AI for Business Transformation

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for AI for Business Transformation is provided by Mr. Laboy Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Laboy, an artificial intelligence strategist, technologist, and data scientist, has collaborated with global brands across multiple sectors to integrate AI solutions for enhanced business growth and performance. Prior to being a learning provider with Appleton Greene, Mr. Laboy served as a Managing Director at Accenture. His diverse career has seen him in roles such as Chief Precision Officer, Chief Data Officer, EVP of Performance and Business Transformation, Chief Strategy Officer, and Senior Partner at an array of consultancies, agencies, and technology firms.
With a solid academic foundation, Mr. Laboy has a Bachelor of Science in Economics, a Master’s in Economics, and an MBA in Finance. He is fluent in English, Spanish, French, and Portuguese. With substantial professional engagements in North America, Europe, Asia, and Latin America, Pedro brings a global perspective to his work. Additionally, he is a former US Army paratrooper.
To request further information about Mr. Laboy through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
AI for Business Transformation
The AI for Business Transformation Training Program is a meticulously designed, comprehensive course aimed at equipping professionals with the knowledge and tools necessary to harness the vast potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in today’s business landscape. Spread across four distinct phases, the program delves deep into foundational AI concepts, emerging technologies, practical applications, and the future trends that are set to shape industries.
Benefits of this program include a robust understanding of how AI can drive innovation, streamline operations, and create competitive advantage. Participants will learn to craft AI strategies, ensure ethical AI deployment, optimize business functions using AI, and stay abreast of rapid technological advancements.
The target audience for this program ranges from business leaders and decision-makers looking to integrate AI into their strategic planning, to managers and professionals keen on understanding AI’s implications in their respective domains. Although tailored for non-technical individuals, IT managers, product developers, and those in data-centric positions will undoubtedly gain significant benefits from the curriculum.
Upon completion, businesses can expect a workforce that’s not only knowledgeable about the latest in AI but also skilled in its practical application. This translates to informed decision-making, innovative product development, enhanced customer experiences, and the ability to navigate and lead in an AI-driven future.
Background
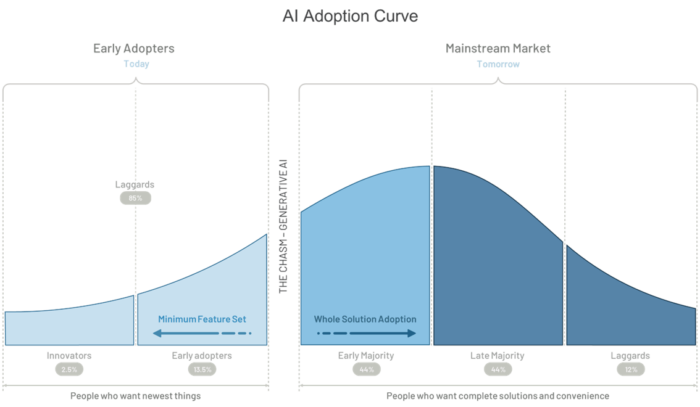
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its emerging subset, Generative AI, are now vital partners in enhancing human expertise within the modern business landscape. No longer confined to the realms of academic research or the imaginative world of science fiction, AI’s true potential is being increasingly recognized and utilized in the corporate sector. This shift, fueled by the abundance of data, advanced machine learning techniques, generative models, and improved computational power, has brought AI from theoretical discussions to practical, strategic applications in boardrooms and core business operations. In the current business environment, AI, especially with the innovative edge of Generative AI, is seen not as a replacement for human intelligence but as a powerful tool that augments and extends our capabilities. It is a transformative force that is reshaping industries by empowering human decision-making with deeper insights, efficiency, and creativity.
Why Now
In today’s digital era, characterized by data’s ubiquity, conditions are ripe for the proliferation and pragmatic application of AI, especially Generative AI. Enterprises today are awash with an unparalleled volume of data. Yet, raw data, without interpretation or business applications, is just untapped potential. AI, including generative models, act as the key, converting this massive data influx into actionable intelligence, domain specific content, and intricate task automation, becoming the bedrock of innovation and business growth. As enterprises grapple with evolving customer needs, the need to deliver tailored, efficient, and innovative solutions grows. AI stands at the forefront of this challenge, enabling businesses to not only meet but consistently exceed these customer expectations. Integrating AI is not just a strategic edge—it is a growth engine for the enterprise.
Financial and Business Benefits
Embracing AI for Competitive Advantage: The rise of AI, particularly the groundbreaking Generative AI, presents an unparalleled opportunity for growth and innovation in the business world. Companies that proactively adopt and integrate AI into their operations are setting themselves up for a future of success. They are not only maintaining pace with technological advancements but also positioning themselves at the forefront of their industries. By leveraging AI, businesses can enhance their product offerings, streamline services, and create unmatched customer experiences, giving them a significant edge over competitors. This isn’t just about staying relevant; it’s about leading the charge in a constantly evolving market. The financial benefits are clear: improved market positioning, enhanced profitability, and business scalability. Organizations that harness the transformative power of AI are not just keeping up—they’re setting the pace, ensuring their place at the top in an increasingly AI-driven marketplace. In the realm of AI, proactive engagement is key to turning potential business challenges into substantial financial gains.
Curriculum
AI for Business Transformation – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 AI Fundamentals
- Part 1 Month 2 AI Strategy
- Part 1 Month 3 AI Governance
- Part 1 Month 4 AI Architecture
- Part 1 Month 5 Generative AI
- Part 1 Month 6 AI Knowledge Management
- Part 1 Month 7 AI Workforce and Workflows
- Part 1 Month 8 AI in Business Functions
- Part 1 Month 9 AI Business Innovation
- Part 1 Month 10 Ethical Considerations and Bias
- Part 1 Month 11 AI Continuous Improvement
- Part 1 Month 12 Future Trends
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene AI for Business Transformation corporate training program.
AI for Business Transformation – Part 1 – Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 AI Fundamentals – Embarking on the AI journey requires a strong foundational knowledge, particularly for business leaders aiming to leverage AI to drive value within their organizations. This introductory session is meticulously designed to decode the intricate world of artificial intelligence, making its foundational principles accessible and relevant to business leaders from all sectors. This session begins with a historical perspective, tracing AI’s evolution from its nascent stages in academia to the sophisticated algorithms shaping today’s digital landscape. Understanding the milestones in AI’s development is critical for grasping the pace of current innovations and anticipating future trends. As we dive into the terminologies and concepts that form AI’s backbone, participants will unravel the nuances of machine learning, neural networks, computer vision, generative AI, and natural language processing. Each term will be demystified through engaging narratives that contextualize these concepts within the business environment, complemented by visuals that illustrate their functionality. In addition to theoretical understanding, this session will showcase AI’s transformative power across a range of industries and business functions. Participants will explore real-world case studies demonstrating AI’s applications, from streamlining supply chains to customizing user experiences. These examples serve not only to inspire but also to instill a pragmatic perspective on AI’s practical benefits and its strategic integration into various business models. Moreover, this program will confront AI’s limitations head-on, discussing the ethical considerations and potential pitfalls of AI integration. It’s essential for business leaders to recognize these boundaries to set realistic expectations and to foster responsible AI adoption within their operations. Interactive expert-led discussions will offer attendees the opportunity to address their queries, ensuring a clear understanding of AI’s implications for their specific business needs. By the end of this foundational module, participants will have acquired a comprehensive understanding of AI’s history, capabilities, and limitations.
- Part 1 Month 2 AI Strategy – The transformative power of artificial intelligence in the business sphere is no longer just theoretical—it’s a practical reality that is redefining the way we think about innovation, competitive advantage, and strategic growth. This session is engineered to take participants beyond the buzzwords and into the heart of AI’s tangible business applications and the strategic imperatives that unlock its comprehensive benefits. As we delve into the session, business leaders will engage with a structured and methodical approach to embedding AI into their strategic initiatives. Through a series of interactive workshops, the participants will actively participate in the exploration of AI’s real-world implications across a variety of business models. We will dissect several use case studies to extract valuable lessons and best practices, illuminating the pathways through which AI can create value and drive business growth. The session is designed to be highly collaborative, encouraging dialogue and exchange of ideas among attendees. This collaborative atmosphere will serve as a crucible for refining the understanding of how AI capabilities can be most effectively aligned with specific business objectives. Participants will learn to sift through the plethora of AI technologies and identify those that offer the most significant return on investment for their unique business context. As we progress, attendees will be tasked with engaging in exercises that mirror the challenges and decisions they will face in their respective organizations. These exercises will hone their skills in strategy formulation, focusing on how to marry AI’s technological potential with the strategic direction of their business. They will leave with not only a theoretical framework but practical experience in drafting strategies that incorporate AI. By the end of the session, participants will be equipped not just with an understanding but with a practitioner’s insight into formulating and executing AI strategies. They will have the knowledge needed to propel their organizations forward, utilizing AI not as an auxiliary tool but as a central pillar in their strategy to achieve innovation, efficiency, and a significant competitive advantage in their markets.
- Part 1 Month 3 AI Governance – The promise of artificial intelligence carries with it an intricate web of governance challenges, ethical considerations, and the need for vigilance in data privacy and security. This session is crafted to take participants on a deep dive into the essential governance frameworks that underpin responsible and effective AI deployment. As we navigate the complexities of AI in the business world, understanding the balance between innovation and ethical responsibility is paramount. Participants will engage with the foundations of regulatory compliance, exploring the global landscape of legislation that shapes AI development and deployment. The session will highlight key principles of data management, including data quality, integrity, and the critical importance of securing sensitive information. This journey into the governance of AI will enable attendees to not only meet regulatory demands but also to exceed them, setting new standards for best practice in their industries. Central to our discussions will be the ethical implications of AI. As we examine the transformative impact of AI, we will confront the ethical dilemmas that arise with such a powerful tool. Interactive discussions will challenge participants to consider the consequences of AI decisions, the importance of building trust with stakeholders, and the role of AI in shaping the future of work and society. Potential biases inherent in AI systems will be another focal point, as we scrutinize the origins of these biases and the measures needed to mitigate them. Participants will gain insights into how to build fairness into their AI systems, ensuring that their AI initiatives are inclusive and equitable. Security protocols cannot be overlooked, and this session will ensure that attendees are well-versed in the best practices for safeguarding AI systems against breaches and misuse. As the threats evolve, so too must the defenses, and we will provide a comprehensive overview of current and emerging security challenges in AI. By the conclusion of this module, participants will not only comprehend but also be ready to implement governance strategies that are robust, ethical, and forward-thinking. They will be prepared to champion AI projects that are at the forefront of innovation, while also being exemplary in terms of security, privacy, and ethical considerations. Attendees will leave with the knowledge and tools necessary to ensure that their AI initiatives are not only successful but also aligned with the highest standards of governance and ethical responsibility.
- Part 1 Month 4 AI Architecture – In the intricate dance of integrating AI into business, the stage upon which all algorithms perform is the technological infrastructure. This session is carefully designed to unpack the complexities and evolving nature of AI technology infrastructures that stand as the backbone of any successful AI deployment. As businesses strive for a competitive edge, the ability to build and manage a robust, adaptable, and scalable technology environment is critical. Participants will embark on a journey through the latest in cloud-based AI solutions, on-premises deployments, and hybrid models, gaining a clear understanding of the strengths and considerations of each. This exploration is tailored to provide the knowledge necessary for making informed decisions about which infrastructural paths will best support their AI ambitions. AI Cloud solutions, with their promise of scalability and flexibility, will be a primary focus. Attendees will learn how cloud environments can be leveraged to drive efficiency and innovation, offering a detailed look at service models like Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). They will explore how these models can accelerate AI initiatives while being cost-effective and minimizing the burden on in-house IT resources. However, cloud is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and we will delve into the nuances of on-premises infrastructures that some organizations might prefer due to their unique requirements for control, security, or data sovereignty. Attendees will examine the trade-offs and potential synergies of on-premises environments, becoming adept at evaluating when and how they might be the appropriate choice for hosting AI applications. The session will further address the intricacies of designing AI architectures that align with specific business needs and constraints. Participants will be encouraged to think critically about how to construct AI systems that are not just functional but optimized for the unique demands of their business context. By the end of this session, participants will possess a clear vision of how to conceptualize AI infrastructures. They will leave equipped with the insights to identify AI solutions that are not only resilient and flexible but also impeccably aligned with overarching business strategies and objectives. This module ensures that business leaders are not just observers but active participants in the creation of an AI-ready enterprise.
- Part 1 Month 5 Generative AI – The landscape of artificial intelligence is continually expanding, and at its vanguard are generative AI, large language models, and a broad spectrum of emergent technologies. These tools are not merely enhancing current operations; they are redefining the potential of entire industries. This session is designed to demystify these cutting-edge technologies, offering participants a thorough understanding of their mechanisms, capabilities, and the transformative impact they can unleash within various business sectors. Generative AI stands as one of the most exciting developments in the field, with its ability to create new content — from realistic images and text to synthetic data and innovative designs. Participants will delve into the principles that drive these generative models, including text-to-text, text-to-image, and text-to-voice models. Attendees will engage with real-world examples that showcase how generative AI is being harnessed across sectors such as media, marketing, and product development to create novel solutions and experiences. Participants will gain an in-depth perspective on how these models function, their training processes, and the nuances of their language understanding and generation capabilities. Through hands-on workshops and expert-led discussions, attendees will learn about the broad applications of these models in automating customer service, generating insightful data analyses, and even aiding in creative writing and content creation. As we probe further into the realm of emerging AI technologies, this session will also shine a light on the latest advancements and their implications for the future of business. Topics such as quantum computing’s role in AI and edge AI will be unpacked to provide a comprehensive picture of the AI technological horizon. By the end of this module, participants will not only have gained an appreciation for the sophistication and possibilities presented by these technologies but will also be equipped with the knowledge to thoughtfully consider how they might be leveraged to drive innovation and growth within their own organizations. The session aims to prepare attendees to be at the forefront of adopting these technologies, ensuring they are well-positioned to lead their businesses into a future where AI is not just a tool but a catalyst for enduring success.
- Part 1 Month 6 AI Knowledge Management – In the rapidly advancing realm of artificial intelligence, it is essential for business leaders and technologists to stay abreast of the latest tools and techniques that drive AI effectiveness and innovation. This session is carefully crafted to delve into the cutting-edge aspects of AI knowledge management, fine-tuning of models, and the art of prompt engineering—skills critical for leveraging AI to its maximum potential. The session begins with an exploration of AI knowledge management—the methodologies by which AI systems are fed, curated, and updated with information. This process is foundational to ensuring AI models retain relevancy and accuracy over time. Participants will learn how to manage the influx of data and insights in a way that AI systems can assimilate and utilize effectively, thereby enhancing their functionality and application in business contexts. Model fine-tuning is the next pillar of this session. Attendees will gain an understanding of how pre-trained models, such as those used in Generative AI, can be tailored to specific organizational needs. Fine-tuning allows businesses to customize general AI models to their unique datasets and challenges, resulting in greater precision and performance. Through practical exercises, participants will explore the steps involved in fine-tuning and learn how to implement this practice to achieve their strategic objectives. Prompt engineering stands as a revolutionary approach in the interaction with AI, particularly with sophisticated language models. It involves crafting inputs to AI systems in a way that elicits the most accurate and useful outputs. This segment of the session will focus on the strategies behind effective prompt design, enabling attendees to communicate with AI in a manner that leverages the model’s capabilities to the fullest. Interactive workshops will guide participants through the nuances of prompt engineering, helping them to understand how to ask the right questions and provide the right information to AI to optimize the responses received. By the conclusion of this session, participants will not just understand these advanced AI concepts but will be capable of applying them directly to their business challenges. They will emerge as savvy navigators of the AI landscape, equipped with the knowledge and skills to harness the power of Generative AI, model finetuning, and more. This will empower them to envision innovative solutions and applications, ultimately driving business growth and maintaining a competitive edge in an AI-driven marketplace.
- Part 1 Month 7 AI Workforce and Workflows – Artificial Intelligence is not just transforming the tools we use in business; it is revolutionizing the very fabric of workforce dynamics and operational methodologies. This profound shift calls for leaders to reassess and reconfigure the traditional paradigms of work. This session is meticulously designed to guide participants through the complex landscape of AI-induced change within the workforce, equipping them with the foresight and strategies necessary to lead a successful transition. The session sets the stage by addressing the impacts of AI on current job roles and operations. Participants will investigate how AI applications, by automating mundane and repetitive tasks, can liberate the workforce to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors, thereby enhancing job satisfaction and productivity. The discussion will extend to understanding AI’s role in augmenting human capabilities, showcasing how collaboration between humans and AI can create unprecedented efficiencies and innovation opportunities. A core focus of this session will be on navigating the transition within the workforce that AI necessitates. We will dissect case studies illustrating successful integrations of AI into various business models, scrutinizing the approaches and mindsets that facilitated these transitions. Through interactive discussions and expert insights, participants will be armed with the knowledge to lead change management initiatives, addressing the concerns and expectations of their teams. Upskilling the workforce to work alongside AI will be a critical component of this session. Attendees will be exposed to strategies for identifying skill gaps and creating development programs that empower employees to thrive in an AI-enhanced environment. We will delve into the latest educational platforms and frameworks for continuous learning, ensuring that the human element of the business evolves in step with technological advancements. The final segment of this session will focus on workflow redesign. Participants will learn how to re-engineer processes and operational structures to maximize the benefits of AI integration. By its conclusion, attendees will be proficient in developing a comprehensive strategy that not only adopts AI technology but also optimizes the collaborative potential of humans and machines. They will leave prepared to steer their organizations toward a future where AI acts as an enabler of growth, innovation, and job enrichment, ensuring a seamless synthesis of technology with human ingenuity.
- Part 1 Month 8 AI in Business Functions – In this dynamic era, Artificial Intelligence stands as a beacon of innovation across all functions of business. This session will focus on how AI can be leveraged to revolutionize departmental operations and enhance business capabilities. With a focus on functions such as marketing, sales, customer service, human resources, and finance, we aim to equip participants with a deep understanding of how AI can be instrumental in driving efficiency and fostering innovation within various business units. This module is thoughtfully structured to dissect the impact of AI within the ecosystem of an organization. Attendees will delve into the transformative role of AI in marketing, learning how it can personalize customer experiences, automate content delivery, and optimize campaign strategies. In sales, the discussion will revolve around AI’s ability to enhance lead qualification, forecast sales trends, and streamline customer relationship management processes. In customer service, the discussion will focus on how AI can enhance product adoption, self-service options, and support ticket prioritization, significantly improving response times and overall customer satisfaction. The narrative will then shift to the realm of human resources, where participants will explore how AI is redefining talent acquisition, employee engagement, and performance analytics. We will also touch upon AI’s influence in finance, discussing automated fraud detection, risk management, and accounting operations automation. This session will be laden with real-world examples to solidify the understanding of AI’s practical applications. Interactive discussions will provide a platform for attendees to engage with thought leaders and peers, thereby enhancing their learning through collective insights. Hands-on activities will further cement their knowledge by simulating AI integration scenarios, allowing participants to experience the decision-making process firsthand. As the session culminates, participants will be proficient in identifying and unleashing AI opportunities within their specific domains. They will leave with a roadmap to pilot AI-driven transformations tailored to their unique business functions. This will empower them to drive forward initiatives that not only streamline operations but also deliver unprecedented value to customers. Ultimately, attendees will emerge as champions of change, poised to embed AI strategically within their business practices to achieve a competitive edge in the market.
- Part 1 Month 9 AI Business Innovation – The ninth session of our comprehensive AI training program is meticulously designed to navigate the complexities of AI integration in the product and service development lifecycle. As the market landscape rapidly changes with increasing consumer demands for smarter, more intuitive products and services, AI has become a linchpin in the quest for innovative product design and delivery. This session is dedicated to imparting an in-depth understanding of how AI can serve as a springboard for innovation, significantly enhancing how businesses conceptualize, develop, and deploy new products and services. Our aim is to guide participants through the myriad of ways in which AI can revolutionize product development. Attendees will gain critical insights into the process of infusing AI to elevate new product or service features, increase functionality, and ultimately enhance the end-user experience. We will unpack the role of AI in each stage of product and service development, from the drawing board where ideas are born, through the intricate development phase, and onto the market launch. Through a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical case studies, participants will learn about the latest AI tools and methodologies that can predict market trends, automate design processes, and provide actionable insights to create products that resonate with consumers. We will delve into topics such as AI-driven data analytics for understanding customer needs, machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance, and the use of neural networks for improving product and service quality. This interactive session will be enriched with hands-on workshops where participants will engage in simulated AI product and service development scenarios, providing a realistic practice ground for the skills they have acquired. Collaborative discussions with industry experts will further hone their ability to strategically implement AI, ensuring that they are able to navigate potential challenges and embrace best practices for success. By the end of this session, attendees will be well-equipped with the competencies required to lead AI-centric product and service development projects. They will have a clear vision of how to integrate cutting-edge AI technologies to maintain market relevance, gain a competitive edge, and achieve heightened levels of customer satisfaction. With these capabilities, participants will be prepared to propel their organizations forward, leveraging AI not just as a tool, but as a transformative force in the journey of product and service innovation.
- Part 1 Month 10 Ethical Considerations and Bias – In the rapidly advancing field of artificial intelligence, navigating the complexities of ethical deployment, recognizing inherent biases, and effectively measuring the impact of AI implementations are paramount. The session is carefully designed to address these significant facets head-on. This session’s goal is to impart a nuanced understanding of the ethical challenges and considerations that come with the integration of AI systems. We aim to provide a thorough grounding in recognizing and mitigating biases that may arise in AI algorithms and datasets. Throughout this intensive session, we will engage participants in a series of case studies that bring to light the ethical quandaries faced by organizations across different sectors. Attendees will analyze real-world scenarios where AI has posed ethical dilemmas, dissecting how different approaches to resolution can lead to varying outcomes. These narratives will serve as a backdrop for deep discussions led by experts in AI ethics, offering insights into the latest thinking and best practices in the field. A substantial portion of the session will be devoted to the issue of bias in AI. Bias can manifest in many forms, from the data used to train algorithms to the design of the AI systems themselves. Participants will be exposed to the techniques for identifying biases and the methodologies employed to ensure AI systems operate fairly and impartially. Interactive activities will challenge attendees to apply these techniques, fostering a hands-on understanding of the process. Measuring AI’s impact goes beyond the bottom line; it encompasses the assessment of societal, ethical, and business outcomes. We will explore tools and frameworks that help quantify the efficiency gains from AI, the enhancement of customer experiences, and the broader societal implications such as job displacement or privacy concerns. We will also consider the challenges of measuring intangible benefits and the importance of aligning AI metrics with overall business goals. By the conclusion of this session, participants will emerge with a robust toolkit of ethical guidelines, bias mitigation strategies, and measurement techniques. They will be well-equipped to oversee AI implementations that are not only innovative and impactful but also aligned with the core values of responsibility, fairness, and transparency. This ensures that the organizations they represent can foster trust and maintain a competitive edge in an AI-driven future.
- Part 1 Month 11 AI Continuous Improvement – Embarking on a journey of AI integration is not just about initial success—it’s about sustaining performance and ensuring continuous alignment with evolving business goals. Our meticulously crafted session is poised to take participants deeper into the realm of AI operational excellence. This essential training component focuses on the vigilant oversight of AI systems, teaching participants to not only anticipate and respond to challenges but also to harness opportunities for perpetual refinement and enhancement. Participants will be exposed to the strategic importance of continuous monitoring in maintaining the efficacy of AI deployments. They will gain practical knowledge of advanced tools and methodologies that are critical in detecting deviations in performance, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on improvement potential. This session will cover the spectrum of monitoring, from basic oversight to advanced analytical techniques that can predict issues before they impact business operations. We will explore a series of real-world scenarios, drawing from a reservoir of case studies that demonstrate the power of a proactive approach to AI system maintenance. Attendees will actively engage in interactive discussions that foster a profound understanding of how continuous monitoring is a cornerstone of AI systems’ health and longevity. Through this session, participants will cultivate the skills necessary for establishing robust monitoring frameworks that ensure AI systems remain up-to-date, effective, and fully optimized. We will delve into strategies for periodic reassessment of AI models to keep them in sync with dynamic market trends and internal business changes. Furthermore, this training will emphasize the importance of iterative improvements, enabling AI systems to evolve and scale as part of the organization’s growth trajectory. By the end of this immersive session, participants will emerge as competent overseers of AI systems, armed with the knowledge and techniques to guarantee that these systems consistently deliver maximum value.
- Part 1 Month 12 Future Trends – The dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence is in constant flux, with new trends and technologies emerging at a breakneck pace. This session is the capstone of our comprehensive training program, designed to prepare participants for the future of AI and equip them with strategies to maintain a competitive advantage. The primary aim of this session is to provide participants with a panoramic view of the upcoming trends in AI, examining the technologies poised to disrupt the market and exploring their practical applications. Our focus is on equipping attendees with the knowledge and foresight to anticipate changes, leverage new opportunities, and navigate potential challenges that AI innovations may present. Throughout this session, we will explore carefully curated presentations that spotlight cutting-edge AI technologies. These presentations will dissect the mechanics and implications of these advancements, from quantum computing’s role in AI to the rise of autonomous systems to the power of edge AI, and will provide an understanding of how such technologies will impact business in the future. Interactive discussions will serve as a platform for a deeper dive into these topics, encouraging attendees to exchange ideas and consider the implications of AI trends within their own industries. This collaborative environment will foster a community of thought leaders who are well-versed in the language of tomorrow’s AI innovations. An integral component of this session is the development of strategies for staying at the vanguard of AI advancements. We will outline actionable steps businesses can take to cultivate a culture of continuous learning and agility, ensuring they can swiftly adapt to the AI evolution. This includes insights into investing in talent development, fostering innovation, and developing a resilient mindset towards technological change. By the end of this session, participants will not only understand the horizon of AI but also how to effectively align these insights with their strategic planning. Attendees will leave with a comprehensive toolkit that includes knowledge of future AI trends, insights into potential business impacts, and strategies for ensuring their organizations remain ahead of the curve in a world where AI is not just a tool, but a game-changer.
Methodology
AI for Business Transformation
Phase 1: Laying the Foundation
In the swiftly evolving landscape of modern business, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth, innovation, and competitive advantage. Phase 1 of this program, Laying the Foundation, is meticulously constructed to provide participants with a robust introduction to the multifaceted world of AI, ensuring a deep foundational understanding that will serve as the bedrock for all future AI-related endeavors within their organizations.
Understanding that knowledge is the precursor to mastery, this phase begins with an immersive dive into the essentials of AI. It is not simply about acquainting participants with the terminology but about instilling a profound appreciation for the transformative power of AI technologies. The journey commences with AI Fundamentals, a module specifically designed to bridge the gap between abstract AI concepts and tangible business impact. Leaders will emerge from this session not only with a grasp of AI’s capabilities but with a vision of its potential to redefine the very nature of their business operations.
The education continues with AI Strategy, a session that translates the theoretical aspects of AI into practical, actionable strategies. Participants will explore a tapestry of AI applications, witnessing firsthand the versatility of AI across various industry sectors. By examining real-world case studies, they will uncover how AI strategies are crafted and executed, aligning technological capability with business objectives. This session is about empowering leaders with the knowledge to not only envision AI initiatives but to drive them to fruition, ensuring alignment with broader business goals for maximum return on investment.
AI Governance rounds out the first phase, addressing the complex web of considerations that underpin responsible AI deployment. In an age where data is both currency and commodity, managing it with integrity is paramount. This session delves into the legislative frameworks that govern AI, the ethical dilemmas it may present, and the security protocols necessary to safeguard sensitive data. Attendees will engage with the moral questions posed by AI, from algorithmic bias to the broader societal impacts of automation, emerging with a comprehensive understanding of how to navigate these challenges thoughtfully and strategically.
By the end of Phase 1, participants will not only recognize the areas within their operations ripe for AI integration but will also be equipped with the critical thinking skills necessary to question, evaluate, and strategize. This foundational knowledge is essential, for it allows business leaders to make informed decisions about where and how to deploy AI solutions effectively. As they progress through the program, the insights gained here will underpin their learning, enabling them to approach AI not just as a tool but as a transformative force capable of reshaping the very fabric of their business models.

Phase 2: AI Technical Acumen
Phase 2, AI Technical Acumen, propels participants deeper into the technicalities of AI, showcasing cutting-edge innovations and providing a hands-on approach to understanding and leveraging these technologies for strategic business outcomes.
AI Architecture, the fourth session, delves into the architectural decisions critical to effective AI implementation. Participants will explore the significance of developing AI systems that are not just technologically advanced but also strategically aligned with business objectives. This session aims to demystify the technical infrastructure of AI, highlighting how a well-designed system can facilitate scalability, reliability, and business agility. By understanding the key components and considerations in AI architecture, leaders will be better equipped to make strategic decisions that enable seamless AI integration and drive long-term business value.
The fifth session, Generative AI, immerses attendees in the exciting advancements that are at the forefront of AI today. This session provides a deep dive into generative models, large language models like GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer), and other novel AI technologies that hold the potential to revolutionize industries. Participants will engage with the implications of these technologies, learning how they can be harnessed to create new business models, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. The session will also touch upon the practical aspects of adopting these technologies, including the necessary considerations for responsible and ethical deployment.
In the sixth session, AI Knowledge Management, the focus shifts to the meticulous process of optimizing AI models. This involves an in-depth look at knowledge and data management strategies, methods for fine-tuning models to align with specific business needs, and the art of prompt engineering to elicit the best performance from AI systems. Participants will gain insights into the lifecycle of AI model management, from development to deployment and maintenance, ensuring they deliver consistent and reliable results that align with organizational goals.
Throughout Phase 2, the emphasis is on not just understanding AI technologies but also on mastering the strategic application of these technologies within a business context. By the end of this phase, participants will possess a robust technical understanding of AI, paired with the practical skills to guide their organizations through the complexities of adopting and benefiting from these emerging technologies.

Phase 3: AI Implementation & Integration
In Phase 3, Implementation & Integration, the curriculum moves from theoretical understanding to the tangible integration of AI into the daily operations of a business. This phase is critical for participants to translate their acquired knowledge into actionable strategies that affect change within their organizations.
Session 7, AI Implications for Workforce and Workflows, tackles the transformative impact AI has on the workforce and operational workflows. Participants will explore strategies to manage the transition within their teams, focusing on upskilling and reskilling initiatives, as well as the redesign of workflows to accommodate new AI-driven processes. The session will offer insights into change management, illustrating how to cultivate an AI-ready culture that embraces continuous learning and adaptability. By navigating the intersection of human and artificial intelligence, leaders will learn how to enhance collaboration between AI systems and their human counterparts to optimize efficiency and innovation.
In Session 8, AI in Business Functions, the training program dives into the deployment of AI across various business areas such as marketing, sales, customer service, HR, and more. This session will provide a look at how AI is transforming traditional roles and functions, presenting both opportunities for growth and potential challenges. Attendees will learn from real-life examples and case studies that demonstrate how AI is used to streamline operations, make data-driven decisions, and create new value for customers and stakeholders. Participants will walk away with a set of best practices and a keen understanding of how to avoid common pitfalls in AI adoption across business functions.
Session 9, AI in Business Innovation, emphasizes the role of AI in driving innovation in the design and development of products and services. This session will guide participants through the process of integrating AI into the product lifecycle, from ideation to launch. It will cover the use of AI for ideation, product analytics, customer insights, automated design processes, and customization. Participants will understand how to leverage AI to stay ahead of market trends, meet customer demands with greater precision, and differentiate their products in a crowded marketplace. The session aims to arm leaders with the knowledge to make strategic decisions that align product and service development with the possibilities made possible by AI technologies.
Through this Phase 3, participants are empowered with the practical skills and strategic insights needed to lead AI implementation initiatives. They will leave equipped with the capabilities to bridge the gap between AI potential and real-world business transformation, ensuring their organizations not only adapt to the AI revolution but thrive in it.

Phase 4: Monitoring, Evaluation, & Future Trends
Phase 4: Monitoring, Evaluation, & Future Trends is the capstone of the AI for Business Transformation program, where participants focus on the stewardship of AI after deployment, ensuring its ethical application, and preparing for what’s next in the rapidly evolving field of AI.
Session 10, Ethical Considerations, Bias, and Measuring AI Impact, prompts a deep dive into the ethical landscape of AI technology. In this critical session, participants grapple with the complex ethical questions AI presents, such as privacy concerns, bias in algorithmic decision-making, and the broader societal impacts of AI implementation. They will learn how to measure the impact of AI not just in business performance terms, but also in ethical dimensions, ensuring that their AI deployments improve societal outcomes as well as bottom lines. Through interactive case studies and discussions, leaders will formulate strategies to identify and mitigate bias and establish best practices for ethical AI use.
In Session 11, Monitoring AI Systems and Continuous Improvement, the spotlight is on the lifecycle management of AI systems. The session equips participants with the tools and knowledge necessary to maintain, monitor, and continuously improve AI systems once they are in operation. Attendees will explore various methodologies to track the performance of AI, understand feedback mechanisms, and apply iterative improvements to ensure AI systems evolve with the changing needs of the business and its customers. This session is about creating a sustainable AI environment that fosters ongoing learning and development.
The final session, Session 12, AI Future Trends and Staying Ahead, propels participants into the future, highlighting the latest trends and potential breakthroughs on the AI horizon. This forward-looking session ensures that participants are not only equipped to handle the AI of today but are also primed to anticipate and leverage the AI of tomorrow. Discussion will focus on cutting-edge research, emerging technologies, and potential new market opportunities created by advancements in AI. As a culmination of the program, this session leaves participants with a sense of preparedness and excitement for the future, ready to lead their organizations in the next wave of AI innovation.
Through Phase 4, participants gain the confidence and competence to ensure their AI initiatives remain effective, responsible, and forward-facing. They will emerge as leaders who not only understand how to implement and manage AI but also how to steer their organizations through ethical considerations and towards the bright future that AI promises.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Government Sector
History
Decentralization and Devolution
Over the past few decades, there has been a major shift in power and responsibility from the federal government to state and local governments. This decentralization has aimed to improve efficiency and accountability in service delivery. However, it has also led to challenges in ensuring equal standards across different jurisdictions. Critics argue that decentralization has weakened federal oversight and left vulnerable populations reliant on uneven state and local services. There are also capacity issues at local levels in terms of resources, expertise, and implementation of federal mandates.
Digital Transformation
Governments at all levels have undertaken digital modernization efforts to improve online public services and data utilization. Adoption of digital technologies like cloud computing and AI has aimed to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance transparency. However, the transition has been uneven, with many agencies and jurisdictions lagging. Barriers include funding constraints, lack of technical skills, and challenges in integrating complex legacy IT systems. Cybersecurity threats have increased with digitization, requiring significant investments in network security. Digital divides also persist, limiting equitable citizen access to e-government services.
Economic Cycles
Government budgets and services have been deeply impacted by economic boom and bust cycles over the past 30 years. Tax revenues declined sharply during recessions, forcing major spending cuts, hiring freezes, and deferred investments. Slow economic recoveries squeezed budgets further at all levels. Some state and local governments still have not restored per-capita expenditures to pre-2008 crisis levels. Countercyclical stimulus spending by the federal government has helped mitigate recessions’ depth but also contributed to rising national debt.
Public Spending
There are growing debates around optimal levels of government spending and taxation. Initiatives to privatize public services and limit government’s role have conflicted with calls to strengthen social services and increase investments in areas like infrastructure, education, and R&D. Pressures to balance budgets and address rising healthcare and pension costs have led to austerity measures. However, some argue this has reduced crucial public services and protections. There are no easy solutions, requiring prudent fiscal management alongside strategic investments in services that promote broad prosperity.
Regulatory Overhaul
Sweeping deregulation efforts have aimed to reduce bureaucratic red tape and compliance costs for businesses and other regulated entities. Results have been mixed. While deregulation has spurred innovation and growth in some sectors, there have also been consequences like workplace safety declines, environmental damages, and financial system risks. More balanced regulatory reform efforts are focused on streamlining reporting requirements while still protecting the public interest.
Political Polarization
Increasing partisanship and polarization in government has made consensus-building and effective policy-making extremely difficult. There is deep divide on fundamental issues like taxation, spending priorities, social programs, environmental regulation, and immigration. This has led to policy flip-flops, confusion for regulators and businesses, and an erosion of institutional norms that allow government to function. Restoring a spirit of compromise and evidence-based policy will be critical.
Current Position
Bureaucratic Inertia
Entrenched bureaucratic structures create inertia that makes implementing policy changes or reforms difficult. Outdated protocols, redundant processes, and institutional silos across agencies all contribute to inefficiency. Transitioning to more agile, iterative approaches that leverage technology will be essential. However, funding constraints and risk-averse cultures are barriers within many government organizations.
E-Governance
The shift towards electronic governance and digitized public services is well underway but remains uneven. Leaders have emerged in areas like automated tax filing, digital record access and online regulatory transactions. However, other services still rely on slow paper-based processes. Integrating complex legacy technology systems across agencies has also proved challenging. Overall, more investment is needed to modernize government operations and ensure equitable citizen access.
Health and Education
The U.S. lags other advanced economies in key health and education metrics despite high per capita spending. Insufficient funding, rising inequality, and fractured policy contribute. Public health systems struggle with cost pressures and uneven access to care. Outcomes like life expectancy and chronic disease rates are concerning. In education, school quality and higher ed affordability vary widely by state and community. College completion rates are stagnating. Targeted investments and reforms are essential to improve service delivery in these critical areas.
Infrastructure
The overall state of core U.S. infrastructure is poor and deteriorating. There is a growing backlog of maintenance across transport networks, water systems, parks, schools and other public facilities. Both funding and coordinated long-term planning are lacking. This creates safety risks, impacts economic productivity, and contributed to the underlying weaknesses exposed by COVID-19. Upgrading and modernizing infrastructure must become an urgent priority.
Data Utilization
Governments have vast amounts of administrative, operational, and survey data. However, this data is often scattered in silos. Better data integration through enterprise data lakes and AI-driven analytics could transform policy development, program evaluation, regulatory oversight, forecasting, and service delivery. Lack of data standards and privacy protections are barriers. Developing the tools and talent to fully harness government data remains a key opportunity.
Cybersecurity
Protection of sensitive government data and critical infrastructure from cyber threats is vitally important but challenging. Agency technology systems are often outdated and vulnerable legacy IT systems. The distributed nature of government systems also creates security coordination issues. Threats from sophisticated state actors and hackers are rising. Large investments in network security, rapid response capabilities and IT workforce training continue to be high priorities.
Future Outlook
Policy Innovation
Emerging policy innovations could help tackle pressing issues more effectively. Social policy experiments, behavioral approaches, predictive analytics, and new funding models could generate better solutions. For example, new fintech and blockchain applications may expand access to capital and financial services. Improved foresight capabilities can aid long-term policy planning. A culture encouraging evidence-based creative problem solving will be valuable.
Regulatory Framework for AI
As government adopts more AI tools, developing proper regulations and controls will be essential. Key priorities include data privacy, algorithmic transparency, accountability for AI decisions, and avoiding coded biases. Expert bodies have called for risk-based AI governance distinguishing between low and high-risk use cases. The adaptable regulatory approach should promote AI innovation while ensuring public protections.
AI in Public Services
AI could help improve delivery of health, education, and social services. In healthcare, AI can assist with clinical decision-making, administration, and public health surveillance. It can tailor education to individual students, assist teachers, and inform policy. For social programs it can help match services to needs, predict risks, and verify eligibility efficiently. To realize this potential, governments must provide the necessary data access and funding.
Smart Cities
Urban AI applications can help manage transportation, utilities, emergency response and sustainability challenges stemming from rapid urbanization and population growth. AI-enabled smart cities can utilize real-time data optimization across traffic systems, power grids, and public infrastructure to improve safety, environmental performance, and livability. However, these systems require upgrades to digital infrastructure and capabilities.
Automation and AI
AI-driven automation can streamline high volume administrative tasks in areas like tax processing, benefit administration, regulatory compliance, permitting, and fee collection. This would allow agencies to reassign human resources towards complex decision-making and oversight roles. It would require significant investments in integrating AI into legacy government IT systems and retraining staff.
Ethical AI
To implement fair, transparent and accountable AI systems, governments must establish rigorous testing, auditing and reporting standards. Regulatory and procurement guidelines can help ensure purchased AI services adhere to ethical principles and civil rights laws. Maintaining human oversight and understanding of automated decisions will be critical for public trust. Workforce skills in data and ethics literacy will need development.

Education
History
Educational Policy Shifts
Major education reforms over the past 30 years have aimed to improve student outcomes through standards-based accountability. Policies like No Child Left Behind (2001) and Common Core (2009) expanded standardized testing to gauge school performance. This data-driven approach has been controversial, with critics arguing it narrows curricula and encourages teaching to the test. The charter school movement starting in the 1990s also introduced school choice options and market-based competition between schools. The impact on overall student achievement has been debated.
Technological Integration
Education technology usage grew substantially since the 1990s but unevenly. Interactive whiteboards, laptops, and online learning platforms entered classrooms and administration. Positive impacts on student engagement and personalized learning occurred, but mostly in well-resourced schools. Insufficient teacher training and student access to technology hampered effectiveness and exacerbated disparities. Lack of interoperability between platforms also created challenges. Overall, education technology remains an area of high potential but requires greater strategic implementation.
Funding Fluctuations
Education funding, primarily from property taxes and state/federal contributions, is highly susceptible to economic cycles. Recessions routinely force deep cuts to K-12 and higher education budgets. The recovery frequently lags, leaving schools under-resourced. Periodic infusions through programs like Race to the Top helped but were not sustained. Overall education budgets remain below optimal levels to support student success, teacher development, and infrastructural needs.
Investment Priorities
Debates persist around optimal education spending priorities. Teacher salaries lag behind other professions, contributing to shortages. However, facilities, instructional materials, support staff, and student services are also underfunded in many districts. Politically, raising teacher pay garners support but actual state allocations often remain insufficient. More data-driven, strategic funding approaches are needed to balance investments based on evidence of what improves outcomes.
Curriculum Overhauls
Frequent state-level curriculum changes and debates over standards for subjects like science, history, and sex education have created challenges. Rapid policy shifts allow insufficient time for educators to adapt instruction and materials. Curriculum battles based more on partisan ideology than expert standards have disrupted teaching and learning continuity. Maintaining consistency while encouraging innovation requires better policy balance.
Partisan Debates
Education policy has become highly politicized and polarized. Debates over charter schools, teacher tenure, school choice, and curriculum standards frequently fall along partisan lines. Union opposition and ideological disagreements stall policy progress, harming students. Reducing education policy volatility and building bipartisan consensus around evidence-based reforms remains an ongoing challenge.
Current Position
Institutional Inertia
Entrenched educational models and school district bureaucracies make adopting new instructional approaches or implementing reforms difficult. Teacher training programs provide limited exposure to new methods and technologies. Tight budgets also constrain innovation and system upgrades. Pilot programs demonstrating positive results frequently stall at the scaling up stage due to these inertia barriers.
E-Learning Platforms
Adoption of learning management systems, digitized instructional content, and online learning options has expanded significantly. Benefits like improved student engagement, personalized pace, and interactive media are clear. But usage is uneven, student access and results vary considerably, and best practices around optimal blending with in-person instruction are still emerging. Usage soared out of necessity during the pandemic but integrating technology in effective, equitable ways remains an ongoing process.
Quality and Accessibility
Wide disparities persist in educational quality and resources, negatively impacting disadvantaged student populations. Inequities exist across income, geographic, and racial/ethnic lines. Advanced courses, technology, qualified teachers, support services, and physical infrastructure are often concentrated in advantaged districts and schools. These structural inequities contribute significantly to achievement gaps and hinder social mobility.
Infrastructure
School facilities and technology infrastructure require major upgrades in many districts to meet modern educational demands. Aging buildings create unhealthy environments and lack accommodations for new technology. Digital connectivity, devices, and software/platforms are outdated or non-interoperable in many schools. Infrastructure gaps disadvantage students and make adopting promising new instructional technologies challenging. Upgrading education infrastructure should be an urgent priority.
Data Analytics in Education
The use of data analytics to inform instruction, policy, and operations decisions is growing but remains limited. Few districts utilize learning analytics to personalize education. Instead, data usage tends to focus more on high-stakes testing for accountability. Privacy concerns, lack of staff capacity, and access to quality consolidated data all constrain more impactful utilization. Leveraging data and AI strategically remains a key opportunity to improve student outcomes.
Cybersecurity in Schools
K-12 cybersecurity profiles are generally low, with insufficient staff, outdated network infrastructure, and lack of end-user training. Higher ed faces threats to valuable research data. Recent cyber attacks have compromised sensitive student records and district systems. Lack of compliance with privacy laws like FERPA and COPPA is also common. Significant upgrades to security policies, tools, and training are needed across educational institutions.
Future Outlook
Innovative Learning Models
Emerging reforms like student-centered, competency-based, and experiential learning aim to develop knowledge and metacognitive skills. Growth in micro-credentialing and skills-based certificates may accelerate. Applying cognitive science to inform personalization and integrate project-based learning holds promise. Policy and institutional barriers to scaling these models remains challenging however.
Framework for Educational Technology
Creating standards and oversight mechanisms for ethical, effective implementation of education technologies will be critical as usage expands. Areas like efficacy validation, accessibility, privacy, and appropriate use need governance. Teachers require training and support to evaluate and integrate new tools. Students also need enhanced digital literacy.
AI in Personalized Learning
AI-driven solutions have significant potential to tailor educational experiences to student strengths and needs. Adaptive learning systems dynamically customize content and assessment as students progress. Intelligent tutors identify gaps and supply supplemental activities. Chat-based apps offer 24/7 support. To be effective, AI tools must provide transparency and protect student privacy.
Technology-Enhanced Learning Environments
Interactive educational simulations, augmented reality, virtual field trips and gamified learning via technology are already enhancing student engagement. As these immersive digital environments evolve, teachers can leverage them to stimulate learning and build collaborative problem-solving skills. Teachers require ongoing training to leverage these new environments optimally.
Automation in Administration
AI and process automation tools can significantly alleviate time-consuming administrative tasks related to record-keeping, report generation, and compliance monitoring. This would allow educators to dedicate more time towards instruction, curriculum development, and advisory roles. However, role displacement concerns will need to be mitigated as automation expands.
Ethical Considerations
The appropriate design and transparent use of AI is essential to ensure fairness and build trust. Algorithmic bias issues found in some educational applications like grading systems underscore the need for rigorous testing. Schools must safeguard student privacy as digital learning expands. Developing principled standards for educational AI will be critical.

Healthcare
History
Policy and Regulation Changes
Major healthcare reforms over the past 30 years aimed to expand access and reduce costs, with mixed results. The introduction of Medicare Part D in 2006 helped seniors afford prescriptions. The Affordable Care Act (2010) cut the uninsured rate through Medicaid expansion and healthcare exchanges, but premiums continue rising. Reforms like accountable care organizations and value-based purchasing tried to cut costs and improve care coordination. However, overall healthcare spending continues to outpace inflation.
Technological Advancements
Healthcare technology advanced considerably but not without challenges. Electronic health records (EHRs) were adopted to improve care coordination and data collection. However, systems remain fragmented across providers. Telemedicine expanded access but reimbursement issues persist. Precision medicine shows promise but reimbursement limits adoption. Technologies that improve patient care have emerged but integrating them smoothly into clinical workflows remains difficult.
Cost of Care
Healthcare costs have risen steadily, straining households, businesses, and government budgets. Key drivers include high drug prices, administrative waste, chronic illnesses, fee-for-service payment models, and lack of transparency around pricing. Cost growth has outpaced inflation for decades. Despite reforms, current cost trajectory remains financially unsustainable for the healthcare system.
Funding for Public Health
Public health funding has been inconsistent, leading to underinvestment in prevention and emergency preparedness. Agency budgets were cut during recessions, including the global health security programs that could have lessened the COVID-19 pandemic’s severity. Rural hospital closures have increased due to limited public health funding and high uninsured rates in those areas. Overall, lack of stable public health financing has created system vulnerabilities.
Healthcare Policy Gridlock
Deep partisan divisions have made passing major healthcare legislation extremely challenging at the federal level. The ACA barely passed along party lines. Repeal efforts failed. But reforms to address issues like high drug prices remain stalled, though both parties recognize the need. Ongoing policy stalemates on healthcare reform pose serious problems for patients and the healthcare system.
Pharmaceutical Regulation
Regulating drug safety, efficacy, pricing, and marketing remains complex. The opioid over-prescription crisis highlighted system failures in balancing pain treatment with addiction risks. High drug prices drive treatment access issues but reforms to control costs struggle in Congress. Meanwhile consumer drug advertising continues driving over-utilization. Strengthening evidence-based regulation of the pharmaceutical industry remains a challenge.
Current Position
System Fragmentation
The healthcare system remains highly fragmented, leading to coordination issues and cost inefficiencies. Patients transitioning between providers often experience gaps in care. Duplicative services drive overutilization. Interoperability problems limit data sharing between healthcare IT systems. Attempts to integrate via consolidated systems like ACOs have shown limited progress so far.
E-Health and Mobile Health
Adoption of e-health and mobile health tools is growing but still developing. Telemedicine usage surged during the pandemic but faces unclear reimbursement post-COVID. mHealth apps have proliferated but struggle with data integration into EHRs. Patient engagement with digital health records remains relatively low. Private sector innovators lead in this space, presenting interoperability challenges.
Access and Equity
Despite reforms, healthcare access and health disparities persist, especially regarding race and geography. Rural hospital closures have increased access gaps. Medicaid expansion helped but 14 states still have not adopted it. Racial gaps exist in insurance rates, maternal mortality, and chronic disease management. The healthcare system still does not adequately serve the needs of all populations.
Infrastructure and Capacity
COVID-19 exposed capacity limitations in staffing, hospital beds, emergency supplies, and public health infrastructure. Nursing shortages are especially acute. Rural areas are particularly underserved. Resilience gaps and coordination failures between the public and private sectors emerged during the pandemic, underscoring the need for infrastructure improvements.
Big Data in Healthcare
Leveraging healthcare data analytics to inform clinical and operational decisions remains limited but full of potential. Fragmented systems, skills gaps, privacy concerns, and lack of data standards slow adoption. Applications like clinical decision support, predictive population health analytics, and inventory optimization currently demonstrate fragmented progress. But room for improvement using healthcare data is vast.
Cybersecurity Measures
Cyber threats to protected health information are increasing as systems digitize. Recent high-profile ransomware attacks have disrupted facilities. But cybersecurity funding lags among providers. Gaps exist in HIPAA compliance, staff training, patching of medical devices, and incident response plans. Significant cybersecurity improvements across the healthcare ecosystem are urgently needed.
Future Outlook
Health Policy Innovations
Future reforms may expand the shift towards value-based care and care coordination among teams and settings. Increased transparency around outcomes and costs could also help improve quality while engaging patients more in their care. Innovations like biopharmaceutical advances, individualized medicine, decentralization of care to community settings, and digital health all have transformative potential.
Regulatory Framework for Health Technology
Developing a robust evidence-based regulatory framework will be crucial as innovative technologies proliferate. Currently healthcare technology is regulated by multiple agencies like the FDA and FCC, creating potential gaps. Clear regulatory guidance and standards will help ensure patient safety, data security, efficacy validation, and ethical use as AI, robotics, biosensors, and genomic testing advance.
AI in Diagnosis and Treatment
AI has significant potential to enhance diagnosis accuracy, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. Applications are emerging in areas like medical imaging, robotic surgery, medication adherence tracking, virtual nursing assistants, and early disease detection. But to improve care, AI systems must integrate smoothly into clinical workflows. Extensive validation and user training are also critical.
AI in Public Health
AI could strengthen public health surveillance, prediction models, information dissemination, and program administration. Early disease outbreak detection, real-time tracking of community health trends, data-driven resource allocation, health risk modeling, and tailored health campaigns are all promising applications if deployed thoughtfully.
Automation in Healthcare Processes
AI and automation tools can help streamline administrative tasks and clinical workflows to improve efficiency. Document processing, scheduling, billing and claims management, and pharmacy dispensing are prime areas for automation. This could free up staff time to focus on patients and higher value tasks. Change management regarding any workforce disruption will be a key consideration however.
Ethical AI Use
Transparency, accountability, and fairness must be core principles guiding healthcare AI. Eliminating algorithmic bias and ensuring clinical decision-support tools are explainable will be important to build provider trust in AI. Privacy must be safeguarded carefully. Technological advancement alone cannot resolve healthcare’s systemic issues – thoughtfully human-centered solutions focused on equitable access and outcomes will be essential.

Media and Publishing
History
Shifts in Media Consumption
The rise of the internet and mobile devices has profoundly disrupted traditional media consumption patterns. Newspaper circulation declined sharply as readers migrated online. Broadcast television audiences fragmented as cable and streaming video options exploded. Digital platforms like social media and aggregators gained prominence in news and content distribution. Media companies scrambled to adapt business models and operations to the digital landscape with mixed success.
Monetization and Business Models
As print advertising revenues plummeted, media companies tried multiple approaches to replace lost income. Paywalls, subscriptions, branded content, video, podcasts, e-commerce, and content syndication to third-party platforms emerged as new digital monetization models. Some companies succeeded in the transition, while many struggled to convert analog dollars to digital dimes profitably. Legacy cost structures posed major challenges. New competitors like Google and Facebook captured the majority of digital ad spending.
Revenue Decline in Print
The mass migration of audiences and advertisers away from print media had devastating financial consequences for that sector. U.S. newspaper advertising revenue dropped from $60 billion in 2000 to below $16 billion in 2020. Magazine ad spending fell from $15 billion to $4 billion over the same period. Thousands of newsroom jobs were cut and numerous publications folded, eroding media diversity and accountability journalism. Digital subscription and contribution revenues have offset some but not all print losses.
Investment in Digital Media
Major investments were made in digital news and content operations, with varying outcomes. Some companies succeeded by pivoting business models early like The New York Times. Other newspaper and magazine companies struggled to adapt, facing shrinking revenues and heavy debt burdens. Venture investment in digital media startups was substantial but highly competitive economics and reliance on platforms created instability.
Regulatory Changes
Media regulation evolved but struggled to keep pace with digital disruption. Antitrust scrutiny around media consolidation increased but mergers continued. Copyright frameworks were unprepared for the rise of aggregators. Privacy regulations like GDPR imposed major compliance burdens. Calls for regulation of platforms like Google and Facebook have grown but with limited impact so far on their market dominance.
Ethical Journalism
Intensifying commercial pressures combined with digital distribution networks strained journalistic ethics and standards. The 24-hour news cycle and clickbait content tactics prioritized speed and sensationalism over accuracy. Misinformation proliferated on digital platforms. But a counter-trend also emerged emphasizing credible reporting and audience trust to maintain relevance. How to sustain ethical journalism remains an ongoing challenge.
Current Position
Industry Consolidation
Media consolidation has accelerated across print, broadcast, and digital sectors. Publishers and stations operate under larger conglomerates focused on synergies and cost efficiencies. This consolidation narrows diversity of ownership and editorial voices as resources concentrate regionally and nationally. But scale also enables technology investments needed to compete.
Adaptation to New Technologies
Integrating audience analytics, content management systems, and multimedia capabilities to support digital workflows has been both an operational necessity and challenge. Transitioning legacy print staff to expand digital skills continues. Audiences now expect continually updated, optimized content accessible across platforms and devices – a major shift from fixed print production cycles. Ongoing technology adoption and evolution is imperative for relevance.
Content Quality and Diversity
Balancing generalized content to maximize audience scale with specialized material to engage niche users is a key challenge. Quality original reporting and diverse viewpoints tend to build loyalty but are expensive to produce at scale. Social platforms incentivize mass viral content over public interest newsgathering. Maintaining excellence despite economic headwinds has forced difficult trade-offs at many outlets.
Infrastructure for Digital Distribution
Reliable, affordable broadband connectivity remains lacking in some communities, limiting access to digital content. Vulnerabilities in network infrastructure pose cybersecurity threats to media operations. Transitioning from print production and distribution facilities to modernized digital infrastructure has proceeded unevenly, especially among newspaper chains still balancing print and digital assets. Ongoing infrastructure investment is essential but costly.
Data-Driven Journalism
Leveraging audience analytics and big data tools to guide editorial decision-making and product development is growing but uneven. While data insights are crucial, some caution that allowing audience size metrics to dictate coverage priorities can skew quality and public service values. Achieving the right balance remains a key challenge.
Cybersecurity and Information Integrity
Digital systems have increased vulnerability to hacking, malware and misinformation. Media outlets must guard against cyber intrusions and inference campaigns aimed at disrupting operations or manipulating content. Maintaining journalistic integrity and earning audience trust around source vetting and verification has become even more critical in countering misinformation proliferating online.
Future Outlook
Media Literacy and Education
Initiatives to improve public media literacy, especially digital news discernment, will be increasingly important. Schools, libraries, civic groups and media companies themselves have roles to play in fostering skills to identify credible news sources and avoid manipulation by misinformation. Technologies like AI fact-checking bots could assist but human judgment remains essential.
Regulation of Digital Platforms
With policymakers pressuring Big Tech over antitrust, privacy, and content issues, increased regulation of platforms including content algorithms is expected. Areas like transparency, content moderation, media compensation, and data portability may be addressed. But regulating private platforms while maintaining free expression rights presents major complexities that require nuanced solutions.
AI in Content Personalization
Using AI to customize content recommendation and curation based on individual user interests and behaviors has strong potential to improve engagement and satisfaction. However, safeguarding against ‘filter bubbles’ that isolate users from diverse perspectives will be important. Human editorial judgment must balance data-driven personalization to serve public as well as user needs.
Automation of News Production
AI-assisted news production could expand editorial output but raises ethics concerns. Automated writing using data and algorithms risks amplifying biases or inaccuracies if not carefully structured and edited. AI is better equipped for rote tasks like sports/financial summaries than original reporting. Protecting uniqueness and quality of human storytelling must remain the priority, with technology as an augmenting rather than replacing force.
Advanced Analytics for Audience Engagement
Innovative applications of machine learning, predictive analytics, and neuroscience to analyze and predict audience engagement offer valuable insights for media strategizing if applied thoughtfully. But over-reliance on metrics over journalistic judgment can be counterproductive. Understanding true audience desires, beyond superficial clicks, remains essential.
Ethical Challenges of AI
Thoughtful oversight is critical as AI capabilities like personalized content bots and generative deepfake media mature. Editorial standards must safeguard against inaccuracies or market-driven manipulation. Transparency around the use of automated systems is essential to maintain audience trust. Technology enables much but upholding integrity, ethics and quality in reporting endures as media’s core mandate.

Professional Services
History
Market Globalization
Professional services rapidly globalized to follow multinational clients. Firms established offices worldwide through mergers and partnerships. Service delivery models adapted to local cultures and regulations. Global talent recruitment accelerated. While increasing complexity, globalization enabled sector revenue growth and knowledge sharing. Offshoring of back-office functions also emerged to reduce costs.
Service Diversification
Firms diversified beyond core offerings to provide integrated solutions as client needs evolved. Consulting firms expanded into technology implementation. Accounting firms offered supply chain and HR consulting. Legal firms developed ancillary services like contract management and compliance. Advertising agencies became full marketing partners. Talent management firms provided additional HR services. Diversification drove revenue growth but also increased competition.
Competitive Pricing Pressure
Pricing pressure intensified significantly with increased competition. Established firms faced growing competition from niche specialists and offshore providers offering services at reduced cost. Some services like contract staffing became commoditized. Automation of basic tasks also enabled new low-cost providers. Maintaining profit margins became challenging for many firms.
Economic Cycles
Demand for professional services has been cyclical, closely tracking GDP growth. Recessions forced clients to reduce spending on discretionary services to cut costs. But downturns also created opportunities like bankruptcy advisory and strategic realignment consulting. Overall, economic volatility, and the uncertainty it created for clients, posed major revenue challenges. Firms adapted their talent and services mix accordingly.
Compliance and Regulation
Regulatory burdens on professional services increased substantially over the past 30 years. Anti-money laundering, data security/privacy, and financial reporting regulations added considerable compliance complexity. Geopolitical factors also complicated delivering consistent services across borders. Keeping up with diverse and shifting regulations required significant investments.
Ethical Standards
Maintaining high ethical standards amidst competitive pressures presented ongoing challenges, occasionally resulting in scandals like Enron-era accounting fraud. Corporate social responsibility expectations also rose around areas like sustainability and diversity. Balancing business objectives with public responsibilities remained tricky terrain to navigate for many firms.
Current Position
Talent Management
Demand for skilled talent outpaced supply across most professional services. Attracting and retaining top performers became highly competitive. Lack of skilled labor triggered wage growth and staff churn. Firms evolved benefits and culture to appear more desirable. Building strong talent pipelines from colleges and employee referrals helped. But aging workforces also created looming talent gaps.
Technological Adaptation
Adoption of digital tools to enhance service delivery accelerated, including customer relationship management (CRM), cloud computing, data analytics and AI. Significant investment went towards developing proprietary tools and platforms to improve productivity, insights and quality. Resistance from traditional professionals towards technology-driven change management emerged as an obstacle.
Client Expectations
Clients expected more value, transparency, collaboration, and vertical expertise from service providers. Firms developed specialized industry capabilities beyond generalist consulting to address this. More data-driven and customized engagements were also demanded by clients. Meeting rising expectations required better understanding each client’s strategic context.
Remote Services
Online collaboration platforms enabled a shift towards remote professional services delivery even pre-pandemic. But adoption surged out of necessity during COVID-19, compressing the transition from years to months. Many clients now expect virtual delivery to continue. While increasing flexibility, remote work also challenges collaboration, talent development, and innovation. Hybrid models are likely.
Digital Transformation
Cloud platforms, data analytics, and AI came to play a central role in operations, service delivery, and decision-making. Substantial investment went into digitizing processes and building proprietary digital platforms. Change management was still required to get traditional professionals comfortable with new tools. Ongoing digital R&D and platform refinement continues.
Data Security and Privacy
With high-profile cyberattacks and growing privacy regulations, data security became critically important and challenging. Firms implemented employee training, role-based access controls, network monitoring, encryption, and incident response plans. However, threat vectors continued evolving rapidly. Vigilance around protecting client data is now ingrained throughout the sector.
Future Outlook
Service Innovation
Demand for expert guidance on digital transformation, analytics, customer experience, and sustainability will likely drive service innovation. Creative new business models like flexible staffing mixes, niche platforms, and outcome-based pricing may emerge. Digital tools will enable smaller agile competitors to gain share. Large incumbents will respond with their own innovations.
Regulatory Adaptation
With growing adoption of AI, platforms, and data-driven services, regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to protect consumers while fostering responsible innovation. Self-regulation may work in some areas like ethical AI principles. But tighter controls will likely come, especially for high-risk applications like autonomous legal and financial services. Firms must actively engage with policymakers on effective adaptable governance.
AI in Decision-Making
AI-supported decision-making using predictive analytics, optimization algorithms, and natural language generation can enhance the scope, accuracy, and speed of professional advisory services. But to build trust, transparency and human judgement will need to guide automation. Where outputs directly inform sensitive client decisions, extensive validation is essential.
Automated Legal and Accounting Services
For routine legal tasks like contract review and basic tax preparation, AI automation can improve efficiency and accuracy while reducing costs. This could expand service access for underserved groups. However, displacing legal and accounting roles will require managing workforce impacts. Handling complex service aspects still requires human skills and ethical discernment.
Advanced Automation in Recruitment
AI shows strong potential to transform recruiting by improving candidate matching, reducing biases, and taking over high-volume administrative tasks. Functions like resume review, interview scheduling, assessment, and onboarding can be enhanced by automation. But recruiters will need to be selective in using AI to avoid dehumanizing the hiring process which requires interpersonal dynamism.
Ethical Implications of AI
To maintain trust and uphold social responsibility, the professional services sector must ensure ethics inform AI application decisions. Responsible practices around transparency, bias elimination, security, and workforce impacts are paramount, even if profit incentives pressure firms to move fast. Guidance and governance mechanisms are still developing, requiring thought leadership from incumbents.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

Los Angeles, CA
History
Over the past three decades, Los Angeles has undergone an economic transformation. Traditionally reliant on aerospace and defense, the city’s business mix diversified significantly. The entertainment industry continued to thrive. Trade rose through the regional ports complex. Tech and biotech sectors emerged as new pillars. Tourism, hospitality, fashion, and financial services expanded as well. However, the city also faced challenges from the decline of the defense industry, the 2008 recession, and the COVID-19 pandemic.
The 1990s saw contraction of the once-dominant aerospace sector following the Cold War’s end. California defense spending fell by 60% during that decade. Many aerospace firms downsized or exited. This produced spillover losses in manufacturing, finance, and logistics industries tied to defense spending. The city’s business leaders formed public-private partnerships to attract investment in new growth industries.
Already the hub of the entertainment world, Los Angeles solidified its position through major studio investments in digital production and distribution capabilities. Media, streaming and tech convergence strengthened L.A.’s hold on Hollywood. The city became a center for video game development. Music, fashion and digital influencer industries also grew significantly as entertainment expanded beyond film/TV.
International trade expanded through the L.A. port complex, creating associated growth in logistics, warehousing and distribution. This helped offset manufacturing job losses. Alongside entertainment, trade remains a cornerstone of the region’s economy. However, automation and competition from other ports present challenges.
High-tech and biotech development emerged in areas like Silicon Beach, Pasadena, and Santa Monica. Venture investment flowed to Southern California, creating startups and attracting Big Tech satellite offices. Once centered in Northern California, the tech industry spread statewide with L.A. as a key hub. Aerospace and medical research also spun off advanced technologies in fields like drones, space, and health data.
The 2008 recession brought severe losses in real estate, construction, retail, and finance. But the region’s economic diversity enabled bounce-back through industries like entertainment. The pandemic triggered another downturn, especially in hospitality and retail. But growth in tech and professional services cushioned the blow. Overall, L.A. has worked to reduce reliance on any one dominant industry.
Current Position
Los Angeles has a diverse business mix spread across trade, tech, entertainment, tourism, apparel, and professional services. Entertainment remains the chief export, constituting over 7% of U.S. GDP. But the tech sector is rising quickly, garnering the most venture investment of any U.S. metro. Trade, tourism, fashion, and construction add billions more annually. Still, economic disparities persist, requiring more inclusive development.
Trade continues to grow, led by the adjacent ports of L.A. and Long Beach which handle approximately 40% of containerized imports nationally. Associated warehousing and logistics industries employ hundreds of thousands regionally. However, trade faces headwinds like increased automation and foreign competition requiring strategic adaptation.
The technology scene has exploded, spanning Internet companies, media tech, aerospace, biotech, and more. Over $100 billion has flowed to local startups since 2010. The tech workforce has increased by 22% since 2013 with key hubs in Santa Monica, Venice, Hollywood, and Playa Vista. Facilitating this growth are local universities like Caltech, UCLA, USC, and Occidental that conduct leading research and supply talent.
Hollywood remains at the core of L.A. business. Major studios like Disney, Universal, Warner Bros., Paramount, and Sony anchor the region’s unrivaled entertainment ecosystem. Streaming has created new massive demand for content locally produced. Music, digital media, gaming, and fashion synergistically feed off this sector. L.A.’s entertainment exports reached a record $65 billion in 2019.
Tourism is a huge economic contributor, attracting over 50 million visitors a year pre-pandemic. The sector is rebounding post-COVID but still faces challenges. Key draws like conventions, concerts, and theme parks have revived. But occupancy rates and overseas visitors remain below past peaks. Sustaining tourism growth requires strategic collaboration between government and businesses.
Professional services, finance, and real estate have all seen major expansions as the economy diversified. Major banks, law firms, accounting giants, and wealth management firms have regional headquarters. Co-working spaces have proliferated to serve startups and remote workers. Commercial and residential development continues apace in urban infill areas like downtown, Hollywood, and Koreatown.
Future Outlook
Los Angeles seems well-positioned for continued growth across key sectors like entertainment and technology. But sustaining prosperity will require supportive policies on infrastructure, housing, sustainability, workforce development, and inclusion. The city’s diversity, culture, universities, and quality of life should continue attracting capital and talent.
The technology industry seems primed for continued expansion. L.A. is now the top U.S. metro for tech-related VC investment and employment growth. The region added over 25,000 tech jobs in 2021 alone. Areas like cybersecurity, fintech, biotech, AI, drones, space tech, 5G, quantum computing, and battery storage could see major advances. Facilitating further growth are research anchors like Caltech, JPL, UCLA, USC, and SpaceX.
Entertainment and digital media will likely continue thriving. Content demand from streaming platforms like Netflix, Prime Video, Disney+, and Hulu is surging. Studios are increasing production capacity. The rise of social media entertainment on YouTube, TikTok, Instagram and Snapchat has also benefited L.A. creators. Supporting infrastructure in gaming, music, fashion, advertising, and digital talent buoys the industry cluster.
The upcoming 2028 Olympic Games provide opportunities to upgrade infrastructure and facilities. Transit projects, airport modernization, public venues, and tourism accommodations can create lasting economic benefits. Sports partnerships with major leagues also promote global business ties. However, ensuring responsible development and community benefits will be critical.
One challenge Los Angeles must address is the affordable housing shortage, which constrains workforce growth and worsens inequality. Relaxing zoning rules to allow more market-rate and subsidized housing near job centers can help. Transit-oriented planning and revitalizing urban neighborhoods are also important for environmental sustainability.
Overall, L.A.’s outlook remains promising. The region has successfully reinvigorated itself through industries like tech and entertainment. But leaders must also look to expand prosperity more inclusively across the diverse populations that call Los Angeles home. The innovation economy holds much potential if growth can be made accessible to all.

San Francisco, CA
History
Over the past three decades, San Francisco has been at the epicenter of the tech revolution that has transformed not just the Bay Area but global business. PC and Internet pioneers like Apple and Netscape spurred an explosion of innovation. By the late 1990s, the ‘dot-com bubble’ led to immense investment and wealth creation along with exuberance-fueled excess. The bubble’s burst led to an early 2000s downturn before the tech ecosystem rebuilt even stronger.
The seeds for Silicon Valley were planted decades before with firms like Hewlett-Packard and Fairchild Semiconductor. But the PC and Internet eras took Bay Area tech to new heights. Hundreds of hardware, software, and Internet firms sprouted, fueled by VC funding. Stanford University and alumni networks offered ideas and talent. San Francisco became the hub for Internet/digital media pioneers.
The dot-com bubble saw large speculative investment flow to Silicon Valley startups before many were ready for primetime. When the bubble popped in 2000-2001, failures abounded. But the shakeout also led to maturation, with Amazon, Google, Salesforce and LinkedIn emerging as industry leaders. The social media wave soon followed with Facebook, Twitter and new innovations.
San Francisco rapidly reinvented itself from a finance and tourism town into a tech epicenter. Venture funding flowed to startups in areas from e-commerce to biotech. Incubators, accelerators, and co-working spaces supported rapid growth. Commercial real estate soared. But tensions also rose over gentrification and widening inequality.
The 2008 recession briefly dampened VC investment and liquidity events. But federal stimulus helped spur a quick rebound. The emergence of smartphones and mobile apps drove the next evolution. Uber, Airbnb, Slack, Pinterest and DoorDash exemplified innovative local startups. Software continues eating the world, expanding tech’s reach.
However, the sector’s success led to severe housing shortages and cost spikes, burdening other local businesses. Tech wealth also exacerbated inequality, especially for marginalized communities. Civic frustrations grew over congestion, public transit stresses, and insufficient community engagement by tech leaders. These issues remain ongoing tensions.
Current Position
Today, San Francisco’s economy centers around the thriving technology sector, with major companies like Salesforce, Uber, Airbnb, Twitter and LinkedIn headquartered locally. Anchored by Silicon Valley giants like Apple, Intel, Google, Meta and Netflix, the Bay Area commands over 50% of total US venture investment. Biotech, finance, tourism, retail and professional services also play key economic roles.
However, the dominance of Big Tech has created imbalances, with runaway housing costs and a crowding-out effect impacting other industries like manufacturing, logistics and entertainment. Lack of affordable housing limits workforce and talent retention across sectors. Congestion and transit overcrowding hinder mobility. Addressing these issues is critical for sustainable prosperity.
The startup and venture capital ecosystems remain highly robust, attracting top entrepreneurs and developers. Co-working spaces have proliferated, enabling new companies to scale efficiently. Accelerators like Y Combinator support promising ventures with funding and advisors. The network of experienced engineers, designers and executives supports young firms. But late-stage valuations show potential frothiness.
Professional services like consulting, legal, marketing and HR expand alongside the tech sector. Recent IPOs and acquisitions have created much local wealth, supporting industries like construction, finance, retail and hospitality. Tourism has partially rebounded post-pandemic but remains constrained by hotel room shortages and high costs. Attracting conferences and events is impeded by high venue expenses.
While technology underpins the region’s dynamism, associated challenges like inequality, housing costs, and congestion threaten to dampen future growth. Maintaining San Francisco’s innovative edge requires making the region more livable and accessible for the full spectrum of workers essential to a thriving business ecosystem. Policy reforms around housing, transit and community engagement are overdue.
Future Outlook
San Francisco seems well-positioned for continued technology sector leadership given the strong local talent pool and access to capital. Emerging technologies like AI, quantum computing, biotech and clean energy should receive substantial investment over the next decade. Google, Meta, Salesforce and LinkedIn will continue anchoring growth via R&D spending and spinoffs.
However, sustaining growth requires making the region more affordable and livable by addressing housing shortages and congestion through supportive public policies. Transit and mobility improvements, workforce housing mandates, commercial development caps in crowded areas, and traffic reduction strategies must be priorities for the city and business community.
If runaway cost-of-living increases can be reined in, San Francisco could see expansions in diverse services from hospitality and entertainment to manufacturing and logistics as lower-margin businesses are not pushed out. Diversification beyond tech would create a more balanced economy. The tech sector itself would benefit from a broader and more inclusive talent pool.
Commercial real estate may face downward price adjustments after surging unsustainably over the past decade. But demand for lab space from biotech and life sciences firms should continue. Mixed-use developments with office, retail and housing could gain favor.
For the innovation ecosystem to keep producing global impact, attracting a diversity of talent is critical. Access to opportunity regardless of background must be strengthened through affordable education and housing pathways. Stronger community connections between new companies and marginalized groups can build understanding.
If San Francisco can undertake reforms that allow economic gains to be more broadly shared, the region is primed for continued leadership in emerging technologies. Sustaining a pipeline of talent and innovation necessitates inclusive policies and business practices that live up to San Francisco’s progressive values while fueling growth.

Dallas, TX
History
Over the past three decades, Dallas has experienced tremendous economic growth and diversification. Once heavily dependent on oil and gas, the city expanded its technology, financial services, and healthcare sectors. Telecom deregulation also catalyzed growth, with Dallas emerging as a major telecom hub. Despite facing challenges from oil busts, recessions, and Covid-19, the region demonstrated resilience.
In the 1990s, Dallas began pivoting away from overreliance on oil and gas. Losses from the savings and loan crisis and oil crash spurred economic diversification. Technology firms were attracted by the region’s central location and competitive business climate. A growing educated workforce supported expansion into sectors like IT, financial services, and accounting.
Deregulation transformed Dallas into a major telecom hub in the 1990s. Firms like Ericsson, Nokia, AT&T and Verizon located operations in the region. An entrepreneurial environment enabled upstarts like Texas Instruments, EDS, and CompUSA to become tech leaders. The tech talent pool and infrastructure established during this period buoyed future growth.
Financial services grew substantially, with institutions like Capital One, TD Ameritrade, and JP Morgan Chase establishing regional hubs. Downtown Dallas also emerged as a major real estate development center, with new corporate campuses, sports stadiums, arts venues, hotels, and residential towers signaling the city’s ascendance.
Healthcare became another economic pillar, led by developments like the Baylor and UTSW medical centers, biotech research, and major hospital expansion. Tourism, conventions, restaurants, arts, and education all saw growth as Dallas became a destination for corporate relocations and investment.
However, dependence on oil and gas still left Dallas vulnerable to energy sector volatility. Recessions in the early 2000s and 2008-2009 brought major losses in real estate, aviation, telecom and finance. In 2020, Covid-19 impacted the region across many industries before substantial fiscal and monetary stimulus aided recovery.
Current Position
Today, Dallas enjoys a diverse business mix spanning technology, financial services, healthcare, aviation, logistics, hospitality, and corporate headquarters. The region is home to 24 Fortune 500 companies including Texas Instruments, AT&T, Southwest Airlines, and McKesson. Prominent business hubs include downtown, Uptown, the Telecom Corridor, Las Colinas, and the Stemmons Corridor.
The DFW International Airport continues fueling growth as a major aviation hub and economic engine. Dallas Love Field also serves as a key regional airport. Collectively, DFW and Love Field provide over 200,000 local jobs. Airline and aviation services account for over $37 billion in annual economic impact.
Financial services, insurance, and real estate represent a major part of Dallas’ economy. JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, TD Ameritrade, and other firms are located in the metro area. The region has one of the nation’s largest concentrations of investment advisors managing over $2 trillion in assets.
Technology remains a significant and growing sector with major firms like AT&T, Texas Instruments, and Microsoft maintaining regional headquarters. Opportunities in areas like AI, IoT, cloud computing, cybersecurity, blockchain, and 5G are attracting startups and investment. The region is now the #4 U.S. tech talent market.
However, challenges like education gaps, housing costs, and transportation constraints must still be addressed for the region to reach its full economic potential and make growth more inclusive. Better harnessing the strengths of the area’s diverse population will maximize human capital.
Future Outlook
Dallas seems poised for strong continued growth given competitive advantages like central location, business-friendly climate, infrastructure, and diverse talent base. Emerging sectors like AI, life sciences, cloud computing, supply chain/logistics, and next-gen telecom should see expansion. Strengthening small business support and talent pipelines will also boost economic dynamism.
Corporate relocations from high-cost coastal cities could accelerate, attracted by Dallas’ affordability, talent pool, and quality of life. Efforts to grow the startup ecosystem through funding, incubators and research collaborations will help diversify the economy beyond established giants. Urban revival across neighborhoods like Uptown and Deep Ellum will create vibrant, amenity-rich hubs.
However, transportation investments like high-speed rail must be priorities to further connect Dallas to other major Texas cities. Environmental sustainability and resilient infrastructure will need emphasis as climate risks mount. Affordable workforce housing near job centers is essential to promoting mobility. Equity and inclusion programs can help maximize diverse talents.
Overall, Dallas has demonstrated an impressive ability to continually reinvent and diversify its economic base. It enjoys advantages in location, infrastructure, universities, and business climate that should sustain expansion across target sectors like technology, biotech and corporate services. With smart investments and policies around talent, quality of life, mobility and sustainability, the region’s future looks bright.

New York City, NY
History
Over the past three decades, New York City has undergone major ebbs and flows across its foundational industries of finance, media, real estate, tourism, and professional services. The city experienced the highs of booming markets in the 1990s and 2010s as well as the lows of recessions in the early 2000s and 2008-2009. Industry mixes shifted as media and tech grew while manufacturing declined. But finance remained the city’s economic engine.
In the 1990s, Wall Street drove tremendous growth as financial markets surged. Securities firms, investment banks and other financial institutions expanded dramatically during this period. The tech/dot-com boom also benefited New York’s emerging Silicon Alley startup ecosystem and media giants. High corporate profits fueled rapid commercial real estate development.
However, the early 2000s recession hit New York’s finance and real estate sectors hard following the tech bubble’s burst. The 9/11 attacks inflicted massive human and economic costs. But resilient tourism, government investment, and gradual Wall Street recovery brought New York back until the next downturn.
The 2008 global financial crisis produced catastrophic losses on Wall Street and throughout New York’s economy. Major investment banks collapsed while others consolidated during the Great Recession. Real estate, media, tourism and retailing also suffered steep declines in revenue and employment. Recovery was slow and uneven across industries and boroughs.
Since 2010, finance has rebounded as trading and banking activity returned along with bull markets. Technology, media, hospitality and professional services expanded as well, diversifying the city’s industry base. Major development transformed areas like Manhattan west side, Brooklyn waterfront, and Hudson Yards. But costs strained other local businesses.
The COVID-19 pandemic sparked another massive disruption starting in 2020 as economic activity and tourism shut down. Office vacancies soared while service and entertainment venues struggled. Finance and tech firms proved more resilient. Uneven federal relief and reopening headwinds have complicated renewal, especially for small businesses and low-income communities.
Current Position
Today, New York remains a global hub for finance, media, real estate, tourism, and professional services. Wall Street firms anchor the economy, employing hundreds of thousands in high-wage jobs recirculating through local businesses. The media, tech, healthcare, education and creative sectors hold major presence as well. However, challenges like high costs and regulation threaten competitiveness.
Wall Street dominates New York’s economy, driving demand for services from law to construction to luxury retail. The securities industry alone employs over 180,000 locally. However, banks face pressures to relocate selected operations and workers to lower-cost cities to reduce expenses. Trading automation and consolidation also affect staffing.
Media, advertising and publishing continue adapting business models to the digital era. Major firms like the New York Times, NBCUniversal, WarnerMedia, Hearst, and Condé Nast anchor the sector alongside startups. However, employment remains below peaks of decades past due to technology disruption.
Technology and innovation development have been bright spots, with growth along Silicon Alley and in Brooklyn. Venture funding, incubators and talent retention efforts aim to strengthen New York’s startup ecosystem versus West Coast tech hubs. Attracting large tech employers is also a priority to diversify the economy.
Hospitality and tourism are slowly recovering from COVID shutdowns but face headwinds. International tourism and business travel are rebounding slower than domestic leisure. Hotel room supply also exceeds still-recovering demand, impacting revenues. Entertainment venues and restaurants face labor shortages. Conventions and meetings show promising signs, however.
Future Outlook
New York City still enjoys formidable advantages in location, infrastructure, talent pool and culture that should sustain its leadership across key industries like finance, media, tourism, real estate and tech. However, improving cost structures and competitiveness is essential for resilient, equitable growth.
The city’s unparalleled stature as a global financial capital seems likely to continue despite mounting competition from cities seeking financial services jobs and firms looking to trim expenses. Regulation and tax incentives will be policy levers to retain banks and trading firms. Cybersecurity and fintech innovation should also see investment.
New York’s dominant media ecosystem appears well positioned for the streaming era as content production booms. Film/tv studios and digital platforms drive strong demand for local talent and support services. advertiser spending is shifting back from tech platforms to premium publishers. NYC now trails only Los Angeles in media sector jobs.
Stronger connecting New York’s research universities and startups can catalyze more local tech innovation. Incentives to grow workforce housing, improve transit and mobility, and resolve infrastructural bottlenecks are also essential for attractiveness. Reducing taxes and bureaucratic obstacles for businesses balances costs.
While virtual communication rose during the pandemic, in-person exchanges and experiences retain unique value. This bodes well for tourism and hospitality as conventions, museums, entertainment and dining continue driving visits. However, affordability improvements can help New York better compete for visitors globally.
If the city can address cost and infrastructure constraints while playing to its strengths in talent, innovation and culture, New York seems poised for sustainable prosperity across diverse sectors. Managing post-pandemic recovery across neighborhoods equitably remains critical as well.

Washington, D.C.
History
As the nation’s capital, Washington D.C.’s economy has been historically dominated by the federal government and related professional services. Over the past three decades, the city has worked to diversify its economic base by fostering growth in technology, hospitality, healthcare, real estate, education, and other private industries. However, the fortunes of D.C. businesses remain closely tied to federal spending and policy direction.
The early 1990s saw downturn in federal hiring and procurement that impacted regional firms dependent on government contracts. In response, business leaders worked to attract private-sector companies in technology, biotech, and other fields to reduce reliance on federal spending. The tech-focused Dulles Technology Corridor emerged.
Under the later 1990s dot-com boom, D.C. saw upticks in IT hiring and office expansion. The emerging tech hub spawned startups and attracted satellite offices from Silicon Valley firms. Venture investment in local tech companies rose significantly during this period.
However, the dot-com bust and 2001-02 recession brought sharp cutbacks as capital dried up. The economic impact rippled through D.C.’s real estate, hospitality and professional services industries. Following the 2008-09 recession, stimulus spending fueled a rebound in government contracting and hiring that buoyed D.C. commerce.
D.C. benefited from surging federal budgets between 2010-2020. Defense, homeland security, healthcare, and technology spending flowed to contractors, consultants, lobbyists, lawyers and more. Commercial real estate boomed with government expansions, lifting the broader local economy. But reliance on federal largess posed risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic and remote work trends hit D.C. harder than peer cities, sparking a sharp downtown office vacancy increase. Constrained federal spending weighs on government services companies. However, solid federal job security and D.C.’s strengths in education, research and quality of life help mitigate losses.
Current Position
Today, Washington D.C. enjoys a diverse mix of public and private sector industries. The federal government remains the metro area’s largest employer, providing over 370,000 local jobs. Government contractors, consultants, law firms and lobbyists form a large professional services ecosystem supported by federal spending.
However, D.C. has developed strong healthcare, education, nonprofit, technology, hospitality and retail sectors as well. The city is home to three top universities in Georgetown, George Washington and Howard. Major corporations like Amazon, Boeing, Pepco, Mars, Danaher and Northrop Grumman all have significant regional operations.
The technology sector has shown robust growth in recent years. The D.C. metro area now holds over 297,000 tech jobs, placing it among the ten largest U.S. tech hubs. Cybersecurity, defense IT, data analytics, aerospace tech and biotech are key strengths. However, tech firms compete intensely for the specialized skillsets the government also recruits.
Travel and tourism-related industries contribute billions to the D.C. economy in typical years. However, conventions, meetings and visits from government officials, associations, lobbyists and foreign dignitaries that account for sizable hospitality revenues have been slow to rebound after COVID-19 shutdowns. Medical and higher education centers buoy activity.
While the region’s educated workforce and resilient economy foster business growth, issues like high costs of living and extreme income inequality pose challenges. As remote work trends persist post-pandemic, attracting and retaining talent demands enhancing amenities, mobility and access to opportunity across neighborhoods.
Future Outlook
Given D.C.’s specialized advantages as the seat of government, education nexus and policy hub, the metro likely will sustain moderate if uneven growth across sectors like technology, professional services, education, healthcare and hospitality. However, diversification beyond direct federal spending remains important for economic resilience.
Near-term federal budgets face pressures from inflation, debt, and partisan disputes over spending priorities. But over the long-term, sustained federal investments in areas like cybersecurity, biotech research, defense technology, energy, and health should underpin government contracting activity and stabilize D.C. commerce.
D.C.’s highly educated workforce, research universities, and proximity to federal R&D funding should support expansion of technology, biotech and advanced sectors. However, competition from tech hubs for skilled talent is intense. Improving mobility, housing affordability and urban amenities can make D.C. more attractive.
Travel and tourism should ramp back up post-pandemic as conventions, meetings and international visits eventually rebound. Hotel and restaurant staffing shortages may pose near-term operational challenges. Retail may struggle with brick-and-mortar declines, but e-commerce growth can offset losses.
With strategic planning and investment, Washington D.C. is poised for continued prosperity based on unique advantages in proximity to government, policy influence, world-class academic and research institutions, specialized skill bases, and vibrant communities. Sustaining growth will depend on smart diversification and enhancing competitiveness for private industries choosing location.
Program Benefits
Marketing
- Enhanced Personalization
- Campaign ideation
- Lead Prioritization
- Sales Automation
- Trend Analysis
- Conversion Optimization
- Engagement Scaling
- Content Creation
- Scalability & Speed
- Message Targeting
Customer Service
- Response Automation
- Chatbot Efficiency
- Sentiment Analysis
- Issue Prediction
- Self-Service Options
- Knowledge management
- Feedback Analysis
- Service Personalization
- Resolution Acceleration
- Upsell Opportunities
Operations
- Cost Reduction
- Error Minimization
- Compliance Monitoring
- Workflow Optimization
- Efficiency Improvement
- Resource Allocation
- Workforce Upskilling
- Decision Support
- Document Management
- Contract Analysis
Testimonials

CFO, Ebony Media
“We highly recommend Mr. Laboy for their exceptional expertise in AI transformation. His AI strategy workshop provided our team with a comprehensive understanding of AI’s business impact and emerging capabilities. His tailored AI workshops played a crucial role in guiding us through identifying the AI use case that would have the greatest business impacts. Mr. Laboy has been an invaluable strategic partner in our AI journey. We confidently endorse their services for any organization seeking to harness the transformative power of AI.”
CEO, Fuel Cycle
“We wholeheartedly recommend Mr. Laboy for his outstanding AI expertise and transformative impact on our business at Fuel Cycle. Their guidance and support have been pivotal in leveraging AI for our business transformation. Mr. Laboy possesses an exceptional depth of knowledge in the field of AI, and their ability to translate that knowledge into actionable strategies has been invaluable. Their tailored solutions have helped us unlock new avenues for growth, efficiency, and innovation. His expertise is a true asset for achieving business excellence through AI-driven solutions.”

Case Study – A Fortune 100 Pharmaceutical Company
Project: AI-Driven Patient Engagement Platform
Challenge: The client, a leading entity in the pharmaceutical sector, faced a significant setback when it was discovered that 50% of prescriptions for a specialized medication were not being filled. This lapse in patient follow-through not only affected patient health outcomes but also resulted in a staggering potential revenue loss of $2 billion annually. Patients reported feeling overwhelmed and uncertain about the process required to manage their treatment with this advanced medication, leading to non-adherence and discontinuation.
Solution: To address this challenge, the consultancy developed a cutting-edge AI solution tailored to enhance patient engagement and adherence. The multi-faceted approach involved:
1. Predictive Analytics: Utilizing AI to sift through vast datasets to identify patients who were at risk of not filling their prescriptions. This proactive measure allowed for early intervention.
2. Personalized Patient Profiles: Leveraging AI to create comprehensive and unique profiles for each patient. These profiles encompassed medical history, demographic information, and behavioral data, ensuring a personalized approach to patient care.
3. Journey Tracking: Monitoring the patient’s journey with real-time tracking to quickly identify and address any roadblocks in their treatment process.
4. AI Concierge Service: Establishing an AI-powered concierge that provided 24/7 support to patients. This virtual assistant guided patients through their treatment regimen, answered queries, and ensured they felt confident in managing their medication.
5. Intelligent Routing: Implementing intelligent automation to seamlessly connect patients with nurse practitioners for human-led support when complex issues arose.
Results: The AI-driven platform revolutionized the way the client engaged with patients. Within the first six months of implementation, the results were noteworthy:
• An increase in revenue of $174 million was a direct result of the improved prescription fill-rate.
• Patient satisfaction scores surged by 22%, as the personalized support and guidance provided by the AI concierge significantly eased patient concerns and improved their treatment experience.
This case study exemplifies the power of AI in transforming patient engagement and adherence. By leveraging advanced analytics and personalized care, the consultancy’s solution not only recuperated lost revenue but also, more importantly, enhanced patient health outcomes.

Case Study – A Fortune 100 Health Insurance Company
Project: AI-Powered Customer Acquisition
Challenge: The client was facing a significant challenge in expanding their customer base due to a lack of access to potential customers. Companies offering the insurer’s health solutions did not share their employee lists, which limited the insurer’s ability to target and engage with potential new members. The inability to identify potential customers in the vast marketplace was a major hurdle in driving up insurance sign-ups and expanding market share.
Solution: To overcome this barrier, an innovative AI solution was developed to harness the power of predictive analytics and data mining. The solution entailed:
1. Predictive Modeling: The AI used advanced algorithms to analyze publicly available data and predict with a high level of accuracy which individuals worked at companies that were offered the insurer’s products.
2. Personalization at Scale: Armed with these insights, the insurer was able to craft personalized content and offers tailored to the interests and needs of these individuals, thereby increasing the relevance and appeal of their communication.
3. Precision Targeting: By focusing on individuals likely to be employed at companies with potential corporate insurance plans, the insurer could more effectively allocate their marketing resources.
4. Data-Driven Campaigns: Marketing campaigns were then launched, utilizing the predictive data to reach out to these potential customers through various channels with customized messaging.
Results: The results of implementing this AI-powered approach were transformative:
• The AI model successfully predicted an individual’s workplace with an impressive 84% accuracy rate.
• The return on advertising spend soared by 53%, indicating a significant increase in the efficiency and effectiveness of the marketing campaigns.
• Most notably, there was an 8% increase in insurance sign-ups, reflecting a substantial growth in the client’s customer base.
This case study demonstrates the potential of AI in revolutionizing customer acquisition strategies. By leveraging cutting-edge technology to identify and target potential customers with precision, the health insurance company not only improved its advertising efficiency but also achieved a remarkable increase in new member enrollment.

Case Study – A Major US Law Firm
Project: AI Optimization of Legal Research and Documentation
Challenge: The client, a prominent US law firm, was grappling with the resource-intensive nature of legal research and case document preparation. The traditional process was cumbersome, involving several days and significant man-hours to gather case law, precedents, and prepare briefs, which led to elevated costs and slower case turnaround times.
Solution: A sophisticated AI-driven solution was implemented to revolutionize the firm’s approach to legal research and documentation. Key components of the solution included:
1. AI-Assisted Legal Research: The AI system was designed to quickly parse through vast amounts of case law to identify relevant precedents and rulings, thereby expediting the research phase.
2. Automated Document Drafting: Utilizing natural language processing, the AI was able to draft briefs and other legal documents, requiring only minimal oversight and input from legal staff.
3. Process Streamlining: By automating routine tasks, the AI allowed legal professionals to focus on more complex, substantive aspects of case preparation.
4. Continual Learning: The AI was equipped with machine learning capabilities, enabling it to improve over time by learning from past research patterns and document drafting.
Results: The integration of AI into the law firm’s operations yielded transformative results:
• Costs associated with case preparation decreased by 33%, as the AI reduced the need for extensive billable hours traditionally spent on research and writing.
• Productivity saw a dramatic 50% increase, with lawyers able to handle more cases simultaneously due to the efficiency of the AI tools.
• Perhaps most significantly, the time required to complete case preparation dropped by 90%, allowing for faster case turnover and the ability to meet client needs more promptly.
This case study highlights the potential for AI to significantly enhance efficiency in the legal field. By automating the laborious aspects of legal work, the law firm not only reduced costs and increased productivity but also improved their capacity to deliver timely legal services to their clients.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.