Flow of Funds

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Flow of Funds is provided by Ms. Grisby Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Ms. Grisby is dedicated to helping businesses optimize their financial and operational processes through innovative accounts receivable management solutions. Her company, specializes in providing a comprehensive range of services, including medical billing, corporate training, accounting, and consulting. These offerings are designed to empower organizations to achieve financial stability, reduce risk, and foster stronger customer relationships.
With over a decade of experience in commercial accounts receivable management, commercial credit management, process optimization, and SOP creation, Ms. Grisby brings a wealth of expertise to her work. Her proficiency lies in designing and implementing strategies that enhance cash flow, reduce outstanding debt, and ensure businesses maintain a healthy financial outlook.
A key strength of Ms. Grisby is her ability to collaborate with clients and tailor solutions to meet their unique needs. Whether developing customized training programs, improving financial reporting systems, or resolving complex billing issues, she consistently delivers measurable results. By combining industry best practices with innovative approaches, Ms. Grisby helps businesses streamline operations and achieve sustainable growth.
Ms. Grisby is an active member of the American Academy of Revenue Cycle Consultants (AARCC) and the National Association of Credit Managers, demonstrating her commitment to industry leadership and maintaining the highest standards of professionalism and integrity.
Her professional achievements include:
• Leading and managing high-performing teams to achieve organizational goals at a well-known medical device company.
• Designing and implementing process improvements that increase efficiency and reduce costs.
• Creating comprehensive SOPs to ensure consistency and compliance across operations.
• Developing financial reports that provide actionable insights for decision-making with a leading medical organization.
• Resolving complex accounts receivable and billing issues with innovative solutions for Fortune 500 companies.
• Driving successful KPIs that align with business objectives and enhance performance for leading organizations.
Ms. Grisby believes that effective cash flow management is the cornerstone of business success. She views each client partnership as an opportunity to make a meaningful impact, helping organizations unlock their full potential. Her company is not just a service provider but a strategic partner invested in client success.
Her commitment to continuous learning and innovation enables her to stay ahead in a constantly evolving industry. By adopting new technologies, refining her skills, and exploring forward-thinking solutions, Ms. Grisby consistently delivers exceptional outcomes.
Outside of her professional endeavors, Ms. Grisby actively networks with other professionals, attends industry events, and shares her expertise through workshops and training sessions. She thrives on connecting with like-minded individuals passionate about driving success and creating value.
Ms. Grisby is a results-driven leader dedicated to helping organizations streamline accounts receivable management, improve operational efficiency, and achieve financial excellence.
To request further information about Ms. Grisby through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Flow of Funds Program
The Flow of Funds: A Journey Through Time and the Future Ahead
The flow of funds—the intricate movement of money within and across economies—has been a defining element of human civilization. From the barter systems of ancient marketplaces to the instant, digital transactions of the 21st century, the evolution of money movement mirrors humanity’s progress, ingenuity, and resilience. What began as simple exchanges of goods has transformed into a global network of financial systems, connecting billions of people, businesses, and governments in real-time.
The history of the flow of funds reveals a fascinating narrative of adaptation and innovation. Consider the emergence of coins as a standardized currency in ancient Lydia, or the development of paper money in China, which revolutionized trade by creating a more efficient and portable means of exchange. The establishment of banking systems further catalyzed economic activity, providing a structured mechanism for saving, lending, and investment. These milestones weren’t merely technological advances—they were societal shifts, reflecting the growing complexity of human interaction and the necessity for trust and regulation in financial transactions.
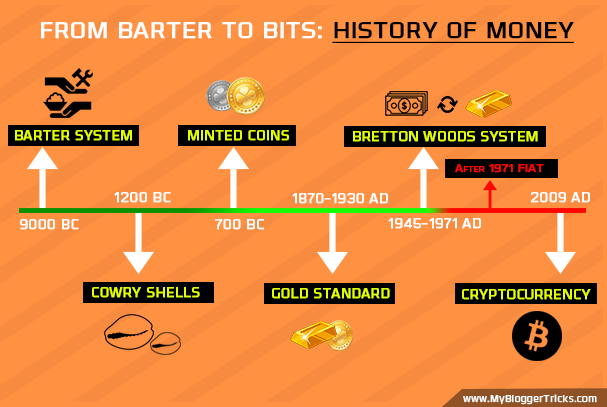
Fast forward to the modern day, and the flow of funds has become a sophisticated, technology-driven phenomenon. Digital wallets, cryptocurrencies, and blockchain technology have redefined how we think about money and financial services. A single smartphone can now execute transactions across the globe in seconds, connecting consumers and businesses in ways unimaginable a few decades ago. This digital transformation brings immense opportunities but also poses challenges, such as cybersecurity threats, regulatory hurdles, and ethical concerns about inequality and inclusion.
The present landscape of money movement is shaped by a confluence of factors. Globalization continues to expand the interconnectedness of financial markets, while geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties create volatility. Central banks’ decisions, like adjusting interest rates to combat inflation, ripple through economies, influencing borrowing costs and investment flows. Meanwhile, technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences are driving the adoption of innovative financial tools and services, making understanding the flow of funds more critical than ever.
As we look to the future, the flow of funds is poised to undergo further transformation. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and decentralized finance (DeFi) promise to disrupt traditional systems, democratizing access to financial services and streamlining operations. At the same time, pressing global challenges like climate change and demographic shifts will influence where and how money is allocated. The need for effective regulation and international cooperation will be paramount as the world grapples with an increasingly complex financial ecosystem.
Understanding the flow of funds—past, present, and future—is more than an academic exercise. It equips individuals, businesses, and policymakers with the knowledge to navigate the ever-changing financial landscape, anticipate challenges, and seize opportunities. As money continues to flow, so too will the possibilities for innovation, growth, and societal advancement.
Flow of Funds – Future Outlook: Forecasting the Financial Landscape
The future of the flow of funds will be defined by the intersection of technological advancements, shifting economic dynamics, and evolving geopolitical realities. These forces, while presenting unprecedented opportunities, also introduce complexities that will shape how money moves globally. From decentralized finance to regulatory challenges, the coming decades promise to reshape the financial landscape profoundly.
Technological Advancements
Technology will remain the most significant driver of change in the flow of funds:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI will revolutionize finance by automating processes like trading, risk management, and fraud detection. Its ability to analyze massive datasets and uncover patterns will enhance decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency. AI-powered tools will enable faster and more informed investment strategies while mitigating risks through predictive analytics.
2. Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain has the potential to upend traditional financial systems by providing decentralized, secure, and transparent transaction platforms. Beyond its use in cryptocurrencies, blockchain is finding applications in supply chain management, identity verification, and smart contracts. These advancements could reduce transaction costs, improve transparency, and foster trust in digital financial ecosystems.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
DeFi seeks to democratize financial services by eliminating intermediaries such as banks and brokers. Through direct peer-to-peer platforms, DeFi has the potential to increase financial inclusion, particularly in underserved regions. Its growth will challenge traditional financial institutions to innovate or risk obsolescence.

Economic Trends
Several global economic shifts will significantly impact the flow of funds:
1. Climate Change:
The urgent need to address climate change will steer capital toward sustainable investments. Green bonds, renewable energy projects, and carbon-reduction initiatives are likely to dominate future financial flows as governments and businesses prioritize environmental sustainability.
2. Demographic Shifts:
Aging populations in developed nations will pressure pension systems and healthcare infrastructure, affecting government spending and private investments. Simultaneously, rising income inequality may require fiscal policies to promote equitable economic growth, redirecting how funds are distributed globally.
3. Globalization and Trade:
While globalization has facilitated interconnected financial markets, its future is uncertain due to geopolitical tensions and trade disputes. Shifts in trade patterns and regional economic alliances will significantly influence cross-border fund flows and investment opportunities.
Geopolitical Risks
1. Geopolitical Tensions:
Conflicts and rivalries between major powers, such as the United States and China, could result in market volatility, currency fluctuations, and disrupted trade routes. These dynamics will directly influence the movement of funds and investment strategies.
2. Cybersecurity Threats:
As digital financial systems expand, the sophistication of cyberattacks poses severe risks to institutions and individuals. Securing sensitive data and preventing financial fraud will become critical priorities for maintaining trust in financial systems.
Regulatory Landscape
1. Evolving Regulations:
Rapid technological change necessitates updated regulations to address emerging issues like data privacy, consumer protection, and financial stability. Governments must balance fostering innovation with mitigating risks to maintain stable financial ecosystems.
2. Cross-Border Regulation:
The globalization of financial markets calls for enhanced international cooperation on regulatory standards. Addressing inconsistencies across jurisdictions will be essential for ensuring smooth cross-border financial operations.
Opportunities and Challenges
While technological advancements promise efficiency and inclusivity, they also raise concerns about privacy, security, and inequality. Climate change, demographic pressures, and geopolitical risks will require innovative financial solutions and collaborative global efforts. By staying informed about these trends and adapting strategies accordingly, individuals, businesses, and policymakers can better navigate the evolving flow of funds and align their decisions with long-term goals.
The Importance of Flow of Funds for Businesses
Understanding and prioritizing the flow of funds is critical for businesses of all sizes. The term refers to the movement of money within and across economies, encompassing transactions, investments, and payments. For businesses, managing the flow of funds effectively is not just about operational efficiency—it is a cornerstone of financial health, strategic planning, and long-term success.
Maintaining Financial Stability
The flow of funds directly impacts a company’s liquidity, or its ability to meet short-term financial obligations. A business must have sufficient cash flow to pay employees, suppliers, and creditors while investing in growth opportunities. Poor cash flow management can lead to operational disruptions, strained relationships with stakeholders, and even insolvency. By closely monitoring and optimizing the flow of funds, businesses can ensure they remain financially stable and resilient to unexpected challenges.
Enhancing Decision-Making
Accurate and timely information about the flow of funds enables better decision-making. Businesses can allocate resources more effectively, identify profitable opportunities, and mitigate risks. For example, understanding patterns in receivables and payables helps companies anticipate cash flow gaps and implement strategies to bridge them, such as securing short-term financing or renegotiating payment terms. Additionally, analyzing the movement of funds can reveal inefficiencies, allowing businesses to streamline operations and improve profitability.
Supporting Strategic Growth
The flow of funds is integral to planning for growth and expansion. Businesses that understand how money moves within their operations and across markets are better positioned to invest in new projects, enter new markets, and develop innovative products or services. For instance, a clear picture of cash inflows and outflows helps a business decide whether to reinvest profits, secure external funding, or pursue mergers and acquisitions. Strategic management of funds also ensures that growth initiatives are sustainable and aligned with long-term goals.

Navigating Economic Uncertainty
The global economy is influenced by factors such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events, all of which affect the flow of funds. Businesses that prioritize this aspect of financial management are better equipped to adapt to changing conditions. For example, during periods of rising interest rates, understanding the cost of borrowing and the availability of capital can help businesses adjust their financial strategies. Similarly, awareness of trade patterns and currency fluctuations enables businesses to mitigate risks associated with international transactions.
Building Stakeholder Confidence
Effective management of the flow of funds demonstrates financial discipline, which is crucial for building trust with stakeholders, including investors, lenders, employees, and customers. Transparent reporting of cash flow and financial performance reassures stakeholders of a company’s stability and reliability. Investors, in particular, value businesses that can demonstrate consistent cash flow, as it indicates the company’s ability to generate returns and weather economic challenges.
Leveraging Technological Advancements
The rise of digital tools, such as automated cash flow management software and blockchain technology, has transformed how businesses manage the flow of funds. By leveraging these advancements, businesses can gain real-time visibility into their financial activities, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. Embracing these technologies not only enhances operations but also positions businesses as innovative and forward-thinking.
Conclusion
Our Flow of Funds program is a lifeline for businesses, influencing their ability to operate, grow, and adapt to a dynamic economic landscape. By placing importance on understanding and managing this critical aspect, businesses can achieve financial stability, make informed decisions, and build a foundation for sustained success. In today’s complex and fast-paced financial environment, prioritizing the flow of funds is not just beneficial—it is essential.

Case Study: Optimizing B2B Accounts Receivable for Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J), a global leader in healthcare, operates across numerous countries and offers a diverse range of consumer health, pharmaceuticals, and medical device products. Serving both consumer and professional markets, J&J faces unique challenges in managing its B2B accounts receivable processes efficiently.
J&J’s accounts receivable management presented several challenges:
1. Diverse Customer Base:
J&J’s customers include hospitals, pharmacies, retailers, and distributors, each with distinct payment terms, invoicing requirements, and billing cycles. Managing this wide variety of customer segments created difficulties in standardizing processes.
2. Complex Invoicing Structure:
The complexity of J&J’s product portfolio and pricing models resulted in intricate invoicing processes. Variations in pricing tiers, discounts, and contractual agreements required tailored invoices for each customer.
3. Global Operations:
Operating in multiple countries introduced complications related to currency conversion, regulatory compliance, and tax requirements. Accounts receivable management across different jurisdictions required systems capable of handling these international nuances.
4. Manual Processes:
Despite being a global conglomerate, J&J relied heavily on manual tasks for invoice generation, reconciliation, and dispute resolution. These labor-intensive processes were time-consuming, prone to errors, and hindered operational efficiency.
To address the challenges of managing accounts receivable efficiently, Johnson & Johnson implemented a comprehensive solution leveraging automation, technology, and process optimization strategies. One significant step was the adoption of a centralized billing platform. This platform consolidated billing information across various business units and regions, enabling standardized invoicing processes. By ensuring consistency and accuracy, the platform streamlined interactions with diverse customer segments.
Automation tools further enhanced the invoicing process by integrating with J&J’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. This allowed for the automatic generation of invoices based on predefined rules, reducing errors and accelerating delivery times. To cater to the specific needs of its varied customer base, J&J developed customized invoicing options, such as electronic invoicing, consolidated billing statements, and customer-specific formats. These tailored solutions not only simplified payment processes but also improved customer satisfaction.
To support secure and efficient payment processing, J&J introduced a global payment gateway. This system facilitated cross-border transactions, supporting multiple currencies and payment methods while ensuring compliance with international regulations. Additionally, J&J invested in advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. Real-time dashboards provided insights into accounts receivable performance, displaying key metrics such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), aging receivables, and payment behaviors. These analytics empowered the company to make proactive decisions and manage risks effectively.
The results of these initiatives were transformative. Streamlined accounts receivable processes and shorter payment cycles significantly improved cash flow management, optimizing liquidity and working capital. Tailored invoicing and efficient payment solutions enhanced customer satisfaction by ensuring accurate and timely invoices, fostering transparency, and strengthening relationships. This contributed to long-term customer loyalty and repeat business.
Operational efficiency also saw a marked improvement due to automation. By reducing manual intervention, J&J achieved substantial cost savings and freed up resources for strategic planning and analysis. Furthermore, the implementation of the global payment gateway ensured compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigated risks associated with cross-border transactions. Enhanced visibility into accounts receivable data supported proactive credit control and robust risk management strategies.
Through these measures, Johnson & Johnson successfully optimized its accounts receivable processes, positioning itself for sustained growth and improved operational performance in the competitive healthcare industry.
Conclusion
Through the integration of automation, technology, and best practices, Johnson & Johnson successfully optimized its B2B accounts receivable processes. Streamlined invoicing, payment systems, and analytics have positioned the company for sustained growth and success in the competitive healthcare industry, while also improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Curriculum
Flow of Funds Program – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Understanding Credit Policies
- Part 1 Month 2 Customer Credit Evaluation
- Part 1 Month 3 Invoicing Processes
- Part 1 Month 4 Payment Terms and Conditions
- Part 1 Month 5 Communication Skills
- Part 1 Month 6 Negotiation Techniques
- Part 1 Month 7 Account Reconciliation
- Part 1 Month 8 Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Part 1 Month 9 Cash Application
- Part 1 Month 10 Aging Analysis
- Part 1 Month 11 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
- Part 1 Month 12 Performance Metrics and Reporting
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Flow of Funds Program corporate training program.
Flow of Funds Program – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Understanding Credit Policies – A comprehensive understanding of a company’s credit policies and procedures is essential for effectively managing accounts receivable. Credit policies define the terms and conditions under which credit is extended to customers, helping to minimize financial risks while fostering strong customer relationships. Clear knowledge of these policies ensures consistency in decision-making, aids in evaluating creditworthiness, and facilitates timely collections. Adherence to established procedures also helps maintain cash flow stability and mitigate bad debt. By aligning credit management practices with company goals, managers can ensure efficient accounts receivable operations while supporting broader financial objectives.
- Part 1 Month 2 Customer Credit Evaluation – Training on customer credit evaluation equips teams with the skills to assess the creditworthiness of potential and existing customers, minimizing the risk of bad debts. This process involves analyzing financial statements, credit scores, payment history, and industry reputation to make informed decisions about extending credit. By understanding these evaluation methods, employees can identify high-risk customers, set appropriate credit limits, and maintain a healthy balance between fostering customer relationships and protecting the company’s financial interests. Comprehensive training ensures consistency in evaluations, reduces exposure to financial risks, and supports the company’s overall cash flow and profitability goals.
- Part 1 Month 3 Invoicing Processes – A thorough understanding of invoicing processes is vital for efficient accounts receivable management. Accurate and timely invoice generation ensures that customers are billed correctly and promptly, reducing delays in payment. Delivery methods should align with customer preferences, whether via email, electronic systems, or traditional mail, to streamline communication. Proper tracking of invoices allows teams to monitor payment statuses, follow up on overdue accounts, and address discrepancies quickly. By mastering these processes, organizations can improve cash flow, enhance customer satisfaction, and minimize errors, creating a foundation for effective financial management and stronger customer relationships.
- Part 1 Month 4 Payment Terms and Conditions – Understanding payment terms and conditions is crucial for effective accounts receivable management and collections. These terms define the agreed-upon timelines and expectations for payments, such as net payment periods (e.g., net 30 days), discounts for early payments, and penalties for late payments. Familiarity with these terms enables teams to communicate payment expectations clearly, encourage timely payments, and manage customer relationships more effectively. Additionally, enforcing penalties and offering early payment discounts can improve cash flow and reduce overdue accounts. A solid grasp of payment terms ensures consistency in collections and strengthens financial stability for the organization.
- Part 1 Month 5 Communication Skills – Strong communication skills are essential for effectively managing accounts receivable and maintaining positive customer relationships. Training should emphasize clear, professional, and empathetic interactions when addressing overdue payments, resolving disputes, or negotiating payment arrangements. Effective communication helps build trust, de-escalate conflicts, and ensure customers feel valued, even in challenging situations. It also aids in conveying payment expectations, reinforcing the importance of timely payments, and reaching mutually beneficial solutions. By developing these skills, teams can improve collection rates, preserve customer loyalty, and foster collaborative relationships that support long-term business success.
- Part 1 Month 6 Negotiation Techniques – Mastering negotiation techniques is crucial for securing payment commitments and resolving disputes while preserving strong customer relationships. Effective negotiation involves understanding the customer’s perspective, identifying mutually beneficial solutions, and remaining firm yet respectful. Techniques such as active listening, presenting flexible payment options, and emphasizing the value of honoring agreements help de-escalate conflicts and encourage cooperation. By demonstrating empathy and professionalism, teams can build trust and secure timely payments without straining relationships. Knowledge of these techniques ensures smoother interactions, minimizes bad debt risks, and supports both financial goals and long-term customer retention.
- Part 1 Month 7 Account Reconciliation – Account reconciliation is a critical process for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring the integrity of accounts receivable. It involves comparing customer payments against invoices to identify and resolve discrepancies, such as overpayments, underpayments, or missing transactions. Timely reconciliation prevents errors from compounding and ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the company’s financial position. Understanding reconciliation techniques enables teams to identify issues early, address customer concerns effectively, and maintain trust. Mastery of this process supports accurate financial reporting, enhances cash flow management, and contributes to the organization’s overall financial stability and compliance with accounting standards.
- Part 1 Month 8 Legal and Regulatory Compliance – Familiarity with legal and regulatory frameworks governing accounts receivable and collections is essential for maintaining compliance and avoiding legal issues. Regulations such as the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) establish guidelines for ethical and lawful collections practices, protecting both businesses and customers. Understanding these laws ensures that collections activities are conducted fairly, professionally, and within legal boundaries. Compliance training helps teams navigate restrictions on communication, privacy, and dispute resolution while minimizing risks of fines or reputational damage. A strong grasp of compliance safeguards the organization and builds trust by demonstrating commitment to ethical financial management.
- Part 1 Month 9 Cash Application – Cash application is a vital component of accounts receivable management, ensuring customer payments are recorded and applied to outstanding invoices accurately and efficiently. Proper training in cash application procedures helps minimize errors, such as misapplied payments or incorrect balances, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction or financial discrepancies. Accurate cash application enhances cash flow management, supports timely account reconciliation, and provides clear visibility into outstanding debts. By mastering this process, teams can maintain reliable financial records, streamline collections, and build trust with customers through transparent and error-free account management.
- Part 1 Month 10 Aging Analysis – Aging analysis is a critical tool in accounts receivable management, enabling businesses to monitor outstanding invoices and identify overdue accounts. By categorizing receivables based on their age, teams can prioritize collection efforts on high-risk or significantly overdue accounts. Understanding aging reports also supports accurate cash flow forecasting, helping organizations anticipate incoming payments and plan accordingly. This analysis allows businesses to address potential bad debts proactively, improve collection efficiency, and maintain healthy financial operations. Mastery of aging analysis equips teams to make informed decisions that optimize receivables management and contribute to overall financial stability.
- Part 1 Month 11 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools – Proficiency in using Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools is essential for efficient accounts receivable and collections management. CRM software allows teams to track customer interactions, record payment commitments, and monitor collections activities in a centralized system. This ensures better organization, real-time access to payment histories, and improved communication with customers. CRM tools also enable proactive follow-ups, strengthen relationships through personalized service, and enhance the accuracy of financial data. By leveraging these tools effectively, businesses can streamline collections processes, foster stronger customer relationships, and improve overall efficiency in managing accounts receivable.
- Part 1 Month 12 Performance Metrics and Reporting – Understanding performance metrics and reporting is essential for effective accounts receivable and collections management. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and collection efficiency ratio provide insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of collections processes. Training should cover how to calculate and interpret these KPIs, as well as generate comprehensive reports for management review. Accurate reporting supports data-driven decision-making, helping identify trends, address inefficiencies, and forecast cash flow. Proficiency in performance metrics ensures that teams can measure progress, optimize strategies, and align collections efforts with organizational financial goals.
Methodology
Flow of Funds Program
The Flow of Funds Program is built on a structured and process-driven methodology designed to help organizations optimize accounts receivable management and align financial operations with organizational goals. This 12-month program unfolds in distinct phases, each addressing a critical aspect of financial management, progressing logically from foundational principles to advanced techniques and sustainable practices. The methodology is characterized by its progressive learning pathway, focus on measurable outcomes, and alignment with strategic objectives.
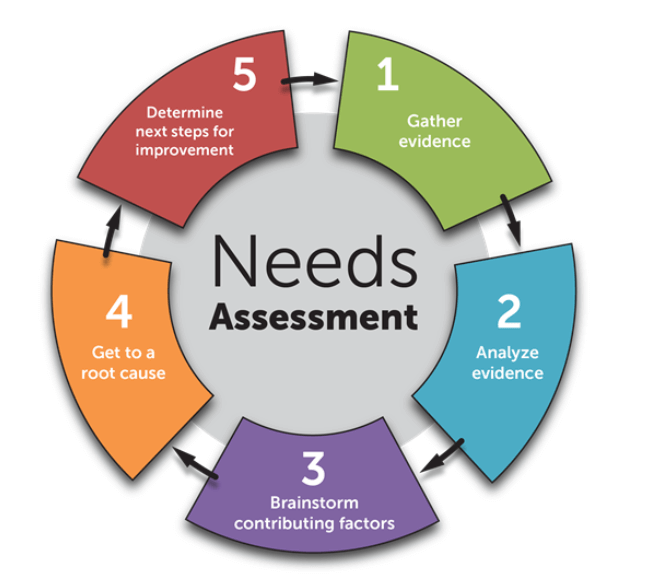
Needs Assessment and Progressive Learning Pathway
The program begins with a thorough needs assessment to identify and prioritize challenges related to the flow of funds. This involves gathering and analyzing data on issues such as financial literacy and economic development. Stakeholders, including individuals, businesses, and communities, are identified, and their needs are ranked based on urgency, potential impact, and feasibility. This ensures that resources are directed toward the most critical areas, laying the groundwork for a focused and impactful program.
Following this assessment, the program is designed to build participants’ expertise incrementally. In the first four months, participants establish a solid understanding of credit policies, customer credit evaluation, invoicing processes, and payment terms. This foundational phase ensures that teams are equipped to make consistent decisions, evaluate creditworthiness effectively, and maintain cash flow stability.
The middle phase, spanning months five through eight, focuses on enhancing operational efficiency through advanced interpersonal and technical skills. Workshops during this phase address communication, negotiation techniques, account reconciliation, and legal compliance. This stage emphasizes fostering trust, maintaining ethical standards, and balancing strong customer relationships with the achievement of financial goals.
The final phase, covering months nine to twelve, introduces practical tools and strategies to streamline operations and ensure sustainability. Participants learn to manage cash application processes, perform aging analysis, and leverage CRM systems to improve efficiency and data accuracy. By the end of the program, participants are equipped to measure performance using key metrics, enabling informed, data-driven decisions that enhance financial management.
Performance Metrics and Continuous Improvement
The methodology prioritizes measurable outcomes, integrating key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and collection efficiency ratios. These metrics are tracked throughout the 12 months, providing continuous insights into progress and highlighting areas for improvement.
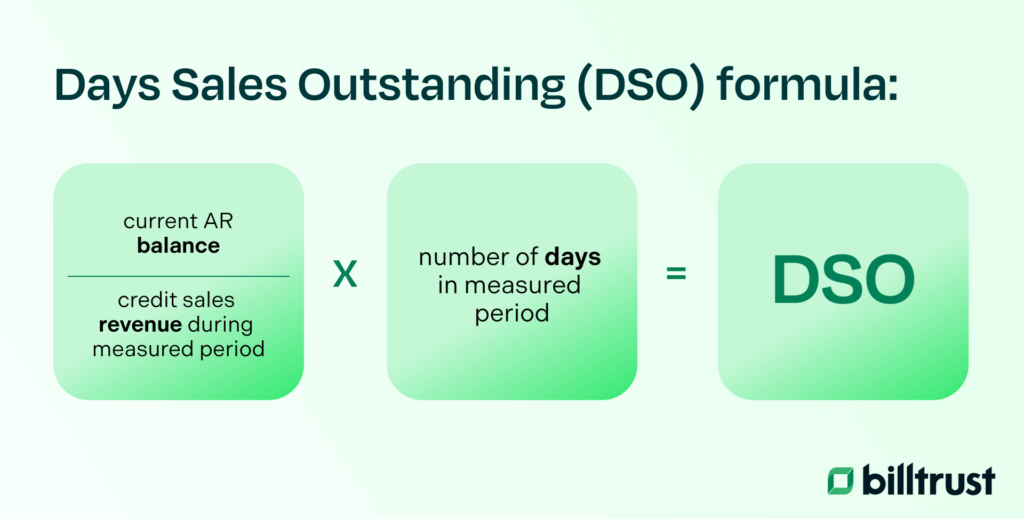
The program also incorporates ongoing monitoring and evaluation, ensuring that activities remain aligned with goals. Data collection and analysis during implementation enable timely adjustments to strategies, enhancing the program’s relevance and effectiveness. This iterative approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling participants to adapt their methods to dynamic business needs.
Alignment with Organizational Objectives
At every stage, the program is aligned with broader organizational financial goals. By improving cash flow management, mitigating risks, and strengthening customer relationships, the program delivers both immediate and long-term benefits.
Workshops are designed to ensure that participants acquire skills directly applicable to their roles, allowing them to address real-world challenges with confidence. Whether through streamlined invoicing processes, efficient collections practices, or CRM tool integration, the program ensures participants contribute meaningfully to their organization’s financial stability and growth.

Sustainability Planning and Documentation
A key focus of the methodology is ensuring that the program’s impact extends beyond its 12-month duration. Sustainability planning is integrated into the final phase, equipping participants with strategies to maintain improvements and ensure the continuity of enhanced financial practices.
Additionally, detailed documentation and regular reporting throughout the program support transparency and accountability. By keeping comprehensive records of activities, financial transactions, and outcomes, participants create a knowledge repository that informs future initiatives and reinforces best practices.
Unique Features of the Methodology
The Flow of Funds Program distinguishes itself through its comprehensive and systematic approach. By integrating progressive learning, performance evaluation, and sustainability planning, this program ensures participants gain both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Its emphasis on measurable outcomes and alignment with organizational goals creates a transformative learning experience that addresses every critical component of accounts receivable management. This holistic approach ensures long-term financial stability and positions organizations for sustained success.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Healthcare
The commercial history of healthcare is a complex tapestry woven with threads of innovation, regulation, and societal expectations. Over time, healthcare has evolved from a personal and often familial responsibility to a sophisticated industry driven by market forces and technological advancements.
The commercialization of healthcare began to accelerate in the mid-20th century, fueled by the rise of insurance as a primary means of paying for medical expenses. As healthcare costs began to escalate, insurance companies became increasingly involved in determining the types of treatments and providers that would be covered. This led to a system that prioritized cost-effectiveness over patient choice, shaping the commercial landscape of healthcare.
The advent of managed care organizations (MCOs) further transformed the industry. By negotiating contracts with providers and establishing networks, MCOs sought to control costs and improve quality. This led to a shift from fee-for-service models to value-based care, where providers are rewarded for achieving positive health outcomes rather than simply delivering services.
Technological advancements have also played a significant role in shaping the commercial history of healthcare. The development of new medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and electronic health records has led to improved patient care but has also contributed to rising costs. The increasing use of technology has also raised concerns about data privacy and security, further complicating the commercial landscape.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on consumerism in healthcare. Patients are becoming more empowered to make informed decisions about their care, and technology is enabling them to access information and compare providers. This trend has led to increased competition among healthcare providers, which can drive down costs and improve quality.
However, the commercialization of healthcare also presents challenges. The pursuit of profits can sometimes lead to ethical dilemmas, such as overtesting or unnecessary procedures. Additionally, the increasing complexity of the healthcare system can make it difficult for patients to navigate and access the care they need.
In conclusion, the commercial history of healthcare is a dynamic and evolving process shaped by a variety of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory changes, and societal expectations. While the pursuit of profits has undoubtedly driven innovation and improved access to care in many ways, it is also important to address the challenges and ethical dilemmas that arise from the commercialization of healthcare.
Current Position
The healthcare industry is currently experiencing a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, economic pressures, and regulatory changes. Several key trends are defining the current commercial position:
• Digital Transformation: The integration of technology into healthcare is accelerating, with electronic health records, telemedicine, and remote patient monitoring becoming increasingly prevalent. This shift is driving efficiency, improving patient access, and creating new business models.
• Value-Based Care: The transition from fee-for-service to value-based care models is gaining momentum. Providers are increasingly incentivized to deliver high-quality care at lower costs, leading to a focus on population health management and outcomes- based payment.
• Consumerism and Patient Empowerment: Patients are becoming more empowered to make informed decisions about their healthcare. This trend is driving increased competition among providers and a greater emphasis on patient experience.
• Rising Costs and Affordability: Healthcare costs continue to rise, putting a strain on individuals, employers, and governments. Efforts to control costs include price transparency, bundled payments, and the development of more affordable healthcare options.
• Regulatory Changes: The healthcare industry is subject to a complex regulatory environment, with changes occurring at both the federal and state levels. These changes can impact the profitability of healthcare organizations and influence the delivery of care.
The current commercial landscape of healthcare is characterized by a tension between the desire for innovation and the need for affordability. While technological advancements offer the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs, they also raise concerns about data privacy, security, and the potential for widening healthcare disparities.
The shift towards value-based care is a positive development, but it requires significant changes in the way healthcare is delivered and measured. Success in this area will depend on the ability of providers to collaborate, share data, and adopt new care models.
Future
The future of the healthcare industry is likely to be shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, economic pressures, and regulatory changes. Several key trends will likely dominate the landscape:
• Continued Technological Advancements: Artificial intelligence, blockchain, and other emerging technologies will continue to transform healthcare. AI-powered diagnostics, personalized medicine, and remote patient monitoring will play a significant role in improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
• Value-Based Care Expansion: The shift towards value-based care models will likely accelerate, with a greater emphasis on population health management and outcomes- based payment. This will require providers to adopt new care models and invest in data analytics and technology.
• Increased Consumerism: Patients will continue to become more empowered consumers, demanding greater transparency, convenience, and personalized care. This trend will drive competition among providers and create opportunities for innovative business models.
• Addressing Affordability: The challenge of rising healthcare costs will persist. Governments, employers, and healthcare providers will need to explore innovative solutions, such as bundled payments, price transparency, and the development of more affordable healthcare options.
• Regulatory Changes: The regulatory environment for healthcare will continue to evolve, with new laws and regulations impacting the industry. These changes may present both opportunities and challenges for healthcare organizations.
The future of healthcare is promising but also fraught with challenges. The potential benefits of technological advancements are immense, but they also raise concerns about data privacy, job displacement, and the widening of healthcare disparities.
The transition to value-based care will require a significant cultural shift within the healthcare industry. Providers will need to focus on outcomes rather than simply delivering services, and this may require new skills and competencies.
The increasing consumerism in healthcare presents both opportunities and challenges. While it can drive innovation and improve patient satisfaction, it can also lead to a fragmented market and higher costs.
Overall, the future of healthcare will be shaped by a complex interplay of factors. By embracing innovation, addressing affordability challenges, and focusing on patient outcomes, the industry can continue to evolve and improve the quality of care while ensuring that it is accessible to all.

Accountancy
The accounting industry has undergone a significant evolution over time, shaped by economic, technological, and societal factors. Its history can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary forms of accounting were used to track assets and liabilities.
In the Middle Ages, the rise of double-entry bookkeeping revolutionized accounting practices, providing a more systematic and accurate method of recording financial transactions. This innovation was particularly important for merchants and traders engaged in international commerce.
With the Industrial Revolution, the accounting profession expanded to meet the growing needs of businesses. Accountants played a crucial role in managing financial resources, assessing business performance, and ensuring compliance with regulations. The development of auditing standards and professional accounting bodies further solidified the accounting profession’s role in the business world.
The 20th century brought significant changes to the accounting industry, including the emergence of new accounting standards, the development of computer technology, and the globalization of markets. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, enacted in response to corporate scandals, introduced stricter regulations for public companies and increased the demand for qualified accountants.
In recent decades, the accounting industry has continued to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing economic conditions. The rise of cloud computing and data analytics has enabled accountants to perform more complex tasks and provide greater value to their clients. Additionally, the increasing globalization of business has led to a demand for
accountants with international expertise.
The accounting profession has played a vital role in the growth and stability of economies throughout history. By providing accurate financial information and ensuring compliance with regulations, accountants have helped businesses make informed decisions and build trust with investors.
The increasing complexity of the business environment and the rapid pace of technological change have presented new challenges and opportunities for the accounting industry. As technology continues to advance, accountants will need to adapt their skills and embrace new tools to remain relevant and competitive.
Current Position
The accounting industry is currently experiencing a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by technological advancements, economic pressures, and regulatory changes. Several key trends are defining the current commercial position:
• Digital Transformation: The integration of technology into accounting practices is accelerating, with cloud-based accounting software, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) becoming increasingly prevalent. This shift is driving efficiency, improving accuracy, and creating new opportunities for accountants.
• Globalization and International Standards: The globalization of business has increased the demand for accountants with international expertise. The adoption of international accounting standards, such as International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), has created a more unified global accounting landscape.
• Regulatory Changes: The accounting industry is subject to a complex regulatory environment, with changes occurring at both the national and international levels. These changes can impact the profitability of accounting firms and influence the services they offer.
• Increasing Competition: The accounting industry is becoming increasingly competitive, with traditional firms facing competition from smaller, boutique firms and online accounting platforms. This competition is driving innovation and forcing firms to differentiate themselves based on their services and expertise.
• Changing Client Needs: The needs of clients are evolving, with a growing demand for
advisory services beyond traditional accounting functions. Accountants are increasingly expected to provide strategic advice, risk management, and other value-added services.
The increasing complexity of the business environment and the rapid pace of technological change have created new challenges and opportunities for accountants.
The shift towards digital transformation is likely to have a significant impact on the accounting profession. Accountants who can effectively leverage technology will be well-positioned to meet the evolving needs of their clients and stay competitive.
The globalization of business and the adoption of international accounting standards have created a more interconnected accounting world. Accountants with international experience and knowledge of different regulatory frameworks will be in high demand.
The increasing competition within the accounting industry is likely to drive innovation and force firms to differentiate themselves based on their services and expertise. Accountants who can provide value-added services beyond traditional accounting functions will be better positioned to succeed.
Future
The accounting industry is poised for significant transformation in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, economic trends, and regulatory changes. Several key trends will likely shape the future landscape:
• Further Technological Advancements: Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation will continue to revolutionize accounting practices. AI-powered tools can automate routine tasks, enhance data analysis, and provide valuable insights.
• Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Accountants will increasingly leverage data analytics and business intelligence tools to provide more strategic advice and support
decision-making. The ability to extract meaningful insights from financial data will become a valuable skill.
• Cloud Computing and Remote Work: The adoption of cloud-based accounting software and the rise of remote work will continue to reshape the way accountants operate. This will create new opportunities for flexible work arrangements and international collaboration.
• Increasing Demand for Advisory Services: As businesses become more complex and face greater challenges, the demand for advisory services from accountants will likely increase. Accountants will need to develop expertise in areas such as risk management, financial planning, and corporate governance.
• Regulatory Changes: The regulatory environment for accounting will continue to evolve, with new standards and regulations emerging. Accountants will need to stay updated on these changes to ensure compliance and provide accurate advice.
The increasing role of technology in accounting will require accountants to develop new skills and adapt to changing work environments. The ability to leverage data analytics and provide strategic advice will be essential for success.
The globalization of business and the adoption of international accounting standards will continue to create opportunities for accountants with international expertise. Additionally, the growing focus on sustainability and corporate social responsibility will likely lead to a demand for accountants with specialized knowledge in these areas.
Overall, the future of the accounting industry is bright, but it will require accountants to be adaptable, innovative, and committed to continuous learning. By embracing technological advancements and developing new skills, accountants can position themselves for success in the evolving landscape.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:
Atlanta, GA
As of November 2024, Atlanta’s economy exhibits a dynamic blend of growth and challenges, reflecting its status as a major economic hub in the southeastern United States.
Atlanta continues to experience robust economic expansion, driven by diverse industries including technology, finance, logistics, and entertainment. The city’s strategic location and well-developed infrastructure have attracted significant investments, fostering job creation and urban development. For instance, GreenBox Systems announced a $144 million investment to construct an automated warehouse in Jackson, Georgia, expected to employ approximately 300 people upon its late 2025 opening.
Additionally, Georgia State University has unveiled plans for a $107 million renovation of its downtown Atlanta campus, aiming to enhance student activity and make the area more welcoming. This project is partly in anticipation of the 2026 World Cup events at the nearby Mercedes-Benz Stadium.
The Atlanta metropolitan area has demonstrated resilience in its labor market. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the civilian labor force in the Atlanta-Sandy Springs-Roswell area was approximately 3.3 million in October 2024, with an unemployment rate of 3.4%. This relatively low unemployment rate indicates a healthy job market, though certain sectors may face labor shortages or wage pressures.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta’s GDPNow model estimated a 2.5% real GDP growth rate for the fourth quarter of 2024, suggesting steady economic expansion. However, the October 2024 Beige Book reported a slight cooling in the regional economy, with declines in tourism following Hurricane Helene, as well as in manufacturing output and commercial real estate.
A recent survey by the Atlanta Regional Commission revealed that the economy has surpassed crime as the top concern among metro Atlanta residents. This shift underscores the community’s heightened focus on economic stability and growth.
Looking ahead, Atlanta’s economy is poised for continued growth, bolstered by ongoing investments and strategic initiatives. The Atlanta Regional Commission’s Metropolitan Transportation Plan outlines a $168 billion blueprint for the region’s future, addressing anticipated population and employment growth through 2050. The plan forecasts the addition of 856,000 jobs by 2050, bringing the total to 4.6 million, with significant contributions from the professional services sector.
In summary, Atlanta’s economy in late 2024 reflects a complex interplay of growth, investment, and emerging challenges. While the city benefits from substantial economic activities and development projects, it must navigate concerns related to economic stability and sector-specific slowdowns to sustain its trajectory of prosperity.
Houston, TX
As of November 2024, Houston’s economy demonstrates resilience and adaptability, reflecting its strategic diversification beyond traditional energy sectors.
Houston’s economy has shown steady growth, with the Greater Houston Partnership reporting that the region has recovered 174% of the jobs lost during the COVID-19 pandemic, adding approximately 280,000 jobs since surpassing pre-pandemic employment levels.
This robust job creation underscores the city’s economic vitality and its capacity to generate employment opportunities across various industries.
Historically known for its oil and gas dominance, Houston is actively diversifying its economic base. The city is becoming a hub for renewable energy, life sciences, and advanced technology sectors. Notably, the Texas Medical Center, the world’s largest medical complex, continues to expand, contributing significantly to the local economy.
Additionally, Houston’s commitment to green energy is evident in its growing solar power generation and the attraction of companies specializing in renewable technologies.
The commercial real estate (CRE) market in Houston remains stable, despite challenges such as loan maturities and potential economic uncertainties. The city’s population growth and inherent resilience support the CRE sector, indicating preparedness to navigate both natural and political challenges.
Furthermore, ambitious redevelopment projects, like the $1 billion plan to transform the Houston Astrodome into a global entertainment destination, highlight ongoing investments in infrastructure and urban revitalization. Houston’s strategic location and port facilities play a crucial role in its economic landscape. In February 2024, exports from the Houston–Galveston District increased to 30.7 million metric tons, continuing a trend of strong growth since 2016. This robust trade activity underscores Houston’s significance as a major player in international commerce.
Despite positive indicators, Houston faces challenges, including the need for infrastructure improvements and addressing rising housing costs. The city is also preparing to weather potential economic downturns, with experts expressing cautious optimism about its ability to overcome future challenges.
Additionally, labor actions, such as the recent dockworkers’ strike affecting major ports, including Houston’s, pose risks to global shipping logistics and the local economy.
In summary, Houston’s economy in late 2024 is characterized by robust job growth, strategic diversification into emerging industries, and significant investments in infrastructure and trade. While challenges persist, the city’s proactive approach to economic development and resilience positions it well for sustained growth and prosperity.

New York, NY
As of November 2024, New York City’s economy exhibits a complex blend of resilience and challenges, reflecting its status as a global financial hub and a center for diverse industries.
The New York City metropolitan area has demonstrated robust job growth, adding approximately 202,900 jobs over the past year, leading all metro areas in the nation. Since the start of 2022, the region has gained 571,900 jobs, surpassing the combined totals of the Dallas and Miami metro areas. This growth underscores the city’s dynamic labor market and its capacity to recover from economic downturns.
The city’s unemployment rate has seen fluctuations, with a recent increase of 0.2 percentage points to 5.0%, marking the first rise in nine months. Despite this uptick, the labor force participation rate has reached a record high of 61.9%, indicating a growing number of residents actively seeking employment.
New York City’s economy is characterized by its diversity, with significant contributions from finance, real estate, technology, and the creative industries. The financial sector, anchored by Wall Street, continues to be a cornerstone, while the tech industry has expanded, attracting startups and established firms alike. The creative sector has also shown resilience, with the city now home to 183,000 small businesses—1,000 more than pre-pandemic levels.
The real estate market remains a critical component of the city’s economy. As of 2023, the total value of all New York City property was assessed at $1.479 trillion, reflecting a 6.1% increase from the previous year. However, the city faces a housing shortage, with a vacancy rate of 1.4% in 2023, the lowest since 1968. This shortage has contributed to high housing costs, with median monthly rents for one-bedroom apartments in Manhattan reaching $4,443.
The city’s budget is the largest municipal budget in the United States, totaling about $112.4 billion in 2024. This budget supports a workforce of 250,000 employees and funds essential services, including education, social services, and public safety. Despite the substantial budget, the city faces fiscal challenges, including a strong imbalance of payments with the federal and state governments. As of 2022, New York City received $0.95 in services for every $1.40 it sent to Washington in taxes, marking it as one of the states that subsidize federal spending in other regions.
The city is currently grappling with several economic challenges. The implementation of a congestion pricing scheme, set to take effect on January 5, 2024, has sparked debate. The plan would impose a $9 fee on vehicles entering Manhattan south of 60th Street to help finance the Metropolitan Transportation Authority’s capital plan and reduce gridlock. Critics argue that it could burden workers and businesses, while proponents believe it will improve commutes and lower tolls.
Additionally, the city’s $7.7 billion Film Production Tax Credit program is under scrutiny following an independent analysis revealing limited financial benefits for taxpayers and small businesses. The study indicates the state recoups only about 31 cents on every dollar invested in the program, leading to calls for more prudent and impactful economic policies.
New York City’s economy in November 2024 reflects a dynamic landscape of growth and challenges. While job creation and sectoral diversity underscore its resilience, issues such as housing shortages, fiscal imbalances, and contentious policy initiatives highlight areas requiring strategic attention. The city’s ability to navigate these complexities will be pivotal in sustaining its economic vitality in the years ahead.
Miami Lakes, FL
As of November 2024, Miami Lakes, Florida, continues to exhibit a robust and diversified economy, underpinned by strategic initiatives and infrastructural developments.
Miami Lakes, encompassing approximately 6.6 square miles, is home to around 30,000 residents and over 1,700 businesses. The town’s strategic location near major interstates and proximity to Miami International Airport and Opa-Locka Airport enhance its appeal for businesses and residents alike. The local economy benefits from a highly educated, diverse, and skilled workforce, contributing to its dynamic business environment.
Key Industries
The town’s economy is bolstered by several key sectors:
• Healthcare and Social Assistance: This sector remains a significant employer, reflecting the town’s commitment to providing quality healthcare services.
• Retail Trade: Retail businesses continue to thrive, catering to the needs of the local population and contributing to the town’s economic vitality.
• Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services: These industries play a crucial role in the town’s economic landscape, offering a range of services that support both local and regional markets.
Between 2021 and 2022, Miami Lakes experienced a slight population increase from 30,582 to 30,621. During the same period, the median household income rose from $84,504 to $90,339, marking a 6.9% increase. This growth indicates a strengthening local economy and improved living standards for residents.
Several significant projects are underway, aimed at enhancing the town’s infrastructure and services:
• Miami Lakes Library Renovation: Scheduled to begin in mid-2024, this $7 million project includes a 5,000-square-foot addition, improved façade, new roof, and updated furniture and fixtures, modernizing the facility for community use.
• Baptist Health South Florida Emergency Center: Construction of a 19,800-square-foot emergency center is in progress, with an anticipated opening in January 2025. This facility aims to enhance local healthcare services, particularly in emergency care.
• Miami Lakes AutoMall Expansion: Plans are underway to build a new showroom and service center, replacing existing structures. The project is expected to commence this year, contributing to the town’s commercial growth.
The Town of Miami Lakes, in collaboration with its Economic Development Committee, is actively fostering a prosperous business climate. Efforts include promoting local business interchange, implementing strategic initiatives to stimulate the economy, and recruiting new businesses to the area. The town maintains one of the lowest business tax rates in South Florida and boasts a low flood insurance rate, making it an attractive location for business investment.
While Miami Lakes enjoys a strong economic position, it faces challenges common to the broader Miami-Dade County area, such as affordable housing shortages. Addressing these issues is crucial for sustaining long-term economic growth and ensuring a high quality of life for residents.
In summary, Miami Lakes’ economy in 2024 is characterized by steady growth, strategic development projects, and proactive economic policies. The town’s commitment to enhancing infrastructure, supporting key industries, and fostering a favorable business environment positions it well for continued prosperity in the coming years.
Program Benefits
Management
- Business Acumen
- Increased Understanding
- Enhanced Leadership
- Effective Communications
- Goal Oriented
- Structure Development
- Team Building
- Increased Confidence
- Personnel Development
- Growth Opportunities
Operations
- Cross-functional Efficiency
- SOP’s
- Policy Creation
- ERP mapping
- Flow Chart Analysis
- Perfomance Improvement
- Customer / Client Retention
- Less Stress
- Build Consistency
- Enhance Understanding
Financials
- Increased Cashflow
- Finance Optimization
- Meet and/or Exceed KPI’s
- Analyze Trends
- Economic Indicators
- Enhanced Reporting
- Cashflow Projections
- Strategy Implementation
- Financial Strength
- Promote Confidence
Testimonials

Testimonial 1
Content here…

Testimonial 2
Content here…

Testimonial 3
Content here…

Testimonial 4
Content here…

Testimonial 5
Content here…
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.