Strategic Innovation

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Strategic Innovation is provided by Mr. Puro MBA BBA Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. Puro, Founder/President of Puro Consulting, is a strategic leader with 25+ years of experience in strategic and project management. A U.S. Air Force Veteran, he is a leadership expert and has successfully implemented numerous multi-million-dollar I.T. projects with a cumulative ROI of over $75M. As a strategist, Mr. Puro helps businesses mitigate risks, accelerate growth, and eradicate complexities.
In 2020, Mr. Puro transitioned from working for several Fortune 500 companies and launched Puro Consulting to help enterprises in the automotive, manufacturing, FinTech, insurance, and government sectors. He helps leaders realign teams, improve processes, and perfect their visions.
Stepping into the I.T. industry in 1990 and, after some time in operations and programming, he switched to project management. As a strategic leader, Mr. Puro helps organizations devise and implement winning strategies to raise global sales, accelerate expansion, and add value.
Mr. Puro is an alumnus of Davenport University and holds a Bachelor of Business Administration and Master of Business Administration degrees with a focus on strategic management. An internationally recognized Certified Senior Project Manager (CSPM), Project Management Professional (PMP), & Scrum Master Certified (SMC), he also holds a graduate certificate in Strategic Innovation and Change from the University of Denver.
To request further information about Mr. Puro through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Strategic Innovation
The Strategic Innovation training course is a comprehensive, 12-module program designed to provide company leadership and stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of key principles and practices of strategic innovation. Delivered monthly over the course of one year, this training program provides participants with the opportunity to learn and apply the latest tools, techniques, and frameworks for driving growth, competitiveness, innovation in their organizations, and respond to rapidly changing business environments.
This course covers the fundamentals of strategic innovation, including identifying new business opportunities, understanding customer needs, and creating and implementing innovative solutions through project management best practices. Students will learn how to develop and apply a strategic innovation framework, assess market trends and disruptions, and create a culture of innovation within their organization. The course also covers best practices for managing risk and uncertainty, and for creating and sustaining a supportive environment for innovation.
Upon completion of the course, participants will have a deep understanding of the key principles of strategic innovation and the skills necessary to drive innovation initiatives within their organizations. They will also have the tools and frameworks to help them lead change and transformation, and to create and sustain a culture of innovation in their organizations. Connecting strategy and innovation in the new normal for organizational success and it is my belief this course will provide a roadmap for leadership.
Fundamentals participants will take away from attending the Strategic Innovation Course:
• Develop skills and knowledge to identify and evaluate opportunities for innovation within an organization.
• Learn to apply design thinking principles to generate and evaluate innovative ideas.
• Develop and implement a business model innovation strategy to drive growth and competitive advantage.
• Understand the impact of digital transformation on business models and competitive advantage.
• Analyze case studies and examples to see how strategic innovation can be applied in practice.
• Engage with fellow students through interactive exercises and group discussions to share knowledge and perspectives.
• Receive feedback on your understanding of the material through formative assessments, such as quizzes and surveys.
• Apply your skills and knowledge to a real-world problem through a final project that requires you to develop and implement a strategic innovation plan.
• Gain a competitive edge in the job market by developing skills and knowledge in strategic innovation that can be applied in a variety of industries and organizational settings.
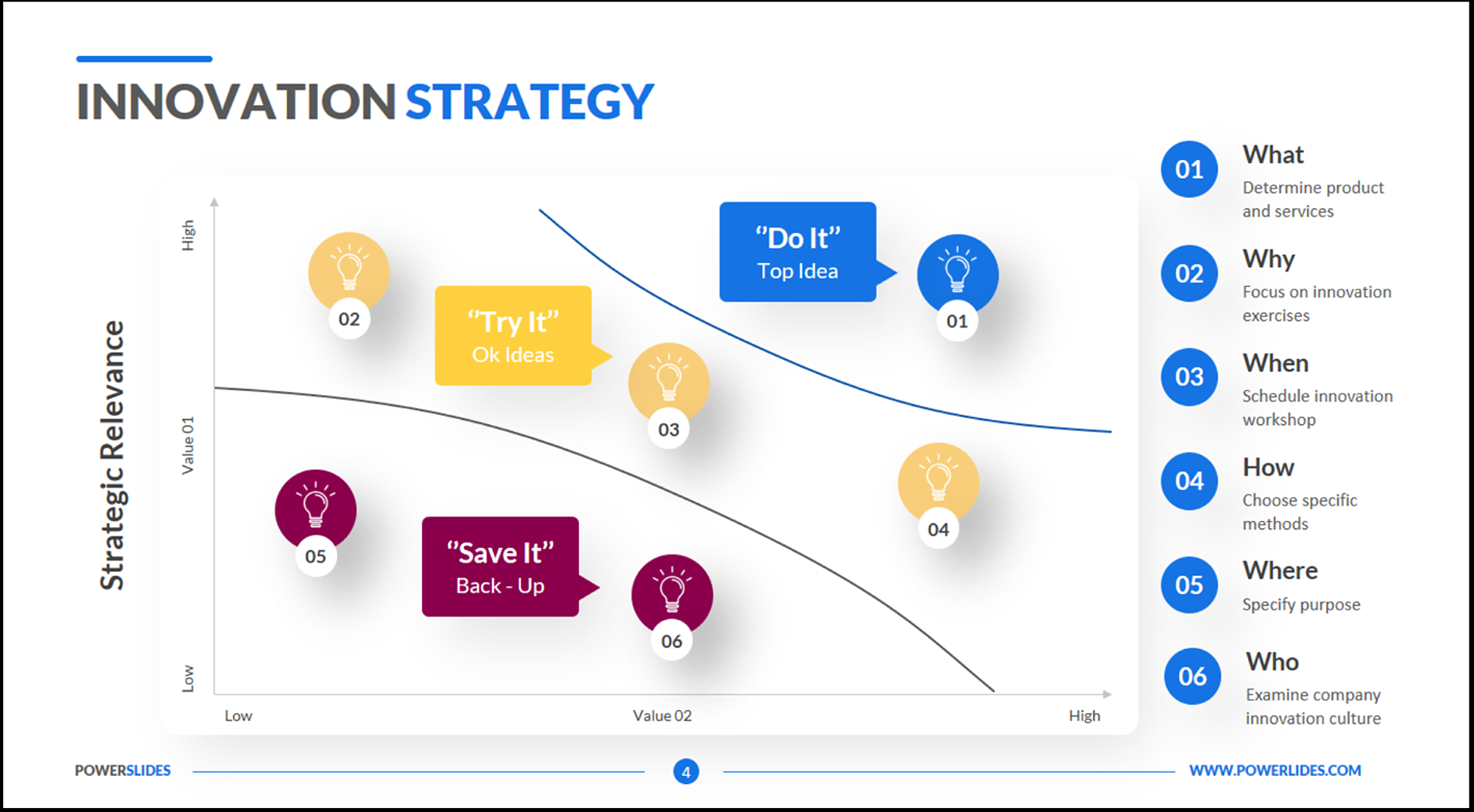
Curriculum
Strategic Innovation – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Strategic Management
- Part 1 Month 2 Strategic Innovation
- Part 1 Month 3 Project Management
- Part 1 Month 4 Emerging Trends
- Part 1 Month 5 Environment Scanning
- Part 1 Month 6 Problem Solving
- Part 1 Month 7 Evaluation
- Part 1 Month 8 Integration
- Part 1 Month 9 Remote Teams
- Part 1 Month 10 Implementation
- Part 1 Month 11 Competition
- Part 1 Month 12 Developing a Culture of Innovation
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Strategic Innovation corporate training program.
Strategic Innovation – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Strategic Management – Module 1 “Strategic Management” aims to provide participants with a comprehensive understanding of the key concepts and principles of strategic innovation and project management. The module is designed to equip learners with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage innovation projects in their organizations and help them achieve their strategic goals. The module begins by defining the terms strategic innovation and project management and explaining their importance in today’s business environment. It covers the different types of innovation and how they can be used to achieve strategic goals. The module also explores the key principles of project management, including planning, execution, monitoring, and control. Participants will also learn about the different tools and techniques used in project management, including Gantt charts, critical path analysis, and risk management. They will also be introduced to different project management methodologies, such as Agile and Waterfall, and learn how to select the right methodology for their projects. In addition to the theoretical concepts, the module includes practical examples and case studies to illustrate the application of strategic innovation and project management in real-world scenarios. Participants will also engage in interactive activities and quizzes to reinforce their learning and test their understanding. By the end of the module, participants will have a clear understanding of the key concepts and principles of strategic innovation and project management. They will be able to apply this knowledge to their own work, helping their organizations to achieve their strategic goals through effective innovation management.
- Part 1 Month 2 Strategic Innovation – Module 2 provides understanding the Importance of Strategic Innovation is a crucial module in any training course that aims to equip learners with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the dynamic business world. The module begins by defining strategic innovation as the process of identifying and implementing new ideas, products, services, and business models to create and sustain a competitive advantage. The module then delves into the importance of strategic innovation in the current business landscape, highlighting how it can help organizations to stay ahead of the curve and outperform their competitors. The module outlines the numerous benefits of strategic innovation, such as helping organizations to better understand their customers and their changing needs, anticipating, and responding to market trends and disruptions, improving operational efficiency, and boosting employee engagement and creativity. Additionally, the module provides a detailed overview of how strategic innovation can help organizations to achieve their long-term strategic goals, such as expanding into new markets, diversifying their product/service offerings, and enhancing their brand reputation. The module also discusses the key challenges that organizations face when trying to implement strategic innovation initiatives, including resistance to change, limited resources, and a lack of alignment between innovation and overall business strategy. The module provides practical strategies and best practices for overcoming these challenges, such as creating a culture of innovation, leveraging external partnerships and collaborations, and aligning innovation initiatives with the organization’s core mission and values. Overall, this module provides learners with a solid understanding of the importance of strategic innovation in today’s business landscape and equips them with the knowledge and skills needed to develop and implement successful strategic innovation initiatives in their own organizations. By the end of the module, learners will have gained a deep appreciation for the strategic value of innovation and will be able to apply their newfound knowledge to drive sustainable growth and success in their organizations.
- Part 1 Month 3 Project Management – Module 3 – project management provides an overview of the key principles and best practices for managing projects effectively. Project management is a critical skill that helps businesses achieve their goals, by ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. The module begins by introducing the key concepts and terminology of project management, including the project life cycle, project charter, work breakdown structure, and project plan. It then explores the importance of stakeholder management, communication, and risk management, and provides guidance on how to develop and implement effective project controls. The module also covers the importance of project leadership, team building, and motivation. It provides tips on how to manage project teams effectively, including how to delegate tasks, provide feedback, and manage conflicts. Finally, the module discusses the use of technology in project management, including project management software, collaboration tools, and other digital technologies that can improve project outcomes. It provides guidance on how to select and use the appropriate technology for different types of projects, and how to ensure that technology is integrated effectively into project management processes. By the end of the module, participants will have a comprehensive understanding of the key principles and practices of project management and will be able to apply these concepts to their own work environments. They will be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage projects effectively, and to lead project teams to success.
- Part 1 Month 4 Emerging Trends – Emerging Trends in Innovation and Project Management focuses on the latest developments in innovation and project management. This module provides learners with an overview of emerging trends and their impact on organizations, including new technologies and changing consumer preferences. The module begins by defining innovation and project management and their importance in driving organizational success. Learners will gain an understanding of the key principles of innovation and project management, including their interdependence and the importance of effective communication and collaboration among team members. The module then delves into the latest trends in innovation and project management, including the rise of agile methodologies, cloud computing, IoT, the increasing importance of data analytics, and the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in project management. Learners will explore the benefits and challenges associated with these emerging trends and gain insights into how they can be applied in their own organizations. The module also explores how the pandemic has impacted innovation and project management, with a focus on remote work and virtual collaboration. Learners will gain an understanding of how organizations have adapted to the new normal and what strategies have been successful in navigating the challenges presented by the pandemic. Throughout the module, learners will engage in a variety of activities and exercises designed to enhance their understanding of the topics covered. These include case studies, group discussions, and interactive simulations that allow learners to apply the concepts they have learned in a practical setting. By the end of the module, learners will have a solid understanding of the latest trends in innovation and project management and how they can be leveraged to drive organizational success. They will also have gained practical skills and tools that they can apply in their own work to become more effective project managers and innovators.
- Part 1 Month 5 Environment Scanning – Module 5 provides that Environmental scanning is a critical process that enables organizations to identify and evaluate external and internal factors that can affect their operations, performance, and competitiveness. This module on environmental scanning provides a comprehensive overview of the importance of environmental scanning in organizational decision-making, the different types of environmental factors that can impact an organization, the benefits of conducting environmental scanning, and the key steps involved in conducting an environmental scan. The module begins by defining environmental scanning and highlighting its significance in the context of organizational decision-making. It explains how environmental scanning helps organizations to stay informed about the various factors that can impact their operations, such as economic, political, social, and technological factors. The module also covers the different types of environmental factors that can affect an organization, such as internal, micro, and macro-environmental factors. The module goes on to describe the benefits of conducting environmental scanning, including improved decision-making, identification of opportunities and threats, better risk management, and enhanced organizational agility. The module explains how environmental scanning enables organizations to stay ahead of the competition by identifying emerging trends and changes in the market. Finally, the module covers the key steps involved in conducting an environmental scan, including defining the scope of the scan, identifying the relevant environmental factors, collecting, and analyzing data, and developing recommendations based on the scan findings. It also emphasizes the importance of ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the environmental scan remains relevant and up to date. Overall, the course module on environmental scanning provides a valuable introduction to this critical process and equips learners with the knowledge and skills they need to conduct effective environmental scans in the context of strategic innovation and project management.
- Part 1 Month 6 Problem Solving – Module 6 is covers Ideation and Problem Solving in Innovation which provides a comprehensive overview of the ideation process and the tools and techniques used for problem solving in innovation. This module is designed for professionals seeking to enhance their problem-solving skills and develop a creative mindset to drive innovation within their organization. The module begins by defining ideation and its importance in the innovation process. Participants will learn about the various ideation techniques, such as brainstorming and mind mapping. The module will also explore the benefits and challenges of ideation, and how to overcome ideation barriers. The module then focuses on problem-solving techniques, starting with problem identification and defining the problem statement. Participants will learn how to conduct a root cause analysis, generate solutions, and evaluate the best options. The module will also cover techniques such as SWOT analysis, 5 why’s, Pareto analysis, and Fishbone diagram to help identify and analyze the root cause of problems. In addition, the module will also cover the concept of design thinking, an approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy and human-centered design. Participants will learn about the five stages of design thinking: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test, and how to apply them to real-world scenarios. Throughout the module, participants will engage in interactive exercises, case studies, and discussions to apply the concepts and techniques covered in the module. By the end of the module, participants will have a solid understanding of ideation and problem-solving techniques and be equipped with the tools and strategies to develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
- Part 1 Month 7 Evaluation – Module 7 on Measuring and Evaluating Impact is designed to help individuals understand the importance of measuring the impact of their innovation efforts and how to do so effectively. The module will cover key topics such as identifying key performance indicators, setting measurable goals, and analyzing data to evaluate success. The first section of the module will focus on the importance of setting measurable goals and identifying key performance indicators. Participants will learn how to establish specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for their innovation initiatives. They will also learn how to identify and track key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be used to monitor progress and evaluate success. The second section of the module will cover data collection and analysis. Participants will learn how to collect relevant data and analyze it effectively to evaluate the impact of their innovation initiatives. They will also learn how to use tools such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews to gather feedback from stakeholders and use that feedback to inform decision-making. The final section of the module will focus on communicating impact and using data to inform future innovation efforts. Participants will learn how to effectively communicate their impact to stakeholders and use data to inform future innovation initiatives. They will also learn how to identify areas for improvement and adjust their innovation strategies accordingly. By the end of this module, participants will have a solid understanding of how to measure and evaluate the impact of their innovation efforts. They will have the skills and knowledge needed to set measurable goals, identify key performance indicators, analyze data, and use that data to inform future innovation initiatives. This module is ideal for anyone involved in innovation, whether they are working in a startup, a large corporation, or a non-profit organization.
- Part 1 Month 8 Integration – Module 8 on Integrating AI and Technology in Strategic Innovation aims to provide participants with a comprehensive understanding of the potential applications of artificial intelligence (AI) and technology in the innovation process. The module highlights the impact of technology and AI on the innovation landscape and how organizations can leverage these advancements to achieve strategic objectives. The course begins by introducing participants to the fundamentals of AI and technology, their evolution over time, and their role in shaping the innovation landscape. Participants will gain a thorough understanding of the various forms of AI, including machine learning, natural language processing, and their applications in innovation. The module explores the ways in which AI and technology can enhance the ideation and prototyping stages of the innovation process, enabling organizations to develop and test new ideas and concepts more efficiently. Participants will learn how to leverage AI-powered tools and techniques to identify emerging trends, predict future market demands, and build customer-centric solutions. The module also highlights the potential impact of AI and technology on project management, providing participants with insights on how to use these tools to manage resources, optimize processes, and improve project outcomes. Participants will learn how to integrate AI and technology into their project management workflows, improving collaboration and communication within their teams. Overall, this module is designed to equip participants with the knowledge and skills required to integrate AI and technology into their strategic innovation efforts effectively. By the end of the course, participants will have gained a thorough understanding of the potential applications of AI and technology in innovation, as well as the best practices for implementing these tools and techniques.
- Part 1 Month 9 Remote Teams – Module 9 Managing Remote and Global Innovation Teams focuses on the skills and techniques needed to successfully manage innovation teams in a remote and global environment. With the growing trend of remote work and globalization, it has become increasingly important for companies to adapt to this changing landscape and develop strategies to effectively manage their remote and global innovation teams. The module begins by exploring the challenges and benefits of managing remote and global innovation teams. Participants will learn how to establish clear communication channels, build trust, and create a culture of collaboration within the team. They will also learn how to effectively manage time zones, language barriers, and cultural differences. The course also covers best practices for remote and global project management, including setting goals, establishing timelines, and tracking progress. Participants will learn how to use various tools and technologies to support remote collaboration and project management, such as project management software, video conferencing, and virtual collaboration platforms. Additionally, the module covers the importance of diversity and inclusion in remote and global innovation teams. Participants will learn how to foster a culture of inclusion, promote diversity, and mitigate biases in team dynamics. Throughout the module, participants will have opportunities to engage in interactive activities and case studies to practice their skills and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios. By the end of the module, participants will have a deeper understanding of the challenges and benefits of managing remote and global innovation teams, as well as the skills and tools needed to effectively manage these teams.
- Part 1 Month 10 Implementation – Module 10 on Implementing Strategic Innovation is designed to provide participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to successfully implement strategic innovation initiatives within their organizations. The course covers a range of topics including the strategic planning process, idea generation and selection, project management, and risk management. The module starts by discussing the importance of having a clear strategic vision and plan, and how this can help organizations identify areas where strategic innovation can be implemented. Participants will learn about the key components of a strategic plan, including the mission, vision, and values, as well as the steps involved in developing a strategic plan. Next, the course covers the ideation and selection process for innovation projects. Participants will learn about various tools and techniques for generating ideas, evaluating them, and selecting the most promising ones for further development. The module also covers the importance of involving key stakeholders in the ideation process and obtaining their buy-in to ensure successful implementation. The course then delves into project management, covering topics such as developing a project charter, creating project plans, and monitoring and controlling project progress. Participants will learn about various project management tools and techniques, including the use of Gantt charts, critical path analysis, and risk management strategies. In addition to project management, the course also covers risk management. Participants will learn how to identify and assess risks associated with innovation projects and develop strategies to mitigate or manage them. The module also covers the importance of monitoring and evaluating the success of innovation projects and making adjustments as necessary. Finally, the course concludes with a discussion on how to effectively communicate and implement innovation initiatives within organizations. Participants will learn about the importance of clear communication and engagement with stakeholders, as well as strategies for overcoming resistance to change. By the end of this course, participants will have gained a comprehensive understanding of the key components involved in implementing strategic innovation initiatives within organizations. They will be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to successfully plan, execute, and evaluate innovation projects, and to effectively communicate and engage stakeholders throughout the process.
- Part 1 Month 11 Competition – Module 11 highlights that the business world is constantly evolving, and it can be challenging for companies to stay ahead of the competition. This training course on staying ahead of the competition focuses on strategic innovation practices to help businesses gain a competitive advantage. The module begins by defining strategic innovation and its importance in the business world. It also explores different types of innovation, such as product innovation, process innovation, and business model innovation, and how they can be used to stay ahead of the competition. The next section of the module delves into the process of conducting an environmental scan to identify potential opportunities and threats in the market. Participants will learn how to identify different types of environmental factors that can impact an organization, such as economic, social, technological, and legal factors. They will also gain an understanding of the benefits of conducting environmental scanning and the key steps involved in conducting an environmental scan. The module then moves on to ideation and problem-solving techniques to help businesses generate new and innovative ideas. Participants will learn how to use brainstorming, mind mapping, and other techniques to generate creative solutions to problems. The final section of the module covers measuring and evaluating impact. Participants will learn how to define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of their innovation initiatives and make data-driven decisions. They will also gain an understanding of the importance of continuous learning and improvement to stay ahead of the competition. By the end of this online training course module, participants will have gained a comprehensive understanding of strategic innovation practices and how to implement them to stay ahead of the competition. They will be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to identify opportunities, generate new ideas, test and validate assumptions, and measure success to drive business growth and success.
- Part 1 Month 12 Developing a Culture of Innovation – Module 12 is the module on developing a culture of innovation, which aims to help participants create a work environment that fosters innovation and creativity. Through this course, learners will understand how to build a culture that supports innovation, encourages risk-taking, and promotes collaboration. They will also learn how to establish processes for idea generation, prototyping, and testing. The course will cover various topics related to developing a culture of innovation, including understanding the importance of innovation, identifying barriers to innovation, and creating a shared vision for innovation. Participants will also learn how to develop and communicate innovation strategies, foster a culture of continuous improvement, and create a supportive environment for innovation. The course will start with an overview of the innovation process and the importance of innovation in organizational growth and success. The learners will then explore the factors that contribute to a culture of innovation, including leadership, vision, collaboration, and risk-taking. They will also learn how to identify and overcome barriers to innovation, such as resistance to change, fear of failure, and lack of resources. Next, the course will cover strategies for generating, evaluating, and implementing innovative ideas. Participants will learn how to create cross-functional teams, establish idea generation processes, and develop effective prototyping and testing methods. They will also learn how to measure and evaluate the impact of their innovations and make necessary adjustments to their strategies. Throughout the course, participants will engage in various activities and exercises to reinforce the concepts they learn. They will also have access to case studies, best practices, and real-world examples of organizations that have successfully developed cultures of innovation. By the end of the course, participants will have a clear understanding of how to create and sustain a culture of innovation within their organizations. They will be equipped with the skills, knowledge, and tools needed to develop and implement innovative ideas that can drive growth and success.
Methodology
Strategic Innovation
Program Planning
The Strategic Innovation training course is a comprehensive, 12-module program designed to provide company leadership and stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of the key principles and practices of strategic innovation. Delivered monthly over the course of one year, this training program provides students with the opportunity to learn and apply the latest tools, techniques, and frameworks for driving growth, competitiveness, innovation in their organizations, and respond to rapidly changing business environments.
The learning objectives for the strategic innovation course are built around the main goal of the course, which is designed to equip participants with the skills and knowledge needed to develop and implement innovative strategies to drive growth and competitive advantage. The cognitive domain of learning is a combination of higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation, as well as lower-order thinking skills such as knowledge and comprehension.
The main learning objectives for the strategic innovation course include:
• Identifying and evaluating opportunities for innovation within an organization
• Applying design thinking principles to generate and evaluate innovative ideas.
• Define strategic innovation and its purpose.
• Developing and implementing a culture of innovation strategy
• Apply project management principles to innovation projects.
• Evaluating the success of innovation initiatives using metrics and key performance indicators
Designing the course structure: Based on the learning outcomes and needs assessment, the course structure has been designed to be most effective for our learners. This includes determining the course content, instructional methods, assessment strategies, and evaluation methods. The course structure will be aligned with the learning outcomes and students will find the course engaging and interactive.

Program Development
This course covers the fundamentals of strategic innovation, including identifying new business opportunities, understanding customer needs, and creating and implementing innovative solutions through project management best practices. Students will learn how to develop and apply a strategic innovation framework, assess market trends and disruptions, and create a culture of innovation within their organization. The course also covers best practices for managing risk and uncertainty, and for creating and sustaining a supportive environment for innovation.
The learning objectives have been aligned with the overall goal of the course and guide the design of the course content, instructional methods, and assessment strategies. The course content will include real-world case studies and examples to help participants apply the principles of strategic innovation in practice. I will also provide instructional methods to include lectures, interactive exercises, and group discussions. Assessment strategies include quizzes, assignments, and a final project that requires participants to apply the skills and knowledge learned in the course to a real-world problem.
By focusing on these learning objectives, participants can develop the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the field of strategic innovation and apply their learned knowledge in practical ways to benefit their organization.
Lastly, assessment strategies have been developed to measure the achievement of the learning outcomes. This will include quizzes, exams, assignments, and projects. The assessment strategies will be aligned with the learning outcomes and are designed to provide meaningful feedback to the participants.

Program Implementation
The method behind the Process Implementation Stage of the program is intended to use a phased implementation focused on meeting the program goals and objectives.
When implementing an online program for strategic innovation, it is important to focus on developing and delivering content that equips participants with the skills and knowledge needed to develop and implement innovative strategies to drive growth and competitive advantage. The content of the program will cover topics such as design thinking, ideation, business model innovation, and transformation. Real-world case studies and examples will be used to help participants apply the principles of strategic innovation in practice. Instructional methods may include video lectures, interactive exercises, and group discussions.
To ensure successful implementation of the program, it is important to have a clear understanding of the goals and objectives of the course, as well as the intended audience. The program has been structured in a way that is accessible and engaging for participants, with clear and concise content delivered in a way that is easy to understand and apply.
Overall, implementing an online program for strategic innovation requires careful planning and attention to detail, with a focus on developing and delivering high-quality content. By focusing on these key elements, the program will help drive growth and competitive advantage for organizations and individuals alike.

Program Review
The course will be evaluated to determine its effectiveness in achieving the learning outcomes. This will be done through surveys throughout the course. The evaluation will also consider the feedback from the participants using formative and summative assessment strategies. The results of the evaluation will be used to improve the course for future iterations.
Formative assessment strategies can include quizzes, surveys, and other interactive exercises that help participants understand and apply the principles of strategic innovation. These assessments provide feedback on areas where participants may need additional support or guidance.
Summative assessment strategies, such as a final project, will be used to evaluate participants’ understanding of the material and their ability to apply it in practical ways. This will be done by requiring participants to develop and implement a strategic innovation plan for a real-world problem.
In addition to these assessment strategies, it is important to gather feedback from participants on the overall effectiveness of the program. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of feedback to help identify areas for improvement and opportunities for future growth.
Overall, reviewing and assessing the program for strategic innovation requires careful consideration of the program’s goals and objectives, as well as the intended audience. By using a combination of formative and summative assessment strategies, and gathering feedback from participants, we can ensure that the program is effective in equipping participants with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the field of strategic innovation.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Technology
The commercial history of the technology sector can be traced back to the 1950s, with the development of the first mainframe computers. These large machines were primarily used by governments and large corporations for data processing and scientific research. In the 1960s, the advent of the minicomputer brought computing power to smaller businesses and organizations.
The 1970s saw the rise of personal computers, which brought computing power to individuals and smaller businesses. The introduction of the Apple II in 1977 and the IBM PC in 1981 paved the way for the modern PC industry. This era also saw the development of computer networking, which enabled computers to communicate with each other and share resources.
The 1990s saw the rise of the internet and the World Wide Web. This created new opportunities for businesses to reach customers and conduct commerce online. The dot-com boom of the late 1990s saw many new internet-based businesses emerge, but also led to a market crash in 2000 when many of these businesses failed.
In the 2000s, the rise of mobile devices and the mobile internet led to the development of new business models and the emergence of new technology giants. Companies like Apple, Google, and Facebook became household names, and new technologies like cloud computing and big data analytics emerged.
Today, the technology sector continues to evolve and grow, with new technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things shaping the future of the industry. Companies are using innovative approaches to disrupt traditional industries and create new markets. Strategic innovation has become essential for businesses to stay competitive in this rapidly changing landscape.
The technology sector is a rapidly evolving industry that has seen significant growth and innovation in recent years. The current commercial position of the technology sector is strong, with several key trends and developments driving growth and investment.
One major driver of the technology industry’s current commercial position is the rise of digital transformation across various industries. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in many sectors, including healthcare, education, and retail. This has led to increased demand for technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics, which have become essential for companies to stay competitive and meet changing consumer needs.
Another key factor driving the technology industry’s commercial position is the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT refers to the interconnectivity of physical devices and objects, which can communicate and exchange data with each other over the internet. This technology has significant potential to drive efficiency and productivity in various industries, from manufacturing to transportation to healthcare. The market for IoT devices and services is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the coming years, with estimates predicting that the number of IoT-connected devices will reach 75 billion by 2025.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another area of significant growth and investment in the technology sector. AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision have the potential to transform many industries, including healthcare, finance, and retail. The market for AI technologies is expected to reach $126 billion by 2025, driven by increased demand for automation, data analytics, and personalized customer experiences.
Cybersecurity is also a critical area of focus for the technology industry’s current commercial position. With the increased use of digital technologies and the rise of cyber threats, companies across various industries are investing in cybersecurity solutions to protect their data and systems. The global cybersecurity market is projected to reach $270 billion by 2026, with significant growth in areas such as cloud security, threat intelligence, and identity and access management.
Overall, the technology industry’s current commercial position is driven by a combination of digital transformation, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. These trends are creating significant opportunities for companies to innovate, grow, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
The technology sector is constantly evolving and shaping the future of various industries. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, it is important to understand the future commercial position of the sector. This executive summary will focus on the future commercial position of the technology sector.
One of the most significant trends that will impact the technology sector in the future is the continued growth of the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT involves the connection of devices to the internet, enabling them to communicate with each other and perform various tasks without human intervention. This technology has the potential to revolutionize industries such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, by providing real-time data and insights that can be used to optimize processes and improve decision-making.
Another trend that will impact the future of the technology sector is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). AI has the potential to automate a wide range of tasks and processes, from customer service to manufacturing, and will become an increasingly important tool for businesses looking to improve efficiency and productivity. As AI continues to evolve, it will become even more powerful, enabling businesses to analyze vast amounts of data and make more accurate predictions.
In addition to IoT and AI, the future of the technology sector will also be shaped by the continued growth of cloud computing. Cloud computing has already transformed the way businesses store and access data, and as the technology continues to evolve, it will become even more powerful, enabling businesses to store and process vast amounts of data in real-time.
The growth of blockchain technology is another trend that will shape the future of the technology sector. Blockchain has the potential to transform industries such as finance, healthcare, and logistics, by providing a secure and transparent platform for storing and sharing data.
In summary the future commercial position of the technology sector looks promising, as emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, cloud computing, and blockchain continue to evolve and shape the way businesses operate. As these technologies become more advanced and more widely adopted, they will provide businesses with new opportunities to innovate and grow. However, businesses will need to stay on top of these trends and be prepared to adapt quickly to the changing landscape if they want to stay ahead of the competition.
Banking and Financial Services
The financial sector has a rich history of innovation, driven by advances in technology, changes in regulatory frameworks, and shifts in consumer behavior. Over the years, financial institutions have implemented numerous innovations to improve efficiency, increase profits, and better serve their customers. For example, the introduction of ATMs in the 1960s revolutionized the way people access their money, while the advent of online banking in the 1990s transformed the way people manage their finances.
More recently, the rise of fintech startups has disrupted the traditional banking landscape, offering consumers new ways to save, invest, and access credit. Fintech innovation has given rise to new business models, such as peer-to-peer lending, mobile payments, and robo-advisors. In response, traditional financial institutions have also embraced digital transformation, partnering with fintech startups, or creating their own digital products and services.
In addition to technological advances, the financial sector has also seen significant regulatory changes over the years, particularly in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis. The Dodd-Frank Act, for example, introduced a range of new regulations aimed at improving transparency and accountability in the banking sector. These changes have presented both challenges and opportunities for financial institutions, requiring them to adapt their operations to comply with new rules while also exploring new business opportunities.
In the current landscape, the financial sector is facing unprecedented levels of disruption and change. The rise of digital technology, the emergence of new fintech players, and changing consumer expectations have all contributed to a rapidly evolving industry. To remain competitive, financial institutions must embrace strategic innovation, developing new products and services, exploring new markets, and streamlining their operations.
One area where financial institutions are increasingly investing in innovation is customer experience. Today’s consumers expect a seamless, personalized experience across all channels, from online and mobile banking to in-branch interactions. To meet these expectations, financial institutions are investing in technologies such as AI, chatbots, and predictive analytics to deliver more personalized, proactive customer experiences.
Another area where strategic innovation is taking place in the financial sector is in the realm of payments. With the rise of mobile and digital payments, traditional payment methods such as cash and checks are becoming less relevant. Financial institutions are exploring new payment technologies such as blockchain and biometrics, to make payments faster, cheaper, and more secure.
The future of the financial sector is likely to be shaped by continued advances in technology, changing consumer behavior, and ongoing regulatory changes. Financial institutions that embrace strategic innovation will be better positioned to capitalize on these trends, developing new products and services, improving efficiency, and driving growth.
One area of innovation that is expected to have a significant impact on the financial sector in the coming years is AI and machine learning. Financial institutions are already using these technologies to automate routine tasks, improve fraud detection, and deliver more personalized customer experiences. As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, they are likely to enable even more sophisticated applications in areas such as risk management, investment analysis, and fraud prevention.
Another area where strategic innovation is likely to play a key role is in sustainability and social responsibility. Financial institutions are increasingly under pressure to address issues such as climate change and income inequality, and consumers are demanding more socially responsible investment options. To meet these challenges, financial institutions are exploring new products and services, such as green bonds and impact investing funds, that align with the values of socially conscious consumers.
In conclusion, the financial sector is in the middle of a significant change, driven by technology, changing consumer behavior, and regulatory changes. To remain competitive, financial institutions must embrace strategic innovation.

Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is poised for significant growth and transformation in the future, and this growth will be driven by several key factors. One of the most critical factors driving growth in the sector is the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Robotics. These technologies are transforming the manufacturing industry by enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and cost savings.
Another critical factor driving growth in the manufacturing sector is the increasing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices. With a growing emphasis on sustainability, manufacturers are exploring new ways to reduce waste, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. This has led to the development of new manufacturing processes and materials that are more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
The manufacturing sector is also poised for significant growth in the future due to the increasing focus on customization and personalization. Consumers today are looking for products that meet their specific needs and preferences, and this has led to a shift towards mass customization in the manufacturing sector. This trend is driving manufacturers to adopt flexible and agile manufacturing processes that can quickly adapt to changing consumer demands.
Finally, the manufacturing sector is expected to benefit significantly from the increasing adoption of 3D printing technology. 3D printing is a game-changing technology that allows manufacturers to produce complex parts and components in a more efficient and cost-effective manner. As this technology continues to evolve, it is expected to transform the manufacturing industry by enabling more localized and on-demand production.
In conclusion, the manufacturing sector is poised for significant growth and transformation in the future, driven by technological innovations, sustainability, customization, and 3D printing. Manufacturers who embrace these trends and invest in the necessary technologies and processes will be well-positioned to succeed in the future. An online strategic innovation course can provide manufacturers with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape and stay ahead of the competition.
The manufacturing sector has a rich history of innovation that has driven growth and progress for centuries. The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries saw the development of machines that could automate production processes and increase efficiency. This led to a surge in manufacturing productivity and paved the way for mass production, enabling the production of goods on a scale never seen. This period of innovation transformed the manufacturing sector and laid the foundation for the technological advancements that followed.
In the 20th century, manufacturing experienced several significant shifts. World War II played a major role in driving innovation in manufacturing, as factories were repurposed to produce military equipment on a massive scale. After the war, the demand for consumer goods increased, leading to the development of new technologies such as assembly lines, just-in-time manufacturing, and lean manufacturing. These advancements helped to streamline production processes and reduce costs, making manufacturing more efficient and accessible.
The latter half of the 20th century saw the emergence of computer-controlled production processes, which allowed for more precise and sophisticated manufacturing techniques. The development of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software revolutionized the manufacturing process, allowing for the creation of complex and intricate products. The advent of robotics and automation further enhanced manufacturing productivity and efficiency, enabling factories to produce goods faster and with greater accuracy.
In recent years, the manufacturing sector has undergone another major shift with the rise of Industry 4.0. This movement is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics into the manufacturing process. Industry 4.0 has the potential to transform manufacturing once again, by allowing for greater customization, flexibility, and agility. It enables manufacturers to monitor production processes in real-time, optimize performance, and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and productivity.
The manufacturing sector has undergone significant changes over the years, with advancements in technology and innovation leading the way. There are several trends and factors that are likely to shape the industry’s position and success.
One key trend is the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices. Consumers are becoming more aware of environmental issues and are increasingly seeking out products and companies that prioritize sustainability. This has led to a rise in eco-friendly materials and production methods, as well as an emphasis on reducing waste and energy consumption in manufacturing processes. In the future, companies that prioritize sustainability are likely to have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Another trend that is shaping the future of manufacturing is the rise of automation and artificial intelligence. As technology continues to advance, more and more tasks are becoming automated, and machines can perform complex tasks that were once only possible for humans. This has the potential to greatly increase efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing process, while also reducing costs. However, it also raises concerns about job loss and the need for workers to have specialized skills to operate and maintain the machinery.
The future of manufacturing is also likely to be shaped by global economic and political factors. The ongoing trade disputes between major world powers, such as the United States and China, have already impacted the industry, with tariffs and trade barriers affecting supply chains and pricing. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of resilience and agility in manufacturing, as disruptions to supply chains and manufacturing processes have created challenges for companies around the world.
Looking ahead, companies in the manufacturing sector will need to adapt to these trends and challenges to remain competitive. This will require a focus on innovation and the ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions. Companies that prioritize sustainability, invest in automation and technology, and have a strong understanding of global economic and political factors are likely to be the most successful in the future.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

San Francisco
San Francisco is known as the technology hub of the world, with a high concentration of technology companies such as Apple, Google, and Facebook, as well as a growing fintech sector.
San Francisco remains a major center for strategic innovation and commercial success in the 21st century. The city continues to attract entrepreneurs, investors, and talent from around the world, thanks to its history of innovation, supportive business environment, and diverse ecosystem.
San Francisco’s strategic position on the West Coast of the United States gives it access to a large and growing market of consumers and businesses. The city is home to some of the world’s leading technology companies, such as Apple, Google, and Facebook, which have helped to fuel the growth of the local economy and create new opportunities for innovation.
San Francisco has a thriving startup ecosystem, with thousands of innovative companies working on cutting-edge technologies and ideas. The city is home to some of the most successful startups in the world, including Uber, Airbnb, and Lyft, which have disrupted traditional industries and transformed the way people live and work.
In addition to technology and startups, San Francisco is also a center for innovation in biotechnology and healthcare. The city is home to several top research institutions and biotech companies, which are developing new treatments and cures for diseases.
The future commercial position of San Francisco as it relates to strategic innovation is likely to be shaped by a few factors, including emerging technologies, global competition, and changing economic and political conditions.
One key trend that is likely to shape the future of strategic innovation in San Francisco is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to transform a wide range of industries, from healthcare to transportation to finance, and could create new opportunities for innovation and growth in the city.
Another important factor is the increasing globalization of the economy, which is creating new opportunities for San Francisco to expand its reach and influence. The city’s position on the West Coast of the United States makes it well-positioned to connect with growing markets in Asia and the Pacific, and to leverage its strategic partnerships and alliances to drive innovation and growth.
At the same time, San Francisco will need to navigate a number of challenges in order to maintain its position as a leading hub for strategic innovation. These challenges include rising costs of living and doing business, which could make it difficult for startups and entrepreneurs to succeed, as well as increased competition from other innovation hubs around the world.

New York City
New York City is the financial capital of the world, with a concentration of major financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, and Citigroup. It also has a large manufacturing sector, particularly in industries such as fashion and transportation.
New York City’s commercial history has been closely tied to strategic innovation. From its earliest days as a colonial trading center, the city has been a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, attracting some of the brightest minds and most ambitious entrepreneurs from around the world.
In the early 20th century, New York City continued to be a leader in strategic innovation, with the rise of the financial sector driving economic growth and investment in new technologies and ideas. The city’s stock exchanges, banks, and investment firms helped to fuel the growth of industries ranging from automobiles to aviation, and the city became known as the financial capital of the world.
Today, New York City remains a leader in strategic innovation, with a vibrant startup ecosystem, world-class universities and research institutions, and a diverse and dynamic economy. The city is home to some of the world’s most successful startups, including WeWork, Etsy, and Squarespace, as well as some of the largest and most influential companies in the world, such as Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan Chase, and Amazon.
New York City’s position as a global leader in strategic innovation is supported by a range of resources and infrastructure, including incubators, accelerators, venture capital firms, and a large and diverse talent pool. The city’s rich history of entrepreneurship and innovation continues to attract entrepreneurs, investors, and talent from around the world, making it a key center for strategic innovation in the 21st century.
New York City remains a leading center for strategic innovation, with a diverse and dynamic economy that spans a wide range of industries and sectors. The city’s position as a global financial and cultural capital has helped to attract a range of entrepreneurs, investors, and talent from around the world, driving innovation and growth across a range of fields.
One key area of strength for New York City in the current commercial landscape is the tech sector. The city is home to a growing number of startups, incubators, and accelerators, and has emerged as a leading hub for industries ranging from fintech to e-commerce to media and entertainment. Major tech companies such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon have established large offices in the city, helping to fuel innovation and growth.
The future commercial position of New York City as a hub for strategic innovation looks promising, as the city continues to invest in infrastructure, resources, and policies to support entrepreneurship, innovation, and growth. New York’s strong position in a range of key industries, combined with its rich history of entrepreneurship and innovation, sets the stage for continued growth and success in the years to come.
One key area of focus for New York City’s future commercial position is the tech sector. The city has already emerged as a leading hub for startups and tech companies.
New York City’s continued strength in finance, media, and advertising also bodes well for its future commercial position. These industries are likely to continue to evolve and innovate in the years to come, and New York’s position as a global capital in these areas will help to attract investment and talent from around the world.
Boston
Boston is home to many prestigious universities and research institutions, making it a hub for innovation and technology companies. It also has a strong financial sector, with many mutual funds and investment firms headquartered in the city.
Boston has a long and storied commercial history that is closely intertwined with strategic innovation, particularly in the areas of technology, healthcare, and education. The city’s position as a leading center of innovation and entrepreneurship can be traced back to the 19th century when Boston emerged as a hub for manufacturing and technology.
In the mid-20th century, Boston’s strategic innovation continued to flourish, particularly in the fields of healthcare and education. The city’s renowned hospitals and medical schools, including Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, became centers of groundbreaking research and development, driving innovation in areas such as genetics, immunology, and drug discovery.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, Boston’s strategic innovation continued to evolve, with a focus on building new companies and industries around emerging technologies. This included the development of the biotech industry in the 1980s and 1990s, as well as the emergence of a range of tech startups and incubators in the 2000s and 2010s.
Overall, Boston’s commercial history has been closely tied to strategic innovation, particularly in the areas of technology, healthcare, and education. This has helped to establish the city as a leading center for innovation and entrepreneurship, with a diverse and dynamic economy that continues to drive growth and success in the 21st century.
The current commercial position of Boston as it relates to strategic innovation is strong, building on its rich history of innovation and entrepreneurship. The city continues to be a hub for cutting-edge research and development, particularly in the fields of biotech, healthcare, and technology. Boston is also home to a diverse range of startups and established companies.
In the technology sector, Boston continues to be a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship. The city is home to a growing number of startups, as well as established tech giants such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook. Boston’s strengths in this area are driven in large part by its world-class universities, including MIT and Harvard, which are at the forefront of research in areas such as artificial intelligence and robotics.
Boston’s commercial position is also supported by its strong financial and professional services sectors. The city is home to a range of leading banks, investment firms, and law firms, as well as a growing number of fintech startups. This helps to provide the funding and support that is essential for strategic innovation and growth.
The future commercial position of Boston is strong, with the city well positioned to continue to drive growth and success in key industries. Boston’s strengths in biotech, healthcare, and technology are likely to remain a key focus for strategic innovation in the years ahead, supported by ongoing investments in research and development, infrastructure, and talent.
In the technology sector, Boston is likely to remain a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and cybersecurity. The city’s world-class universities and research institutions will continue to play a key role in driving innovation in these areas, supported by a growing ecosystem of startups and established companies. Boston is also likely to see continued growth in the fintech sector, driven by a growing number of startups and partnerships with traditional financial institutions.
Seattle
Seattle is known for being the headquarters of several major technology companies, including Amazon and Microsoft. It also has a growing biotechnology and healthcare industry.
Seattle has a rich commercial history of strategic innovation, driven in large part by the city’s thriving technology sector. The city has been a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship for decades, with a range of companies and startups driving growth in key industries such as software, cloud computing, and e-commerce.
One of the key factors that has contributed to Seattle’s commercial success is the presence of several large technology companies, including Microsoft and Amazon. These companies have played a significant role in driving innovation and growth in the city, helping to attract talent, investment, and resources. Microsoft, for example, was founded in the city in the 1970s, and has since grown into one of the world’s largest and most successful software companies. Amazon, meanwhile, has played a key role in the growth of the e-commerce industry, and has become one of the world’s largest online retailers.
Seattle’s commercial history has also been shaped by the presence of a range of startups and smaller technology companies. The city has a thriving startup ecosystem, with a range of incubators, accelerators, and venture capital firms supporting growth and innovation.
Seattle’s commercial success has also been supported by the city’s strong research and development community. Seattle is home to several world-class research institutions, which have played a significant role in driving innovation and development in areas such as biotech and healthcare.
Seattle’s current commercial position is strong as it continues to be a hub for strategic innovation, particularly in the technology industry. The city is home to some of the world’s largest and most successful technology companies, including Amazon, Microsoft, and Boeing, and has a thriving startup ecosystem that supports growth and innovation in a range of industries.
One of the key drivers of Seattle’s commercial success is its technology sector. The city has become a hub for software development, cloud computing, and e-commerce, with several large technology companies headquartered in the area. Amazon, for example, has continued to expand its presence in the city, with plans to build new office towers and a second headquarters in the area. Microsoft, meanwhile, has continued to develop new software and services, including its cloud computing platform, Azure.
Seattle’s startup ecosystem is also a key contributor to its current commercial position. The city has successful venture capital firms that support early-stage companies and has produced a number of successful startups in recent years. These startups are focused on a range of industries, from biotech to fintech, and are helping to drive growth and innovation in the area.
Seattle is well positioned to continue to be a leader in strategic innovation in the future, building on its existing strengths in the technology sector and startup ecosystem.
Seattle’s startup ecosystem is also poised for growth in the future, with a range of new companies and industries likely to emerge in the coming years. The city’s venture capital firms and incubators will continue to support early-stage companies, helping to drive growth and innovation in a range of sectors. Additionally, Seattle’s strengths in areas such as e-commerce and logistics could lead to the development of new industries and business models in the future.
Chicago
Chicago has a diverse economy, with a strong manufacturing sector that includes companies such as Boeing and Caterpillar. It also has a growing fintech industry, with companies such as Enova and Avant headquartered in the city.
Chicago has a long commercial history that spans several industries, including finance, transportation, and manufacturing. However, its history in strategic innovation has been relatively modest in comparison to some other major US cities, where I can see an opportunity.
Recently, Chicago has begun to develop a reputation as a center for innovation in a range of industries, particularly in technology and entrepreneurship. Additionally, Chicago has seen significant growth in areas such as fintech, healthcare, and logistics, with notable companies emerging in these sectors.
Chicago’s position as a major transportation hub has also played a role in its commercial history and innovation. The city’s location at the crossroads of the country’s rail and highway systems has made it a major center for logistics and transportation, with major companies in these industries based in the city.
Chicago is currently positioning itself as a hub for strategic innovation, with initiatives and programs aimed at supporting and growing innovative industries in the city.
One of the key areas of growth in Chicago’s innovation ecosystem has been the technology sector. The city has a growing startup scene, with incubators, accelerators, and co-working spaces supporting early-stage companies.
Additionally, a number of large technology companies have established a presence in Chicago, including Google, Facebook, and Salesforce. These companies have cited the city’s deep pool of talent and its central location as reasons for their presence in Chicago.
One of the key areas of growth in Chicago’s innovation ecosystem is likely to be in the technology sector. The city has a growing startup scene and has established itself as a hub for fintech, with companies developing new financial technologies and services. Additionally, Chicago has a strong legacy in the transportation and logistics industries, which could position the city as a leader in developing new technologies for the transportation sector, such as autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure.
Chicago is also likely to continue to grow as a center for advanced manufacturing and research. The city’s strengths in these areas could attract new companies and investment, particularly as the demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies continues to grow.
Program Benefits
Information Technology
- Enhanced collaboration
- Improved efficiency
- Increased innovation
- Improved communication
- Reduced costs
- Improved quality
- Faster delivery
- Decision-making
- Increased productivity
- Risk management
Management
- Improved performance
- Goal alignment
- Reduced risk
- Increased profitability
- Enhanced agility
- Decision making
- Increased efficiency
- Resource utilization
- Enhanced innovation
- Improved competitive edge
Operations
- Improved efficiency
- Enhanced collaboration
- Increased flexibility
- Reduced waste
- Improved quality
- Better resource allocation
- Faster delivery
- Increased scalability
- Enhanced risk management
- Customer satisfaction
Testimonials

DENSO International America, Inc.
Mr. Puro is proud to have successfully led the launch of an ERP solution across 10 North America locations. This achievement was the result of months of planning, collaboration, and hard work by a dedicated team of professionals. They were able to achieve our goals on time, within budget, and with a high level of quality.
From the outset, Mr. Puro knew that this project would be challenging. They faced complex technical requirements, diverse stakeholder interests, and a tight schedule of 5 years. To overcome these challenges, Mr. Puro focused on building strong relationships with key stakeholders, including internal teams and external vendors. By fostering open communication, setting clear expectations, and maintaining a collaborative approach, Mr. Puro was able to build trust and consensus among the team.
Throughout the project, Mr. Puro demonstrated an eye for detail, ensuring that every aspect of the solution met the company’s high standards for quality and functionality. Mr. Puro also proactively managed risks and issues, anticipating potential roadblocks, and developing contingency plans to mitigate them.
Overall, Mr. Puro is proud to have played a critical role in the successful launch of this ERP solution. It is evidence to the power of collaboration, project planning, project management, hard work, and dedication. Mr. Puro is excited to see the positive impact that this solution will have on their business and their customers in the years to come.

DENSO International America, Inc.
Mr. Puro was thrilled to have successfully completed a major reorganization for our North American division. This achievement required significant planning, coordination, and leadership to transition our decentralized location-based teams to a more functional alignment, resulting in a 15% reduction in spending.
From the beginning, Mr. Puro recognized that this reorganization would require a deep understanding of our business processes and a clear vision for how to align their resources to better support our strategic objectives. Through careful analysis and stakeholder engagement, Mr. Puro was able to identify opportunities to consolidate roles, streamline processes, and improve efficiency.
To achieve these goals, Mr. Puro worked closely with my team to communicate the vision for the reorganization, address concerns, and build consensus. Mr. Puro also invested in staff development and training to ensure that everyone was prepared for the changes ahead.
Throughout the reorganization, Mr. Puro maintained a sharp focus on metrics, tracking progress against key performance indicators and adjusting as needed. He also worked closely with our finance team to monitor spending and ensure that they were staying on track with our targets.
Overall, Mr. Puro is proud to have played a critical role in this reorganization, which has improved our operations, reduced costs, and positioned us for success in the years ahead. It is a testament to the power of strategic thinking, strong leadership, and a commitment to excellence.

DENSO International America, Inc.
Mr. Puro am proud to have successfully completed the implementation of a cloud-based help desk system, which replaced an older Lotus Notes-based system and provided a return on investment of over 20%.
From the beginning, Mr. Puro recognized that this project would require a significant investment in time, resources, and expertise. However, he was confident that the benefits of a modern, cloud-based solution would far outweigh the costs. Through careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and execution, he was able to deliver a solution that exceeded our expectations.
To achieve these goals, Mr. Puro worked closely with his IT team and external vendors to develop a comprehensive implementation plan, which included data migration, system configuration, and user training. Mr. Puro also engaged key stakeholders across the business to ensure that the new system met their needs and requirements.
During the implementation, Mr. Puro maintained a focus on ROI, tracking key performance indicators and ensuring that they were realizing the expected benefits. By leveraging cloud-based technology, they were able to improve system performance, increase accessibility, and reduce maintenance costs.
Mr. Puro was excited to have played a critical role in this project, which had significantly improved their IT infrastructure and provided a substantial return on investment. It is a demonstration to the power of strategic planning, innovation, project management, effective collaboration, and a focus on business outcomes.
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.












