers to pursue employment opportunities within factories.
Throughout the 20th century, manufacturing continuously evolved and adapted to dynamic technological advancements. Assembly lines, mechanization, and subsequent automation fundamentally reshaped production processes, fostering enhanced efficiency and output. Mass production techniques facilitated the manufacture of consumer goods at an unprecedented magnitude, thereby augmenting affordability and accessibility for a wider populace.
The post-World War II era witnessed the pivotal role of the manufacturing industry in economic recovery. Nations such as Japan and Germany painstakingly reconstructed their manufacturing sectors, focusing on quality and precision engineering. Consequently, these nations emerged as industrial powerhouses, assuming global leadership in automotive manufacturing, electronics, and machinery.
Current Position
The manufacturing industry retains its pivotal position within global economies, propelling innovation, stimulating economic growth, and generating substantial employment opportunities. It operates across diverse sectors, encompassing automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, electronics, textiles, and more. The industry is characterized by an unwavering commitment to innovation, advanced manufacturing techniques, and the adoption of digital technologies. Manufacturers fervently invest in automation, robotics, and data analytics to amplify efficiency, productivity, and product quality.
The industry has also embraced sustainable manufacturing practices, which have assumed prominence. Manufacturers increasingly focus on waste reduction, energy conservation, and adopting eco-friendly production processes. Sustainability aligns with global environmental goals, engenders cost savings, and bolsters brand reputation.
Moreover, the manufacturing industry plays an instrumental role in job creation and economic development, fostering a diverse workforce comprising engineers, technicians, and assembly line workers possessing a broad range of skill sets. These jobs confer stability and contribute to the prosperity of local communities.
The manufacturing sector further benefits from the opportunities presented by globalization and international trade. Companies gain access to global markets, enabling them to reach a broader customer base and expand their operations. International collaborations and intricate supply chains have become indispensable for manufacturers seeking to source materials, access novel technologies, and penetrate emerging markets.
Manufacturing constitutes approximately 16% of the world’s GDP, with leading manufacturing countries significantly contributing to this figure. As per 2018 data from the World Economic Forum, China is the world’s largest manufacturing economy, accounting for 28.4% of global manufacturing output. It is followed by the United States (16.6%), Japan (7.2%), Germany (5.8%), and South Korea (3.3%).
In terms of employment, manufacturing continues to serve as a substantial job provider globally. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), manufacturing employment represented 13.6% of total global employment in 2021, bolstering livelihoods and fostering economic stability.
However, the manufacturing industry confronts a multitude of challenges. Rapid technological advancements necessitate continuous adaptation and upskilling of the workforce. Manufacturers must invest in comprehensive training programs to equip employees with the requisite skills to operate and maintain advanced machinery and embrace digital technologies.
Furthermore, manufacturers must navigate the complexities of global competition and evolving consumer demands. They must display agility and responsiveness to market trends, fostering innovation and diversifying their product offerings to meet ever-evolving customer expectations.
In conclusion, the manufacturing industry’s contributions to the global economy, job creation, and innovation are of paramount significance. Manufacturers are poised to continue driving economic growth and shaping the future trajectory of industries worldwide by prioritizing sustainable practices, adopting digital technologies, and remaining responsive to market dynamics.
Future Outlook
The future of the manufacturing industry presents an amalgamation of challenges and opportunities. Technology will continue to play a pivotal role, with transformative trends such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and Additive Manufacturing (3D printing) reshaping production processes and supply chains.
The proliferation of personalized manufacturing, wherein products can be tailored to individual customer preferences, is poised to become increasingly prevalent. This paradigm shift towards customization necessitates manufacturers to embrace flexible and agile production systems.
Furthermore, sustainability will remain an enduring focus, with manufacturers striving to minimize their environmental impact and advocate for circular economy principles. Energy-efficient processes, recycling initiatives, and using renewable materials shall be imperative for fostering sustainable manufacturing practices.
Statistics underscore the potential impact of these trends on the manufacturing industry. A November 2021 report titled “The Internet of Things: Catching up to an accelerating opportunity” by McKinsey & Company posits that the IoT could unlock a global economic value ranging from $5.5 trillion to $12.6 trillion by 2030.
Moreover, the future of manufacturing holds substantial promise in terms of job creation. The “Future of Jobs Report,” released by the World Economic Forum in May 2023, estimates a net increase of 25% in manufacturing-related employment by 2027, owing to the heightened adoption of new and frontier technologies.
Manufacturing continues to stand as a critical driver of economic growth and innovation. The industry’s ability to adapt to technological advancements, embrace sustainability, and respond to shifting market dynamics will undeniably shape its success in the future. With personalized manufacturing, sustainable practices, and the potential for significant economic growth and job creation, the manufacturing industry is poised to leave an indelible impact on the future of industries worldwide.

Food and Beverage
History
The food and beverage industry has a rich and diverse commercial history that dates back to ancient civilizations. This industry has been crucial throughout the ages in nourishing populations, stimulating trade, and shaping cultural practices worldwide.
In ancient times, societies recognized the importance of food production and distribution. Civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans developed agricultural techniques and culinary practices that laid the foundation for the modern food and beverage industry. These early cultures cultivated crops, raised livestock, and devised methods for processing and preserving food, enabling the establishment of markets and trade networks.
The Middle Ages saw the emergence of guilds and specialized professions related to food production. Bakers, brewers, and butchers formed guilds to regulate their respective trades, ensuring quality standards and fair competition. The guilds played a vital role in disseminating knowledge and refining techniques, contributing to the growth and sophistication of the food and beverage industry.
The exploration and colonization of new territories in the 15th and 16th centuries expanded the global food trade. European powers sought spices, exotic fruits, and other valuable commodities from distant lands. This era of exploration led to the establishment of extensive trade networks and the exchange of culinary traditions and ingredients between different cultures, enriching the global food landscape.
The 18th and 19th centuries Industrial Revolution brought significant advancements to the food and beverage industry. Mechanization and steam power revolutionized milling, brewing, and canning processes, increasing production efficiency and scale. This era witnessed the rise of large-scale food processing facilities, enabling the mass production and preservation of goods.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the birth of consumer culture and the growth of branded food and beverage products. Companies such as Nestlé, Coca-Cola, and Kellogg’s capitalized on packaging, advertising, and transportation advancements to create global brands and reach a broader customer base. This era also saw the rise of food regulations and safety standards, ensuring the quality and integrity of products.
The mid-20th century marked a period of technological advancements and scientific discoveries that transformed the food and beverage industry. Innovations such as refrigeration, pasteurization, and the development of synthetic additives revolutionized food preservation and extended shelf life. The rise of supermarkets and the proliferation of convenience foods further changed consumer habits and expanded the industry’s reach.
In recent decades, the food and beverage industry has witnessed a growing focus on sustainability, health, and ethical practices. Consumers increasingly demand organic, locally sourced, and ethically produced food and beverages. This shift has driven innovation in farming methods, food processing techniques, and the development of alternative and plant-based products.
The food and beverage industry continues to evolve rapidly in response to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and global challenges. From farm to fork, this industry remains a vital and dynamic force in economies worldwide, providing sustenance, employment, and culinary experiences that shape cultures and societies.
Current Position
The food and beverage industry holds a prominent position within the global market, serving as a vital component of economies worldwide. It encompasses various sectors, including food production, processing, packaging, distribution, and hospitality. With its pivotal role in nourishing populations and catering to consumer demands, the industry continuously evolves to meet changing preferences and trends.
Innovation is a key driver within the food and beverage industry, as companies strive to develop new products, enhance production techniques, and improve overall efficiency. Technological advancements, such as automation and digitalization, have revolutionized food manufacturing processes, increasing productivity and product quality. Moreover, the industry strongly emphasizes research and development to create healthier, more sustainable, and convenient food options.
Sustainability has emerged as a critical focus area for the food and beverage industry. Companies actively address environmental concerns by implementing sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes sourcing locally produced ingredients, reducing waste and packaging materials, implementing energy-efficient operations, and promoting responsible farming and fishing practices. By embracing sustainability, companies contribute to a healthier planet and enhance their brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
The food and beverage industry is a significant employer globally, providing diverse job opportunities across various sectors. Millions of jobs worldwide are supported, from agricultural workers and food scientists to chefs and restaurant staff. These jobs contribute to local economies, provide livelihoods, and support the growth of communities.
Globalization and international trade have greatly impacted the food and beverage industry. Companies have expanded their operations to reach international markets, establishing global supply chains and forging partnerships with suppliers worldwide. This enables access to a broader customer base, facilitates the exchange of culinary traditions and flavors, and supports the growth of emerging markets. Regarding economic contribution, food systems contribute $10 trillion or over 12% of global GDP and over 40% of all jobs in 2022 data from the World Economic Forum.
Challenges within the food and beverage industry are diverse and ever-present. The sector must navigate evolving consumer preferences, dietary trends, and regulatory requirements. Rising concerns over food safety and transparency necessitate stringent quality control measures, traceability systems, and ethical sourcing practices. Additionally, the industry constantly needs adaptation and innovation to meet the demands of a diverse consumer base.
In conclusion, the food and beverage industry plays a vital role in global economies, catering to consumer needs, driving innovation, and providing employment opportunities. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and responding to market dynamics, companies within the industry are well-positioned to continue shaping the future of food and beverage worldwide while contributing to economic growth and societal well-being.
Future Outlook
The future of the food and beverage industry presents a dynamic landscape filled with various challenges and opportunities. Technology is set to play a crucial role in shaping the industry, with transformative trends such as digitalization, automation, and data analytics revolutionizing production, distribution, and consumer engagement.
One of the significant trends shaping the future of the food and beverage industry is the increasing demand for healthier, more sustainable, and personalized food options. Consumers are becoming more conscious of their dietary choices, seeking products that align with their nutritional needs and lifestyle preferences. This shift towards personalization necessitates food and beverage manufacturers to invest in flexible production processes that accommodate customization and adapt to changing consumer demands.
Additionally, sustainability will continue to be a driving force in the food and beverage industry. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of food production and are demanding more eco-friendly practices. Manufacturers are expected to focus on reducing waste, adopting energy-efficient technologies, implementing sustainable sourcing and packaging methods, and promoting circular economy principles throughout the supply chain.
Moreover, technological advancements will enable greater transparency and traceability in the food and beverage industry. Blockchain technology, for instance, can enhance food safety by providing an immutable record of the entire supply chain, ensuring product authenticity and reducing the risk of contamination. This increased transparency will foster consumer trust and enable brands to build stronger customer relationships.
According to market research, the food and beverage industry is poised for substantial growth in the coming years. The Global Food Automation Market Report 2022 predicts the food automation market will reach $17.46 billion in 2026 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.63%, driven by the increasing adoption of automation solutions in food processing and packaging. Furthermore, the global plant-based protein market is expected to explode, driven by the rising popularity of vegan and vegetarian diets.
The food and beverage industry’s future also holds promising job creation opportunities. As new technologies are integrated into the industry, there will be a demand for skilled professionals in areas such as food science, data analytics, and sustainability. This shift in the workforce will require upskilling and reskilling initiatives to ensure a capable and adaptable workforce.
The food and beverage industry, focusing on personalized nutrition, sustainability, and technological advancements, is positioned to impact the future of the global economy significantly. By embracing emerging technologies, adopting sustainable practices, and meeting the evolving needs of consumers, the industry can drive economic growth, innovation, and positive environmental change.
Retail
History
The Retail industry has a vibrant and ever-evolving commercial history that reflects the evolution of consumer culture and economic systems. From ancient marketplaces to modern shopping malls, retail has played a central role in connecting producers with consumers and satisfying society’s diverse needs and desires.
The origins of retail can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where marketplaces and bazaars served as gathering places for trade and commerce. Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, and the Roman Empire boasted bustling market squares where merchants sold various goods, including food, clothing, and household items. These early forms of retail laid the foundation for the development of organized trade and consumer-focused commerce.
In the Middle Ages, the growth of towns and cities in Europe gave rise to specialized retail shops. Craftsmen and artisans established workshops and storefronts, offering goods produced by their own hands. Guilds and merchant associations played a significant role in regulating trade, ensuring quality standards, enhancing consumer trust, and fostering retail growth.
The Renaissance period witnessed the emergence of the first department stores. In cities like Paris and London, entrepreneurial merchants opened grand establishments that housed a wide range of merchandise under one roof. These early department stores aimed to provide a unique shopping experience, attracting customers with luxurious interiors, attentive staff, and an array of products to choose from.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought transformative changes to the retail industry. Advances in manufacturing and transportation led to the mass production and distribution of goods, fueling retail growth on a large scale. The rise of urbanization, the expansion of railway networks, and improved logistics enabled retailers to reach broader markets and supply an increasingly diverse array of products.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the advent of modern retail formats and innovations. Introducing self-service stores, pioneered by retailers such as F.W. Woolworth and Clarence Saunders, revolutionized the shopping experience. Customers could browse and select products, providing greater convenience and lower prices.
The mid-20th century witnessed the rise of supermarkets and discount stores. Chains like Kroger and Walmart leveraged economies of scale, efficient supply chains, and competitive pricing to become dominant players in the retail landscape. The post-World War II era also saw the emergence of shopping malls, offering a wide range of retailers and entertainment options in one location.
With the advent of the internet and e-commerce in the late 20th century, retail underwent a significant transformation. Online retailers like Amazon and Alibaba disrupted traditional brick-and-mortar retail models, offering convenience, vast product selections, and personalized shopping experiences. The digital era also facilitated the rise of omnichannel retailing, where customers can seamlessly shop across multiple platforms and touchpoints.
In recent years, retail has faced the challenges posed by changing consumer preferences, sustainability concerns, and the impact of technology. Retailers are increasingly embracing experiential retail concepts, focusing on creating immersive in-store experiences to differentiate themselves from online competitors. Sustainability and ethical sourcing have also become critical considerations, with consumers demanding transparency and eco-friendly practices from retailers.
As the retail industry continues to evolve, it adapts to new technologies, shifts in consumer behavior, and societal trends. From traditional mom-and-pop stores to global e-commerce giants, retail remains a vital sector of the economy, shaping consumer culture and driving economic growth.
Current Position
The retail industry is prominent in the global marketplace, serving as a vital link between manufacturers and consumers. It encompasses many businesses, including traditional retail outlets, e-commerce platforms, and hybrid models integrating online and offline shopping experiences. The industry plays a critical role in fulfilling consumer needs and preferences by offering diverse products and services.
The retail industry has undergone significant transformation in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behavior. The rise of e-commerce and mobile shopping has revolutionized how consumers browse, purchase, and receive products. Retailers have adapted by investing in robust online platforms, enhancing the user experience, and leveraging data analytics to personalize marketing efforts and improve customer satisfaction.
Customer experience has become a focal point for the retail industry. Retailers are investing in creating seamless, convenient, personalized shopping experiences to attract and retain customers. This includes strategies such as immersive in-store experiences, click-and-collect options, fast and reliable delivery services, and customized recommendations based on customer preferences. By prioritizing customer satisfaction, retailers can build brand loyalty and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Sustainability has also gained prominence within the retail industry. Consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental and social issues, demanding more sustainable and ethically produced products. Retailers respond by adopting sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly packaging, responsible sourcing, waste reduction, and energy-efficient store designs. Embracing sustainability aligns with consumer values and contributes to brand reputation and long-term business viability.
The retail industry is a significant employer globally, providing diverse job opportunities across various roles and skill levels. The sector supports millions of jobs worldwide, from sales associates and visual merchandisers to logistics personnel and digital marketers. In October 2022, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that over 15.8 million people were employed in retail positions at physical stores alone. It’s important to note that this data excludes retail workers in other parts of the businesses, such as corporate headquarters, distribution centers, call centers, and innovation labs. Retail jobs also often serve as entry-level positions, offering valuable training and career development opportunities for individuals entering the workforce.
Globalization and international trade have greatly impacted the retail industry. Companies are expanding their reach beyond national borders, establishing partnerships with international suppliers, and leveraging global sourcing networks. This enables retailers to access a wider range of products, offer competitive pricing, and cater to diverse consumer preferences. Cross-border e-commerce has opened new markets, allowing retailers to reach customers in different regions and countries.
In terms of economic contribution, the global retail market generated sales of over $27 trillion in 2022, according to Statista. The retail industry drives consumption, supports other sectors of the economy, and contributes to job creation and tax revenues. Leading countries in the retail industry include the United States, China, Japan, Germany, and the United Kingdom, where robust consumer markets, infrastructure, and technological advancements contribute to their competitive advantage.
However, the retail industry faces several challenges. Competition is fierce, both from traditional retailers and e-commerce giants. Retailers must continually innovate, adapt to changing consumer trends, and invest in technology to stay relevant. They must also navigate regulatory complexities, manage supply chain disruptions, and address cybersecurity concerns to ensure the security of customer data.
In conclusion, the retail industry plays a crucial role in the global economy by connecting manufacturers and consumers. Retailers can thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape by embracing technological advancements, prioritizing customer experience, and adopting sustainable practices. The industry’s ability to anticipate and meet consumer demands will continue to shape its commercial position and drive its future success.
Future Outlook
The retail industry is poised for a dynamic and transformative future, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and evolving market dynamics. As digitalization reshapes the retail landscape, companies must adapt to emerging trends and embrace innovative strategies to thrive in this changing environment.
E-commerce will continue to be a major force shaping the future of the retail industry. The growth of online retail and the increasing popularity of mobile shopping has fundamentally changed consumer expectations. To stay competitive, retailers must invest in robust online platforms, seamless omnichannel experiences, and personalized digital marketing strategies. Integrating augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies will also enhance the online shopping experience, allowing customers to virtually try on products or visualize how furniture and decor items would look in their homes.
Store-based retail will transform as retailers seek to create unique and immersive shopping experiences. Physical stores will increasingly serve as showrooms, where customers can interact with products and receive personalized assistance. Retailers will leverage interactive displays, IoT devices, and AI-powered chatbots to enhance customer engagement and deliver tailored recommendations. In-store technologies, such as contactless payments and self-checkout options, will also enable frictionless checkout processes.
Sustainability and ethical practices will become paramount in the retail industry. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental and social impact of their purchases. Retailers must adopt sustainable sourcing and manufacturing practices, reduce packaging waste, and offer eco-friendly product alternatives. Embracing sustainability will resonate with environmentally conscious consumers and contribute to long-term brand loyalty and differentiation.
Data analytics and AI will play a pivotal role in retail’s future. Retailers will leverage customer data to gain insights into preferences, behaviors, and purchase patterns, enabling them to deliver personalized marketing campaigns and tailored product recommendations. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants will provide real-time customer support, answer inquiries, and guide purchase decisions. Predictive analytics will also drive inventory management, demand forecasting, and supply chain optimization, helping retailers reduce costs, minimize stockouts, and improve operational efficiency.
The rise of direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands will continue to disrupt the retail industry. D2C companies leverage digital platforms to establish direct customer relationships, bypassing traditional retail channels. These brands focus on delivering unique value propositions, cultivating brand loyalty, and providing exceptional customer experiences. Traditional retailers must innovate and find ways to differentiate themselves to compete effectively in this changing landscape.
According to industry reports (Verified Market Research), the global retail market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years and reach $41.3 trillion by 2030. This will be driven by increasing consumer spending, urbanization, and rising disposable incomes. E-commerce is expected to continue its strong growth trajectory.
In conclusion, the future of the retail industry is marked by the integration of online and offline experiences, personalized marketing, sustainability, and technological innovation. Retailers can thrive in this rapidly evolving landscape by embracing digital transformation, leveraging data-driven insights, and focusing on customer-centric strategies. Adapting to changing consumer preferences, delivering exceptional experiences, and building meaningful connections with customers will be essential for success in the future retail industry.

Distribution and Logistics
History
The Distribution & Logistics industry has a rich and intricate commercial history that parallels the development of trade and transportation networks throughout human civilization. From ancient trading routes to modern supply chains, this industry has played a fundamental role in connecting producers with consumers and facilitating the movement of goods.
The roots of distribution and logistics can be traced back to the ancient world, where civilizations like the Phoenicians, Egyptians, and Romans established trading networks spanning vast distances. These early traders and merchants devised methods for organizing and transporting goods, relying on caravans, ships, and even early forms of packaging to facilitate trade and distribution.
The Middle Ages witnessed the rise of trade routes, such as the Silk Road, linking Europe, Asia, and Africa. These routes fostered the exchange of goods, knowledge, and cultural practices, facilitating economic growth and shaping the world as we know it today. Merchants and traders developed sophisticated systems for inventory management, warehousing, and transportation, establishing the foundation for modern logistics practices.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about significant advancements in distribution and logistics. The steam engine revolutionized transportation, enabling the development of railways, steamships, and later, motor vehicles. These transportation innovations allowed for the rapid movement of goods across long distances, reducing transit times and expanding markets.
The advent of mass production techniques in the late 19th century further transformed distribution and logistics. As factories increased output, efficient systems for storing, organizing, and delivering goods became essential. Warehouses, distribution centers, and specialized logistics companies emerged to manage the flow of products from manufacturers to retailers and consumers.
The 20th century saw the continued evolution of distribution and logistics, driven by technological advancements. The introduction of refrigeration and cold chain logistics enabled the transportation and preservation of perishable goods, opening new markets and expanding consumer choices. The development of containerization in the mid-20th century revolutionized global trade, streamlining cargo handling and reducing costs.
The rise of information technology in the late 20th century and the early 21st century brought about a paradigm shift in distribution and logistics. Electronic data interchange (EDI) and the adoption of transportation management systems (TMS) allowed for real-time tracking and optimization of shipments. Implementing barcode technology and RFID tags improved inventory accuracy and enhanced supply chain visibility.
Today, the Distribution & Logistics industry continues to adapt and innovate in response to globalization, e-commerce, and evolving consumer expectations. The rise of online retail and the demand for fast and efficient delivery services have led to the development of sophisticated logistics networks, last-mile delivery solutions, and the integration of artificial intelligence and automation in warehousing and transportation.
Current Position
The distribution and logistics industry holds a crucial position within the global economy, facilitating the movement of goods and services across various sectors. It encompasses multiple activities: transportation, warehousing, inventory management, packaging, and supply chain optimization. The industry plays a pivotal role in ensuring the timely delivery of products, enabling businesses to meet customer demands efficiently.
The distribution and logistics industry has experienced significant growth and transformation in an increasingly interconnected world. Rapid technological advancements, particularly in automation, robotics, and data analytics, have revolutionized the industry’s operations. These technological innovations have enhanced efficiency, increased supply chain visibility, improved inventory management, and optimized transportation routes, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Sustainability has emerged as a critical focus area for the distribution and logistics industry. Companies are adopting eco-friendly practices to minimize their carbon footprint and reduce environmental impact. This includes implementing energy-efficient transportation methods, optimizing route planning to reduce emissions, using recyclable packaging materials, and exploring alternative fuel options. By prioritizing sustainability, companies contribute to environmental preservation, enhance their brand reputation, and meet the growing expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
The industry is a significant source of employment globally, offering diverse job opportunities. The distribution and logistics sector employs millions of people worldwide, from truck drivers and warehouse personnel to logistics coordinators and supply chain managers. These jobs contribute to economic growth, support local communities, and require diverse skills, from operational management to technological proficiency.
Globalization and international trade have greatly influenced the distribution and logistics industry. As businesses expand their operations to new markets and collaborate with international partners, efficient supply chain networks become paramount. Companies increasingly rely on global transportation systems, integrated customs processes, and advanced tracking technologies to streamline the flow of goods across borders. This enables businesses to access a wider customer base, source materials from diverse locations, and meet the demands of a global marketplace.
Regarding economic contribution, the distribution and logistics industry represents a significant portion of global GDP. Allied Market Research state that the global logistics market was valued at $9,833.8 billion in 2022. The industry enables the efficient movement of goods and services, supporting economic activities in various sectors such as retail, manufacturing, e-commerce, and healthcare. Leading countries in distribution and logistics include the United States, China, Germany, Japan, and the United Kingdom, where robust infrastructure, technological advancements, and strategic geographic locations contribute to their competitive advantage.
However, the distribution and logistics industry also faces several challenges. These include navigating complex regulatory frameworks, addressing security concerns, managing supply chain disruptions, and adapting to changing consumer expectations. Additionally, technological advancements require ongoing workforce training and upskilling investments to ensure employees can leverage new tools and systems effectively.
In conclusion, the distribution and logistics industry is critical in global trade, supply chain management, and economic growth. By embracing technological advancements, prioritizing sustainability, and responding to the demands of a global marketplace, companies within the industry are well-positioned to continue driving efficiency, enhancing customer satisfaction, and shaping the future of distribution and logistics worldwide.
Future Outlook
The distribution and logistics industry is on the cusp of a transformative era driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations. As supply chains become increasingly complex and global, the industry faces challenges and opportunities that will shape its future landscape.
Technology will continue to be a key driver of change in the distribution and logistics industry. The rise of automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI) will revolutionize warehouse operations, transportation, and last-mile delivery. Automated systems will optimize inventory management, streamline order fulfillment, and enhance operational efficiency, ultimately reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, data analytics and predictive modeling will be crucial in supply chain optimization. Advanced analytics tools will enable real-time tracking, demand forecasting, and route optimization, enhancing visibility and agility across the supply chain. This data-driven approach will allow companies to make informed decisions, reduce lead times, minimize stockouts, and improve overall supply chain performance.
E-commerce will continue to be a significant force driving growth in the distribution and logistics industry. The rapid expansion of online retail and the increasing popularity of same-day and next-day delivery services have pressured logistics providers to optimize their operations. Fulfillment centers and distribution networks are being reconfigured to handle the growing volume of e-commerce orders, and logistics companies are investing in innovative solutions to meet the rising demand for fast and efficient deliveries.
Sustainability and environmental concerns are also shaping the future of the distribution and logistics industry. Consumers are increasingly conscious of the carbon footprint associated with transportation and logistics operations. As a result, companies are exploring eco-friendly practices such as alternative fuel vehicles, route optimization for fuel efficiency, and packaging optimization to reduce waste. Sustainability initiatives contribute to environmental conservation and present an opportunity for companies to enhance their brand image and meet consumer expectations.
The growing importance of omnichannel retailing will also influence the future of the distribution and logistics industry. With consumers expecting a seamless shopping experience across multiple channels, companies invest in integrated supply chain solutions that effectively handle online orders, brick-and-mortar store replenishment, and direct-to-consumer shipments. This shift towards omnichannel fulfillment requires logistics providers to adopt flexible and scalable systems that adapt to changing customer preferences and market dynamics.
According to industry reports, the global logistics market is expected to witness significant growth in the coming years, where it is estimated to reach $16,794.7 billion by 2032 according to Allied Market Research, a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2023 to 2032. Drivers of the growth include a demand for efficient supply chain solutions and the evolution of e-commerce. Additionally, the market for drone delivery services is expected to expand, with the global drone logistics and transportation market projected to reach $53.32 billion by 2031.
In conclusion, the distribution and logistics industry is undergoing a transformative phase fueled by technological advancements, e-commerce growth, sustainability imperatives, and changing consumer expectations. By embracing automation, leveraging data analytics, adopting sustainable practices, and optimizing supply chain networks, companies in this industry can position themselves for success in the future. The ability to navigate these evolving trends and deliver efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric solutions will be crucial for the industry’s growth and competitiveness in the global marketplace.

Banking and Financial Services
History
The Banking & Financial Services industry has a long and dynamic commercial history that spans centuries, reflecting the development of economic systems and the evolution of financial practices. This industry has played a crucial role in facilitating trade, investment, and economic growth from ancient moneylenders to modern global financial institutions.
The origins of banking can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early forms of financial services emerged. In Mesopotamia, merchants and temple authorities acted as moneylenders, providing loans and facilitating trade by exchanging commodities for promissory notes. Ancient Egypt saw the establishment of grain banks and temples that held deposits and extended credit to individuals and businesses.
During the Middle Ages, banking practices began to take shape in various parts of the world. The Italian city-states, such as Florence and Venice, became prominent financial centers where banks facilitated trade and financed ventures. The Medici family in Florence gained renown as influential bankers, supporting artists, merchants, and even governments through their financial services.
The 17th and 18th centuries witnessed the establishment of modern banking institutions. The Bank of England, founded in 1694, became a model for central banks worldwide, issuing currency, managing government debt, and stabilizing the financial system. Private banks also proliferated during this period, providing services such as deposits, loans, and money transfers to individuals and businesses.
The 19th century brought significant developments to the banking and financial services industry. The rise of industrialization and global trade created a demand for more complex financial instruments and services. Investment banks emerged, facilitating the issuance of stocks and bonds to raise capital for businesses and governments. Commercial banks expanded their reach, providing a broader range of services to meet the growing needs of businesses and consumers.
The early 20th century saw the establishment of regulatory frameworks to safeguard the banking sector’s stability. Central banks were granted expanded powers to regulate money supply, manage interest rates, and oversee the financial system. The Great Depression in the 1930s led to further economic reforms, including creating deposit insurance to protect customers’ funds and separating commercial and investment banking activities.
Post-World War II, technological advancements revolutionized the banking industry. The introduction of computers and electronic data processing enabled faster transaction processing and improved record-keeping. The rise of credit cards and automated teller machines (ATMs) transformed how individuals accessed and managed their finances.
The late 20th century and early 21st century witnessed the globalization and consolidation of the banking industry. Financial deregulation and advancements in communication technology allowed banks to expand their operations globally and offer a wider range of financial services. Investment banking, wealth management, insurance, and other specialized services became integral parts of many banking institutions.
The digital revolution of the late 20th century and early 21st century brought about further transformations in the banking and financial services industry. Online banking and mobile banking platforms emerged, providing customers with convenient access to their accounts and a range of financial services. FinTech (Financial Technology) companies disrupted traditional banking models, offering innovative payment solutions, lending, investment, and personal finance management solutions.
In recent years, the industry has faced challenges such as financial crises, increased regulatory scrutiny, and the need to address cybersecurity threats. Banks and financial institutions focus on enhancing transparency, risk management, and customer experience to rebuild trust and adapt to changing customer expectations.
The Banking & Financial Services industry continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing regulatory landscapes, and shifts in global economic dynamics. It is critical in allocating capital, supporting economic growth, and providing essential financial services to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide.
Current Position
The banking and financial services industry is vital in the global economy, providing essential financial products, services, and infrastructure that support economic growth, investment, and wealth management. It encompasses various institutions, including commercial banks, investment banks, asset management firms, insurance companies, and fintech companies. The industry is critical in facilitating transactions, managing risk, and allocating capital across various sectors.
Technological advancements have significantly transformed the banking and financial services industry. Digital banking, mobile payment systems, and online investment platforms have revolutionized how customers interact with financial institutions. Banks invest in digital transformation initiatives, enhance their online and mobile banking capabilities, and leverage data analytics and artificial intelligence to personalize services, detect fraud, and improve operational efficiency.
Customer experience has become a key focus area for the industry. Financial institutions are adopting customer-centric approaches to provide seamless, convenient, and personalized experiences across all touchpoints. This approach includes streamlining account opening processes, offering intuitive self-service options, and providing personalized financial advice and solutions. Banks and financial services firms can build trust, loyalty, and long-term customer relationships by prioritizing customer satisfaction and convenience.
Sustainability and responsible finance have gained prominence within the banking and financial services industry. Institutions increasingly integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their investment decisions and risk management practices. They are developing sustainable finance products and services, supporting initiatives such as renewable energy projects, and promoting responsible lending practices. Embracing sustainability aligns with societal and regulatory expectations and offers long-term financial benefits and risk mitigation.
The banking and financial services industry is a significant employer. According to the International Labor Organization, over 52 million people were estimated to be employed in the financial services sector in 2019. The industry offers diverse roles and skill sets, from financial analysts and wealth managers to risk management professionals and technology specialists, while providing various career opportunities. Banks and financial institutions contribute to job creation, professional development, and economic stability in their communities.
Globalization and international finance are integral to the banking and financial services industry. Financial institutions operate across borders, facilitating international trade, foreign investments, and capital flows. They provide services such as trade finance, foreign exchange, and cross-border payments, enabling businesses and individuals to conduct transactions globally. International collaborations, regulatory frameworks, and financial networks have become essential for banks to operate efficiently in the global marketplace.
In terms of economic contribution, the banking and financial services industry represents a significant portion of global GDP, at least 20% and up to 25%, according to most leading financial data analytics companies. The impact of the financial sector on economic growth is significant. It is a critical intermediary, mobilizing savings, allocating capital, and providing financial products and services to individuals, businesses, and governments. Leading financial centers include New York, London, Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Singapore, where financial institutions, regulatory frameworks, and deep markets contribute to their global prominence.
However, the banking and financial services industry also faces several challenges. Rapid technological advancements, cybersecurity threats, and evolving regulatory requirements necessitate continuous investment in digital infrastructure, data security, and compliance. Institutions must also navigate market volatility, manage risks, and adapt to changing customer expectations and market dynamics.
In conclusion, the banking and financial services industry plays a crucial role in the global economy, facilitating financial transactions, managing risk, and supporting economic growth. By embracing digital transformation, prioritizing customer experience, and integrating sustainability, institutions can drive innovation, build trust, and navigate the complexities of the evolving financial landscape. The industry’s ability to adapt to changing demands and leverage technological advancements will shape its commercial position and define its future success.
Future Outlook
The banking and financial services industry is on the brink of a transformative era driven by technological advancements, changing customer expectations, and regulatory developments. As digitalization and innovation reshape the sector, banks and financial institutions must adapt to emerging trends and embrace new strategies to stay competitive and meet evolving customer needs.
Technology will continue to be a major driver of change in the banking and financial services industry. The rise of digital banking, mobile payments, and fintech disruptors has shifted customer preferences and expectations. Banks must invest in robust digital platforms, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and seamless omnichannel experiences to cater to the growing demand for convenient, secure, personalized financial services.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will revolutionize various aspects of the industry, including customer service, risk assessment, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants will provide personalized and real-time customer support. At the same time, advanced analytics and ML algorithms will enable banks to analyze large volumes of data, improve credit scoring models, and detect patterns that can enhance risk management and fraud prevention.
Open banking and the rise of application programming interfaces (APIs) will promote collaboration and innovation in the banking sector. Banks can partner with fintech companies and third-party providers to offer customers a broader range of services, such as personal finance management tools, investment platforms, and customized financial solutions. Open banking also allows for seamless data sharing, giving customers a holistic view of their financial information across multiple accounts and institutions.
Sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations will become increasingly important for the banking and financial services industry. Customers are seeking responsible and ethical financial institutions that align with their values. Banks must integrate ESG factors into their investment decisions, offer sustainable finance solutions, and disclose their environmental and social impacts to build trust and attract socially conscious customers.
Regulatory compliance will continue to shape the future of the banking and financial services industry. Implementing PSD2, GDPR, and AML/KYC requirements emphasizes data privacy, security, and transparency. Banks must invest in robust compliance systems, enhance data protection measures, and ensure regulatory compliance to maintain customer trust and avoid hefty penalties.
The rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology presents opportunities and challenges for the banking industry. While cryptocurrencies offer the potential for faster and more secure transactions, they also raise concerns about financial stability, money laundering, and regulatory oversight. Banks must navigate this evolving landscape, exploring partnerships and collaborations with blockchain-based platforms while ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Allied Market Research reports that the global banking and financial services market will generate $520.02 billion by 2027. Increasing international trade, economic growth, and adopting digital banking services will drive this generation. Fintech investments are also expected to rise, with the global fintech market projected to become a $1.5 Trillion Industry by 2030, according to the Boston Consulting Group.
In conclusion, the future of the banking and financial services industry lies in embracing digital transformation, leveraging advanced technologies, and meeting customer expectations for convenience, personalization, and transparency. By investing in innovative solutions, collaborating with fintech partners, and incorporating sustainability and ESG principles, banks can position themselves for success in this rapidly evolving landscape. The ability to adapt to regulatory changes, provide secure and seamless digital experiences, and deliver responsible financial services will be key to driving growth and staying competitive in the future banking and financial services industry.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:
New York, US
History
Introduction:
New York City, often hailed as the “Big Apple,” boasts a storied commercial history that has propelled it to become one of the world’s foremost economic centers. From its origins as a Dutch trading post to its current status as a global metropolis, New York City has played a pivotal role in shaping the commercial landscape of the United States.
From Dutch Trading Post to Global Hub:
In the early 17th century, New York City, then known as New Amsterdam, was established as a fur trading outpost by the Dutch West India Company. Its strategic location at the mouth of the Hudson River provided easy access to trade routes and fueled its initial economic growth.
The British takeover of New Amsterdam in 1664 marked a turning point, and the city was renamed New York. Under British rule, New York City flourished and expanded. Its port became a crucial trading hub for goods, connecting North America to Europe and the Caribbean. Agricultural products, timber, and manufactured items flowed through the port, further bolstering the city’s economic vitality.
Industrial Revolution and Economic Transformation:
The 19th century witnessed significant developments in New York City’s commercial landscape. The construction of the Erie Canal in 1825 established a direct water route connecting the city to the Great Lakes region, stimulating trade and fostering the growth of industries such as shipping, manufacturing, and finance.
The rise of the Industrial Revolution propelled New York City’s economic growth even further. The city became a manufacturing center, with industries such as textiles, printing, and machinery thriving. Waves of immigrants worldwide flocked to New York City, seeking employment opportunities and contributing to its economic dynamism.
Financial Powerhouse and Global Influence:
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, New York City solidified its position as a financial powerhouse. Wall Street emerged as the epicenter of American finance, with major banks, investment firms, and stock exchanges taking root. The New York Stock Exchange, founded in 1792, grew into the world’s leading stock market.
New York City’s commercial prominence continued to soar throughout the 20th century. Iconic skyscrapers such as the Empire State Building and the Chrysler Building transformed the city’s skyline, symbolizing its economic might and ambition.
The city’s diverse economy encompassed sectors ranging from finance and commerce to media, entertainment, and fashion. New York City became a global hub for advertising, publishing, television, and film production, cementing its cultural and creative capital status.
Adaptation to Changing Times:
New York City has maintained its leading position as a global city in recent decades. It has embraced technological innovation, fostered a thriving startup scene, and attracted businesses from diverse industries. Neighborhoods like Silicon Alley in Manhattan and DUMBO in Brooklyn have become magnets for tech companies and digital entrepreneurs.
New York City’s commercial history exemplifies its spirit of ambition, entrepreneurship, and resilience. It remains a symbol of opportunity and economic vitality, attracting talented individuals, businesses, and investors worldwide and continuing to shape the global commercial landscape.
Current Position
Today, New York City occupies a prominent commercial position as a global economic powerhouse and one of the world’s leading financial centers. According to the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, in 2020, the New York metropolitan area generated a GDP of approximately US$1.022 trillion, representing around 4.9% of the nation’s US$20.894 trillion economic output for that year.
New York City’s economic strength lies in its diverse and robust sectors, including finance, professional services, technology, media, tourism, and creative industries. Wall Street, the iconic financial district, is the heart of the global financial sector. Major banks, investment firms, and insurance companies facilitate domestic and international trade, investment, and capital flows.
The city’s professional services industry thrives, concentrating on legal, accounting, consulting, advertising, and public relations firms. New York City’s professional services sector caters to a wide range of industries, providing expertise and support for businesses locally and globally.
New York City also stands at the forefront of technological innovation, serving as a hub for the technology industry. Its vibrant startup ecosystem, centered around Silicon Alley, attracts talent and investment across various fields, including fintech, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and cybersecurity. The city’s connections with academia, research institutions, and major corporations create fertile ground for groundbreaking advancements and disruptive business models. New York City’s thriving tech scene, diverse talent pool, and robust infrastructure solidify its reputation as a global technology hub.
Furthermore, New York City remains a major center for media and entertainment, hosting film and television production studios, publishing houses, advertising agencies, and digital media companies. Its vibrant arts, fashion, design, and theater sectors set trends and captivate audiences worldwide. New York City’s cultural vibrancy, multicultural richness, and access to global markets ensure that it remains a hub of creativity and innovation.
The city’s robust tourism industry is a cornerstone of its commercial success, attracting millions of domestic and international visitors annually. New York City’s iconic landmarks, cultural institutions, culinary scene, and major events contribute to its appeal as a premier destination for business and leisure travelers alike.
Despite its commercial strengths, New York City faces challenges that must be addressed for sustainable growth and competitiveness. Affordability, particularly regarding housing and the cost of living, poses constraints for residents and businesses. Addressing affordability is crucial for attracting and retaining talent and maintaining a diverse workforce.
Infrastructure, particularly transportation systems, requires significant investments and upgrades to accommodate a growing population and ensure efficient mobility. Investing in resilient infrastructure to mitigate climate change risks, such as flooding and extreme weather events, is essential.
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly impacted New York City’s economy, particularly in sectors such as tourism, hospitality, and retail. The restrictions on travel, social distancing measures, and changing consumer behavior have affected businesses and employment. New York City has been implementing measures to support affected industries, stimulate recovery, and adapt to new economic realities.
Despite these challenges, New York City’s resilience, economic diversification, and entrepreneurial spirit position it for continued commercial success. Adapting to changing global dynamics, supporting innovation and entrepreneurship, investing in infrastructure, and addressing affordability concerns are crucial for future growth and competitiveness.
Future Outlook
New York City’s commercial future shines brightly, propelled by its unwavering spirit of innovation, unparalleled economic diversity, and global influence. The city’s financial sector, technology ecosystem, creative industries, and tourism sector all contribute to its commercial prowess and global impact.
New York City’s financial sector, anchored by Wall Street, will remain a leading global financial hub. The city’s robust regulatory framework, deep pool of financial talent, and access to capital will continue to attract financial institutions and investors worldwide. Navigating complex markets, embracing technological advancements, and fostering collaborations will sustain New York City’s position as the economic epicenter of the world.
The city’s technology sector is poised for rapid growth, driven by innovation, entrepreneurship, and access to capital. New York City’s vibrant startup ecosystem will continue to attract talent and investment across various industries, including fintech, artificial intelligence, e-commerce, health tech, and media tech. The city’s strong ties with academia, research institutions, and major corporations will create a fertile ground for groundbreaking technological advancements and disruptive business models. New York City’s thriving tech scene, diverse talent pool, and robust infrastructure will solidify its reputation as a global technology hub.
Moreover, New York City’s creative industries will significantly influence its economic prowess and global influence. The city’s dynamic arts, fashion, design, and media sectors will continue to set trends and captivate audiences worldwide. New York City’s iconic fashion shows, Broadway productions, world-class museums, and thriving film and television production studios will sustain its reputation as a premier destination for creativity and innovation across multiple disciplines.
The tourism industry will remain vital to New York City’s commercial success. Its famous attractions, cultural institutions, culinary scene, and major events will continue to attract millions of visitors from around the globe. New York City’s commitment to hosting international conferences, sports competitions, and cultural festivals will further enhance its tourism potential and showcase its capabilities on a global stage.
To ensure its future success, New York City must address key challenges. Prioritizing affordable housing initiatives will be crucial to maintaining a diverse and vibrant workforce, ensuring that economic opportunities are accessible to all. Enhancing transportation infrastructure, expanding public transportation networks, and embracing sustainable mobility solutions will alleviate congestion and improve connectivity. New York City’s commitment to environmental sustainability, such as reducing carbon emissions and investing in renewable energy, will reinforce its resilience and position as a leader in combating climate change.
As a global metropolis, New York City is responsible for addressing global challenges and contributing to social and economic development. New York City can amplify its global influence and reputation by championing diversity and inclusion, supporting social justice initiatives, and fostering collaborations with other cities. The city’s commitment to corporate social responsibility, ethical business practices, and sustainability will further enhance its commercial future and solidify its position as a progressive beacon.
In conclusion, New York City’s commercial future remains robust and promising, driven by its relentless pursuit of innovation, economic diversity, and global connectivity. The city’s financial sector, technology ecosystem, creative industries, and tourism sector all contribute to its commercial prowess and global influence. By embracing emerging technologies, fostering entrepreneurship, and prioritizing sustainability, New York City is poised to shape its future as a dynamic, inclusive, and influential city. It continues to set trends, attract investments, and inspire the world with unparalleled energy and entrepreneurial spirit.
London, UK
History
Introduction:
London, a city steeped in a vibrant and diverse history, has transformed into a thriving global metropolis, offering boundless opportunities. From its modest beginnings as a Roman settlement in AD 43, London has witnessed centuries of evolution, shaping the dynamic city it is today.
A Center of Commerce, Innovation, and Cultural Exchange:
London has always been a hub of commerce, innovation, and cultural exchange, fostering prosperity and growth. The city flourished as a bustling trading center during the Middle Ages, strategically located along the River Thames. Merchants from across the globe flocked to London’s markets, exchanging goods and ideas. This early focus on trade established the bedrock for the city’s future economic vitality.
The Birth of a Financial Powerhouse:
In the 17th century, London emerged as a financial powerhouse, marked by the establishment of the Royal Exchange and the birth of the modern stock market. The city’s growing influence in finance attracted merchants and investors from far and wide, seeking opportunities for prosperity and growth. This era marked a pivotal turning point, cementing London’s position as a global economic hub.
The Industrial Revolution and Unprecedented Growth:
The 18th and 19th centuries witnessed London’s unprecedented growth during the Industrial Revolution, fueled by advancements in manufacturing and trade. The city’s population swelled as people migrated to the capital in search of better lives and employment opportunities. With the construction of canals and railways, London became the epicenter of Britain’s industrial might, driving the nation’s economic prosperity. The magnificent Victorian architecture that adorns the cityscape is a testament to this era of progress and success.
Triumphs and Challenges of the 20th Century:
The 20th century brought both triumphs and challenges to London. The city played a crucial role during World War II, enduring the sustained bombing campaign known as the Blitz. Despite the devastation, London showcased remarkable resilience and determination during the subsequent recovery and reconstruction, underscoring its unwavering spirit.
Post-war, London witnessed significant social and cultural changes. It became a magnet for youth culture and music, epitomized by iconic movements like the Swinging Sixties and the British Invasion in the music scene. The cultural impact of London during this period resonated globally, as the city became synonymous with creativity and progressive thinking.
London’s Financial Sector and Notable Developments:
London’s financial sector experienced remarkable developments in the latter half of the 20th century. The establishment of the International Stock Exchange in 1967 and the deregulation of financial markets in the 1980s, under Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher’s government, positioned London as a global economic powerhouse. The city’s financial district, the City of London or the Square Mile, thrived, attracting international banks, investment firms, and financial institutions. London became a magnet for financial talent and expertise, with individuals flocking to the city to pursue lucrative careers in finance.
Current Position
London’s Current Position as a Leading Global Center:
Today, London stands tall as a leading international urban center, renowned for its economic prowess, cultural vibrancy, and unparalleled opportunities. The city’s current status is exemplified by its significant contribution to the UK’s GDP, with the London region accounting for approximately 23% of the nation’s economic output in 2021 (Source: Statista).
London’s economic strength is deeply rooted in its diverse sectors, including finance, professional services, tourism, technology, and the creative industries. The Square Mile is a world-renowned financial center, housing major banks, investment firms, and the London Stock Exchange. It pulsates with economic activity, facilitating billions of pounds worth of transactions on a daily basis. London’s financial services sector employs a vast number of professionals and plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade and investment.
London is also home to prestigious educational institutions, attracting international students and enriching its talent pool. Renowned universities such as Imperial College London, the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE), and University College London (UCL) offer top-quality education and research opportunities. These institutions foster knowledge exchange and attract talented individuals worldwide, further enhancing London’s diverse and skilled workforce.
Addressing Challenges and Navigating the Future:
However, despite its strengths, London faces several economic challenges that require attention to ensure continued growth and prosperity. One significant challenge is the impact of Brexit, the UK’s departure from the European Union. The process of disentanglement has introduced uncertainties and complexities affecting various sectors, including finance, trade, and investment.
London’s financial services sector, a longstanding pillar of the city’s economy, has been particularly affected by Brexit. The loss of passporting rights, which previously allowed UK-based financial institutions to operate freely across the EU, has necessitated the establishment of new regulatory frameworks and has disrupted established relationships with European partners. To mitigate these challenges, London needs to forge new global partnerships, expand trade networks beyond the EU, and demonstrate its resilience as a global financial hub.
Another economic challenge facing London is the issue of high living costs and affordability. Soaring property prices and the rising cost of goods and services have created affordability constraints for businesses and individuals alike. This challenge can hinder talent attraction and retention, as well as place strains on business operating costs and competitiveness.
Furthermore, London’s success as a global city has also led to issues such as congestion, inadequate infrastructure, and environmental concerns. While extensive, the city’s transportation network needs help coping with increasing demand and population growth. Investments in infrastructure projects, such as Crossrail, aim to address these challenges, but ongoing efforts are necessary to ensure efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted London’s economy, as it has impacted cities worldwide. Various sectors, including tourism, hospitality, and retail, experienced disruptions. While recovery efforts are underway, uncertainties surrounding the potential long-term economic repercussions remain a challenge that needs to be navigated.
London’s Resilience and Future Outlook:
Despite these challenges, London’s resilience and adaptability are its strengths. The city has a proven track record of successfully navigating turbulent times and emerging stronger. To overcome its economic challenges, London must continue fostering an environment that supports innovation, encourages investment, and attracts global talent.
Future Outlook
Looking to the future, London’s prospects as a global economic powerhouse remain promising. The city’s ability to adapt, innovate, and capitalize on its strengths positions it for continued growth and prosperity in the years to come.
London’s financial sector, although navigating the post-Brexit landscape, is expected to maintain its prominence as a global financial hub. The city will continue to forge new partnerships and establish relationships beyond the EU, leveraging its robust regulatory framework, deep talent pool, and global connectivity to attract businesses and investment. London’s financial technology (fintech) sector, in particular, is poised to thrive as advancements in digital innovation and the adoption of technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence reshape the financial landscape.
Moreover, London’s diversification into emerging sectors, including technology and the creative industries, will drive its future economic growth. The city’s technology ecosystem will expand, with substantial investments in startups and scale-ups across various tech domains. London’s reputation as a center for innovation, coupled with access to capital and talent, will fuel the growth of disruptive technologies, creating new business opportunities and driving job creation. The city hosts numerous tech startups, incubators, and accelerators, providing fertile ground for entrepreneurial endeavors. London’s vibrant tech scene encompasses diverse fields such as artificial intelligence, fintech, biotechnology, and clean energy, attracting local and international investors eager to tap into the city’s innovation potential.
The creative industries also contribute significantly to London’s economic landscape. The city’s theaters, music venues, art galleries, and film production studios have a global reputation for excellence. London’s creative talent, combined with its rich cultural heritage and supportive infrastructure, enables it to attract artists, designers, and creative professionals from around the world. The creative industries contribute to London’s economy and enhance its cultural vitality, making it a hub for artistic expression and cultural exchange.
London’s tourism sector continues to flourish, drawing visitors from around the globe. The city’s rich historical landmarks, iconic attractions, and world-class museums make it a top destination for travelers. The British Museum, the Tower of London, Buckingham Palace, and the Tate Modern are just a few examples of the city’s must-visit sites. London’s vibrant cultural scene, with festivals, theater productions, and live music events, further enhances its appeal to tourists seeking immersive experiences.
To ensure its future success, London must address several key areas. Investing in affordable housing initiatives is crucial to tackle the city’s affordability crisis and retain a diverse workforce. Enhancing transportation infrastructure, expanding connectivity, and prioritizing sustainable transportation options will help alleviate congestion and facilitate smoother movement across the city. Promoting environmental sustainability and mitigating the impacts of climate change are also vital for London’s long-term prosperity. The city aims to become carbon neutral by 2030, focusing on renewable energy, sustainable transport, and green infrastructure. London will continue to attract investments in clean technologies and drive innovation in sustainability practices, creating a greener and more resilient city for future generations.
As a global metropolis, London is also responsible for addressing global challenges. Taking a leadership role in sustainability efforts, promoting social responsibility, and championing human rights can further enhance London’s worldwide reputation and influence. Collaborating with other cities and sharing best practices can contribute to tackling common challenges faced by urban centers worldwide.
In conclusion, London’s journey from its Roman origins to its status as a thriving global metropolis has been shaped by centuries of history, innovation, and resilience. The city’s economic prowess, cultural vibrancy, and diverse talent pool position it as a beacon of opportunity and a global leader. While London faces challenges, ranging from the impact of Brexit to affordability concerns, its ability to adapt, innovate, and embrace change ensures its continued growth and success. With a focus on fostering innovation, promoting sustainability, and nurturing inclusivity, London is poised to shape its future as a dynamic and influential city on the global stage.

Tokyo, Japan
History
Introduction:
Tokyo, the capital city of Japan, boasts a centuries-long commercial history that has propelled it to the forefront of global economic centers. From its modest origins as a small fishing village named Edo to its current status as a bustling metropolis, Tokyo has established itself as a dominant force in the world economy.
The Rise of Edo as a Political and Economic Center:
In the 17th century, Edo emerged as the political nucleus of Japan when the Tokugawa shogunate established its government there. This stability ushered in an era of peace and remarkable economic growth. Edo became a thriving hub for trade and commerce, attracting merchants from all corners of Japan.
The Transformation into Tokyo and the Meiji Restoration:
During the late 19th century Meiji Restoration, Japan experienced a swift modernization and Westernization process. Edo was renamed Tokyo and designated as the new capital. The government implemented policies to promote industrialization and international trade, fueling the city’s economic expansion.
Resilience and Growth in the 20th Century:
Tokyo witnessed significant growth in the early 20th century following the devastating Great Kanto Earthquake of 1923. The city’s resilience was demonstrated through swift reconstruction efforts, resulting in a surge of economic development. Tokyo became a bustling center for manufacturing and commerce, with thriving industries such as textiles, machinery, and electronics contributing to its economic prosperity.
Post-WWII Transformation and Financial Hub:
The post-World War II era marked a turning point for Tokyo’s recovery and transformation. The city emerged as a major financial and business hub, bolstered by government policies focused on economic development. Tokyo’s stock exchange, the Tokyo Stock Exchange, rose to prominence, attracting investors and companies from around the globe.
The Economic Boom and Technological Advancements:
In the latter half of the 20th century, Tokyo experienced an unparalleled economic boom. The city became a leader in technology and innovation, with major electronics and automobile companies establishing their headquarters within its boundaries. This era, famously known as the “Japanese economic miracle,” propelled Tokyo’s global standing and cemented its reputation as an economic powerhouse.
Expansion of Tokyo’s Financial Sector:
Tokyo’s financial sector expanded rapidly with the establishment of international banks, investment firms, and financial institutions. The city’s financial district, centered around Marunouchi and Nihonbashi, thrived as a bustling center for business and finance.
Current Position
Tokyo’s Current Position as a Leading Global Hub:
Today, Tokyo is a global economic powerhouse and a prominent financial center. Its significance is reflected in its substantial contribution to Japan’s GDP, with Tokyo generating a gross prefectural domestic product of approximately 115.7 trillion Japanese yen in the 2019 fiscal year, accounting for about 21 percent of the nation’s GDP (Source: Statista).
Tokyo’s economic strength is deeply rooted in its diverse sectors: finance, technology, manufacturing, retail, and tourism. The city hosts a multitude of financial institutions, with the Tokyo Stock Exchange serving as one of the largest in the world. Tokyo’s financial sector is vital in facilitating domestic and international trade, investment, and capital flows.
Technological advancements have propelled Tokyo’s reputation as a center for innovation and research. The city is home to numerous tech companies, startups, and research institutions contributing to breakthroughs in electronics, robotics, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence. Tokyo’s technological prowess attracts global talent and fosters an environment of entrepreneurship and innovation.
Tokyo’s manufacturing sector remains robust, encompassing industries such as automobiles, electronics, machinery, and pharmaceuticals. This sector meets domestic demand, drives Japan’s exports, and contributes to the nation’s trade balance. Tokyo’s manufacturing companies are renowned for their high-quality products and advanced production processes.
The retail industry in Tokyo is vibrant and diverse, catering to a wide range of consumer needs. Luxury shopping districts like Ginza and Omotesando attract domestic and international shoppers, while traditional markets, department stores, and innovative concept stores offer diverse retail experiences.
Tourism plays a significant role in Tokyo’s economy, drawing millions of visitors annually. The city’s rich cultural heritage, historic landmarks, world-class museums, and vibrant entertainment districts make it a popular choice for travelers. The tourism industry supports various sectors, including hospitality, food and beverage, retail, and transportation.
Challenges and Path to Sustainable Growth:
Despite its strengths, Tokyo faces certain economic challenges that require attention to ensure sustainable growth and competitiveness. One significant challenge is the high cost of living and limited land availability. Tokyo’s property prices and living expenses rank among the highest globally, posing affordability constraints for individuals and businesses. The high cost of doing business can hinder entrepreneurship and talent attraction.
Another challenge Tokyo faces is its aging population and shrinking workforce. Japan’s declining birth rate and aging demographics impact the city’s labor market and productivity. Tokyo must implement policies and initiatives that encourage workforce participation, enhance productivity, and attract skilled professionals from domestic and international talent pools.
Addressing urbanization-related issues such as traffic congestion, public transportation capacity, and environmental sustainability is vital. Tokyo’s transportation network, including its renowned subway system, needs help meeting a growing population’s demands. Investments in infrastructure projects, such as expanding railway lines and improving transportation efficiency, are necessary to ensure smooth mobility and reduce congestion within the city.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted Tokyo’s economy, particularly in sectors such as tourism, hospitality, and retail. Restrictions on international travel have affected tourism revenues and overall economic growth. Tokyo has been implementing recovery efforts, supporting affected businesses, and stimulating domestic tourism.
Future Outlook
Tokyo’s future as a global economic powerhouse holds immense potential, driven by its unique strengths and unwavering commitment to innovation. The city’s ability to adapt to changing dynamics, leverage emerging technologies, and foster international collaborations positions it for continued growth and prosperity in the coming years.
Tokyo’s financial sector, renowned for its stability and efficiency, will maintain its status as a global financial hub. Despite economic fluctuations and evolving regulatory landscapes, Tokyo’s robust infrastructure, deep market liquidity, and highly skilled workforce will continue to attract businesses and investors. The city’s fintech sector is poised for significant growth, propelled by digital innovation and adopting technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Tokyo’s fintech ecosystem will streamline financial services, enhance customer experiences, and stimulate new business models, reinforcing its position as a global fintech leader.
Tokyo’s commitment to nurturing emerging sectors, such as technology and innovation, will fuel its economic expansion. The city will continue attracting investments in startups and scale-ups, driving breakthroughs in electronics, robotics, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence. Tokyo’s vibrant startup ecosystem, supported by incubators, accelerators, and venture capital firms, will foster entrepreneurship and attract domestic and international investors seeking to capitalize on the city’s innovation potential.
The creative industries will also be crucial in shaping Tokyo’s economic landscape. The city’s dynamic arts, fashion, design, and entertainment sectors enjoy global acclaim for their creativity and excellence. Tokyo’s fusion of traditional craftsmanship with contemporary aesthetics and its embrace of cutting-edge technology makes it a magnet for artists, designers, and creative professionals worldwide. The city’s vibrant cultural scene, encompassing fashion weeks, art festivals, anime expos, and film production studios, contributes to its economic growth and positions Tokyo as a global trendsetter and cultural hub.
The tourism industry in Tokyo is set to thrive, attracting visitors with its unique blend of ancient traditions and futuristic marvels. The city’s iconic landmarks, such as the Imperial Palace, Meiji Shrine, and Tokyo Tower, along with its vibrant neighborhoods like Shibuya and Shinjuku, offer diverse experiences for travelers. Tokyo’s rich culinary scene, encompassing traditional and innovative cuisine, adds to its allure as a global gastronomic destination. The city’s commitment to hosting international events, including the Olympic Games, further enhances its tourism potential and provides a platform to showcase its strengths on a global stage.
To ensure its future success, Tokyo must address several key areas. Affordable housing is crucial to accommodate a diverse workforce and maintain social inclusivity. Enhancing transportation infrastructure, including expanding public transportation networks and promoting sustainable mobility options, will facilitate smoother movement within the city and reduce congestion. Tokyo’s commitment to sustainability should involve promoting renewable energy, investing in green infrastructure, and implementing eco-friendly practices across sectors, ensuring a more sustainable and resilient future for the city.
As a global metropolis, Tokyo is responsible for addressing global challenges and promoting social progress. Taking a leadership role in sustainability efforts, embracing diversity and inclusion, and supporting human rights will enhance Tokyo’s worldwide reputation and influence. Collaborating with other cities within Japan and globally to share best practices and tackle common urban challenges will foster innovation and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
In conclusion, Tokyo’s journey from its modest origins to a thriving global metropolis exemplifies its resilience, technological prowess, and unwavering pursuit of excellence. Tokyo’s economic strength, cultural richness, and commitment to innovation position it as a formidable player on the global stage. By embracing emerging technologies, fostering innovation, and prioritizing sustainability, Tokyo is poised to shape its future as a dynamic, inclusive, and influential city, captivating the world with its blend of tradition and cutting-edge advancements.

Sydney, Australia
History
Introduction:
Sydney, the largest city in Australia, has a vibrant commercial history that has propelled it into a major economic center in the Asia-Pacific region. From its origins as a British penal colony to its present-day status as a global city, Sydney has experienced significant commercial development and growth.
From Penal Colony to Commercial Hub:
Established as a penal settlement by the British in 1788, Sydney’s early economy revolved around agriculture and basic goods production to support its growing population. The city’s importance as a maritime trade hub began flourishing as ships from Europe and Asia frequented its harbor. Exporting wool, timber, and agricultural products was pivotal in Sydney’s initial commercial development.
The Gold Rush and Economic Prosperity:
The discovery of gold in New South Wales in the mid-19th century brought a wave of prosperity to Sydney. The city became a major center for gold trading and the gateway for migrants seeking fortunes in the goldfields. This influx of people and wealth fueled the expansion of businesses, services, and infrastructure, cementing Sydney’s growing economic significance.
The Rise of a Metropolis:
By the late 19th century, Sydney had blossomed into a bustling metropolis. Manufacturing, shipping, and finance industries drove the city’s economic growth. Major banks and financial institutions established themselves in Sydney, setting the stage for its emergence as a financial center.
Growth in the 20th Century:
The 20th century witnessed further commercial development in Sydney. The city’s harbor played a pivotal role in trade and transportation, with shipping and cargo industries rising in prominence. The Port of Sydney became a vital link between Australia and the rest of the world, facilitating the import and export of goods.
Post-World War II Urbanization and Industrialization:
The post-World War II era brought rapid urbanization and industrialization to Sydney. Its population swelled, and new manufacturing, construction, and services sectors thrived. Sydney became a center for automotive production, textiles, and consumer goods.
Diversification and Expansion:
In recent decades, Sydney’s economy has continued to diversify and expand. The services sector, encompassing finance, professional services, tourism, and education, has emerged as a driving force. The city has also become a regional hub for technology, innovation, and startups, attracting local and international investment.
Sydney’s iconic landmarks, such as the Sydney Opera House and Sydney Harbour Bridge, have not only become symbols of the city but also major tourist attractions, contributing to its thriving tourism industry.
Sydney’s commercial history exemplifies transforming from a colonial outpost to a dynamic and cosmopolitan global city. Its strategic location, natural harbor, and diverse economy have positioned Sydney as a trade, finance, and innovation hub, solidifying its status as one of the world’s leading economic centers.
Current Position
Today, Sydney stands as a prominent commercial center and a key economic hub in the Asia-Pacific region. According to .id consulting, the greater Sydney area contributed approximately AU$ 490 billion to Australia’s GDP in the year ending June 2022, representing around 22.75% of the nation’s total GDP.
Sydney’s economic strength is rooted in its diverse sectors, including finance, professional services, tourism, technology, manufacturing, and creative industries. The city has a thriving financial sector, with major banks, investment firms, and financial institutions operating in its central business district. Sydney’s financial services sector is crucial in supporting domestic and international trade, investment, and wealth management.
The professional services industry in Sydney is vibrant and diverse, attracting global companies and skilled professionals who contribute expertise to various sectors and drive economic growth.
Sydney’s tourism industry is a vital pillar of its commercial success. Iconic attractions such as the Sydney Opera House, Bondi Beach, and the Sydney Harbour Bridge draw millions of visitors annually. The city’s vibrant cultural scene, world-class restaurants, and diverse events and festivals make it a popular destination for domestic and international tourists. The tourism industry supports hospitality, retail, transportation, and entertainment businesses.
Sydney also emerges as a technology and innovation hub, fostering entrepreneurship and technological advancements. The city’s tech sector encompasses startups, research institutions, and initiatives in fintech, biotech, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. With government support and university collaboration, Sydney’s startup ecosystem attracts entrepreneurs and investors looking to leverage the city’s innovation potential.
Furthermore, Sydney’s manufacturing sector focuses on advanced manufacturing, aerospace, defense, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. The city’s manufacturing companies are known for their high-quality products, innovation, and advanced technologies. Sydney’s manufacturing prowess supports domestic consumption, exports, and job creation.
Despite its strengths, Sydney faces challenges that must be addressed to ensure sustainable growth and competitiveness. The high cost of living and housing affordability pose constraints for individuals and businesses. Transportation and infrastructure limitations strain the city’s mobility and productivity. Environmental sustainability concerns require action to mitigate climate change and attract sustainable investment.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted Sydney’s economy, particularly in tourism, hospitality, and retail sectors. Recovery efforts, support for affected businesses, and stimulating domestic tourism are essential for economic recovery.
Future Outlook
Sydney’s commercial future is promising, driven by its status as a global business hub, strong economic foundations, and strategic location. The city’s ability to foster innovation, embrace emerging technologies, and capitalize on its diverse industries positions it for continued growth and prosperity.
Sydney’s financial sector will remain a leading financial hub in the Asia-Pacific region. Fintech growth and digital banking solutions will strengthen the financial ecosystem, promoting efficiency and innovation in financial services.
The city’s technology sector is poised for further development, driven by a supportive startup ecosystem, government initiatives, and research and development capabilities. Sydney’s tech scene will lead in areas such as cybersecurity, software development, artificial intelligence, and clean technologies.
Sydney’s creative industries contribute to its commercial future, attracting artists, designers, and creatives worldwide. The city’s vibrant cultural landscape positions it as a global hub for artistic expression and cultural exchange.
Sydney’s tourism industry will continue to thrive, drawing visitors with its iconic landmarks, diverse experiences, and culinary excellence. Major events, conferences, and festivals will showcase the city’s capabilities and foster economic growth.
Sydney must invest in infrastructure development, prioritize sustainability, foster entrepreneurship, and nurture talent through education and skills development initiatives to ensure its future success. Embracing diversity, engaging with neighboring cities and regions, and addressing social and environmental issues will enhance Sydney’s reputation and global standing.
In conclusion, Sydney’s commercial future is bright, driven by its dynamic business environment, innovation ecosystem, and cultural richness. The city’s financial services, technology-driven industries, creative sectors, and tourism industries contribute to its commercial success. By embracing technological advancements, nurturing entrepreneurship, and prioritizing sustainability and social progress, Sydney is poised to shape its future as a vibrant, inclusive, and globally connected city, attracting investments, talent, and opportunities worldwide.

São Paolo, Brazil
History
Introduction:
São Paulo, the largest city in Brazil and one of the world’s most populous cities boasts a dynamic commercial history that has shaped its role as a major economic hub in Latin America. From its humble beginnings as a small village to its present-day status as a bustling metropolis, São Paulo’s journey of commercial development has been nothing short of remarkable.
From Village to Coffee Powerhouse:
Founded in the 16th century by Portuguese colonizers, São Paulo initially faced limitations due to its inland location. However, the 19th century marked a turning point with the growth of coffee production in the surrounding region. Coffee became São Paulo’s primary export, driving its economic expansion. Entrepreneurs and landowners invested in coffee plantations, accumulating substantial wealth and giving rise to a prosperous coffee elite. São Paulo became the heart of Brazil’s coffee industry, attracting migrants from across the country seeking employment opportunities and contributing to the city’s rapid population growth.
Industrialization and Economic Transformation:
By the early 20th century, São Paulo had evolved into a major industrial center. Fueled by its coffee wealth, the city made significant investments in manufacturing, establishing factories in textiles, food processing, and machinery production. São Paulo’s industrialization created jobs, stimulated urban development, and attracted workers from other parts of Brazil, further propelling its economic growth.
Becoming a Commercial Hub:
Throughout the 20th century, São Paulo’s commercial importance continued to expand. The city’s strategic location and robust transportation infrastructure, including railways and highways, facilitated the movement of goods and connected São Paulo to other regions of Brazil. This infrastructure played a key role in positioning São Paulo as a distribution center, enabling the city to trade and distribute coffee and a wide range of goods from various industries.
Diversification and Rise of the Services Sector:
In addition to manufacturing, São Paulo became a financial and services hub. The city’s financial district, centered around Avenida Paulista, became home to numerous banks, investment firms, and corporate headquarters. São Paulo’s services sector, including finance, insurance, real estate, and professional services, played a vital role in its economic growth.
Cultural Diversity and Entrepreneurial Spirit:
São Paulo’s commercial history is closely intertwined with its cultural diversity and entrepreneurial spirit. Immigrants from various countries, particularly Europe, arrived in São Paulo and contributed to the city’s economic development. These immigrant communities established businesses, brought new skills and technologies, and enriched São Paulo’s cultural landscape.
Recent Decades and Commercial Expansion:
In recent decades, São Paulo has embraced its status as a global city and a Latin American center for finance, commerce, and culture. The city has expanded its services sector, focusing on technology, innovation, and creative industries. São Paulo has become a haven for startups, incubators, and coworking spaces, reflecting its growing reputation as an entrepreneurship and innovation hub.
São Paulo’s commercial history illustrates its transformation from a coffee-driven economy to a diversified and cosmopolitan metropolis. The city’s economic growth, cultural diversity, and entrepreneurial environment have firmly established it as a major economic powerhouse and a prominent global city in Latin America.
Current Position
Today, São Paulo maintains a prominent commercial position in Latin America. Known as Brazil’s financial and business center, São Paulo plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy.
São Paulo’s economy is diverse and robust, encompassing finance, manufacturing, services, and commerce sectors. The city is the headquarters for numerous national and multinational companies, making it an important center for business and investment.
An indicator of São Paulo’s commercial strength is its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), São Paulo contributed approximately R$699.28 billion to Brazil’s GDP in 2017, accounting for 10.6% of the nation’s total GDP that year.
The financial sector is a major contributor to São Paulo’s commercial prowess. The city is home to Brazil’s largest stock exchange, B3 (formerly BM&FBOVESPA), and numerous banks, investment firms, and insurance companies. The financial district in downtown São Paulo buzzes with activity, attracting domestic and international investors.
São Paulo’s manufacturing sector is significant, spanning textiles, automotive, machinery, electronics, and food processing. The city’s industrial parks and manufacturing zones house numerous factories and production facilities. São Paulo’s manufacturing prowess supplies domestic markets and contributes to Brazil’s overall trade balance through exports.
The services sector plays a vital role in São Paulo’s commercial landscape. The city boasts a vibrant professional services industry, encompassing legal, accounting, consulting, and advertising firms. São Paulo’s cultural scene, with major events, festivals, and international conferences, further bolsters the services sector.
Additionally, São Paulo has become an attractive destination for technology and innovation. The city is home to numerous tech startups, incubators, and accelerators, fostering an environment of entrepreneurship and technological advancement. The tech industry’s growth has contributed to São Paulo’s economic diversification, positioning it as a regional hub for innovation.
Nevertheless, São Paulo faces significant challenges that require attention and proactive measures. Socioeconomic inequality is a key challenge, reflected in the stark contrasts between affluent neighborhoods and areas of poverty. Ensuring access to quality education, healthcare, and basic services for all population segments is crucial. São Paulo is implementing policies and initiatives to reduce inequality and improve social inclusion.
Infrastructure issues also pose challenges to São Paulo’s economic growth. Rapid urbanization and population growth have strained existing infrastructure, resulting in problems like traffic congestion, inadequate public transportation, and insufficient housing. São Paulo’s transportation system, including roads and public transit, requires substantial investments and improvements to meet the demands of a growing population. Efforts are underway to expand and upgrade transportation networks, including the construction of new metro lines and bus rapid transit systems and the implementation of sustainable mobility solutions.
Environmental sustainability is another challenge for São Paulo. The city’s rapid urban expansion has pressured natural resources and contributed to environmental degradation. Urgent attention and sustainable solutions are required to address issues such as air pollution, water scarcity, and waste management. São Paulo is actively implementing environmental policies and initiatives to mitigate the impact of urbanization, promote sustainable practices, and preserve green spaces.
Governance and bureaucracy challenges can hinder business development and investment in São Paulo. Streamlining administrative processes, reducing red tape, and improving transparency are essential for fostering a favorable business environment and attracting domestic and foreign investment.
To address these challenges, São Paulo is committed to promoting sustainable and inclusive economic growth. The government and private sector are collaborating on initiatives to reduce inequality, improve access to education and healthcare, and provide social support programs for vulnerable communities. Efforts are also underway to invest in infrastructure development, including transportation and housing, to enhance residents’ quality of life and support economic activities.
Furthermore, São Paulo actively engages in sustainable urban planning and environmental conservation efforts. The city is investing in renewable energy sources, implementing waste management strategies, and promoting sustainable practices in industries and businesses.
By tackling these challenges head-on, São Paulo aims to create a more equitable, sustainable, and prosperous future for its residents. The city’s commitment to inclusive growth and sustainable development will contribute to its long-term success as a leading global economic center in Latin America.
Future Outlook
Sao Paulo, driven by its role as a thriving economic powerhouse in Latin America, holds immense potential for its commercial future. The city’s adaptability, diverse industries, and entrepreneurial spirit position it for continued growth and prosperity. By leveraging its strengths, embracing innovation, and fostering sustainability, Sao Paulo is set to shape its future as a dynamic and globally connected metropolis.
Financial Hub and Digital Innovation:
Sao Paulo’s financial sector, supported by a robust banking system and capital markets, is poised to maintain its leading position in Latin America. The city’s deep pool of financial talent, strong regulatory framework, and access to capital attract domestic and international financial institutions. B3, Sao Paulo’s stock exchange, serves as a hub for regional trading, while the vibrant fintech ecosystem fosters digital innovation in financial services, driving financial inclusion and digital transformation.
The Technology Trajectory:
Sao Paulo’s technology sector is on a rapid ascent, fueled by a thriving startup ecosystem and a focus on digital innovation. The city embraces various fields, including software development, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and health tech. Incubators, accelerators, and venture capital firms support Sao Paulo’s startup community, nurturing entrepreneurship and attracting investment. With its large consumer market and entrepreneurial culture, Sao Paulo has become a catalyst for technological disruption, positioning itself as a hub for innovation and technological advancement in Latin America.
Cultural Capital and Artistic Expression:
Sao Paulo’s creative industries play a significant role in its commercial landscape, showcasing its cultural richness and creativity. The vibrant arts, fashion, design, and entertainment sectors attract global attention through Sao Paulo Fashion Week, art festivals, design fairs, and film production studios. Sao Paulo’s multiculturalism, creative talent, and entrepreneurial drive foster a dynamic, innovative ecosystem, solidifying the city’s position as a cultural capital and a hub of artistic expression.
Tourism and Beyond:
Sao Paulo’s tourism industry presents abundant growth opportunities, capitalizing on its cultural heritage, vibrant nightlife, and diverse attractions. Architectural landmarks such as the Sao Paulo Cathedral and the Sao Paulo Museum of Art provide unique experiences for visitors. The city’s renowned culinary scene, a fusion of international flavors and local cuisine, adds to its allure as a gastronomic destination. Sao Paulo’s commitment to hosting major events, conferences, sports competitions, and cultural festivals further elevates its tourism potential, showcasing its capabilities on a global stage.
Sustainable Development and Social Progress:
To ensure its future success, Sao Paulo must address key areas. Investments in infrastructure development, including transportation networks and digital connectivity, will enhance mobility, reduce congestion, and boost productivity. The city’s commitment to reducing social inequalities, improving education and healthcare systems, and fostering inclusive growth will pave the way for social progress and equal economic opportunities. By promoting sustainable practices, environmental conservation, and adopting renewable energy, Sao Paulo will bolster its resilience to climate change and contribute to a greener future.
Global Collaborations and Ethical Practices:
As a global metropolis, Sao Paulo is responsible for addressing global challenges and contributing to social and economic development. Sao Paulo can promote knowledge sharing, innovation, and inclusive growth by fostering collaborations with other cities, regions, and industries. Embracing corporate social responsibility, supporting ethical business practices, and championing social causes will enhance Sao Paulo’s reputation and influence on the global stage.
Conclusion:
Sao Paulo’s commercial future is promising, driven by its economic strength, cultural richness, and entrepreneurial dynamism. The city’s financial sector, technology-driven industries, creative sectors, and tourism industry all contribute to its commercial success. By embracing innovation, nurturing entrepreneurship, and prioritizing sustainability and social progress, Sao Paulo is poised to shape its future as a vibrant, inclusive, and globally connected metropolis, attracting investments, talent, and opportunities from around the world.
Program Benefits
Finance
- Improved Performance
- Enhanced Capital
- Cashflow Optimization
- Process Streamlining
- Financial Reporting
- Forecasting Accuracy
- Budget Control
- Profit Maximization
- Prioritization Planning
- Revenue Growth
Management
- Informed Decision-Making
- Streamlined Operations
- Increased Productivity
- Effective Communication
- Cost Reduction
- Enhanced Visibility
- Growth Enabler
- Stakeholder Satisfaction
- Accelerated Innovation
- Strategic Alignment
Marketing
- Competitive Advantage
- Improved Conversion
- Enhanced CRM
- Scalable Sales
- Higher Profitability
- Better Forecasting
- Enhanced Negotiation
- Stronger Pipeline
- Efficient Prospecting
- Effective Upselling
Testimonials
Cook Medical
“Mr. Cody is an experienced professional who’s detailed and collaborative approach allows him to capture critical client requirements to deliver quality services. He draws on his vast previous experience to develop creative and innovative solutions for complex problems. I would have no hesitation in recommending Mr. Cody as he is a very diligent, committed, and talented professional who always strives for excellent results. I would also welcome the opportunity to work with Mr. Cody on future project endeavours.”

Pembroke Alliance
“Mr. Cody has proven invaluable to our client businesses across diverse industries and sectors, enabling them to achieve a distinct competitive advantage. Through his guidance, these businesses have experienced transformative results, undergoing significant improvements through continuous improvement initiatives, and empowering their employees’ personal and professional growth. It’s clear that Mr. Cody’s passion for Operational Excellence goes beyond theory. While his depth of knowledge in Operational Excellence tools and techniques is vast, he excels in translating these concepts into tangible solutions that deliver immediate impact. This approach ensures that businesses can swiftly implement strategies, leading to improved efficiency, productivity, and overall performance.”

Abbott Laboratories
“I would highly recommend Mr. Cody as someone to do business with. A relentlessly positive professional, who is always extremely accountable and passionate about his work. Mr. Cody is a good-spirited, results-driven individual with a focus on sustainable improvements, while following excellent people leadership processes. His strong analytical capability, demonstrated in multiple projects, coupled with his great appreciation for operational excellence principles & processes were crucial in root cause identification of complex problems and driving significant year-on-year cost improvements. Mr. Cody always completed every project to the highest level and took pride in this. He was a wonderful mentor and loved helping others see and reach their potential. It was a pleasure to work alongside Mr. Cody.”
Prodieco Advanced Engineering Solutions
Prodieco Advanced Engineering Solutions brought Mr. Cody on board in a consultant capacity to support the reduction of manufacturing-related quality nonconformances and improve first-pass yield. Mr. Cody quickly identified and drove a number of standardisation and de-risking initiatives. Following a 3-month period where there was 1 day consultation per week, the rate of manufacturing-related quality nonconformances fell by 31% in comparison to historical data. Additionally, sharing lessons learned and improving culture resulted in other areas of the business (not in the scope of the project) also demonstrating improvement. Overall, there was a 42% reduction in quality nonconformances across the site.
Boston Scientific
“Mr. Cody is a great role model, a pleasure to work with, and an excellent engineer.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.

















