Professional Services Advisor

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Professional Services Advisor is provided by Dr. Cherry Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability. 

Personal Profile
Prior to his advisory, academic and training career, Dr. Cherry had significant senior management experience, at general manager and managing director level, across manufacturing and service industries. His strong commercial acumen and strategic thinking, coupled with formal business and technical tertiary qualifications, have allowed him to achieve significant revenue and profitability growth through his senior career. Dr Cherry has worked in senior management, executive director, and non-executive director roles across multinationals, listed and private companies as well as not-for-profits. A strong strategic mind-set, coupled with an ability to lead senior and middle management teams have been the keys to Dr Cherry’s commercial success in business, across a range of industries. Throughout his career, Dr Cherry has demonstrated his capability to affect change, turnaround, re-engineer and grow businesses both organically and via acquisition. He has leveraged this corporate experience and success into his professional services career and provides strategic advisory and training services at senior management and board level to clients globally. Outside his professional career, Dr Cherry was a founding director of the Cure Brain Cancer Foundation, established to fund advances in brain tumour treatment and research. He also lectures and supervises at undergraduate and postgraduate levels across several Australian and Irish universities and business schools.
Dr Cherry holds an honours degree in Chemical Engineering, a Master of Commerce degree with a marketing major and a Doctor of Business Administration degree where he researched trust in the professional services context.
To request further information about Dr. Cherry through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive Summary

Professional Services Advisor
Trusted Advice for the Trusted Professional Services Advisor
The Professional Services Advisor program has been developed after working with professional services firms for more than twenty years, as referral partners or as clients, understanding their challenges and those of their clients. It is also informed by doctoral research into trust in the professional services context.
Professional services encompass industries providing specialised professional, scientific, and technical activities, primarily to other businesses or organisations. The Professional Services Advisor program has been developed for and specifically targeted to organisations providing engineering consulting services, management consulting services, legal services, accounting services, scientific and environmental research services, architectural and surveying services, advertising and market research services and other professional services.
According to recent research, key professional services challenges include predicting resource requirements, maintaining profitability, and the retention of employees and clients. As a result, professional services firms need to be on the lookout for some of the following telltale signs: complex operations, bureaucracy, leadership gaps, poor client retention, poor talent retention, inability to predict project resourcing needs, limited data and visibility, outdated legacy systems, ineffective change management and decreasing profitability. This program provides professional services leaders (both aspiring and incumbent) with comprehensive practical skills and tools to effectively face these challenges, covering trust and communication, leadership, services marketing and client development and retention.

The professional services sector consistently highlights staff retention and development as major and growing challenges. Indeed, Deloitte Digital (2023) confirms that, “research demonstrates that fostering trust, opportunities for growth, and employee well-being are the keys to increased workforce retention and satisfaction.” The business expertise of staff is a major source of competitive advantage and needs to be nurtured, developed and retained. The Professional Services Advisor program addresses this need across in a very targeted manner, via the Effective Communication, Becoming Persuasive, Effective Leadership, People Development and Managing Change modules (Modules 2, 3, 4, 5 & 6).
Another regularly cited professional services pain point relates to client retention and business development in increasingly saturated and competitive markets. IBM (2024) highlights that, “Customer retention must be a top priority for leaders of any company wanting to remain competitive.” All services organisations understand the intangible nature of their offerings. This intangibility means that trust is a vital component of the relationship between providers and their clients. What is less understood is how trust is defined and indeed developed. So important is trust, being a determinant of loyalty and commitment, it features as Module 1 in this program, Services Trust. Services Trust, along with the modules covering Becoming Persuasive, Advisory Services, Market Targeting. Market Positioning, Your Brand, Business Development and Client Management (Modules 1, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 & 12) all provide refined guidance on strengthening client relationships and retention.
Another important issue facing professional services providers centres on how and when to expand their high-value advisory services. Firms may seek to diversify revenue streams or benefit from high growth areas, regionally or indeed globally. Only practices with laser-like clarity on their Advisory Services, Market Targeting, Market Positioning, Brand and Business Development (Modules 7, 8, 9, 10 & 11) can expect to have ongoing success in the refinement and development of their offers to targeted clients. Dentons, the global law firm, has consistently shown the benefits of identification of key sectors, with Boyajian (2023) commenting that their, “global platform and breadth has positioned us well for strong growth despite market challenges.”
Increasingly, technology developments represent both a challenge and an opportunity for professional services firms. Leveraging the opportunity relies on firms making informed decisions on how to ensure they add value in their advisory services, as viewed by the client, the customer. The Economic Times (2023) recently reported that, “Top high-value consulting firms like McKinsey, BCG and Bain, along with tech majors such as Accenture and IBM, as well as professional services firms like Deloitte, EY and PwC, are investing tens of millions of dollars and actively forming partnerships with IT companies and startups while creating internal teams to develop solutions for clients and internal needs.” Decisions in areas of automation, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud and data analytics (to name a few) require application of the same skills highlighted above, as firms seek to expand their high-value advisory services, viz, Advisory Services, Market Targeting, Market Positioning, Brand and Business Development (Modules 7, 8, 9, 10 & 11).
This program seeks to provide professional services practitioners with refined exposure to the skills and tools necessary to build a successful career and practice, whilst addressing their micro and macroenvironmental challenges. To do so, it addresses the major needs areas of trust and communication (Modules 1, 2 & 3), leadership (Modules 4, 5 & 6), marketing in the very specific professional services context (Modules 7, 8, 9 & 10) and acquiring and keeping clients (Modules 11 & 12).
Curriculum
Professional Services Advisor – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Services Trust
- Part 1 Month 2 Effective Communication
- Part 1 Month 3 Becoming Persuasive
- Part 1 Month 4 Effective Leadership
- Part 1 Month 5 People Development
- Part 1 Month 6 Managing Change
- Part 1 Month 7 Advisory Services
- Part 1 Month 8 Market Targeting
- Part 1 Month 9 Market Positioning
- Part 1 Month 10 Your Brand
- Part 1 Month 11 Business Development
- Part 1 Month 12 Client Management
Deleted:
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Professional Services Advisor corporate training program.
Professional Services Advisor – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Services Trust – The foundation need for trusted advisor status is well acknowledged amongst professional services providers. Across international borders we see the concept of trust and the value associated with the profession documented via the aims and objectives of their industry associations. The trust term is a relative one, what does it mean in absolute terms and what are its determinants? Trust is certainly a complex term, due to the myriad of interactions between the two parties to the relationship, professional services providers, and their clients. This module of the curriculum allows participants to gain insights around the key question, do clients believe their professional services provider is their most trusted advisor and what are the determinants of that trust? Various definitions for trust exist, what is the most appropriate for you, and your practice?
- Part 1 Month 2 Effective Communication – Professional services organisations are paid for their insights, so need to communicate very well. The prior module highlighted this need as a significant determinant of trust in the relationship between professional services providers and their clients. To achieve this, participants will learn how to use active listening techniques, adopt behaviours to enhance working relationships and use effective questioning skills. Participants can also expect to identify and develop their own personal communication style. Skills around giving and receiving appropriate feedback will also be explored, as well how to deal with difficult communication situations.
- Part 1 Month 3 Becoming Persuasive – With effective communication as our starting point, this module focuses in on developing the participant’s ability to influence, to persuade. Recent research confirms that the ability to persuade is one of the top five soft skills sought in business along with creativity, collaboration, adaptability, and emotional intelligence. This module will equip the participant with the skills and frameworks necessary to persuade with confidence and accelerate the leadership journey. It offers a practical introduction to persuasion theory and persuasive communication and provides an applied understanding of the psychology of persuasion and the art of rhetoric. This will be achieved by exploring classical and contemporary ideas of persuasion with an emphasis on recent social, and psychological theory and research. Participants will also practise critical skills in analysing, organising, information gathering, goal setting, evaluating, and public speaking.
- Part 1 Month 4 Effective Leadership – This module focuses on the nature and practice of leadership and the development of the leadership capabilities necessary to operate effectively in complex and rapidly changing organisational environments. It deals with a variety of leader behaviours and capabilities reflecting self-leadership, the leadership of others, and leadership within broader organisational and business contexts. Participants can expect to analyse their own leadership skills, develop capabilities for career success and collaborate effectively to critically reflect on and inform leadership practice.
- Part 1 Month 5 People Development – We may only become effective leaders if we can also develop those who work with and for us. Such development is the foundation for building human capital in professional services organisations. It commences at induction and continues to retirement or departure. Across the professional services sector, human resource development is a strategic issue, not just operational and applies to all staff – full-time, part-time, casuals, contractors and temporary. This module provides participants with practical frameworks for developing human resource plans and policies, learning and development strategies, organisational induction plans and orientation, training programs, development and learning and the evaluation of same.
- Part 1 Month 6 Managing Change – This module examines the role of change in the management of professional services organisations. It explores the nature and processes of organisational change and focuses on technological, administrative, and process innovation as well as on contemporary techniques and procedures used to understand, initiate, plan, and implement change. It is shaped by concerns over the need to combine consistent structures for predictable and efficient operations and personnel employment with flexibility and timely adaptability in order to respond to shifts in the environment. Participants develop a practical and effective understanding of the key processes and components in managing change for application within their own organisation.
- Part 1 Month 7 Advisory Services – Whilst at first glance this module might seem self-evident to those already in the professional services sector, it is important to take a first principles look at why you do what you do, or indeed should do. This module reviews and explores the nature and characteristics of the consulting industry, major practice areas in consulting and the value creation activities of consultants. It discusses the main success factors of consulting. It also allows participants to explore methods of consultancy project design and management, and integrative problem-solving applying the principles of design thinking and different performance measures.
- Part 1 Month 8 Market Targeting – A fundamental requirement for professional services success is achieving laser-like clarity around the clients we choose to serve. All too often a firm’s decisions in this area are legacy related (they are our clients because they came with the firm we acquired) or vague rather than explicit. Participants will develop an understanding of what segments actually are, identifying the various segments in their market and ultimately, make explicit, well-reasoned decisions for the segment(s) that should be targeted.
- Part 1 Month 9 Market Positioning – Once decisions have been made around which client segments are to be served, the firm then needs to decide how it will differentiate its offering for each segment and what position it wants to occupy in the minds of its clients. Participants will work to develop a clear, distinctive, and memorable positioning, providing clarity on the reasons why clients choose to do business with them. The key here is to put as much distance between the firm and its competitors as possible.
- Part 1 Month 10 Your Brand – In professional services markets, offering consistent quality and satisfying services are key challenges. These challenges are driven by the intangibility, heterogeneity, variability, and perishability of service offerings. Because of the nature of services, professional services firms must adopt strategies to market their service offerings which are different from tangible goods. There is a growing range of touchpoints, where clients experience service marketing techniques. Therefore, services marketers require a deep understanding of issues such as service design and delivery, service quality measurement and internal marketing. Participants will critically analyse and evaluate their service offerings and service delivery processes with a focus on creating strategic options to improve service quality, satisfaction, firm performance, and brand services competitively.
- Part 1 Month 11 Business Development – Business development, or let’s call it as it is, consultative selling, is often considered an anathema within professional services firms. But it doesn’t have to be, we’re just providing our targeted segments (i.e., those who are likely to value what we have to offer) with the opportunity to benefit from our services. How can that be repugnant? Participants will develop an understanding of the consultative selling process, learn the types of questions to uncover client needs, understand the process to present their services, understand different people’s styles, learn in-depth questioning, using SPIN and differentiate between confirming the business versus doing the deal.
- Part 1 Month 12 Client Management – Strategic client management assists firms develop continuous, positive relationships with clients based on the quality of service offering and value. This module is a logical follow-on from the prior consultative sales program, which focused specifically on developing individual sales skills. Whereas the Strategic Client Management program focuses on the development of effective and formal client plans. Participants will gain an effective understanding of the definition of strategic client management, make distinctions between relationship levels (transactional, strategic and partnership clients), learn and apply the various buyer and influencer roles, and learn the skills to focus on, in approaching clients as problem solvers (reactive) and client developers (proactive). Finally, participants will create strategic client management frameworks to ensure they are working on clients, not just in clients.
Methodology

Professional Services Advisor
This program seeks to provide professional services practitioners with refined exposure to the skills and tools necessary to build a successful career and practice, whilst addressing their micro and macroenvironmental challenges. To do so, it addresses the major needs areas of trust and communication (Modules 1, 2 & 3), leadership (Modules 4, 5 & 6), marketing in the very specific professional services context (Modules 7, 8, 9 & 10) and acquiring and keeping clients (Modules 11 & 12).
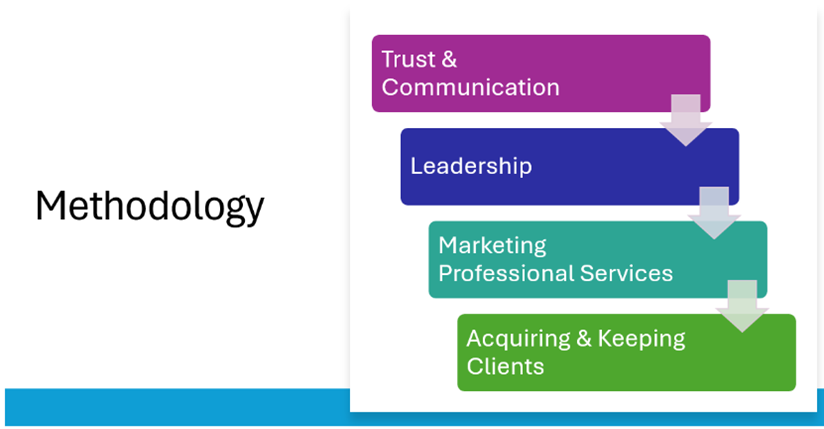
Trust & Communication (Modules 1, 2 & 3)
The first three modules provide professional services practitioners with an effective grounding in client trust and how it can be developed, tools to develop effective client interactions and the ability to influence, to persuade. The foundation need for trust in relationships with clients is well understood in the professional services sector. However, what is much less understood is how this trust is defined and indeed developed. Drawing on the current research on trust, participants will learn how to bridge this gap. Effective communication is not what we say, it is what the other person hears. This module has been designed to provide tools to ensure communication effectiveness, after all we are being paid for these insights, so need to make sure they are refined, targeted and valued. The third module develops participants’ ability to persuade, via exploration of classical and contemporary ideas on rhetoric and persuasion.
Leadership (Modules 4, 5 & 6)
The leadership modules move participants beyond management of self to management of others, encompassing effective leadership, people development and effective change management. Participants will analyse their own management style against best practice and further develop these skills and capabilities. The people development module provides participants with up-to-date and practical frameworks to develop human resource policies, plans and practices. The change management module utilises contemporary techniques and processes which participants will use to effect change within their own organisation.
Marketing Professional Services (Modules 7, 8, 9 & 10)
Modules 7 through 10 explore marketing from a very focused professional services standpoint. Firstly, by considering the nature and characteristics of advisory/consultancy services and value creation activities of trusted advisors. Participants will then use proven models to segment and then target attractive client groupings. Explicit decisions are then taken with regard to positioning and branding for the practice/professional services practitioners which are most likely to resonate with targeted client groups.
Acquiring and Keeping Clients (Modules 11 & 12)
The final two modules deal with business development at both the tactical and strategic level. Module 11 allows participants to better understand consultative selling and further refine their own style. The final module provides participants with an understanding of the importance of strategic client relationships and management, and tools and approaches to ensure they are effectively fostering the correct relationship – across the continuum from transactional to partnerships.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:

Professional Services Sector
The overall professional services sector consists of industries providing services which include scientific research; architectural, engineering and technical; legal and accounting; advertising; market research and statistics; management and related consulting; veterinary; and other professional services. North America is the largest regional market for such services, followed by Western Europe, and then the Asia Pacific region. According to recent research, key professional services challenges include predicting resource requirements, maintaining profitability, and the retention of employees and clients. As a result, professional services firms need to be on the lookout for some of the following telltale signs: complex operations, bureaucracy, leadership gaps, poor client retention, poor talent retention, inability to predict project resourcing needs, limited data and visibility, outdated legacy systems, ineffective change management and decreasing profitability.
This program provides professional services leaders (both aspiring and incumbent) with comprehensive practical skills and tools to effectively face these challenges, covering trust and communication, leadership, services marketing and client development and retention.
The following paragraphs review each of the major industries which comprise the professional services sector, highlighting current position and outlook.

Engineering Consulting Services
Engineering consulting services industry firms provide engineering consulting services, which typically relate to the design, development and use of infrastructure projects, machinery, processes, and systems. Industry firms offer advisory services, feasibility studies, preparation of preliminary and final plans and designs, technical services during project construction phases, and inspection and evaluation of construction and engineering projects.
The Engineering Consulting Services industry has heavy regulation. Firms are subject to a range of regulations, including practitioner qualifications, codes of ethics, building and design regulations, environmental policies and insurance coverage. Industry bodies provide some assistance for engineering consultants and promote and educate members involved in engineering consulting.
Engineering consulting firms reap the benefits from rising capital expenditure on non-residential construction, driven by an increasing number of industrial complexes and transport buildings, including airport terminals and train stations. Firms are differentiating themselves by offering services throughout a project’s life cycle, including engineering, procurement, construction and management (EPCM).
The major drivers of the industry include the level of activity in the construction industry, public sector capital expenditure, consolidation within the industry as larger firms seek to expand and the emergence of multidisciplinary firms to operate as one-stop shops.
Management Consulting Services
Management consulting industry firms provide clients with advice and strategies to solve a range of complex business issues. These issues include financial performance, business strategy and operational structure. Management consultants aim to improve a client’s overall business performance.
Consolidation has risen over the past few years as larger firms have been acquiring smaller consulting practices. These firms have pursued acquisitions to expand client bases and develop their exposure to high-value and specialised consulting work, widening profit margins. Even so, small management consulting firms and sole proprietors continue to comprise most of the management consulting firms, serving niche markets and smaller clients. In recent years, a raft of new small firms and sole proprietors has contributed to growing enterprise numbers.
Industry performance is largely driven by consulting services’ diverse nature supporting management consultancies’ revenue, overall business confidence, public sector demand, firms benefiting from more clients adopting IT and telecommunications technology and major players consolidating via acquisition to build scale and broaden service offerings.
Legal Services
Legal services industry firms primarily provide legal advice and representation and prepare legal documents. Solicitors, barristers and legal aid offices typically provide these services. Alternative dispute resolution, conveyancing and intellectual property services are also included in the industry. The industry does not include services provided by in-house legal teams.
Legal service providers have faced mixed conditions over the past few years. Business confidence has been volatile over the period, prompting varied demand from downstream markets. Uncertain economic conditions have contributed to constrained demand for value-added services, like legal work relating to expansionary activity and IPOs as clients have sought to limit discretionary spending. On the flip side economic headwinds have boosted the need for restructuring and insolvency expertise. Constant legal requirements for downstream businesses have stabilised fluctuations in demand.
Larger firms have introduced more professional services to complement their legal work to maintain competitiveness with big accounting firms that are doing the same thing. The complexity of legal services designates a relatively high average profit margin for legal service providers. This figure is inflated by the large amount of sole proprietors in the industry that use profit as imputed wages. The continued need for core legal services despite economic uncertainty has benefited law firm profit margins.

Accounting Services
Accountancy firms provide accounting services, including auditing accounting records, preparing financial statements, preparing tax returns and bookkeeping. In conjunction with these services, industry companies may also offer business advice and assistance. The level of regulation in the accounting services industry is high. The industry requires close monitoring because of the importance of accurate financial reporting and ensuring appropriate measures are undertaken when compiling or auditing a company’s accounts.
Revenue in the industry has crept upwards in recent years, despite mixed operating conditions. Audit and tax services have remained a dependable source of revenue for accounting firms, as some businesses legally require these services. Nonetheless, swelling price competition has limited the profit margins associated with providing these services. Climbing demand for industry-specific advisory services has buoyed revenue in recent years, with many accounting firms expanding their advisory services.
Accounting firms are increasingly incorporating technology like data analytics and cloud-based accounting into their processes, which has expanded value-added services. These value-added services have larger profit margins than traditional tax and audit processing, encouraging firms to diversify.
Industry performance has recently been impacted by uncertain business conditions, with firms forces to cut costs to maintain profitability. Technological changes have had a mixed impact. Data analytics and technology consulting have been added to their offer and technological investments have added further income streams and allowed for productivity gains. On the flipside, client uptake of cloud-based accounting poses a threat to firms that provide traditional accounting services. Increased price-based competition continues to impact industry profit margins.

Scientific and Environmental Research Services
Scientific and environmental research services operators primarily provide scientific testing services to customers in the agricultural, mining, manufacturing and construction sectors. Industry firms also collect, analyse and forecast meteorological information. Other industry segments include pollution monitoring services, forensic sciences and general laboratory operations that may undertake testing for product safety and quality.
Key drivers for this industry include growing global demand within the mining sector, continued demand for scientific research services has also supported industry revenue, driven by investment in medical products, agriculture and chemical products, and IT and computing research. Farmers also continue to rely on trusted weather providers during volatile weather conditions. Consequently, profit margins continue to grow due to high demand an effective cost management.

Architectural and Surveying Services
Architectural industry firms provide architectural design and drafting services, landscape design services and town planning services. Industry operators also provide consultation on land zoning and building code regulations.
Architectural services firms have endured challenging conditions in recent years. In response to uncertain economic conditions because of the pandemic and subsequent supply chain issues, many downstream clients delayed or cancelled projects, dropping demand for architectural services. Tumbling business confidence and construction activity have contributed to a limited number of new projects in recent years. This trend has intensified competition and put downward pressure on prices, further reducing architects’ ability to lift revenue. Nonetheless, climbing demand from institutional construction has buoyed industry revenue in recent times.
Architecture firms have faced mounting competition from vertically integrated firms, including large building construction and engineering consulting firms, in recent years. Some clients tend prefer firms that offer integrated services, as these operators can provide a full suite of services for projects at a lower price due to greater economies of scale. This trend has proven difficult for small architecture firms and sole proprietors, which make up the bulk of the industry. These smaller architecture firms often do not have the scale or brand recognition to acquire other firms or compete on tenders for substantial developments. Instead, larger integrated firms looking to expand their capabilities have increasingly acquired these boutique architecture firms in recent years.
Industry performance is driven by growing institutional building construction activity, which has benefitted large architecture firms. Inflationary pressures and interest hikes have stifled demand from a range of construction markets. Dwindling profit margins have forced some architects out of the industry. However, growing environmental awareness has encouraged a greater focus on green architecture.

Advertising and Market Research Services
Advertising industry companies provide clients with advertising services, such as creating advertising campaigns and materials. Industry revenue relates to the revenue received from developing and producing advertising campaigns rather than revenue from client billings.
The transition to digital advertising is underpinning growth for advertising agencies. Digital advertising services are surging at the expense of traditional print and broadcast advertising services. Many larger advertising firms are focusing on providing integrated services for clients. This is prompting a flurry of merger and acquisition activity.
The ways that advertising agencies implement strategies for clients to reach their audiences are changing. Mass media advertising’s high costs and the fragmentation of consumer media viewing habits are prompting some clients to expand their below-the-line advertising, like targeted email, SMS and direct mail campaigns. New forms of media, alongside changing media usage trends, are also affecting advertising agencies’ operating conditions. Advertising firms are responding to these trends by transforming their traditional advertising strategies. Most major and middling advertising agencies are developing or acquiring complementary public relations, market research and analytics, digital advertising and web development businesses. Advertising agencies are expected to continue changing their services alongside ongoing media fragmentation over the coming years. Greater investment will be required to adjust to new mobile and online advertising trends.

Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

New York
New York City, a global economic powerhouse, boasts a vibrant commercial landscape characterised by diverse industries and robust financial services. Over the past decade, the city has seen significant growth in sectors such as finance, technology, and professional services, fuelled by innovation and a dynamic entrepreneurial spirit. With its unparalleled infrastructure, access to capital, and diverse talent pool, New York continues to attract businesses from around the world, solidifying its status as a premier commercial destination. Over the past decade, the city has witnessed significant transformations in its economic landscape, with the professional services sector playing a pivotal role in shaping its trajectory.
One of the defining trends in New York City’s professional services sector has been its adaptation to the digital age. As technology continues to revolutionise industries, firms in fields such as finance, law, consulting, and accounting have embraced digital innovation to enhance their services and stay competitive on a global scale. From the adoption of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to the development of digital platforms for client engagement, New York City’s professional services firms have been at the forefront of leveraging technology to drive efficiency and deliver value to their clients.
Moreover, the city’s status as a global financial hub has bolstered its professional services sector, particularly in areas such as investment banking, asset management, and financial advisory services. Despite facing challenges such as regulatory changes and market volatility, New York City’s financial services firms have demonstrated resilience and adaptability, maintaining their leadership positions in an increasingly interconnected and competitive global marketplace.
In addition to traditional sectors, emerging industries have also contributed to the vibrancy of New York City’s professional services landscape. The rise of fintech startups, for instance, has created new opportunities for collaboration and innovation, as established firms seek to tap into the entrepreneurial spirit and technological expertise prevalent in the city’s startup ecosystem.
Furthermore, New York City’s professional services sector has played a vital role in driving economic growth and fostering entrepreneurship. Through the provision of advisory services, legal counsel, and strategic guidance, professional services firms have supported the expansion of businesses across various sectors, from small startups to multinational corporations. This ecosystem of support and expertise has facilitated the city’s reputation as a magnet for talent and investment, attracting professionals from around the world eager to contribute to its dynamic economy.
Looking ahead, New York City’s professional services sector is poised to continue its evolution, driven by ongoing technological advancements, shifting market dynamics, and evolving client needs. As the city navigates the complexities of a post-pandemic world and embraces the opportunities of the digital age, its professional services firms remain integral to its economic resilience and global competitiveness.

London
London, a global financial hub, thrives on a rich tapestry of commercial activities. Over the last decade, the city has showcased resilience amidst challenges like Brexit, retaining its position as a magnet for international businesses. London’s diverse economy encompasses finance, technology, professional services, and more, fuelled by innovation and a robust regulatory framework. With world-class infrastructure and a deep talent pool, London remains a premier destination for businesses seeking growth and opportunity. London has remained a cornerstone of global commerce, with its professional services sector playing a pivotal role in sustaining its economic vibrancy amidst a rapidly changing landscape. From finance and law to consulting and accounting, the city’s professional services firms have demonstrated resilience in the face of challenges while embracing innovation to maintain their competitive edge.
One of the notable developments in London’s professional services sector has been its response to regulatory changes and geopolitical uncertainties. The aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis ushered in a new era of regulatory scrutiny, prompting financial institutions and legal firms to adapt their practices to comply with evolving regulations. Despite initial challenges, London’s professional services sector has demonstrated agility in navigating regulatory complexities, leveraging its expertise to help clients navigate an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Moreover, London’s status as a global financial centre has underpinned the growth of its professional services sector, particularly in areas such as investment banking, asset management, and insurance. Despite concerns surrounding Brexit and the subsequent reorientation of financial services, London has maintained its position as a hub for financial innovation and expertise, attracting talent and investment from around the world.
In addition to traditional sectors, London’s professional services landscape has also been shaped by the rise of technology and digital disruption. Firms across various industries have embraced digital transformation, leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing to enhance their service offerings and improve operational efficiency. In response, professional services firms in London have invested in digital capabilities, recognising the importance of staying ahead of the curve in an increasingly digitised world.
Furthermore, London’s professional services sector has played a crucial role in supporting entrepreneurship and innovation. From providing legal counsel to startups to offering strategic advice to growing businesses, professional services firms have been instrumental in nurturing London’s thriving startup ecosystem. The city’s access to capital, diverse talent pool, and supportive regulatory environment have further bolstered its reputation as a global hub for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Looking ahead, London’s professional services sector faces both opportunities and challenges. While geopolitical uncertainties and regulatory changes continue to pose risks, the city’s reputation as a centre of excellence and innovation remains unparalleled. By embracing digital transformation, fostering collaboration, and maintaining its commitment to excellence, London’s professional services firms are well-positioned to navigate the challenges of the future and continue driving the city’s economic growth and prosperity.
Sydney
Sydney, a dynamic economic centre, has witnessed substantial growth in diverse industries over the past decade. Renowned for its finance, technology, and professional services sectors, the city continues to attract investment and talent from around the globe. With its strategic location in the Asia-Pacific region, vibrant startup ecosystem, and commitment to innovation, Sydney offers unparalleled opportunities for businesses looking to expand and thrive in a competitive market landscape.
One of the key trends shaping Sydney’s professional services sector has been its increasing specialisation and expertise in niche areas. As the city continues to attract investment and talent from around the world, professional services firms have capitalised on opportunities to provide specialised services tailored to the needs of various industries. Whether it’s fintech advisory services, environmental consulting, or digital marketing expertise, Sydney’s professional services sector has demonstrated agility in responding to evolving market demands and emerging trends.
Moreover, Sydney’s status as a regional financial hub has fuelled the growth of its professional services sector, particularly in areas such as investment banking, wealth management, and insurance. The city’s proximity to the Asia-Pacific region, coupled with its robust regulatory framework and stable economic environment, has attracted multinational corporations and financial institutions, further cementing Sydney’s position as a leading financial centre.
In addition to traditional sectors, Sydney’s professional services landscape has been invigorated by the rise of technology and digital innovation. Firms have embraced digital transformation, leveraging technologies such as data analytics, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing to enhance their service offerings and streamline operations. This shift towards digitalisation has not only improved efficiency but has also opened new avenues for collaboration and client engagement.
Furthermore, Sydney’s professional services sector has played a crucial role in supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups. From providing legal advice on business structures to offering strategic consulting services, professional services firms have been instrumental in helping startups navigate the complexities of starting and scaling a business. The city’s vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem, coupled with the availability of skilled professionals, has contributed to Sydney’s reputation as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Looking ahead, Sydney’s professional services sector is poised for further growth and evolution. With increasing globalisation, technological advancement, and changing consumer preferences, firms will need to continue adapting to stay relevant and competitive in the market. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and maintaining a commitment to excellence, Sydney’s professional services firms are well-positioned to drive economic growth and prosperity in the years to come.

New Delhi
New Delhi, the bustling capital of India, boasts a thriving commercial landscape marked by robust economic growth and increasing globalisation. Over the past decade, the city has witnessed significant expansion across sectors such as finance, technology, and professional services. With its burgeoning startup ecosystem, skilled workforce, and government initiatives aimed at fostering entrepreneurship, New Delhi presents abundant opportunities for businesses seeking to tap into the vast potential of the Indian market.
One of the notable trends in New Delhi’s professional services sector has been its increasing integration with global markets. As India’s capital city and a key business hub, New Delhi has attracted multinational corporations seeking to establish a presence in the country. Professional services firms have capitalised on this trend by providing a range of services tailored to the needs of international clients, including market entry strategies, regulatory compliance, and cross-border transactions.
Moreover, New Delhi’s professional services sector has benefited from the country’s economic liberalisation and reforms initiated in the early 1990s. These reforms have facilitated the growth of sectors such as finance, insurance, and consulting, creating opportunities for professional services firms to expand their offerings and tap into new markets. Additionally, initiatives such as Make in India and Digital India have further propelled growth, driving demand for specialised services in areas such as technology consulting and digital transformation.
In addition to serving multinational clients, New Delhi’s professional services firms have played a crucial role in supporting domestic businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). With India’s rapidly expanding economy and entrepreneurial spirit, there has been a growing demand for advisory services, legal counsel, and financial planning among SMEs looking to navigate regulatory complexities and scale their operations.
Furthermore, New Delhi’s professional services sector has been at the forefront of technological innovation, leveraging advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and cloud computing to enhance service delivery and drive efficiency. Firms have invested in digital infrastructure and talent development to stay competitive in an increasingly digitised marketplace, offering clients innovative solutions to address their evolving needs.
Looking ahead, New Delhi’s professional services sector is poised for continued growth and evolution. As the city continues to attract investment and talent, professional services firms will need to adapt to changing market dynamics and embrace new technologies to remain competitive. By fostering collaboration, nurturing talent, and maintaining a commitment to excellence, New Delhi’s professional services sector can continue to drive economic growth and prosperity in the years to come.

Mumbai
Mumbai, India’s financial capital, stands as a beacon of commerce and industry, epitomising the country’s economic dynamism. Over the past decade, the city has experienced remarkable growth across diverse sectors, including finance, technology, and professional services. With its vibrant stock exchanges, burgeoning fintech scene, and bustling port, Mumbai continues to attract investors and businesses, underscoring its status as a global commercial hub and a driving force behind India’s economic resurgence.
One of the defining features of Mumbai’s professional services sector has been its deep-rooted connection to the financial industry. As home to the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), National Stock Exchange (NSE), and numerous financial institutions, Mumbai has long been the epicentre of India’s financial activities. Over the past decade, the city’s financial services sector has experienced significant expansion, with firms specialising in investment banking, asset management, and insurance witnessing robust growth amidst increasing capital inflows and market liberalisation.
Moreover, Mumbai’s professional services sector has been a driving force behind India’s emergence as a global outsourcing destination. The city’s vibrant business process outsourcing (BPO) industry, coupled with its skilled workforce and advanced infrastructure, has attracted multinational corporations seeking cost-effective solutions for back-office operations, customer support, and IT services. This has led to the proliferation of IT consulting firms and technology service providers, further fuelling Mumbai’s economic growth and employment opportunities.
In addition to traditional sectors, Mumbai’s professional services landscape has been reshaped by the rise of digital innovation and entrepreneurship. Firms have embraced technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and blockchain to enhance service delivery and improve operational efficiency. This has led to the emergence of fintech startups, digital marketing agencies, and e-commerce platforms, contributing to Mumbai’s reputation as a hotbed of innovation and creativity.
Furthermore, Mumbai’s professional services sector has played a pivotal role in supporting the city’s vibrant real estate market. With a growing demand for commercial and residential properties, real estate advisory firms, legal services, and property management companies have experienced increased activity, facilitating transactions and investments across the city’s diverse neighbourhoods and business districts.
Looking ahead, Mumbai’s professional services sector is poised for further growth and diversification. As India continues to position itself as a global economic powerhouse, professional services firms in Mumbai will need to adapt to evolving market dynamics, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions. By leveraging their expertise, embracing innovation, and fostering collaboration, Mumbai’s professional services sector can continue to drive economic prosperity and cement the city’s position as a leading commercial hub on the world stage.
Program Benefits
Management
- Profitability
- Business Adaptability
- Streamlined Operations
- Trust Development
- Change Management
- Problem Solving
- Improved Communication
- Remove Waste
- Project Management
- Refined Metrics
Human Resources
- Talent Retention
- Improved Culture
- Engaged Team
- Skilled Resources
- Employee Satisfaction
- Team Building
- Team Empowerment
- Embracing Change
- Skills Development
- Employer Branding
Marketing
- Client Management
- Client Retention
- Valuable Segments
- Client Targeting
- Service Quality
- Business Development
- Market Positioning
- Strategic Partnerships
- Sales Effectiveness
- Value Creation
Testimonials

Studio Mondo, General Manager
“Studio Mondo and I have worked with Dr Cherry for over ten years. During this time, he has been invaluable across all areas of our business from Human Resources, Marketing and Financial. His wealth of experience has offered guidance and support that has allowed us to grow and achieve our strategic goals. He has been a huge part of our success, and any business would be lucky to have his expertise.”

Michael Johnson Associates, Chairman
“Michael Johnson Associates appointed Dr Cherry as Chief Adviser to the partnership at a time of great challenge to the practice. He was a highly influential voice as we navigated major changes in our market and our ownership structure. He was a calming influence and a constant source of encouragement. The current success of our practice is due in no small measure to Dr Cherry’s invaluable contribution.”

Integrity and Values, Managing Director
“When you meet someone who really listens and makes excellent measured decisions you watch poetry in motion. Dr Cherry may be my client, yet I believe I learned more about being a great consultant and the art of giving without hooks. Thank you, Dr Cherry, for your willingness to help one of my colleagues and the generosity with which you gave of your time and expertise. I would recommend Dr Cherry if you wanted to grow your business and ensure that grow is solid and will be there in five or more years.”

Macquarie Business School, Head Dept. of Marketing & Management
“Following a call for nominations from full-time staff in the Dept. of Marketing and Management of adjunct teaching staff in the Dept. who have unequivocally demonstrated sustained excellence in their teaching over time, I am pleased to write this congratulatory letter to you.
Specifically, on the evidence supplied by Associate Professor Chris Baumann in a range of units including MKTG208 Marketing Management, MKTG811 Brand Management and, in previous years, MKTG101 Marketing Principles and MKTG205 Business to Business Marketing, for example, he notes that you see sessional/adjunct teaching as the opportunity to give back and that you clearly model professionalism, honesty and integrity for our students. This includes prompt responses to student queries and your balanced interplay between teaching marketing theory aligned with practical lessons. In addition, it seems you go above-and-beyond with your careers-related discussions with students, providing them with advice of how to successfully transition into the workforce.
On behalf of the Dept., thank you for your sustained and valued efforts in and beyond the classroom. Our students are the more enriched as a result of your teaching. Thank you.”

Michael Johnson Associates, Partner
“We engaged Dr Cherry to assist us as part of a strategy to improve our productivity and profitability. In the time that he has worked with us, Dr Cherry very quickly understood our business and its challenges, and with minimal disruption to our day-to-day operations, helped us determine where our issues lay, and presented us with achievable recommendations to improve the way we run our business. He very quickly established trusting relationships with each member of staff, and this has greatly helped us in commencing to implement the change processes necessary to develop and implement our new business improvement strategies. Dr Cherry’s wide-ranging experience in business consulting across a range of industries gives him a perspective that enables him to quickly cut through to the issues. I don’t believe that we could have so quickly and easily developed and implemented the changes required without his assistance.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or if you would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.







